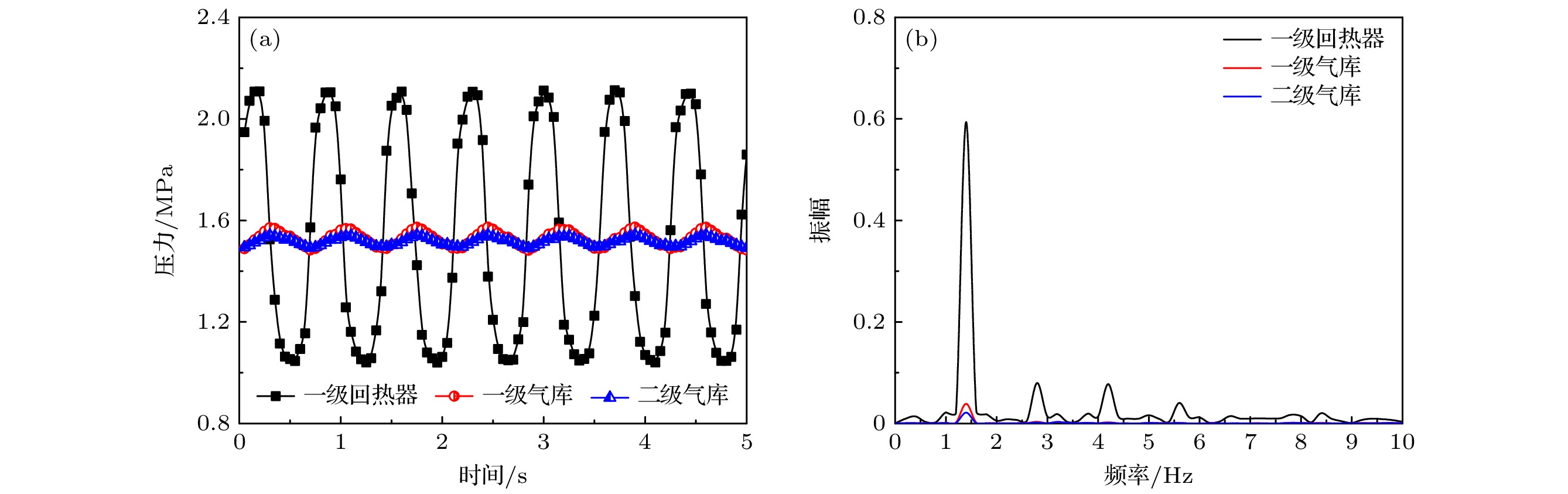
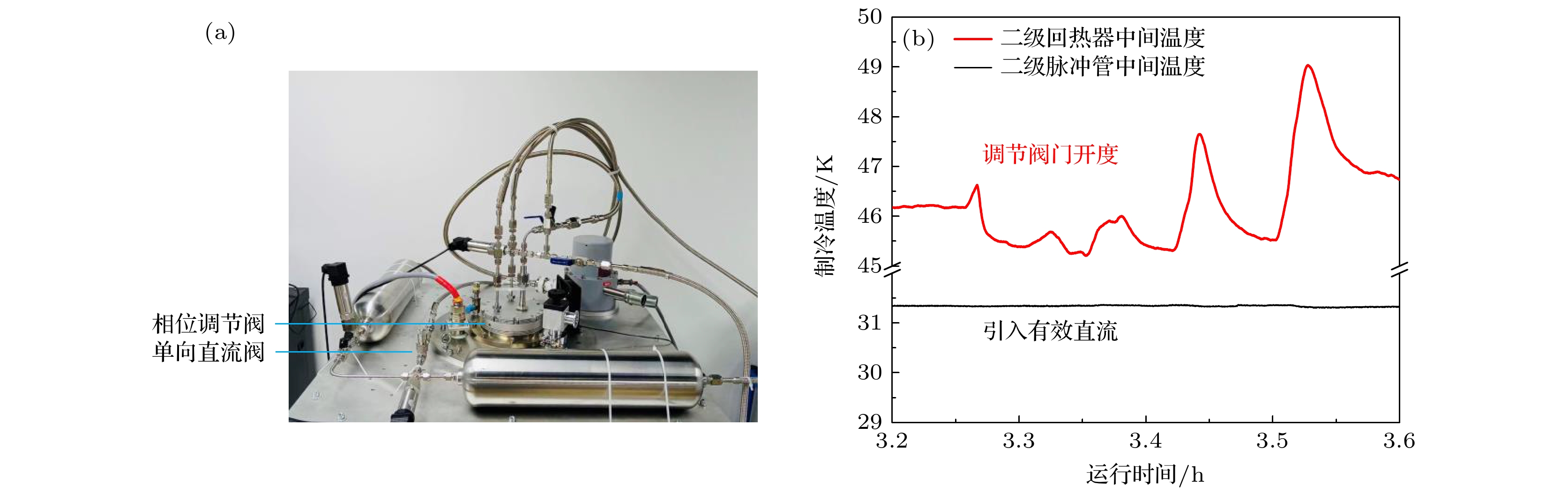
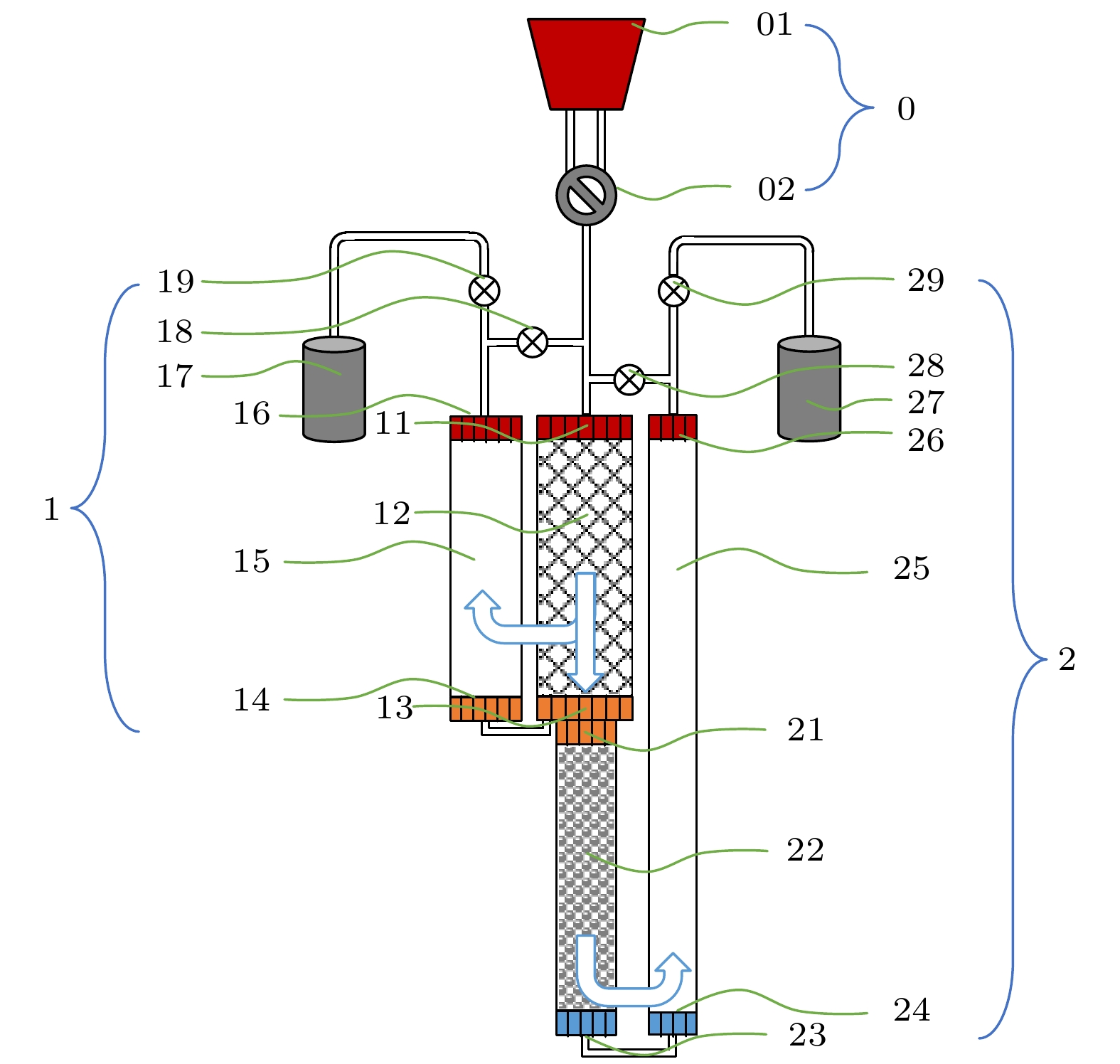
-
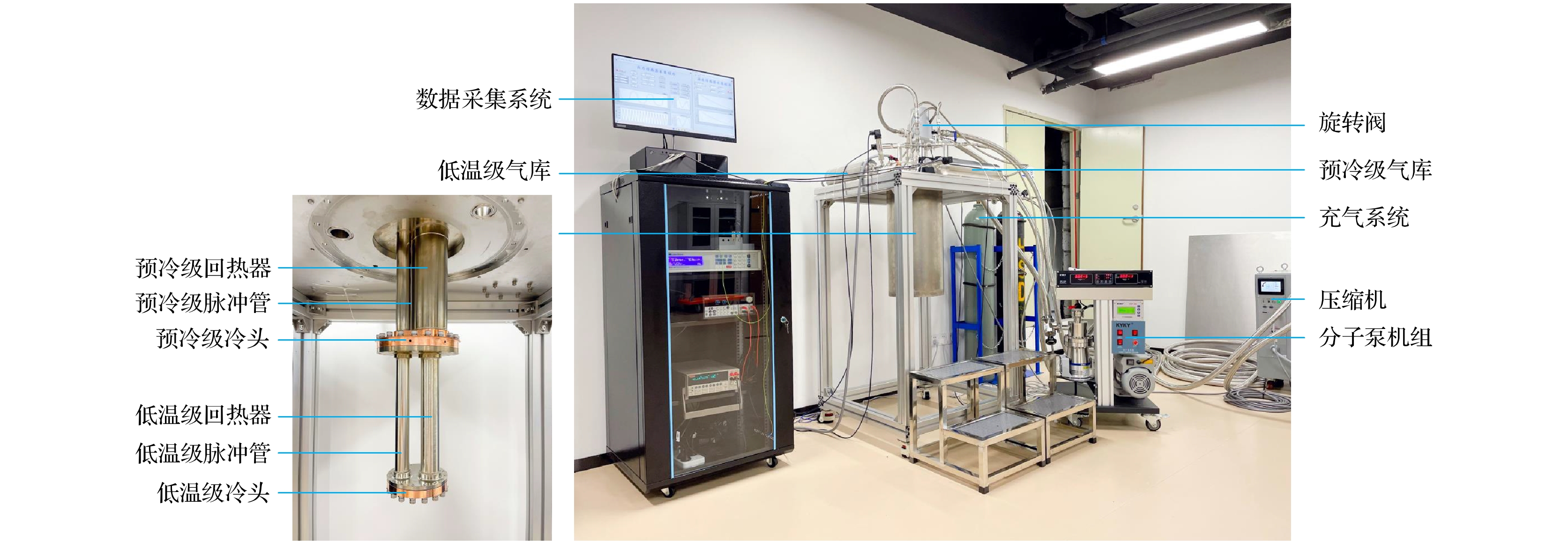
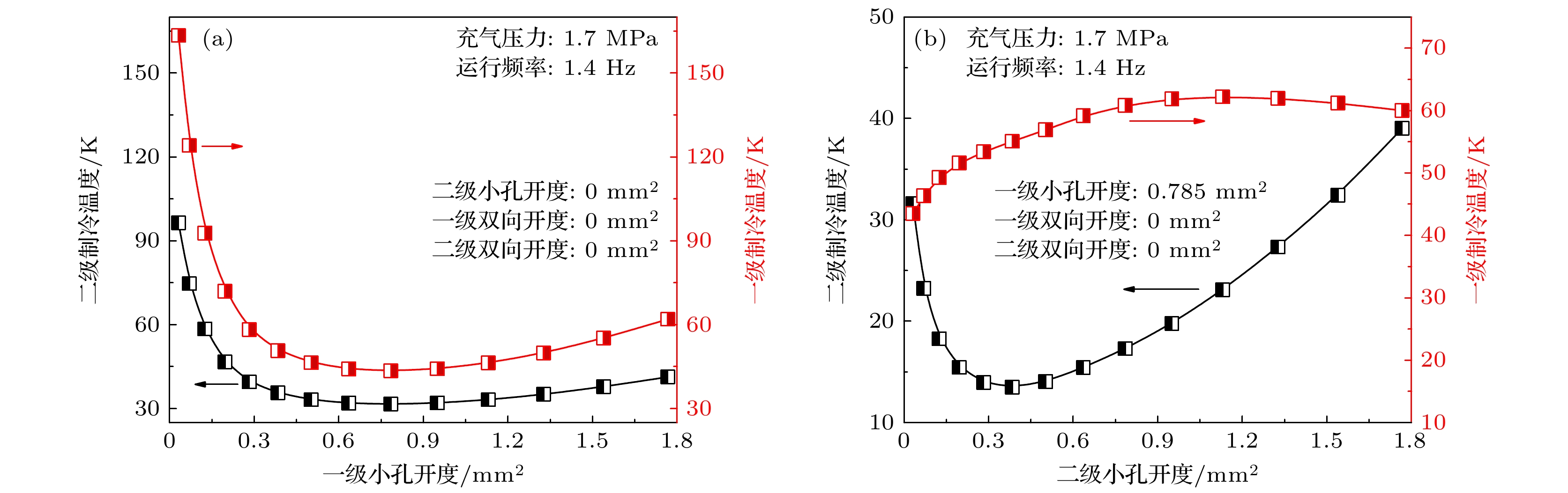
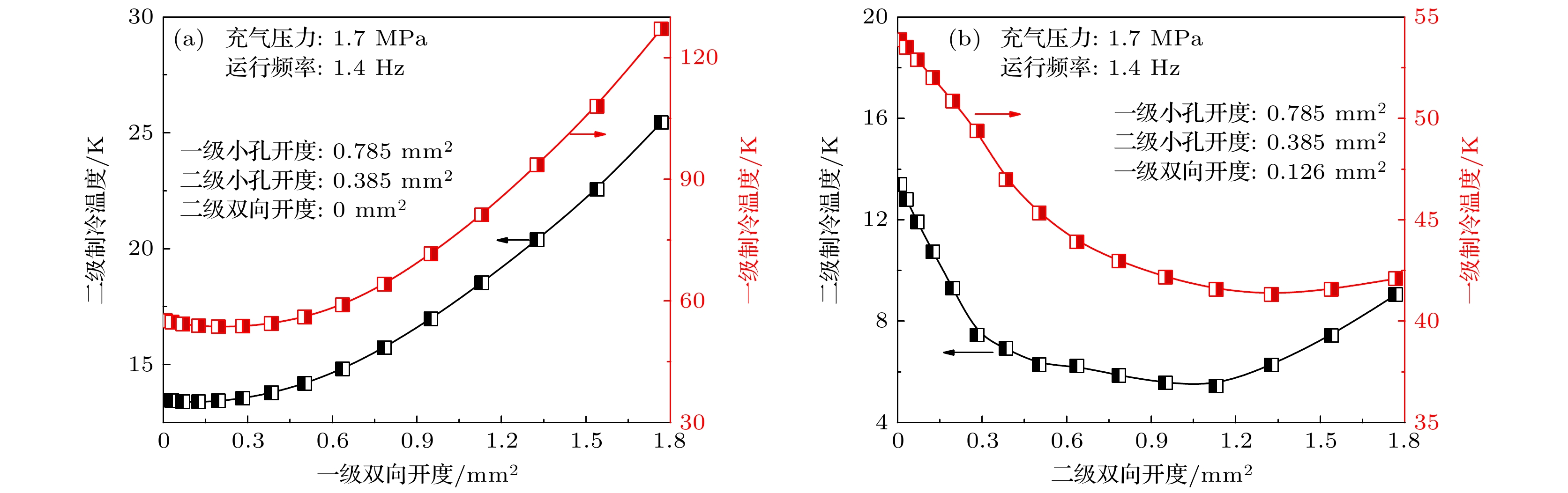
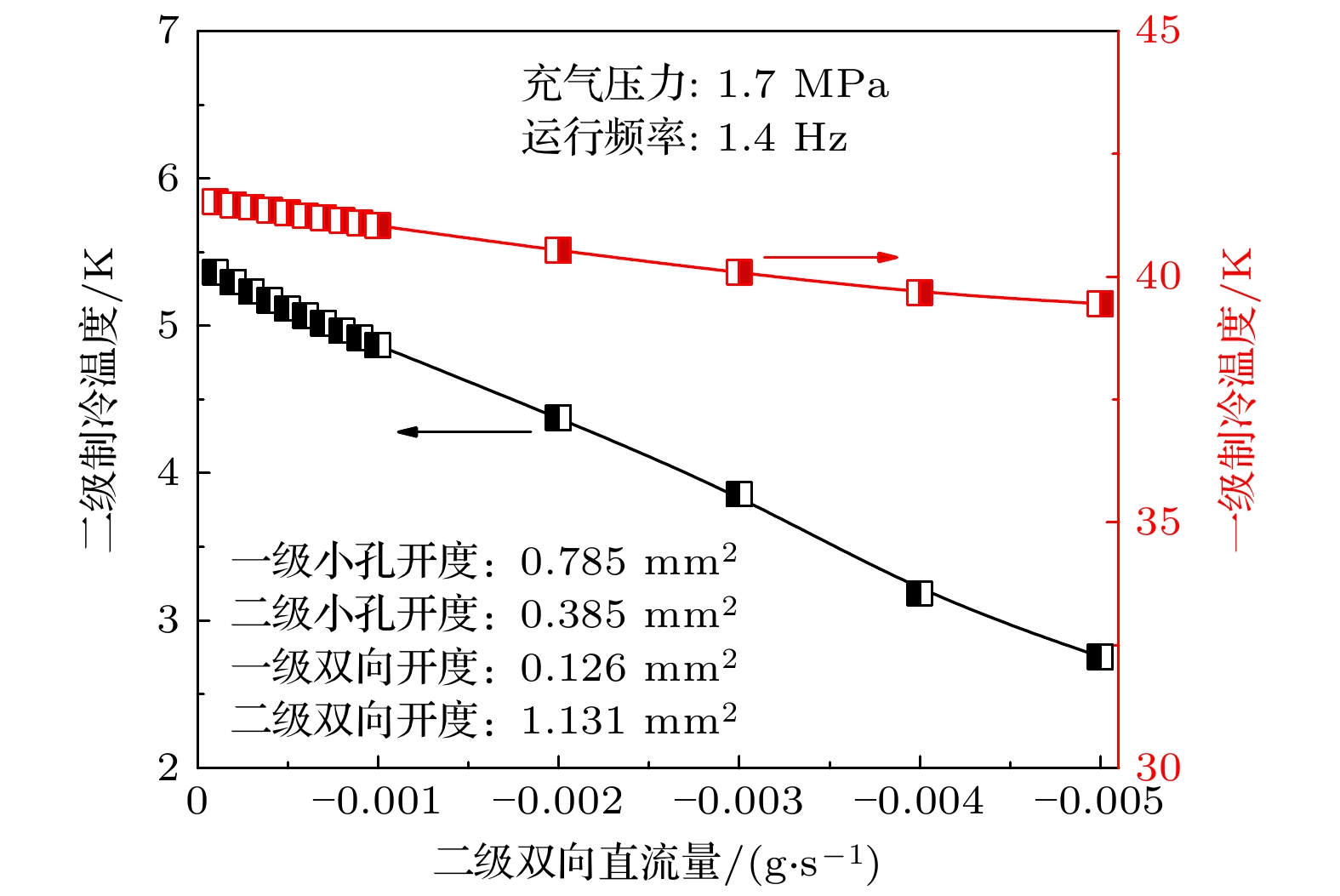
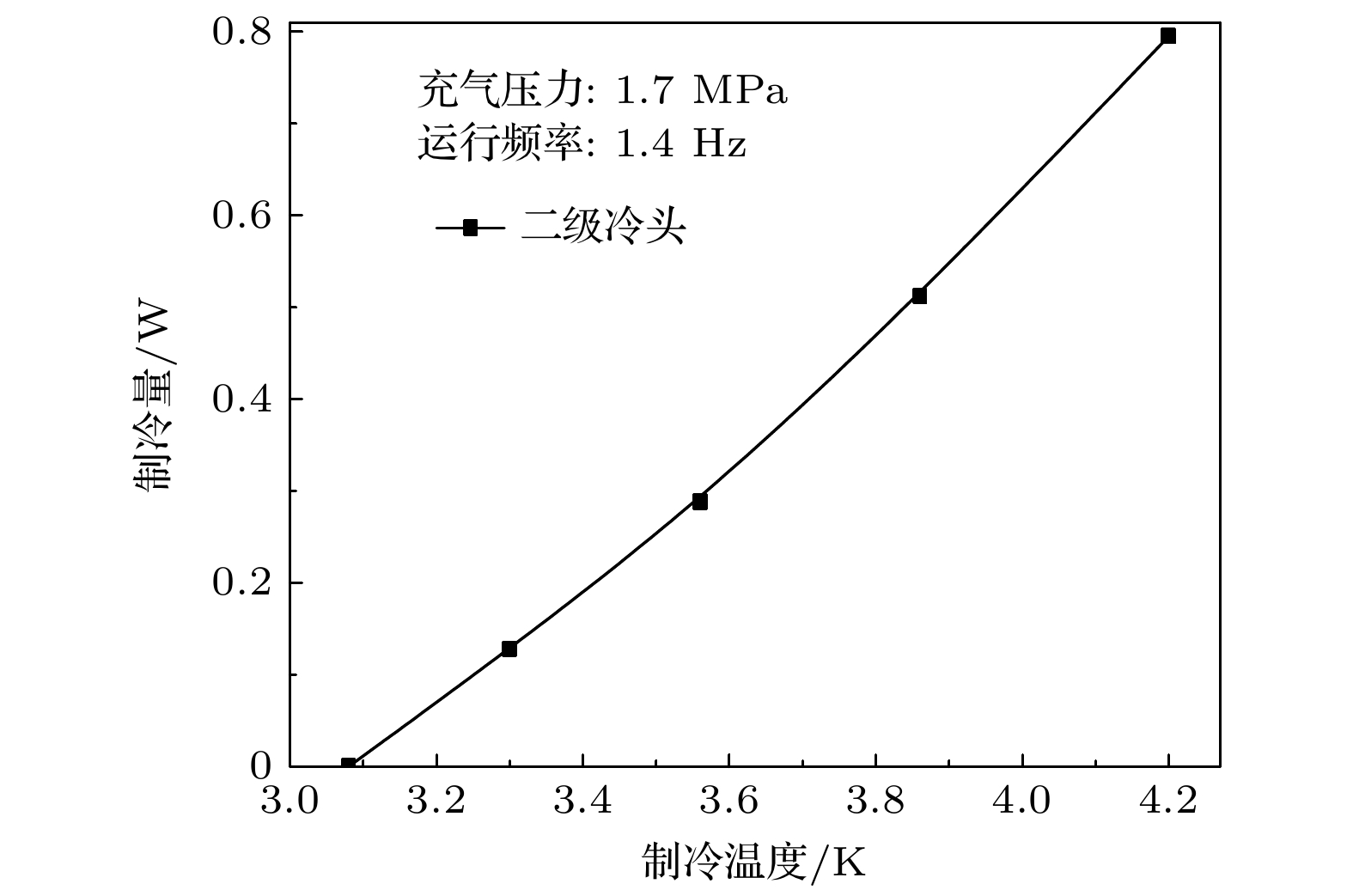
Owing to the advantages of large cooling capacity, low vibration and high reliability, GM-type pulse tube cryocoolers at liquid helium temperature have important applications in frontier fields of condensed matter physics research, quantum computing, etc. The phase shifter has an important influence on the cooling performance of pulse tube cryocooler. Previous researches on the phase shifter of GM-type pulse tube cryocooler mainly focused on the effect of a single phase shifter on the performance of the cryocooler at liquid helium temperature. In this paper, based on Sage software, a simulation model of a 4 K two-stage gas-coupled GM-type pulse tube cryocooler is first designed and constructed. The influence of the phase shifters of the two stages on the first-stage and the second-stage temperatures are calculated. The adjustment and optimization process of the cryocooler to obtain the liquid helium temperature is studied. Numerical simulations are given below. 1) The lowest temperature of the model is only about 100 K when the phase shifters of the two stages are closed. The lowest temperature of the model can be reduced to 2.7 K by optimizing the first-stage orifice valve, the second-stage orifice valve, the first-stage double-inlet valve and the second-stage double-inlet valve in sequence. 2) The first-stage orifice valve, the second-stage orifice valve, and the second-stage double-inlet valve have a significant effect on reducing the cooling temperature of the second stage, while the first-stage double-inlet valve has little effect on reducing the temperature of the second stage. 3) The first-stage orifice valve and the second-stage double-inlet valve have a significant effect on reducing the cooling temperature of the first stage, and the first-stage double-inlet valve has little effect on reducing the temperature of the first stage. The second-stage orifice valve will worsen the first stage performance. Finally, an experimental system is constructed. The lowest temperature of the experimental prototype can reach 3.1 K, and the cooling capacity of 0.8 W can be produced at 4.2 K, which is presently the best result obtained by the domestic two-stage gas-coupled valve-separated GM type pulse tube cryocooler. This research can not only promote the independent construction of domestic 4 K refrigeration platform, but also support the relevant frontier basic scientific research and the development of important scientific instruments and equipment. In the future, the structure of the first-stage cold-end heat exchanger and the impedance matching between the compressor and the cryocooler will be improved, and the gas coupling characteristics inside the cryocooler will be studied theoretically and experimentally in depth.
-
Keywords:
- pulse tube cryocooler /
- GM type /
- liquid helium temperature /
- two-stage gas-coupled
[1] 俎红叶, 程维军, 王亚男, 王晓涛, 李珂, 戴巍 2023 72 080701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zu H Y, Cheng W J, Wang Y N, Wang X T, Li K, Dai W 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 080701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Yang B, Gao Z Z, Xi X T, Chen L B, Wang J J 2022 J. Low Temp. Phys. 206 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Radebaugh R 2009 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 21 164219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Gifford W, Longsworth R 1964 J. Eng. Ind. 86 264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Radebaugh R 1990 Adv. Cryog. Eng. 35 1191
[6] Matsubara Y, Gao J L 1994 Cryogenics 34 259
[7] Tanida K, Gao J L, Yoshimura N, Matsubara Y 1996 Adv. Cryog. Eng. 41 1503
[8] Wang C, Thummes G, Heiden C 1997 Cryogenics 37 857
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wang C, Heiden C, Thummes G 1998 Cryogenics 38 689
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chen G B, Qiu L M, Zheng J Y, Yan P D, Gan Z H, Bai X, Huang Z X 1997 Cryogenics 37 271
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Chen G B, Zheng J Y, Qiu L M, Bai X, Gan Z H, Yan P D, Yu J P, Jin T, Huang Z X 1997 Cryogenics 37 529
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Qiu L M, He Y L, Gan Z H, Chen G B 2006 AIP Conf. 823 845
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 成渝 2006 硕士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学)
Cheng Y 2006 M. S. Thesis (Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology
[14] 闫磊 2007 硕士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学)
Yan L 2007 M. S. Thesis (Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology
[15] Jiang N, Lindemann U, Giebeler F, Thummes G 2004 Cryogenics 44 809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wang C 2016 Cryocoolers 19 299
[17] Qiu L M, Zhang K H, Dong W Q, Gan Z H, Wang C, Zhang X J 2012 Int. J. Refrig. 35 2332
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Schmidt B, Vorholzer M, Dietrich M, Falter J, Schirmeisen A, Thummes G 2017 Cryogenics 88 129
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Schmidt J A, Schmidt B, Dietzel D, Falter J, Thummes G, Schirmeisen A 2022 Cryogenics 122 103417
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Japanese 4 K Two-stage GM Type Pulse Tube Cryocoolers https://www.shicryogenics.com/products/cryocoolers/ [2023-6-29
[21] American 4 K Two-Stage GM Type Pluse Tube Cryocoolers https://www.cryomech.com/cryocoolers/pulse-tube-cryocoolers/ [2023-6-29
[22] Wang C 1997 Cryogenics 37 207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wang C 1997 Cryogenics 37 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang C, Thummes G, Heiden C 1997 Cryogenics 37 159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Qiu L M, Thummes G 2002 Adv. Cryog. Eng. 47 625
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Qiu L M, Thummes G 2002 Cryogenics 42 327
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Kim K, Zhi X Q, Qiu L, Nie H L, Wang J J 2017 Int. J. Refrig. 77 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Liu X M, Chen L B, Wu X L, Yang B, Wang J, Zhu W X, Wang J J, Zhou Y 2020 Sci. China Technol. Sci. 63 434
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Gedeon D 2016 Sage User’s Guide: Stirling, Pulse-Tube and Low-T Cooler Model Classes v11 Edition (Athens: Gedeon Associates) p6
[30] 戴巍, 罗二仓 2005 低温工程 144 24
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dai W, Luo E C 2005 Cryog. Eng. 144 24
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Pan C Z, Zhang T, Zhou Y, Wang J J 2016 Cryogenics 77 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 4 K GM型脉冲管制冷机主要结构参数
Table 1. Main structural parameters of the 4 K GM-type pulse tube cryocooler.
参数 数值 一级回热器外径/长度/(mm/mm) 60/210 一级脉冲管外径/长度/(mm/mm) 44/210 一级气库容积/L 3 二级回热器外径/长度/(mm/mm) 33/210 二级脉冲管外径/长度/(mm/mm) 25/450 二级气库容积/L 3 表 2 与其他同类主流制冷机产品比较
Table 2. Comparison with mainstream products of 4 K GM-type pulse tube cryocoolers.
生产厂商 降温
时间/h最低
温度/K制冷量 Sumitomo RP-182 B2 S 2 < 2.8 1.5 W@4.2 K Cryomech PT415* 2 2.8 1.35 W@4.2 K 本文 3 3.1 0.8 W@4.2 K 注: *表示阀分离型 -
[1] 俎红叶, 程维军, 王亚男, 王晓涛, 李珂, 戴巍 2023 72 080701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zu H Y, Cheng W J, Wang Y N, Wang X T, Li K, Dai W 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 080701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Yang B, Gao Z Z, Xi X T, Chen L B, Wang J J 2022 J. Low Temp. Phys. 206 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Radebaugh R 2009 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 21 164219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Gifford W, Longsworth R 1964 J. Eng. Ind. 86 264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Radebaugh R 1990 Adv. Cryog. Eng. 35 1191
[6] Matsubara Y, Gao J L 1994 Cryogenics 34 259
[7] Tanida K, Gao J L, Yoshimura N, Matsubara Y 1996 Adv. Cryog. Eng. 41 1503
[8] Wang C, Thummes G, Heiden C 1997 Cryogenics 37 857
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wang C, Heiden C, Thummes G 1998 Cryogenics 38 689
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chen G B, Qiu L M, Zheng J Y, Yan P D, Gan Z H, Bai X, Huang Z X 1997 Cryogenics 37 271
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Chen G B, Zheng J Y, Qiu L M, Bai X, Gan Z H, Yan P D, Yu J P, Jin T, Huang Z X 1997 Cryogenics 37 529
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Qiu L M, He Y L, Gan Z H, Chen G B 2006 AIP Conf. 823 845
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 成渝 2006 硕士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学)
Cheng Y 2006 M. S. Thesis (Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology
[14] 闫磊 2007 硕士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学)
Yan L 2007 M. S. Thesis (Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology
[15] Jiang N, Lindemann U, Giebeler F, Thummes G 2004 Cryogenics 44 809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wang C 2016 Cryocoolers 19 299
[17] Qiu L M, Zhang K H, Dong W Q, Gan Z H, Wang C, Zhang X J 2012 Int. J. Refrig. 35 2332
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Schmidt B, Vorholzer M, Dietrich M, Falter J, Schirmeisen A, Thummes G 2017 Cryogenics 88 129
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Schmidt J A, Schmidt B, Dietzel D, Falter J, Thummes G, Schirmeisen A 2022 Cryogenics 122 103417
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Japanese 4 K Two-stage GM Type Pulse Tube Cryocoolers https://www.shicryogenics.com/products/cryocoolers/ [2023-6-29
[21] American 4 K Two-Stage GM Type Pluse Tube Cryocoolers https://www.cryomech.com/cryocoolers/pulse-tube-cryocoolers/ [2023-6-29
[22] Wang C 1997 Cryogenics 37 207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wang C 1997 Cryogenics 37 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang C, Thummes G, Heiden C 1997 Cryogenics 37 159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Qiu L M, Thummes G 2002 Adv. Cryog. Eng. 47 625
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Qiu L M, Thummes G 2002 Cryogenics 42 327
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Kim K, Zhi X Q, Qiu L, Nie H L, Wang J J 2017 Int. J. Refrig. 77 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Liu X M, Chen L B, Wu X L, Yang B, Wang J, Zhu W X, Wang J J, Zhou Y 2020 Sci. China Technol. Sci. 63 434
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Gedeon D 2016 Sage User’s Guide: Stirling, Pulse-Tube and Low-T Cooler Model Classes v11 Edition (Athens: Gedeon Associates) p6
[30] 戴巍, 罗二仓 2005 低温工程 144 24
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dai W, Luo E C 2005 Cryog. Eng. 144 24
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Pan C Z, Zhang T, Zhou Y, Wang J J 2016 Cryogenics 77 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 10699
- PDF Downloads: 375
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: