-
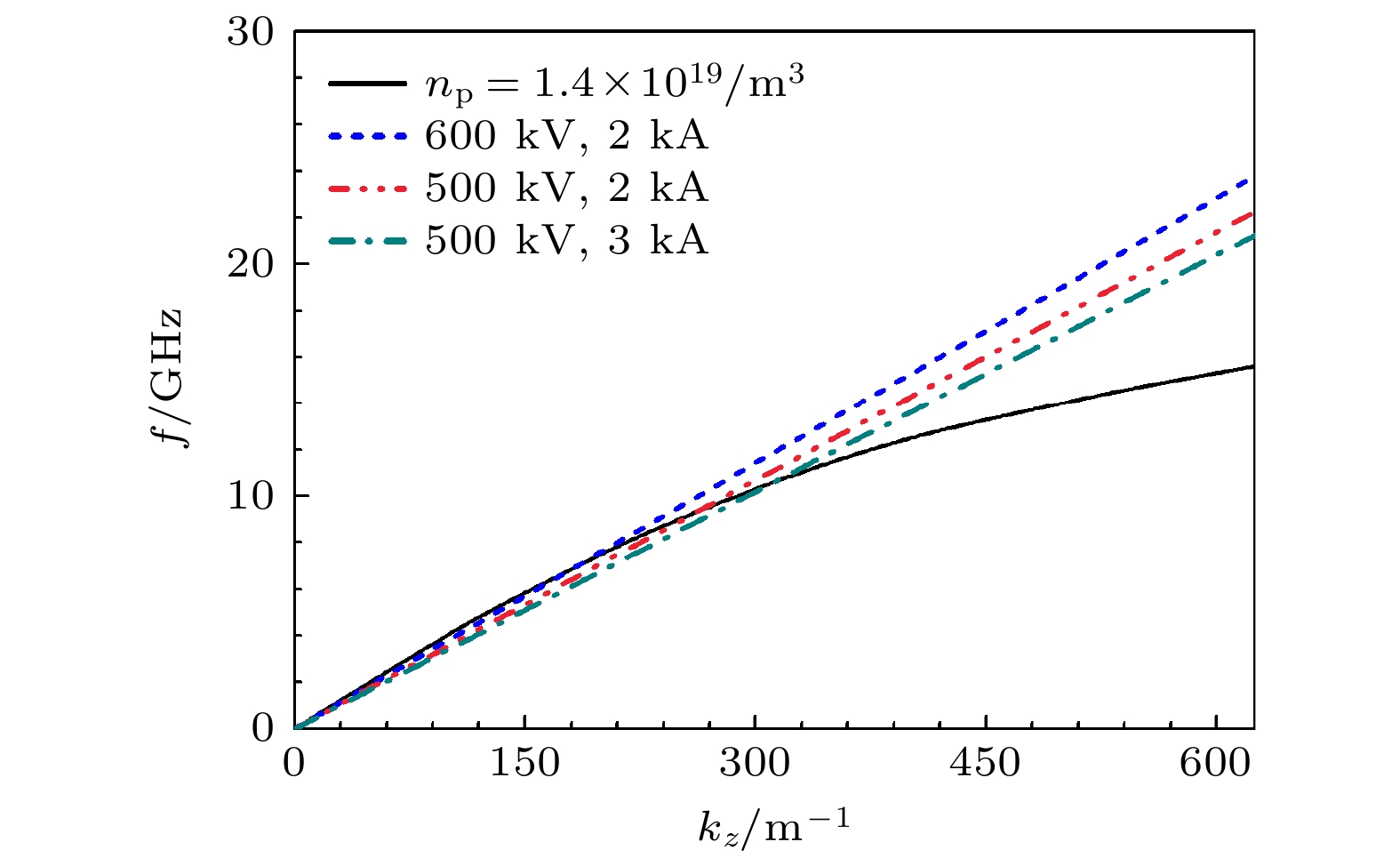
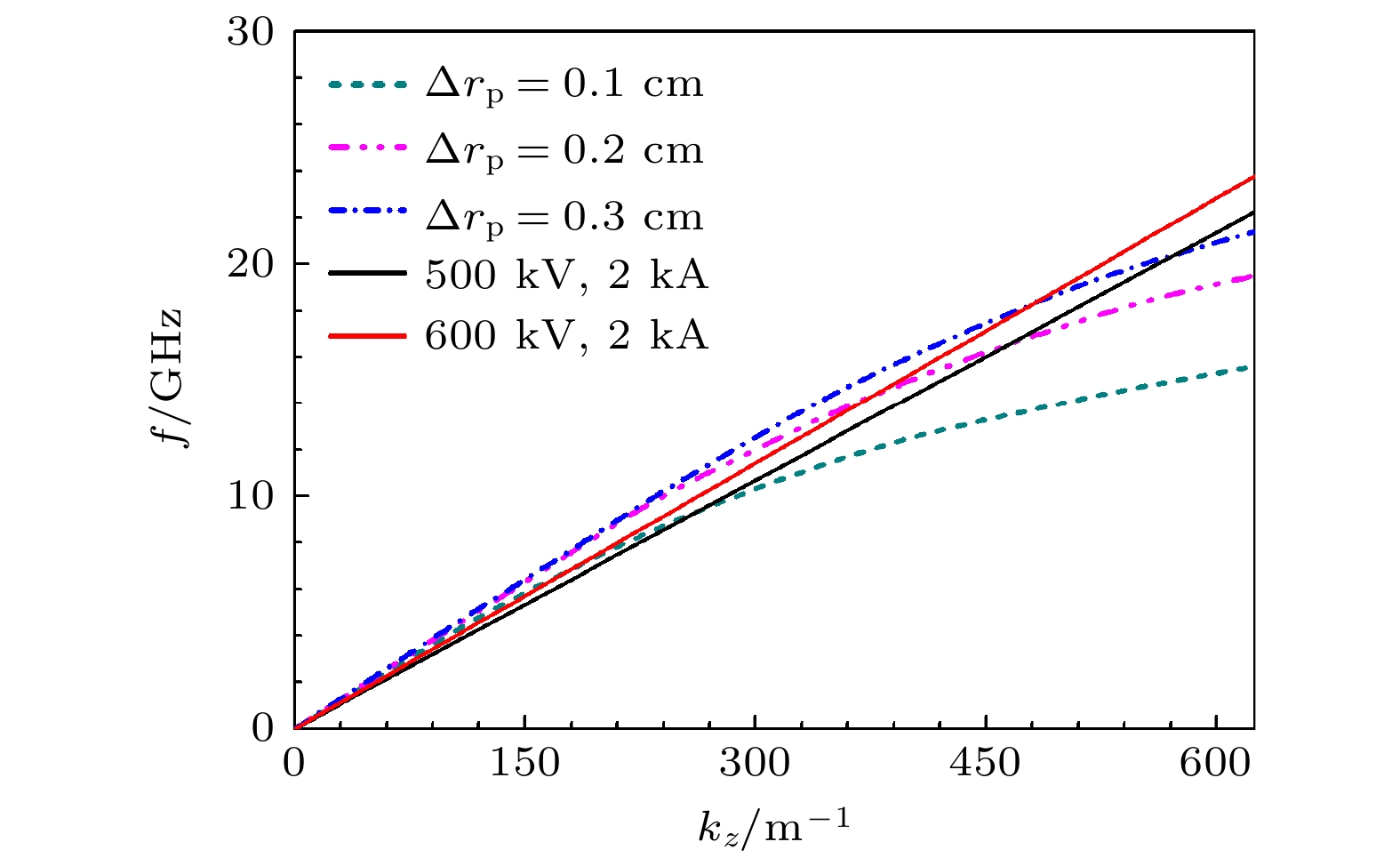
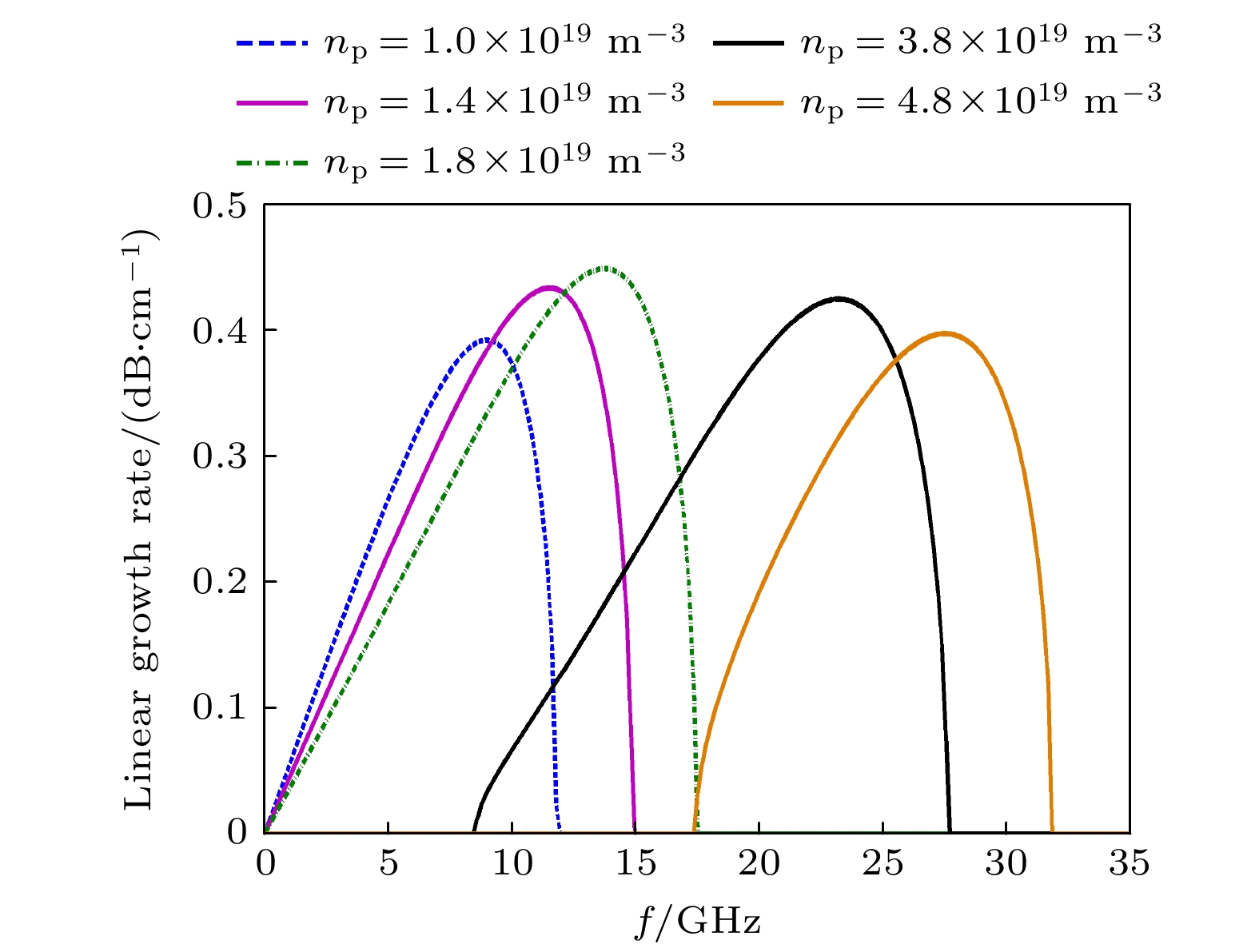
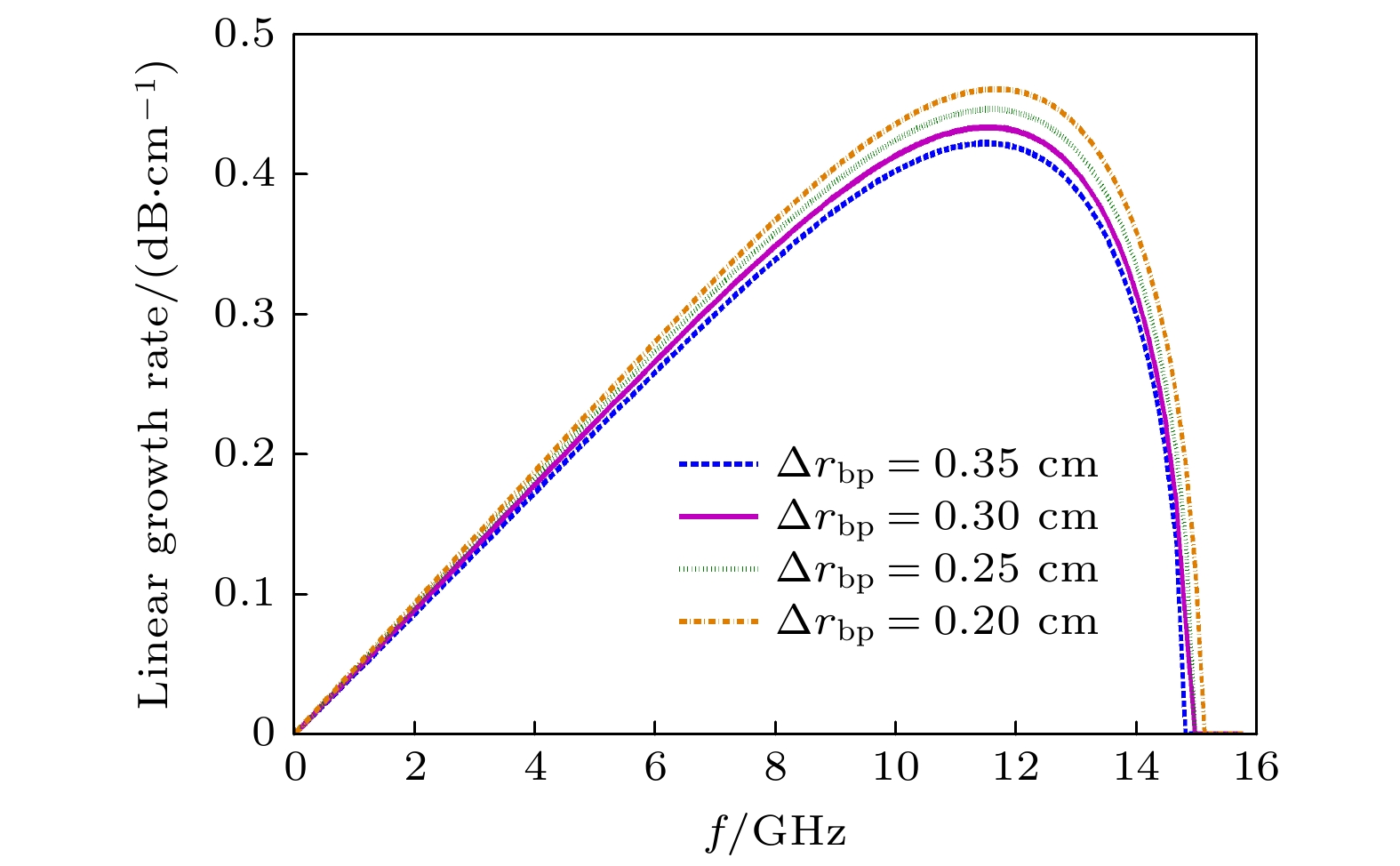
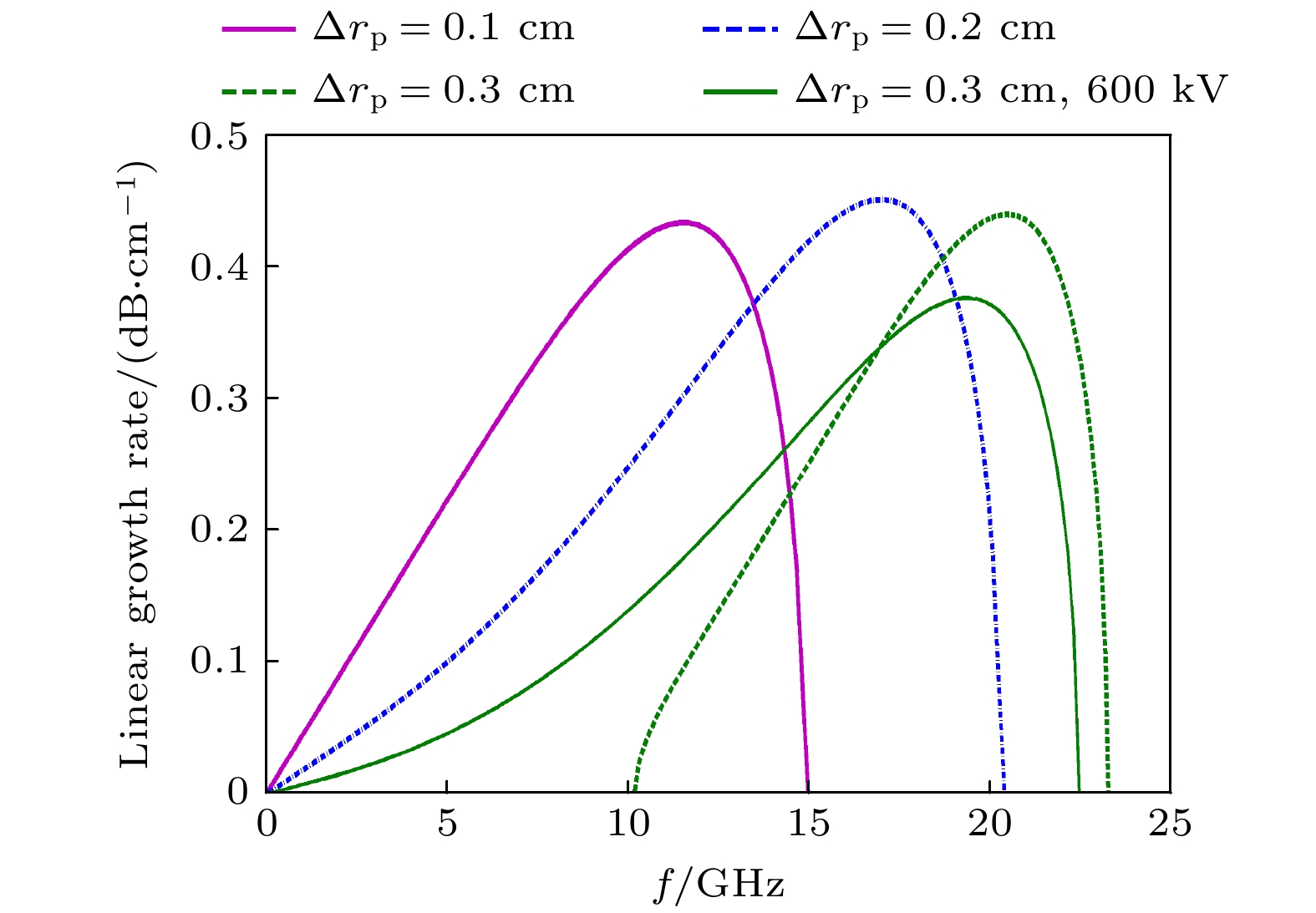
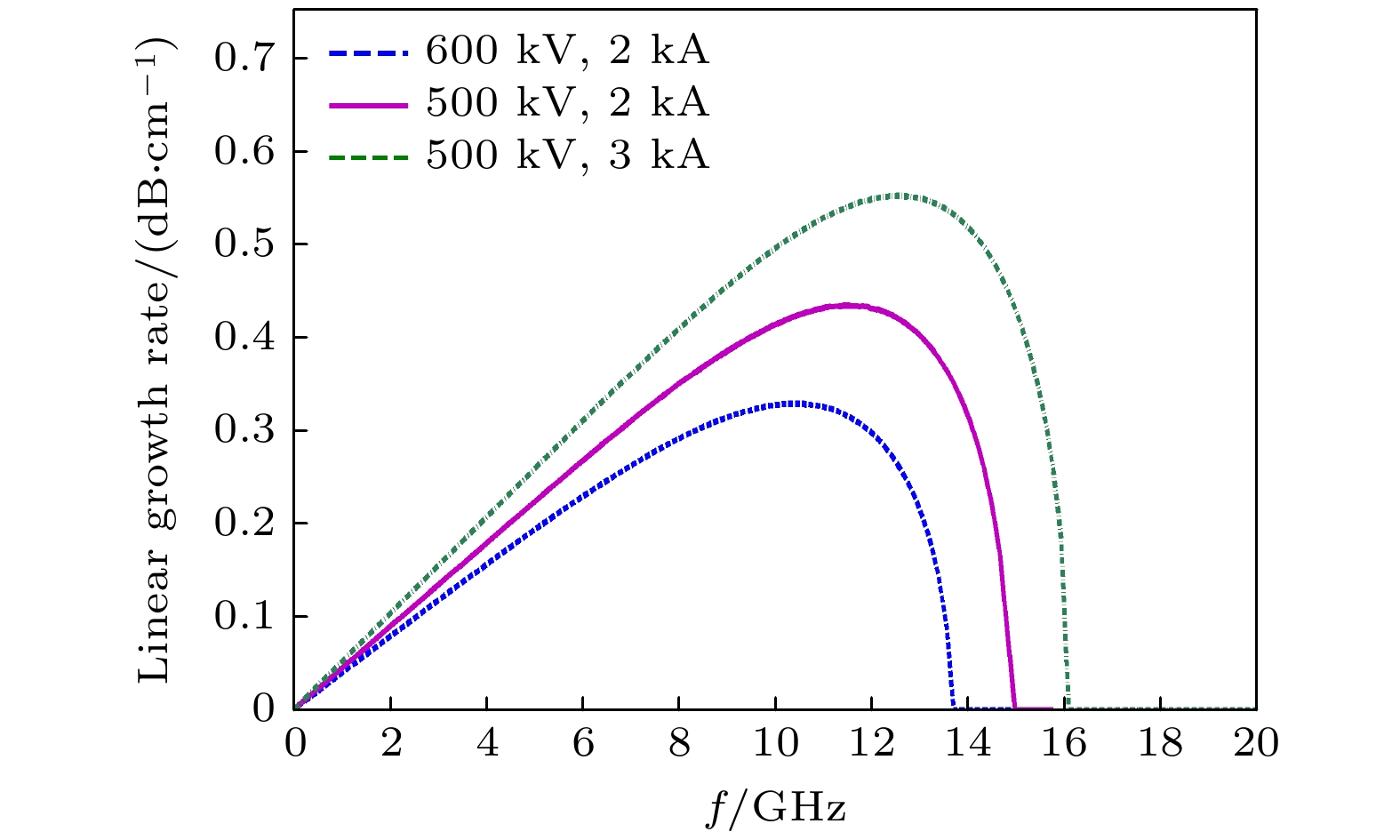
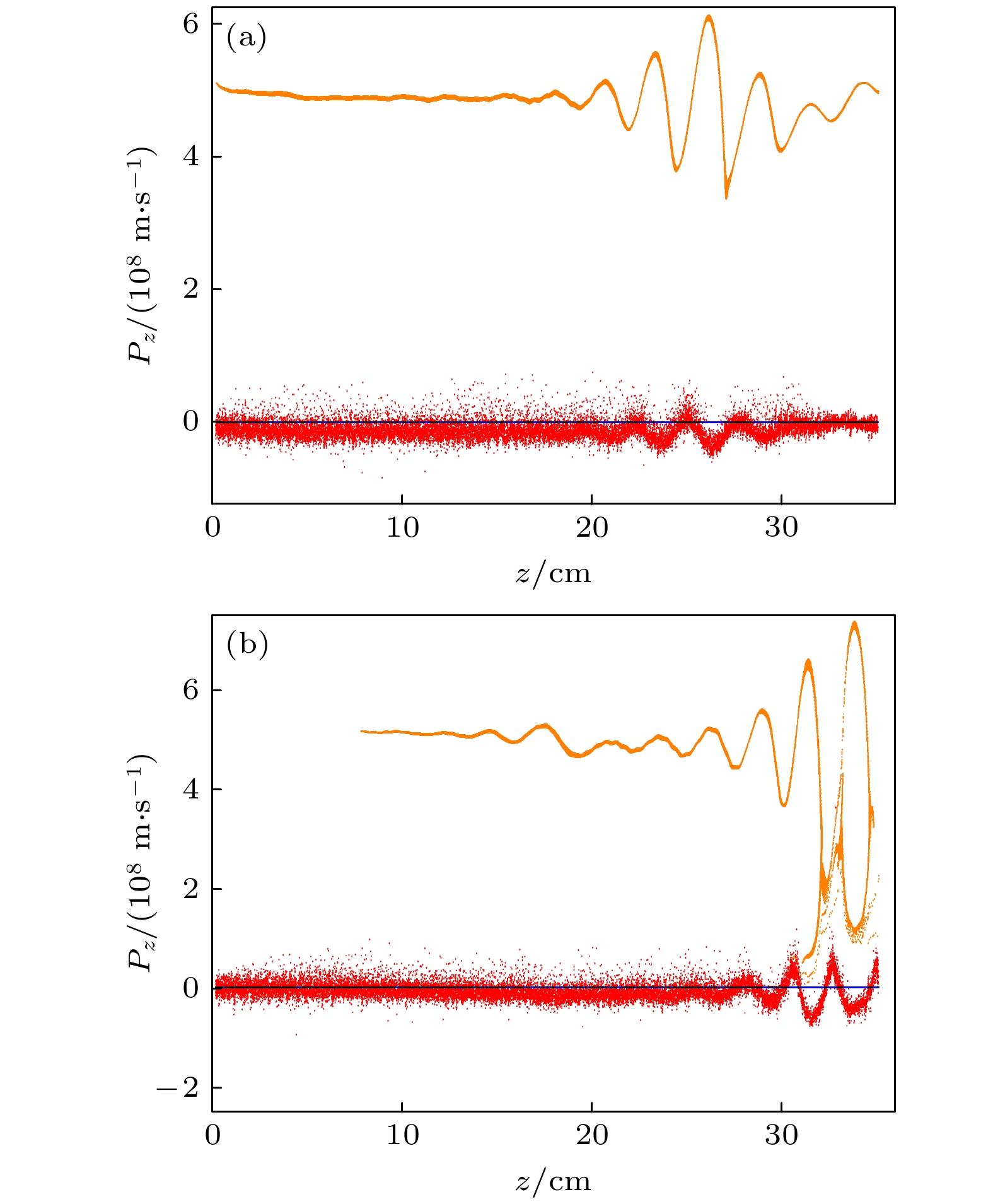
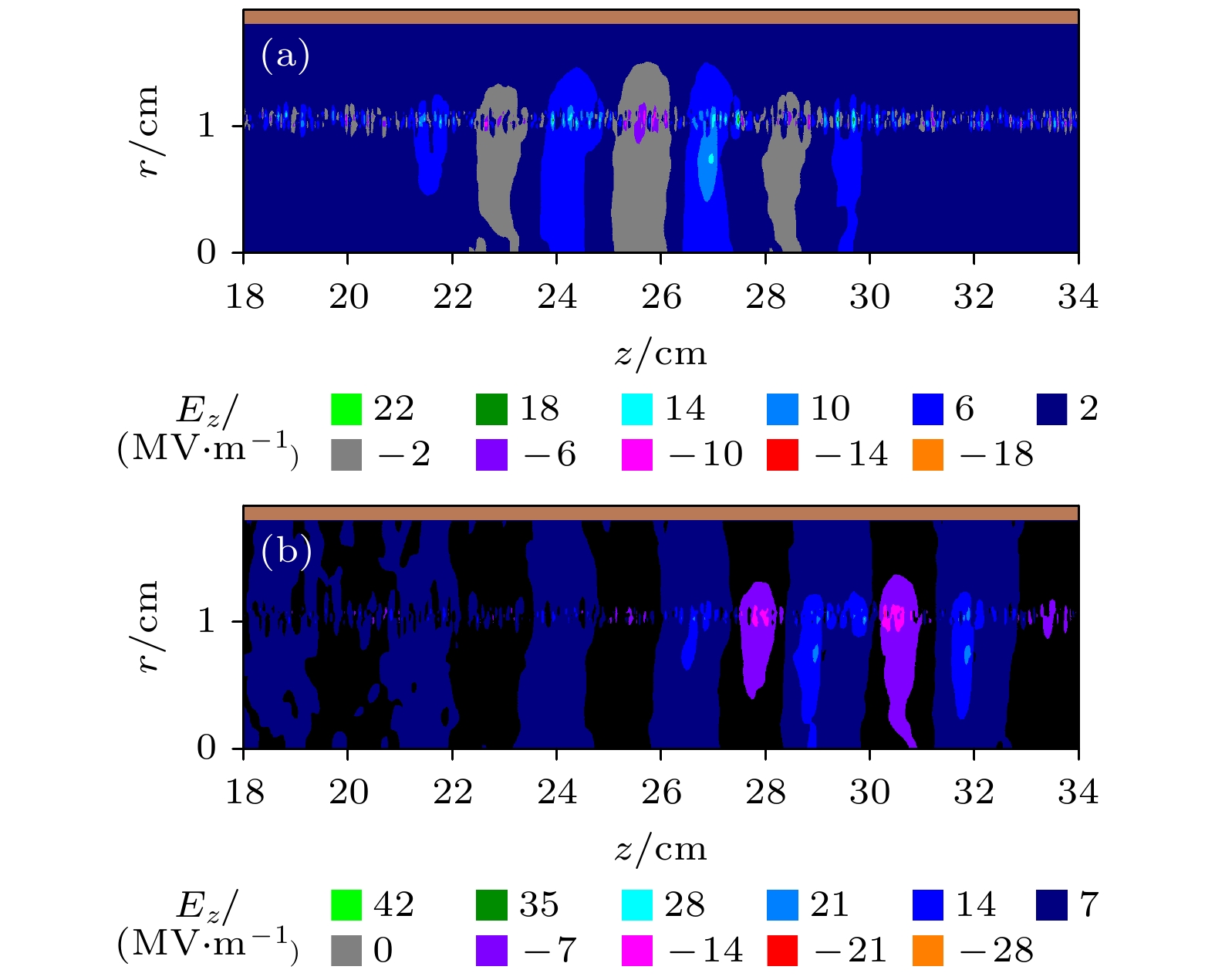
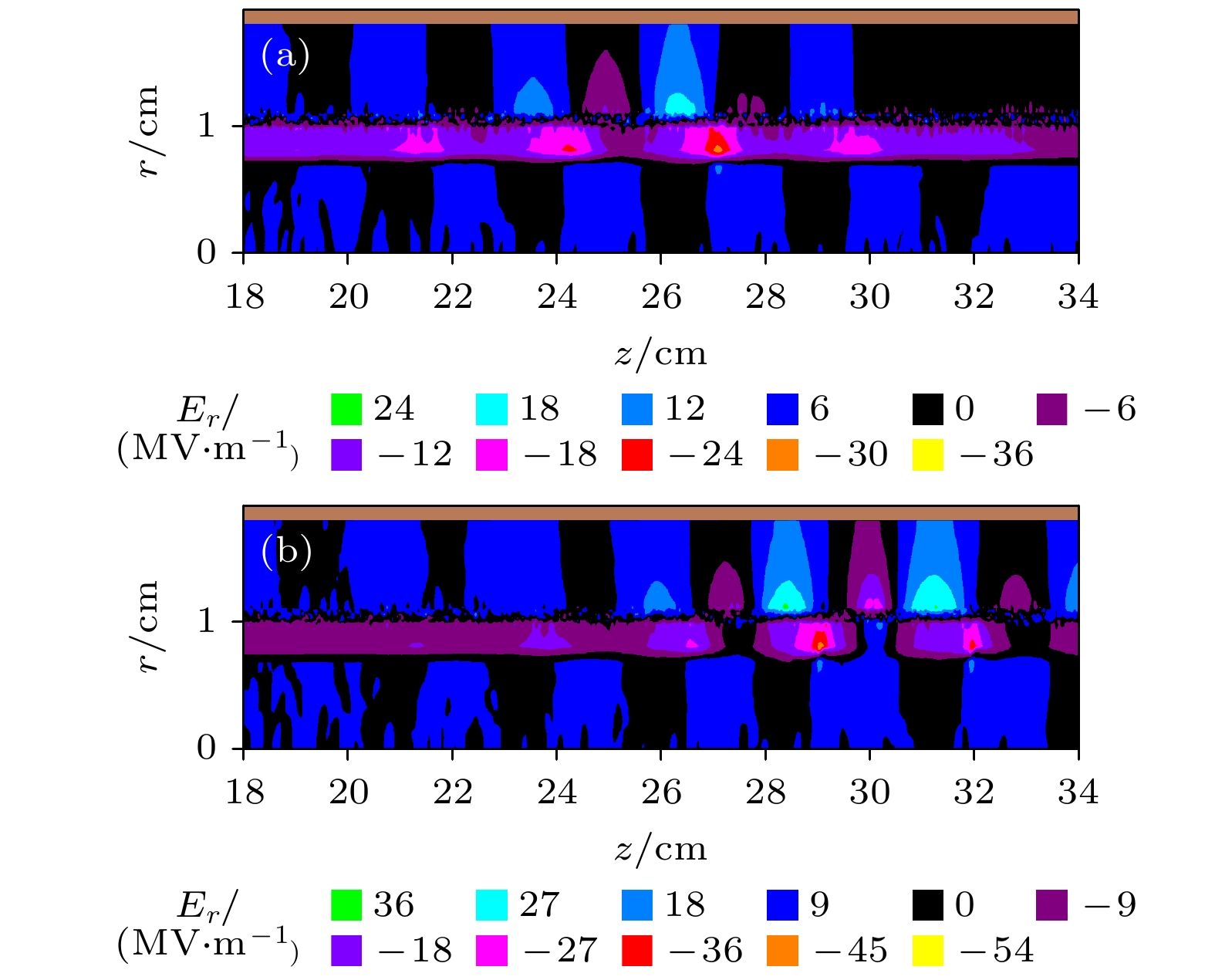
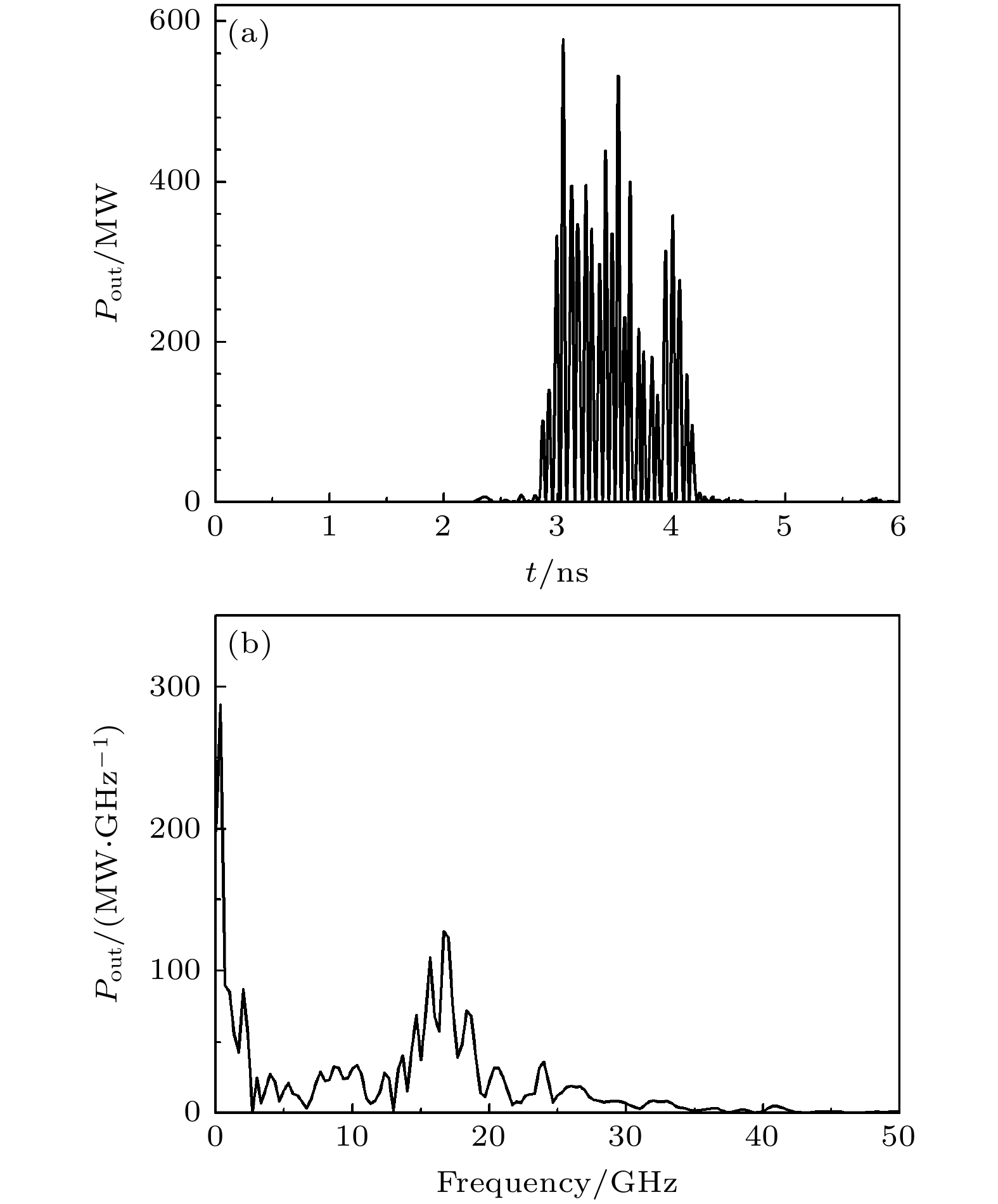
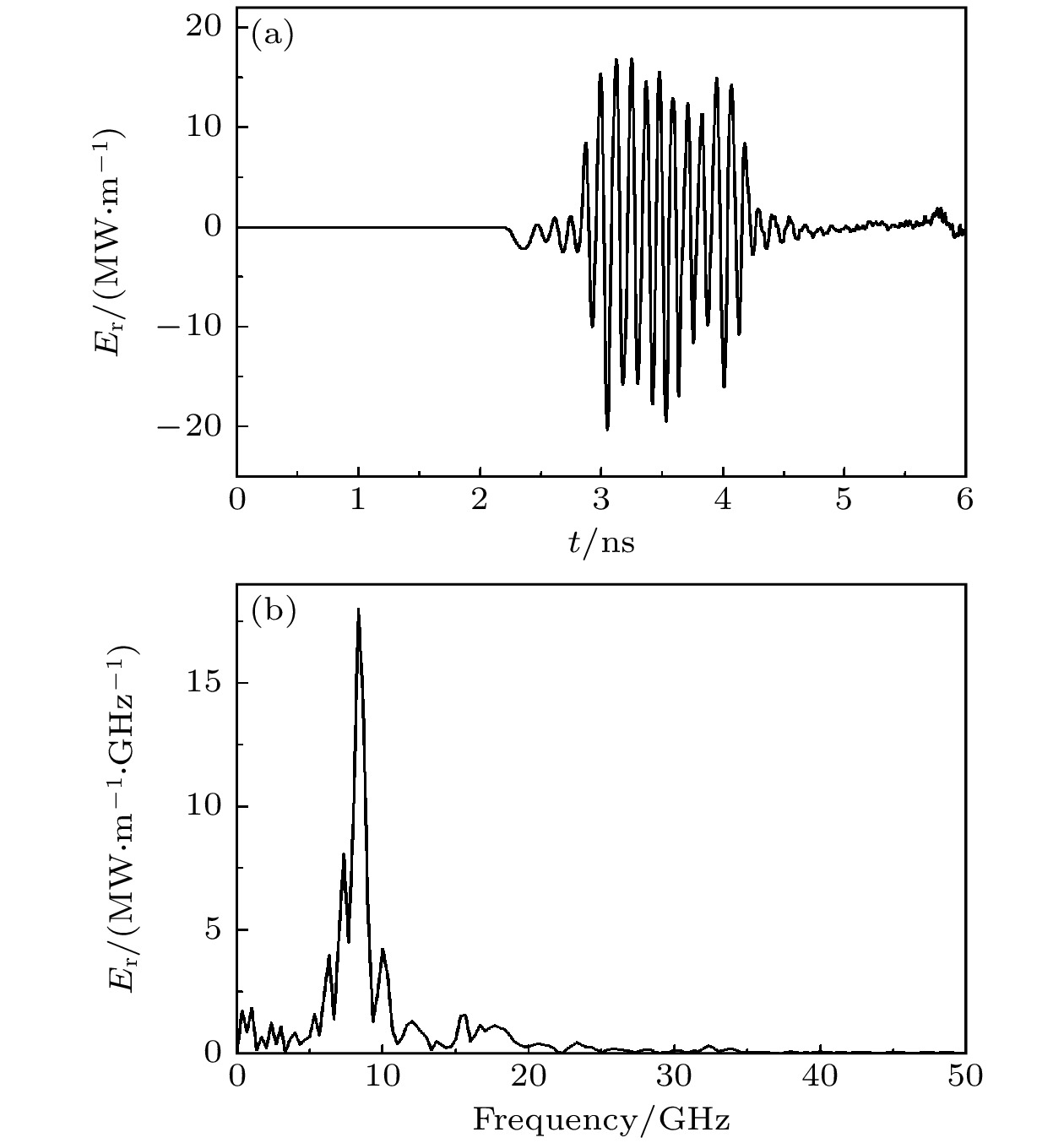
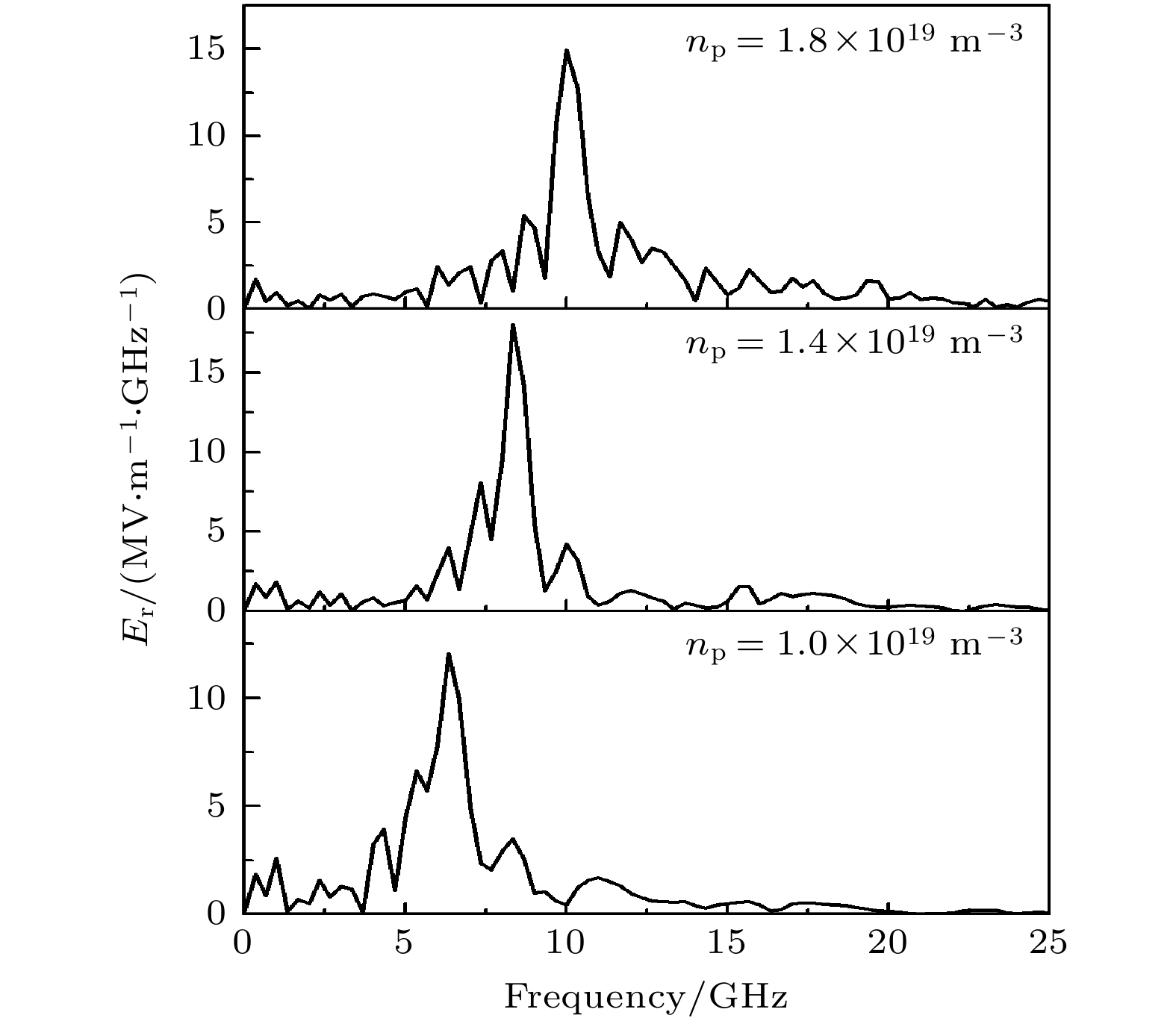
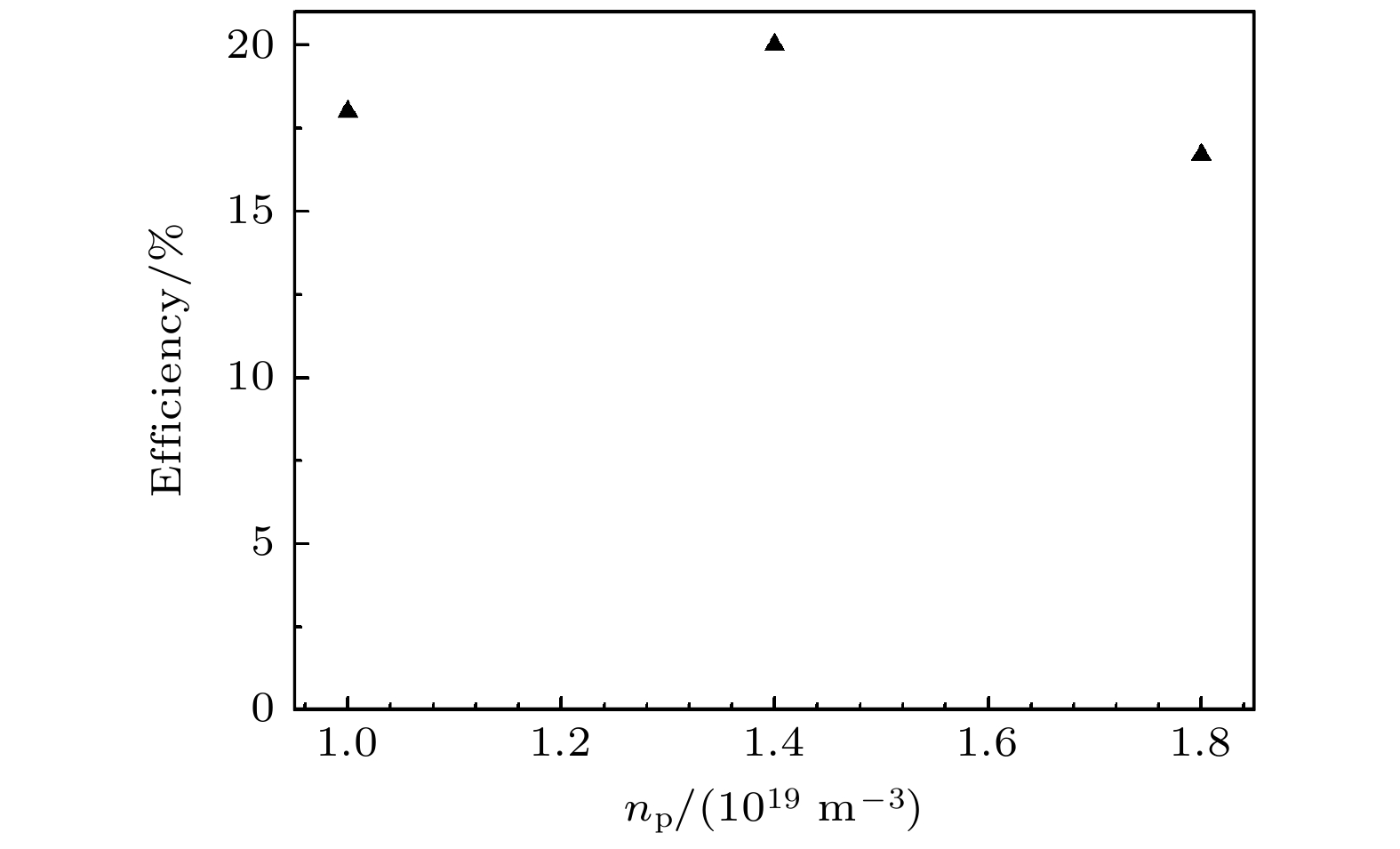
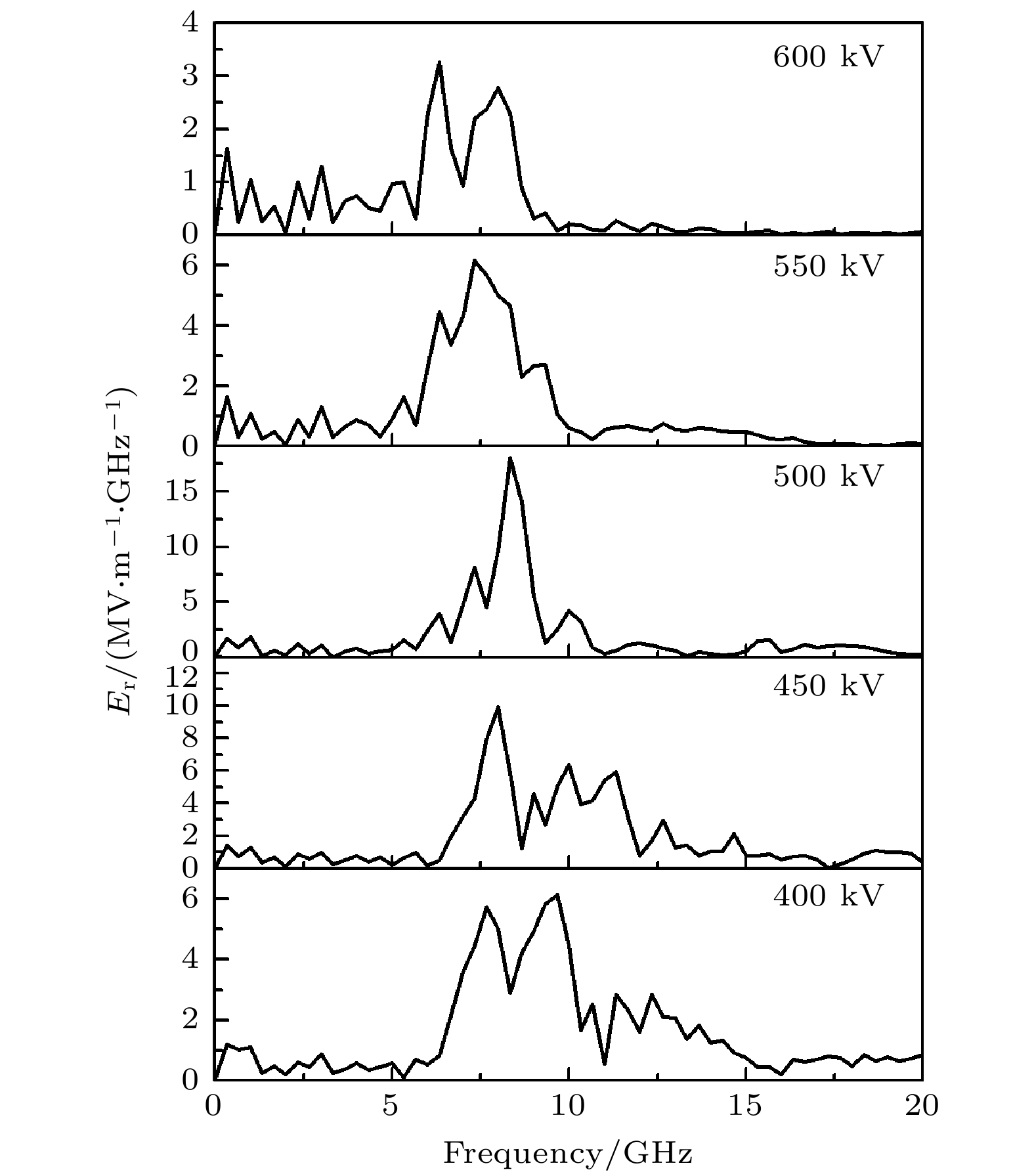
The physical mechanism and output properties of the plasma relativistic microwave noise amplifier (PRNA) are studied numerically by using the all electromagnetic particle-in-cell (PIC) code. Firstly, the dispersion relation between the operating mode and the slow space charge wave of relativistic electron beam without coupling is simulated and analyzed. Simulation results show that both the plasma density np and radial thickness Δrp affect the dispersion characteristics markedly and their increasing can lead the frequency at the beam-wave resonant point to be enhanced. The beam voltage and current also affect the resonant frequency, but the effect is relatively slight. Secondly, variation of the linear growth rate and the bandwidth are then evaluated by using the linear theory. Calculations show that the PRNA has the virtue of wideband output. Its bandwidth can reach a GHz level. By adjusting the plasma parameters np and Δrp, the relativistic electron beam voltage and current, the operating frequency can be tuned over a wide frequency range. Therefore the PRNA also has virtue of fine frequency tunability. Based on the above calculation results, the whole PIC simulations of the PRNA are then carried out to verify the virtues of wideband microwave output and frequency tunability. The basic features of the field distributions of the operating in the evolution process and out coupling process are given. The bunching process and the energy release process of relativistic electron beam are also plotted. Simulations show that with a plasma density of 1.4×1019 /m3, beam voltage and current of 500 kV and 2 kA and applied magnetic field of 2.0 T, 200 MW output microwave with efficiency about 20% can be obtained. The frequency ranges from about 7.0 to 9.0 GHz, the band width reaches 2 GHz. And the output mode is the TEM mode of the coaxial waveguide. Both np and Δrp affect the dispersion relations markedly and the output frequency increases clearly with np and Δrp increasing. The influence of beam voltage and current on the output frequency are both relatively small and the gap distance between the plasma and electron beam has little effect on the output frequency. The research results will provide useful reference for further designing the PRNA.
-
Keywords:
- relativistic microwave noise amplifier /
- plasma /
- dispersion relation /
- numerical simulation
[1] Kuzelev M V, Mukhametzyanov F Kh, Rabinovich M S, Rukhadze A A, Strelkov P S, Shkvarunets A G 1982 Sov. Phys. JETP 56 780
[2] Kuzelev M V, Loza O T, Ponomarev A V, Rukhadze A A, Strelkov P S, Shkvarunets A G, Ulyanov D K 1996 Sov. Phys. JETP 82 1102
[3] Bogdankevich L S, Kuzelev M V, Rukhadze A A 1981 Sov. Phys. Usp. 24 1
[4] Kuzelev M V, Rukhadze A A 2000 Plasma Phys. Rep. 26 231
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Carmel Y, Lou W R, Antonsen Jr T M, Rodgers J, Levush B, Destler W W, Granatstein V L 1992 Phys. Fluids B 4 2286
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Shkvarunets A G, Kobayashi S, Weaver J, Carmel Y, Rodgers J, Antonsen Jr T M, Granatstein V L, Destler W W, Ogura K, Minami K 1996 Phys. Rev. E 53 2045
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 王宇, 陈再高, 雷奕安 2013 62 125204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y, Chen Z G, Lei Y A 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 125204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ponomarev A V, Strelkov P S, Shkvarunets A G 1998 Plasma Phys. Rep. 24 48
[9] Strelkov P S, Ul’yanov D K 2000 Plasma Phys. Rep. 26 303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Barker R J, Schamiloglu E 2001 High-Power Microwaves Sources and Technologies (New York: Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineer, Inc.) pp25–27
[11] Prather W D, Baum C E, Torres R J, Sabath F, Nitsch D 2004 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 46 335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 黄裕年, 任国光 2002 微波学报 18 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huan Y N, Ren G G 2002 J. Microwaves 18 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Strelkov P S, Tarakanov V P, Mikh D E D, Ivanov I E, Shumeiko D V 2019 Plasma Phys. Rep. 45 345
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Ernyleva S E, Litvin V O, Loza O T, Bogdankevich I L 2013 Prob. At. Sci. Technol. 2013 3
[15] Ernyleva S E, Litvin V O, Loza O T, Bogdankevich I L 2014 Tech. Phys. 59 1228
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ernyleva S E, Loza O T 2017 Phys. Wave Phenom. 25 56
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Ulyanov D K, Bogdankevich I L, Ernyleva S E, Andreev S E 2019 Plasma Phys. Rep. 45 980
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Kartashov I N, Kuzelev M V 2021 Plasma Phys. Rep. 47 548
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Buleyko A B, Ponomarev A V, Loza O T, Ulyanov D K, Andreev S E 2021 Phys. Plasmas 28 023303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Buleyko A B, Ponomarev A V, Loza O T, Ulyanov D K, Sharypov K A, Shunailov S A, Yalandin M I 2021 Phys. Plasmas 28 023304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Kuzelev M V, Loza O T, Rukhadze A A, Strelkov P S, Shkvarunets A G 2001 Plasma Phys. Rep. 27 669
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] Kuzelev M V, Mukhametzyanov F Kh, Rabinovich M S, Rukhadze A A, Strelkov P S, Shkvarunets A G 1982 Sov. Phys. JETP 56 780
[2] Kuzelev M V, Loza O T, Ponomarev A V, Rukhadze A A, Strelkov P S, Shkvarunets A G, Ulyanov D K 1996 Sov. Phys. JETP 82 1102
[3] Bogdankevich L S, Kuzelev M V, Rukhadze A A 1981 Sov. Phys. Usp. 24 1
[4] Kuzelev M V, Rukhadze A A 2000 Plasma Phys. Rep. 26 231
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Carmel Y, Lou W R, Antonsen Jr T M, Rodgers J, Levush B, Destler W W, Granatstein V L 1992 Phys. Fluids B 4 2286
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Shkvarunets A G, Kobayashi S, Weaver J, Carmel Y, Rodgers J, Antonsen Jr T M, Granatstein V L, Destler W W, Ogura K, Minami K 1996 Phys. Rev. E 53 2045
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 王宇, 陈再高, 雷奕安 2013 62 125204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y, Chen Z G, Lei Y A 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 125204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ponomarev A V, Strelkov P S, Shkvarunets A G 1998 Plasma Phys. Rep. 24 48
[9] Strelkov P S, Ul’yanov D K 2000 Plasma Phys. Rep. 26 303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Barker R J, Schamiloglu E 2001 High-Power Microwaves Sources and Technologies (New York: Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineer, Inc.) pp25–27
[11] Prather W D, Baum C E, Torres R J, Sabath F, Nitsch D 2004 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 46 335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 黄裕年, 任国光 2002 微波学报 18 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huan Y N, Ren G G 2002 J. Microwaves 18 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Strelkov P S, Tarakanov V P, Mikh D E D, Ivanov I E, Shumeiko D V 2019 Plasma Phys. Rep. 45 345
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Ernyleva S E, Litvin V O, Loza O T, Bogdankevich I L 2013 Prob. At. Sci. Technol. 2013 3
[15] Ernyleva S E, Litvin V O, Loza O T, Bogdankevich I L 2014 Tech. Phys. 59 1228
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ernyleva S E, Loza O T 2017 Phys. Wave Phenom. 25 56
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Ulyanov D K, Bogdankevich I L, Ernyleva S E, Andreev S E 2019 Plasma Phys. Rep. 45 980
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Kartashov I N, Kuzelev M V 2021 Plasma Phys. Rep. 47 548
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Buleyko A B, Ponomarev A V, Loza O T, Ulyanov D K, Andreev S E 2021 Phys. Plasmas 28 023303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Buleyko A B, Ponomarev A V, Loza O T, Ulyanov D K, Sharypov K A, Shunailov S A, Yalandin M I 2021 Phys. Plasmas 28 023304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Kuzelev M V, Loza O T, Rukhadze A A, Strelkov P S, Shkvarunets A G 2001 Plasma Phys. Rep. 27 669
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 6418
- PDF Downloads: 65
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: