-
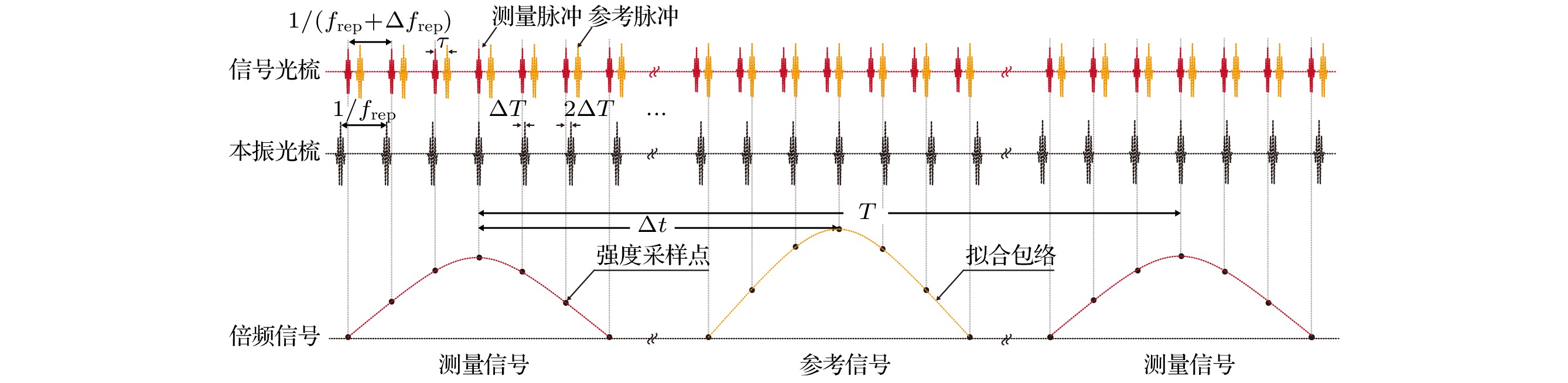
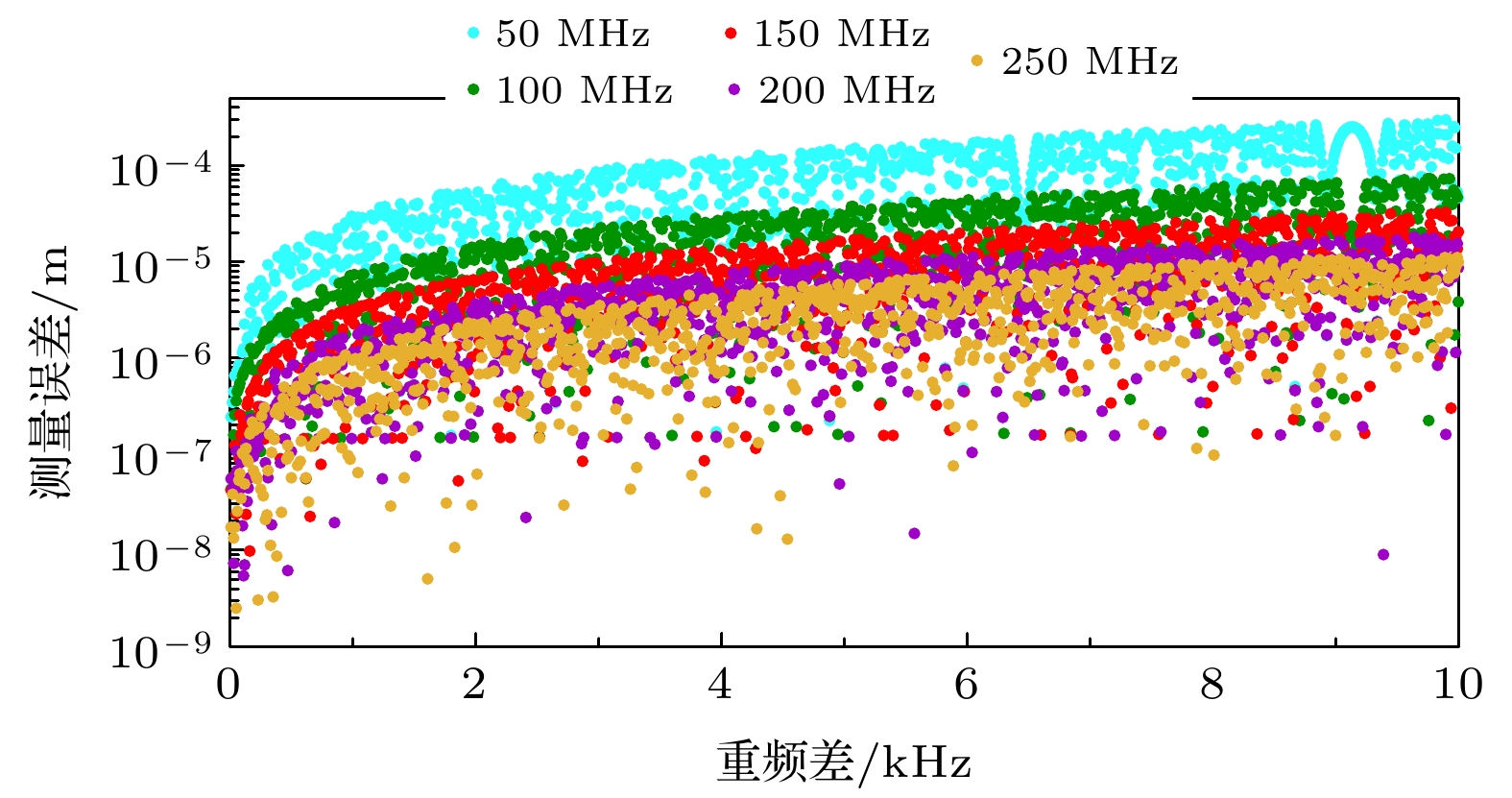
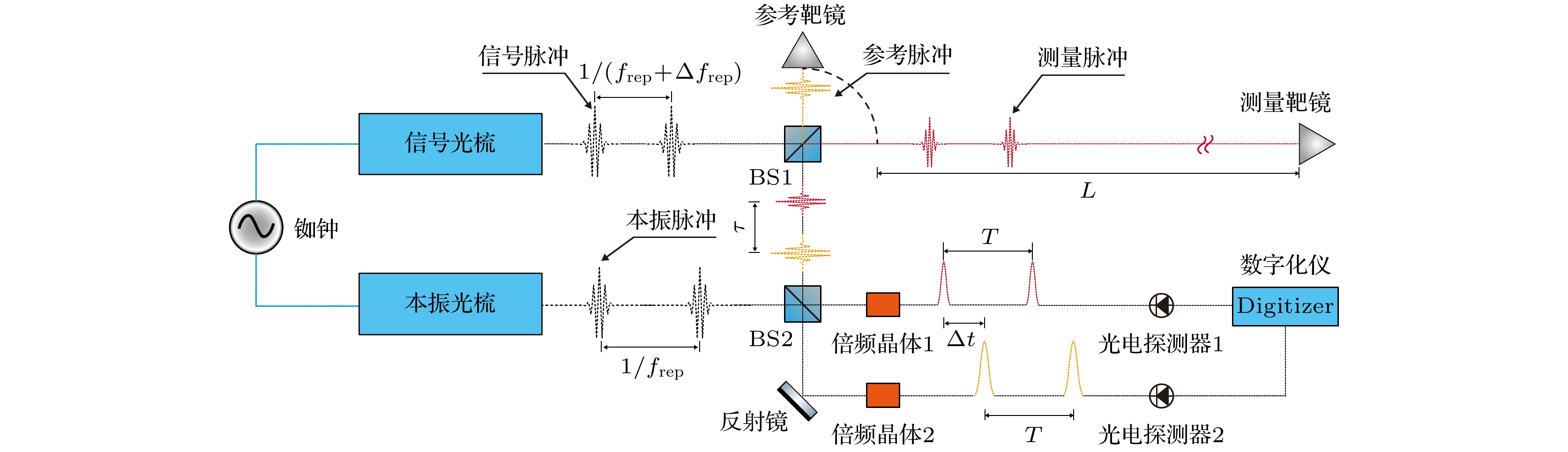
Absolute distance measurement based on the asynchronous optical sampling with using a dual-comb system has the characteristics of large range, fast measurement speed, and high accuracy, which has wide application prospects in the field of precision measurement of geometric quantities, such as the space technology, equipment manufacturing, etc. Recently, the invention of the femtosecond frequency comb is a milestone in the field of precision length measurement. Many approaches to the absolute distance measurement have been proposed. Among them, the dual-comb system with asynchronous optical sampling can realize a length measurement with fast speed, high accuracy, and long range. Especially, the temporal method combining the asynchronous optical sampling with nonlinear intensity cross-correlation can effectively avoid influencing of the carrier-envelope offset frequency on the ranging accuracy in the measurement process. The time-of-flight information can be obtained by the time interval between the reference pattern and the measurement pattern. Even so, the selection of the repetition rate and the difference of repetition rates will strongly influence the temporal sampling interval of the measurements. Therefore, the theoretical model and key parameters for the ranging are numerically studied for the non-linear asynchronous optical sampling by using a dual-comb system of absolute distance measurement. After analysis, the effects of source parameters (repetition frequency and repetition frequency difference), fine fitting of second harmonic signal, and timing jitter on ranging accuracy are studied respectively. The numerical analysis results show that the method of choosing a reasonable repetition frequency and repetition frequency difference is beneficial to the improvement of the ranging accuracy. When the sampling interval of the dual-comb system is a constant, the time value between the reference and measurement patterns can be obtained by the interpolation method of fine curve fitting, and it will further improve the ranging accuracy. In addition, the time jitter of the femtosecond pulses is also an important factor that can affect the ranging accuracy. By changing the difference in the repetition rate, the measurement speed can also be improved. After that, the cumulative ranging error caused by time jitter can be reduced. Therefore, the appropriate increasing of measurement speed can effectively reduce the influence of timing jitter on ranging.
-
Keywords:
- absolute distance measurement /
- optical frequency comb /
- asynchronous optical sampling /
- numerical analysis
[1] Schmitt R H, Peterek M, Morse E, Knapp W, Galetto M, Härtig F, Goch G, Hughes B, Forbes A, Estler W T 2016 CIRP Ann. -Manuf. Techn. 65 643
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 谭久彬 2020 中国工业和信息化 6 18
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tan J B 2020 China Ind. Inf. Technol. 6 18
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 郑联语, 朱绪胜, 姜丽萍 2013 航空制造技术 7 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zheng L Y, Zhu X S, Jiang L P 2013 Aeron. Manuf. Technol. 7 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 华卿, 周维虎, 许艳 2012 计测技术 32 1
Hua Q, Zhou W H, Xu Y 2012 Metrol. Meas. Technol. 32 1
[5] Hansch T W 2006 Rev. Mod. Phys. 78 1297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Hall J L 2006 Rev. Mod. Phys. 78 1279
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 张伟鹏, 杨宏雷, 陈馨怡, 尉昊赟, 李岩 2018 67 090701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang W P, Yang H L, Chen X Y, Yu H Y, Li Y 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 090701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhang R, Zhu Z, Wu G 2019 Opt. Express 27 34269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Liu Y, Lin J, Yang L, Wang Y, Zhu J 2018 Opt. Express 26 26618
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 王国超, 颜树华, 杨俊, 林存宝, 杨东兴, 邹鹏飞 2013 62 070601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang G C, Yan S H, Yang J, Lin C B, Yang D X, Zou P F 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 070601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 邢书剑, 张福民, 曹士英, 王高文, 曲兴华 2013 62 170603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xing S J, Zhang F M, Cao S Y, Wang G W, Qu X H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 170603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Minoshima K, Matsumoto H 2000 Appl. Optics 39 5512
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Ye J 2004 Opt. Lett. 29 1153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Nam J K, Woo K S 2006 Opt. Express 14 5954
[15] Lee J, Kim Y J, Lee K, Lee S, Kim S W 2010 Nat. Photonics 4 716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 吴翰钟, 曹士英, 张福民, 邢书剑, 曲兴华 2014 63 100601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu H Z, Cao S Y, Zhang F M, Xing S J, Qu X H 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 100601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 刘亭洋, 张福民, 吴翰钟, 李建双, 石永强, 曲兴华 2016 65 020601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu T Y, Zhang F M, Wu H Z, Li J S, Shi Y Q, Qu X H 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 020601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 王国超, 李星辉, 颜树华, 谭立龙, 管文良 2021 70 040601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang G C, Li X H, Yan S H, Tan L L, Guan W L 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 040601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Coddington I, Swann W C, Nenadovic L, Newbury N R 2009 Nat. Photonics 3 351
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Liu T A, Newbury N R, Coddington I 2011 Opt. Express 19 18501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Lee J, Han S, Lee K, Bae E, Kim S, Lee S, Kim S W, Kim Y J 2013 Meas. Sci. Technol. 24 45201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhang H Y, Wei H Y, Wu X J, Yang H L, Li Y 2014 Opt. Express 22 6597
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Shi H S, Song Y J, Liang F, Xu L M, Hu M L, Wang C Y 2015 Opt. Express 23 14057
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Lin B, Zhao X, He M, Pan Y, Chen J, Cao S, Lin Y, Wang Q, Zheng Z, Fang Z 2017 IEEE Photonics J 9 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Li Y, Cai Y, Li R, Shi H, Tian H, He M, Song Y, Hu M 2019 Chin. Opt. Lett. 17 091202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Shiraki E, Nishizawa N 2011 Proceedings of the International Quantum Electronics Conference and Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics Pacific Rim Sydney, Australia, August 28−September 1, 2011 p894
[27] Lazaridis P, Debarge G, Gallion P 1995 Opt. Lett. 20 1160
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Paschotta R 2004 Appl. Phys. B 79 153
[29] Wang Y, Tian H, Ma Y, Song Y, Zhang Z 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 4382
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Benedick A J, Fujimoto J G, Kärtner F X 2012 Nat. Photonics 6 97
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
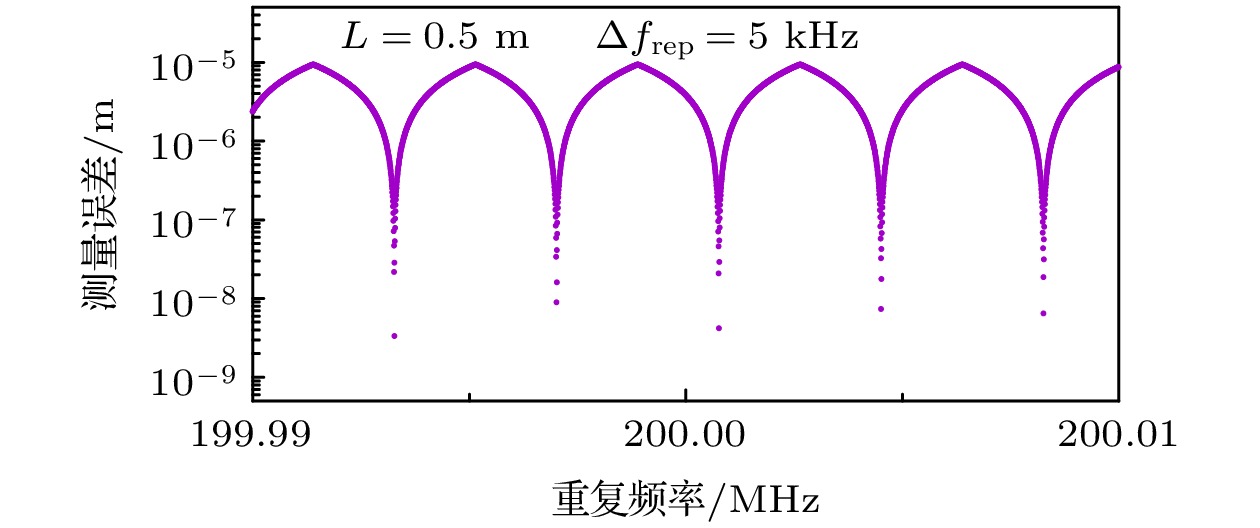
图 5 重频差对仿真测距精度的影响及其现象解释 (a)微调重频差对仿真测距精度的影响; (b)脉冲重合示意图
Figure 5. Effect of repetition frequency difference on the simulated ranging accuracy and its phenomenon explanation; (a) Effect of fine-tuning the repetition frequency difference on the simulated ranging accuracy; (b) schematic of pulse overlap.
表 1 重频差、测距精度与重合因子的关系
Table 1. Relationships among repetition frequency difference, ranging accuracy and overlap factor.
重频差/Hz 测量误差/μm 重合因子n 4981.2 9.163 0.5095 4983.2 4.497 0.7591 4990.8 0.263 0.9859 4999.4 0.052 0.9973 5001.2 7.343 0.3919 5005.4 0.112 0.0059 表 2 重复频率、测距精度与重合因子的关系
Table 2. Relationships among repetition frequency difference, ranging accuracy and overlap factor.
重复频率/MHz 测量误差/μm 重合因子n 199.993275 0.003 0.0002 199.995125 9.254 0.4938 199.996665 0.183 0.9048 199.997020 0.009 0.9995 200.001665 4.482 0.2390 200.007320 4.724 0.7482 表 3 不同时间抖动对仿真测距精度的影响
Table 3. Effect of different timing jitter on simulated ranging accuracy
时间抖动/fs 测量周期/ms 最大标准差/μm 10 0.500 71.252 0.200 48.116 0.125 29.148 1 0.500 6.296 0.200 4.517 0.125 2.431 0.013 0.500 0.069 0.200 0.039 0.125 0.023 -
[1] Schmitt R H, Peterek M, Morse E, Knapp W, Galetto M, Härtig F, Goch G, Hughes B, Forbes A, Estler W T 2016 CIRP Ann. -Manuf. Techn. 65 643
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 谭久彬 2020 中国工业和信息化 6 18
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tan J B 2020 China Ind. Inf. Technol. 6 18
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 郑联语, 朱绪胜, 姜丽萍 2013 航空制造技术 7 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zheng L Y, Zhu X S, Jiang L P 2013 Aeron. Manuf. Technol. 7 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 华卿, 周维虎, 许艳 2012 计测技术 32 1
Hua Q, Zhou W H, Xu Y 2012 Metrol. Meas. Technol. 32 1
[5] Hansch T W 2006 Rev. Mod. Phys. 78 1297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Hall J L 2006 Rev. Mod. Phys. 78 1279
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 张伟鹏, 杨宏雷, 陈馨怡, 尉昊赟, 李岩 2018 67 090701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang W P, Yang H L, Chen X Y, Yu H Y, Li Y 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 090701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhang R, Zhu Z, Wu G 2019 Opt. Express 27 34269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Liu Y, Lin J, Yang L, Wang Y, Zhu J 2018 Opt. Express 26 26618
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 王国超, 颜树华, 杨俊, 林存宝, 杨东兴, 邹鹏飞 2013 62 070601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang G C, Yan S H, Yang J, Lin C B, Yang D X, Zou P F 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 070601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 邢书剑, 张福民, 曹士英, 王高文, 曲兴华 2013 62 170603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xing S J, Zhang F M, Cao S Y, Wang G W, Qu X H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 170603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Minoshima K, Matsumoto H 2000 Appl. Optics 39 5512
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Ye J 2004 Opt. Lett. 29 1153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Nam J K, Woo K S 2006 Opt. Express 14 5954
[15] Lee J, Kim Y J, Lee K, Lee S, Kim S W 2010 Nat. Photonics 4 716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 吴翰钟, 曹士英, 张福民, 邢书剑, 曲兴华 2014 63 100601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu H Z, Cao S Y, Zhang F M, Xing S J, Qu X H 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 100601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 刘亭洋, 张福民, 吴翰钟, 李建双, 石永强, 曲兴华 2016 65 020601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu T Y, Zhang F M, Wu H Z, Li J S, Shi Y Q, Qu X H 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 020601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 王国超, 李星辉, 颜树华, 谭立龙, 管文良 2021 70 040601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang G C, Li X H, Yan S H, Tan L L, Guan W L 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 040601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Coddington I, Swann W C, Nenadovic L, Newbury N R 2009 Nat. Photonics 3 351
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Liu T A, Newbury N R, Coddington I 2011 Opt. Express 19 18501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Lee J, Han S, Lee K, Bae E, Kim S, Lee S, Kim S W, Kim Y J 2013 Meas. Sci. Technol. 24 45201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhang H Y, Wei H Y, Wu X J, Yang H L, Li Y 2014 Opt. Express 22 6597
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Shi H S, Song Y J, Liang F, Xu L M, Hu M L, Wang C Y 2015 Opt. Express 23 14057
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Lin B, Zhao X, He M, Pan Y, Chen J, Cao S, Lin Y, Wang Q, Zheng Z, Fang Z 2017 IEEE Photonics J 9 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Li Y, Cai Y, Li R, Shi H, Tian H, He M, Song Y, Hu M 2019 Chin. Opt. Lett. 17 091202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Shiraki E, Nishizawa N 2011 Proceedings of the International Quantum Electronics Conference and Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics Pacific Rim Sydney, Australia, August 28−September 1, 2011 p894
[27] Lazaridis P, Debarge G, Gallion P 1995 Opt. Lett. 20 1160
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Paschotta R 2004 Appl. Phys. B 79 153
[29] Wang Y, Tian H, Ma Y, Song Y, Zhang Z 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 4382
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Benedick A J, Fujimoto J G, Kärtner F X 2012 Nat. Photonics 6 97
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 11353
- PDF Downloads: 310
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: