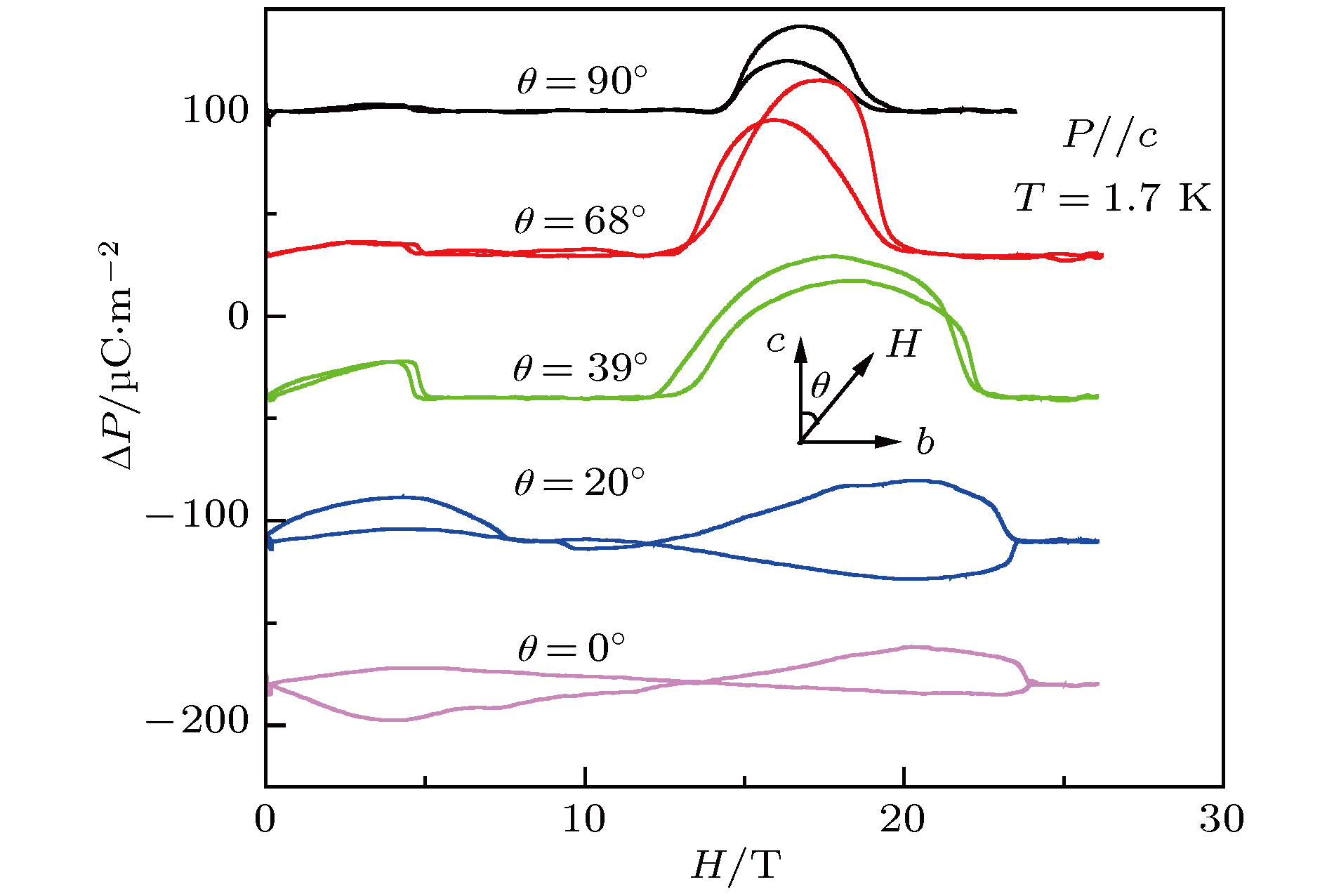
-
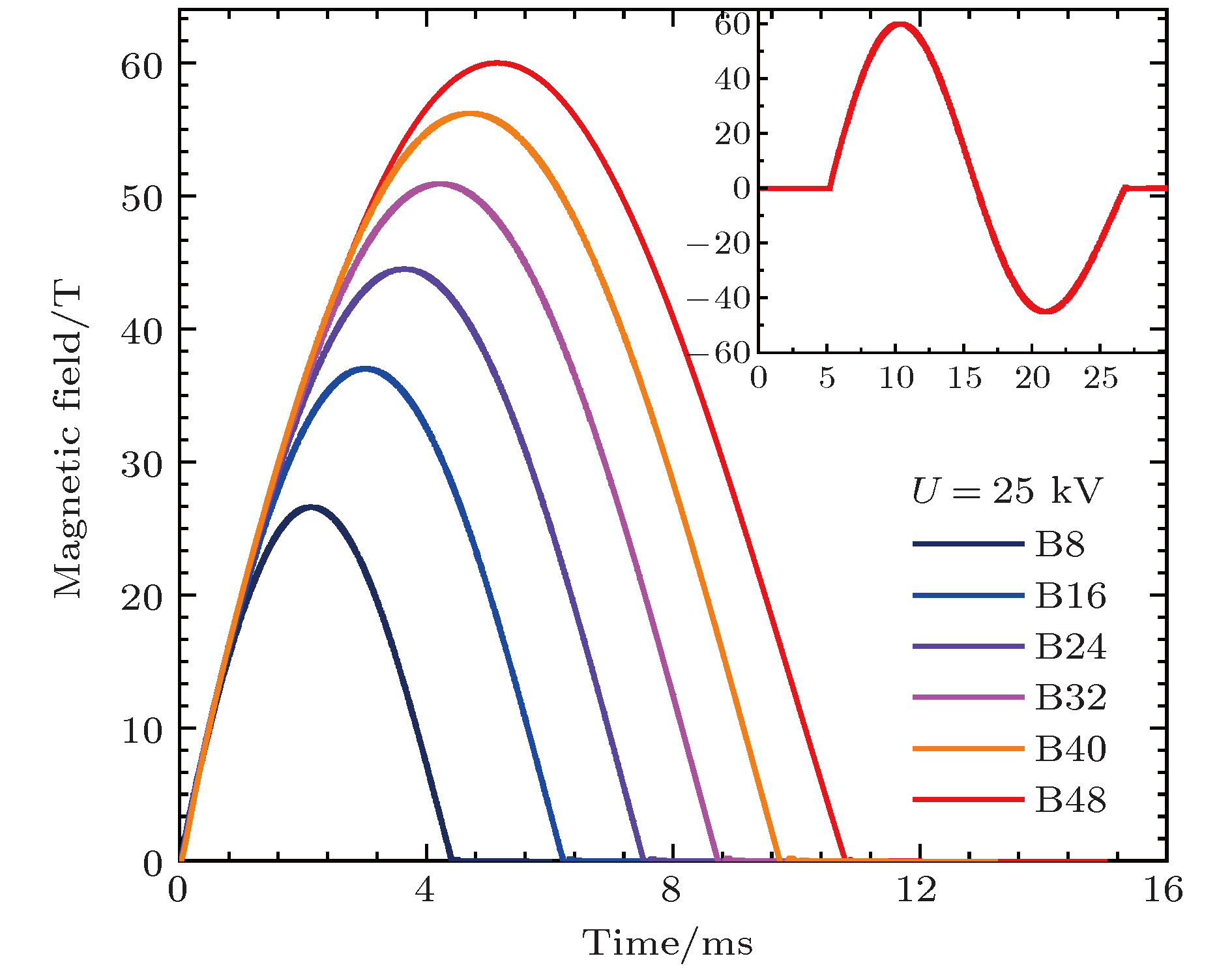
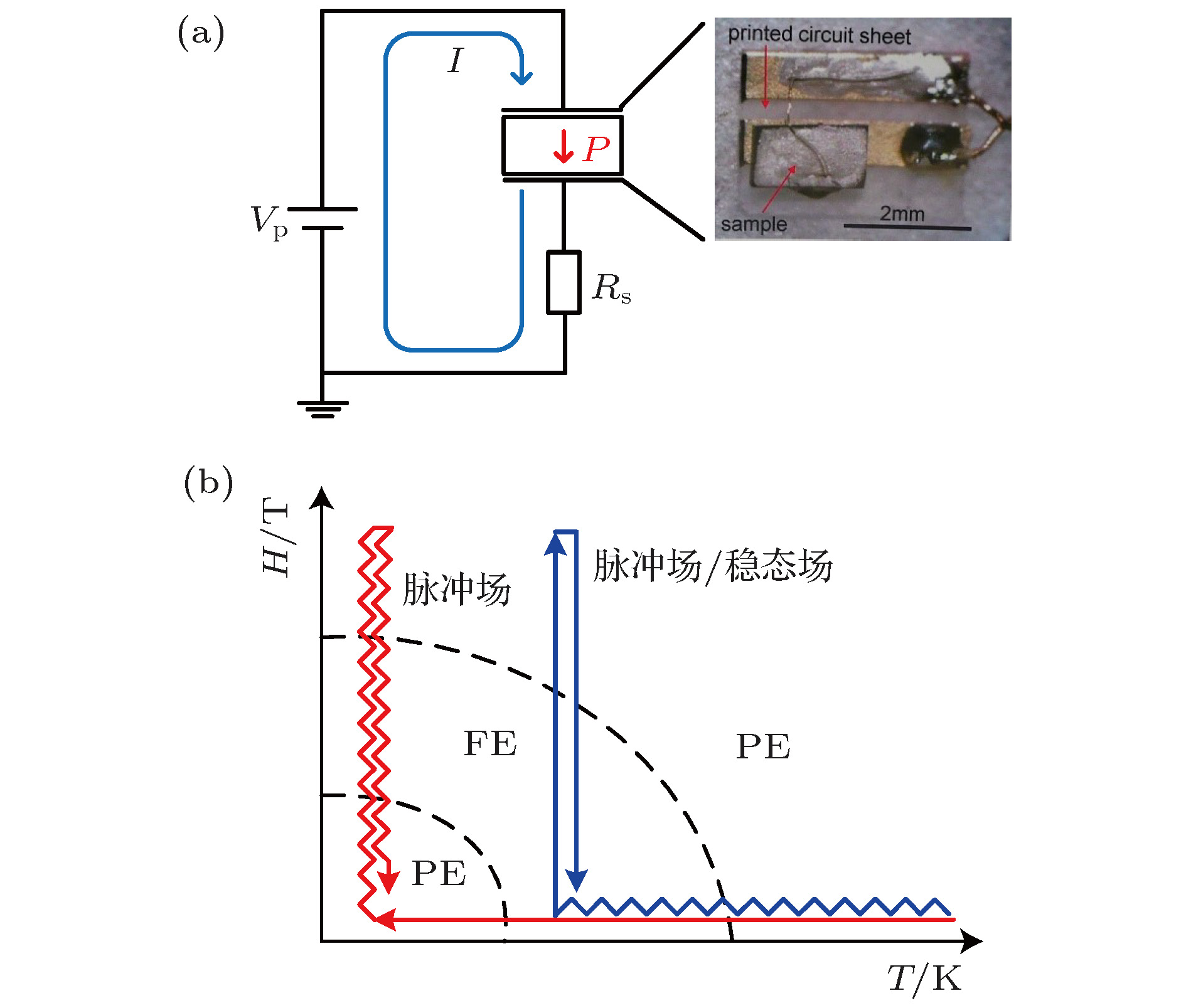
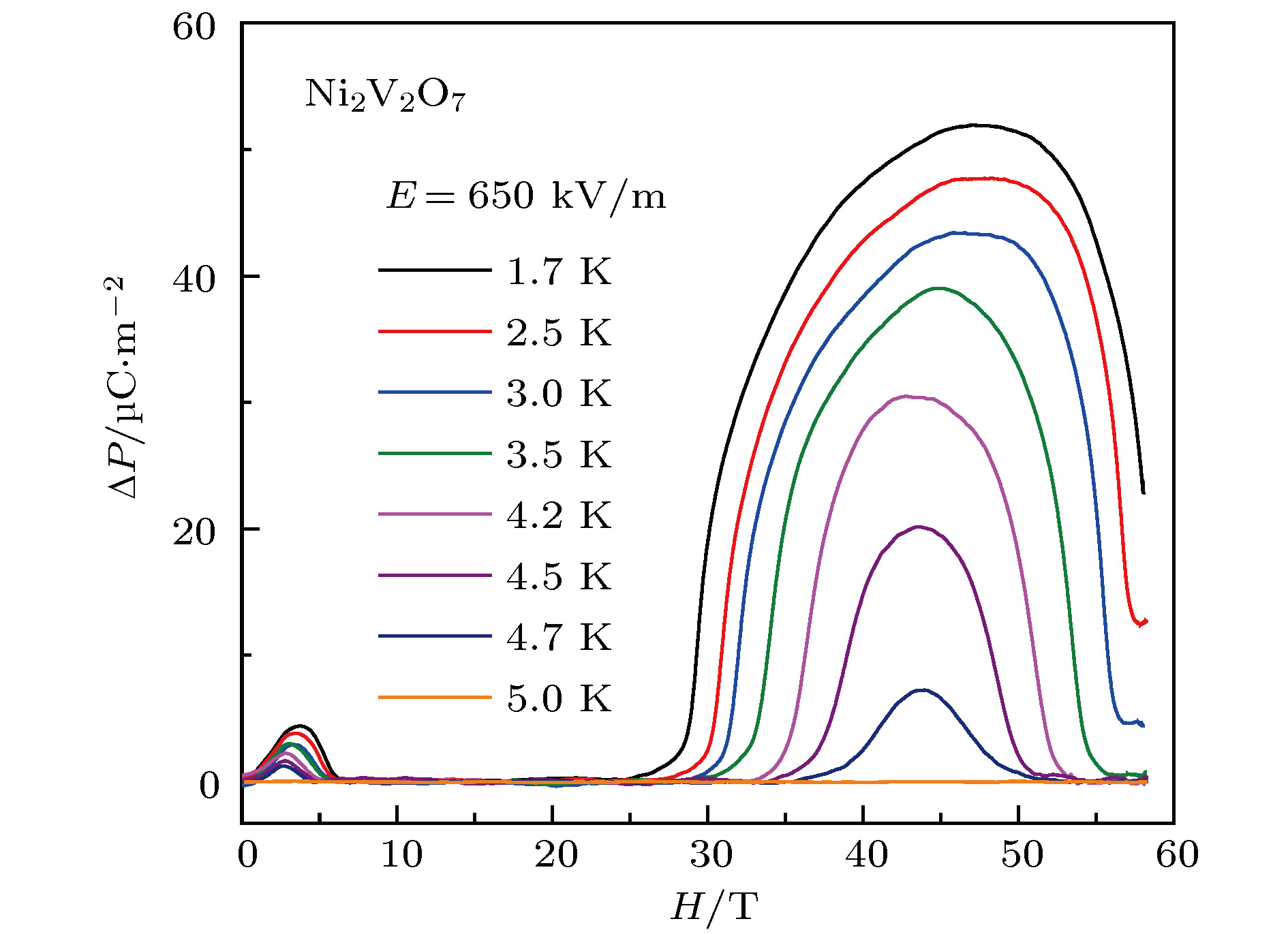
Multiferroic materials, which exhibit the coexistence of ferromagnetic, ferroelectric, or ferroelastic orders, are of particular interest for not only fundamental physics but also potential applications. An important physical property of multiferroic materials, especially those with magnetically driven ferroelectricity, is known as a strong magnetoelectric coupling between the magnetic order and the ferroelectric order. The external magnetic fields can directly interact with spins or magnetic moments of the materials and lead the spontaneous ferroelectricity to be suppressed, and in some cases result in field-induced ferroelectricity in a higher field. Depending on the exchange interactions, these ferroelectric phase transitions may take place in a critical magnetic field as high as several tens of tesla. The standard electric-polarization measurement based on a commercial PPMS system is limited by the strength of the static field consequently. As an extremely experimental condition, pulsed magnetic fields can be used to reveal new physical phenomena in multiferroic materials. Due to the short pulse duration and the effect of eddy current, this measurement technique under pulsed high magnetic fields is still a challenge to date although a few laboratories have developed it in recent years. Wuhan National High Magnetic Field Center (WHMFC) of China is a newly built pulsed-field laboratory. This experimental station is equipped with the many measuring instruments such as for measuring electric transport, magnetization, electron spin resonance, magneto-optics, and high pressure, which were established after the national assessment at the end of 2014. Recently, using a pyroelectric technique we successfully constructed an electric-polarization measurement system based on the large-scaled facility at the WHMFC. The nondestructive magnet driven by discharging a 1.25 MJ capacitor bank can generate a pulsed field up to 60 T. By tuning the charging energy and voltages, the pulse duration time can be modulated from 4.3 ms to 10.8 ms. A helium-3 cryogenic system equipped on this facility can achieve a lowest temperature down to 0.5 K. A high-precision rotation probe is designed and fabricated with angle varying from –5° to 185° for an angular-dependent study. The pyroelectric current is detected by a shunt resistor of 10 kΩ and the electric polarization is derived by integrating the pyroelectric current over the time. The resulting data have a good accuracy and quality which are helpful in detecting weak ferroelectric phase transitions induced by pulsed fields with a fast field sweep rate. In this paper, we introduce this measurement system in detail including the method, principle and its advantages in comparison with those in static fields. Recent study and progress of magnetoelectric multiferroic materials under high magnetic fields are also reported. [1] Schmid H 1994 Ferroelectrics 162 317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Scott J F 2007 Nat. Mater. 6 256
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Fiebig M J 2005 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 38 123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Schmid H 2008 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 20 434201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Ouyang Z W, Sun Y C, Wang J F, Yue X Y, Chen R, Wang Z X, He Z Z, Xia Z C, Liu Y, Rao G H 2018 Phys. Rev. B 97 144406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Liu Y J, Wang J F, Sun X F, Zhou J S, Xia Z C, Ouyang Z W, Yang M, Liu C B, Chen R, Cheng J G, Kohama Y, Tokunaga M, Kindo K 2018 Phys. Rev. B 97 214419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yin L, Ouyang Z W, Wang J F, Yue X Y, Chen R, He Z Z, Wang Z X, Xia Z C, Liu Y 2019 Phys. Rev. B 99 134434
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhang X X, Xia Z C, Ke Y J, Zhang X Q, Cheng Z H, Ouyang Z W, Wang J F, Huang S, Yang F, Song Y J, Xiao G L, Deng H, Jiang D Q 2019 Phys. Rev. B 100 054418
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 刘沁莹, 王俊峰, 左华坤, 杨明, 韩小涛 2019 68 230701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Q Y, Wang J F, Zuo H K, Yang M, Han X T 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 230701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Liu Y J, Wang J F, He Z Z, Lu C L, Xia Z C, Ouyang Z W, Liu, R. Chen C B, Matsuo A, Kohama Y, Kindo K, Tokunaga M 2018 Phys. Rev. B 97 174429
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Chen R, Wang J F, Ouyang Z W, He Z Z, Wang S M, Lin L, Liu J M, Lu C L, Liu Y, Dong C, Liu C B, Xia Z C, Matsuo A, Kohama Y, Kindo K 2018 Phys. Rev. B 98 184404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] He Z Z, Yamaura J I, Ueda Y, Cheng W D 2009 Phys. Rev. B 79 092404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Matsubara M, Manz S, Mochizuki M, Kubacka T, Iyama A, Aliouane N 2015 Science 348 1112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Abe N, Taniguchi K, Ohtani S, Takenobu T, Iwasa Y, Arima T 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 99 227206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Cabrera I, Kenzelmann M, Lawes G, Chen Y, Chen W C, Erwin R, Gentile T R, Leão J B, Lynn J W, Rogado N, Cava R J, Broholm C 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 087201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Rogado N, Lawes G, Huse D A, Ramirez A P, Cava R J 2002 Solid State Commun. 124 229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Fina I, Fàbrega L, Martí X, Sánchez F, Fontcuberta J 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 107 257601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Akaki M, Iwamoto H, Kihara T, Tokunaga M, Kuwahara H 2012 Phys. Rev. B 86 060413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Catalan G, Scott J F 2009 Adv. Mater. 21 2463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Tokunaga M, Akaki M, Ito T, Miyahara S, Miyake A, Kuwahara H, Furukawa N 2015 Nat. Commun. 6 5878
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Chen R, Wang J F, Ouyang Z W, Tokunaga M, Luo A Y, Lin L, Liu J M, Xiao Y, Miyake A, Kohama Y, Lu C L, Yang M, Xia Z C, Kindo K, Li L 2019 Phys. Rev. B 100 140403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
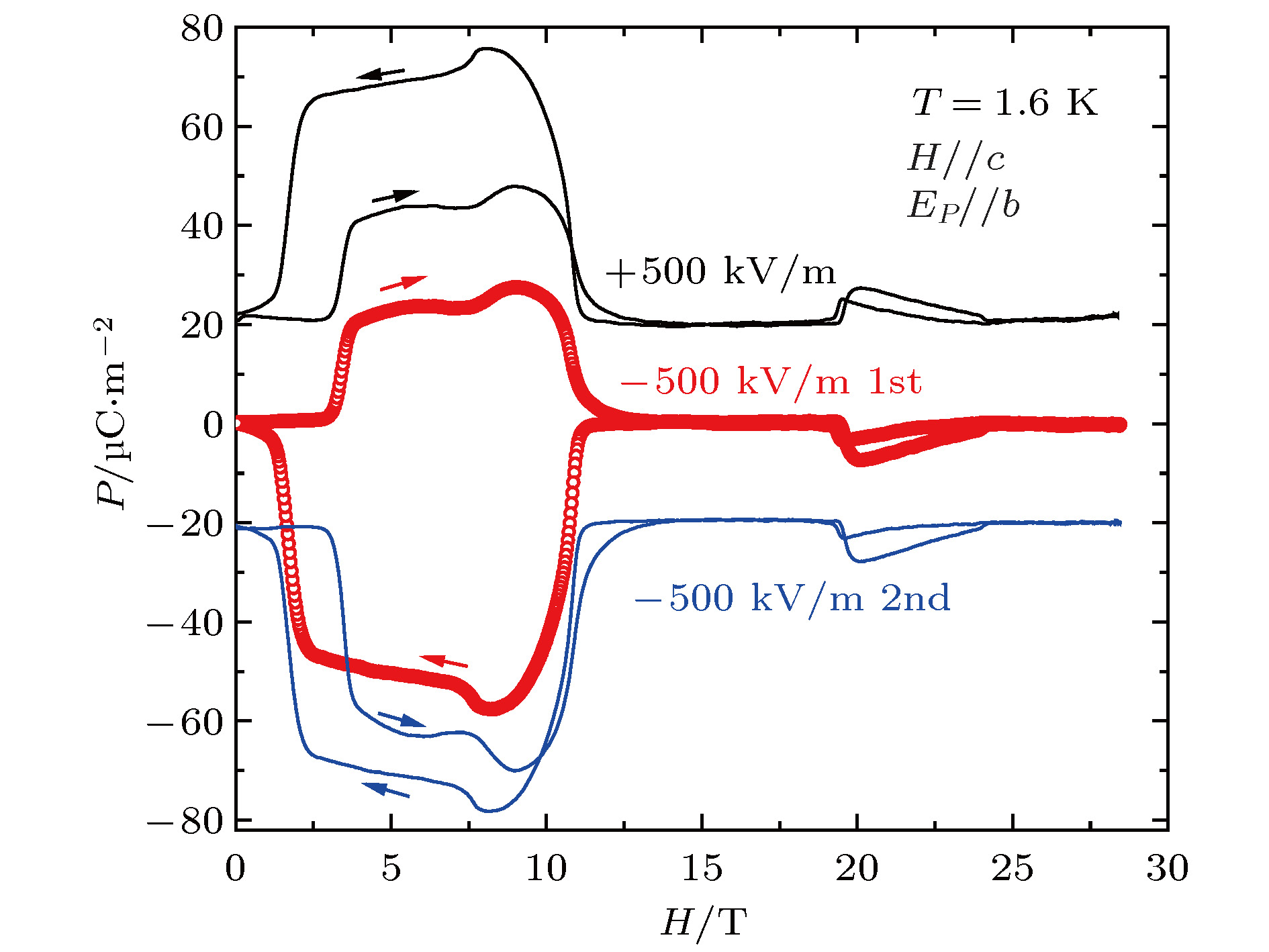
图 7 Ni3V2O8在不同偏置电压下的电极化反转及磁电记忆效应研究(首先, 施加+500 kV/m的电场, 测量1.6 K下的电极化强度; 接着, 施加–500 kV/m的电场, 进行两次连续的脉冲磁场电极化测量)
Figure 7. Study on polarization reversal and magnetoelectric memory effect of Ni3V2O8 in different voltages (First, an electric field of +500 kV/m is applied to measure the electric polarization at 1.6 K. Then, two successive pulsed fields are performed by applying an electric field of –500 kV/m).
-
[1] Schmid H 1994 Ferroelectrics 162 317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Scott J F 2007 Nat. Mater. 6 256
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Fiebig M J 2005 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 38 123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Schmid H 2008 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 20 434201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Ouyang Z W, Sun Y C, Wang J F, Yue X Y, Chen R, Wang Z X, He Z Z, Xia Z C, Liu Y, Rao G H 2018 Phys. Rev. B 97 144406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Liu Y J, Wang J F, Sun X F, Zhou J S, Xia Z C, Ouyang Z W, Yang M, Liu C B, Chen R, Cheng J G, Kohama Y, Tokunaga M, Kindo K 2018 Phys. Rev. B 97 214419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yin L, Ouyang Z W, Wang J F, Yue X Y, Chen R, He Z Z, Wang Z X, Xia Z C, Liu Y 2019 Phys. Rev. B 99 134434
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhang X X, Xia Z C, Ke Y J, Zhang X Q, Cheng Z H, Ouyang Z W, Wang J F, Huang S, Yang F, Song Y J, Xiao G L, Deng H, Jiang D Q 2019 Phys. Rev. B 100 054418
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 刘沁莹, 王俊峰, 左华坤, 杨明, 韩小涛 2019 68 230701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Q Y, Wang J F, Zuo H K, Yang M, Han X T 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 230701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Liu Y J, Wang J F, He Z Z, Lu C L, Xia Z C, Ouyang Z W, Liu, R. Chen C B, Matsuo A, Kohama Y, Kindo K, Tokunaga M 2018 Phys. Rev. B 97 174429
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Chen R, Wang J F, Ouyang Z W, He Z Z, Wang S M, Lin L, Liu J M, Lu C L, Liu Y, Dong C, Liu C B, Xia Z C, Matsuo A, Kohama Y, Kindo K 2018 Phys. Rev. B 98 184404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] He Z Z, Yamaura J I, Ueda Y, Cheng W D 2009 Phys. Rev. B 79 092404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Matsubara M, Manz S, Mochizuki M, Kubacka T, Iyama A, Aliouane N 2015 Science 348 1112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Abe N, Taniguchi K, Ohtani S, Takenobu T, Iwasa Y, Arima T 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 99 227206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Cabrera I, Kenzelmann M, Lawes G, Chen Y, Chen W C, Erwin R, Gentile T R, Leão J B, Lynn J W, Rogado N, Cava R J, Broholm C 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 087201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Rogado N, Lawes G, Huse D A, Ramirez A P, Cava R J 2002 Solid State Commun. 124 229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Fina I, Fàbrega L, Martí X, Sánchez F, Fontcuberta J 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 107 257601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Akaki M, Iwamoto H, Kihara T, Tokunaga M, Kuwahara H 2012 Phys. Rev. B 86 060413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Catalan G, Scott J F 2009 Adv. Mater. 21 2463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Tokunaga M, Akaki M, Ito T, Miyahara S, Miyake A, Kuwahara H, Furukawa N 2015 Nat. Commun. 6 5878
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Chen R, Wang J F, Ouyang Z W, Tokunaga M, Luo A Y, Lin L, Liu J M, Xiao Y, Miyake A, Kohama Y, Lu C L, Yang M, Xia Z C, Kindo K, Li L 2019 Phys. Rev. B 100 140403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 14687
- PDF Downloads: 190
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: