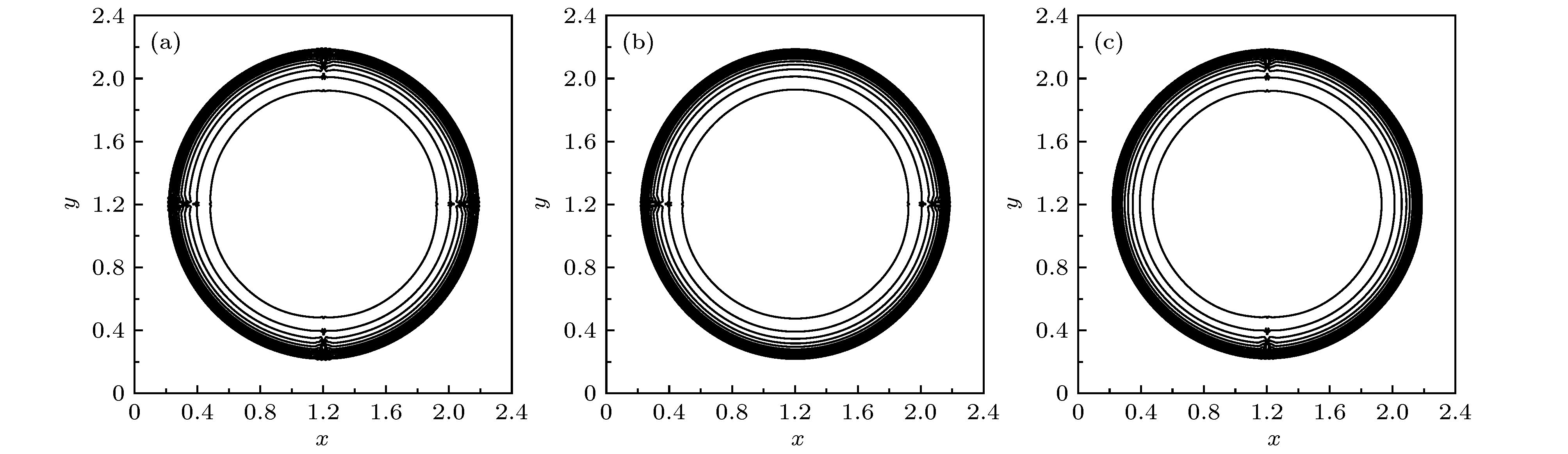
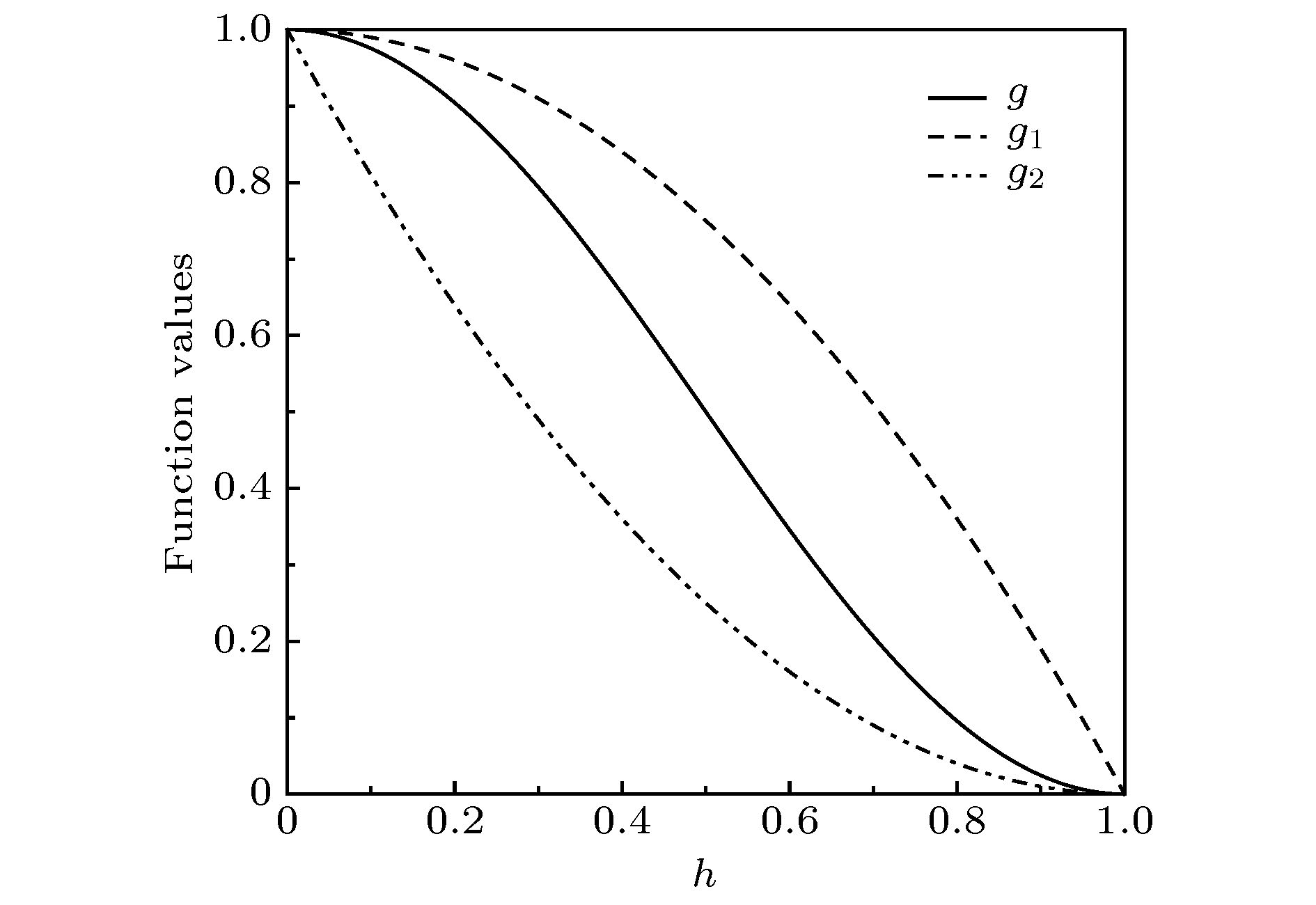
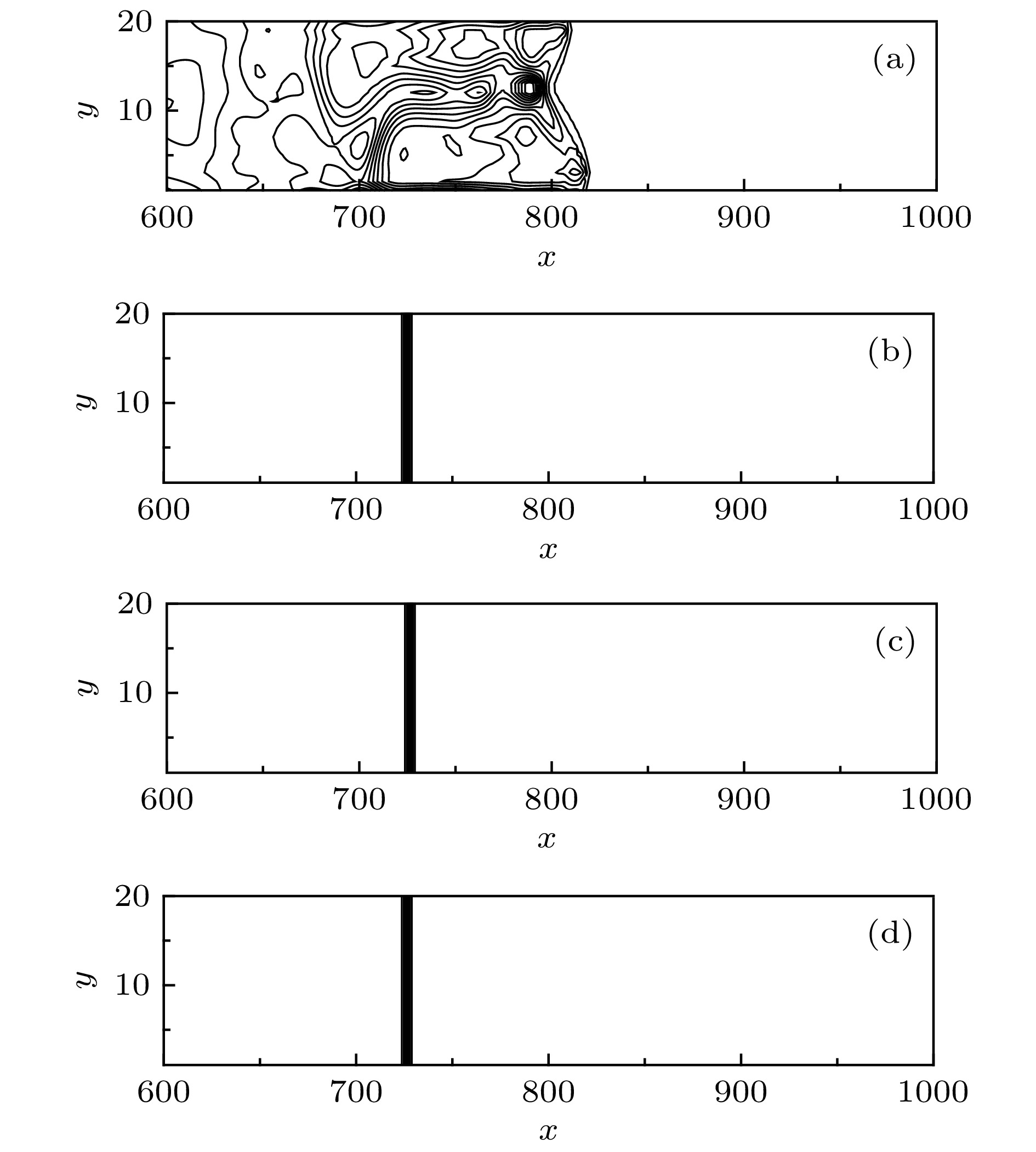
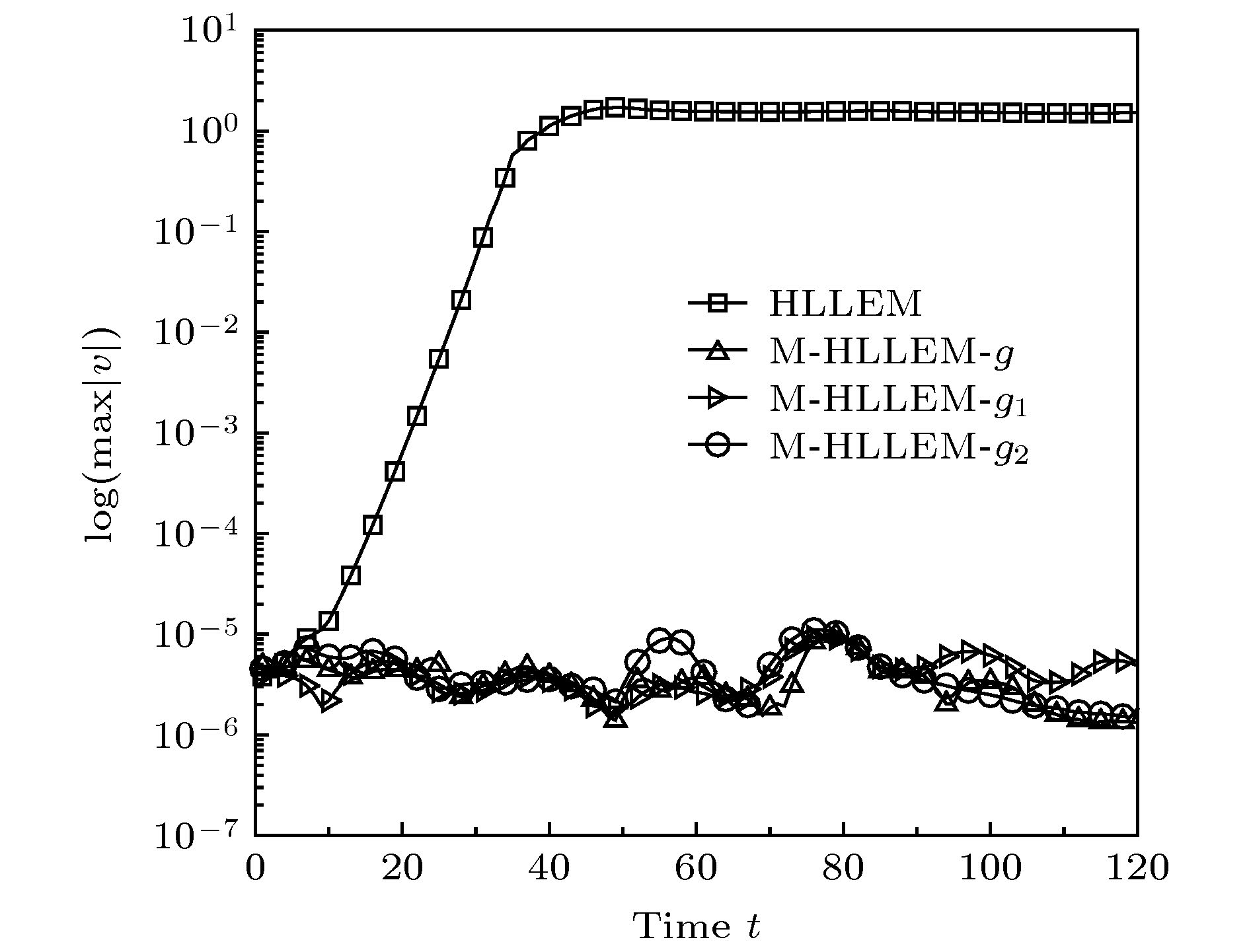
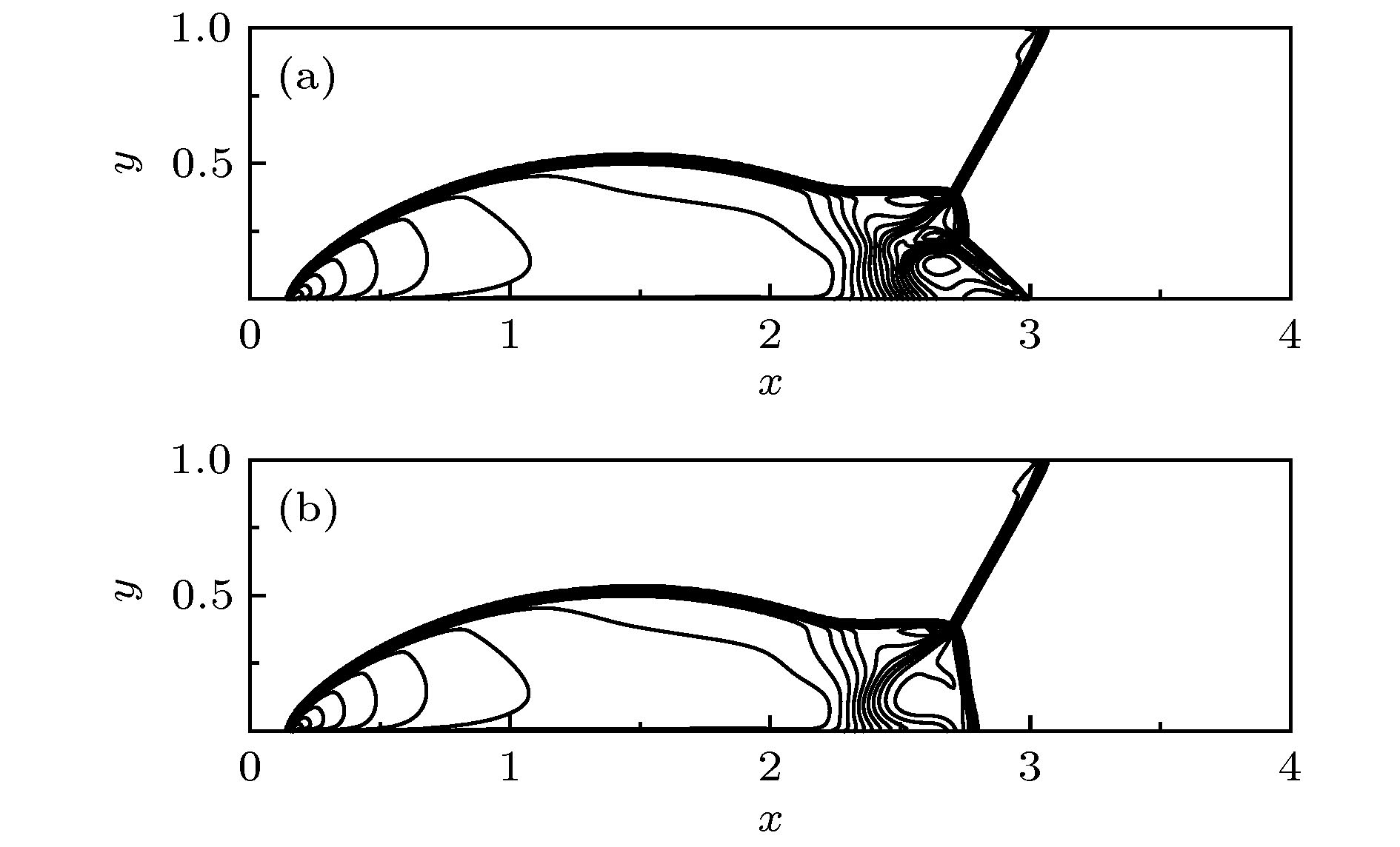
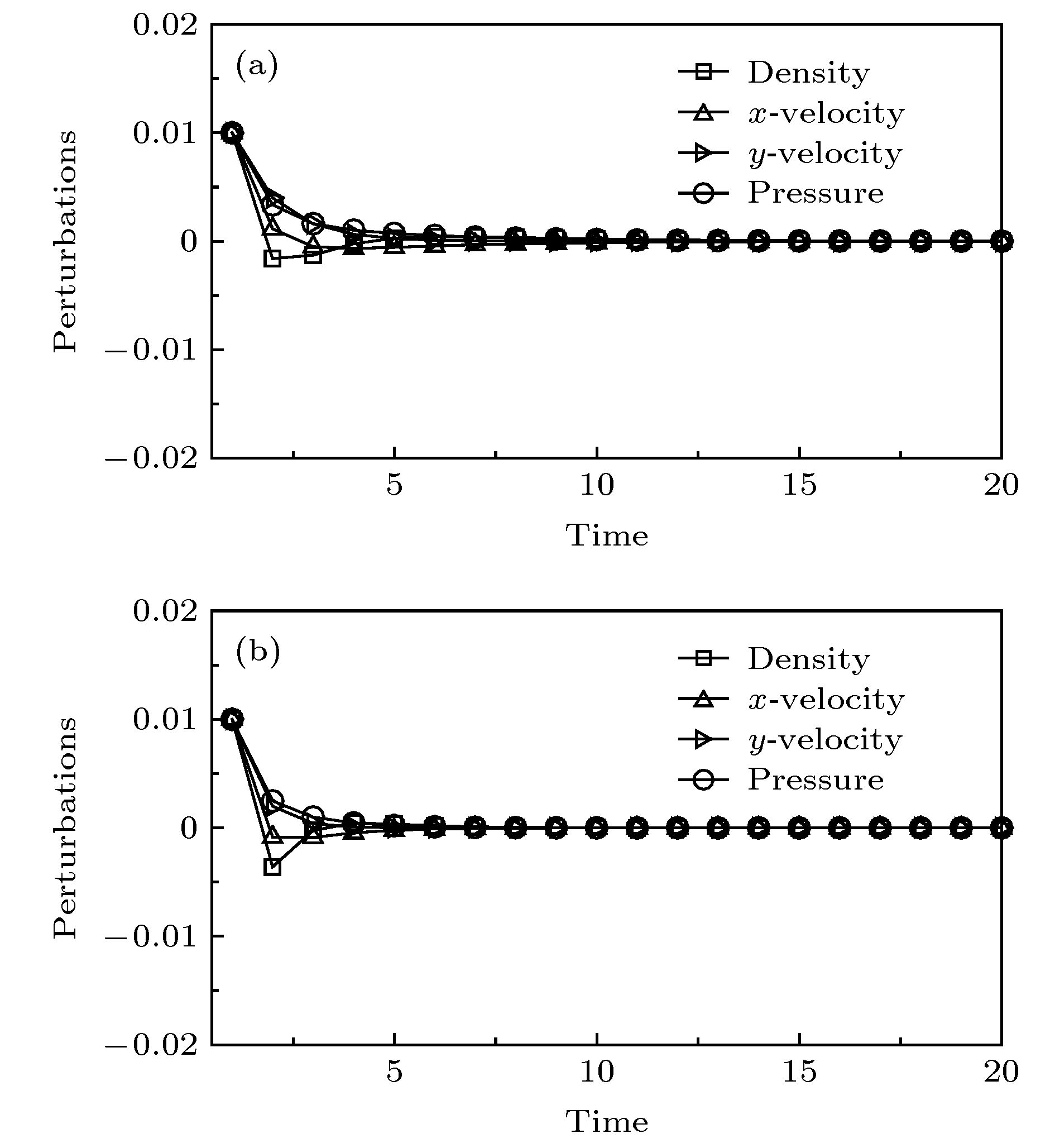
-
使用低耗散激波捕捉格式对高超声速流动问题进行数值模拟时经常会遭受不同形式的激波不稳定性. 本文基于二维无黏可压缩Euler方程, 对低耗散HLLEM格式进行激波稳定性分析. 结果表明: 激波面横向通量中切向速度的扰动增长诱发了格式的不稳定性. 通过增加耗散来治愈HLLEM格式的激波不稳定性. 为了避免引入过多的耗散进而影响剪切层的分辨率, 定义激波探测函数和亚声速区探测函数, 使得只有在计算激波层亚声速区的横向数值通量时才增加耗散, 其余地方的数值通量依然采用低耗散的HLLEM格式来计算. 稳定性分析和数值模拟的结果表明, 改进的HLLEM格式不仅保留了原格式高分辨率的优点, 还大大提高了格式的鲁棒性, 在计算强激波问题时能够有效地抑制不稳定现象的发生.Reliable numerical simulations for hypersonic flows require an accurate, robust and efficient numerical scheme. The low-dissipation shock-capturing methods often suffer various forms of shock wave instabilities when used to simulate hypersonic flow problems numerically. For the two-dimensional(2D) inviscid compressible Euler equations, the stability analysis of the low-dissipation HLLEM scheme is conducted. The odd and even perturbations are added to the initial state in the streamwise direction and the transverse direction respectively, and the evolution equations of perturbations are deduced to explore the mechanism of instability inherent in the HLLEM scheme. The results of stability analysis show that the perturbations of density and shear velocity in the flux transverse to the shock wave front are undamped. Due to the symmetry, the 2D Sedov blast wave problem is computed to prove the multidimensionality of the shock instability. In the one-dimensional case which is free from the instability, the undamped property of density perturbation is also existent but no shear velocity is found. The conclusion can be drawn as follows: the shock instability of HLLEM scheme is triggered by the perturbation growth of shear velocity in the flux transverse to the shock wave front. Based on the conclusion of stability analysis, the instability of HLLEM scheme is cured by adding the shear viscosity to the transverse flux. In order to avoid affecting the resolution of the shear layer due to the introduction of too high shear viscosity, two functions to detect the shock wave and the subsonic regimes are defined, so that the shear viscosity is only added to the transverse flux in the subsonic regime of the shock layer, while the rest of numerical fluxes are still computed by the original HLLEM scheme. The results of stability analysis and some challenging numerical test problems show that the modified HLLEM scheme not only retains the merits of the original HLLEM, such as, resolving contact discontinuity and shear wave accurately, but also has greatly improved its robustness, inhibiting the unstable phenomena from occurring effectively when computing the strong shock wave problems.
-
Keywords:
- hypersonic flow /
- low dissipation scheme /
- tangential dissipation /
- shock instability
[1] Tchuen G, Fogang F, Burtschell Y, Woafo P 2014 Comput. Phys. Commun. 185 479
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 全鹏程, 易仕和, 武宇, 朱杨柱, 陈植 2014 63 084703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Quan P C, Yi S H, Wu Y, Zhu Y Z, Chen Z 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 084703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Quirk J J 1994 Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 18 555
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Gressier J, Moschetta J M 2000 Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 33 313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Dumbser M, Moschetta J M, Gressier J 2004 J. Comput. Phys. 197 647
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 谢文佳, 李桦, 潘沙, 田正雨 2015 64 024702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xie W J, Li H, Pan S, Tian Z Y 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 024702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Shen Z J, Yan W, Yuan G W 2016 J. Comput. Phys. 309 185
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kim S D, Lee B J, Lee H J, Jeung I S 2009 J. Comput. Phys. 228 7634
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wu H, Shen L J, Shen Z J 2010 Commun. Comput. Phys. 8 1264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Shen Z J, Yan W, Yuan G W 2014 Commun. Comput. Phys. 15 1320
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ren Y X 2003 Comput. Fluids 32 1379
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Rodionov A 2017 J. Comput. Phys. 345 308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Rodionov A 2019 Comput. Fluids 190 77
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Rodionov A 2018 J. Comput. Phys. 361 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Chen S S, Yan C, Lin B X, Liu L Y, Yu J 2018 J. Comput. Phys. 373 662
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Simon S, Mandal J C 2018 Comput. Fluids 174 144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Simon S, Mandal J C 2019 J. Comput. Phys. 378 477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Xie W J, Li W, Li H, Tian Z Y, Pan S 2017 J. Comput. Phys. 350 607
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Fleischmann N, Adami S, Hu X Y, Adams N 2020 J. Comput. Phys. 401 109004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Einfeldt B, Munz C D, Roe P L, Sjögreen B 1991 J. Comput. Phys. 92 273
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Chauvat Y, Moschetta J M, Gressier J 2005 Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 47 903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Kitamura K, Roe P L, Ismail F 2009 AIAA J. 47 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Xu K, Li Z W 2001 Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 371
[24] Huang K, Wu H, Yu H, Yan D 2011 Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 65 1026
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Woodward P, Colella P 1984 J. Comput. Phys. 54 115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] Tchuen G, Fogang F, Burtschell Y, Woafo P 2014 Comput. Phys. Commun. 185 479
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 全鹏程, 易仕和, 武宇, 朱杨柱, 陈植 2014 63 084703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Quan P C, Yi S H, Wu Y, Zhu Y Z, Chen Z 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 084703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Quirk J J 1994 Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 18 555
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Gressier J, Moschetta J M 2000 Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 33 313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Dumbser M, Moschetta J M, Gressier J 2004 J. Comput. Phys. 197 647
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 谢文佳, 李桦, 潘沙, 田正雨 2015 64 024702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xie W J, Li H, Pan S, Tian Z Y 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 024702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Shen Z J, Yan W, Yuan G W 2016 J. Comput. Phys. 309 185
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kim S D, Lee B J, Lee H J, Jeung I S 2009 J. Comput. Phys. 228 7634
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wu H, Shen L J, Shen Z J 2010 Commun. Comput. Phys. 8 1264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Shen Z J, Yan W, Yuan G W 2014 Commun. Comput. Phys. 15 1320
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ren Y X 2003 Comput. Fluids 32 1379
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Rodionov A 2017 J. Comput. Phys. 345 308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Rodionov A 2019 Comput. Fluids 190 77
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Rodionov A 2018 J. Comput. Phys. 361 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Chen S S, Yan C, Lin B X, Liu L Y, Yu J 2018 J. Comput. Phys. 373 662
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Simon S, Mandal J C 2018 Comput. Fluids 174 144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Simon S, Mandal J C 2019 J. Comput. Phys. 378 477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Xie W J, Li W, Li H, Tian Z Y, Pan S 2017 J. Comput. Phys. 350 607
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Fleischmann N, Adami S, Hu X Y, Adams N 2020 J. Comput. Phys. 401 109004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Einfeldt B, Munz C D, Roe P L, Sjögreen B 1991 J. Comput. Phys. 92 273
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Chauvat Y, Moschetta J M, Gressier J 2005 Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 47 903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Kitamura K, Roe P L, Ismail F 2009 AIAA J. 47 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Xu K, Li Z W 2001 Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 371
[24] Huang K, Wu H, Yu H, Yan D 2011 Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 65 1026
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Woodward P, Colella P 1984 J. Comput. Phys. 54 115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 9252
- PDF下载量: 124
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: