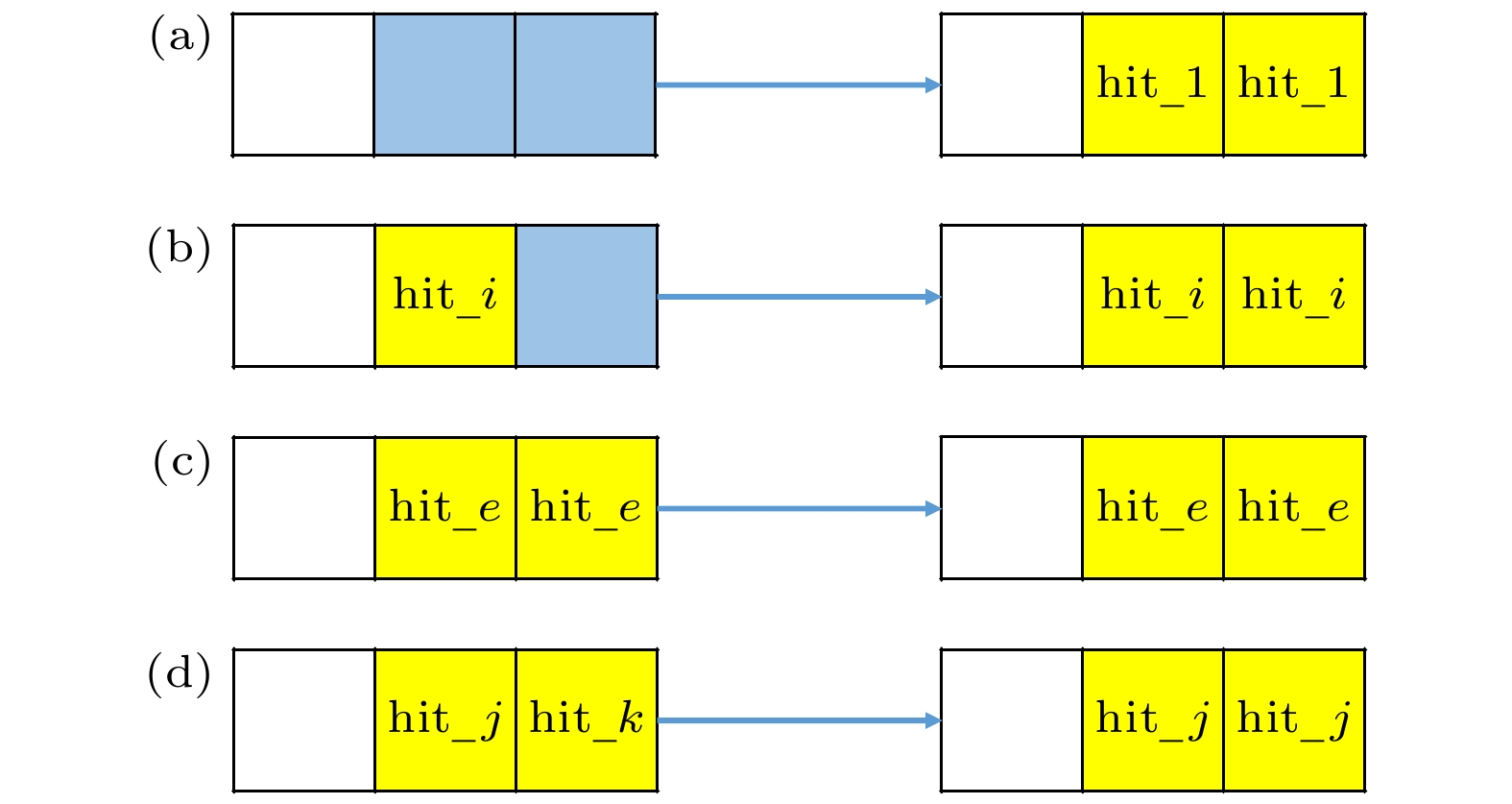
-
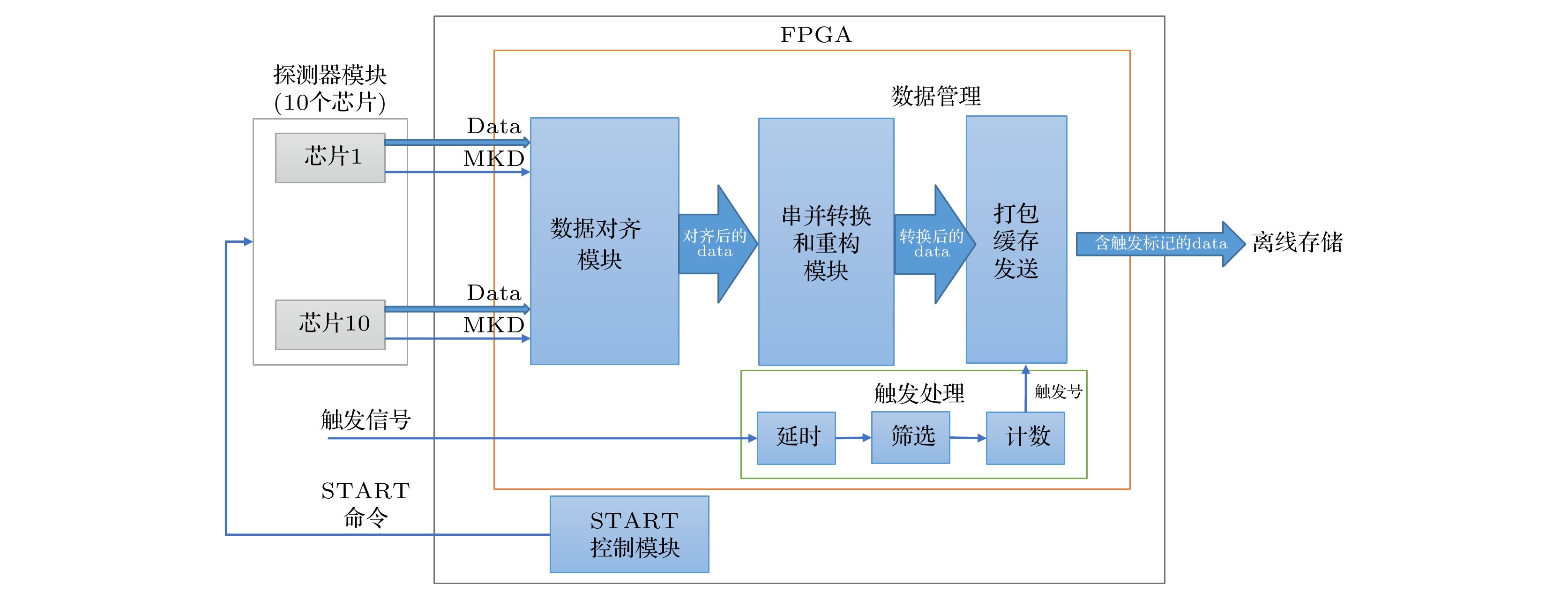
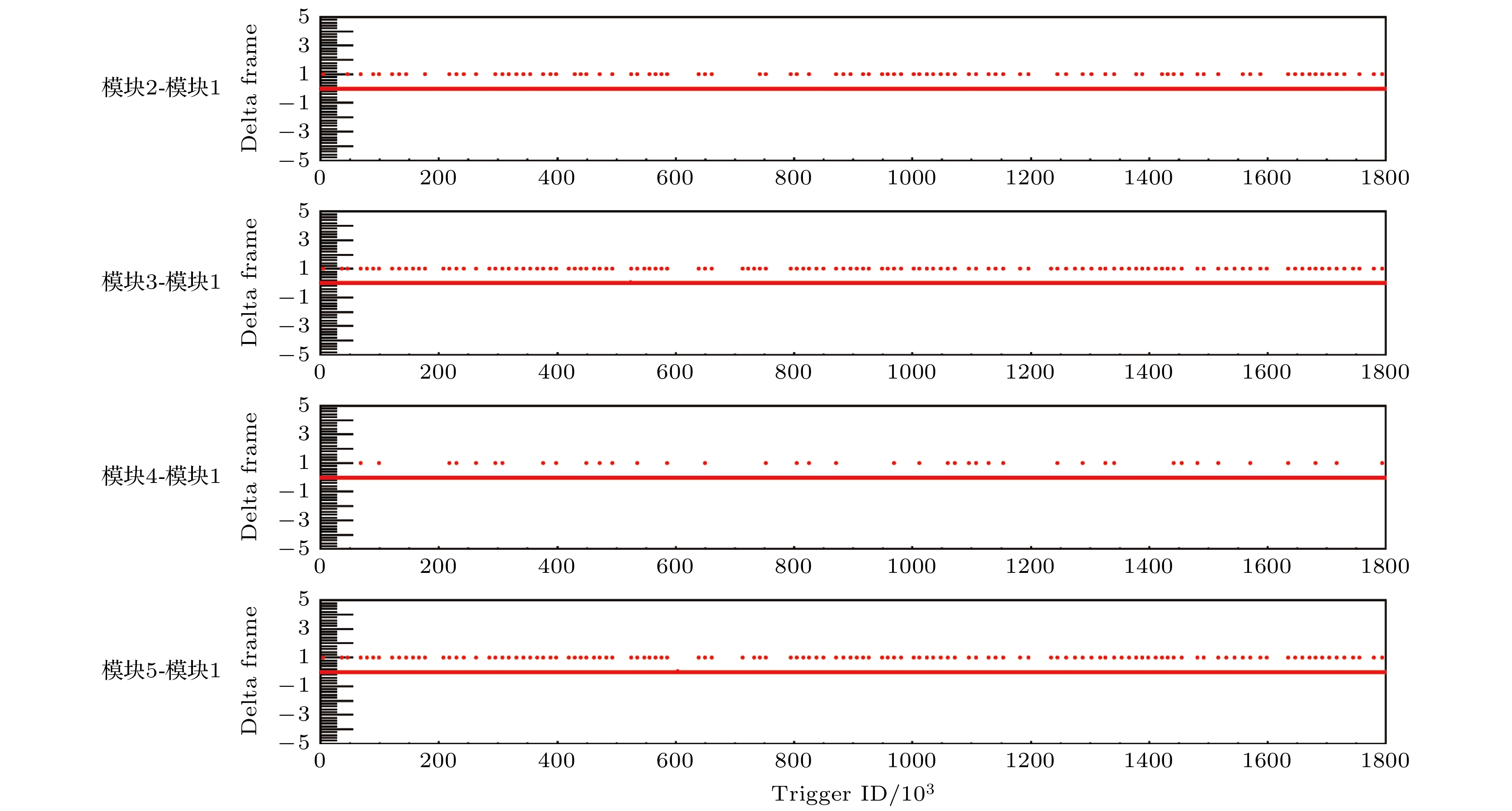
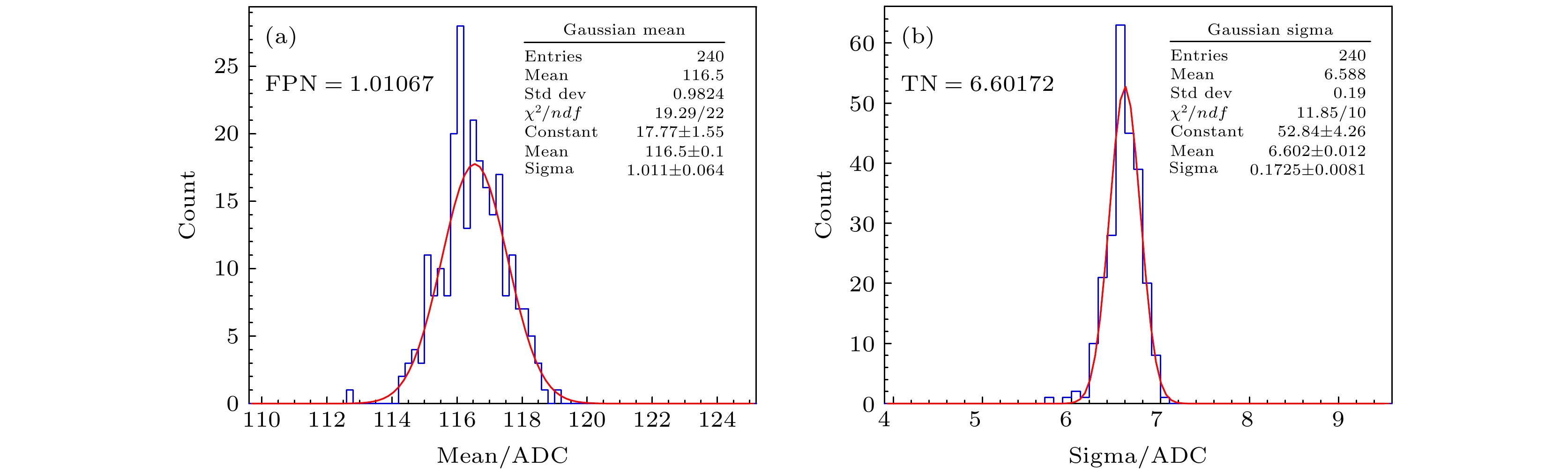
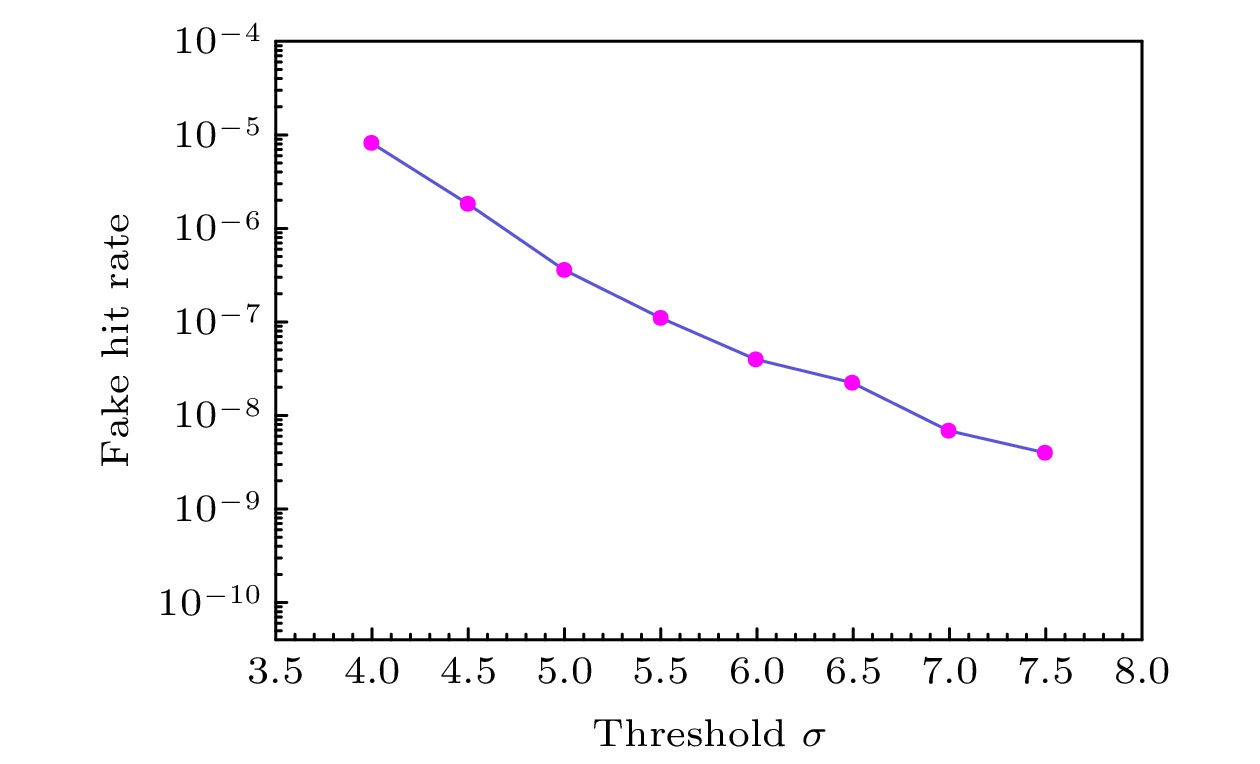
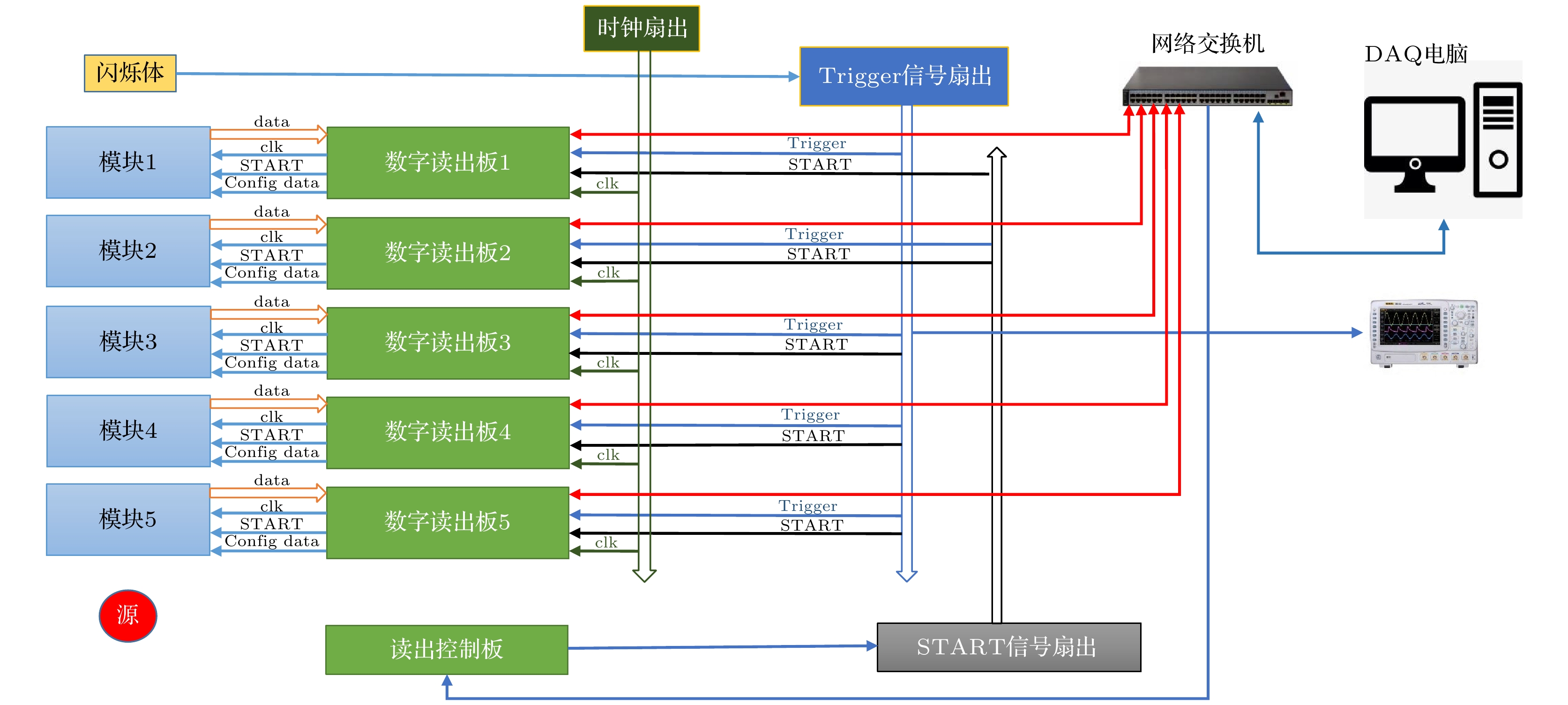
硅像素探测器因具有优异的空间分辨率、极高的耐计数能力和较低的功耗等优点, 近年来已被广泛应用于高能对撞机实验的顶点探测器和内径迹探测器. 基于MIMOSA28芯片的硅像素探测器研究是北京谱仪Ⅲ漂移室内室的升级预研方案之一, 该方案计划建造一个漂移室内室1/10规模的模型. 探测模块是该模型的基本探测单元. 为了对探测模块的性能进行研究, 搭建了实验室测试系统. 该系统主要由五层探测模块、读出电子学系统以及数据获取系统组成. 本文围绕带有触发标记的连续数据读出方法的实现、探测模块的噪声水平和放射源响应测试以及击中位置重建算法研究展开. 测试结果验证了探测模块工作性能良好, 触发读出逻辑正确, 而且重建算法准确有效, 为后续探测模块性能的进一步研究奠定了基础.Silicon pixel detectors are widely used as vertex detectors or inner trackers in high-energy collider experiments because of their excellent spatial resolution, extremely high counting capability and low power consumption. The study of the silicon pixel detector based on the monolithic active pixel sensor (MAPS) is one of the R&D schemes for upgrading the inner chamber of the Beijing spectrometer Ⅲ (BESⅢ) drift chamber (MDC). It is planned to build a 1/10 scale prototype of the inner chamber. The detector module is the basic component of the prototype, consisting of ten MIMOSA28 chips thinned to 50 μm, a flexible cable and a carbon fiber support. In order to study the performance of the module, a test system is set up. The system is composed mainly of five-layer modules, readout electronics and data acquisition system. This article focuses on the realization of the continuous data readout method with trigger marking function, the measurement of the noise level of the detector modules, the module response test by a radioactive source, and the study of the hit reconstruction algorithm. The test of trigger readout logic verifies the correctness of the continuous readout method with trigger marking. It can be concluded that analyzing consecutive three frames data (the previous frame, the current frame and the next frame) of each valid trigger will not lead to effective hit data loss. The noise level of the detector module is tested. The results show that the fixed pattern noise (FPN) is 0.253 mV, and the temporal noise (TN) is 1.65 mV. The fake hit rate is less than
$ {10}^{-5} $ that can be ignored when the chip threshold is set to be above 4σ of noise. Two algorithms for hit reconstruction (i.e. adjacent method and comparison method) are studied and compared. When the average number of fired pixels caused by each hit is 2.562 and more than four hits in each frame of data, the adjacent method can find all of the fired pixels to be faster. During the test, the detector module and the electronics are proved to work well. These studies lay a foundation for further testing the performance of the detector prototype.[1] Weste N H E, Eshraghian K 1985 NASA STI/Recon Technical Report A 85 47028
[2] MacMillen D, Camposano R, Hill D, Williams T W 2000 IEEE Trans.Comput.Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 19 1428
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Greiner L, Anderssen E, Matis H S, Ritter H G, Schambach J, Silber J, Stezelberger T, Sun X, Szelezniak M, Thomas J, Videbaek F, Vu C, Wieman H 2011 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 650 68
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Contin G, Anderssen E, Greiner L, Schambach J, Silber J, Stezelberger T, Sun X, Szelezniak M, Vu C, Wieman H, Woodmansee S 2015 JINST 10 C03026
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Brüning O, Burkhardt H, Myers S 2012 Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 67 705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Schukraft J 2012 Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 370 917
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Mager M 2016 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 824 434
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Keil M 2015 JINST 10 C03012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhou Y, Lu Y P, Wu Z G, Shi T, Ju X D, Dong J, Zhu H B, Ouyang Q 2020 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 980 164427
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wei W, Zhang J, Ning Z, Lu Y P, Fan L, Li H S, Jiang X S, Lan A K, Ou-Yang Q, Wang Z, Zhu K J, Chen Y B, Liu P 2016 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 835 169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Zhang C 2009 Chin. Phys. C 33 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Harris F A 2006 Nucl. Phys. B 162 345
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Hu G C, Baudot J, Bertolone G, et al. 2010 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 623 480
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Contin G, Greiner L, Schambach J, Szelezniak M, Anderssen E, Bell J, Cepeda M, Johnson T, Qiu H, Ritter H G, Silber J, Stezelberger T, Sun X M, Tran C, Vu C, Wieman H, Wilson K, Witharm R, Woodmansee S, Wolf J 2018 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 907 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ultimate user manual, Himmi A, Doziere G, Bertolone G, Dulinski W, Coll-edani C, Dorokhov A, Hu Ch, Morel F, Pham H, Valin I, Wang J http://www.iphc.cnrs.fr/IMG/pdf/Ultimate_UserManual.pdf [2021-3-9]
[16] Valin I, Hu-Guo C, Baudot J, Bertolone G, Besson A, Colledani C, Clau G, Dorokhov A, Dozière G, Dulinski W, Gelin M, Goffe M, Himmi A, Jaaskel-ainen K, Morel F, Pham H, Santos C, Senyukov S, Specht M, Voutsinas G, Wang J, Winter M 2012 JINST 7 C01102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Highland V L 1975 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. 129 497
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Szelezniak M A, Deptuch G W, Guilloux F, Heini S, Himmi A 2007 IEEE J. Sensor 7 137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 7 Series FPGAs Data Sheet: Overview, Xinlinx https://www.xilinx.com/support/documentation/data_sheets/ds180_7 Series_Overview.pdf[2021-4-19]
[20] Mathieson K, Passmore M S, Seller P, Prydderch M L, O’Shea V, Bates R L, Smith K M, Rahman M 2002 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 487 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 6 探测模块的噪声水平(1 ADC=0.25 mV) (a) 传输曲线的Mean值分布(FPN为1.01067 ADC, 转换成电压值为0.253 mV); (b) 传输曲线的Sigma值分布(TN为6.60172 ADC, 转换成电压值为1.65 mV)
Fig. 6. Noise level of detector module (1 ADC unit = 0.25 mV): (a) Mean distribution of transmission curve (FPN is 1.01067 ADC, converted into the voltage is 0.253 mV); (b) Sigma distribution of transmission curve (TN is 1.01067 ADC, converted into the voltage is 1.65 mV).
表 1 两种算法的复杂度比较
Table 1. Comparison of the complexity of the two algorithms.
相邻法 比较法 循环次数 $4 \times M \times N$ $({ { {M^2} \times {N^2} - M \times N} })/{2}$ 时间复杂度T(N) O(N) O(N2) -
[1] Weste N H E, Eshraghian K 1985 NASA STI/Recon Technical Report A 85 47028
[2] MacMillen D, Camposano R, Hill D, Williams T W 2000 IEEE Trans.Comput.Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 19 1428
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Greiner L, Anderssen E, Matis H S, Ritter H G, Schambach J, Silber J, Stezelberger T, Sun X, Szelezniak M, Thomas J, Videbaek F, Vu C, Wieman H 2011 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 650 68
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Contin G, Anderssen E, Greiner L, Schambach J, Silber J, Stezelberger T, Sun X, Szelezniak M, Vu C, Wieman H, Woodmansee S 2015 JINST 10 C03026
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Brüning O, Burkhardt H, Myers S 2012 Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 67 705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Schukraft J 2012 Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 370 917
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Mager M 2016 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 824 434
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Keil M 2015 JINST 10 C03012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhou Y, Lu Y P, Wu Z G, Shi T, Ju X D, Dong J, Zhu H B, Ouyang Q 2020 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 980 164427
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wei W, Zhang J, Ning Z, Lu Y P, Fan L, Li H S, Jiang X S, Lan A K, Ou-Yang Q, Wang Z, Zhu K J, Chen Y B, Liu P 2016 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 835 169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Zhang C 2009 Chin. Phys. C 33 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Harris F A 2006 Nucl. Phys. B 162 345
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Hu G C, Baudot J, Bertolone G, et al. 2010 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 623 480
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Contin G, Greiner L, Schambach J, Szelezniak M, Anderssen E, Bell J, Cepeda M, Johnson T, Qiu H, Ritter H G, Silber J, Stezelberger T, Sun X M, Tran C, Vu C, Wieman H, Wilson K, Witharm R, Woodmansee S, Wolf J 2018 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 907 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ultimate user manual, Himmi A, Doziere G, Bertolone G, Dulinski W, Coll-edani C, Dorokhov A, Hu Ch, Morel F, Pham H, Valin I, Wang J http://www.iphc.cnrs.fr/IMG/pdf/Ultimate_UserManual.pdf [2021-3-9]
[16] Valin I, Hu-Guo C, Baudot J, Bertolone G, Besson A, Colledani C, Clau G, Dorokhov A, Dozière G, Dulinski W, Gelin M, Goffe M, Himmi A, Jaaskel-ainen K, Morel F, Pham H, Santos C, Senyukov S, Specht M, Voutsinas G, Wang J, Winter M 2012 JINST 7 C01102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Highland V L 1975 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. 129 497
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Szelezniak M A, Deptuch G W, Guilloux F, Heini S, Himmi A 2007 IEEE J. Sensor 7 137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 7 Series FPGAs Data Sheet: Overview, Xinlinx https://www.xilinx.com/support/documentation/data_sheets/ds180_7 Series_Overview.pdf[2021-4-19]
[20] Mathieson K, Passmore M S, Seller P, Prydderch M L, O’Shea V, Bates R L, Smith K M, Rahman M 2002 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 487 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 8294
- PDF下载量: 102
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: