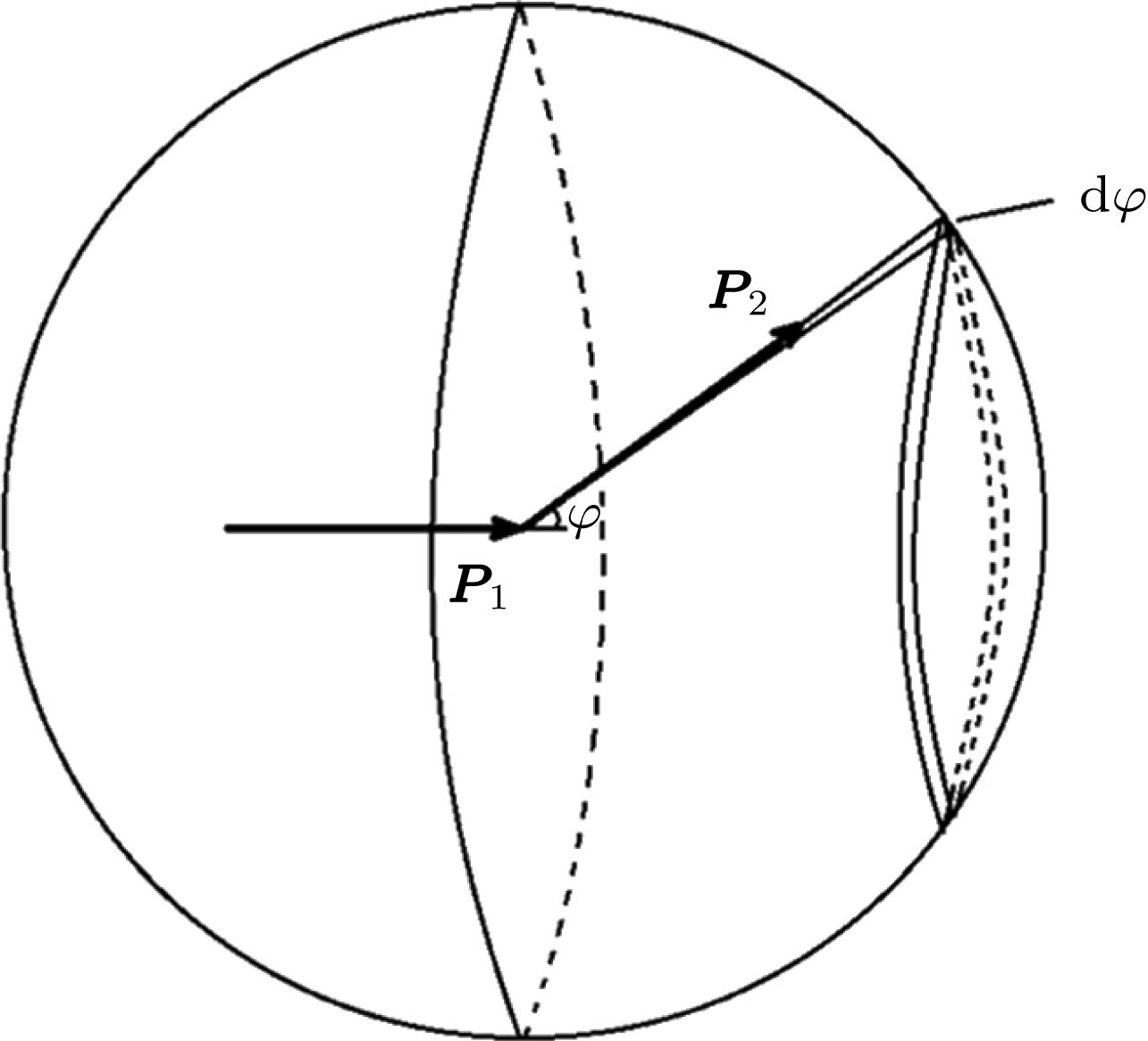
-
惯性约束聚变(ICF)是实现受控热核聚变可能途径之一. 聚变中子源项是氘氚激光等离子体物理设计与分析的重要参数之一, 其准确性直接影响分析结果的可靠性. 目前国内外对于ICF氘氚聚变反应产生的中子源项研究主要基于解析公式法, 在温度和反应类型等方面适用范围有限. 本文采用粒子云概念对氘、氚粒子云团开展了随机抽样与时空网格划分, 然后基于麦克斯韦速率分布律对氘氚聚变反应开展了多普勒能量展宽效应分析与微分截面温度修正工作, 耦合蒙特卡罗方法和离散纵标方法, 开展了激光等离子体中D-T粒子云团聚变反应率的数值模拟工作. 研究结果显示, 与原核数据库截面相比, D-T, D-D, T-D截面经修正后多普勒温度效应显著. 在20—100 keV的等离子体温度范围内, 相较传统的解析公式法, 本文模拟结果更符合最新的ENDF核数据库的氘氚反应截面数据, 且与解析公式法结果在低能区存在较大误差, 可能是计算方法不同与低温截面差异过大原因导致.Inertial confinement fusion (ICF) is one of the possible ways to realize controlled thermonuclear fusion. The fusion neutron source term is one of the important parameters in the physical design and analysis of laser plasma. The accuracy of the fusion neutron source term directly affects the reliability of the analysis results. At present, the neutron source term of deuterium-tritium fusion reaction in ICF is mainly based on formula method. It has limited applications in temperature and reaction type. Because of a large quantity of data, it is impossible to simulate the fusion reaction of each particle. In this paper, the concept of particle cloud is introduced, that is, the collection of the like particles with the same position and speed, and it is considered that the action of particle cloud is the same reaction. Because the particles should satisfy the Maxwell velocity distribution at a certain temperature and the direction is all around the circumference angle, the collision cross sections between the incident particle and different target particles are different. Therefore, the design program takes all the possible velocities, polar angles and direction angles, reads the collision cross sections between deuterium and tritium and makes corrections, and obtains the multi-temperature differential correction cross sections of deuterium and tritium fusion with Doppler energy broadening. On these bases, Monte Carlo method and discrete ordinate method method are used. A numerical simulation program for the fusion rate of D-T particles in laser plasma is developed in this paper. It is found that there are significant differences between the DT, DD, TD cross sections and the original cross sections after Doppler broadening. In a range of plasma temperature between 20 keV and 100 keV, the simulation results are more consistent with the cross section data of ENDF/B-VI and ENDF/B-VII databases of deuterium-tritium fusion reaction than those from the analytical formula method. There is a large error between the numerical simulation results and the analytical formula method in the low energy region. It may be caused by the difference of calculation methods and too big difference among the used fusion cross sections at low temperature.
-
Keywords:
- laser plasma /
- deuterium-tritium fusion reaction /
- differential cross-section temperature correction /
- Monte Carlo method /
- discrete ordinate method
[1] Nuckolls J H 1982 Phys. Today 35 24
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Johnson T H 2005 Proc. IEEE 72 548
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Brysk H 1973 Plasma Phys. 15 611
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Davis J, Petrov G M, Petrova T, Willingale L, Maksimchuk A, Krushelnick K 2010 Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 52 045015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Petrov G M, Higginson D P, Davis J, et al. 2013 Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 55 105009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Ditmire T, Zweiback J, Yanovsky V P, et al. 1999 Nature 398 6727
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Bang W, Dyer G, Quevedo H J, Bernstein A C, Gaul E, Donovan M, Ditmire T 2013 Phys. Rev. E 87 023106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bang W, Barbui M, Bonasera A, et al. T 2013 Phys. Rev. E 88 033108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Jung D, Falk K, Guler N, et al. 2013 Phys. Plasmas 20 056706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Ni M, Wang Y, Yuan B, Jiang J, Wu Y 2013 Fusion Eng. Des. 88 2422
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Nie B, Ni M, Wei S 2017 J. Hazardous Mater. 327 135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Nie B, Ran G, Zeng Q, Du H, Li Z, Chen Y, Zhu Z, Zhao X, Ni M, Li F 2019 Energ. Sci. Eng. 7 457
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] He M Q, Cai H B, Zhang H, et al. 2015 Phys. Plasmas 22 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Pomerantz I, Mccary E, Meadows A R, et al. 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 113 184801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Fausser C, Puma A L, Gabriel F, Villari R 2012 Fusion Eng. Des. 87 787
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 林尊琪 2006 第五届全国光子学大会会议论文集 黄山 2004年10月18日 p4
Lin Z Q 2006 The Proc. the Fifth National Conference on Photonics Huangshan, China, October 18, 2004 p4 (in Chinese)
[17] 樊铁栓, 黄钢, 冯玉清 2005 原子能科学技术 39 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fan T S, Huang G, Feng Y Q 2005 At. Energ. Sci. Technol. 39 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Xu B, Ma Y, Yang X, Tang W, Wang S, Ge Z, Zhao Y, Ke Y 2017 Laser and Particle Beams 35 366
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bosch H S, Hale G M 1992 Nucl. Fusion 32 611
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] https://t2.lanl.gov/nis/data/endf/ [2019−3−28]
-
-
[1] Nuckolls J H 1982 Phys. Today 35 24
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Johnson T H 2005 Proc. IEEE 72 548
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Brysk H 1973 Plasma Phys. 15 611
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Davis J, Petrov G M, Petrova T, Willingale L, Maksimchuk A, Krushelnick K 2010 Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 52 045015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Petrov G M, Higginson D P, Davis J, et al. 2013 Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 55 105009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Ditmire T, Zweiback J, Yanovsky V P, et al. 1999 Nature 398 6727
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Bang W, Dyer G, Quevedo H J, Bernstein A C, Gaul E, Donovan M, Ditmire T 2013 Phys. Rev. E 87 023106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bang W, Barbui M, Bonasera A, et al. T 2013 Phys. Rev. E 88 033108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Jung D, Falk K, Guler N, et al. 2013 Phys. Plasmas 20 056706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Ni M, Wang Y, Yuan B, Jiang J, Wu Y 2013 Fusion Eng. Des. 88 2422
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Nie B, Ni M, Wei S 2017 J. Hazardous Mater. 327 135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Nie B, Ran G, Zeng Q, Du H, Li Z, Chen Y, Zhu Z, Zhao X, Ni M, Li F 2019 Energ. Sci. Eng. 7 457
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] He M Q, Cai H B, Zhang H, et al. 2015 Phys. Plasmas 22 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Pomerantz I, Mccary E, Meadows A R, et al. 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 113 184801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Fausser C, Puma A L, Gabriel F, Villari R 2012 Fusion Eng. Des. 87 787
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 林尊琪 2006 第五届全国光子学大会会议论文集 黄山 2004年10月18日 p4
Lin Z Q 2006 The Proc. the Fifth National Conference on Photonics Huangshan, China, October 18, 2004 p4 (in Chinese)
[17] 樊铁栓, 黄钢, 冯玉清 2005 原子能科学技术 39 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fan T S, Huang G, Feng Y Q 2005 At. Energ. Sci. Technol. 39 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Xu B, Ma Y, Yang X, Tang W, Wang S, Ge Z, Zhao Y, Ke Y 2017 Laser and Particle Beams 35 366
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bosch H S, Hale G M 1992 Nucl. Fusion 32 611
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] https://t2.lanl.gov/nis/data/endf/ [2019−3−28]
计量
- 文章访问数: 14499
- PDF下载量: 114
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: