-
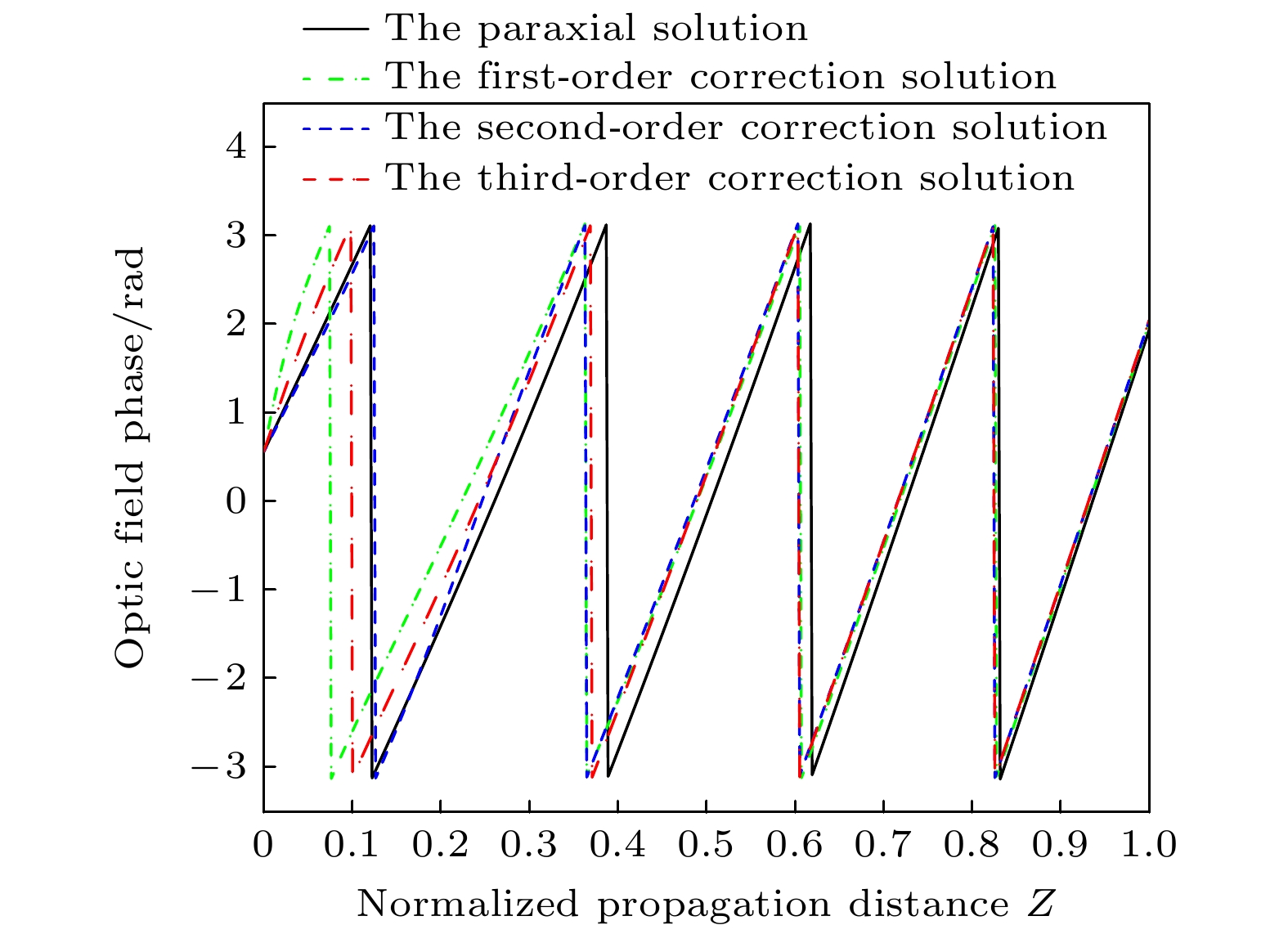
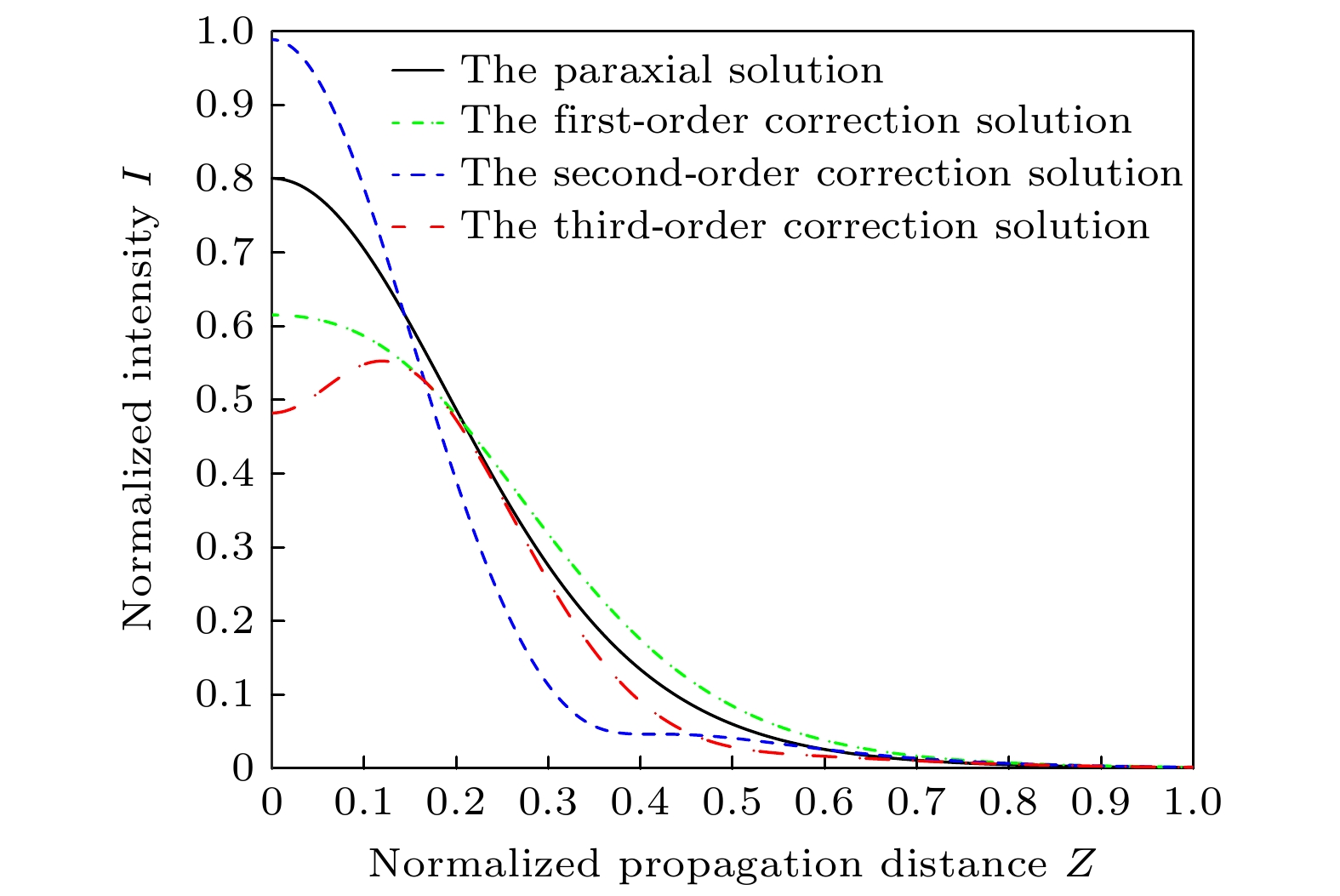
Generalized parabolic beams have various optical morphologies. They can be used in different research fields, such as component design, aero-optics, and microwave wireless power transmission. Studying the near-field transmission characteristics of these beams is important for improving utilization efficiency. We develop a more accurate theoretical framework to precisely understand the propagation behaviors of complex light fields in the near-field range, especially to break through the limitations of conventional near-axis approximation. This framework fully reveals the propagation mechanism of parabolic beams and their energy transmission modes. Here, based on the principle of independent propagation and the virtual source method, a group of virtual sources are introduced to analyze generalized parabolic beams. These beams can be expanded into the superposition of infinite continuous integer Bessel beams. Then, by combining the Weber integral formula and the Fourier Bessel transform, we rigorously derive an integral expression for generalized parabolic beams during near-field propagation. This expression breaks through the limitation of the traditional paraxial approximation and contains all the key propagation parameters of the family of beams. Based on this integral expression, the intensity distribution and phase characteristics of the generalized parabolic beam along the optical axis are further calculated and analyzed to reveal its energy transfer mode and phase characteristics. By comparing the paraxial approximate solution with the nonparaxial corrected solution for generalized parabolic beams, the far-field propagation of generalized parabolic beams is found to be the same when the propagation distance is sufficiently long. Such simulation results indirectly confirm the correctness of the obtained theoretical solution. The simple paraxial approximation theory can be used conveniently to calculate the far-field propagation of generalized parabolic beams. However, large errors exist when paraxial theory is used to calculate the near-field distribution of generalized parabolic beams. Although calculating nonparaxial propagation is especially complex, the nonparaxial correction solution is necessary when generalized parabolic beams are used in near-field research. Such research results not only deepen the understanding of the propagation mechanism of generalized parabolic beams but also lay a theoretical foundation for studying the precise propagation behaviors of other complex light fields in near-field optics.
-
Keywords:
- generalized parabolic beams /
- virtual sources /
- paraxial approximation /
- superposition principle
[1] Durnin J, Miceli J J, Eberly J H 1987 Phys. Rev. Lett. 58 1499
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Durnin J 1987 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 4 651
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Gutiérrez-Vega J C, Iturbe-Castillo M D, Chávez-Cerda S 2000 Opt. Lett. 25 1493
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Sosa-Sánchez C T, Silva-Ortigoza G, Juárez-Reyes S A, et al. 2017 J. Opt. 19 085604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Bandres M A, Gutirrez-Vega J C, Chvez-Cerda S 2004 Opt. Lett. 29 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Khonina S N, Ustinov A V, Chávez-Cerda S 2018 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 35 1511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Liang Y S, Yan S H, Wang Z J, Li R Z, Cai Y N, He M R, Yao B L, Lei M 2020 Rep. Prog. Phys. 83 032401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Gu S Y, Yu X H, Bai C, Min J W, Li R Z, Yang Y L, Yao B L 2022 Front. Phys. 10 1111023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Deschamps G A 1971 Electron. Lett. 7 684
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Felsen L B 1976 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 66 751
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Seshadri S R 2002 Opt. Lett. 27 998
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Borghi R, Santarsiero M 1997 Opt. Lett. 22 262
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li Y J, Lee H, Wolf E 2004 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 21 640
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Song L B, Ren Z J, Fan C J, Qian Y X 2021 Opt. Commun. 499 127307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Gori F, Guattari G, Padovani C 1987 Opt. Commun. 64 491
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Seshadri S R 2002 Opt. Lett. 27 1872
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yan S H, Yao B L, Lei M, Dan D, Yang Y L, Gao P 2012 Opt. Lett. 37 4774
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Seshadri S R 2003 Opt. Lett. 28 595
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Khonina S N, Ustinov A V, Porfirev A P 2019 Opt. Commun. 450 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 陈鑫淼, 李海英, 吴涛, 孟祥帅, 黎凤霞 2023 72 100302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen X M, Li H Y, Wu T, Meng X S, Li F X 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 100302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 岳东宁, 董全力, 陈民, 赵耀, 耿盼飞, 远晓辉, 盛政明, 张杰 2023 72 125201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yue D N, Dong Q L, Chen M, Zhao Y, Geng P F, Yuan X H, Sheng Z M, Zhang J 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 125201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 尹培琪, 许博坪, 刘颖华, 王屹山, 赵卫, 汤洁 2024 73 095202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yin P Q, Xu B P, Liu Y H, Wang Y S, Zhao W, Tang J 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 095202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] Durnin J, Miceli J J, Eberly J H 1987 Phys. Rev. Lett. 58 1499
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Durnin J 1987 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 4 651
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Gutiérrez-Vega J C, Iturbe-Castillo M D, Chávez-Cerda S 2000 Opt. Lett. 25 1493
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Sosa-Sánchez C T, Silva-Ortigoza G, Juárez-Reyes S A, et al. 2017 J. Opt. 19 085604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Bandres M A, Gutirrez-Vega J C, Chvez-Cerda S 2004 Opt. Lett. 29 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Khonina S N, Ustinov A V, Chávez-Cerda S 2018 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 35 1511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Liang Y S, Yan S H, Wang Z J, Li R Z, Cai Y N, He M R, Yao B L, Lei M 2020 Rep. Prog. Phys. 83 032401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Gu S Y, Yu X H, Bai C, Min J W, Li R Z, Yang Y L, Yao B L 2022 Front. Phys. 10 1111023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Deschamps G A 1971 Electron. Lett. 7 684
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Felsen L B 1976 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 66 751
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Seshadri S R 2002 Opt. Lett. 27 998
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Borghi R, Santarsiero M 1997 Opt. Lett. 22 262
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li Y J, Lee H, Wolf E 2004 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 21 640
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Song L B, Ren Z J, Fan C J, Qian Y X 2021 Opt. Commun. 499 127307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Gori F, Guattari G, Padovani C 1987 Opt. Commun. 64 491
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Seshadri S R 2002 Opt. Lett. 27 1872
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yan S H, Yao B L, Lei M, Dan D, Yang Y L, Gao P 2012 Opt. Lett. 37 4774
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Seshadri S R 2003 Opt. Lett. 28 595
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Khonina S N, Ustinov A V, Porfirev A P 2019 Opt. Commun. 450 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 陈鑫淼, 李海英, 吴涛, 孟祥帅, 黎凤霞 2023 72 100302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen X M, Li H Y, Wu T, Meng X S, Li F X 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 100302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 岳东宁, 董全力, 陈民, 赵耀, 耿盼飞, 远晓辉, 盛政明, 张杰 2023 72 125201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yue D N, Dong Q L, Chen M, Zhao Y, Geng P F, Yuan X H, Sheng Z M, Zhang J 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 125201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 尹培琪, 许博坪, 刘颖华, 王屹山, 赵卫, 汤洁 2024 73 095202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yin P Q, Xu B P, Liu Y H, Wang Y S, Zhao W, Tang J 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 095202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 1822
- PDF Downloads: 46
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: