-
Display devices based on new generation of light source have become the mainstream of the market due to the advantages of large color gamut, high brightness, and high resolution. Blue light, as one of the three primary colors, is an indispensable part of the display system. Its parameters, such as wavelength, spectral width, brightness affect the color gamut of the display system from different aspects. Strong blue light can damage the retinal cells of the human eye and affect the biological rhythm. Therefore, it is needed to consider how to reduce the blue light hazard when designing the display system. Display devices, represented by mobile phones and TV are an important part for human-computer interaction. In order to reduce the blue light hazard, anti-blue hazard mode is usually used and this mode will affect the color gamut of display device. To measure the color gamut and blue light hazards in a display system with the blue light protection mode is necessary. We propose a theory of measuring the characteristic points of display devices to obtain the stereoscopic color gamut. Several mainstream mobile phones currently on the market are used as experimental samples to measure the stereoscopic color gamut and blue light hazard value. Based on the results, we propose the measurement standard of the conversion ratio between the color gamut and the blue light hazard to evaluate the quality of the anti-blue hazard mode.
-
Keywords:
- display /
- stereoscopic color gamut /
- blue light hazard
[1] Sun Y, Zhang C, Yang Y L, Ma H M, Sun Y B 2019 Curr. Opt. Photonics 3 590
[2] Wu T Z, Sher C W, Lin Y, Lee C F, Liang S J, Lu Y J, Huang C S W, Guo W J, Kuo H C, Chen Z 2018 Appl. Sci. 8 1557
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Hosoumi S, Yamaguchi T, Inoue H, Nomura S, Yamaoka R, Sasaki T, Seo S 2017 SID Symposium, Seminar, and Exhibition 2017, Display Week 2017 Los Angeles U.S.A. May 21–26, 2017 p13
[4] Lin S Y, Tan G J, Yu J H, Chen E G, Weng Y L, Zhou X T, Xu S, Yan F Q, Guo T L 2019 Opt. Express 27 28480
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhao J Y, Yan Y L, Gao Z H, Du Y X, Dong H Y, Yao J N, Zhao Y S 2019 Nat. Commun. 10 870
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] ITU-R Recommendation BT-2020 2012 Parameter Values for Ultra-high Definition Television Systems for Production and International Programme Exchange
[7] ITU-R Recommendation BT-709 1990 Parameter values for the HDTV standards for production and international programme exchange
[8] 灯和灯系统的光生物安全 第2部分: 非激光光辐射安全相关的制造要求指南
GB/T 30117.2—2013 2013 Photobiological Safety of Lamps and Lamp Systems—Part 2: Guidance on Manufacturing Requirements Relating to Non-laser Optical Radiation Safety (in Chinese)
[9] BSI Standards Publication, PD IEC-TR 62741-2-2009 2009 Photobiological Safety of Lamps and Lamp Systems—Part 2: Guidance on Manufacturing Requirements Relating to Non-laser Optical Radiation Safety
[10] CIE 2000 CIE Collection in Photobiology and Photochemistry 2000 138/1 CIE TC 6-14 report: Blue-light Photochemical Retinal Hazard
[11] Noell W K, Walker V S, Kang B S, Berman S 1966 Invest. Ophth. 5 450
[12] Ham W T, Mueller H A, Ruffolo J J, Clarke A M 1979 Photochem. Photobiol. 29 735
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wenzel A, Grimm C, Samardzijia M, Reme C E 2005 Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 24 275
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Enezi J A, Revell V, Brown T, Wynne J, Schlangen L, Lucas R 2011 J. Biol. Rhythms 26 314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Brainard G C, Hanifin J P, Greeson J M, Byrne B, Glickman G, Gerner E, Rollag M D 2001 J. Neurosci. 21 6405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Baczynska K, Price L 2013 Lighting Res. Technol. 45 40
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 刘婕 2014 硕士学位论文 (上海: 复旦大学)
Liu J 2014 M. S. Thesis (Shanghai: Fudan University) (in Chinese)
[18] Nie J X, Chen Z Z, Jiao F, Zhan J L, Chen Y F, Chen Y Y, Pan Z J, Kang X N, Wang Y Z, Wang Q, Zhou T H, Dang W M, Dong W T, Zhou S Z, Yu X, Zhang G Y, Shen B 2021 Opt. Laser Technol. 135 106709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhang J J, Guo W H, Xie B, Yu X J, Luo X B, Zhang T, Yu Z H, Wang H, Jin X 2017 Opt. Laser Technol. 94 193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wang G, Yang Y H, Dong T H, Gu C, Xu L C 2018 Fifth International Symposium on Laser Interaction with Matter (Changsha, China) November 11–13, 2018
[21] 王聪 2020 硕士学位论文(合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
Wang C 2020 M. S. Thesis (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China) (in Chinese)
[22] 中国电子技术标准化研究赛西实验室 2018 激光电视视觉健康测试证书TC(2018)016
CESI Laboratory 2018 Testing Certificate of laser TV vision health TC(2018)016 (in Chinese)
[23] Chen H W, Lee J H, Lin B Y, Chen S, Wu S T 2018 Light Sci. Appl. 7 17168
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
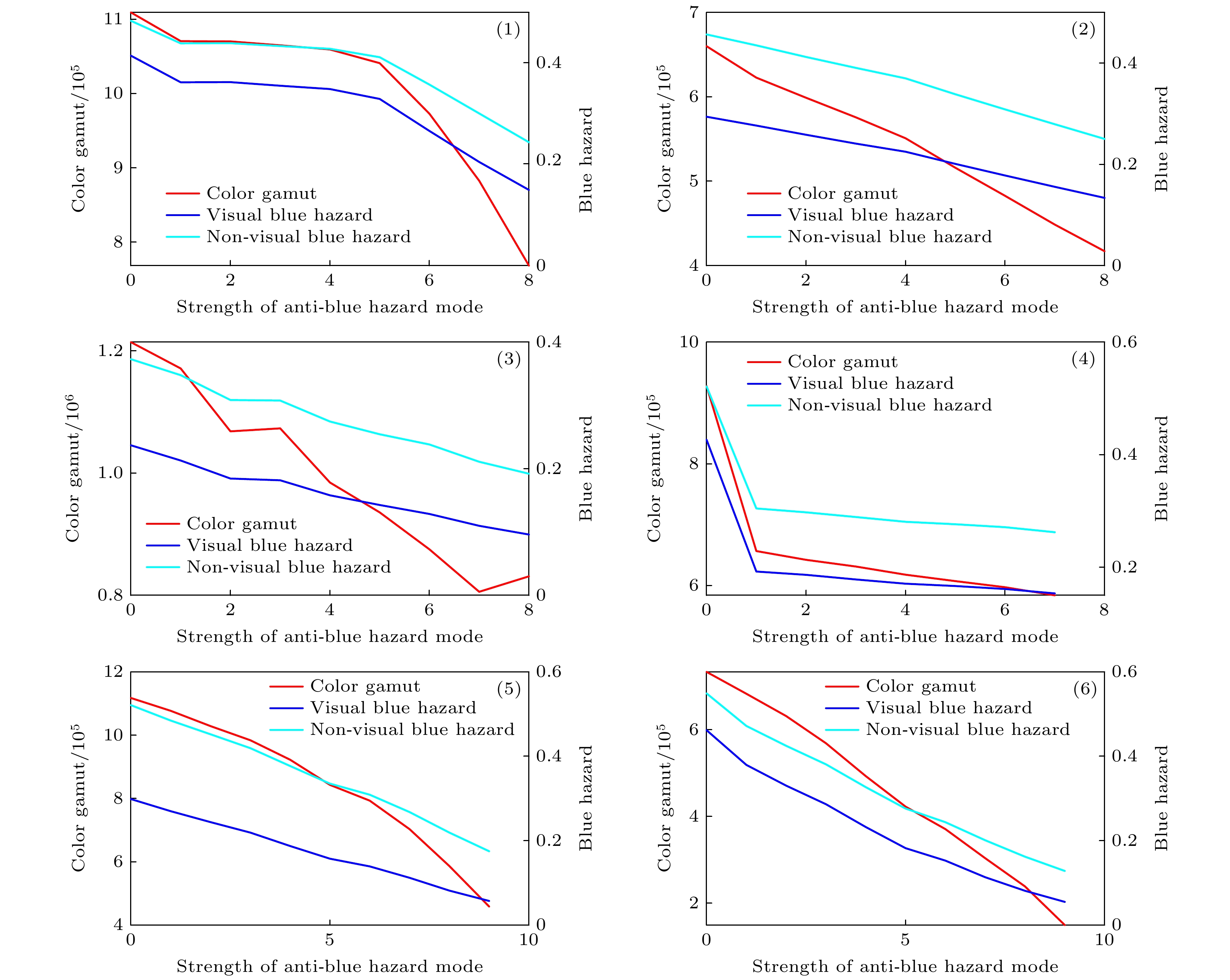
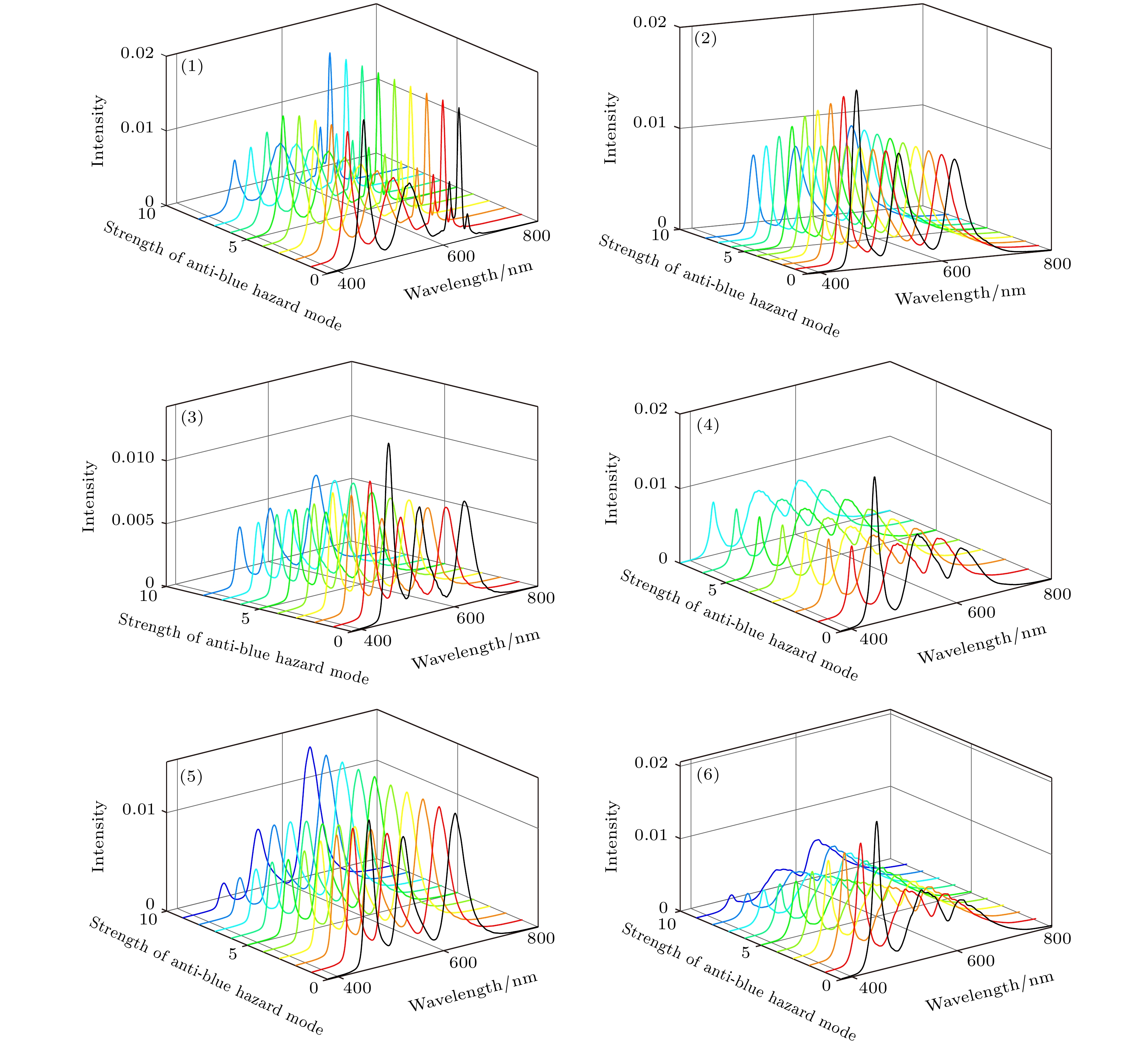
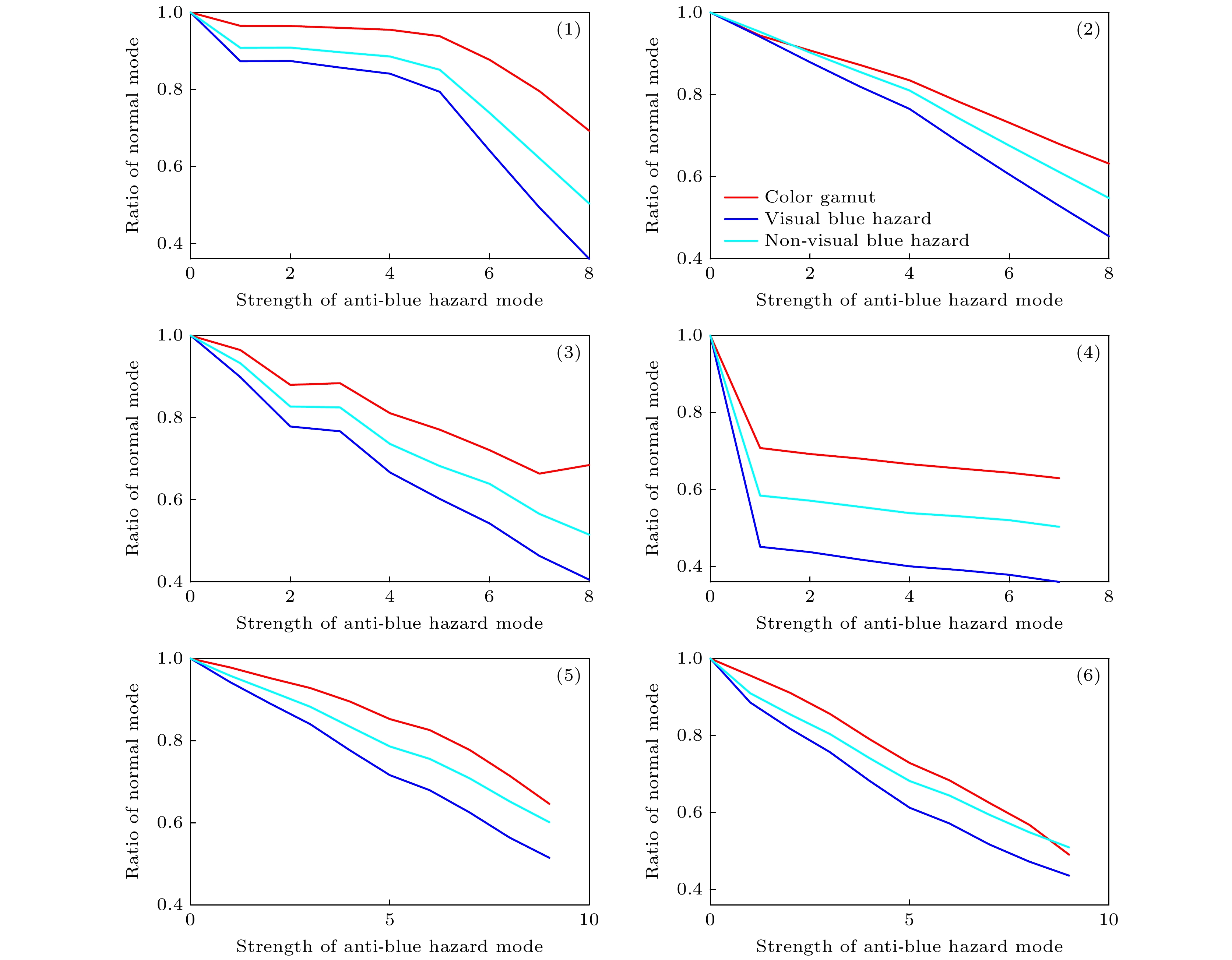
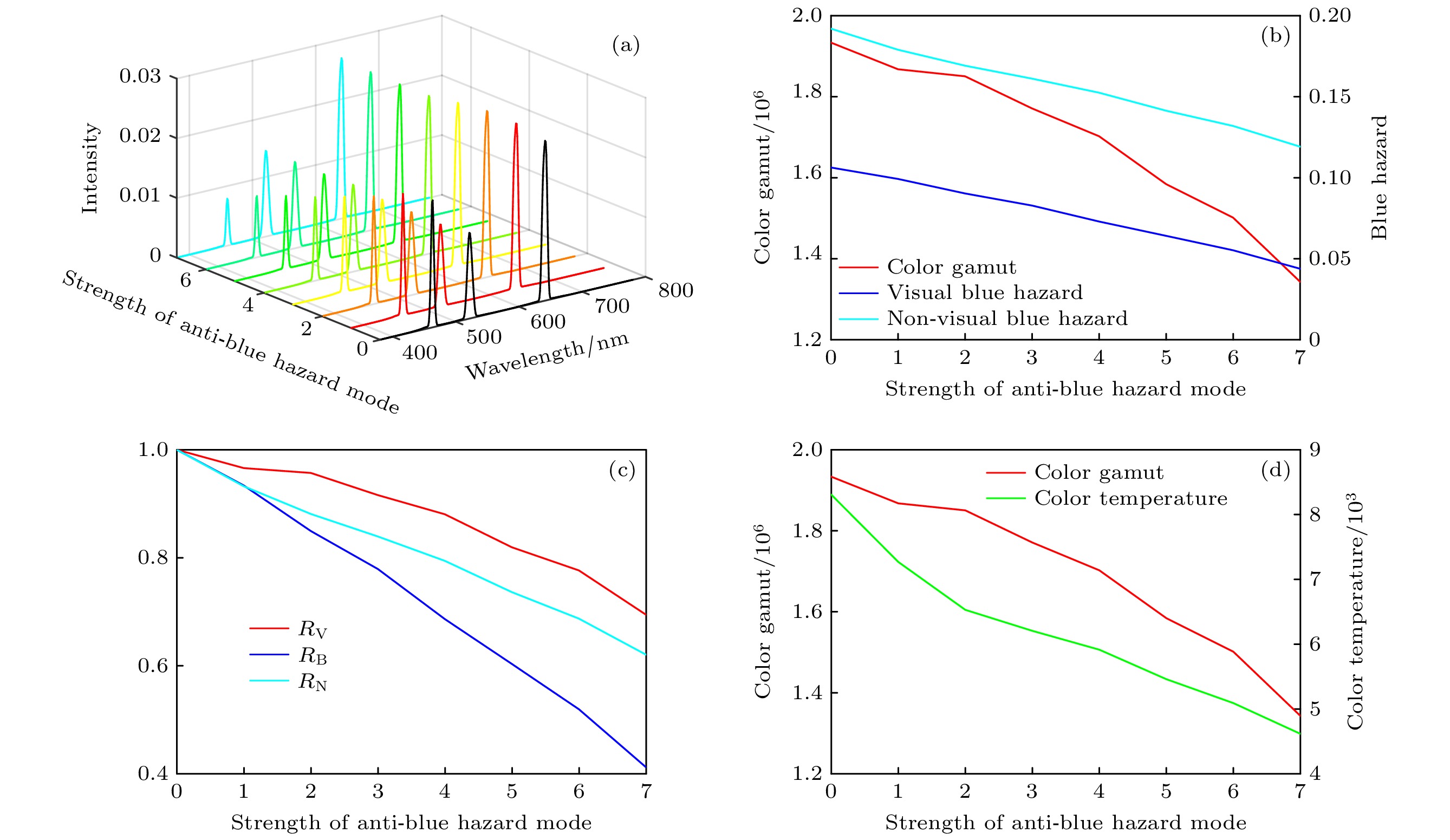
图 9 防蓝光模式强度的变化对激光电视参数的影响 (a) 光谱强度分布, 三基色中心波长分别为464 nm, 520 nm, 660 nm; (b)色域及两种蓝光危害, 蓝光危害通过白场光谱强度分布计算得到;
$ \left(\text{c}\right){R}_{\text{V}}, {R}_{\text{B}}, {R}_{\text{N}} $ 参数; (d)色域-色温曲线Figure 9. The influence of the strength of the anti-blue hazard mode on the parameters of laser TV: (a)Spectral power distribution, the peak wavelength of three primaries are 464 nm, 520 nm and 660 nm;(b)color gamut and two kinds of blue hazard, the blue light hazard is calculated from the white field spectral distribution; (c)
$ {R}_{\text{V}}, {R}_{\text{B}}, {R}_{\text{N}} $ parameter;(d) color gamut-color temperature curve.表 1
$ {L}_{\text{B}} $ 和$ {E}_{\text{B}} $ 与蓝光危害等级的关系Table 1. The relationship between
$ {L}_{\text{B}} $ ,$ {E}_{\text{B}} $ and the blue light hazard level.危害等级 IR0 IR1 IR2 IR3 ${{L} }_{\rm{B} }/$(${\rm{W} }{\cdot}{\rm{m} }^{-2}{\cdot} {\rm{s}{\rm{r} } }^{-1}$) ≤ 100 ${100—10}^{4}$ ${10}^{4}—4\times {10}^{6}$ > $ 4\times {10}^{6} $ ${{E} }_{\rm{B} }/$(${\rm{W} }{\cdot}{\rm{m} }^{-2}$) ≤ 800 ${800—10}^{3}$ ${10}^{3}—4\times {10}^{5}$ > $ 4\times {10}^{5} $ 表 2 几种设备的相关参数
Table 2. The parameters of experimental device.
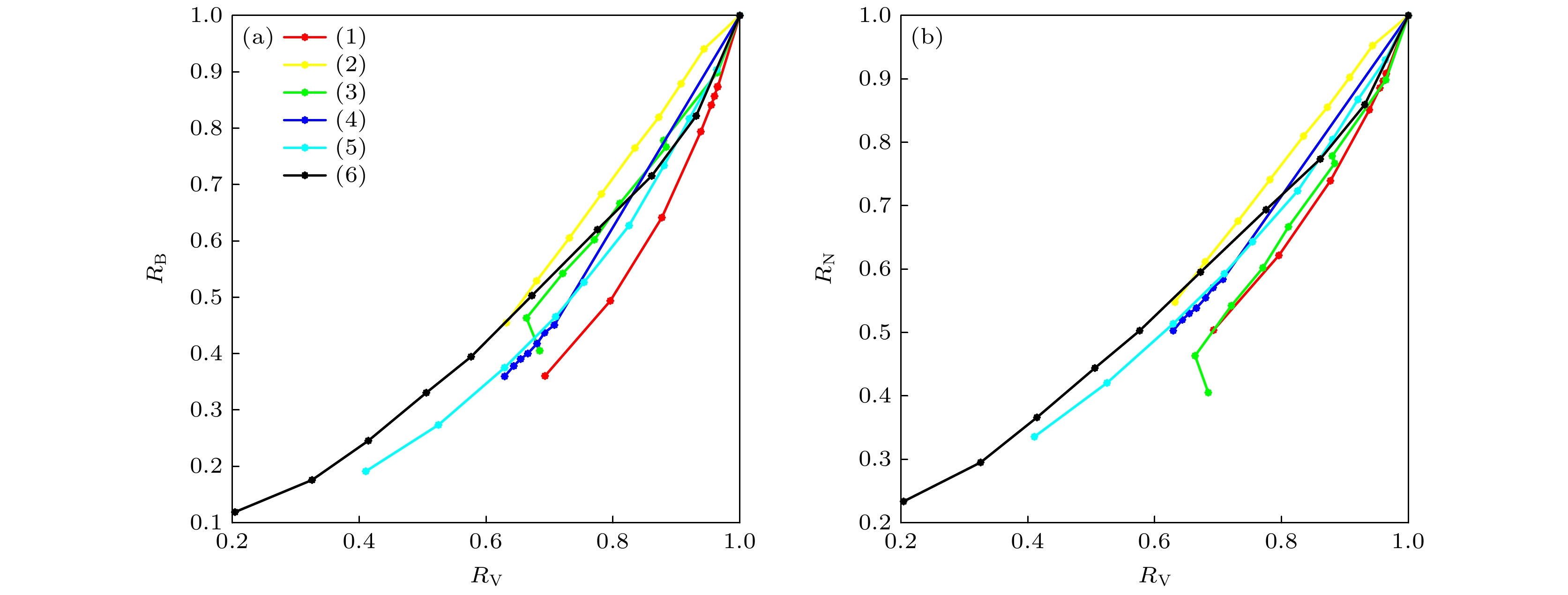
设备编号 屏幕种类 发布年份 (1) 液晶 2019 (2) OLED 2020 (3) OLED 2020 (4) 液晶 2019 (5) OLED 2021 (6) LED 2018 表 3 6台显示器色域和两种蓝光危害比例的线性拟合及相关系数
Table 3. Linear fitting and correlation coefficients of 6 display devices, between the ratio of color gamut and the ratio of two kinds of blue light hazards.
设备编号 $ {\boldsymbol{R}}_{\bf{V}} $-$ {\boldsymbol{R}}_{\bf{B}} $斜率 相关系数 $ {\boldsymbol{R}}_{\bf{V}} $-$ {\boldsymbol{R}}_{\bf{N}} $斜率 相关系数 (1) 2.3497 0.9265 1.7796 0.9511 (2) 1.4591 0.9969 1.2003 0.9955 (3) 1.7335 0.9748 1.3875 0.9788 (4) 1.7865 0.9943 1.3726 0.9970 (5) 1.5859 0.9242 1.2532 0.9598 (6) 1.2695 0.9223 1.0724 0.9513 -
[1] Sun Y, Zhang C, Yang Y L, Ma H M, Sun Y B 2019 Curr. Opt. Photonics 3 590
[2] Wu T Z, Sher C W, Lin Y, Lee C F, Liang S J, Lu Y J, Huang C S W, Guo W J, Kuo H C, Chen Z 2018 Appl. Sci. 8 1557
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Hosoumi S, Yamaguchi T, Inoue H, Nomura S, Yamaoka R, Sasaki T, Seo S 2017 SID Symposium, Seminar, and Exhibition 2017, Display Week 2017 Los Angeles U.S.A. May 21–26, 2017 p13
[4] Lin S Y, Tan G J, Yu J H, Chen E G, Weng Y L, Zhou X T, Xu S, Yan F Q, Guo T L 2019 Opt. Express 27 28480
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhao J Y, Yan Y L, Gao Z H, Du Y X, Dong H Y, Yao J N, Zhao Y S 2019 Nat. Commun. 10 870
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] ITU-R Recommendation BT-2020 2012 Parameter Values for Ultra-high Definition Television Systems for Production and International Programme Exchange
[7] ITU-R Recommendation BT-709 1990 Parameter values for the HDTV standards for production and international programme exchange
[8] 灯和灯系统的光生物安全 第2部分: 非激光光辐射安全相关的制造要求指南
GB/T 30117.2—2013 2013 Photobiological Safety of Lamps and Lamp Systems—Part 2: Guidance on Manufacturing Requirements Relating to Non-laser Optical Radiation Safety (in Chinese)
[9] BSI Standards Publication, PD IEC-TR 62741-2-2009 2009 Photobiological Safety of Lamps and Lamp Systems—Part 2: Guidance on Manufacturing Requirements Relating to Non-laser Optical Radiation Safety
[10] CIE 2000 CIE Collection in Photobiology and Photochemistry 2000 138/1 CIE TC 6-14 report: Blue-light Photochemical Retinal Hazard
[11] Noell W K, Walker V S, Kang B S, Berman S 1966 Invest. Ophth. 5 450
[12] Ham W T, Mueller H A, Ruffolo J J, Clarke A M 1979 Photochem. Photobiol. 29 735
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wenzel A, Grimm C, Samardzijia M, Reme C E 2005 Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 24 275
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Enezi J A, Revell V, Brown T, Wynne J, Schlangen L, Lucas R 2011 J. Biol. Rhythms 26 314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Brainard G C, Hanifin J P, Greeson J M, Byrne B, Glickman G, Gerner E, Rollag M D 2001 J. Neurosci. 21 6405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Baczynska K, Price L 2013 Lighting Res. Technol. 45 40
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 刘婕 2014 硕士学位论文 (上海: 复旦大学)
Liu J 2014 M. S. Thesis (Shanghai: Fudan University) (in Chinese)
[18] Nie J X, Chen Z Z, Jiao F, Zhan J L, Chen Y F, Chen Y Y, Pan Z J, Kang X N, Wang Y Z, Wang Q, Zhou T H, Dang W M, Dong W T, Zhou S Z, Yu X, Zhang G Y, Shen B 2021 Opt. Laser Technol. 135 106709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhang J J, Guo W H, Xie B, Yu X J, Luo X B, Zhang T, Yu Z H, Wang H, Jin X 2017 Opt. Laser Technol. 94 193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wang G, Yang Y H, Dong T H, Gu C, Xu L C 2018 Fifth International Symposium on Laser Interaction with Matter (Changsha, China) November 11–13, 2018
[21] 王聪 2020 硕士学位论文(合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
Wang C 2020 M. S. Thesis (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China) (in Chinese)
[22] 中国电子技术标准化研究赛西实验室 2018 激光电视视觉健康测试证书TC(2018)016
CESI Laboratory 2018 Testing Certificate of laser TV vision health TC(2018)016 (in Chinese)
[23] Chen H W, Lee J H, Lin B Y, Chen S, Wu S T 2018 Light Sci. Appl. 7 17168
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 8211
- PDF Downloads: 88
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: