-
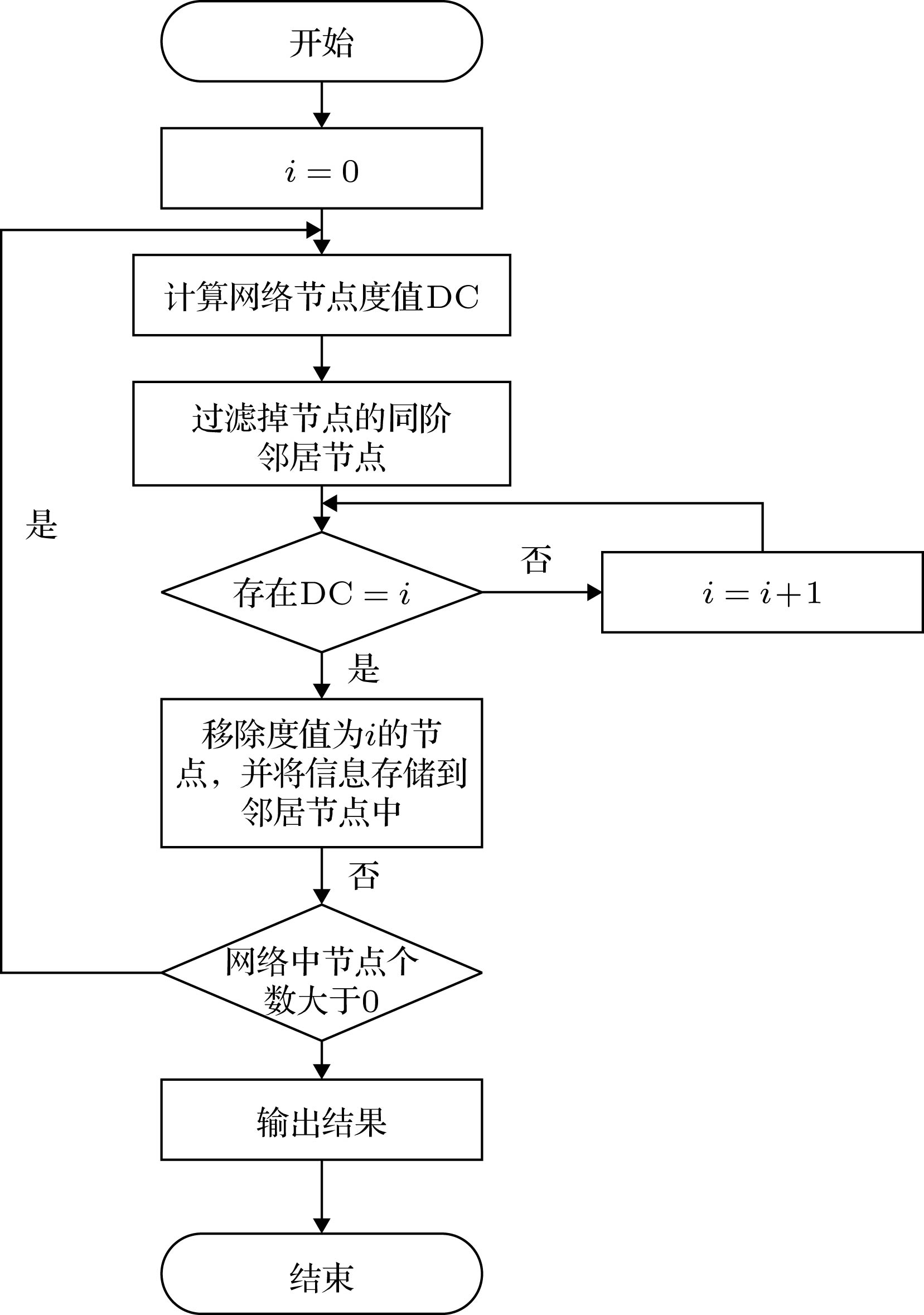
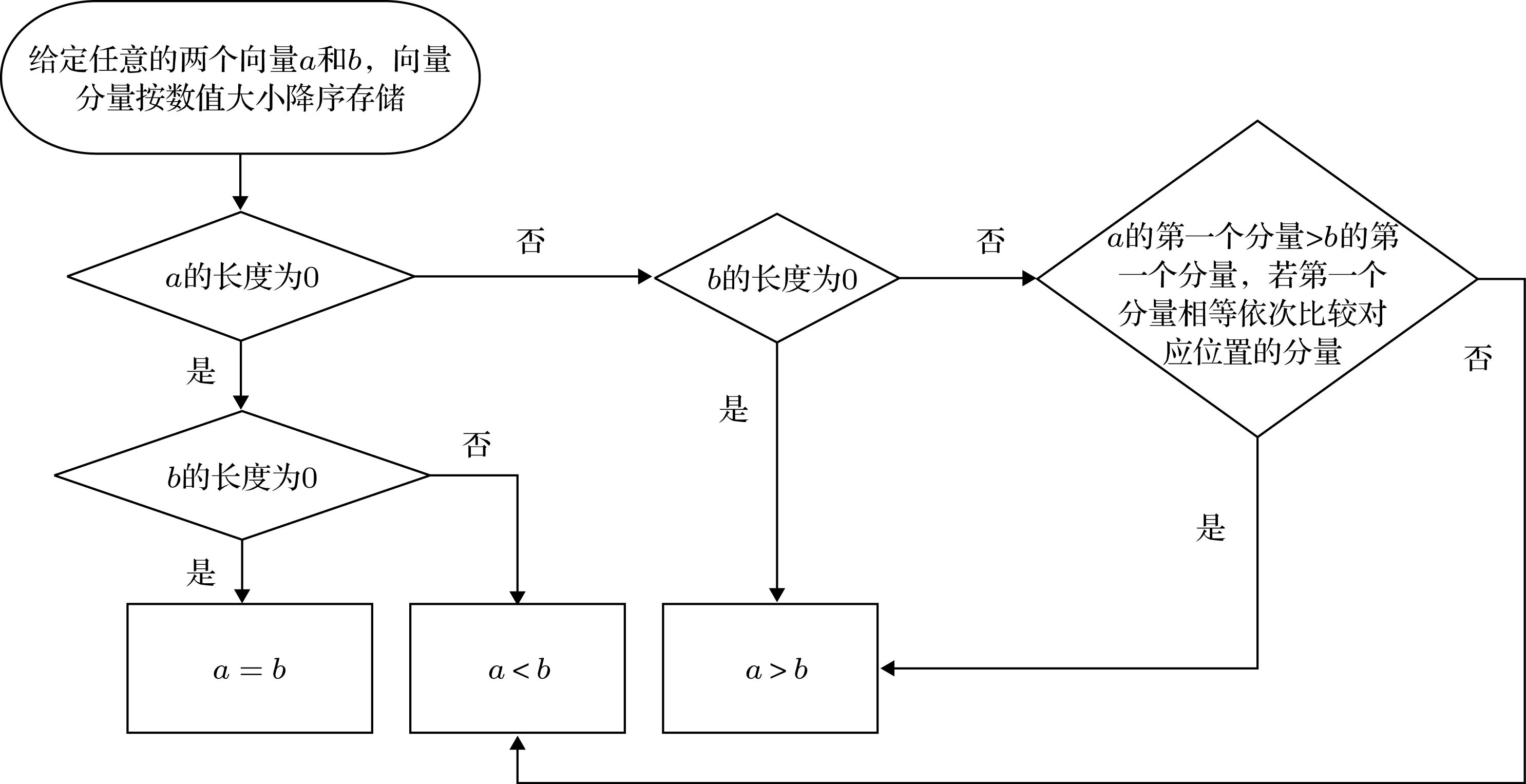
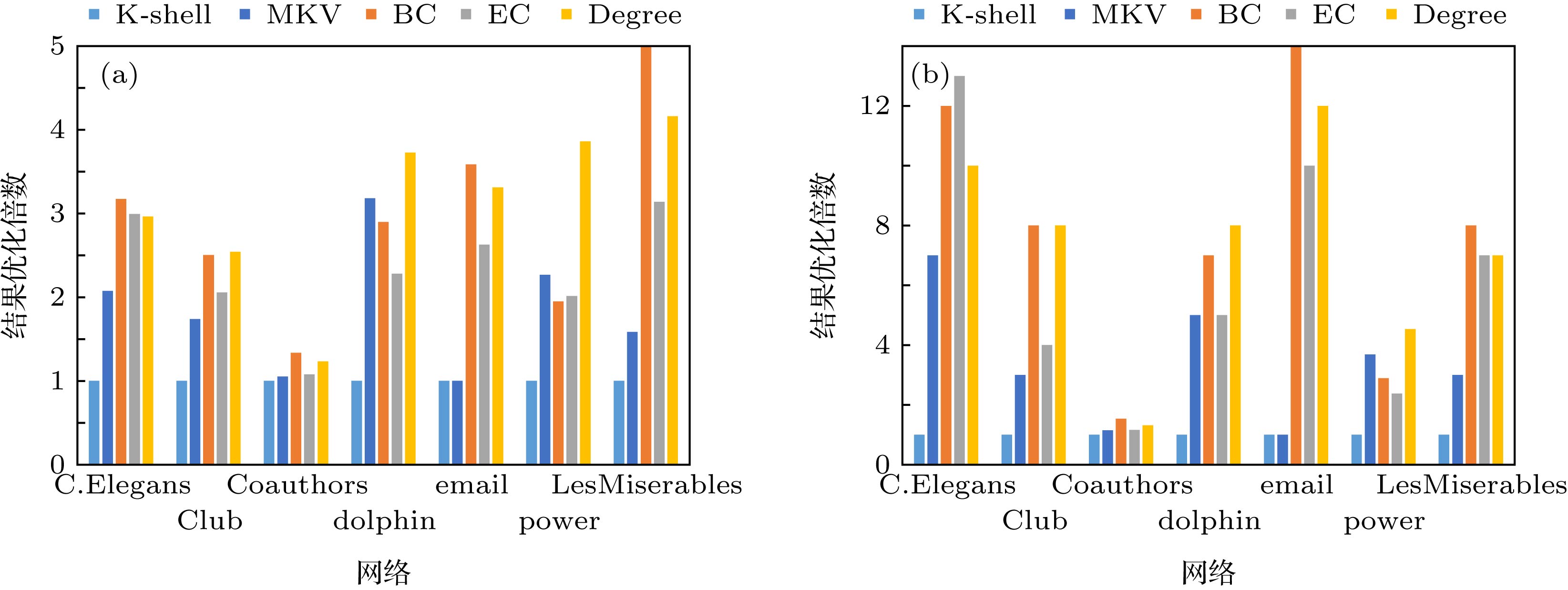
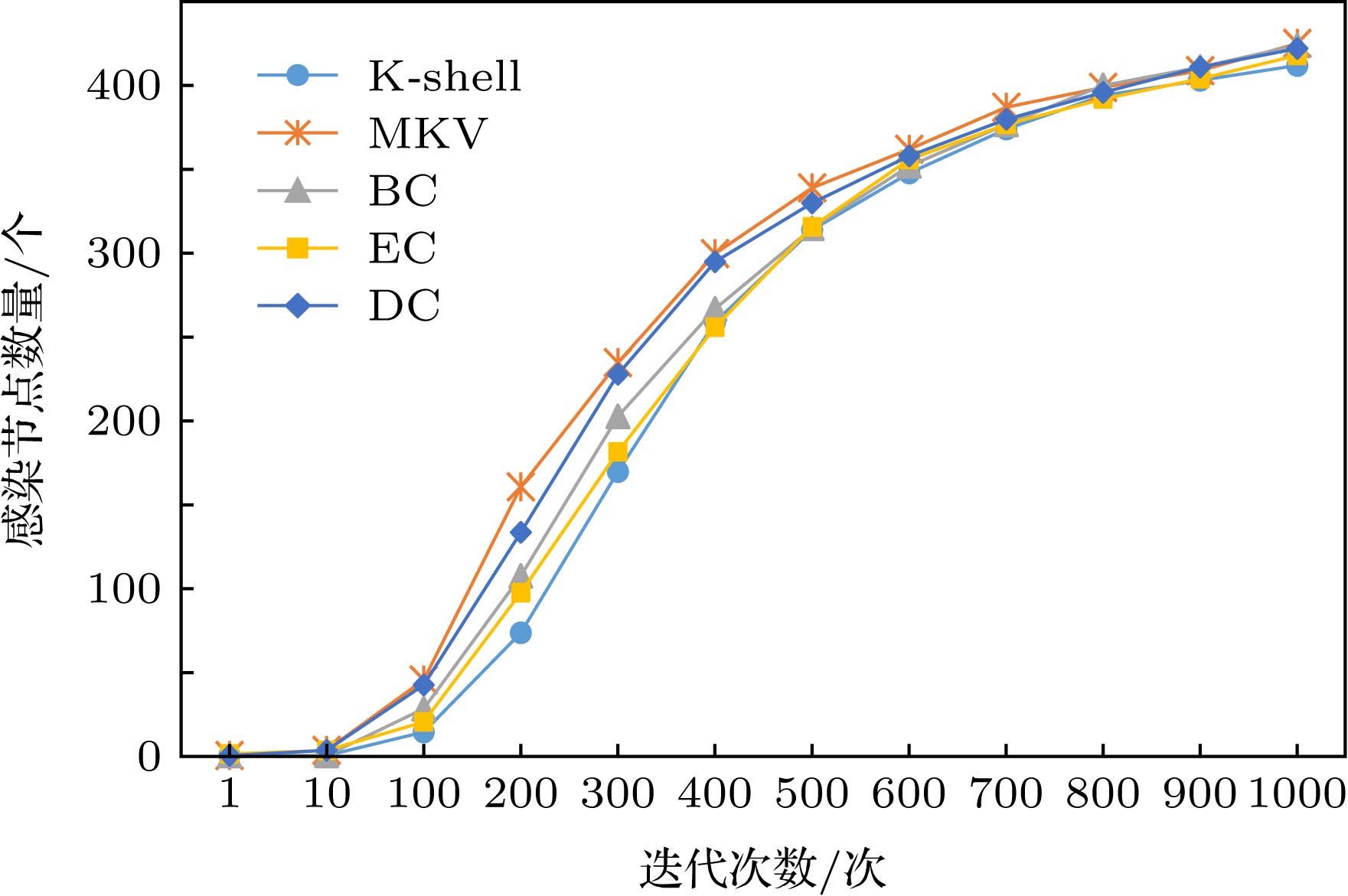
The K-shell has important theoretical significance and application value in measuring the importance of nodes in complex networks. However, in the K-shell method, most of nodes possess an identical K-shell value so that the relative importance of the identical K-shell nodes cannot be further compared with each other. Therefore, based on the K-shell value of nodes in the complex network and the K-shell values of multi-order neighbors in complex networks, in this paper we use the vectors to represent the relative importance of node in each of complex networks, which is named multi-order K-shell vector. Multi-order K-shell vector centrality defines a vector indicating the number of multi-order neighbors with different K-shells and groups them into elements of the vector. Each vector infers to not only the original K-shell of the given node but also the number of its multi-order neighbors and their K-shell values, which indicates the propagation capability of the given node. An approach to comparing two multi-order K-shell vectors is also presented, which is used to sort the vectors to evaluate the node importance. The method is explored by comparing several existing centrality methods. Through the experiments of SI propagation and static attack experiments in seven real-world networks, it is found that multi-order K-shell vector centrality provides low computational complexity, effectively evaluates nodes with high propagation capability, which confirms the improved performance in susceptible infected model propagation experiments. On the other hand, the static attack experiments show that the multi-order K-shell vector tends to preferentially select the core structure with powerful propagation capability in the network. The multi-order K-shell vector greatly improves the difference rate of node centrality under the premise of preserving the K-shell structure information, as well as balancing the importance measure of nodes in the complex network and the structure evaluation of propagation capability. The multi-order K-shell vector is not appropriate for all types of networks when considering the result of network attacking. For the networks with low clustering coefficients and high average path lengths, multi-order K-shell vector method is dominant and the effect is relatively obvious. By contrast, multi-order K-shell vector surpasses most of centrality approaches when spreading information is our priority. In a few networks, eigenvector centrality presents a slightly better performance with a larger computational complexity. The proposed centrality measure is therefore of great theoretical and practical importance.
-
Keywords:
- centrality /
- multi-order K-shell vector /
- susceptible infected model /
- static attack
[1] Barabasi A L, Albert R 1999 Science 286 509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Newman M, Girvan M 2004 Phys. Rev. E 69 423
[3] Ai J, Su Z, Li Y, Wu C X 2019 Physica A 527 121155
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ai J, Liu Y Y, Su Z, Zhang H , Zhao F Y 2019 Europhys. Lett. 126 38003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Brin S, Page L 2012 Computer Networks 56 3825
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Newman M 2010 Networks: An introduction (Oxford: Oxford University Press) p327
[7] Cohen R, Erez K, Ben-Avraham D, Havlin S 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 86 3682
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Keeling M J, Rohani P, Pourbohloul B 2008 Clinical Infectious Diseases 47 864
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Moreno Y, Nekovee M, Pacheco A F 2004 Phys. Rev. E 69 066130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 张彦超, 刘云, 张海峰, 程辉, 熊菲 2011 60 050501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y C, Liu Y, Zhang H F, Cheng H, Xiong F 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 050501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Li H, Gao G, Chen R 2019 Int. J. Software Engineer. Knowledge Engineer. 29 93
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 刘建国, 任卓明, 郭强, 汪秉宏 2013 62 178901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu J G, Ren Z M, Guo Q, Wang B H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 178901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 任晓龙, 吕琳媛 2014 科学通报 59 1175
Ren X L, Lü L Y 2014 Chin. Sci. Bull. 59 1175
[14] Chen D, Lin Y L, Shang M S 2012 Fuel and Energy Abstracts 391 1777
[15] Freeman L C 1977 Sociometry 40 35
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Opsahl T, Agneessens F, Skvoretz J 2010 Social Networks 32 245
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Kitsak M, Gallos L K, Havlin S, Liljeros F, Muchnik L, Stanley H E, Makse H A 2010 Nat. Phys. 6 888
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 罗仕龙, 龚凯, 唐朝生, 周靖 2017 66 188902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Luo S L, Gong K, Tang C S, Zhou J 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 188902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Jiang L C, Zhao X, Ge B, Xiao W, Ruan Y 2019 Physica A 516 58
[20] Gong K, Kang L 2018 J. Syst. Sci. Inf. 6 366
[21] 朱晓霞, 赵雪, 刘萌萌 2017 计算机应用研究 34 2582
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu X X, Zhao X, Liu M M 2017 Application Research of Computers 34 2582
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 李慧嘉, 严冠, 刘志东, 李桂君, 章祥荪 2017 中国科学: 数学 47 16
Li H J, Yan G, Liu Z D, Li G J, Zhang X S 2017 Scientia Sinica Mathematica 47 16
[23] 李慧嘉, 李爱华, 李慧颖 2017 计算机学报 40 15
Li H J, Li A H, Li H Y 2017 Chinese Journal of Computers 40 15
[24] Zhang J P, Xu H, Yang J, Lun L J 2018 ICPCSEE Zhengzhou, China, September 21−24, 2018 p28
[25] 王浩, 张赞, 李磊, 汪萌 2016 电子学报 44 2330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H, Zhang Z, Li L, Wang M 2016 Acta Electronica Sinica 44 2330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Ai J, Zhao H, Carley K M, Su Z, Li H 2013 Eur. Phys. J. B 86 163
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Freeman L C 1979 Social Networks 1 215
[28] Brandes U 2001 Math. Sociology 25
[29] E.Knuth D 1993 The Stanford GraphBase: A Platform for Combinatorial Computing (Vol.1)
[30] Watts D J, Strogatz S H 1998 Nature 393 440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Guimera R, Danon L, Diaz-Guilera A, Giralt F, Arenas A 2003 Phys. Rev. E 68 065103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Newman M 2006 Phys. Rev. E 74 036104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Lusseau D, Schneider K, Boisseau O, Haase P, Slooten E, Dawson S 2003 Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 54 396
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Duch J, Arenas A 2005 Phys. Rev. E 72 027104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Zachary W W 1977 J. Anthropol. Res. 33 452
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] 汪小帆, 李翔, 陈关荣 2012 网络科学导论 (北京: 高等教育出版社) 第306−307页
Wang X F, Li X, Chen G R 2012 Network Science: an Introduction (Beijing: Higher Education Press) pp306−307 (in Chinese)
-
表 1 本文中用到的几个网络基本信息
Table 1. Several basic network information used in this paper.
网络 节点数量 边数量 平均度值 聚集系数 平均路径长度 同配系数 LesMiserables 77 254 6.597 0.736 2.641 –0.4756 PowerGrid 4941 6594 2.669 0.107 18.989 0.4616 Email 1134 6556 11.563 0.526 1.992 –0.0436 Coauthor 1589 2742 3.451 0.878 5.823 0.0035 Dolphin 62 159 5.129 0.303 3.357 –0.1652 C.Elegans 453 4596 9.007 0.657 2.664 –0.1085 Club 34 78 2.29 0.588 2.408 –0.2145 表 2 中心性的区分度在不同网络中的取值情况(越大越好)
Table 2. Value of Centrality Distinction in Different Networks(the larger, the better).
DR BC EC Degree K-shell MKV C.Elegans 66.225% 88.962% 8.830% 2.208% 40.839% Club 61.765% 79.412% 32.353% 11.765% 47.059% Coauthors 9.880% 29.264% 1.447% 0.692% 9.880% Dolphin 87.097% 96.774% 19.355% 6.452% 70.968% Email 62.346% 94.533% 4.586% 0.970% 53.263% Power 59.279% 86.217% 0.324% 0.101% 8.561% LesMiserables 41.558% 67.532% 23.377% 10.390% 37.662% -
[1] Barabasi A L, Albert R 1999 Science 286 509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Newman M, Girvan M 2004 Phys. Rev. E 69 423
[3] Ai J, Su Z, Li Y, Wu C X 2019 Physica A 527 121155
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ai J, Liu Y Y, Su Z, Zhang H , Zhao F Y 2019 Europhys. Lett. 126 38003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Brin S, Page L 2012 Computer Networks 56 3825
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Newman M 2010 Networks: An introduction (Oxford: Oxford University Press) p327
[7] Cohen R, Erez K, Ben-Avraham D, Havlin S 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 86 3682
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Keeling M J, Rohani P, Pourbohloul B 2008 Clinical Infectious Diseases 47 864
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Moreno Y, Nekovee M, Pacheco A F 2004 Phys. Rev. E 69 066130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 张彦超, 刘云, 张海峰, 程辉, 熊菲 2011 60 050501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y C, Liu Y, Zhang H F, Cheng H, Xiong F 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 050501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Li H, Gao G, Chen R 2019 Int. J. Software Engineer. Knowledge Engineer. 29 93
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 刘建国, 任卓明, 郭强, 汪秉宏 2013 62 178901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu J G, Ren Z M, Guo Q, Wang B H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 178901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 任晓龙, 吕琳媛 2014 科学通报 59 1175
Ren X L, Lü L Y 2014 Chin. Sci. Bull. 59 1175
[14] Chen D, Lin Y L, Shang M S 2012 Fuel and Energy Abstracts 391 1777
[15] Freeman L C 1977 Sociometry 40 35
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Opsahl T, Agneessens F, Skvoretz J 2010 Social Networks 32 245
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Kitsak M, Gallos L K, Havlin S, Liljeros F, Muchnik L, Stanley H E, Makse H A 2010 Nat. Phys. 6 888
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 罗仕龙, 龚凯, 唐朝生, 周靖 2017 66 188902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Luo S L, Gong K, Tang C S, Zhou J 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 188902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Jiang L C, Zhao X, Ge B, Xiao W, Ruan Y 2019 Physica A 516 58
[20] Gong K, Kang L 2018 J. Syst. Sci. Inf. 6 366
[21] 朱晓霞, 赵雪, 刘萌萌 2017 计算机应用研究 34 2582
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu X X, Zhao X, Liu M M 2017 Application Research of Computers 34 2582
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 李慧嘉, 严冠, 刘志东, 李桂君, 章祥荪 2017 中国科学: 数学 47 16
Li H J, Yan G, Liu Z D, Li G J, Zhang X S 2017 Scientia Sinica Mathematica 47 16
[23] 李慧嘉, 李爱华, 李慧颖 2017 计算机学报 40 15
Li H J, Li A H, Li H Y 2017 Chinese Journal of Computers 40 15
[24] Zhang J P, Xu H, Yang J, Lun L J 2018 ICPCSEE Zhengzhou, China, September 21−24, 2018 p28
[25] 王浩, 张赞, 李磊, 汪萌 2016 电子学报 44 2330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H, Zhang Z, Li L, Wang M 2016 Acta Electronica Sinica 44 2330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Ai J, Zhao H, Carley K M, Su Z, Li H 2013 Eur. Phys. J. B 86 163
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Freeman L C 1979 Social Networks 1 215
[28] Brandes U 2001 Math. Sociology 25
[29] E.Knuth D 1993 The Stanford GraphBase: A Platform for Combinatorial Computing (Vol.1)
[30] Watts D J, Strogatz S H 1998 Nature 393 440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Guimera R, Danon L, Diaz-Guilera A, Giralt F, Arenas A 2003 Phys. Rev. E 68 065103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Newman M 2006 Phys. Rev. E 74 036104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Lusseau D, Schneider K, Boisseau O, Haase P, Slooten E, Dawson S 2003 Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 54 396
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Duch J, Arenas A 2005 Phys. Rev. E 72 027104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Zachary W W 1977 J. Anthropol. Res. 33 452
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] 汪小帆, 李翔, 陈关荣 2012 网络科学导论 (北京: 高等教育出版社) 第306−307页
Wang X F, Li X, Chen G R 2012 Network Science: an Introduction (Beijing: Higher Education Press) pp306−307 (in Chinese)
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 13287
- PDF Downloads: 96
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: