-
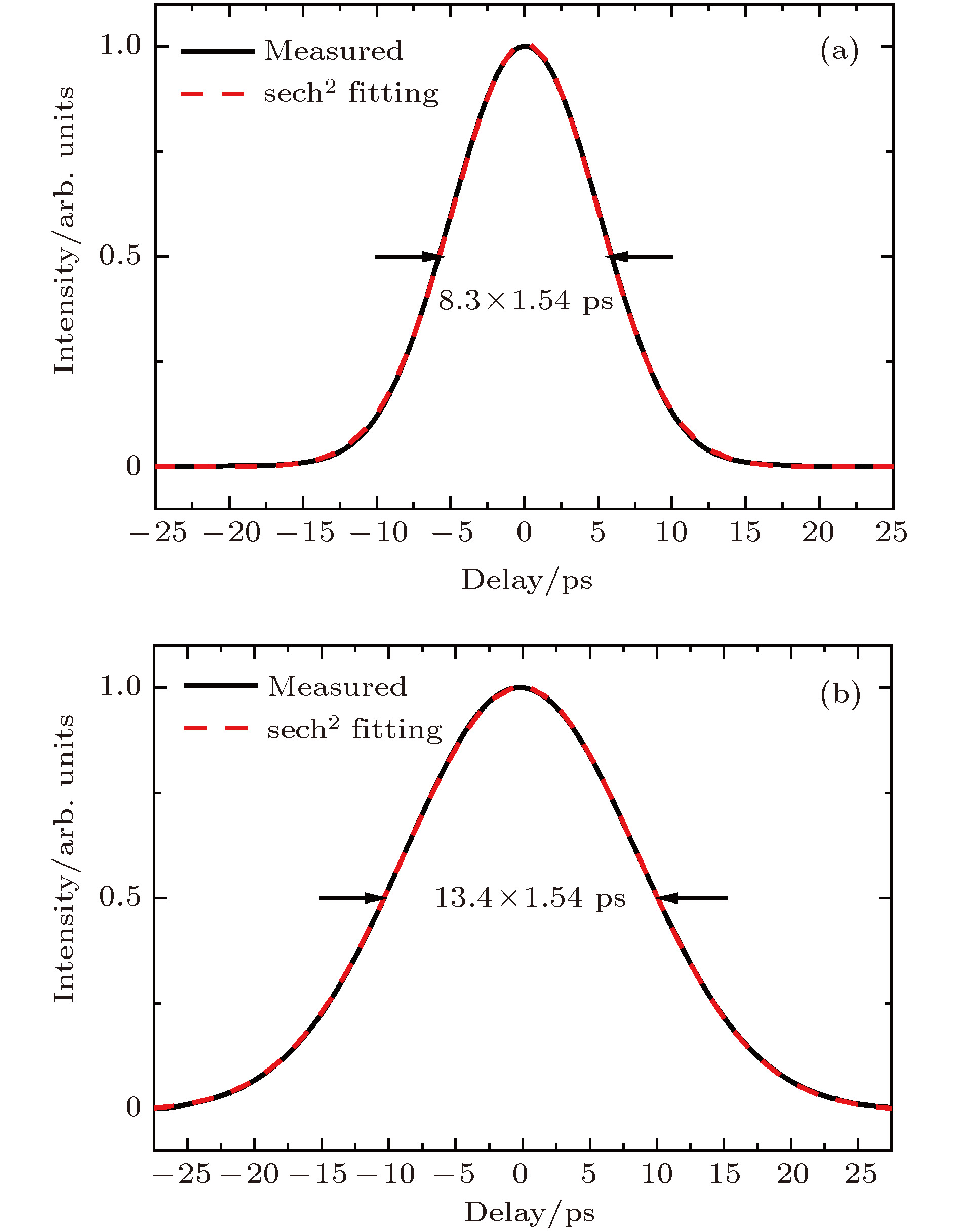
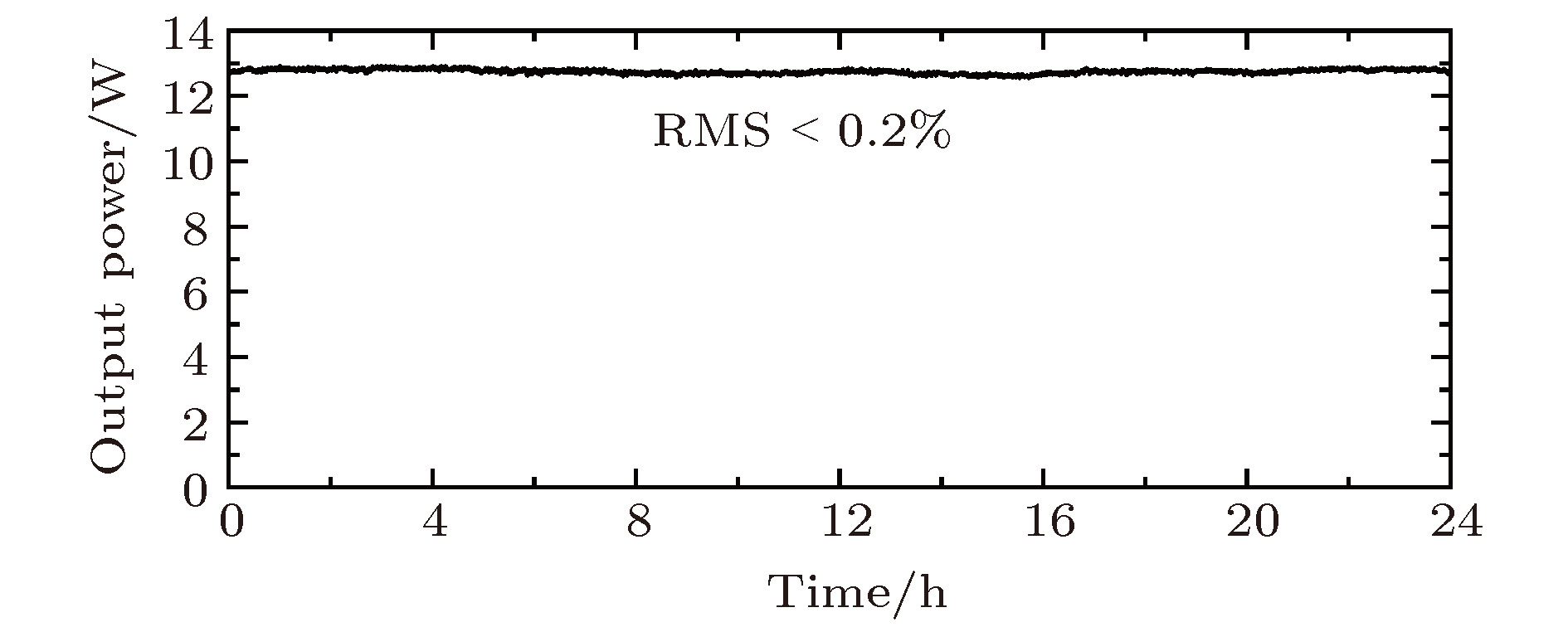
Picosecond laser with high-repetition-rate and high pulse energy is widely favorite in many scientific and industrial applications. Some nonlinear crystals can be used to efficiently convert a near-infrared laser into a green laser or an ultraviolet laser which has a higher photon energy and a smaller focal area. Especially for high-quality and high-speed transparent hard material fabrication, green or ultraviolet picosecond laser has been found to possess unique advantages. In this paper, the experiments on high-efficiency second-harmonic-generation (SHG) and third-harmonic-generation (THG) by using a home-made all-solid-state picosecond laser amplifier and an LBO crystal are reported. The picosecond laser amplifier consists of a seed source, a regenerative amplifier and a two-stage single-pass amplifier. The seed source is a commercial all-solid-state picosecond oscillator with a pulse duration of 8.3 ps and a repetition rate of 68 MHz. The repetition rate is reduced from 68 MHz to 500 kHz by an electro-optic Pockels cell (PC), and the period doubling bifurcation is minimized by reducing the duration of high voltage in PC. Both the regenerative amplifier and the two-stage single-pass amplifier are pumped by three 30-W continuous-wave fiber-coupled laser diodes. After the regenerative amplifier, the seed laser is amplified to 4.86 W with a repetition rate of 500 kHz at 1064 nm. Then the laser power is increased to 23.2 W by a two-stage single-pass amplifier, and the M2 value of the amplified laser in the X direction and in the Y direction are 1.330 and 1.235, respectively. The final pulse duration is 13.4 ps, which is slightly stretched in the amplification chain compared with the seed pulse duration (8.3 ps). For high-efficiency SHG and THG from near-infrared to green and ultraviolet, we carefully study the optical characteristics of some nonlinear crystals, such as LBO, BBO, BIBO, CLBO, etc., and we find that the LBO crystal, which has a high damage threshold, small walk-off and high nonlinear coefficient, is the best choice for both SHG and THG. Then the parameters of the two crystals for SHG and THG are specially designed according to the phase matching condition, the walk-off and the laser parameter. As a result, a 4-mm-long type-I phase matching LBO with cutting angle of θ = 90° and φ = 11.6° is used for SHG, and a 3-mm-long type-II phase matching LBO with cutting angle of θ = 42.2° and φ = 90° is used for THG. Finally, we realize high-efficiency frequency conversion with SHG power of 12.7 W at 532 nm and THG power of 9.25 W at 355 nm. The corresponding optical-optical conversion efficiencies reach 54.7% and 39.6%, respectively.
-
Keywords:
- nonlinear optics /
- frequency conversion /
- diode-pumped lasers /
- amplifiers
[1] Erny C, Heese C, Haag M, Gallmann L, Keller U 2009 Opt. Express 17 1340
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 王鹏, 赵环, 王兆华, 李德华, 魏志义 2006 55 4161
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang P, Zhao H, Wang Z H, Li D H, Wei Z Y 2006 Acta Phys. Sin. 55 4161
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 何会军, 蒋建旺, 程梦尧, 宋贾俊, 王兆华, 方少波, 魏志义 2018 光子学报 47 0914002
He H J, Jiang J W, Cheng M Y, Song J J, Wang Z H, Fang S B, Wei Z Y 2018 Acta Photon. Sin. 47 0914002
[4] Muhammad N, Whitehead D, Boor A, Oppenlander W, Liu Z, Li L 2012 Appl. Phys. A 106 607
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Weck A, Crawford T H R, Wilkinson D S, Haugen H K, Preston J S 2008 Appl. Phys. A 90 537
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 张菲, 段军, 曾晓雁, 李祥友 2009 中国激光 36 3143
Zhang F, Duan J, Zeng X Y, Li X Y 2009 Chin. J. Las. 36 3143
[7] Rauch T, Delmdahl R, Pfeufer V, Mondry M 2009 Laser Tech. J. 6 20
[8] Norreys P A, Zepf M, Moustaizis S, Fews A P, Zhang J, Lee P, Bakarezos M, Danson C N, Dyson A, Gibbon P, Loukakos P, Neely D, Walsh F N, Wark J S, Dangor A E 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 76 1832
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Liu J X, Wang W, Wang Z H, Lü Z G, Zhang Z Y, Wei Z Y 2015 Appl. Sci. 5 1590
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Offerhaus H L, Godfried H P, Witteman W J 1996 Opt. Commun. 128 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Dörring J, Killi A, Morgner U, Lang A, Lederer M, Kopf D 2004 Opt. Express 12 1759
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 毛小洁, 秘国江, 庞庆生, 邹跃 2013 中国激光 38 1002004
Mao X J, Bi G J, Pang Q S, Zou Y 2013 Chin. J. Las. 38 1002004
[13] Zhu P, Li D J, Liu Q Y, Chen J, Fu S J, Shi P, Du K M, Loosen P 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 4716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Borsutzky A, Briinger R, Huang C H, Wallenstein R 1991 Appl. Phys. B 52 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ghotbi M, Sun Z, Majchrowski A, Michalski E, Kityk I V, Ebrahim Z M 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett. 89 173124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ueda K, Orii Y,Takahashi Y, Okada G, Mori Y, Yoshimura M 2016 Opt. Express 24 30465
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Guo L, Wang G L, Zhang H B, Cui D F, Wu Y C, Lu L, Zhang J Y, Huang J Y, Xu Z Y 2007 Appl. Phys. B 88 197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Yoshida H, Fujita H, Nakatsuka M, Yoshimura M, Sasaki T, Kamimura T, Yoshida K 2006 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 45 766
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 王正平, 滕冰, 杜晨林, 许心光, 傅琨, 许贵宝, 王继扬, 邵宗书 2003 52 2176
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Z P, Teng B, Du C L, Xu X G, Fu K, Xu G B, Wang J Y, Shao Z S 2003 Acta Phys. Sin. 52 2176
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wu Y C, Sasaki T, Nakai S, Yokotani A, Tang H G, Chen C T 1993 Appl. Phys. Lett. 62 2614
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wu B C, Chen N, Chen C T, Deng D Q, Xu Z Y 1989 Opt. Lett. 14 1080
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Chen L Y, Bai Z X, Pan Y L, Chen M, Li G 2013 Opt. Eng. 52 086107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 1 全固态皮秒激光放大器及SHG与THG光路图(HR, 高反镜; DM, 双色镜; LD, 二极管激光器; HT 1064 HR 532, 在1064 nm处高透, 在532 nm处高反)
Figure 1. Structure of all-solid-state picosecond laser amplifier, SHG and THG (HR, high reflectivity mirror; DM, dichroic mirror; LD, laser diode; HT 1064 HR 532: high transmittance @ 1064 nm and high reflectivity @ 532 nm).
表 1 非线性晶体参数
Table 1. Parameters of nonlinear crystal.
晶体 透射范围/nm 损伤阈值/GW·cm–2 deff 11/pm·V–1 deff 22/pm·V–1 走离角1/mrad 走离角2/mrad LBO 160—2600 36.3[18] 0.83 (xy) 0.53 (yz) 7.06 (xy) 9.30 (yz) BBO 185—2600 18.27[18] 2.01 2.02 55.86 72.33 KDP 177—1700 20[18] 0.26 0.32 28.06 30.12 BIBO 286—2500 3.4[19] 2.96 (yz) 3.9 (yz) 25.74 (yz) 67.86 (yz) CLBO 180—2570 27.3[18] 0.38 0.52 31.41 37.16 CBO 170—3000 26[20] 1.01 (xz) 1.19 (xy) 31.17 (xz) 16.25 (xy) 注: 1, 1064 nm倍频输出532 nm的条件下; 2, 1064 nm与532 nm和频输出355 nm的条件下 -
[1] Erny C, Heese C, Haag M, Gallmann L, Keller U 2009 Opt. Express 17 1340
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 王鹏, 赵环, 王兆华, 李德华, 魏志义 2006 55 4161
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang P, Zhao H, Wang Z H, Li D H, Wei Z Y 2006 Acta Phys. Sin. 55 4161
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 何会军, 蒋建旺, 程梦尧, 宋贾俊, 王兆华, 方少波, 魏志义 2018 光子学报 47 0914002
He H J, Jiang J W, Cheng M Y, Song J J, Wang Z H, Fang S B, Wei Z Y 2018 Acta Photon. Sin. 47 0914002
[4] Muhammad N, Whitehead D, Boor A, Oppenlander W, Liu Z, Li L 2012 Appl. Phys. A 106 607
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Weck A, Crawford T H R, Wilkinson D S, Haugen H K, Preston J S 2008 Appl. Phys. A 90 537
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 张菲, 段军, 曾晓雁, 李祥友 2009 中国激光 36 3143
Zhang F, Duan J, Zeng X Y, Li X Y 2009 Chin. J. Las. 36 3143
[7] Rauch T, Delmdahl R, Pfeufer V, Mondry M 2009 Laser Tech. J. 6 20
[8] Norreys P A, Zepf M, Moustaizis S, Fews A P, Zhang J, Lee P, Bakarezos M, Danson C N, Dyson A, Gibbon P, Loukakos P, Neely D, Walsh F N, Wark J S, Dangor A E 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 76 1832
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Liu J X, Wang W, Wang Z H, Lü Z G, Zhang Z Y, Wei Z Y 2015 Appl. Sci. 5 1590
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Offerhaus H L, Godfried H P, Witteman W J 1996 Opt. Commun. 128 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Dörring J, Killi A, Morgner U, Lang A, Lederer M, Kopf D 2004 Opt. Express 12 1759
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 毛小洁, 秘国江, 庞庆生, 邹跃 2013 中国激光 38 1002004
Mao X J, Bi G J, Pang Q S, Zou Y 2013 Chin. J. Las. 38 1002004
[13] Zhu P, Li D J, Liu Q Y, Chen J, Fu S J, Shi P, Du K M, Loosen P 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 4716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Borsutzky A, Briinger R, Huang C H, Wallenstein R 1991 Appl. Phys. B 52 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ghotbi M, Sun Z, Majchrowski A, Michalski E, Kityk I V, Ebrahim Z M 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett. 89 173124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ueda K, Orii Y,Takahashi Y, Okada G, Mori Y, Yoshimura M 2016 Opt. Express 24 30465
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Guo L, Wang G L, Zhang H B, Cui D F, Wu Y C, Lu L, Zhang J Y, Huang J Y, Xu Z Y 2007 Appl. Phys. B 88 197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Yoshida H, Fujita H, Nakatsuka M, Yoshimura M, Sasaki T, Kamimura T, Yoshida K 2006 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 45 766
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 王正平, 滕冰, 杜晨林, 许心光, 傅琨, 许贵宝, 王继扬, 邵宗书 2003 52 2176
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Z P, Teng B, Du C L, Xu X G, Fu K, Xu G B, Wang J Y, Shao Z S 2003 Acta Phys. Sin. 52 2176
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wu Y C, Sasaki T, Nakai S, Yokotani A, Tang H G, Chen C T 1993 Appl. Phys. Lett. 62 2614
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wu B C, Chen N, Chen C T, Deng D Q, Xu Z Y 1989 Opt. Lett. 14 1080
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Chen L Y, Bai Z X, Pan Y L, Chen M, Li G 2013 Opt. Eng. 52 086107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 20616
- PDF Downloads: 581
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: