-
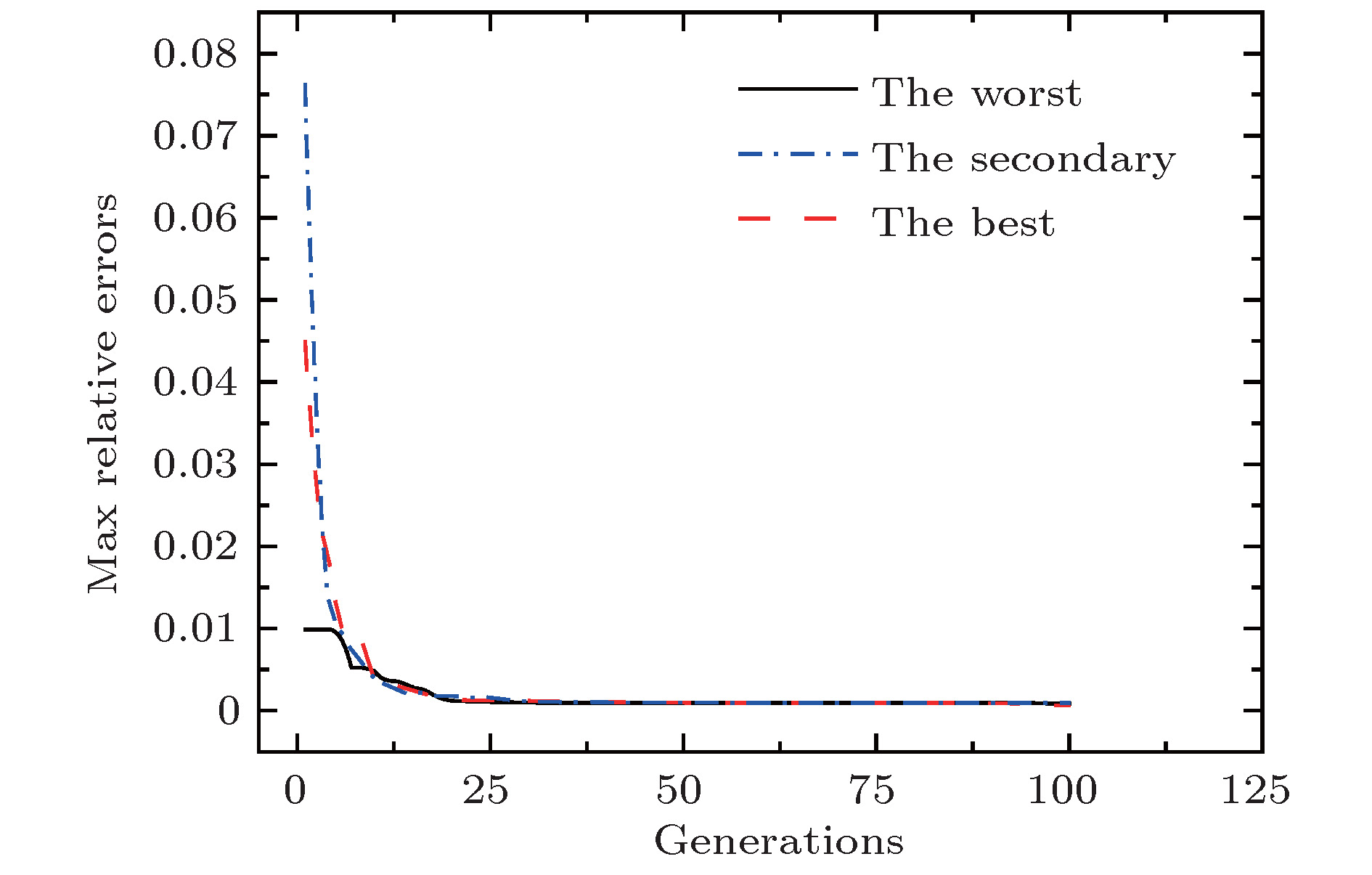
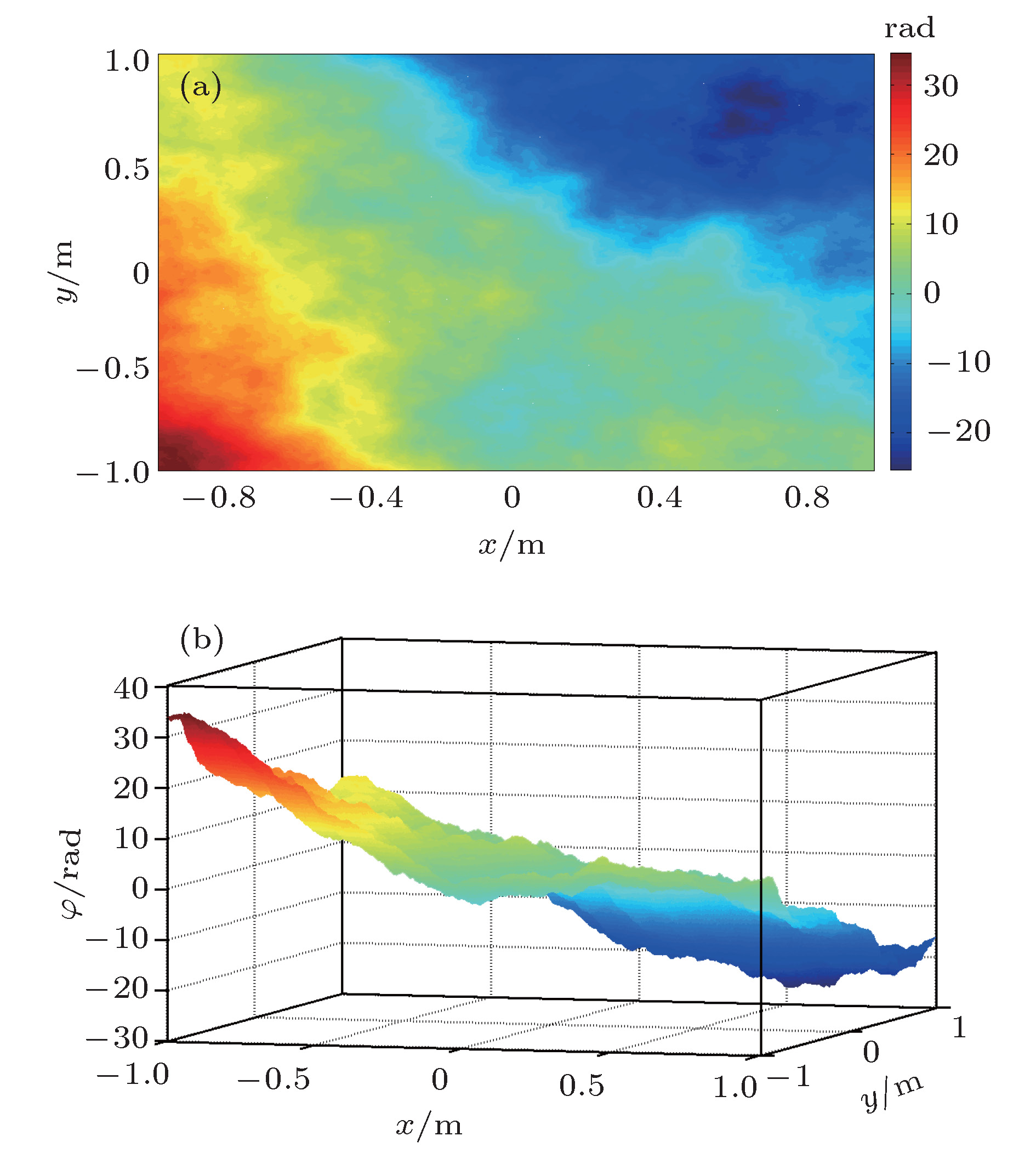
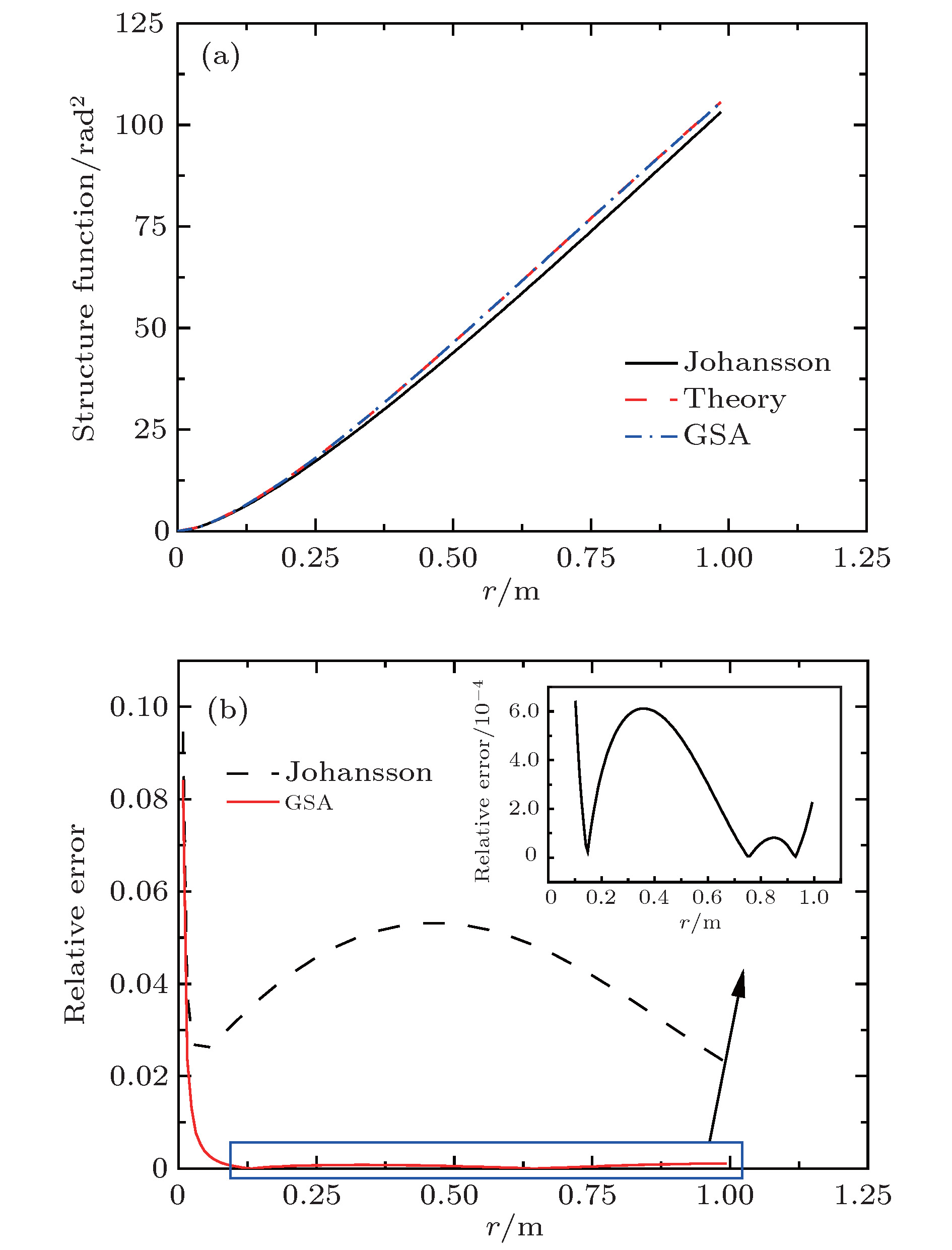
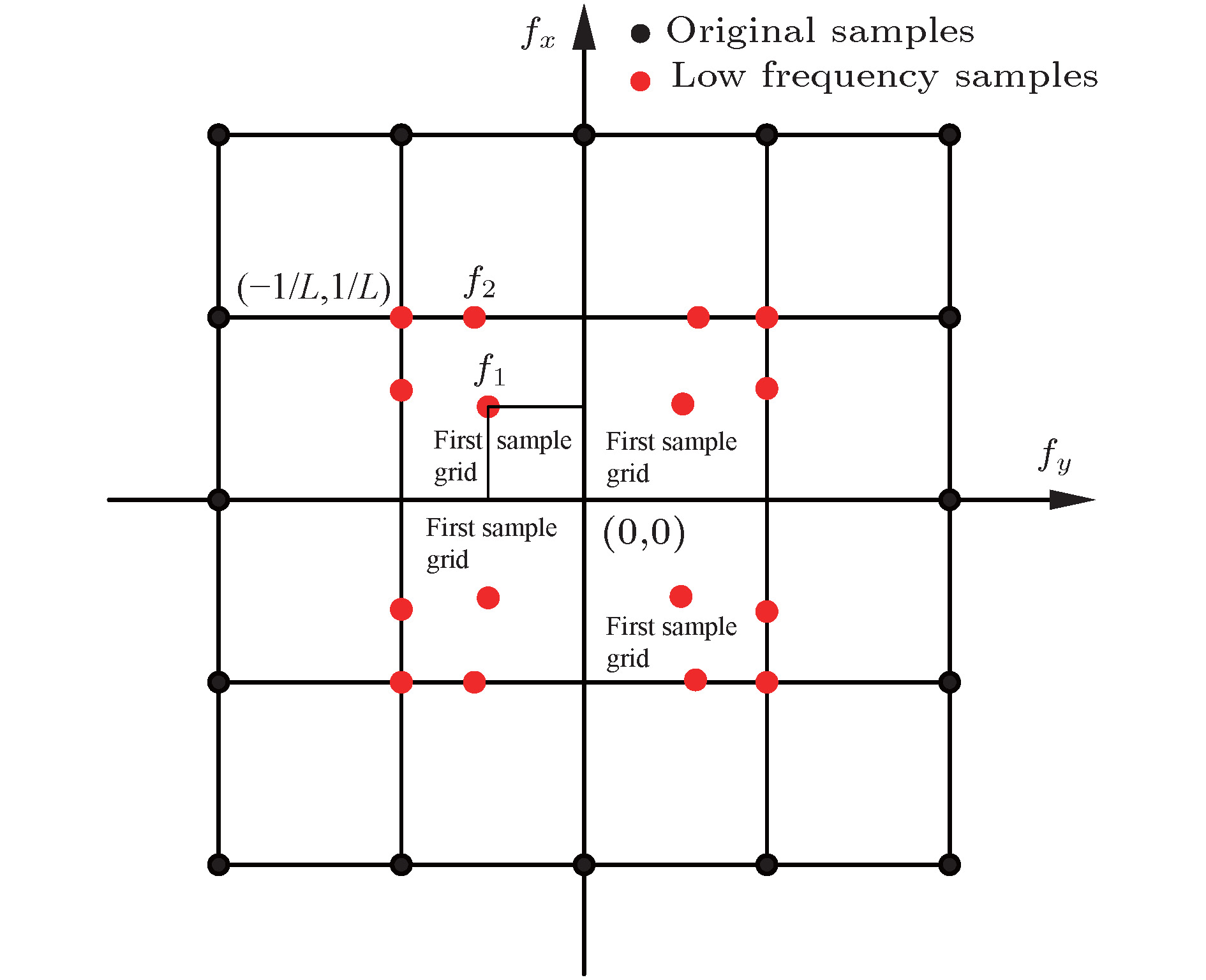
The new techniques in adaptive optics, free space optical(FSO) communication rely on the use of numerical simulations for atmospheric turbulence to evaluate the performance of the system. The simulation of turbulence phase screen is the heart of numerical simulations which produces random wavefront phase perturbations with the correct statistical properties corresponding to models of optical propagation through atmospheric turbulence. The phase-screen simulation techniques can be roughly divided into fast Fourier transform (FFT) method and matrix-based method. Because of a better performance in computation time, the FFT method is generally used for modeling the performance of a real system. But the classical FFT method has a main deficiency of oversample in low frequency region, which leads to the lost of accuracy. To overcome this deficiency, many methods have been proposed for compensating for the oversample of low frequency components, in the last decades. Essentially, these methods achieve a higher accuracy at the expense of computation time. A good compensation method should take into consideration both accuracy and computation time. To achieve higher accurcy and lower computational cost simultaneously, we develop a hybrid method to generate turbulence phase screen, i.e. the classical FFT model is mixed with the sparse spectrum model. We first extract the low frequency region from the frequency grid of FFT model, and resample this region with 16 samples. It is found that the accuracy of phase screen is related to the distribution of these samples, and there must be an optimum distribution that can minimize the relative error between expected structure function and theoretical structure function in the low frequency region. So it permits one to use optimization algorithm to find the optimized distribution of low frequency samples. Here an improved gravity search algorithm is adopted in which the memory of each particle is taken into consideration. The optimization parameters are determined after a lot of tests, and the robustness testing shows that the algorithm is effective. To compare with existing subharmonic method, we choose the same parameters of phase screen as those used in the expanded subharmonic method, generate 1000 phase screens for each method, compute the phase structure function, and we also compare our results with those from the theoretical structure function. The comparison result shows that the curve of phase structure function generated by our method is nearly consistent with the theoretical one, the maximum relative error in low frequency region is about 0.063% which is much better than that from the expanded subharmonic method 5%. Finally in this paper, the computational cost is analyzed, showing that the generation speed for our method is at least 4.5 times as fast as that for the Johansson’s method.
-
Keywords:
- atmospheric optics /
- atmospheric turbulence /
- turbulence phase screen
[1] 季小玲 2010 59 692
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jin X L 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 692
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Fleck J A, Morris J R, Feit M D 1976 Appl. Phys. 10 129
[3] Flatte S M, Wang G Y, Martin J 1993 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 10 2363
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Flatte S M 2000 Opt. Express 10 777
[5] McGlamery B L 1976 Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 74 225
[6] Noll R J 1976 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 66 207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Roddier N 1990 Opt. Eng. 29 1174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wallace J, Gebhardt F G 1986 Proc. SPIE 642 261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Roggemann M C, Welsh B M, Montera D, Rhoadamer T A 1995 Appl. Opt. 34 4037
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Harding C M, Johnston R A, Lane R G 1999 Appl. Opt. 38 2161
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 华志励, 李洪平 2012 光学学报 32 0501001
Hua Z L, Li H P 2012 Acta Optica Sinica 32 0501001
[12] Formwalt B, Cain S 2006 Appl. Opt. 45 5657
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Sriram V, Kearney D 2007 Opt. Express 15 13709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhang B D, Qin S Q, Wang X S 2010 Chin. Opt. Lett. 8 969
[15] Xiang J 2012 Opt. Express 20 681
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 王建新, 白福忠, 宁禹, 黄林海, 姜文汉 2011 60 209501
Wang J X, Bai F Z, Ning Y, Huang L H, Jiang W H 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 209501
[17] Vorontsov A M, Paramonov P V, Valley M T, Vorontsov M A 2008 Waves Random Complex Medium 18 91
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Herman B J, Strugala L A 1990 Proc. SPIE 1221 183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Lane R G, Glindemann A, Dainty J C 1992 Waves Random Complex Medium 2 209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Johansson E M, Gavel D T 1994 Symposium on Astronomical Telescopes and Instrumentation for the 21st Century Kona, Hawaii, March 13-18 1994 p940391
[21] Sedmak G 2004 Appl. Opt. 43 4527
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Charnotskii M 2013 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 30 479
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 蔡冬梅, 王昆, 贾鹏, 王东, 刘建霞 2014 63 104217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cai D M, Wang K, Jia P, Wang D, Liu J X 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 104217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 蔡冬梅, 遆培培, 贾鹏, 王东, 刘建霞 2015 64 224217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cai D M, Ti P P, Jia P, Wang D, Liu J X 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 224217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Xiang J S 2014 Opt. Eng. 53 016110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Rashedi E, Nezamabadi-pour H, Saryazdi S 2009 Information Science 179 2232
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Kennedy J, Eberhart R 1995 Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks Perth, November 27, 1995 p1942
[28] 李春龙, 戴娟, 潘丰 2012 计算机应用 32 2732
Li C L, Dai J, Pan F 2012 J. Comput. Appl. 32 2732
[29] 陈水利, 蔡国榕, 郭文忠, 陈国龙 2007 长江大学学报(自科版)理工卷 4 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen S L, Cai G R, Guo W Z, Chen G L 2007 Journal of Yangtze University(Nat. Sci. Ed.) Sci. & Eng. V 4 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 不同参数及参数值下的最大相对误差
Table 1. The maximum relative errors with different parameters.
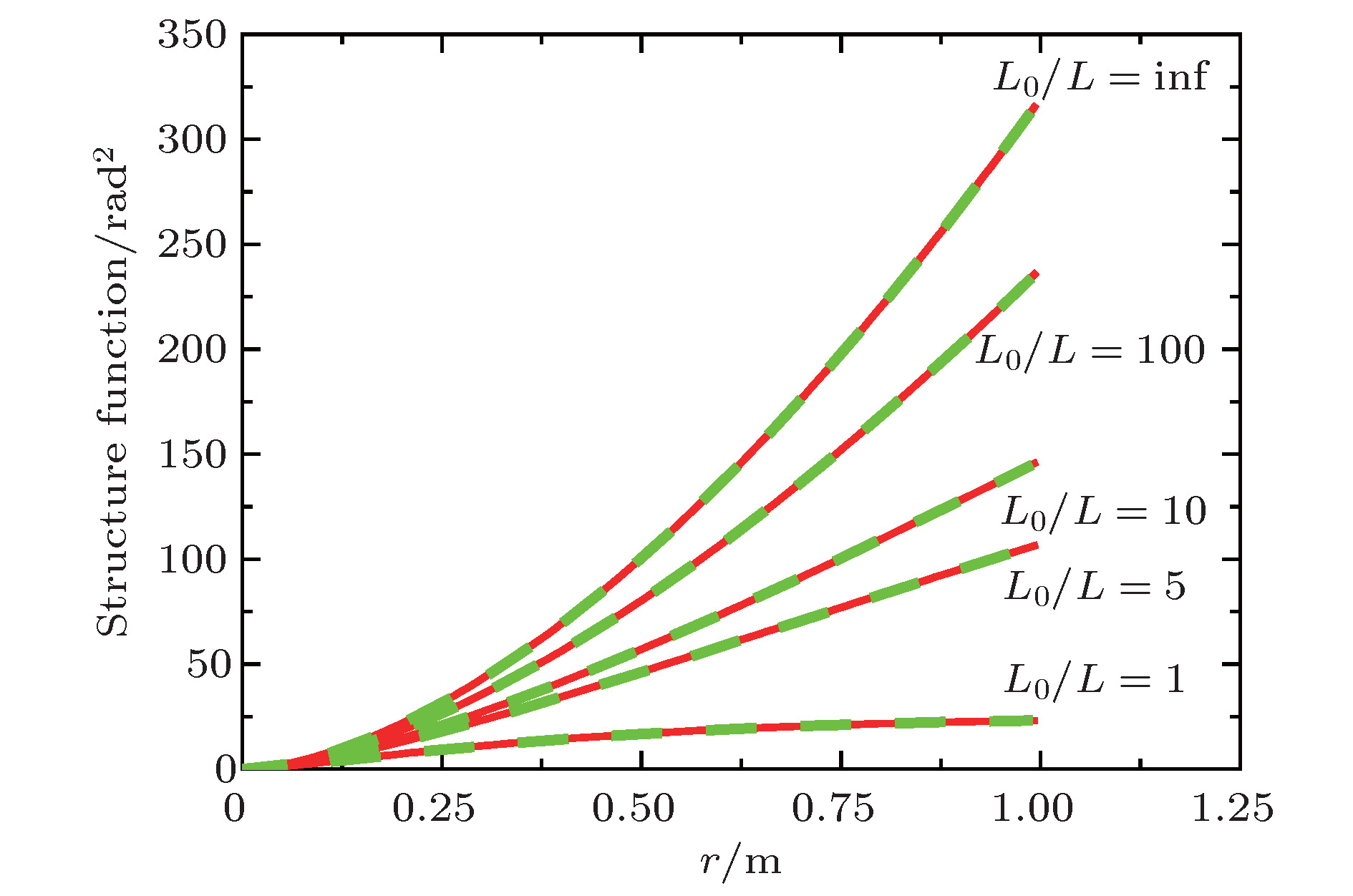
参数类型 参数值 最大相对误差 r0/m 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 1 1.5 εmax 0.00063 0.00063 0.00063 0.00063 0.00063 0.00063 0.00063 L0/m 2 3 4 5 10 20 30 εmax 0.07399 0.16607 0.23083 0.25830 0.00063 0.96574 1.49931 L/m 2 3 4 5 10 20 30 εmax 0.00063 0.23228 0.25830 0.23083 0.07399 0.02327 0.00677 N 32 64 128 256 512 1024 2048 εmax 0.00249 0.00111 0.00071 0.00063 0.00077 0.00084 0.00084 表 2 不同L0/L下的最优参数
Table 2. The optimization parameters with different L0/L.
L0/L (c1, c2) 1 (15.73173, 24.90114) 5 (6.43847, 9.04869) 10 (23.73113, 28.39211) 100 (18.76658, 19.86318) 200 (18.16039, 18.81765) 300 (18.04556, 18.37957) inf (16.56943, 15.80313) -
[1] 季小玲 2010 59 692
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jin X L 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 692
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Fleck J A, Morris J R, Feit M D 1976 Appl. Phys. 10 129
[3] Flatte S M, Wang G Y, Martin J 1993 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 10 2363
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Flatte S M 2000 Opt. Express 10 777
[5] McGlamery B L 1976 Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 74 225
[6] Noll R J 1976 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 66 207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Roddier N 1990 Opt. Eng. 29 1174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wallace J, Gebhardt F G 1986 Proc. SPIE 642 261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Roggemann M C, Welsh B M, Montera D, Rhoadamer T A 1995 Appl. Opt. 34 4037
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Harding C M, Johnston R A, Lane R G 1999 Appl. Opt. 38 2161
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 华志励, 李洪平 2012 光学学报 32 0501001
Hua Z L, Li H P 2012 Acta Optica Sinica 32 0501001
[12] Formwalt B, Cain S 2006 Appl. Opt. 45 5657
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Sriram V, Kearney D 2007 Opt. Express 15 13709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhang B D, Qin S Q, Wang X S 2010 Chin. Opt. Lett. 8 969
[15] Xiang J 2012 Opt. Express 20 681
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 王建新, 白福忠, 宁禹, 黄林海, 姜文汉 2011 60 209501
Wang J X, Bai F Z, Ning Y, Huang L H, Jiang W H 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 209501
[17] Vorontsov A M, Paramonov P V, Valley M T, Vorontsov M A 2008 Waves Random Complex Medium 18 91
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Herman B J, Strugala L A 1990 Proc. SPIE 1221 183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Lane R G, Glindemann A, Dainty J C 1992 Waves Random Complex Medium 2 209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Johansson E M, Gavel D T 1994 Symposium on Astronomical Telescopes and Instrumentation for the 21st Century Kona, Hawaii, March 13-18 1994 p940391
[21] Sedmak G 2004 Appl. Opt. 43 4527
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Charnotskii M 2013 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 30 479
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 蔡冬梅, 王昆, 贾鹏, 王东, 刘建霞 2014 63 104217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cai D M, Wang K, Jia P, Wang D, Liu J X 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 104217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 蔡冬梅, 遆培培, 贾鹏, 王东, 刘建霞 2015 64 224217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cai D M, Ti P P, Jia P, Wang D, Liu J X 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 224217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Xiang J S 2014 Opt. Eng. 53 016110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Rashedi E, Nezamabadi-pour H, Saryazdi S 2009 Information Science 179 2232
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Kennedy J, Eberhart R 1995 Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks Perth, November 27, 1995 p1942
[28] 李春龙, 戴娟, 潘丰 2012 计算机应用 32 2732
Li C L, Dai J, Pan F 2012 J. Comput. Appl. 32 2732
[29] 陈水利, 蔡国榕, 郭文忠, 陈国龙 2007 长江大学学报(自科版)理工卷 4 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen S L, Cai G R, Guo W Z, Chen G L 2007 Journal of Yangtze University(Nat. Sci. Ed.) Sci. & Eng. V 4 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 14220
- PDF Downloads: 78
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: