-
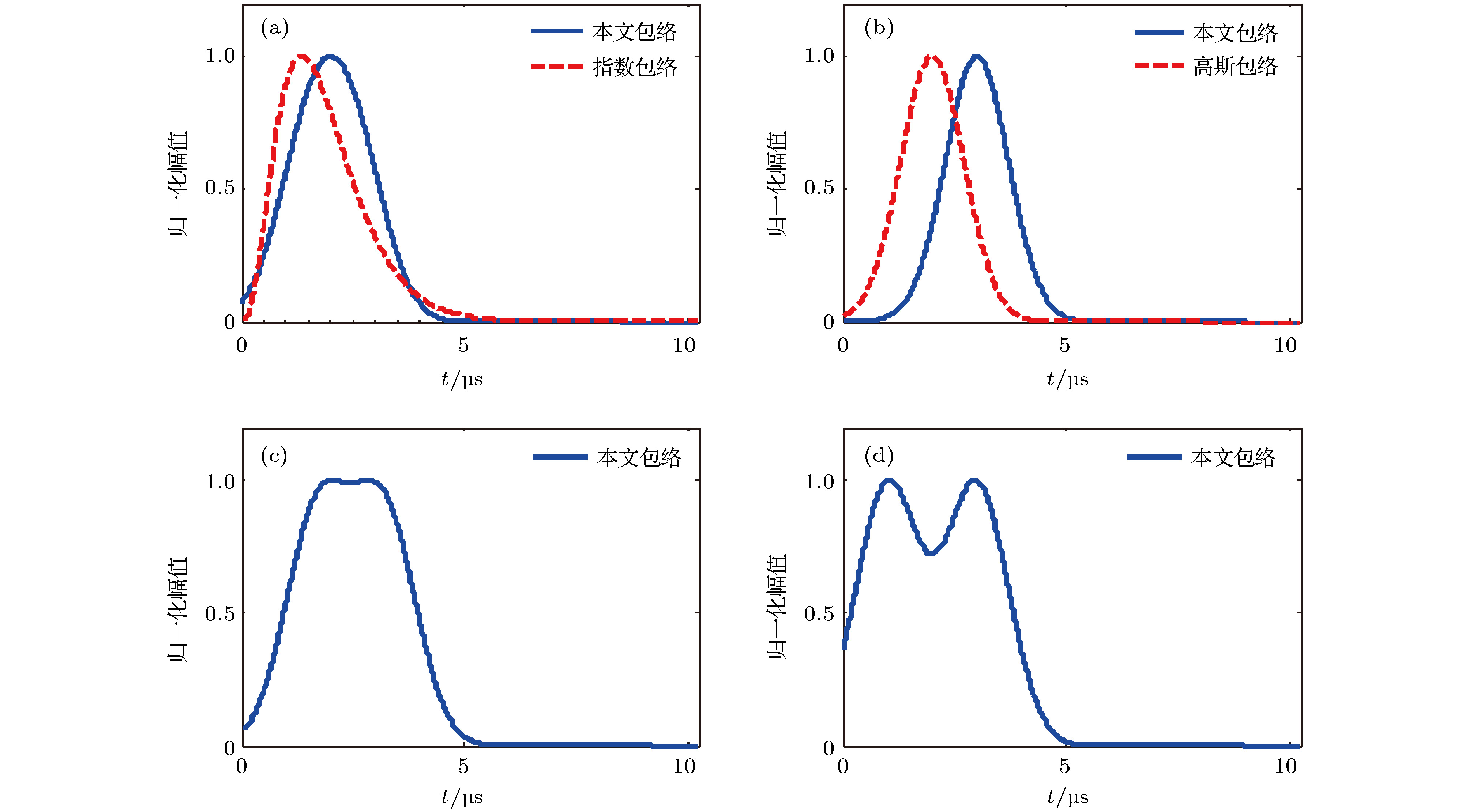
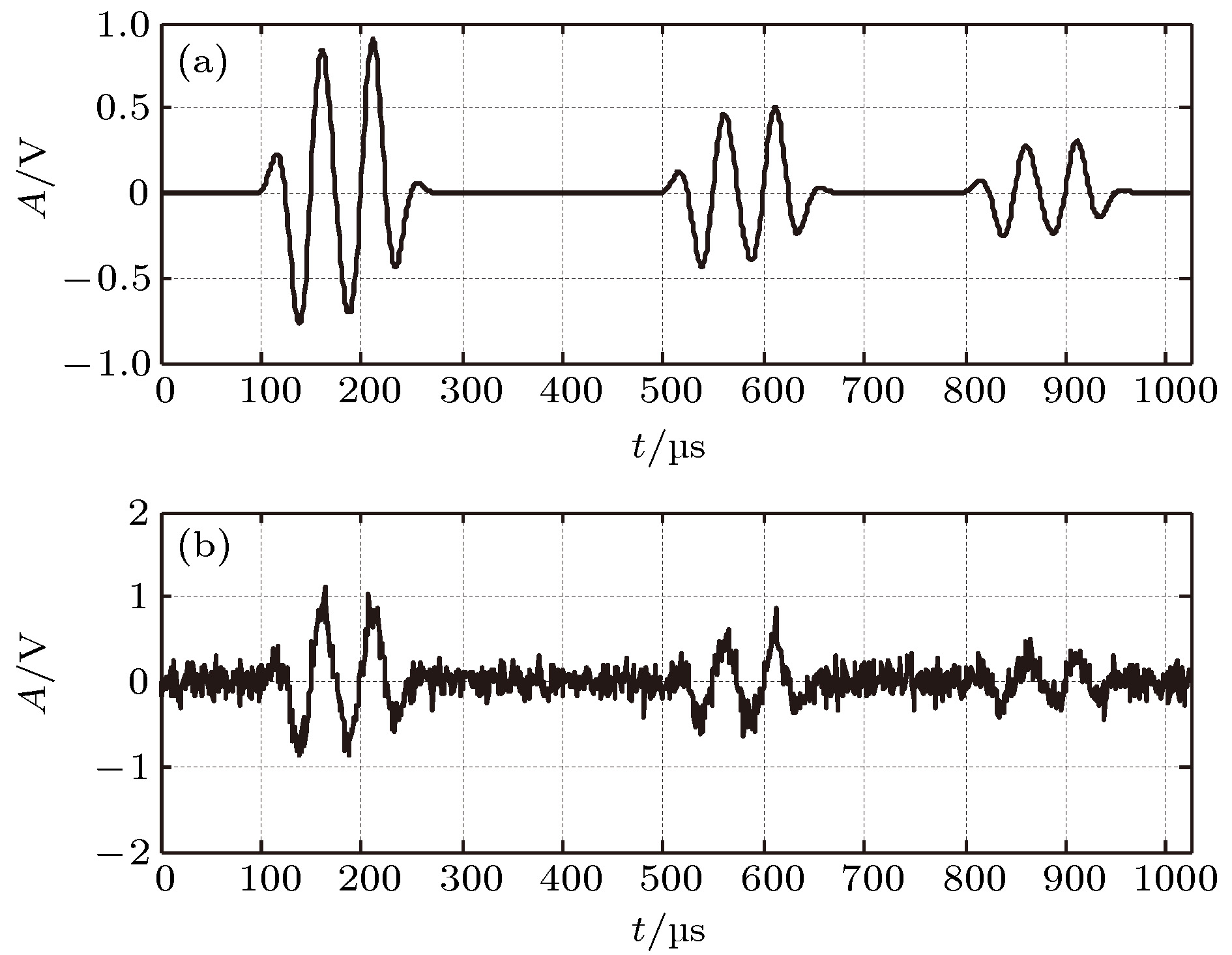
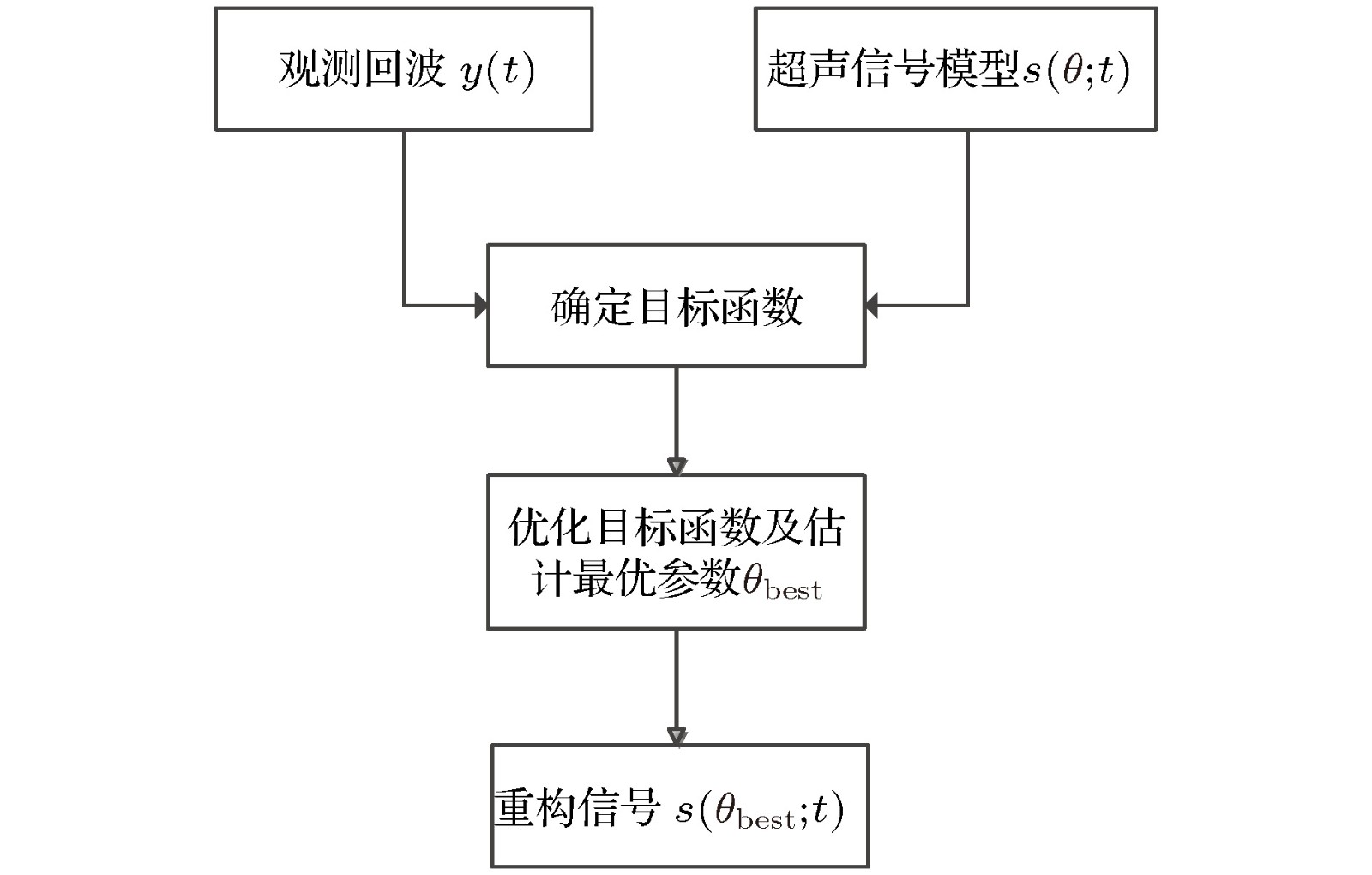
Ultrasonic non-destructive testing, which is one of the most important and rapidly developed non-destructive testing technologies, is widely used in industrial production and other areas. Signal de-noising and feature extraction, whose performance directly affects the evaluation of non-destructive testing results, are the key technologies of ultrasonic non-destructive testing data processing, and also the core elements of ultrasonic non-destructive testing. Therefore, the research on them has important academic significance and practical value. In order to solve the problem of parameter estimation and noise reduction of ultrasonic echo in strong noise background, a novel ultrasonic echo processing method is proposed in this paper. The principle of the proposed method in this paper is as follows. The ultrasonic echo, which is generated by modulating the ultrasonic transducer, has a specific structure, but the noise in practical engineering is usually a Gauss random process, therefore the noise is independent of the ultrasonic signal structure. In this paper, the problem of parameter estimation and noise reduction of ultrasonic echo signal are converted into a function optimization problem by establishing the model of ultrasonic signal, determining the objective function, optimizing the objective function, estimating the parameters, and reconstructing the ultrasonic signal. Firstly, a dual gaussian attenuation mathematical model of ultrasonic signal is established based on practical engineering experience. Secondly, the cosine similarity function, an effective measure of data sequence similarity, is selected as an objective function according to the observed echo and the established ultrasonic signal model. Thirdly, the artificial bee colony algorithm is selected to optimize the objective function to obtain the optimal estimation parameters of the ultrasonic signal from the noisy ultrasonic echo. Fourthly, the estimation of de-noising ultrasonic signal is reconstructed by the optimal parameters based on the established ultrasonic signal mathematical model. The processing results of simulated ultrasonic echoes and measured ultrasonic echoes show that the proposed method can accurately estimate the parameters of ultrasonic signal from strong background noise whose signal-to-noise ratio is lowest, as low as –10 dB. In addition, compared with the adaptive threshold based wavelet method and empirical mode decomposition method, the proposed method in this paper shows the good de-noising performance. Furthermore, compared with the commonly used exponential model and Gaussian model in numerical and simulation analysis, the proposed dual gaussian attenuation mathematical model of ultrasonic signal in this paper can well simulate the measured ultrasonic signal, with a mean square error of 9.4 × 10–5 and normalized correlation coefficient of 0.98.
[1] Fulin J 2017 Mater. Eval. 75 456
[2] Burkov M V, Eremin A V, Lyubutin P S, Byakov A V, Panin S V 2017 Russ. J. Nondestr. Test. 53 817
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Lu Z K, Yang C, Qin D H, Luo Y L 2016 Signal Process. 120 607
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wang X K, Guan S Y, Hua L, Wang B, He X M 2019 Ultrasonics 91 161
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Meng M, Chua Y J, Wouterson E, Ong C P K 2017 Neurocomputing 257 128
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 孙灵芳, 王彤彤, 徐曼菲, 李霞, 朴亨 2017 仪器仪表学报 38 2879
Sun L F, Wang T T, Xu M F, Li X, Pu H 2017 Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 38 2879 (in Chinese)
[7] 王大为, 王召巴 2018 67 210501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang D W, Wang Z B 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 210501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Qi A L, Zhang G M, Dong M, Ma H W, Harvey D M 2018 Ultrasonics 88 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wu J, Zhu J G, Yang L H, Shen M T, Xue B, Liu Z X 2014 Measurement 47 433
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Fang Z H, Hu L, Qin L H, Mao K, Chen W Y, Fu X 2017 Flow Meas. Instrum. 55 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Demirli R, Saniie J 2001 IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferr. 48 787
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Rathee N, Ganotra D 2018 Signal Image Video P. 12 1141
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Kirkpatrick S, Gelatt C D, Vecchi M P 1983 Science 220 671
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Tamizharasan T, Barnabas J K, Pakkirisamy V 2012 P. I. Mech. Eng. B:J. Eng. 226 1159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 李树有, 都志辉, 吴梦月, 朱静, 李三立 2001 50 1260
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li S Y, Du Z H, Wu M Y, Zhu J, Li S L 2001 Acta Phys. Sin. 50 1260
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Hasanoglu M S, Dolen M 2018 Eng. Optimiz. 50 2013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zhan Z H, Zhang J, Li Y, Chung H S H 2009 IEEE Trans. Cybern. 39 1362
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 李一博, 张博林, 刘自鑫, 张振宇 2014 63 160504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y B, Zhang B L, Liu Z X, Zhang Z Y 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 160504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Karaboga D, Ozturk C 2011 Appl. Soft Comput. 11 652
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Kiran M S, Findik O 2015 Appl. Soft Comput. 26 454
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 李广明, 胡志辉 2016 65 230501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li G M, Hu Z H 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 230501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhu J J, Li X L 2017 Healthcare. Technol. Lett. 4 134
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 唐炬, 高丽, 彭莉, 周倩 2007 高电压技术 12 66
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang J, Gao L, Peng L, Zhou Q 2007 High Voltage Eng. 12 66
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 4 不同方法降噪结果对比 (a)黑色实线为含噪回波, 红色虚线为原始信号; (b)本文方法处理结果; (c)小波方法处理结果; (d) EMD方法处理结果
Figure 4. Comparison of de-noising by different methods: (a) Noisy echo plotted in a black solid line, original signal plotted in a red dotted line; (b) signal de-noised by our proposed method; (c) signal de-noised by wavelet method; (d) signal de-noised by EMD method
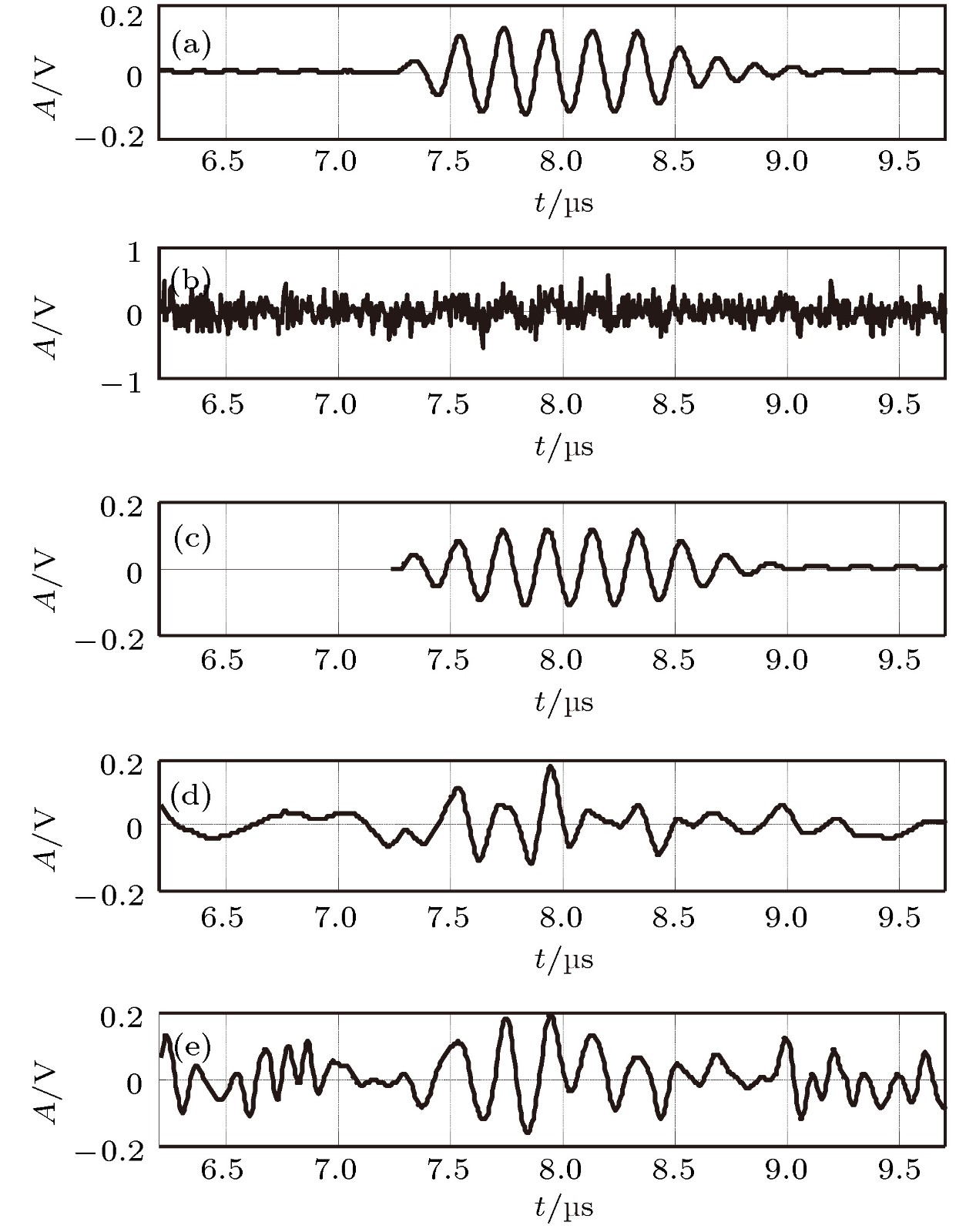
图 7 实测超声回波处理结果对比 (a)实测超声回波; (b)混入系统噪声后的实测超声回波, 信噪比为–10 dB; (c)本文方法结果; (d)小波方法结果; (e) EMD方法结果
Figure 7. Comparison of measured ultrasonic echo processing results: (a) Measured ultrasonic echo; (b) measured ultrasonic echo contaminated by system noise; (c) echo processed by our proposed method; (d) echo processed by wavelet method; (e) echo processed by EMD method.
表 1 渡越时间τ估计误差
Table 1. Estimation error of transit time τ.
输入SNR 实际值/${\text{μ}}{\rm{s}}$ 估计值/${\text{μ}}{\rm{s}}$ 绝对误差/${\text{μ}}{\rm{s}}$ 相对误差/% 100 99.9979 0.0021 0.0021 20 dB 500 499.9789 0.0211 0.0042 800 800.0654 0.0654 0.0082 100 100.1274 0.1274 0.1274 10 dB 500 500.3514 0.3514 0.0703 800 800.4780 0.4780 0.0597 100 100.4791 0.4791 0.4791 0 dB 500 500.7756 0.7756 0.1551 800 802.3819 2.3819 0.2977 100 98.6191 1.3809 1.3809 –10 dB 500 504.4061 4.4061 0.8812 800 — — — 表 2 不同方法降噪结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of denoising results using different methods.
输入SNR 方法 MSE NCC ESNR/dB 本文方法 0 1.0000 49.7149 20 dB 小波方法 0 0.9996 30.5339 EMD方法 0 0.9977 23.3946 本文方法 0 1.0000 42.1588 10 dB 小波方法 0.0001 0.9963 21.3690 EMD方法 0.0002 0.9902 16.8283 本文方法 0 0.9997 32.3540 0 dB 小波方法 0.0010 0.9512 10.1957 EMD方法 0.0014 0.9411 8.8503 本文方法 0.0003 0.9857 15.4456 –10 dB 小波方法 0.0043 0.8439 3.8503 EMD方法 0.0100 0.7149 0.1636 -
[1] Fulin J 2017 Mater. Eval. 75 456
[2] Burkov M V, Eremin A V, Lyubutin P S, Byakov A V, Panin S V 2017 Russ. J. Nondestr. Test. 53 817
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Lu Z K, Yang C, Qin D H, Luo Y L 2016 Signal Process. 120 607
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wang X K, Guan S Y, Hua L, Wang B, He X M 2019 Ultrasonics 91 161
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Meng M, Chua Y J, Wouterson E, Ong C P K 2017 Neurocomputing 257 128
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 孙灵芳, 王彤彤, 徐曼菲, 李霞, 朴亨 2017 仪器仪表学报 38 2879
Sun L F, Wang T T, Xu M F, Li X, Pu H 2017 Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 38 2879 (in Chinese)
[7] 王大为, 王召巴 2018 67 210501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang D W, Wang Z B 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 210501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Qi A L, Zhang G M, Dong M, Ma H W, Harvey D M 2018 Ultrasonics 88 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wu J, Zhu J G, Yang L H, Shen M T, Xue B, Liu Z X 2014 Measurement 47 433
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Fang Z H, Hu L, Qin L H, Mao K, Chen W Y, Fu X 2017 Flow Meas. Instrum. 55 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Demirli R, Saniie J 2001 IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferr. 48 787
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Rathee N, Ganotra D 2018 Signal Image Video P. 12 1141
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Kirkpatrick S, Gelatt C D, Vecchi M P 1983 Science 220 671
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Tamizharasan T, Barnabas J K, Pakkirisamy V 2012 P. I. Mech. Eng. B:J. Eng. 226 1159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 李树有, 都志辉, 吴梦月, 朱静, 李三立 2001 50 1260
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li S Y, Du Z H, Wu M Y, Zhu J, Li S L 2001 Acta Phys. Sin. 50 1260
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Hasanoglu M S, Dolen M 2018 Eng. Optimiz. 50 2013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zhan Z H, Zhang J, Li Y, Chung H S H 2009 IEEE Trans. Cybern. 39 1362
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 李一博, 张博林, 刘自鑫, 张振宇 2014 63 160504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y B, Zhang B L, Liu Z X, Zhang Z Y 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 160504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Karaboga D, Ozturk C 2011 Appl. Soft Comput. 11 652
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Kiran M S, Findik O 2015 Appl. Soft Comput. 26 454
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 李广明, 胡志辉 2016 65 230501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li G M, Hu Z H 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 230501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhu J J, Li X L 2017 Healthcare. Technol. Lett. 4 134
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 唐炬, 高丽, 彭莉, 周倩 2007 高电压技术 12 66
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang J, Gao L, Peng L, Zhou Q 2007 High Voltage Eng. 12 66
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 12051
- PDF Downloads: 182
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: