-
Pulse signal detection is widely used in nuclear explosion electromagnetic pulse detection, lightning signal detection, power system partial discharge detection, electrostatic discharge detection, and other fields. The signal strength becomes weak with the increase of the detection distance and may be submerged in strong Gaussian noise for remote detection. Therefore, the detection and recovery of the weak signals, especially the weak pulse signals, have important applications in signal processing area. Some methods have been reported to detect and estimate weak pulse signals in strong background noise. Coupled Duffing oscillators are usually used in processing periodic signals, though it is still in an exploration stage for aperiodic transient signals. There remain some problems to be solved, for example, the system performance depends on some initial values, results are valid only for the period-doubling bifurcation state, the waveform time domain information cannot be accurately estimated, etc. In this paper, we explain the reasons why there exist these inherent defects in the current weakly coupled Duffing oscillators. In order to solve the above-mentioned problems, a new signal detection and recovery model is constructed, which is characterized by coupling the restoring force and damping force of the two oscillators simultaneously. A large coupling coefficient is applied to the two Duffing oscillators, and a generalized " in-well out-of-synchronization”phenomenon arises between the oscillators which conduces to detecting and recovering the weak pulse signals, and also overcoming the defects mentioned above. Using the metrics of signal-to-noise ratio improvement (SNRI) and waveform similarity, the effects of amplitude and period of periodic driving force, coupling coefficient, step size and damping coefficient on signal detection and waveform recovery are studied. Finally, experiments are performed to detect and recover the following three kinds of pulses: square wave pulses, double exponential pulses, and Gaussian derivative pulses. The input SNR thresholds of these three waveforms are –15, –12, and –16 dB, respectively, under the detection probabilities and waveform similarity all being greater than 0.9 simultaneously. The maximum error of the pulse amplitude and pulse width are both less than 5% of their corresponding true values. In summary, the strongly coupled Duffing system has advantages of being able to operate in any phase-space state and being no longer limited by the initial values. Especially, the time domain waveform of weak pulse signals can be well recovered in the low SNR case, and the error and the minimum mean square error are both very low.
-
Keywords:
- weak pulse signal /
- strongly coupled Duffing oscillators /
- signal detection /
- parameter estimation
[1] Kirsteins I P, Mehta S K, Fay J 1997 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing Munich, Germany, April 21−24, 1997 p483
[2] 吴小培, 冯焕清, 周荷琴, 王涛 2001 生物医学工程学杂志 18 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu X P, Feng H Q, Zhou H Q, Wang T 2001 J. Biomedical. Eng. 18 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Qi L, Tao R, Zhou S Y, Wang Y 2004 Sci. China: Ser. F 47 184
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 刘锋, 徐会法, 陶然 2011 电子与信息学报 33 1864
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu F, Xu H F, Tao R 2011 J. Electr. Inf. Technol. 33 1864
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 王燕, 邹男, 付进, 梁国龙 2013 电子与信息学报 35 1720
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y, Zou N, Fu J, Liang G L 2013 J. Electr. Inf. Technol. 35 1720
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 汪立新, 林孝焰, 吴涛 2007 计算机工程与应用 43 239
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang L X, Lin X Y, Wu T 2007 Comput. Eng. Appl. 43 239
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 樊高辉, 刘尚合, 刘卫东, 魏明, 胡小锋, 张悦 2015 电波科学学报 30 736
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fan G H, Liu S H, Liu W D, Wei M, Hu X F, Zhang Y 2015 Chin. J. Radio. 30 736
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 苏理云, 孙唤唤, 王杰, 阳黎明 2017 64 090503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Su L Y, Sun H H, Wang J, Yang L M 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 090503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 苏理云, 孙唤唤, 李晨龙 2017 电子学报 45 837
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Su L Y, Sun H H, Li C L 2017 Acta Electron. Sin. 45 837
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 王永生, 姜文志, 赵建军, 范洪达 2008 57 2053
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y S, Jiang W Z, Zhao J J, Fan H D 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 2053
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 姚海洋, 王海燕, 张之琛, 申晓红 2017 66 124302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yao H Y, Wang H Y, Zhang Z S, Shen X H 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 124302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 金友渔 2002 电子学报 30 79
[13] 王慧武, 丛超 2016 电子学报 44 1450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H W, Cong C 2016 Acta Electron. Sin. 44 1450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 赖志慧, 冷永刚, 孙建桥, 范胜波 2012 61 050503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lai Z H, Leng Y G, Sun J Q, Fan S B 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 050503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 范剑, 赵文礼, 王万强 2013 62 180502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fan J, Zhao W L, Wang W Q 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 180502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 吴继鹏, 曲银凤, 程学珍 2017 电子测量技术 40 143
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu J P, Qu Y F, Cheng X Z 2017 Electr. Measur. Technol. 40 143
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 李月, 路鹏, 杨宝俊, 赵雪平 2006 55 1672
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y, Lu P, Yang B J, Zhao X P 2006 Acta Phys. Sin. 55 1672
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Yuan Y, Li Y, Mandic D P, Yang B J 2009 Chin. Phys. B 18 958
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 吴勇峰, 张世平, 孙金玮, Peter Rolfe 2011 60 020511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Y F, Zhang S P, Sun J W, Rolfe P 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 020511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 吴勇峰, 张世平, 孙金玮, Peter Rolfe, 李智 2011 60 100509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Y F, Zhang S P, Sun J W, Rolfe P, Li Z 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 100509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 吴勇峰, 黄绍平, 金国彬 2013 62 130505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Y F, Huang S P, Jin G B 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 130505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 张悦, 刘尚合, 胡小锋, 刘卫东, 魏明, 王雷 2015 中国发明专利 201510275506.8
Zhang Y, Liu S H, Hu X F, Liu W D, Wei M, Wang L 2015 CN Patent 201510275506.8 (in Chinese)
[23] 曾喆昭, 周勇, 胡凯 2015 64 070505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zeng Z Z, Zhou Y, Hu K 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 070505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 王晓东, 赵志宏, 杨绍普 2016 噪声与振动控制 36 174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X D, Zhao Z H, Yang S P 2016 Noise Vibra. Contrl. 36 174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Shampine L F, Reichelt M W 1997 SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 18 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 史蒂芬 H. 斯托加茨 著(孙梅, 汪小帆 译)2017 非线性动力学与混沌(北京: 机械工业出版社)第162—163页
Steven H S (translated by Sun M, Wang X F) 2017 Nonlinear Dynamics and chaos (Beijing: Mechanical Industry Press) pp162−163 (in Chinese)
[27] 刘海波, 吴德伟, 金伟, 王永庆 2013 62 050501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu H B, Wu D W, Jin W, Wang Y Q 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 050501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 孙克辉, 谈国强, 盛利元, 张泰山 2004 计算机工程与应用 35 12
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun K H, Tan G Q, Sheng L Y, Zhang T S 2004 Comput. Eng. Appl. 35 12
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
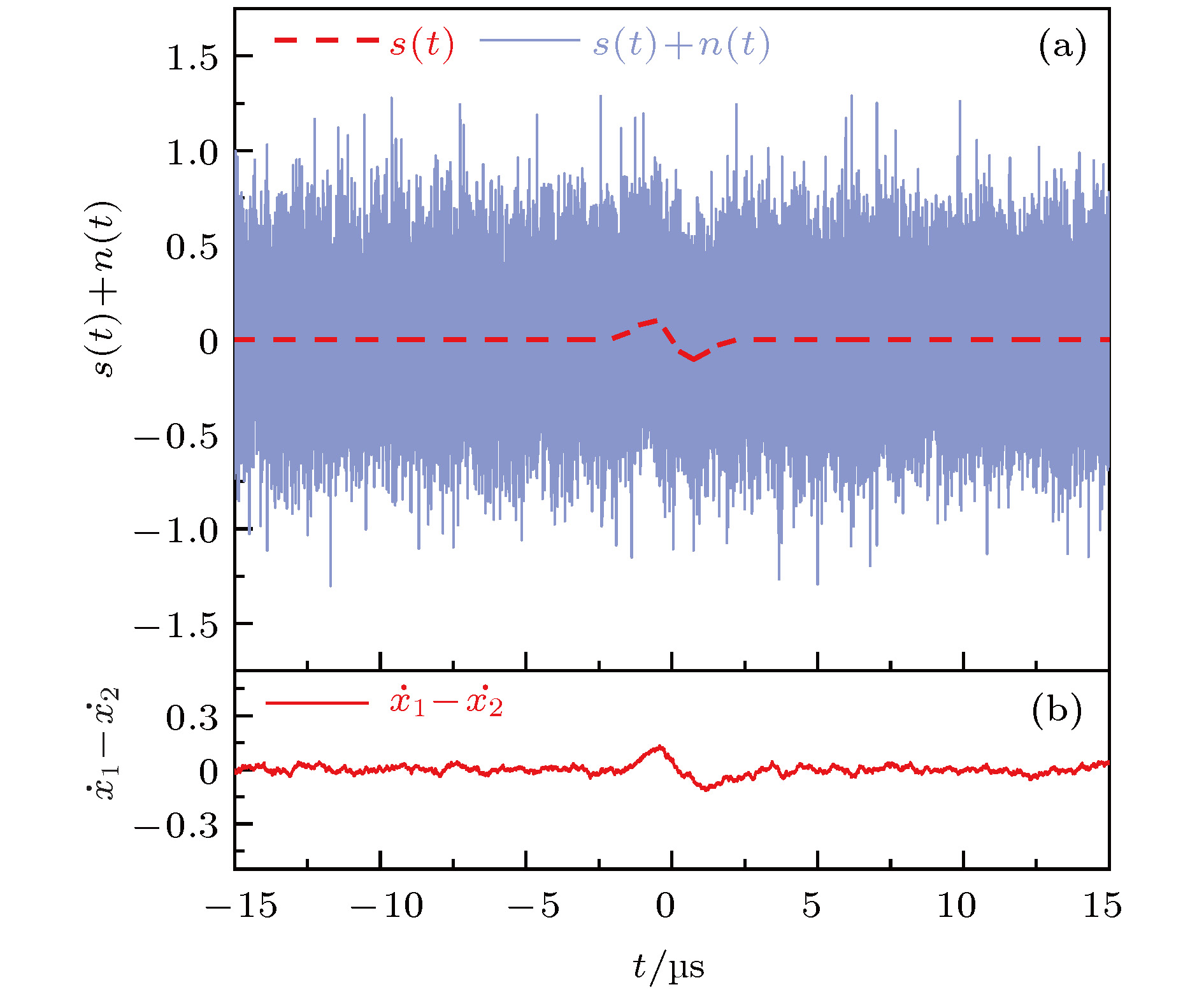
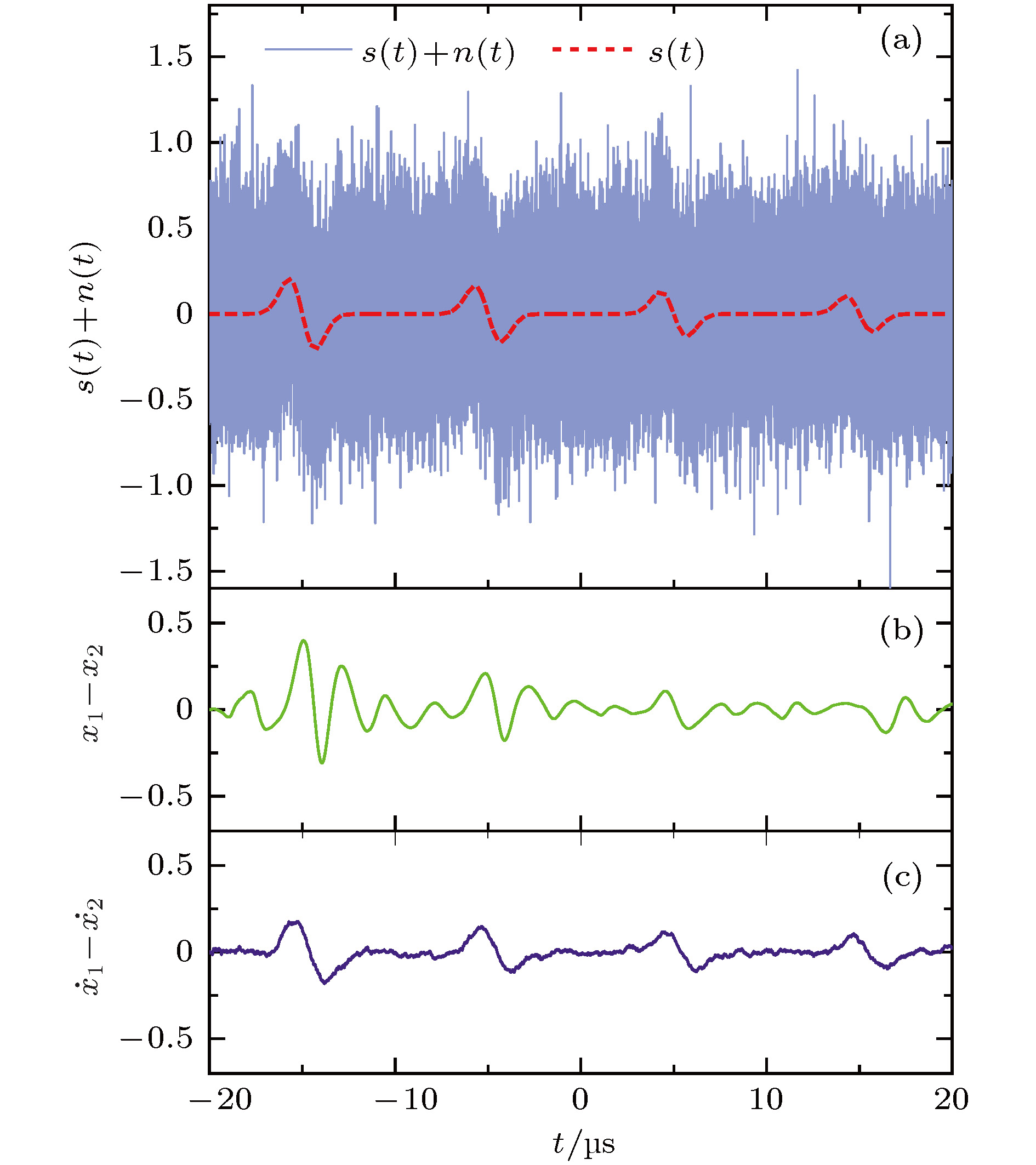
图 1 强耦合Duffing振子检测微弱脉冲信号 (a)输入信号; (b)输出信号; (c)振子1相图; (d)振子2相图; (e)变量
${\dot x_1}$ 时域图; (f)变量${\dot x_2}$ 时域图Figure 1. Detection of weak pulse signal using the strongly coupled Duffing oscillators: (a) Input signal; (b) output signal; (c) phase space of oscillator 1 and (d) oscillator 2; (e) time domain diagram of variable
${\dot x_1}$ and (f)${\dot x_2}$ 表 1 强耦合Duffing振子各参数取值区间与默认值
Table 1. Values range and default values of parameters in strongly coupled Duffing oscillators
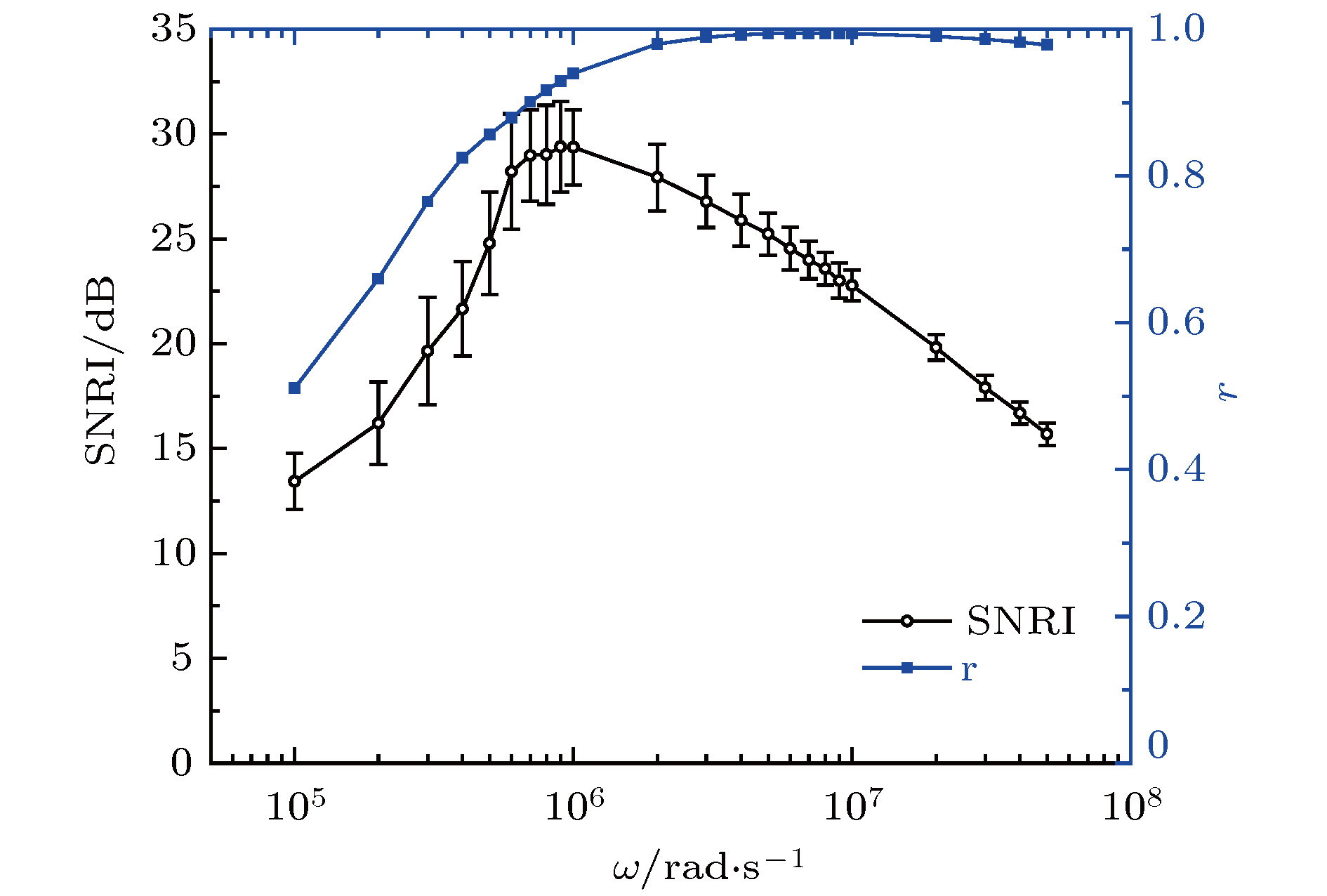
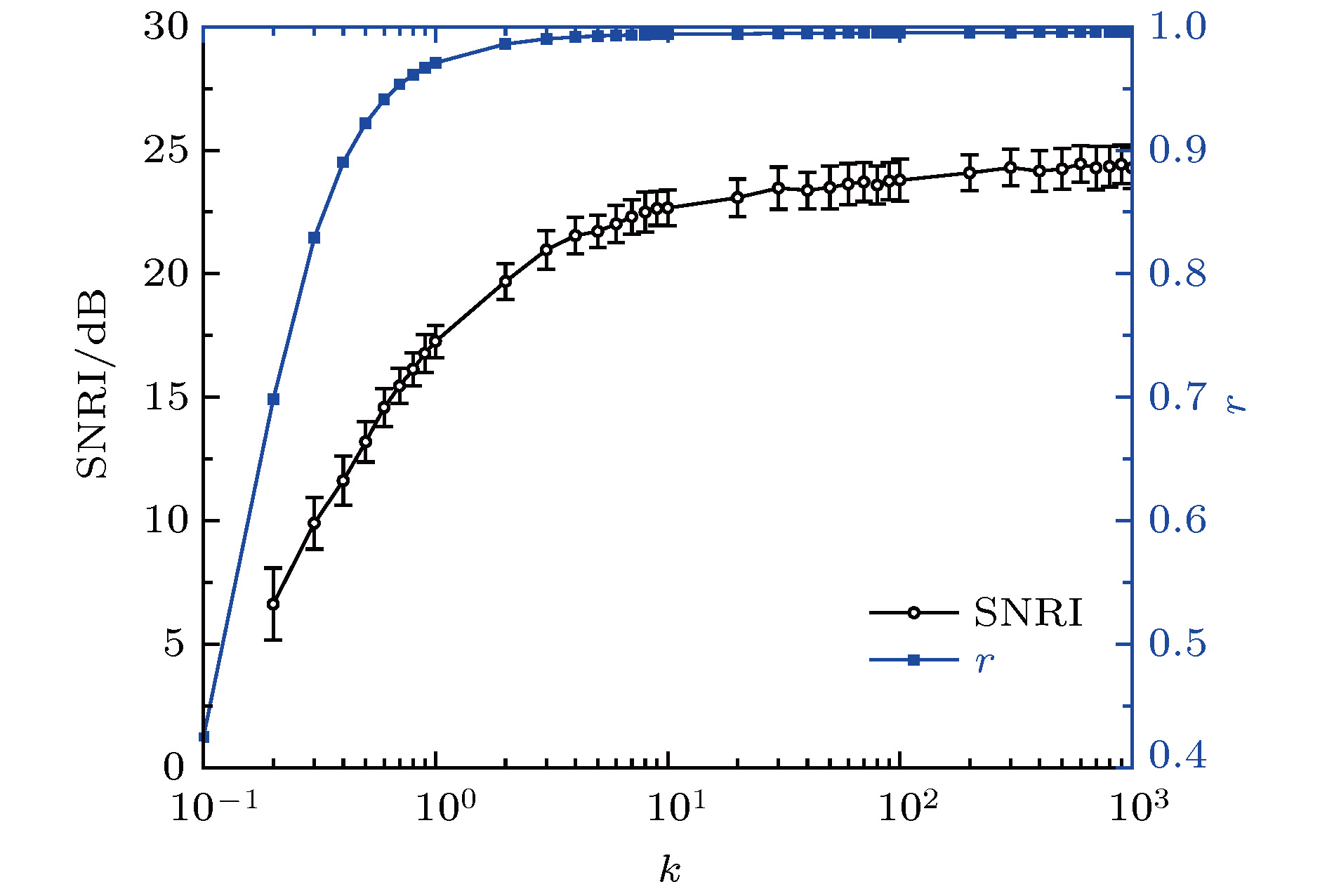
参数 取值区间 默认值 F [0, 2] 0.2 $\omega $/${\rm rad}\cdot {{\rm s}^{-1}} $ [1 × 105, 5 × 107] 5 × 106 k [10–1, 103] 10 $\xi$ [10–2, 102] 0.7 计算步长/ns [20, 1] 1 表 2 波形特征及部分振子参数
Table 2. Waveform characteristics and partial oscillator parameters
脉冲类型 波形时域特征 Duffing振子参数 方波 上升时间0.1 ms $\omega = 50$ rad/s 半高宽1 s 计算步长0.1 ms 双指数脉冲 上升时间3 ${\text{μs}}$ $\omega = 5 \times {10^5}$ rad/s 半高宽25 ${\text{μs}}$ 计算步长10 ns 高斯导数脉冲 上升时间1.5 ${\text{μs}}$ $\omega = 4 \times {10^6}$ rad/s 峰峰宽1.45 ${\text{μs}}$ 计算步长1 ns 表 3 强耦合Duffing振子检测结果
Table 3. Detection results of strongly coupled Duffing oscillators
脉冲类型 输入信噪比/dB –20 –19 –18 –17 –16 –15 –14 –13 –12 –11 –10 方波 检测概率/% 14.0 21.5 41.5 60.5 78.0 91.5 99.0 100 100 100 100 波形相似度r 0.88 0.90 0.92 0.93 0.94 0.95 0.96 0.97 0.97 0.98 0.98 双指数脉冲 检测概率/% 0.5 4.5 5.5 10.0 23.5 51.0 67.5 87.5 95.5 100 100 波形相似度r 0.67 0.71 0.74 0.78 0.81 0.84 0.86 0.88 0.90 0.91 0.92 高斯导数脉冲 检测概率/% 37.5 55.0 73.0 86.5 94.0 99.5 100 100 100 100 100 波形相似度r 0.85 0.87 0.88 0.89 0.90 0.91 0.92 0.92 0.93 0.93 0.93 表 4 脉冲信号幅值估计结果
Table 4. Estimation results of pulse signals amplitude
脉冲类型 输入信噪比/dB –16 –15 –14 –13 –12 –11 –10 方波 真实值 — 0.1125 0.1262 0.1416 0.1589 0.1783 0.2000 估计值 — 0.1114 0.1304 0.1375 0.1641 0.1761 0.1943 误差/% — –0.98 3.34 –2.90 3.29 –1.24 –2.85 MSE/10–4 — 1.26 1.43 0.75 2.04 1.23 2.49 双指数脉冲 真实值 — — — — 0.1589 0.1783 0.2000 估计值 — — — — 0.1586 0.1773 0.2032 误差/% — — — — –0.16 –0.55 1.62 MSE/10–4 — — — — 2.79 6.43 5.03 高斯导数脉冲 真实值 0.1002 0.1125 0.1262 0.1416 0.1589 0.1783 0.2000 估计值 0.1039 0.1180 0.1297 0.1423 0.1595 0.1807 0.1960 误差/% 3.74 4.93 2.78 0.52 0.41 1.35 –2.02 MSE/10–4 0.29 0.89 0.79 1.60 0.82 1.46 0.71 表 5 脉冲信号宽度估计结果
Table 5. Estimation results of pulse signals width
脉冲类型 输入信噪比/dB –16 –15 –14 –13 –12 –11 –10 方波 真实值/s — 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 估计值/s — 1.0011 0.9988 0.9941 0.9984 0.9972 0.9986 误差/% — 0.11 –0.12 –0.59 –0.16 –0.28 –0.14 MSE/10–4 — 1.40 1.11 0.57 0.13 0.56 0.45 双指数脉冲 真实值/${\text{μ}}{\rm s}$ — — — — 25 25 25 估计值/${\text{μ}}{\rm s}$ — — — — 25.22 24.79 24.68 误差/% — — — — 0.89 –0.84 –1.27 MSE — — — — 15.8 3.8 7.7 高斯导数脉冲 真实值/${\text{μ}}{\rm s}$ 1.45 1.45 1.45 1.45 1.45 1.45 1.45 估计值/${\text{μ}}{\rm s}$ 1.38 1.52 1.52 1.47 1.48 1.52 1.46 误差/% –5.02 4.99 4.61 1.43 2.37 4.49 0.34 MSE 0.011 0.023 0.017 0.032 0.024 0.003 0.012 -
[1] Kirsteins I P, Mehta S K, Fay J 1997 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing Munich, Germany, April 21−24, 1997 p483
[2] 吴小培, 冯焕清, 周荷琴, 王涛 2001 生物医学工程学杂志 18 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu X P, Feng H Q, Zhou H Q, Wang T 2001 J. Biomedical. Eng. 18 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Qi L, Tao R, Zhou S Y, Wang Y 2004 Sci. China: Ser. F 47 184
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 刘锋, 徐会法, 陶然 2011 电子与信息学报 33 1864
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu F, Xu H F, Tao R 2011 J. Electr. Inf. Technol. 33 1864
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 王燕, 邹男, 付进, 梁国龙 2013 电子与信息学报 35 1720
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y, Zou N, Fu J, Liang G L 2013 J. Electr. Inf. Technol. 35 1720
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 汪立新, 林孝焰, 吴涛 2007 计算机工程与应用 43 239
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang L X, Lin X Y, Wu T 2007 Comput. Eng. Appl. 43 239
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 樊高辉, 刘尚合, 刘卫东, 魏明, 胡小锋, 张悦 2015 电波科学学报 30 736
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fan G H, Liu S H, Liu W D, Wei M, Hu X F, Zhang Y 2015 Chin. J. Radio. 30 736
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 苏理云, 孙唤唤, 王杰, 阳黎明 2017 64 090503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Su L Y, Sun H H, Wang J, Yang L M 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 090503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 苏理云, 孙唤唤, 李晨龙 2017 电子学报 45 837
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Su L Y, Sun H H, Li C L 2017 Acta Electron. Sin. 45 837
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 王永生, 姜文志, 赵建军, 范洪达 2008 57 2053
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y S, Jiang W Z, Zhao J J, Fan H D 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 2053
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 姚海洋, 王海燕, 张之琛, 申晓红 2017 66 124302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yao H Y, Wang H Y, Zhang Z S, Shen X H 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 124302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 金友渔 2002 电子学报 30 79
[13] 王慧武, 丛超 2016 电子学报 44 1450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H W, Cong C 2016 Acta Electron. Sin. 44 1450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 赖志慧, 冷永刚, 孙建桥, 范胜波 2012 61 050503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lai Z H, Leng Y G, Sun J Q, Fan S B 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 050503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 范剑, 赵文礼, 王万强 2013 62 180502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fan J, Zhao W L, Wang W Q 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 180502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 吴继鹏, 曲银凤, 程学珍 2017 电子测量技术 40 143
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu J P, Qu Y F, Cheng X Z 2017 Electr. Measur. Technol. 40 143
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 李月, 路鹏, 杨宝俊, 赵雪平 2006 55 1672
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y, Lu P, Yang B J, Zhao X P 2006 Acta Phys. Sin. 55 1672
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Yuan Y, Li Y, Mandic D P, Yang B J 2009 Chin. Phys. B 18 958
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 吴勇峰, 张世平, 孙金玮, Peter Rolfe 2011 60 020511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Y F, Zhang S P, Sun J W, Rolfe P 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 020511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 吴勇峰, 张世平, 孙金玮, Peter Rolfe, 李智 2011 60 100509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Y F, Zhang S P, Sun J W, Rolfe P, Li Z 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 100509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 吴勇峰, 黄绍平, 金国彬 2013 62 130505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Y F, Huang S P, Jin G B 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 130505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 张悦, 刘尚合, 胡小锋, 刘卫东, 魏明, 王雷 2015 中国发明专利 201510275506.8
Zhang Y, Liu S H, Hu X F, Liu W D, Wei M, Wang L 2015 CN Patent 201510275506.8 (in Chinese)
[23] 曾喆昭, 周勇, 胡凯 2015 64 070505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zeng Z Z, Zhou Y, Hu K 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 070505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 王晓东, 赵志宏, 杨绍普 2016 噪声与振动控制 36 174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X D, Zhao Z H, Yang S P 2016 Noise Vibra. Contrl. 36 174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Shampine L F, Reichelt M W 1997 SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 18 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 史蒂芬 H. 斯托加茨 著(孙梅, 汪小帆 译)2017 非线性动力学与混沌(北京: 机械工业出版社)第162—163页
Steven H S (translated by Sun M, Wang X F) 2017 Nonlinear Dynamics and chaos (Beijing: Mechanical Industry Press) pp162−163 (in Chinese)
[27] 刘海波, 吴德伟, 金伟, 王永庆 2013 62 050501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu H B, Wu D W, Jin W, Wang Y Q 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 050501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 孙克辉, 谈国强, 盛利元, 张泰山 2004 计算机工程与应用 35 12
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun K H, Tan G Q, Sheng L Y, Zhang T S 2004 Comput. Eng. Appl. 35 12
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 12087
- PDF Downloads: 153
- Cited By: 0



















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: