-
针对目前透过散射介质成像技术中宽谱导致目标信息被淹没于背景干扰中, 且散射对波长的敏感性使得频谱信息混叠产生的色彩畸变严重, 无法实现彩色超分辨率成像的问题, 提出了基于散射光场偏振信息复用的计算偏振彩色傅里叶叠层成像技术. 该技术深入地分析散射场的强度及偏振分布特性, 综合利用散射场中目标与背景干扰的偏振信息差异性和唯一性表征, 结合光场的偏振共模抑制特性和偏振的波长相关性, 分通道实现宽谱散射场中的背景干扰信息和目标信息的有效分离. 此外, 深度挖掘散射光场中频谱信息的差异性, 利用傅里叶叠层技术实现散射光场频谱信息拼接, 进而获得透过散射介质的彩色高分辨率成像效果. 实验结果表明, 该方法不仅能够实现透过散射介质的超分辨率重建, 而且偏振信息的复用对于谱宽造成的信号混叠有明显的抑制作用, 大幅提升了重建图像的信噪比和对比度, 抑制了色彩畸变, 在未来的透过散射介质成像具有良好的应用前景.
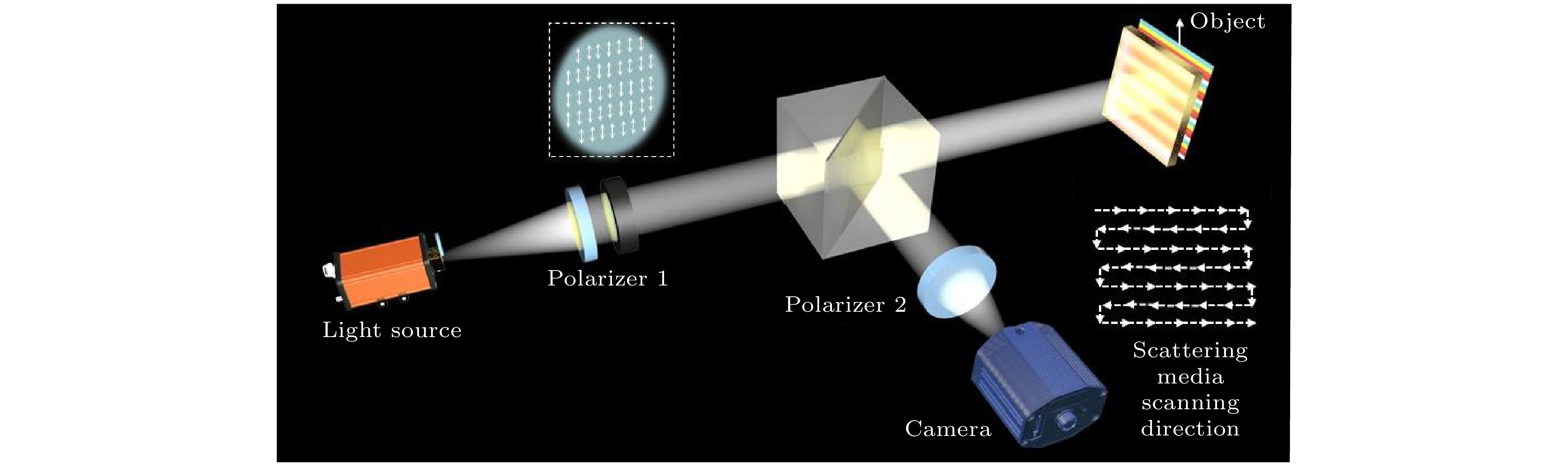
Fourier ptychography for high-resolution imaging has been a revolutionizing technical, since it can provide abundant information about target scene by changing illumination or pupil scanning. However, many objects are covered by dynamic scattering media, such as biological tissues and mist, that disrupts the light paths and forms the scattering wall, let alone high-resolution imaging. It is worth noting that the scatting effect caused by the scattering media will reduce the correlation of scattered light field, which makes the information aliasing difficult to extract. The situation becomes worse if the image scene is in color. Typically, the wavefront shaping, optical transmission matrix, and speckle correlation technique can successfully recover hidden targets form the scattered light field. Notably, the physical model of conventional method is limited by the difficultly in extracting target information from the strong scattering environment, especially in broadband light illumination imaging. Thus, it is limited to achieve super-resolution color imaging through scattering media by utilizing the current techniques. In this work, we present a computational polarized colorful Fourier ptychography imaging approach for super-resolution perspective in broadband dynamic scattering media. In order to address the challenge of current imaging methods that is limited by the width of the light spectrum, the polarization characteristics of the scattered-light-field are explored. After retrieving a series of sub-polarized images, which bring the information about different frequencies caused by the motion of scattering media and are processed by the common-mode rejection of polarization characteristic, our computational approach utilizes the iterative optimization algorithm to recover the scene. Notably, owning to the difference between the target scattering information and background scattering information of scattered light fields with different polarization rotation angles, we can obtain two images in which the target information and the background information are dominant in the scattered field. Afterwards, a series of images containing target information and background information is used to iterate the Fourier ptychographyprogram to update the target image based on the obtained image sequence until the estimation converges. During the updating procedure, the scattering effect can be removed, and the spatial-resolution is improved. Compared with traditional scattering imaging model, the proposed method can perform super-resolution color imaging and descattering under various conditions, and solve the problem of color cases. Furthermore, the proposed method is easy to incorporate into a traditional Fourier Ptychography imaging system to obtain high-fidelity images with better quality and effective detail information. Therefore, the proposed method has the potential to help super-resolution imaging to obtain more practical applications. -
Keywords:
- scattering /
- polarization imaging /
- super-resolution imaging /
- Fourier ptychography /
- computational imaging
[1] Dong Y, Liu S, Shen Y, He H, Ma H 2020 Biomed. Opt. Express 11 4960
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Chen H, Wu X, Liu G, Chen Z, Pu J 2023 Results Phys. 44 106134
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 苏云, 葛婧菁, 王业超, 王乐然, 王钰, 郑子熙, 邵晓鹏 2023 中国光学 16 258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Su Y, Ge J J, Wang Y C, Wang L R, Wang Y, Zheng Z X, Shao X P 2023 Chin. Opt. 16 258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 邓红艳, 苏云, 郑国宪, 赵明, 张月, 田芷铭 2023 光子学报 52 0552219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Deng H Y, Su Y, Zheng G X, Zhao M, Zhang Y, Tian Z M 2023 Acta Photonica Sin. 52 0552219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Bian Y, Li H, Wang Y, Zheng Z, Liu X 2015 Appl. Opt. 54 8241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Li L, Pan A, Li C, Zhao H 2023 Opt. Commun. 537 129393
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 潘安 2020 博士学位论文 (西安: 中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所)
Pan A 2020 Ph. D. Dissertation (Xi’an: Xi’an Institute of Optics & Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
[8] Zheng G, Horstmeyer R, Yang C 2013 Nat. Photonics 7 739
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Ou X, Horstmeyer R, Yang C, Zheng G 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 4845
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wang M Q, Zhang Y Z, Chen Q, Sun J S, Fan Y, Zuo C 2017 Opt. Commun. 405 406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Pan A, Zhang Y, Wen K, Zhou M, Min J, Lei M, Yao B 2018 Opt. Express 26 23119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tian Z, Zhao M, Yang D, Wang S, Pan A 2023 Photonics Res. 11 2072
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Holloway J, Wu Y, Sharma M K, Cossairt O, Veeraraghavan A 2017 Sci. adv. 3 e1602564
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Xiang M, Pan A, Zhao Y, Fan X, Zhao H, Li C, Yao B 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Dong S, Nanda P, Shiradkar R, Guo K, Zheng G 2014 Opt. Express 22 20856
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jiang S, Liao J, Bian Z, Song P, Soler G, Hoshino K, Zheng G 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 811
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Liu Q, Chen Y, Liu W, Han Y, Cao R, Zhang Z, Kuang C, Liu X 2019 Opt. Lasers Eng. 123 45
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Xie Z L, Qi B, Ma H T, Ren G, Tan Y F, He B, Zeng H L, Jiang C 2016 Chin. Phys. Lett. 33 044206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bertolotti J, van Putten E G, Blum C, Lagendijk A, Vos W L, Mosk A P 2015 Conference on Adaptive Optics and Wavefront Control for Biological Systems San Francisco, California, United States , February 7−9, 2015 p93350W
[20] Zhu L, Soldevila F, Moretti C, d’Arco A, Boniface A, Shao X, De Aguiar H B, Gigan S 2022 Nat. Commun. 13 1447
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Gao Y T, Chen J R, Wang A Y, Pan A, Ma C W, Yao B L 2021 Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 64 114211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Bian Y X, Xing T, Deng W J, Xian Q, Qiao H L, Yu Q, Peng J L, Yang X F, Jiang Y N, Wang J X, Yang S M, Shen R B, Shen H, Kuang C F 2022 Infrared Laser Eng. 51 20210891
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Hu H, Jin H, Liu H, Li X, Cheng Z, Liu T, Zhai J 2023 Opt. Laser Technol. 166 109632
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Schechner Y Y, Karpel N 2006 IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 30 570
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Han P, Liu F, Yang K, Ma J, Li J, Shao X 2017 Appl. Opt. 56 6631
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Andreoli D, Volpe G, Popoff S, Katz O, Grésillon S, Gigan S 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 10347
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Tao H C, Lü J G, Liang J Q, Zhao B X, Chen Y P, Zheng K F, Zhao Y Z, Wang W B, Qin Y X, Liu G H, Sheng K Y 2023 Photonics 10 566
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Tyo J S 1998 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 15 359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Yang L, Liang J, Zhang W, Ju H, Ren L, Shao X 2019 Opt. Commun. 438 96
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Luo M R, Cui G, Rigg B 2001 Color Res. Appl. 26 340
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
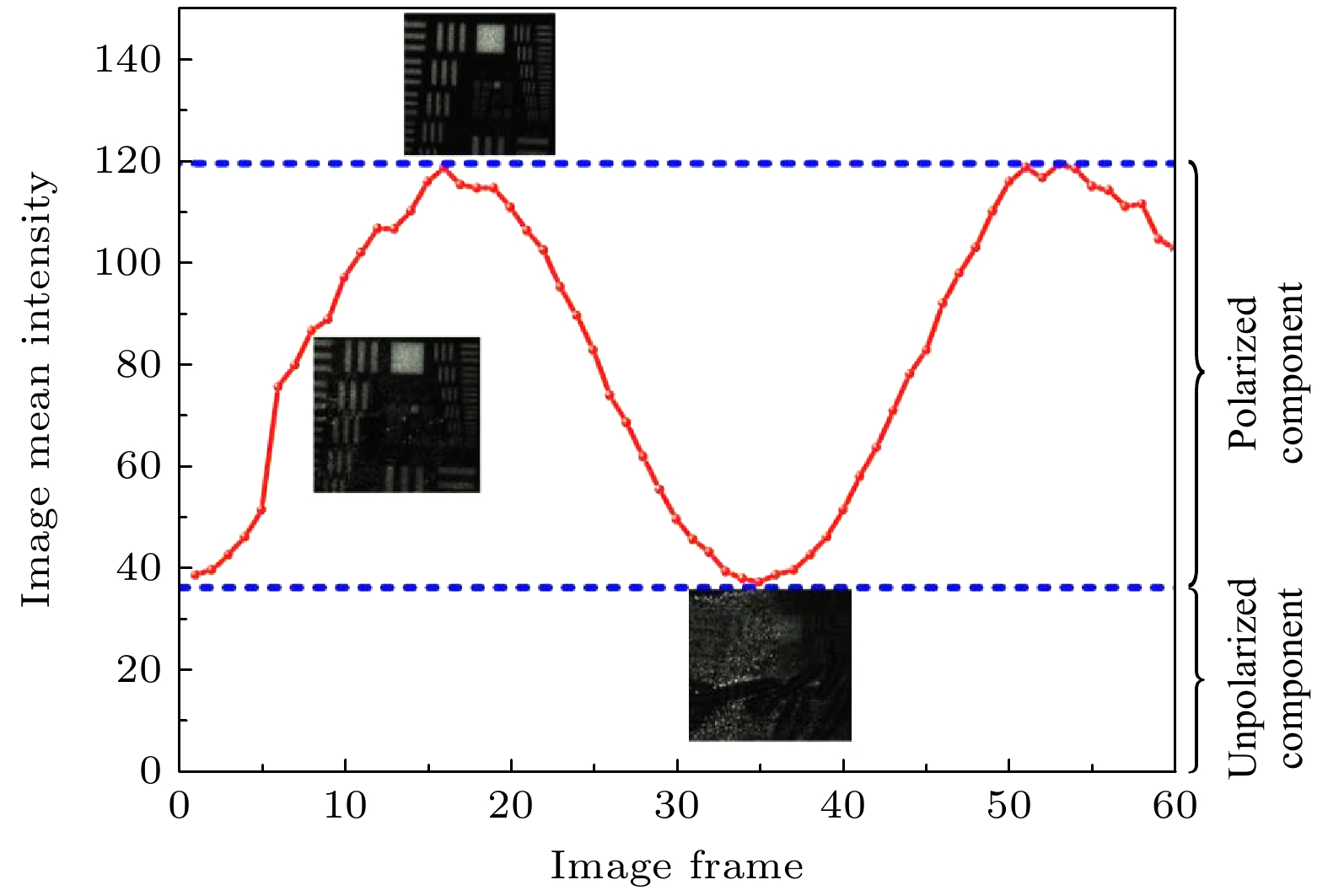
图 3 散射光场偏振特性分布情况 (a) 偏振度图像; (b) 偏振角图像; (c)—(e) RGB三通道的偏振度图像; (f)—(h) RGB三通道的偏振角图像; (i) RGB三通道的偏振角图像子区域的数值分析
Fig. 3. Distribution of polarization characteristics of scattering light field: (a) DoLP images; (b) AoP images; (c)–(e) DoLP images in RGB channel; (f)–(h) AoP images in RGB channel; (i) numerical analysis for sub regions of AoP images in RGB channel.
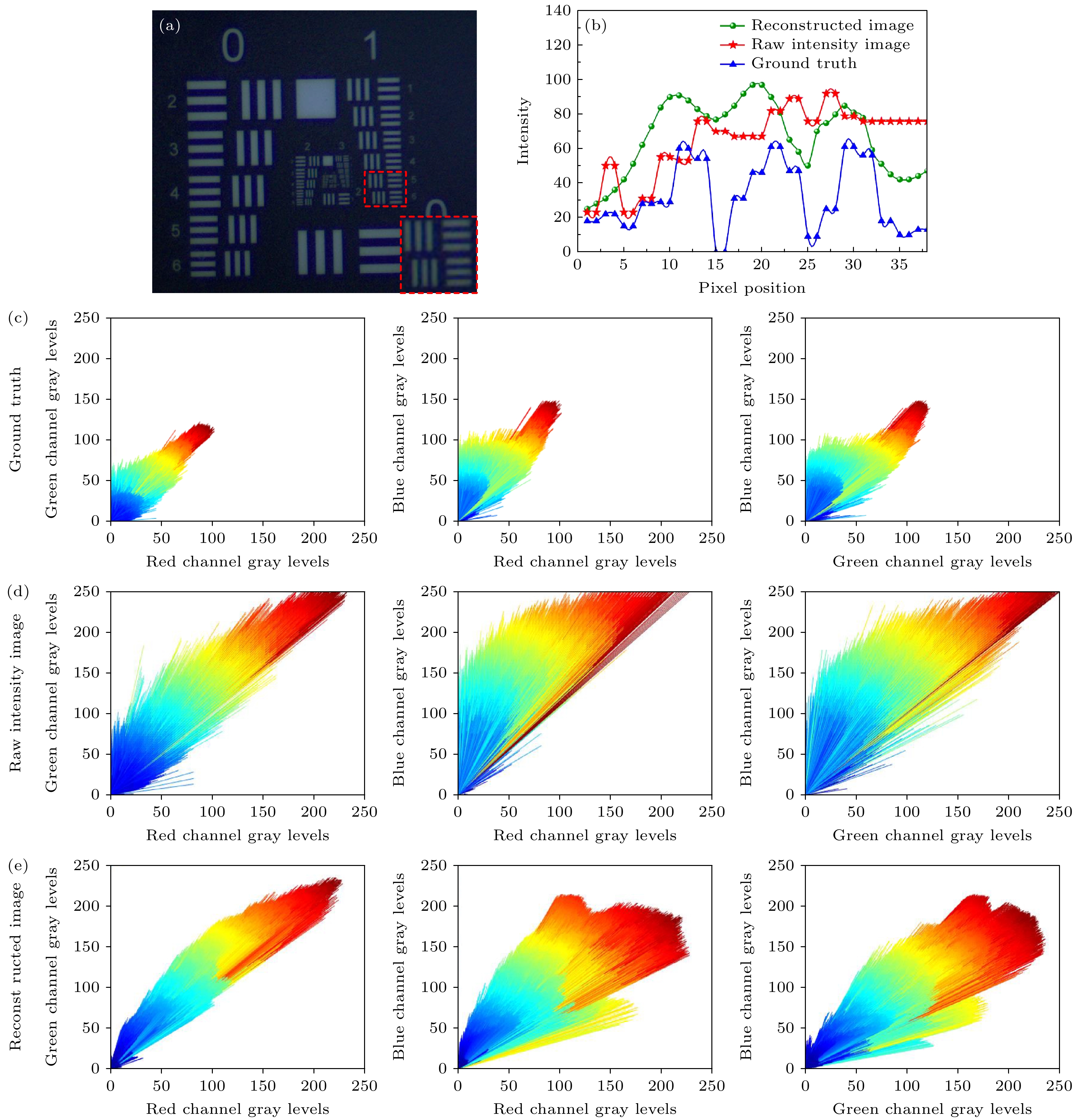
图 5 分辨率靶标的实验结果 (a) 探测器获取的原始强度图像; (b) 本文算法重建所得结果; (c) 原始强度图像的局部放大; (d) 本文重建结果的局部放大; (e) 传统偏振去散射算法重建结果; (f) 传统偏振去散射重建结果的局部放大
Fig. 5. Imaging result of USAF target: (a) Raw intensity image; (b) the reconstructed resulted by proposed method; (c) the details information of the raw image (a); (d) the details information of the image (b); (e) the reconstructed resulted by the traditional polarimetric dehazing method; (f) the details information of the image (e)
图 6 (a) 目标靶板的真值图像; (b) 图5所示的1组6的分辨率线对像素强度值分布图; (c), (d)和(e)分别为图6(a)、图5(a)和图5(b)的R, G, B三通道像素强度统计值
Fig. 6. (a) Ground truth image; (b) the horizontal line plots at the resolution line pair of group 1, element 6; (c), (d) and (e) are the pixel intensity distribution of channel R, G and B of Fig. 6(a), Fig. 5(a) and Fig. 5(b).
图 7 其他目标的重建结果: 纸质、塑料、病叶和编织布, 其中(a)—(c), (d)—(f), (g)—(i), (j)—(l)分别为不同目标的参考图像、直接采集原始强度图像和重建结果; (a1)—(l1), (a2)—(f2)分别为不同目标图像对应区域的细节信息对比结果
Fig. 7. Reconstruction images of different objects (paper, plastic, diseased leaves and woven fabric) using the proposed method: (a)–(c), (d)–(f), (g)–(i), (j)–(l) The ground truth image, raw intensity image and reconstructed image; (a1)–(l1), (a2)–(f2) the detail information of area 1–6 in images.
-
[1] Dong Y, Liu S, Shen Y, He H, Ma H 2020 Biomed. Opt. Express 11 4960
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Chen H, Wu X, Liu G, Chen Z, Pu J 2023 Results Phys. 44 106134
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 苏云, 葛婧菁, 王业超, 王乐然, 王钰, 郑子熙, 邵晓鹏 2023 中国光学 16 258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Su Y, Ge J J, Wang Y C, Wang L R, Wang Y, Zheng Z X, Shao X P 2023 Chin. Opt. 16 258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 邓红艳, 苏云, 郑国宪, 赵明, 张月, 田芷铭 2023 光子学报 52 0552219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Deng H Y, Su Y, Zheng G X, Zhao M, Zhang Y, Tian Z M 2023 Acta Photonica Sin. 52 0552219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Bian Y, Li H, Wang Y, Zheng Z, Liu X 2015 Appl. Opt. 54 8241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Li L, Pan A, Li C, Zhao H 2023 Opt. Commun. 537 129393
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 潘安 2020 博士学位论文 (西安: 中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所)
Pan A 2020 Ph. D. Dissertation (Xi’an: Xi’an Institute of Optics & Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
[8] Zheng G, Horstmeyer R, Yang C 2013 Nat. Photonics 7 739
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Ou X, Horstmeyer R, Yang C, Zheng G 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 4845
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wang M Q, Zhang Y Z, Chen Q, Sun J S, Fan Y, Zuo C 2017 Opt. Commun. 405 406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Pan A, Zhang Y, Wen K, Zhou M, Min J, Lei M, Yao B 2018 Opt. Express 26 23119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tian Z, Zhao M, Yang D, Wang S, Pan A 2023 Photonics Res. 11 2072
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Holloway J, Wu Y, Sharma M K, Cossairt O, Veeraraghavan A 2017 Sci. adv. 3 e1602564
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Xiang M, Pan A, Zhao Y, Fan X, Zhao H, Li C, Yao B 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Dong S, Nanda P, Shiradkar R, Guo K, Zheng G 2014 Opt. Express 22 20856
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jiang S, Liao J, Bian Z, Song P, Soler G, Hoshino K, Zheng G 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 811
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Liu Q, Chen Y, Liu W, Han Y, Cao R, Zhang Z, Kuang C, Liu X 2019 Opt. Lasers Eng. 123 45
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Xie Z L, Qi B, Ma H T, Ren G, Tan Y F, He B, Zeng H L, Jiang C 2016 Chin. Phys. Lett. 33 044206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bertolotti J, van Putten E G, Blum C, Lagendijk A, Vos W L, Mosk A P 2015 Conference on Adaptive Optics and Wavefront Control for Biological Systems San Francisco, California, United States , February 7−9, 2015 p93350W
[20] Zhu L, Soldevila F, Moretti C, d’Arco A, Boniface A, Shao X, De Aguiar H B, Gigan S 2022 Nat. Commun. 13 1447
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Gao Y T, Chen J R, Wang A Y, Pan A, Ma C W, Yao B L 2021 Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 64 114211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Bian Y X, Xing T, Deng W J, Xian Q, Qiao H L, Yu Q, Peng J L, Yang X F, Jiang Y N, Wang J X, Yang S M, Shen R B, Shen H, Kuang C F 2022 Infrared Laser Eng. 51 20210891
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Hu H, Jin H, Liu H, Li X, Cheng Z, Liu T, Zhai J 2023 Opt. Laser Technol. 166 109632
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Schechner Y Y, Karpel N 2006 IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 30 570
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Han P, Liu F, Yang K, Ma J, Li J, Shao X 2017 Appl. Opt. 56 6631
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Andreoli D, Volpe G, Popoff S, Katz O, Grésillon S, Gigan S 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 10347
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Tao H C, Lü J G, Liang J Q, Zhao B X, Chen Y P, Zheng K F, Zhao Y Z, Wang W B, Qin Y X, Liu G H, Sheng K Y 2023 Photonics 10 566
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Tyo J S 1998 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 15 359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Yang L, Liang J, Zhang W, Ju H, Ren L, Shao X 2019 Opt. Commun. 438 96
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Luo M R, Cui G, Rigg B 2001 Color Res. Appl. 26 340
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 5003
- PDF下载量: 309
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: