-
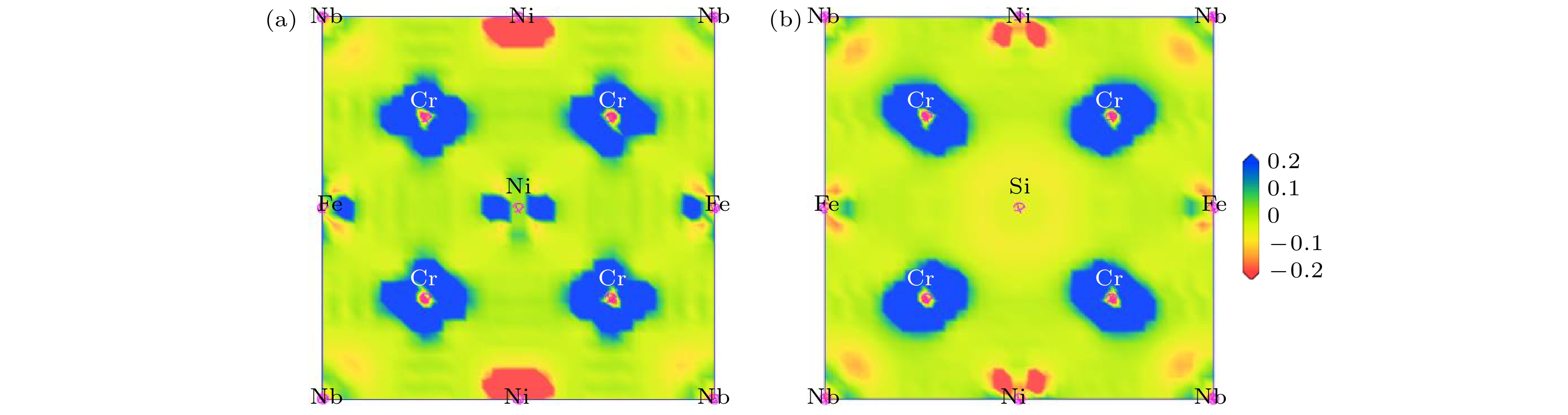
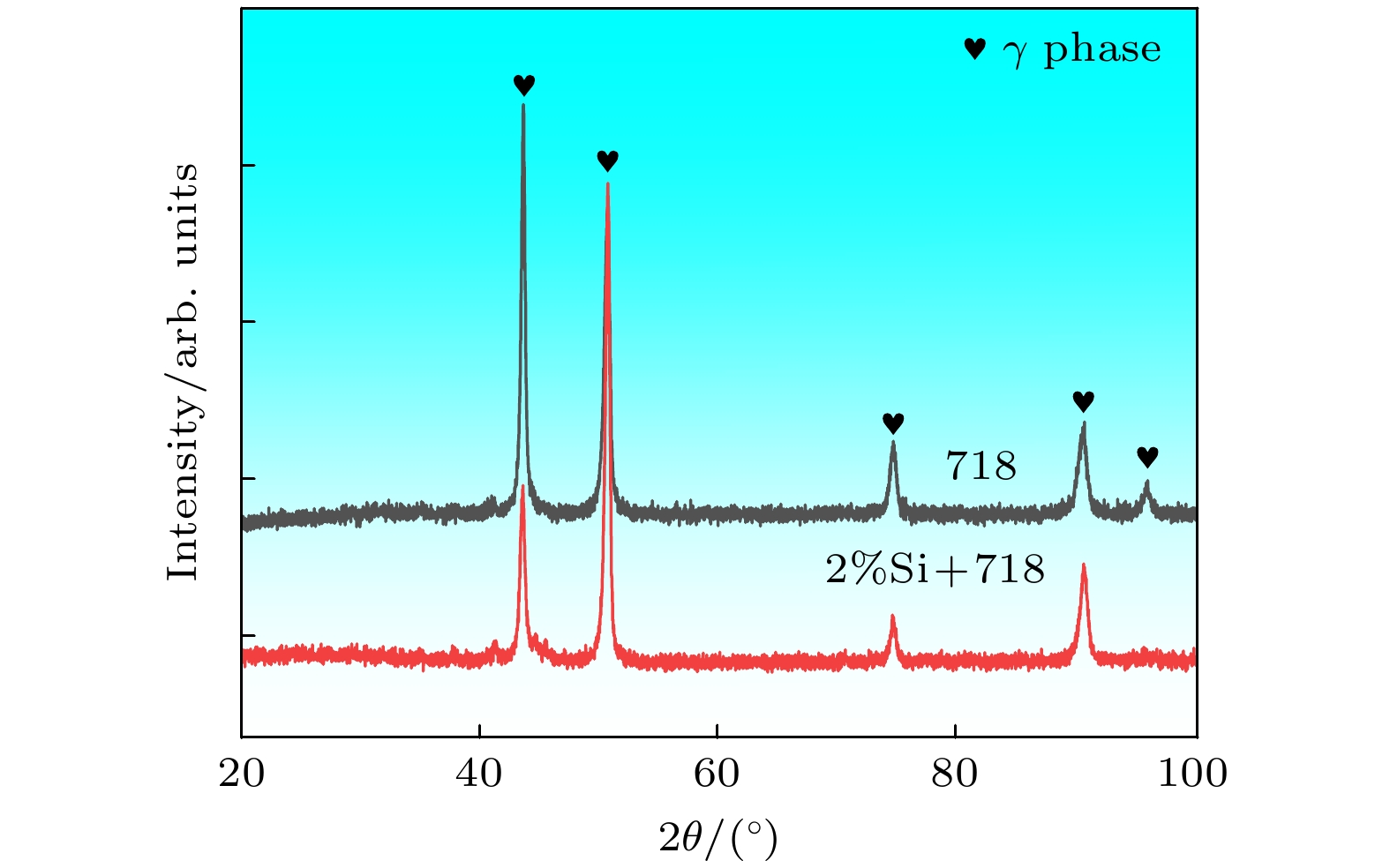
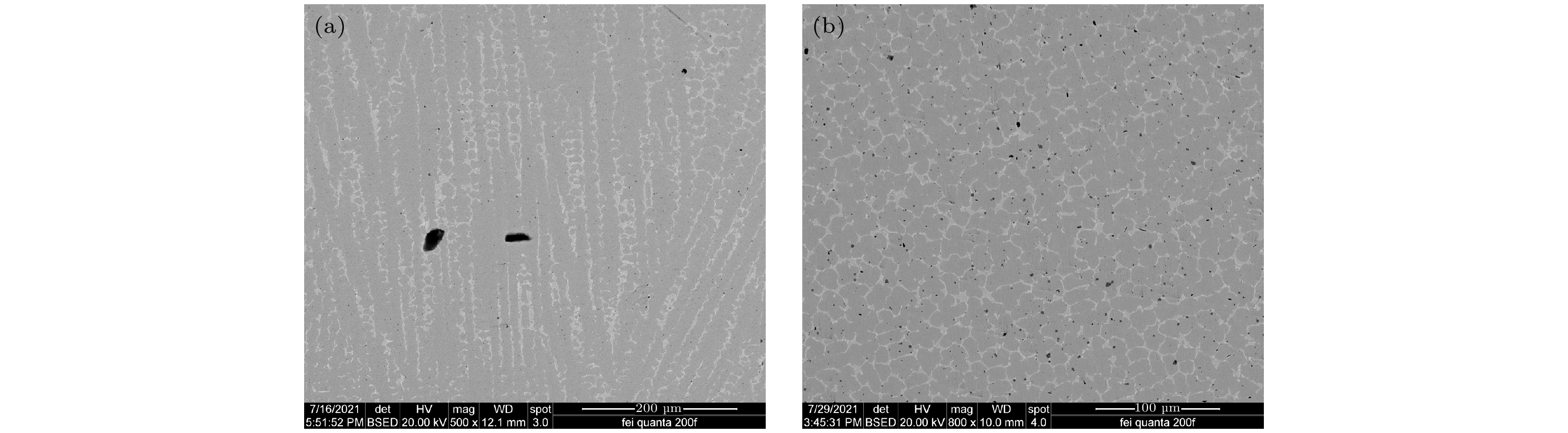
随着航空航天、能源化工等领域的快速发展, 人们对高温合金的性能提出了更高的期望. Inconel 718 (简称IN 718)是目前用量最大的镍基高温合金, 目前国内外关于Si对IN 718合金组织与性能影响的研究, 尤其是在微观尺度上的研究, 还存在大量空白. 本文从第一性原理计算出发研究了Si掺杂对IN 718合金中γ相的影响, 计算了Si掺杂前后γ相的晶格常数、总能量、缺陷形成能、形成热、结合能、态密度和差分电荷密度, 并进行了布居分析. 同时利用等离子熔覆的方法制备了IN 718涂层以及Si质量分数为2%的IN 718涂层, 并对其进行显微组织及相结构的分析. 计算结果表明, Si的掺杂改变了体系内原子的交互作用, 影响了原子之间的价电子数量、电荷密度分布及原子之间键合的强度, 从而扩大了γ相的晶胞体积, 同时降低了γ相的稳定性. 实验结果表明, Si掺杂会使得IN 718合金涂层组织发生由柱状晶向等轴晶的转变, 并降低IN 718合金中γ相的体积分数, 同时, Si掺杂会加剧合金组织内Nb和Cr元素的偏析.
-
关键词:
- Inconel 718合金 /
- 第一性原理 /
- γ相 /
- Si掺杂
Inconel 718 (IN 718) is the most widely used nickel-based high-temperature alloy today. It is widely adopted in important fields such as aerospace, energy and chemicals, and is also one of the few high-temperature alloys, of which some can be fabricated by using additive manufacturing. There is a lack of research on the effect of Si on the structure and properties of IN 718 alloy on a microscopic scale. In this paper, the effect of Si doping on the γ phase in IN 718 alloy is investigated by first-principles calculations through using the CASTEP package. The lattice constants, total energy, defect formation energy, formation enthalpy, cohesive energy, density of states, and electron density difference of the γ phase are calculated before and after Si doping, and population analysis is performed. The calculation of the lattice constant reveals that the doping of Si atoms expands the cell volume of the γ phase supercell, which contributes to a certain solution strengthening effect, and is conducive to the improvement of the hardness of the alloy. The energy and electronic structure calculations show that the Si atoms prefer to occupy the Ni atomic positions in the γ phase. The number of valence electrons between the atoms, the distribution of the charge density, and the strength of the bonds between the atoms also change with Si doping, thus modifying the interaction of the atoms within the γ phase, reducing the stability of the γ phase, and favouring the precipitation of the second phase. Besides, uniform and dense IN 718 coatings with low-coat Si doping are successfully fabricated by using plasma cladding. The experimental results demonstrate that Si doping has no significant effect on the type of matrix structure of IN 718 coatings, but causes a slight expansion of the lattice of the alloy, which is consistent with the calculation result. The addition of Si can result in a transformation of the alloy coating from columnar crystal to equiaxed crystal, refining the grain size of the alloy, while reducing the volume fraction of the γ phase and increasing the volume fraction of the second phase. Moreover, the addition of Si exacerbates the segregation of Nb and Cr elements in the IN 718 coatings.-
Keywords:
- Inconel 718 /
- first principles /
- γ phase /
- Si doping
[1] Pollock T M, Tin S 2006 J. Propuls. Power. 22 361
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Hao L Y, Wen X Z, Lei X W, Yao W J, Wang N 2022 J. Alloys Compd. 920 165996
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Pollock T M 2016 Nat. Mater. 15 809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Nnaji R N, Bodude M A, Osoba L O, Fayomi O S I, Ochulor F E 2019 Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 106 1149
[5] Hosseini E, Popovich V A 2019 Addit. Manuf. 30 100877
[6] Greene G A, Finfrock C C 2001 Oxid. Met. 55 505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Qiao Z, Li C, Zhang H, Liang H, Liu Y, Zhang Y 2020 Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 27 1123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Fu S H, Dong J X, Zhang M C, Xie X S 2009 Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 499 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 赵文超, 周杰, 彭文屹, 危翔, 邓晓华, 章爱生, 于思琪, 孙祖祥, 余飞翔, 高安澜 2022 表面技术 51 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao W C, Zhou J, Peng W Y, Wei X, Deng X H, Zhang A S, Yu S Q, Sun Z X, Yu F X, Gao A L 2022 Surf. Technol. 51 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 陆富刚 2019 硕士学位论文(北京: 北京交通大学)
Lu F G 2019 M. S. Dissertation (Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University
[11] Jia Q, Gu D 2014 Opt. Laser. Technol. 62 161
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tunthawiroon P, Li Y, Tang N, Koizumi Y, Chiba A 2015 Corros. Sci. 95 88
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhang Y L, Li J, Zhang Y Y, Kang D N 2020 J. Alloy. Compd. 827 154131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang A, Li Y, Fan C, Yang K, Li D, Zhao X, Shi C 1994 Scripta Metal. Mater. 31 1695
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 孙文儒, 郭守仁, 卢德忠, 胡壮麒 1996 航空材料学报 2 7
Sun W R, Guo S R, Lu D Z, Hu Z Q 1996 J. Aeronaut. Mater. 2 7
[16] Ma M, Han A, Zhang Z, Lian Y, Zhao C, Zhang J 2021 Corros. Sci. 185 109417
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Huang D, Lu J, Zhuang Y, Tian C, Li Y 2019 Corros. Sci. 158 108088
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 李亚敏, 张瑶瑶, 赵旺, 周生睿, 刘洪军 2022 金属学报 58 241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y M, Zhang Y Y, Zhao W, Zhou S R, Liu H J 2022 Acta. Metall. Sin. 58 241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 张聪 2021 硕士学位论文(昆明: 昆明理工大学)
Zhang C 2021 M. S. Thesis (Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology
[20] Ghosh G, Asta M 2005 Acta. Mater. 53 3225
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Van de Walle A, Ceder G 2002 Rev. Mod. Phys. 74 11
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 张旭昀, 郑冰洁, 郭斌, 吴戆, 王文泉, 王勇 2017 材料导报 31 146
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X Y, Zheng B J, Guo B, Wu Z, Wang W Q, Wang Y 2017 Mater. Rev. 31 146
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
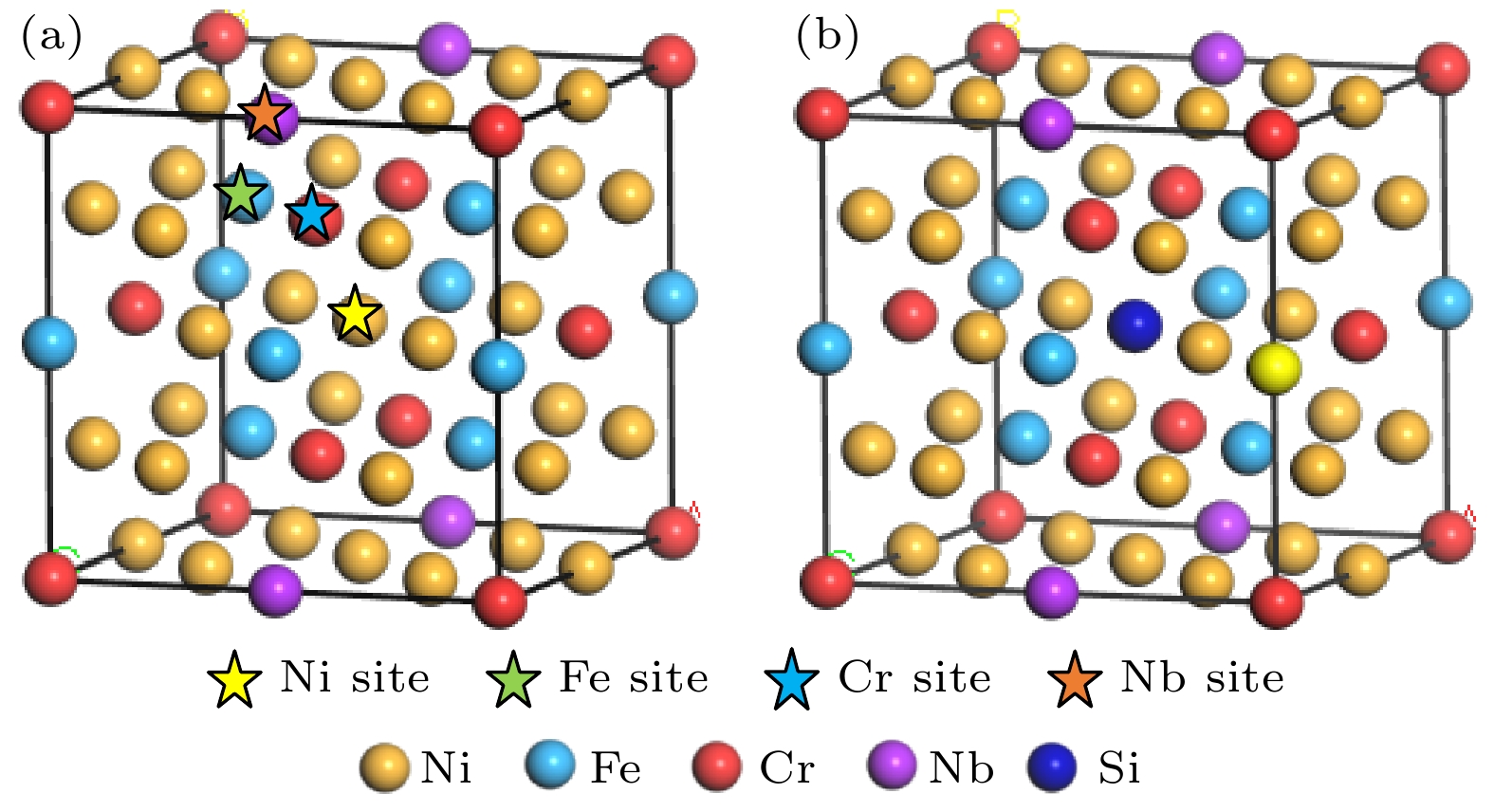
表 1 超晶胞模型的平衡晶格常数及晶胞体积
Table 1. Equilibrium lattice constant and unit cell volume of supercell model.
System Site a/nm b/nm c/nm α/(°) β/(°) γ/(°) V/nm3 Ni19Fe6Cr6Nb — 0.71345 0.72715 0.70223 90.000 90.000 90.000 0.3643 Ni18Fe6Cr6NbSi Ni Site 0.71915 0.71859 0.71627 90.000 90.000 90.000 0.3701 Ni19Fe5Cr6NbSi Fe Site 0.73543 0.73499 0.68475 90.000 90.000 90.314 0.3702 Ni19Fe6Cr5NbSi Cr Site 0.70478 0.73256 0.70599 89.592 89.991 90.003 0.3645 Ni19Fe6Cr6Si Nb Site 6.99468 7.26214 7.01313 90.000 90.000 90.001 0.3562 表 2 体系的总能量、缺陷形成能、形成热与结合能
Table 2. Total energy, defect formation energy, formation enthalpy and cohesive energy of systems.
System Site Ef/eV H/(eV·atom–1) E/(eV·atom–1) Etotal/eV Ni19Fe6Cr6Nb — — –0.213127 –2.929875 –47447.72376 Ni18Fe6Cr6NbSi Ni Site –1.339744 –0.256865 –2.915375 –46241.16350 Ni19Fe5Cr6NbSi Fe Site –1.322440 –0.255194 –2.880194 –46754.74620 Ni19Fe6Cr5NbSi Cr Site –1.226650 –0.252200 –2.892825 –45218.05041 Ni19Fe6Cr6Si Nb Site –1.112683 –0.248639 –2.948639 –45961.73644 表 3 Si掺杂前后体系的原子布居数
Table 3. Atomic populations of systems before and after Si doping.
System Species s p d f Total Charge Ni19Fe6Cr6Nb Ni 0.48 0.83 8.65 0 9.96 0.031 Cr 2.58 6.77 4.96 0 14.32 –0.31 Fe 0.50 0.70 6.72 0 7.92 0.08 Nb 2.26 6.02 3.93 0 12.21 0.79 Ni18Fe6Cr6NbSi Ni 0.49 0.83 8.65 0 9.97 0.02 Cr 2.57 6.77 5.00 0 14.33 –0.33 Fe 0.49 0.67 6.74 0 7.90 0.11 Nb 2.26 6.04 3.94 0 12.24 0.76 Si 1.21 2.61 0.00 0 3.83 0.17 表 4 Si掺杂前后体系键的布居数
Table 4. Overlapping populations of systems before and after Si doping.
System Bond Population Length/nm Ni19Fe6Cr6Nb Fe—Ni 0.06 0.360847 Cr—Fe –0.07 0.350106 Cr—Ni –0.03 0.359244 Ni—Ni –0.03 0.375966 Fe—Nb –0.10 0.434654 Ni—Nb –0.13 0.364001 Cr—Nb –0.46 0.340342 Cr—Cr –0.16 0.419928 Fe—Fe –0.07 0.427230 Ni18Fe6Cr6NbSi Fe—Ni 0.06 0.363710 Cr—Fe –0.12 0.351112 Cr—Ni –0.04 0.363071 Ni—Ni 0.03 0.373913 Fe—Nb –0.13 0.434897 Ni—Nb –0.13 0.356309 Cr—Nb –0.40 0.338983 Cr—Cr –0.33 0.422106 Fe—Fe –0.06 0.418588 Ni—Si 0.02 0.386153 表 5 测量与折算的平衡晶格常数及晶胞体积
Table 5. Measured and converted equilibrium lattice constant and unit cell volume.
System Measurement results Converted results α/(°) β/(°) γ/(°) a/nm b/nm c/nm V/nm3 a/nm b/nm c/nm V/nm3 IN 718 0.36028 0.36021 0.35848 0.0465 0.72056 0.72042 0.71696 0.3721 90.000 90.000 90.000 2Si-IN 718 0.35970 0.35960 0.36114 0.0467 0.71940 0.71920 0.72228 0.3737 90.000 90.000 90.000 表 6 Si掺杂前后合金涂层EDS结果(原子百分数)
Table 6. EDS results (atomic percent) of coating before and after Si doping.
Coating Area Ni Fe Cr Nb Mo Ti Al Si IN 718 Matrix 40.85 38.46 17.42 0.53 1.14 — 1.28 0.32 Second phase 36.08 28.42 14.33 6.89 2.89 1.46 0.56 9.33 2Si-IN 718 Matrix 38.95 40.42 16.06 0.43 1.13 0.69 0.99 1.33 Second phase 34.1 23.6 10.4 12.8 2.73 1.54 0.53 14.3 -
[1] Pollock T M, Tin S 2006 J. Propuls. Power. 22 361
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Hao L Y, Wen X Z, Lei X W, Yao W J, Wang N 2022 J. Alloys Compd. 920 165996
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Pollock T M 2016 Nat. Mater. 15 809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Nnaji R N, Bodude M A, Osoba L O, Fayomi O S I, Ochulor F E 2019 Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 106 1149
[5] Hosseini E, Popovich V A 2019 Addit. Manuf. 30 100877
[6] Greene G A, Finfrock C C 2001 Oxid. Met. 55 505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Qiao Z, Li C, Zhang H, Liang H, Liu Y, Zhang Y 2020 Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 27 1123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Fu S H, Dong J X, Zhang M C, Xie X S 2009 Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 499 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 赵文超, 周杰, 彭文屹, 危翔, 邓晓华, 章爱生, 于思琪, 孙祖祥, 余飞翔, 高安澜 2022 表面技术 51 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao W C, Zhou J, Peng W Y, Wei X, Deng X H, Zhang A S, Yu S Q, Sun Z X, Yu F X, Gao A L 2022 Surf. Technol. 51 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 陆富刚 2019 硕士学位论文(北京: 北京交通大学)
Lu F G 2019 M. S. Dissertation (Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University
[11] Jia Q, Gu D 2014 Opt. Laser. Technol. 62 161
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tunthawiroon P, Li Y, Tang N, Koizumi Y, Chiba A 2015 Corros. Sci. 95 88
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhang Y L, Li J, Zhang Y Y, Kang D N 2020 J. Alloy. Compd. 827 154131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang A, Li Y, Fan C, Yang K, Li D, Zhao X, Shi C 1994 Scripta Metal. Mater. 31 1695
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 孙文儒, 郭守仁, 卢德忠, 胡壮麒 1996 航空材料学报 2 7
Sun W R, Guo S R, Lu D Z, Hu Z Q 1996 J. Aeronaut. Mater. 2 7
[16] Ma M, Han A, Zhang Z, Lian Y, Zhao C, Zhang J 2021 Corros. Sci. 185 109417
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Huang D, Lu J, Zhuang Y, Tian C, Li Y 2019 Corros. Sci. 158 108088
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 李亚敏, 张瑶瑶, 赵旺, 周生睿, 刘洪军 2022 金属学报 58 241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y M, Zhang Y Y, Zhao W, Zhou S R, Liu H J 2022 Acta. Metall. Sin. 58 241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 张聪 2021 硕士学位论文(昆明: 昆明理工大学)
Zhang C 2021 M. S. Thesis (Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology
[20] Ghosh G, Asta M 2005 Acta. Mater. 53 3225
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Van de Walle A, Ceder G 2002 Rev. Mod. Phys. 74 11
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 张旭昀, 郑冰洁, 郭斌, 吴戆, 王文泉, 王勇 2017 材料导报 31 146
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X Y, Zheng B J, Guo B, Wu Z, Wang W Q, Wang Y 2017 Mater. Rev. 31 146
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 5280
- PDF下载量: 65
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: