-
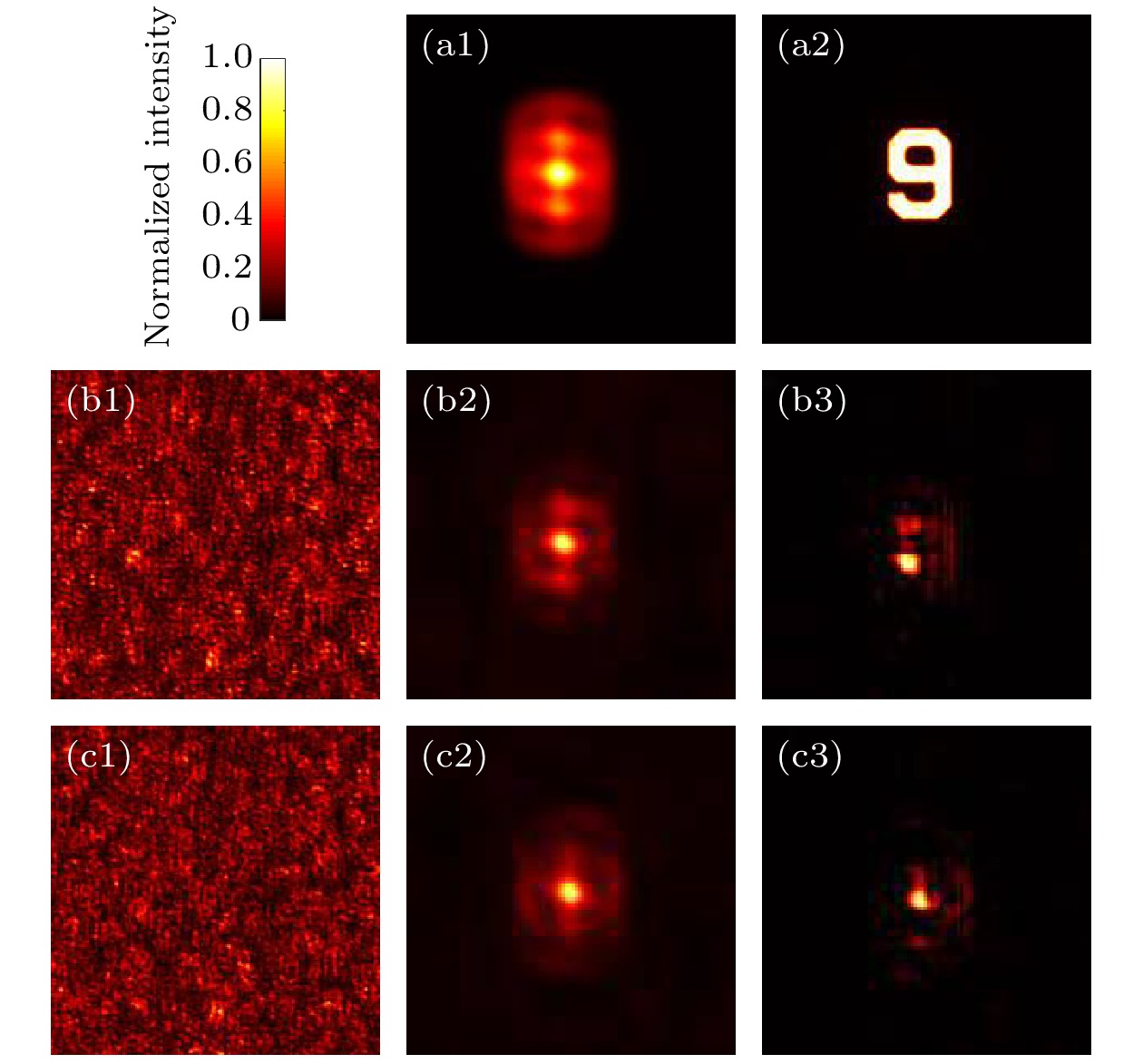
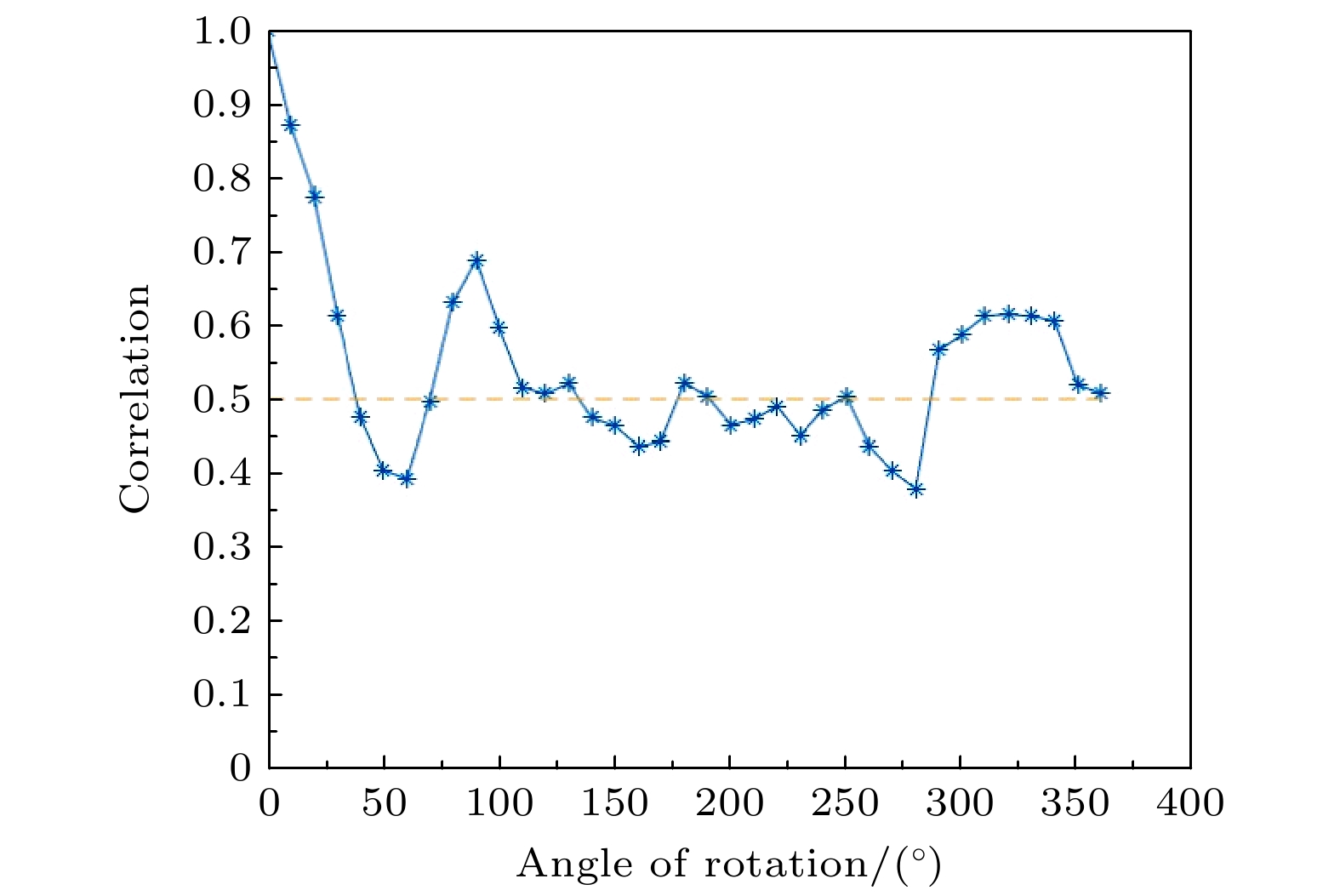
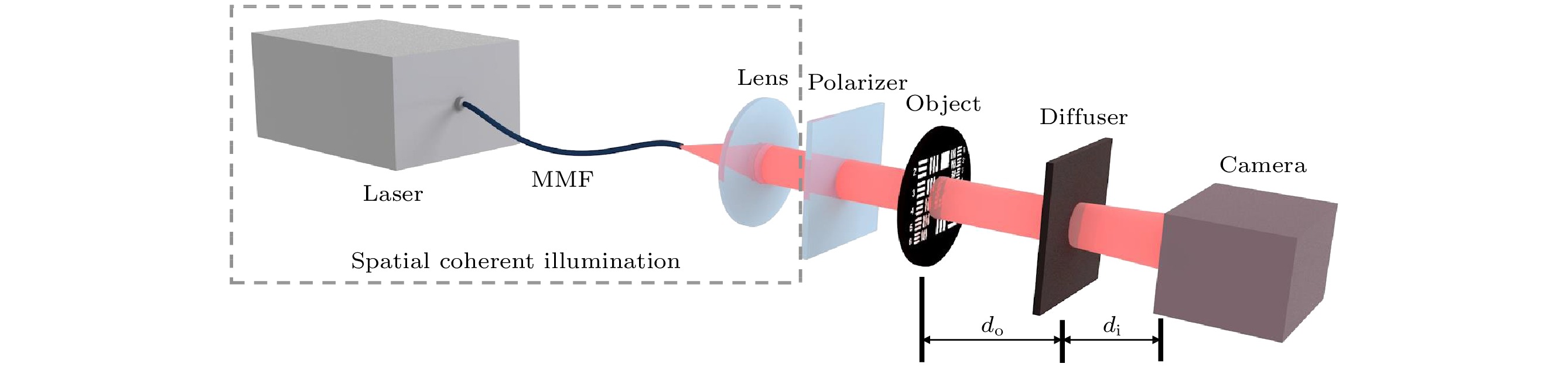
散斑相关成像因为记忆效应的要求, 通常需要空间非相干光源, 这使得成像装置变得复杂且光源利用率低, 同时也限制了这种方法在空间相干光源照射情况下的应用. 本文提出了一种基于空间相干光照明情况下, 通过复用不同偏振方向散斑图案实现的散斑相关成像新方法, 简称偏振复用散射成像. 新方法通过旋转放置在照射光路中的偏振器获得不同偏振方向的散斑图案, 再将这些图案叠加并平均, 最后使用相位恢复算法就可以重建物体图像. 与常规散斑相关成像技术的比较, 本文提出的方法降低了对光源的要求, 提高了光源的利用率, 使得装置更加简单紧凑. 实验结果表明这种方法的可行性, 并具有较强的环境适应性, 从而可拓展散斑相关成像方法的应用范围.Imaging through scattering media, such as clouds, biological tissues, and seawater, has broad application prospects in transportation, medical diagnosis, and information technology. Researchers have proposed various techniques to obtain images from scattered light passing through the scattering media, among which speckle correlation imaging has developed rapidly. Speckle correlation imaging requires non-coherent light sources due to the requirement of memory effect. This requirement makes the imaging device complex, and the light source utilization rate low. Additionally, this method is limited in its application under the illumination of spatially coherent light sources. This paper proposes a new method of speckle correlation imaging based on the illumination of spatially coherent light, which is achieved by multiplexing different polarization direction speckle patterns, called polarization multiplexing scattering imaging. To achieve the decoherence of the light source, previous approaches have used a rotating scattering medium to generate time-varying speckle patterns that are integrated over the shutter time of the camera to eliminate coherent noise, or multiplexed wavelength-dependent speckle multiplexing to achieve this. This paper uses spatially incoherent light sources to obtain different polarization direction speckle patterns by rotating polarizers placed in the illumination path. These patterns are superimposed and averaged, and phase recovery algorithm is used to reconstruct the object image. This experiment uses Ping-Pang (PP) algorithm with fusion error reduction and hybrid input-output algorithm to reconstruct targets quickly and with high quality. The comparison of the reconstruction results of different numbers of reused speckle patterns demonstrates that using more speckle patterns can achieve better image quality. Compared with conventional speckle correlation imaging technology, the proposed method reduces the requirements of light sources, improves the utilization rate of light sources, and makes the device simpler and more compact. Experimental results show that this method is feasible and has strong environmental adaptability, which can expand the application scope of speckle correlation imaging methods.
-
Keywords:
- scattering imaging /
- polarization /
- memory effect /
- autocorrelation
[1] Vellekoop I M, Mosk A P 2007 Opt. Lett. 32 2309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Katz O, Small E, Silberberg Y 2012 Nat. Photonics 6 549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Mosk A P, Lagendijk A, Lerosey G, Fink M 2012 Nat. Photonics 6 283
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhuang H C, He H X, Xie X S, Zhou J Y 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 32696
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Edrei E, Scarcelli G 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 33558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Xie X S, Zhuang H C, He H X, Xu X Q, Liang H W, Liu Y K, Zhou J Y 2018 Sci. Rep. 8 4585
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Popoff S M, Lerosey G, Carminati R, Fink M, Boccara A C, Gigan S 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 100601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Popoff S, Lerosey G, Fink M, Boccara A C, Gigan S 2010 Nat. Commun. 1 81
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hofer M, Brasselet S 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 2137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Freund I, Rosenbluh M, Feng S 1988 Phys. Rev. Lett. 61 2328
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Katz O, Heidmann P, Fink M, Gigan S 2014 Nat. Photonics 8 784
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Li X H, Greenberg J A, Gehm M E 2019 Optica 6 864
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Song P M, Jiang S W, Zhang H, Bian Z C, Guo C F, Hoshino K, Zheng G A 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 3645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Horisaki R, Okamoto Y, Tanida J 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 4032
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Yang W Q, Li G W, Situ G H 2018 Sci. Rep. 8 9614
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ma R, Wang Z, Zhang H H, Zhang W L, Rao Y J 2020 Opt. Lett. 45 4352
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Ma R, Wang Z, Wang W Y, Zhang Y, Liu J, Zhang W L, Gomes A S L, Fan D Y 2021 Opt. Lasers Eng. 141 106567
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 孙雪莹, 刘飞, 段景博, 牛耕田, 邵晓鹏 2021 70 224203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun X Y, Liu F, Duan J B, Niu G T, Shao X P 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 224203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Goodman J W 2006 Speckle Phenomena in Optics: Theory and Applications (Roberts and Company Publishers) pp66–77
[20] Bertolotti J, Van Putten E G, Blum C, Lagendijk A, Vos W L, Mosk A P 2012 Nature 491 232
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Fienup J R 1982 Appl. Optics 21 2758
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Hofer M, Soeller C, Brasselet S, Bertolotti J 2018 Opt. Express 26 9866
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 肖晓, 杜舒曼, 赵富, 王晶, 刘军, 李儒新 2019 68 034201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiao X, Du S M, Zhao F, Wang J, Liu J, Li R X 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 034201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Edrei E, Scarcelli G 2016 Optica 3 71
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
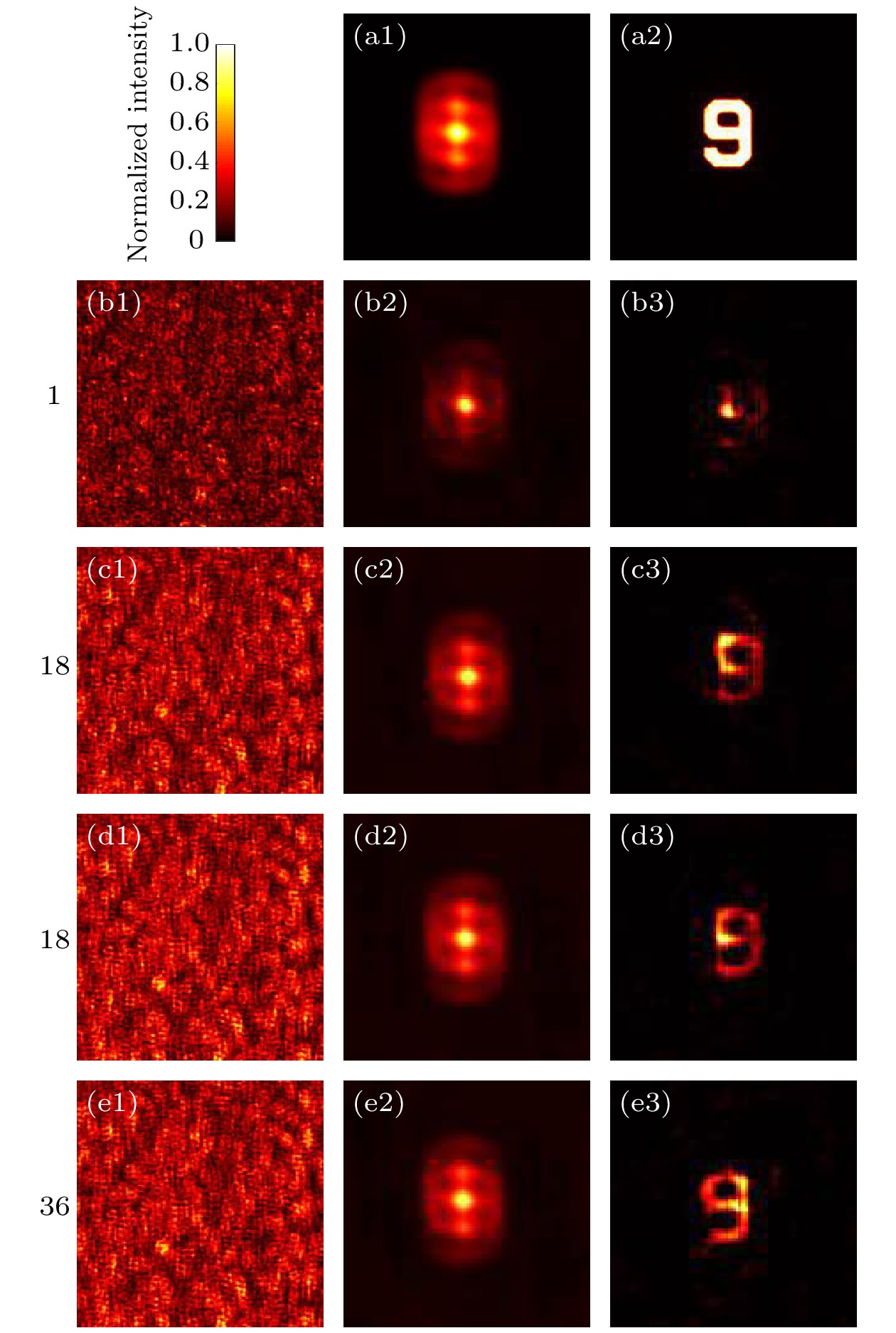
图 4 偏振复用散射相关成像 (a1), (b2), (c2), (d2), (e2)自相关; (a2)物体; (b1), (c1), (d1), (e1)散斑图案; (b3), (c3), (d3), (e3)重建图案
Fig. 4. Polarization multiplexed speckle correlation imaging: (a1), (b2), (c2), (d2), (e2) The autocorrelation; (a2) the object; (b1), (c1), (d1), (e1) speckle pattern; (b3), (c3), (d3), (e3) reconstruction pattern.
-
[1] Vellekoop I M, Mosk A P 2007 Opt. Lett. 32 2309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Katz O, Small E, Silberberg Y 2012 Nat. Photonics 6 549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Mosk A P, Lagendijk A, Lerosey G, Fink M 2012 Nat. Photonics 6 283
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhuang H C, He H X, Xie X S, Zhou J Y 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 32696
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Edrei E, Scarcelli G 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 33558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Xie X S, Zhuang H C, He H X, Xu X Q, Liang H W, Liu Y K, Zhou J Y 2018 Sci. Rep. 8 4585
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Popoff S M, Lerosey G, Carminati R, Fink M, Boccara A C, Gigan S 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 100601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Popoff S, Lerosey G, Fink M, Boccara A C, Gigan S 2010 Nat. Commun. 1 81
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hofer M, Brasselet S 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 2137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Freund I, Rosenbluh M, Feng S 1988 Phys. Rev. Lett. 61 2328
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Katz O, Heidmann P, Fink M, Gigan S 2014 Nat. Photonics 8 784
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Li X H, Greenberg J A, Gehm M E 2019 Optica 6 864
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Song P M, Jiang S W, Zhang H, Bian Z C, Guo C F, Hoshino K, Zheng G A 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 3645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Horisaki R, Okamoto Y, Tanida J 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 4032
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Yang W Q, Li G W, Situ G H 2018 Sci. Rep. 8 9614
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ma R, Wang Z, Zhang H H, Zhang W L, Rao Y J 2020 Opt. Lett. 45 4352
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Ma R, Wang Z, Wang W Y, Zhang Y, Liu J, Zhang W L, Gomes A S L, Fan D Y 2021 Opt. Lasers Eng. 141 106567
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 孙雪莹, 刘飞, 段景博, 牛耕田, 邵晓鹏 2021 70 224203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun X Y, Liu F, Duan J B, Niu G T, Shao X P 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 224203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Goodman J W 2006 Speckle Phenomena in Optics: Theory and Applications (Roberts and Company Publishers) pp66–77
[20] Bertolotti J, Van Putten E G, Blum C, Lagendijk A, Vos W L, Mosk A P 2012 Nature 491 232
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Fienup J R 1982 Appl. Optics 21 2758
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Hofer M, Soeller C, Brasselet S, Bertolotti J 2018 Opt. Express 26 9866
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 肖晓, 杜舒曼, 赵富, 王晶, 刘军, 李儒新 2019 68 034201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiao X, Du S M, Zhao F, Wang J, Liu J, Li R X 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 034201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Edrei E, Scarcelli G 2016 Optica 3 71
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 5571
- PDF下载量: 119
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: