-
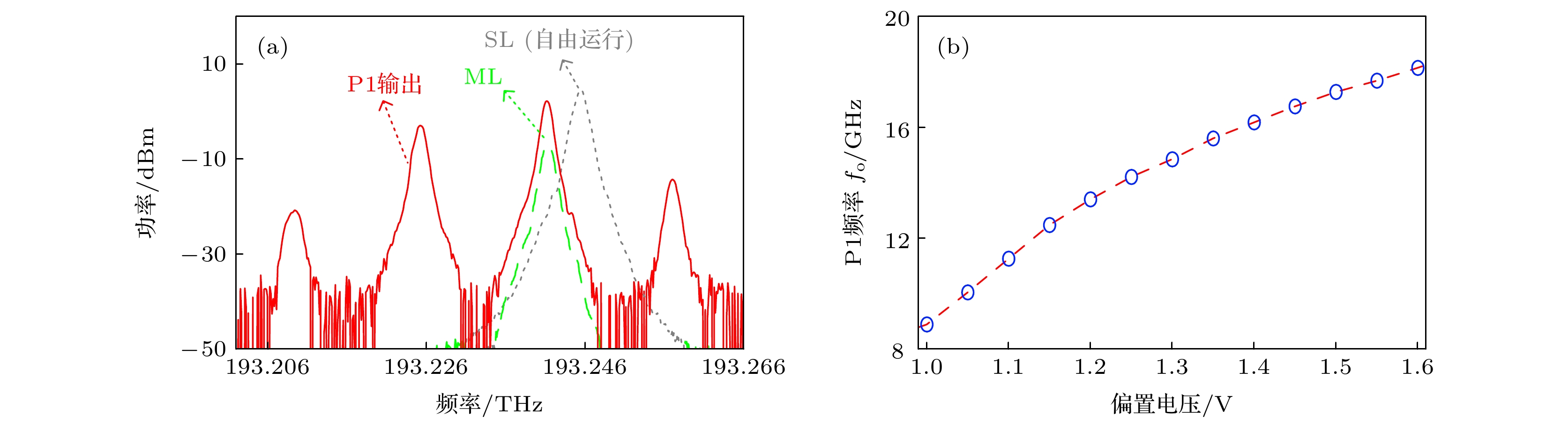
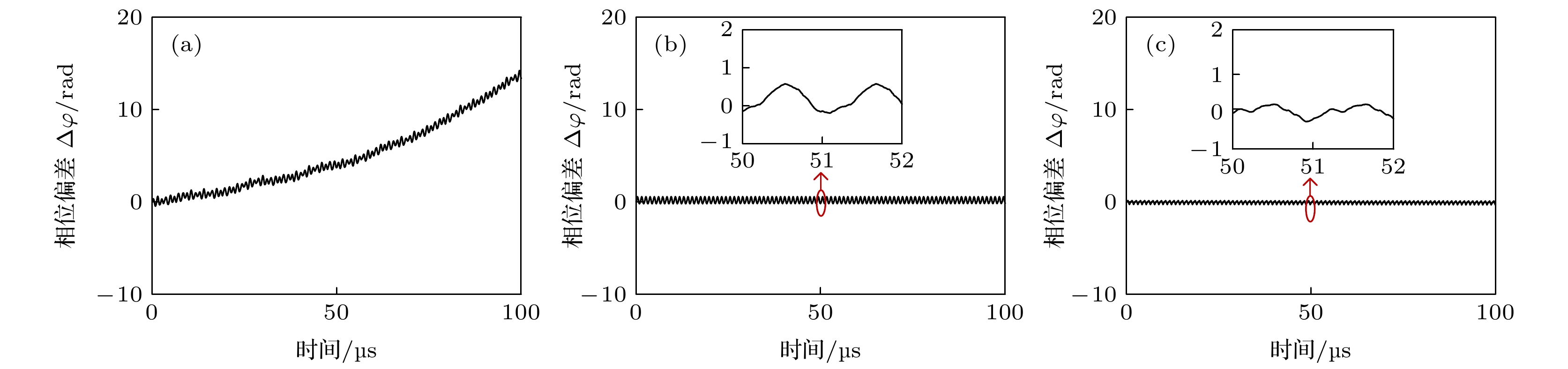
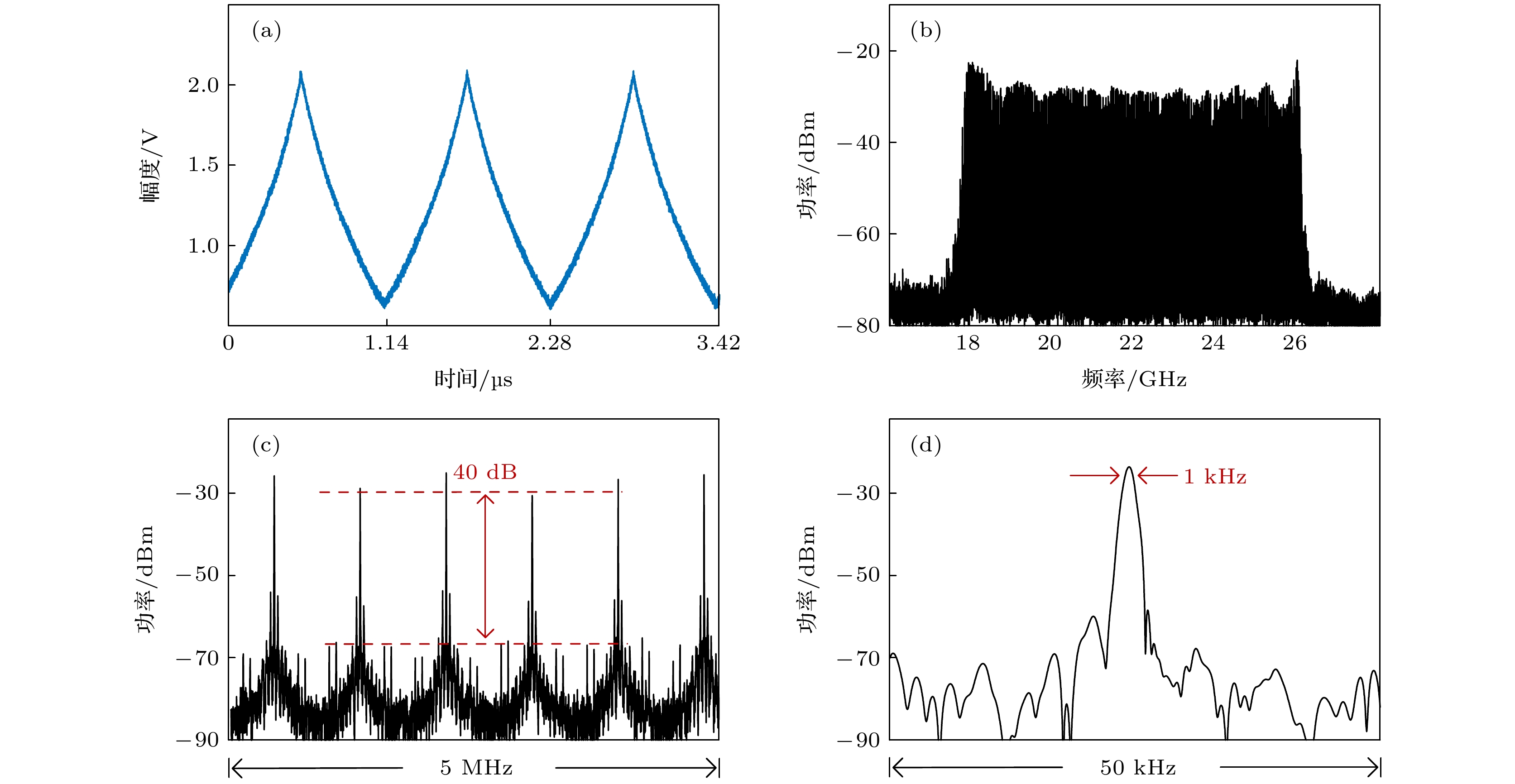
提出了一种基于双路光电反馈下, 光注入半导体激光器的高性能微波线性调频信号产生方案, 并进行了实验验证. 在合适的注入参数下, 光注入半导体激光器可工作于单周期振荡态, 生成频率由注入强度和失谐频率决定的可调谐微波信号. 通过加载波形为类三角波的电压信号控制注入强度, 光注入半导体激光器可生成宽带微波线性调频信号. 进一步通过引入延时匹配的双路光电反馈环路, 来提升光注入半导体激光器生成线性调频信号的质量: 分别基于傅里叶域模式锁定原理和自注入锁定技术, 引入短环光电反馈和长环光电反馈, 以同时实现线性调频信号的梳齿信噪比提升和线宽窄化. 在验证实验中, 本方案产生了带宽为8 GHz (18—26 GHz)的线性调频信号, 其梳齿信噪比达到40 dB, 梳齿线宽为1 kHz. 实验结果证明了本方案能够生成同时具有大带宽、高梳齿信噪比、窄线宽且相位关系稳定的高性能微波线性调频信号.
Linear frequency-modulated (LFM) waveforms have numerous applications in high-resolution radar detection, high-speed wireless communication, and high precision measurement. The generation of LFM microwave signals based on conventional electronic technologies is limited in their center frequency and bandwidth, which are usually less than a few gigahertz. Fortunately, the inherently large bandwidth offered by photonic technology is very hopeful of breaking through the electronic bottleneck. A variety of photonics-based approaches to generating the LFM waveforms have been reported, including the frequency-to-time mapping method and the external modulation method. However, these solutions suffer poor tunability or expensive RF sources. In recent years, the LFM waveform generation based on optically injected semiconductor lasers (OISLs) has attracted increasing attention. By introducing a low-speed electrical signal to control the period-one (P1) dynamics of an OISL, the LFM waveforms with a large bandwidth are generated. Nonetheless, the generated microwave signal has poor spectral purity, which restricts its many practical applications. In this work, a high-performance microwave LFM waveform generation scheme based on an OISL with dual-loop optoelectronic feedback is proposed and demonstrated experimentally. In this scheme, the optical injection strength of an OISL is controlled first by a triangular-like voltage signal to generate LFM waveforms with a large bandwidth. Then, the quality of the generated LFM signal is comprehensively improved by introducing a delay-matched dual-loop optoelectronic feedback structure. Based on the Fourier domain mode locking principle (FDML) and the self-injection locking technique, both a short-delay optoelectronic feedback loop and a long-delay optoelectronic feedback loop are introduced to simultaneously improve the spectral purity and phase stability of the generated LFM signals. In the proof-of-concept experiment, by analyzing the spectral quality and phase deviation of the generated LFM signal, a comb contrast of 40 dB, a comb linewidth of 1 kHz, and a phase deviation ∆φ of less than π/3 are simultaneously obtained. In addition, the parameters such as bandwidth and center frequency of the generated LFM signal generated can be flexibly tuned, and an LFM signal with a large bandwidth up to 8 GHz (18–26 GHz) is generated in the experiment. The proposed scheme features a simple and compact structure, high spectral quality and flexible tuning, thus may find applications in broadband radar and high-speed communication systems. -
Keywords:
- semiconductor lasers /
- optical injection /
- linear frequency-modulated signals /
- optoelectronic feedback
[1] 潘时龙, 张亚梅 2017 科技导报 35 36
Pan S L, Zhang Y M 2017 Sci. Technol. Rev. 35 36
[2] 曹继明, 崇毓华, 梅理, 朱宇鹏, 段宗明 2021 电子科技 34 36
Cao J M, Chong Y H, Mei L, Zhu Y P, Duan Z M 2021 Electron. Sci. Technol. 34 36
[3] 李刚 2019 电子技术与软件工程 15 60
Li G 2019 Electron. Technol. Software Eng. 15 60
[4] McKinney J D 2014 Nature 507 310
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Pan S L, Zhang Y M 2020 J. Lightwave Technol. 38 5450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhang F Z, Guo Q S, Pan S L 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 13848
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 王贝贝, 王志鹏 2021 电视技术 45 90
Wang B B, Wang Z P 2021 Video Eng. 45 90
[8] Zhang H, Zou W W, Chen J P 2015 Opt. Lett. 40 1085
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Sun Y, Wang D Y, Deng C Y, Lu M J, Huang L, Hu G H, Yun B F, Cui Y P 2022 Opt. Lett. 47 1077
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Li R M, Li W Z, Ding M L, Wen Z L, Li Y L, Zhou L J, Yu S S, Xing T H, Gao B W, Luan Y C, Zhu Y T, Guo P, Tian Y, Liang X D 2017 Opt. Express 25 14334
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Zhu D, Yao J P 2015 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 27 1410
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhang Y M, Ye X W, Guo Q S, Zhang F Z, Pan S L 2017 J. Lightwave Technol. 35 1821
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li W Z, Yao J P 2014 J. Lightwave Technol. 32 3573
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhou P, Li N Q, Pan S L 2022 Photonics 9 227
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhou P, Zhang F Z, Guo Q S, Pan S L 2016 Opt. Express 24 18460
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Usechak N G, Suelzer J S, Haefner J W 2017 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 29 1132
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zhou P, Zhang R H, Li K X, Jiang Z D, Mu P H, Bao H L, Li N Q 2020 Opt. Express 28 32647
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Tseng C H, Hung Y H, Hwang S K 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 3334
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhou P, Chen H, Li N Q, Zhang R H, Pan S L 2020 Opt. Lett. 45 1342
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhuang J P, Li X Z, Li S S, Chan S C 2016 Opt. Lett. 41 5764
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhou P, Zhang F Z, Pan S L 2018 J. Lightwave Technol. 36 3726
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Lin X D, Xia G Q, Shang Z, Deng T, Tang X, Fan L, Gao Z Y, Wu Z M 2019 Opt. Express. 27 1217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chan S C, Hwang S K, Liu J M 2006 Opt. Lett. 31 2254
[24] Hao T F, Cen Q Z, Dai Y T, Tang J, Li W, Yao J P, Zhu N H, Li M 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 1839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
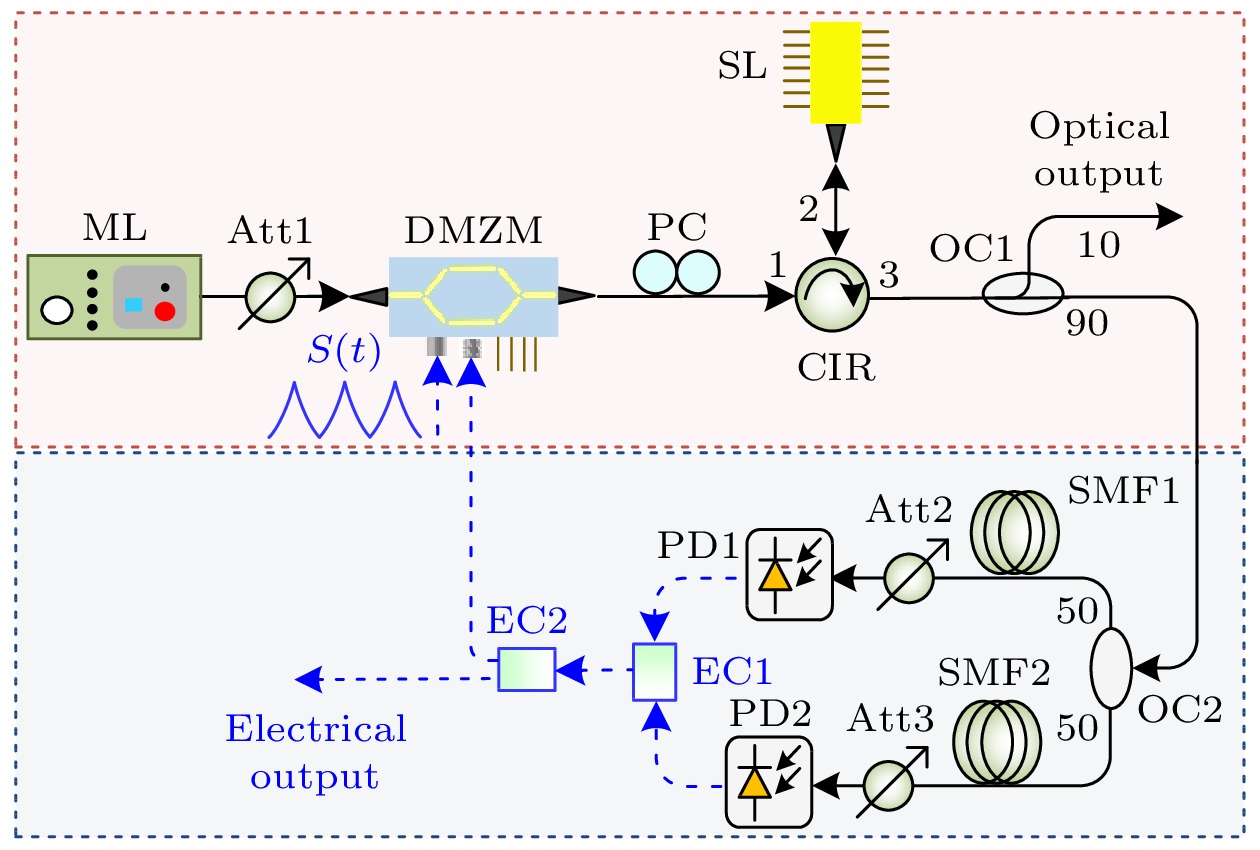
图 1 实验装置示意图(ML, 主激光器; SL, 从激光器; Att, 光衰减器; PC, 偏振控制器; DMZM, 双驱动马赫-曾德尔调制器; S(t), 控制信号; CIR, 光环行器; OC, 光耦合器; SMF, 单模光纤; PD, 光电探测器; EC, 电耦合器)
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of the experimental setup. ML, master laser; SL, slave laser; Att, optical attenuator; PC, polarization controller; DMZM, dual-drive Mach-Zehnder modulator; S(t), control signal; CIR, optical circulator; OC, optical coupler; SMF, single-mode fiber; PD, photodetector; EC, electrical coupler.
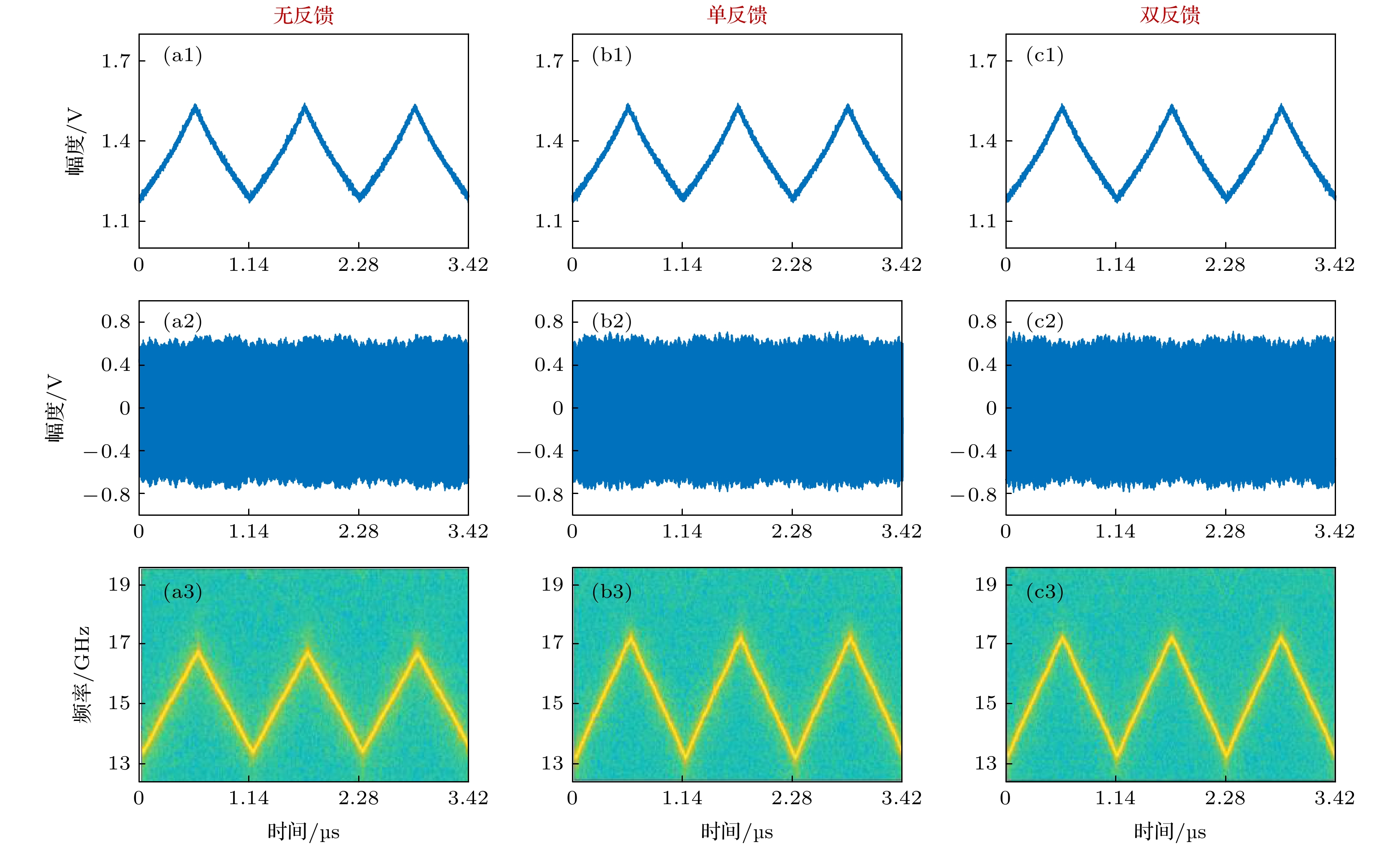
图 3 所产生线性调频信号的结果(控制信号S(t)(第一行); 时域波形(第二行); 瞬时频率(第三行)) (a) 无反馈情形; (b) 单反馈情形; (c) 双反馈情形
Fig. 3. Results of the generated LFM microwave signals (Control signals S(t) (the first row); temporal waveforms (the second row); instantaneous frequencies (the third row)): (a) Without feedback; (b) single-loop feedback; (c) dual-loop feedback.
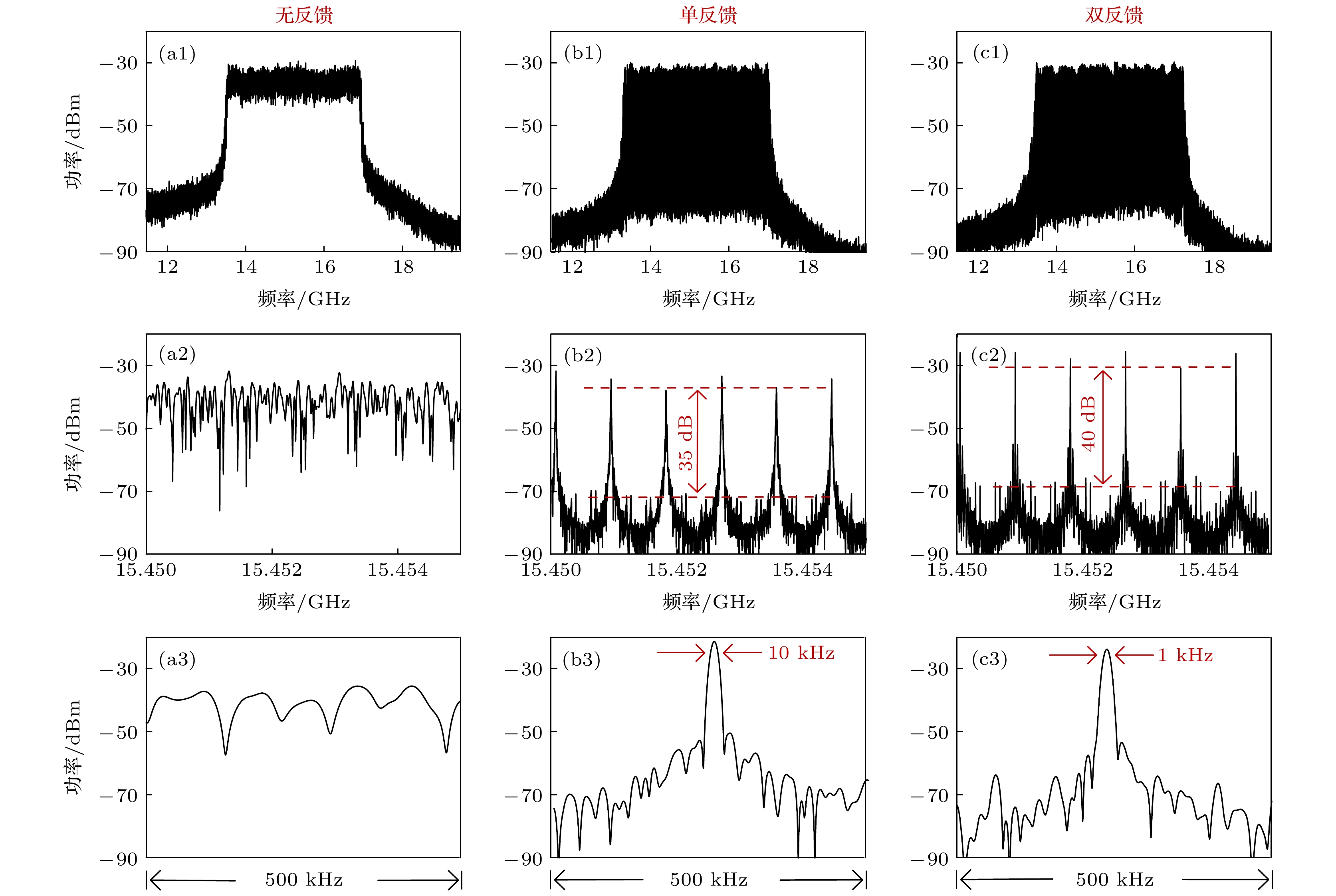
图 4 线性调频信号的频谱图(频谱图(第一行); 细节频谱图(第二、三行)) (a) 无反馈情形; (b) 单反馈情形, 延时τu = 1.14 μs; (c) 双反馈情形, 延时(τu, τd) = (1.14 μs, 25.08 μs)
Fig. 4. Electrical spectra of the generated LFM microwave signals (Electrical spectra (the first row); the zoomed-in views of the electrical spectra (the second and third row)): (a) Without feedback; (b) single-loop feedback with τu = 1.14 μs; (c) dual-loop feedback with (τu, τd) = (1.14 μs, 25.08 μs).
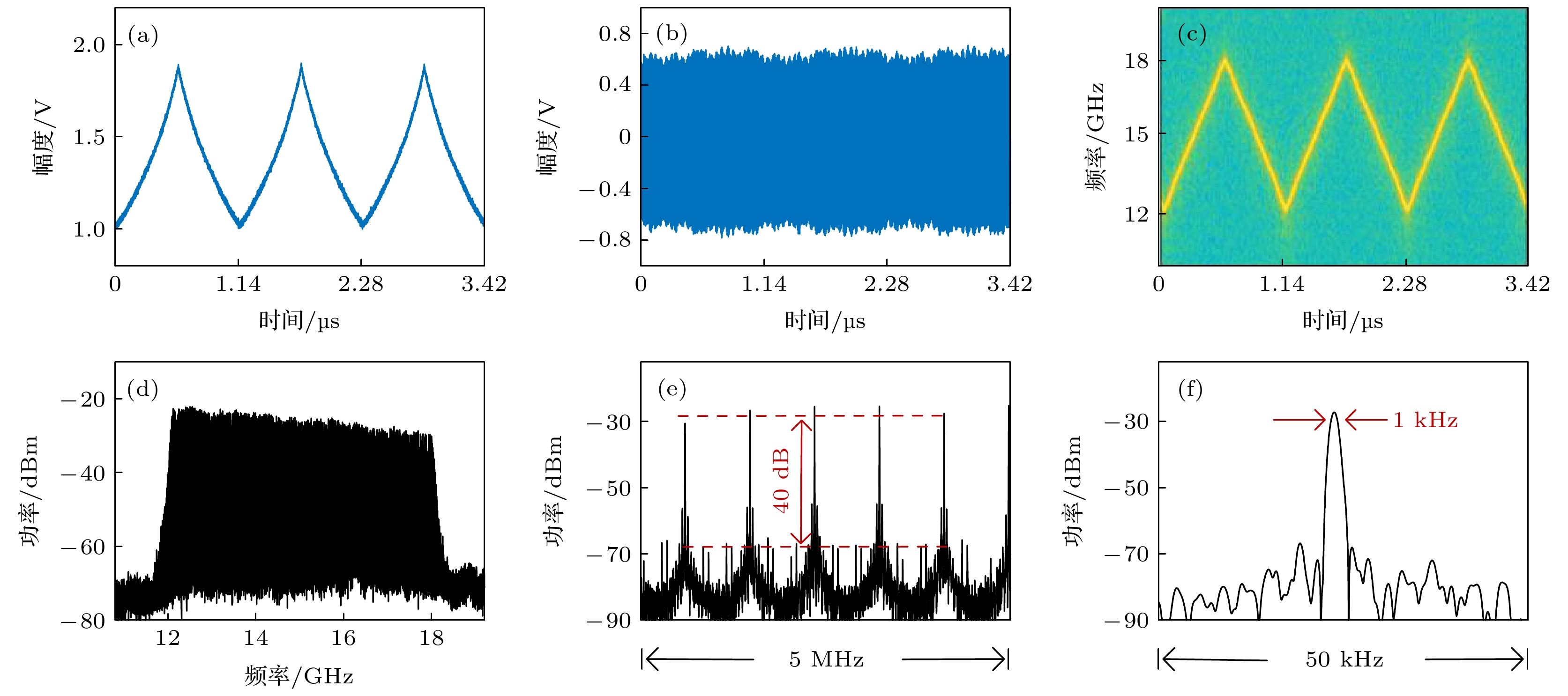
图 6 Ku波段线性调频信号产生结果 (a)控制信号S(t); (b) 时域波形; (c) 瞬时频率; (d) 频谱图; (e) 5 MHz频谱图; (f) 50 kHz频谱图
Fig. 6. Results of the Ku-band LFM microwave signal: (a) Control signal S(t); (b) temporal waveform; (c) instantaneous frequency; (d) electrical spectrum; (e) 5 MHz electrical spectrum; (f) 50 kHz electrical spectrum.
-
[1] 潘时龙, 张亚梅 2017 科技导报 35 36
Pan S L, Zhang Y M 2017 Sci. Technol. Rev. 35 36
[2] 曹继明, 崇毓华, 梅理, 朱宇鹏, 段宗明 2021 电子科技 34 36
Cao J M, Chong Y H, Mei L, Zhu Y P, Duan Z M 2021 Electron. Sci. Technol. 34 36
[3] 李刚 2019 电子技术与软件工程 15 60
Li G 2019 Electron. Technol. Software Eng. 15 60
[4] McKinney J D 2014 Nature 507 310
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Pan S L, Zhang Y M 2020 J. Lightwave Technol. 38 5450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhang F Z, Guo Q S, Pan S L 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 13848
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 王贝贝, 王志鹏 2021 电视技术 45 90
Wang B B, Wang Z P 2021 Video Eng. 45 90
[8] Zhang H, Zou W W, Chen J P 2015 Opt. Lett. 40 1085
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Sun Y, Wang D Y, Deng C Y, Lu M J, Huang L, Hu G H, Yun B F, Cui Y P 2022 Opt. Lett. 47 1077
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Li R M, Li W Z, Ding M L, Wen Z L, Li Y L, Zhou L J, Yu S S, Xing T H, Gao B W, Luan Y C, Zhu Y T, Guo P, Tian Y, Liang X D 2017 Opt. Express 25 14334
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Zhu D, Yao J P 2015 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 27 1410
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhang Y M, Ye X W, Guo Q S, Zhang F Z, Pan S L 2017 J. Lightwave Technol. 35 1821
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li W Z, Yao J P 2014 J. Lightwave Technol. 32 3573
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhou P, Li N Q, Pan S L 2022 Photonics 9 227
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhou P, Zhang F Z, Guo Q S, Pan S L 2016 Opt. Express 24 18460
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Usechak N G, Suelzer J S, Haefner J W 2017 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 29 1132
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zhou P, Zhang R H, Li K X, Jiang Z D, Mu P H, Bao H L, Li N Q 2020 Opt. Express 28 32647
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Tseng C H, Hung Y H, Hwang S K 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 3334
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhou P, Chen H, Li N Q, Zhang R H, Pan S L 2020 Opt. Lett. 45 1342
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhuang J P, Li X Z, Li S S, Chan S C 2016 Opt. Lett. 41 5764
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhou P, Zhang F Z, Pan S L 2018 J. Lightwave Technol. 36 3726
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Lin X D, Xia G Q, Shang Z, Deng T, Tang X, Fan L, Gao Z Y, Wu Z M 2019 Opt. Express. 27 1217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chan S C, Hwang S K, Liu J M 2006 Opt. Lett. 31 2254
[24] Hao T F, Cen Q Z, Dai Y T, Tang J, Li W, Yao J P, Zhu N H, Li M 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 1839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 7418
- PDF下载量: 138
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: