-
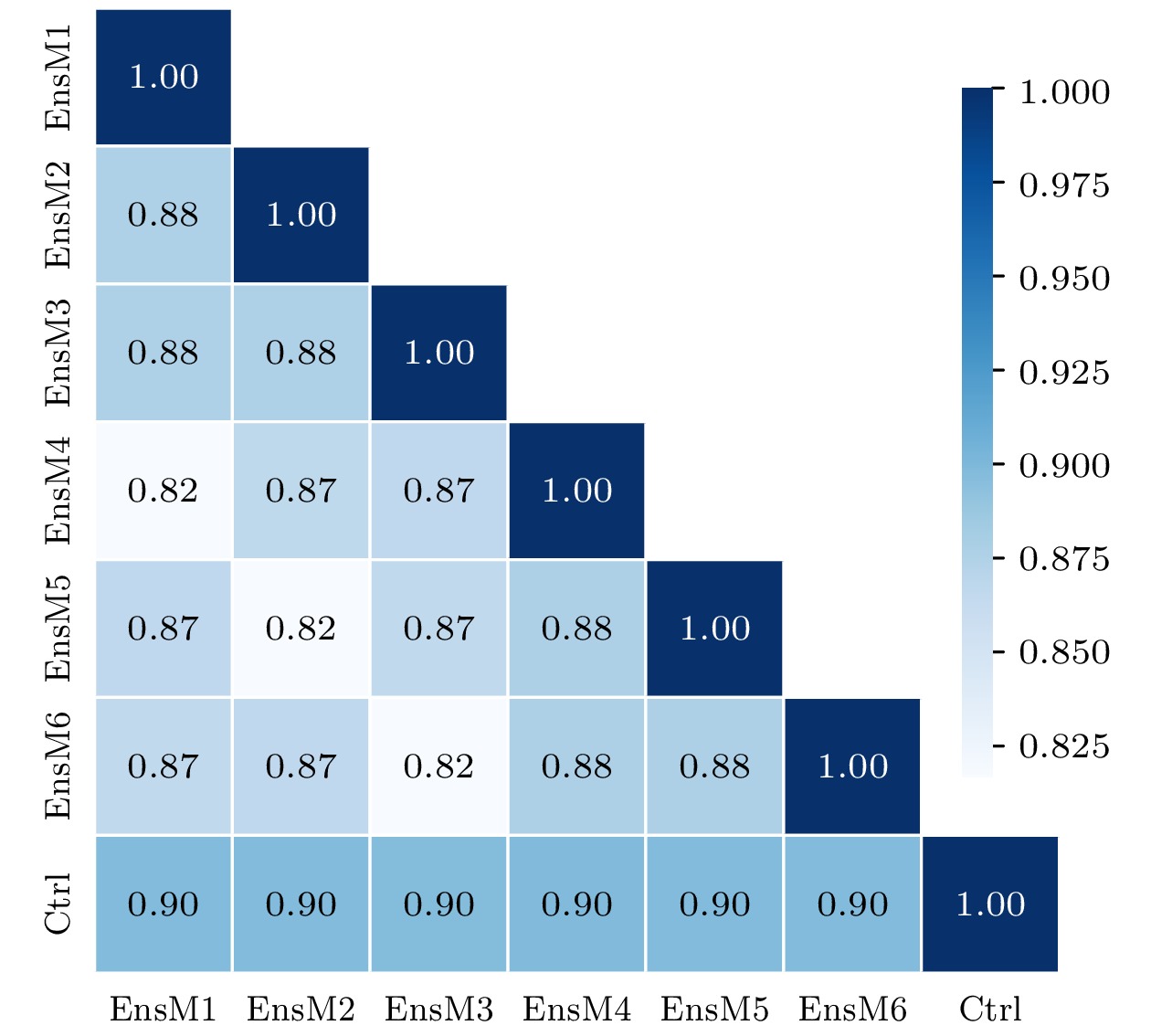
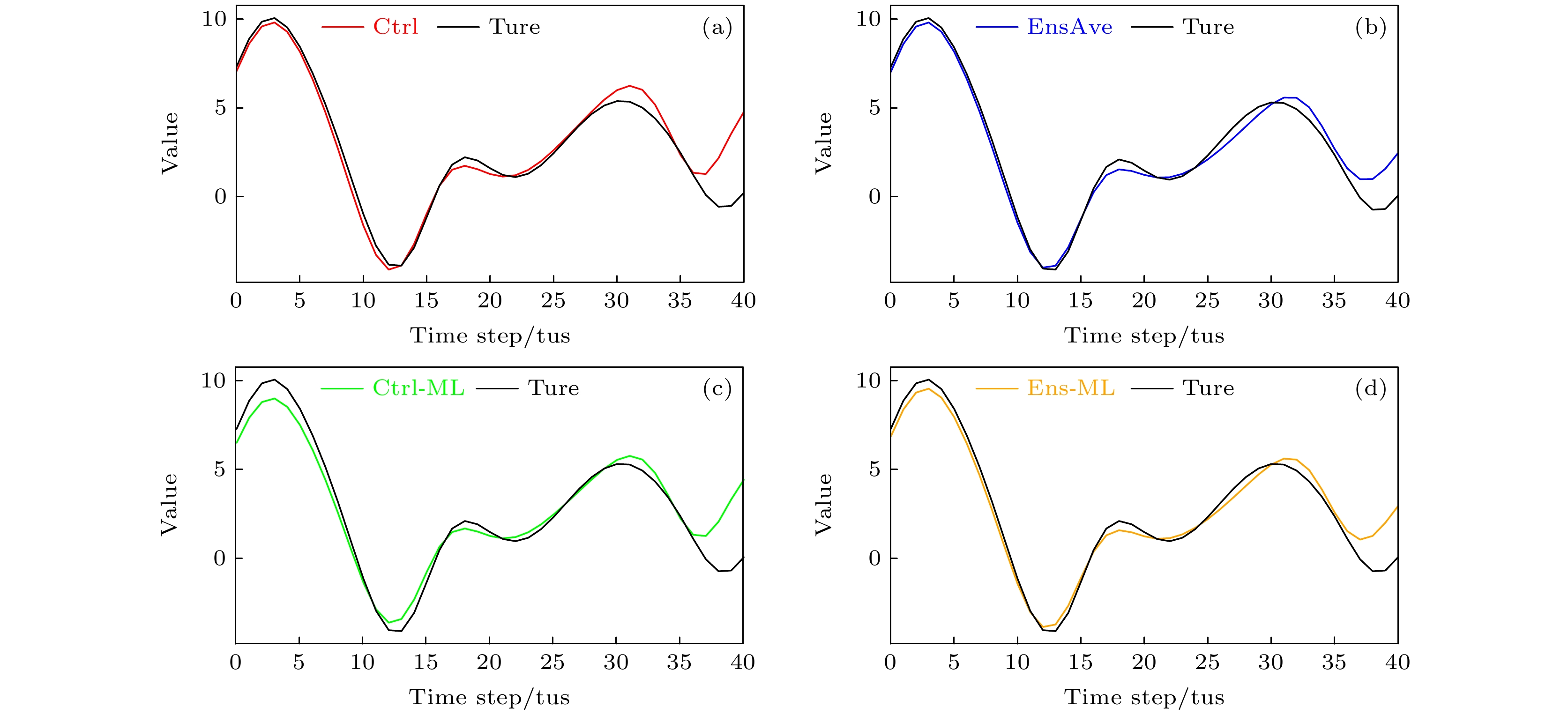
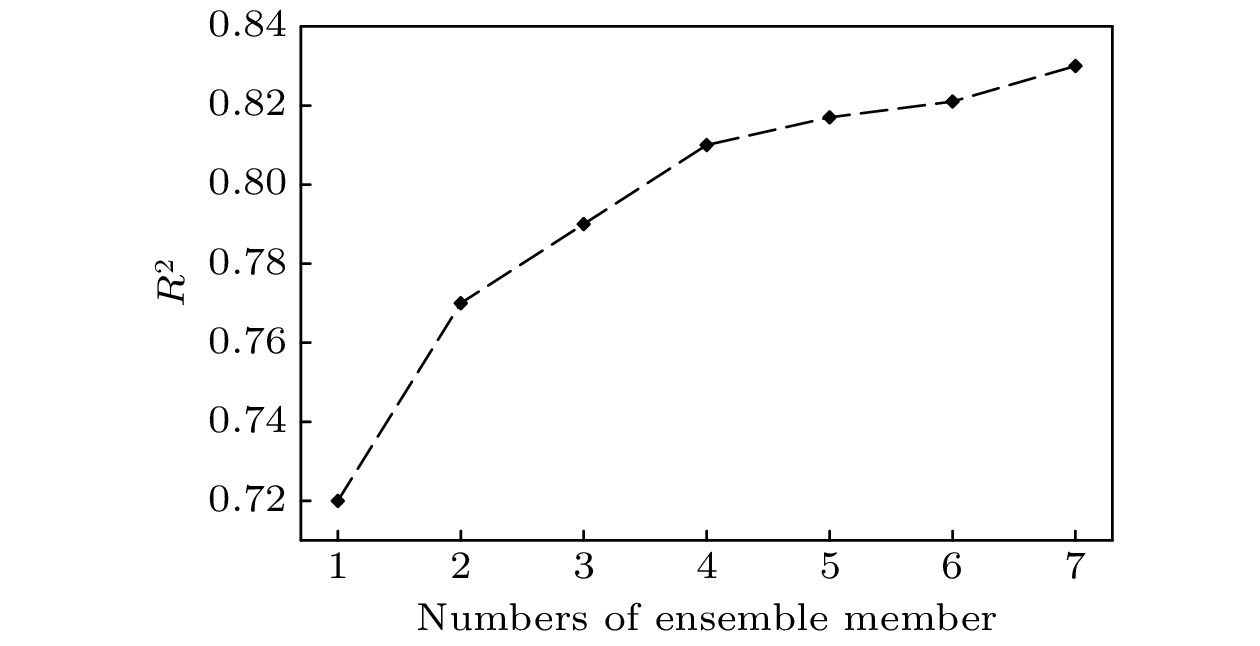
基于Lorenz96模型初步探讨了机器学习算法提高非线性局部Lyapunov向量(NLLV)集合预报效果的可行性和有效性. 结果表明: 基于岭回归算法和NLLV集合预报结果建立的机器学习模型(Ens-ML)能够有效提高整体预报技巧, 而且优于集合平均预报(EnsAve)、控制预报(Ctrl)以及基于Ctrl结果建立的机器学习模型(Ctrl-ML). 同时, 还发现Ens-ML的预报技巧改进程度依赖于集合成员的数量, 即增加集合成员数有助于提高Ens-ML模型的整体预报准确率. 通过对比个例预报表现得到, 随着预报时间延长, Ens-ML, Ctrl-ML和EnsAve的个例预报误差逐渐小于Ctrl. 进一步分析Ens-ML, Ctrl-ML和EnsAve预报的吸引子, 发现它们的概率分布的值域收缩、峰度增大并向平均值靠拢, 尤其Ens-ML的表现更为明显.
-
关键词:
- 机器学习 /
- 非线性局部Lyapunov向量 /
- 集合预报 /
- Lorenz96模型
In this study, the feasibility and effectiveness of machine learning algorithm to improve ensemble forecasts using nonlinear local Lyapunov vectors (NLLVs) are explored preliminarily based on the Lorenz96 model. The results show that the machine learning model (Ens-ML) based on the ridge regression algorithm and the results of NLLV ensemble forecasting can effectively improve the overall forecasting skill. The Ens-ML outperforms the ensemble-averaged forecasting (EnsAve) and control forecasts (Ctrl) as well as the machine learning model based on Ctrl results (Ctrl-ML). It is also found that the improvement of forecasting skill depends on the total number of ensemble members used in the Ens-ML model, i.e. the increase of the number of ensemble members is conducive to the improvement of forecasting skill and to the decrease of overfitting in the early stage. By comparing the performances among different experimental cases, we find that the experimental forecasting errors of Ens-ML, Ctrl-ML and EnsAve are gradually smaller than that of Ctrl as the forecasting time increases. The attractors forecasted by Ens-ML, Ctrl-ML and EnsAve are also analyzed. Their attractor probability distributions show a contraction of the value domain, an increase in kurtosis and a convergence to the mean, especially for Ens-ML.-
Keywords:
- machine learning /
- nonlinear local Lyapunov vectors /
- ensemble forecasting /
- Lorenz96 model
[1] Lorenz E N 1963 J. Atmos. Sci. 20 130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Leith C E 1974 Mon. Wea. Rev. 102 409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Epstein E S 1969 Tellus 21 739
[4] 张立凤, 罗雨 2010 气象科学 30 650
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang L F, Luo Y 2010 Sci. Meteor. Sin. 30 650
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 杜钧, 李俊 2014 气象科技进展 4 6
Du J, Li J 2014 Adv. Meteor. Sci. Tech. 4 6
[6] 段晚锁, 汪叶, 霍振华, 周菲凡 2019 气候与环境研究 24 396
Duan W S, Wang Y, Huo Z H, Zhou F F 2019 Clim. Env. Res. 24 396
[7] 杜钧, 陈静 2010 气象 36 1
Du J, Chen J 2010 Meteor. Mon. 36 1
[8] Toth Z, Kalnay E 1997 Mon. Wea. Rev. 125 3297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Toth Z, Kalnay E 1993 Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 74 2317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Molteni F, Buizza R, Palmer T N, Petroliagis T 1996 Q. J. R. Meteor. Soc. 122 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Bishop C H, Toth Z 1999 J. Atmos. Sci. 56 1748
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Evensen G 2003 Ocean Dyn. 53 343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Duan W, Huo Z 2016 J. Atmos. Sci. 73 997
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Feng J, Ding R, Liu D, Li J 2014 J. Atmos. Sci. 71 3554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ding R Q, Li J, Li B 2017 Adv. Atmos. Sci. 34 1027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Norwood A, Kalnay E, Ide K, Yang S-C, Wolfe C 2013 J. Phys. A:Math. Theor. 46 254021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 李娟, 尉鹏, 戴学之, 赵森, 张博雅, 吕玲玲, 胡京南 2021 环境科学研究 34 872
Li J, Wei P, Dai X Z, Zhao S, Zhang B Y, Lv L L, Hu J N 2021 Res. Env. Sci. 34 872
[18] 贺圣平, 王会军, 李华, 赵家臻 2021 大气科学学报 44 26
He S P, Wang H J, Li H, Zhao J Z 2021 Trans. Atmos. Sci. 44 26
[19] 康俊锋, 谭建林, 方雷, 肖亚来 2021 中国环境科学 41 4016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Kang J F, Tan J L, Fang L, Xiao Y L, 2021 Chi. Env. Sci. 41 4016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 付旭东, 王金艳, 李龙燕, 陈金车, 苏士翔, 常伟, 王明 2021 兰州大学学报(自然科学版) 57 503
Fu X D, Wang J Y, Li L Y, Chen J C, Su S X, Chang W, Wang M 2021 J. Lanzhou Univ. (Natural Sciences) 57 503
[21] 门晓磊, 焦瑞莉, 王鼎, 赵晨光, 刘亚昆, 夏江江, 李昊辰, 严中伟, 孙建华, 王立志 2019 气候与环境研究 24 116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Men X L, Jiao R L, Wang D, Zhao C G, Liu Y K, Xia J J, Li H C, Yan Z W, Sun J H, Wang L Z 2019 Clim. Env. Res. 24 116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Ham Y G, Kim J H, Luo J J 2019 Nature 573 568
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 梁丁, 顾斌, 丁瑞强, 李建平, 钟权加 2018 67 070501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang D, Gu B, Ding R Q, Li J P, Zhong Q J 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 070501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Lorenz E N 1996 Predictability: A problem partly solved. Proc. Seminar on Predictability, Vol. I, Reading, United Kingdom, ECMWF, 1–18.
[25] Feng J, Ding R Q, Li J P, Liu D Q 2016 Adv. Atmos. Sci. 33 1036
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Hou Z, Li J, Ding R, Feng J, Duan W 2018 Clim. Dynam. 51 283
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Feng J, Li J P, Ding R Q, Toth Z 2018 J. Atmos. Sci. 75 1073
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Hoerl A E, Kennard R W 1970 Technometrics 12 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Bager A, Roman M, Algelidh M, Mohammed B 2017 J. Soc. Econo. Stat. 6 30
[30] 胡占占, 陈传法, 胡保健 2021 环境科学学报 41 4228
Hu Z Z, Chen C F, Hu B J 2021 Acta. Sci. Circum. 41 4228
[31] Murphy A H, Epstein E S 1989 Mon. Wea. Rev. 117 572
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
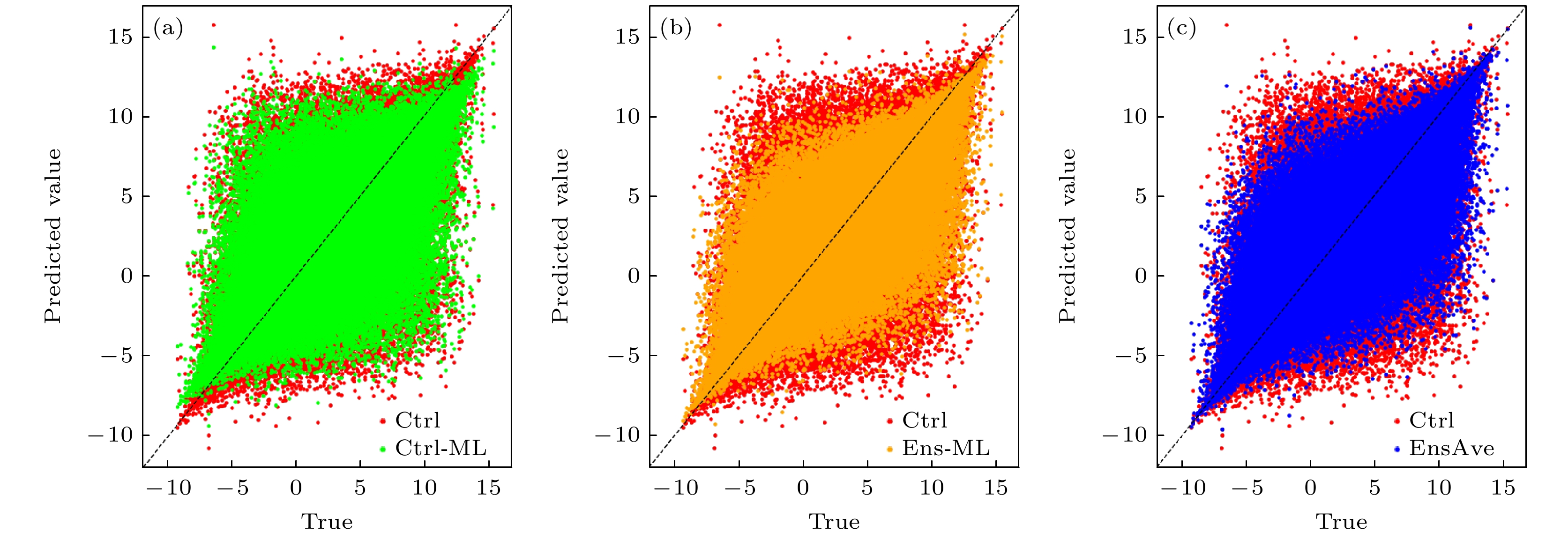
图 9 试验个例在不同时刻的EnsAve, Ctrl-ML和Ens-ML与Ctrl的预报误差 (a)—(c) 0 tus; (d)—(f) 10 tus; (g)—(i) 20 tus; (j)—(l) 30 tus; (m)—(o) 40 tus
Fig. 9. Scatterplot of forecast error at different leading times between the EnsAve, Ctrl-ML, Ens-ML and the Ctrl, respectively: (a)–(c) 0 tus; (d)–(f) 10 tus; (g)–(i) 20 tus; (j)–(l) 30 tus; (m)–(o) 40 tus .
表 1 不同预报方法的预报结果比较
Table 1. Evaluation of forecast results in different forecasting methods.
评价 方法 Ctrl EnsAve Ctrl-ML Ens-ML R² 0.77 0.82 0.78 0.83 MAE 0.90 0.86 0.97 0.85 MSE 3.05 2.40 2.88 2.31 RMSE 1.75 1.55 1.70 1.52 -
[1] Lorenz E N 1963 J. Atmos. Sci. 20 130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Leith C E 1974 Mon. Wea. Rev. 102 409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Epstein E S 1969 Tellus 21 739
[4] 张立凤, 罗雨 2010 气象科学 30 650
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang L F, Luo Y 2010 Sci. Meteor. Sin. 30 650
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 杜钧, 李俊 2014 气象科技进展 4 6
Du J, Li J 2014 Adv. Meteor. Sci. Tech. 4 6
[6] 段晚锁, 汪叶, 霍振华, 周菲凡 2019 气候与环境研究 24 396
Duan W S, Wang Y, Huo Z H, Zhou F F 2019 Clim. Env. Res. 24 396
[7] 杜钧, 陈静 2010 气象 36 1
Du J, Chen J 2010 Meteor. Mon. 36 1
[8] Toth Z, Kalnay E 1997 Mon. Wea. Rev. 125 3297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Toth Z, Kalnay E 1993 Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 74 2317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Molteni F, Buizza R, Palmer T N, Petroliagis T 1996 Q. J. R. Meteor. Soc. 122 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Bishop C H, Toth Z 1999 J. Atmos. Sci. 56 1748
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Evensen G 2003 Ocean Dyn. 53 343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Duan W, Huo Z 2016 J. Atmos. Sci. 73 997
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Feng J, Ding R, Liu D, Li J 2014 J. Atmos. Sci. 71 3554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ding R Q, Li J, Li B 2017 Adv. Atmos. Sci. 34 1027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Norwood A, Kalnay E, Ide K, Yang S-C, Wolfe C 2013 J. Phys. A:Math. Theor. 46 254021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 李娟, 尉鹏, 戴学之, 赵森, 张博雅, 吕玲玲, 胡京南 2021 环境科学研究 34 872
Li J, Wei P, Dai X Z, Zhao S, Zhang B Y, Lv L L, Hu J N 2021 Res. Env. Sci. 34 872
[18] 贺圣平, 王会军, 李华, 赵家臻 2021 大气科学学报 44 26
He S P, Wang H J, Li H, Zhao J Z 2021 Trans. Atmos. Sci. 44 26
[19] 康俊锋, 谭建林, 方雷, 肖亚来 2021 中国环境科学 41 4016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Kang J F, Tan J L, Fang L, Xiao Y L, 2021 Chi. Env. Sci. 41 4016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 付旭东, 王金艳, 李龙燕, 陈金车, 苏士翔, 常伟, 王明 2021 兰州大学学报(自然科学版) 57 503
Fu X D, Wang J Y, Li L Y, Chen J C, Su S X, Chang W, Wang M 2021 J. Lanzhou Univ. (Natural Sciences) 57 503
[21] 门晓磊, 焦瑞莉, 王鼎, 赵晨光, 刘亚昆, 夏江江, 李昊辰, 严中伟, 孙建华, 王立志 2019 气候与环境研究 24 116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Men X L, Jiao R L, Wang D, Zhao C G, Liu Y K, Xia J J, Li H C, Yan Z W, Sun J H, Wang L Z 2019 Clim. Env. Res. 24 116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Ham Y G, Kim J H, Luo J J 2019 Nature 573 568
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 梁丁, 顾斌, 丁瑞强, 李建平, 钟权加 2018 67 070501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang D, Gu B, Ding R Q, Li J P, Zhong Q J 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 070501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Lorenz E N 1996 Predictability: A problem partly solved. Proc. Seminar on Predictability, Vol. I, Reading, United Kingdom, ECMWF, 1–18.
[25] Feng J, Ding R Q, Li J P, Liu D Q 2016 Adv. Atmos. Sci. 33 1036
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Hou Z, Li J, Ding R, Feng J, Duan W 2018 Clim. Dynam. 51 283
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Feng J, Li J P, Ding R Q, Toth Z 2018 J. Atmos. Sci. 75 1073
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Hoerl A E, Kennard R W 1970 Technometrics 12 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Bager A, Roman M, Algelidh M, Mohammed B 2017 J. Soc. Econo. Stat. 6 30
[30] 胡占占, 陈传法, 胡保健 2021 环境科学学报 41 4228
Hu Z Z, Chen C F, Hu B J 2021 Acta. Sci. Circum. 41 4228
[31] Murphy A H, Epstein E S 1989 Mon. Wea. Rev. 117 572
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 7219
- PDF下载量: 103
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: