-
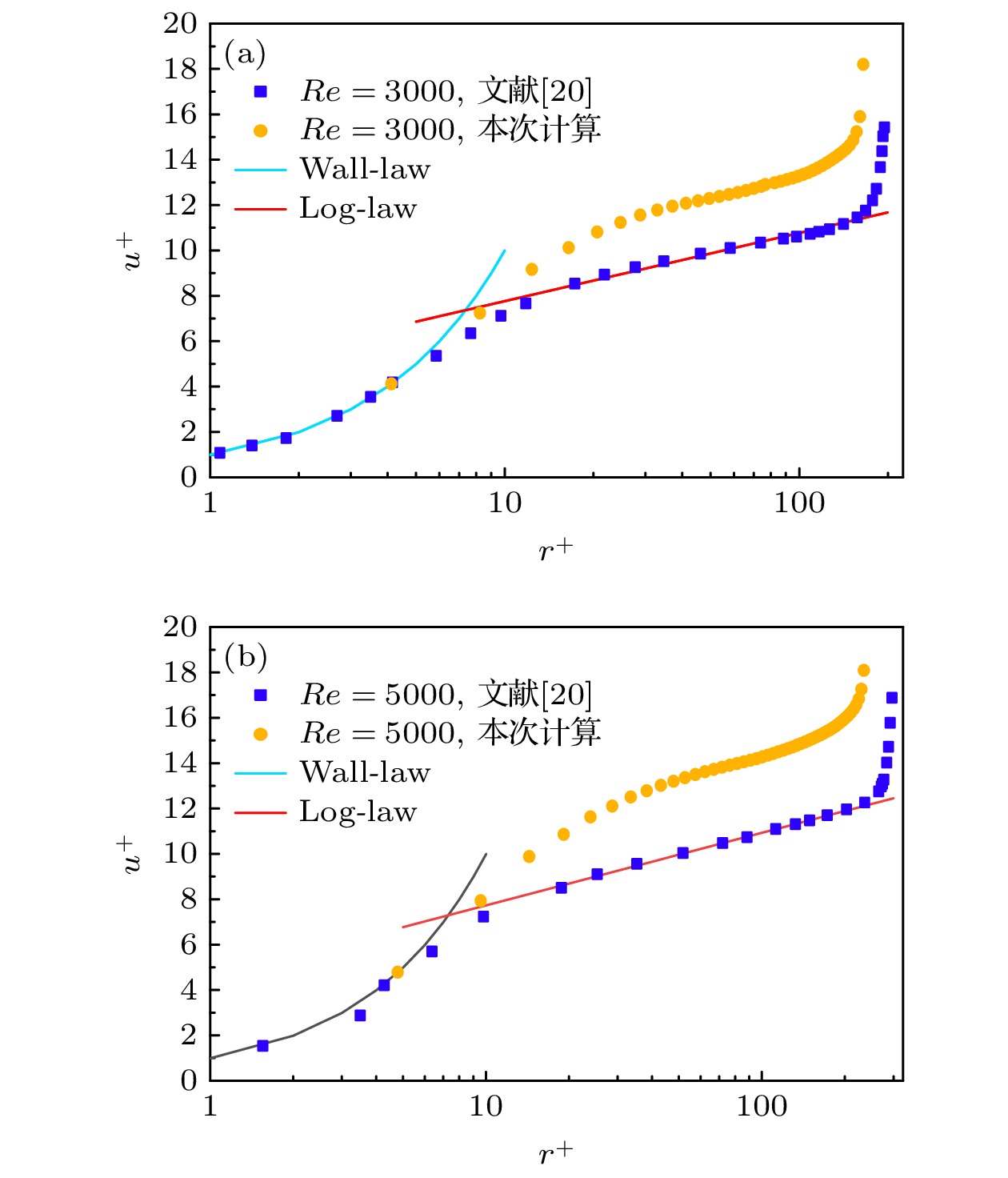
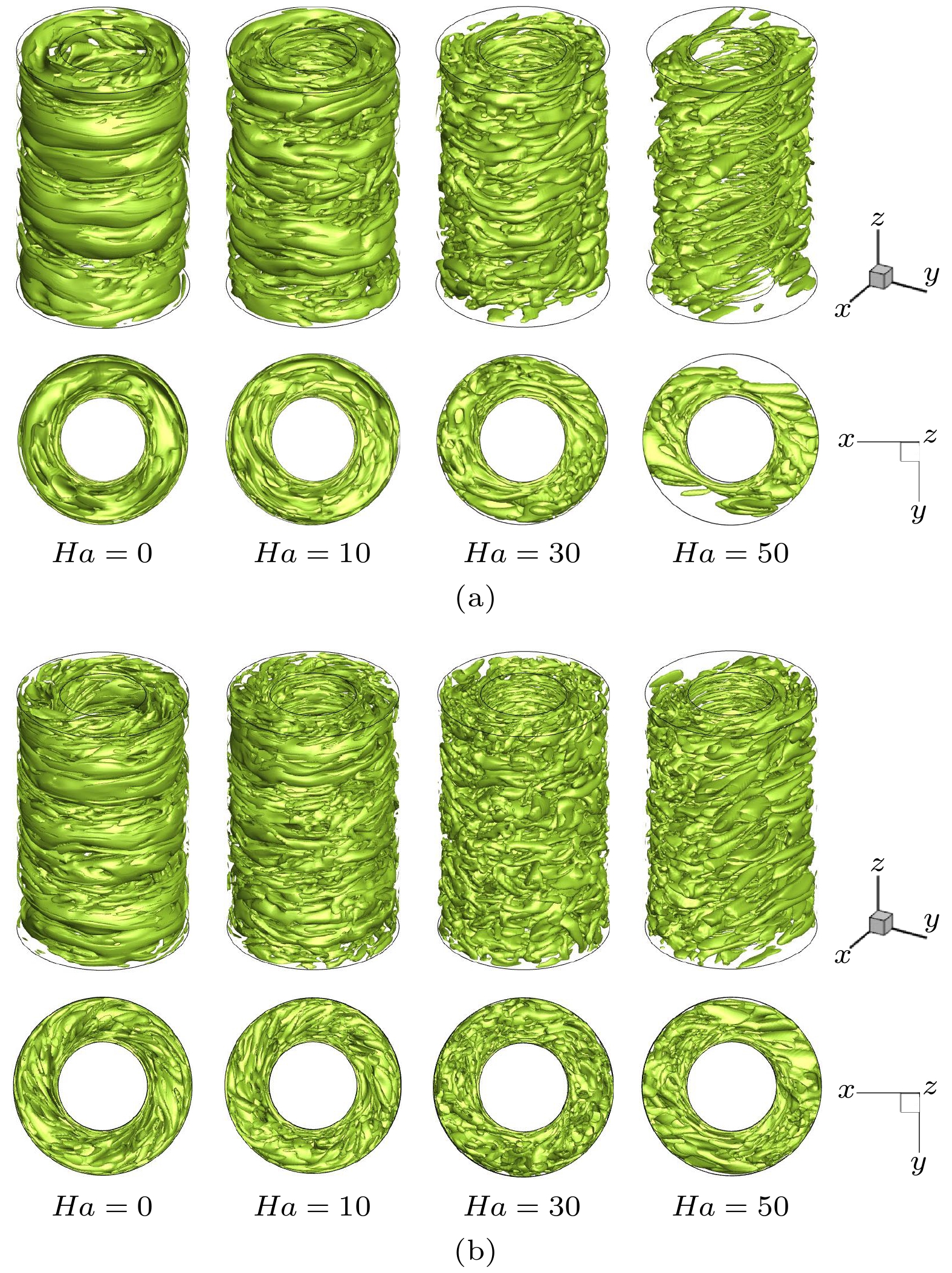
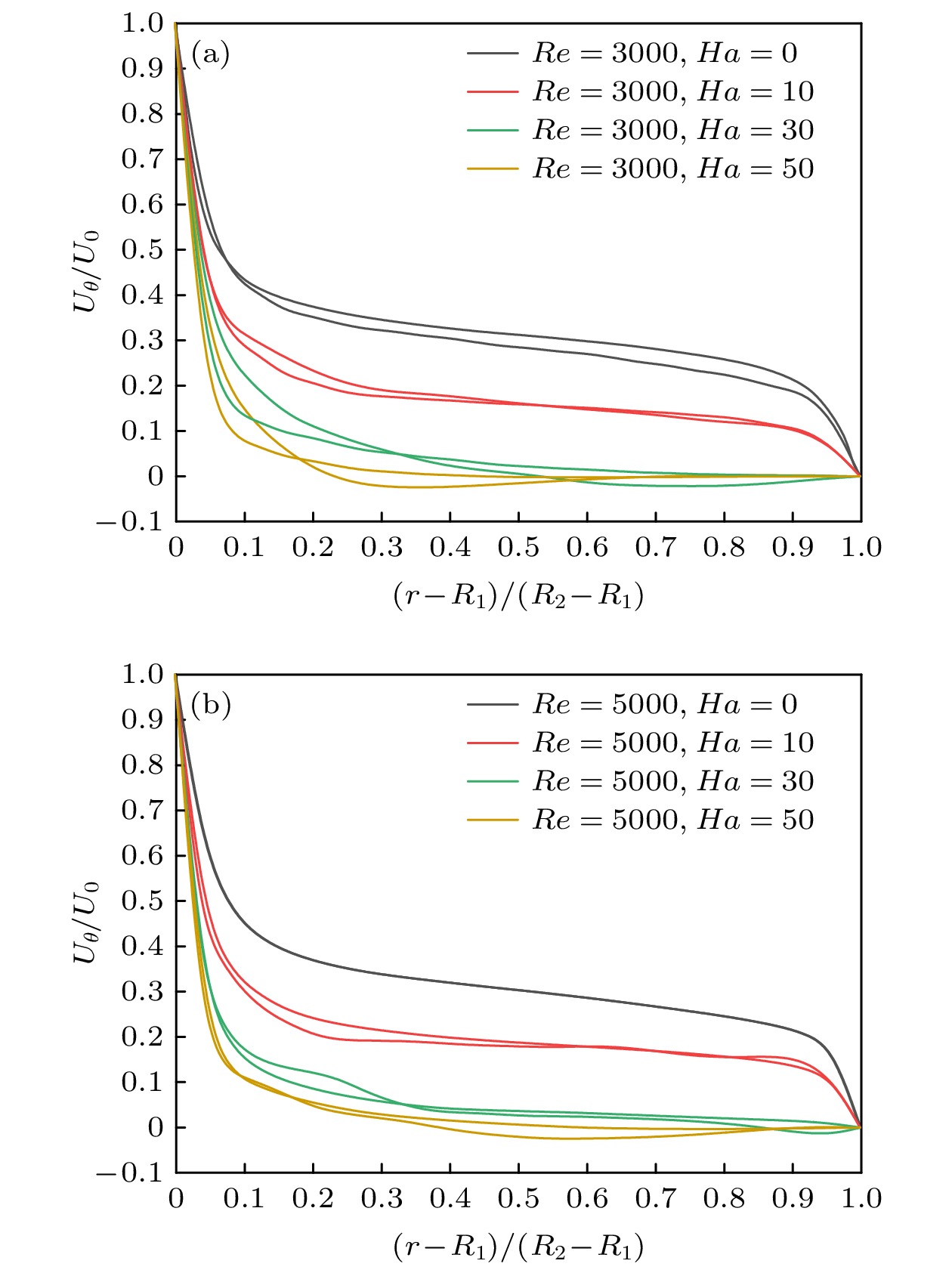
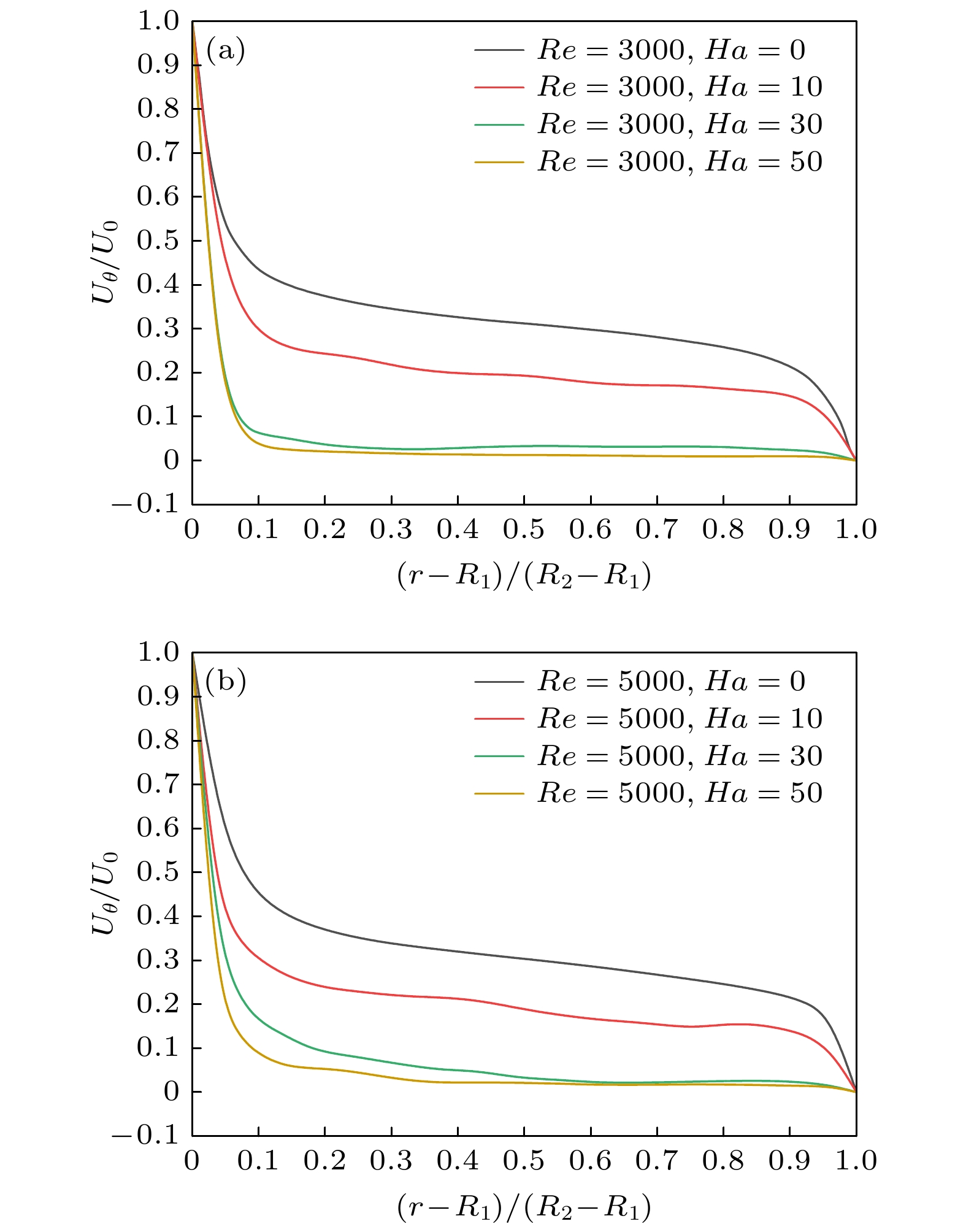
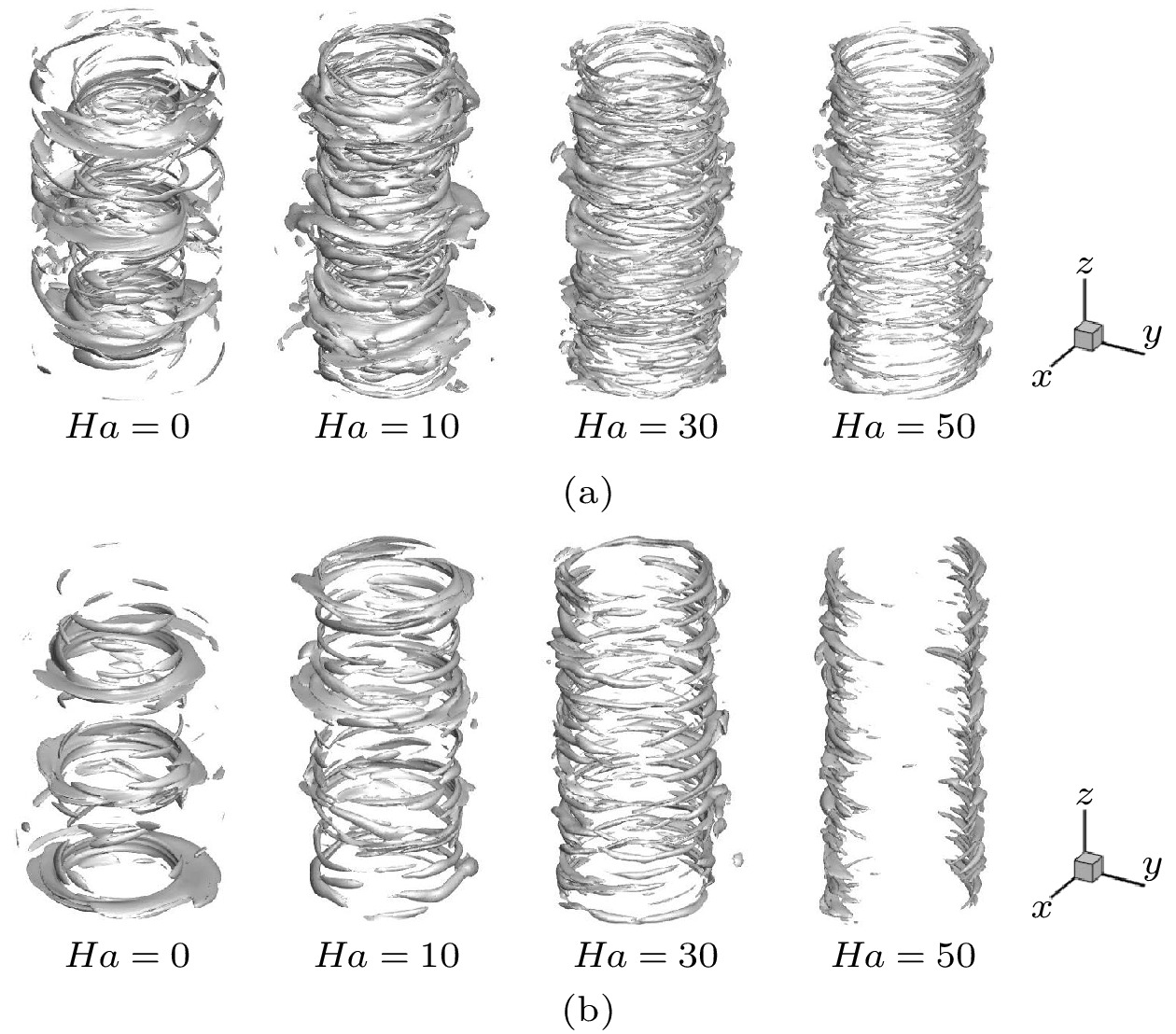
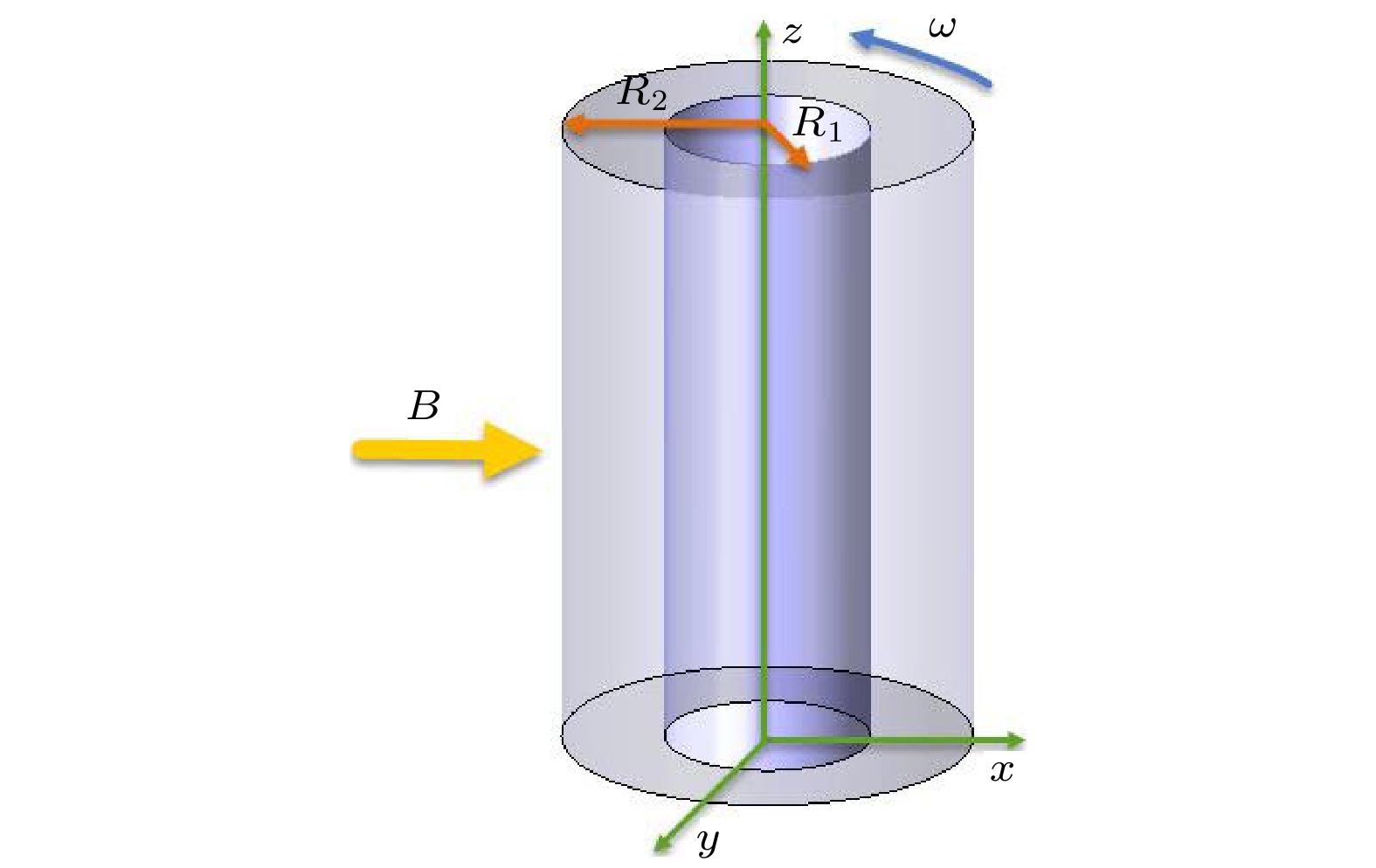
采用大涡模拟方法对横向磁场作用下导电流体Taylor-Couette湍流流动进行数值模拟, 以研究其运动规律. 计算模型为无限长度, 半径比为1/2. 雷诺数分别选取为3000和5000, 磁场加载方式为全局磁场, 哈特曼数取值0—50. 对磁场作用下泰勒涡的演化过程、速度分布和湍动能分布进行分析, 并与轴向磁场作用下泰勒涡演化过程进行对比. 结果表明: 磁场对流场有显著的抑制作用, 扭曲的泰勒涡在横向磁场的作用下破裂成小尺度涡结构, 并沿磁场方向排列; 在外圆筒和垂直于磁场方向的区域, 磁场抑制效果较强; 随着雷诺数的增加, 磁场抑制效果减弱, 在流场不同区域, 流动呈现出不同的特点. 与轴向磁场相比, 横向磁场对流场的抑制效果较弱, 流场分布呈现出明显的各向异性.
-
关键词:
- 横向磁场 /
- Taylor-Couette流动 /
- 湍流 /
- 大涡模拟
By the large eddy simulation method, the turbulent Taylor-Couette flow of conducting fluid under a homogenous transverse magnetic field is investigated through using the computational fluid dynamic software ANSYS Fluent 17.0. The flow is confined between two infinitely long cylinders, thus a periodic boundary condition is imposed in the axial direction. The inner cylinder rotates while the outer one is at rest, and their radius ratio is 1/2. Two Reynolds numbers of 3000 and 5000 are considered in the simulations, and the Hartmann number is varied from 0 to 50. In the present study, we assume a lower magnetic Reynolds number$Re_{\rm m} \ll 1$ , i.e., the influence of the induced magnetic field on the flow is negligible in comparison with the imposed magnetic field. The evolution of Taylor vortices, velocity profile of mean flow, and turbulent kinetic energy distribution under the transverse magnetic field are analyzed and compared with the results of the axial magnetic field counterpart. It shows that the imposed magnetic field has a significant damping effect on the Taylor-Couette flow. The twisted Taylor vortices break into small-scale vortex structures under the transverse magnetic field and they arrange themselves along the magnetic field. The fluctuations which are perpendicular to the magnetic field are suppressed effectively, while the one which is parallel to the magnetic field is nearly uninfluenced, resulting in quasi-two-dimensional elongated structure in the flow field. As anticipated, in a sufficiently strong magnetic field, the turbulent Taylor-Couette flow may eventually decay to a Couette laminar flow. In the outer cylinder and the area perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field, the suppression effect is even stronger than those in any other places and fewer vortices are observed in the simulations. The turbulent kinetic energy is transferred firstly from large eddies to intermediate eddies, then to small eddies, and finally dissipated due to the viscous and Joule effect. As the Reynolds number increases, the suppression effect of the magnetic field weakens, and the flow behaves divergently in different areas of the apparatus. Compared with the axial magnetic field, the transverse magnetic field has a weak suppression effect on the flow field, and the profiles of related variables are obviously anisotropic.-
Keywords:
- transverse magnetic field /
- Taylor-Couette flow /
- turbulence /
- large eddy simulation
[1] Taylor G I 1923 Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 223 289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Andereck C D, Liu S S, Swinney H L 1986 J. Fluid Mech. 164 155
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 叶立, 蔡小舒, 童正明 2012 化工进展 31 1878
Ye L, Cai X S, Tong Z M 2012 Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. 31 1878
[4] Dutta P K, Ray A K 2004 Chem. Eng. Sci. 59 5249
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Collet Y, Magotte O, Van den Bogaert N, Rolinsky R, Loix F, Jacot M, Regnier V, Marie J M, Dupret F 2012 J. Cryst. Growth 360 18
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Li Y, Ruan D, Imaishi N, Wu S, Peng L, Zeng D 2003 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 46 2887
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Gao X, Kong B, Vigil R D 2015 Bioresour. Technol. 198 283
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Gil L V G, Singh H, Da Silva J D S, Santos D P D, Suazo C A T 2020 Biochem. Eng. J. 162 107710
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Kang B K, Song Y H, Park W K, Kwag S H, Lim B S, Kwon S B, Yang W S, Yoon D H 2017 J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 37 3673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Serov A F, Nazarov A D, Mamonov V N, Terekhov V I 2019 Appl. Energy 251 113362
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Donnelly R J, Ozima M 1962 Proc. R. Soc. A 266 272
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tagawa T, Kaneda M 2005 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 14 007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Leng X Y, Kolesnikov Y B, Krasnov D, Li B W 2018 Phys. Fluids 30 015107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Leng X Y, Yu Y, Li B W 2014 Comput. Fluids 105 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhao Y R, Tao J J, Zikanov O 2014 Phys. Rev. E 89 33002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kikura H, Aritomi M, Takeda Y 2005 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 289 342
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Davidson P A 1995 J. Fluid Mech. 299 153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 丁明松, 江涛, 刘庆宗, 董维中, 高铁锁, 傅杨奥骁 2020 69 134702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ding M S, Jiang T, Liu Q Z, Dong W Z, Gao T S, Fu Y A X 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 134702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Kakarantzas S C, Benos L T, Sarris I E, Knaepenc B, Grecos A P, Vlachos N S 2017 Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 65 342
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Dong S 2007 J. Fluid Mech. 587 373
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Cheng W, Pullin D I, Samtaney R 2020 J. Fluid Mech. 890 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 赵斌娟, 谢昀彤, 廖文言, 韩璐遥, 付燕霞, 黄忠富 2020 机械工程学报 56 216
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao B J, Xie Y T, Liao W Y, Han L Y, Fu Y X, Huang Z F 2020 J. Mech. Eng. 56 216
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 杜珩, 阙夏, 刘难生 2014 中国科学技术大学学报 44 761
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Du H, Que X, Liu N S 2014 J. Univ. Sci. Technol. China 44 761
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Leng X Y, Krasnov D, Kolesnikov Y, Li B W 2017 Magnetohydrodynamics 53 159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] Taylor G I 1923 Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 223 289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Andereck C D, Liu S S, Swinney H L 1986 J. Fluid Mech. 164 155
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 叶立, 蔡小舒, 童正明 2012 化工进展 31 1878
Ye L, Cai X S, Tong Z M 2012 Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. 31 1878
[4] Dutta P K, Ray A K 2004 Chem. Eng. Sci. 59 5249
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Collet Y, Magotte O, Van den Bogaert N, Rolinsky R, Loix F, Jacot M, Regnier V, Marie J M, Dupret F 2012 J. Cryst. Growth 360 18
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Li Y, Ruan D, Imaishi N, Wu S, Peng L, Zeng D 2003 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 46 2887
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Gao X, Kong B, Vigil R D 2015 Bioresour. Technol. 198 283
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Gil L V G, Singh H, Da Silva J D S, Santos D P D, Suazo C A T 2020 Biochem. Eng. J. 162 107710
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Kang B K, Song Y H, Park W K, Kwag S H, Lim B S, Kwon S B, Yang W S, Yoon D H 2017 J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 37 3673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Serov A F, Nazarov A D, Mamonov V N, Terekhov V I 2019 Appl. Energy 251 113362
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Donnelly R J, Ozima M 1962 Proc. R. Soc. A 266 272
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tagawa T, Kaneda M 2005 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 14 007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Leng X Y, Kolesnikov Y B, Krasnov D, Li B W 2018 Phys. Fluids 30 015107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Leng X Y, Yu Y, Li B W 2014 Comput. Fluids 105 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhao Y R, Tao J J, Zikanov O 2014 Phys. Rev. E 89 33002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kikura H, Aritomi M, Takeda Y 2005 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 289 342
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Davidson P A 1995 J. Fluid Mech. 299 153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 丁明松, 江涛, 刘庆宗, 董维中, 高铁锁, 傅杨奥骁 2020 69 134702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ding M S, Jiang T, Liu Q Z, Dong W Z, Gao T S, Fu Y A X 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 134702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Kakarantzas S C, Benos L T, Sarris I E, Knaepenc B, Grecos A P, Vlachos N S 2017 Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 65 342
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Dong S 2007 J. Fluid Mech. 587 373
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Cheng W, Pullin D I, Samtaney R 2020 J. Fluid Mech. 890 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 赵斌娟, 谢昀彤, 廖文言, 韩璐遥, 付燕霞, 黄忠富 2020 机械工程学报 56 216
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao B J, Xie Y T, Liao W Y, Han L Y, Fu Y X, Huang Z F 2020 J. Mech. Eng. 56 216
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 杜珩, 阙夏, 刘难生 2014 中国科学技术大学学报 44 761
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Du H, Que X, Liu N S 2014 J. Univ. Sci. Technol. China 44 761
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Leng X Y, Krasnov D, Kolesnikov Y, Li B W 2017 Magnetohydrodynamics 53 159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 8422
- PDF下载量: 101
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: