-
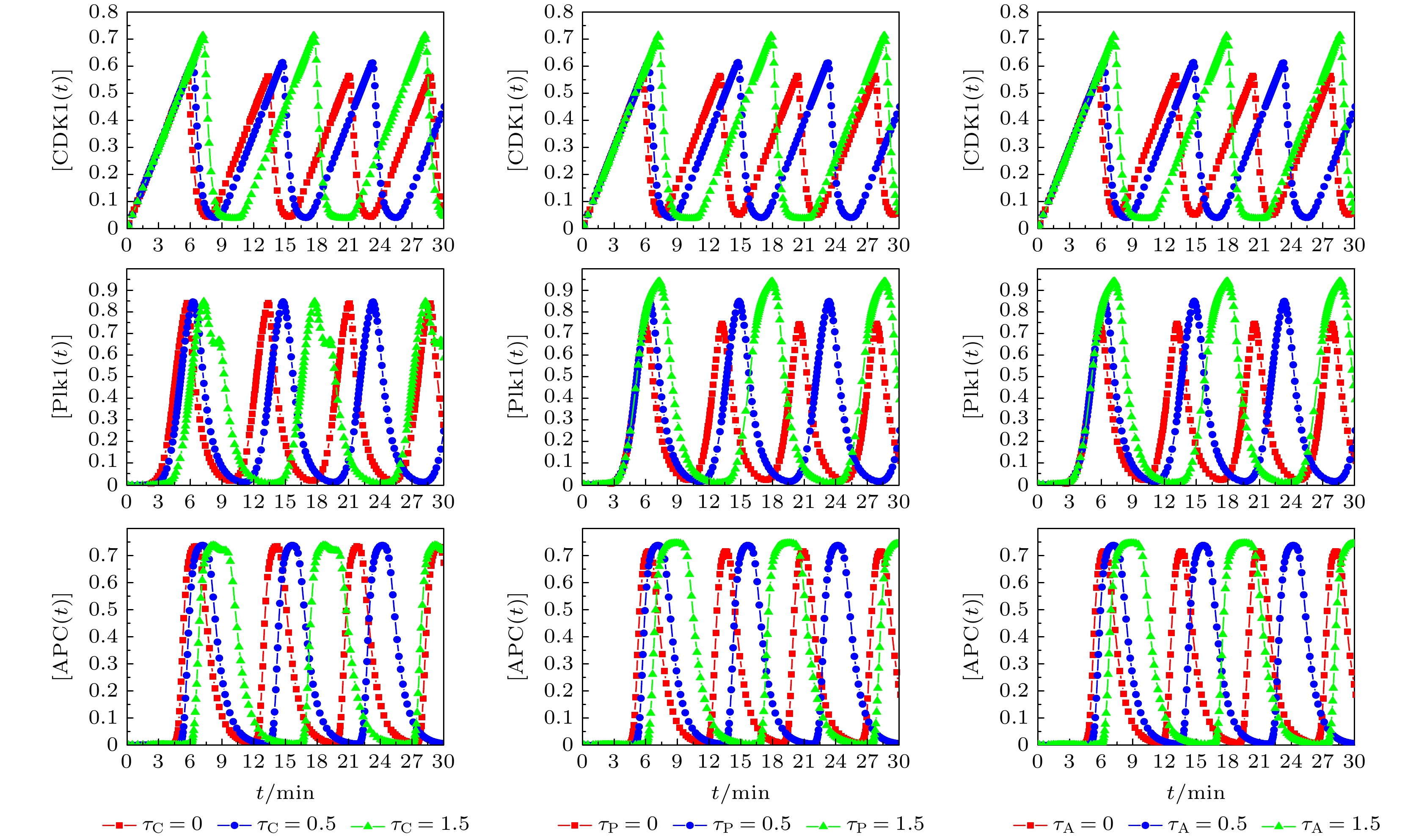
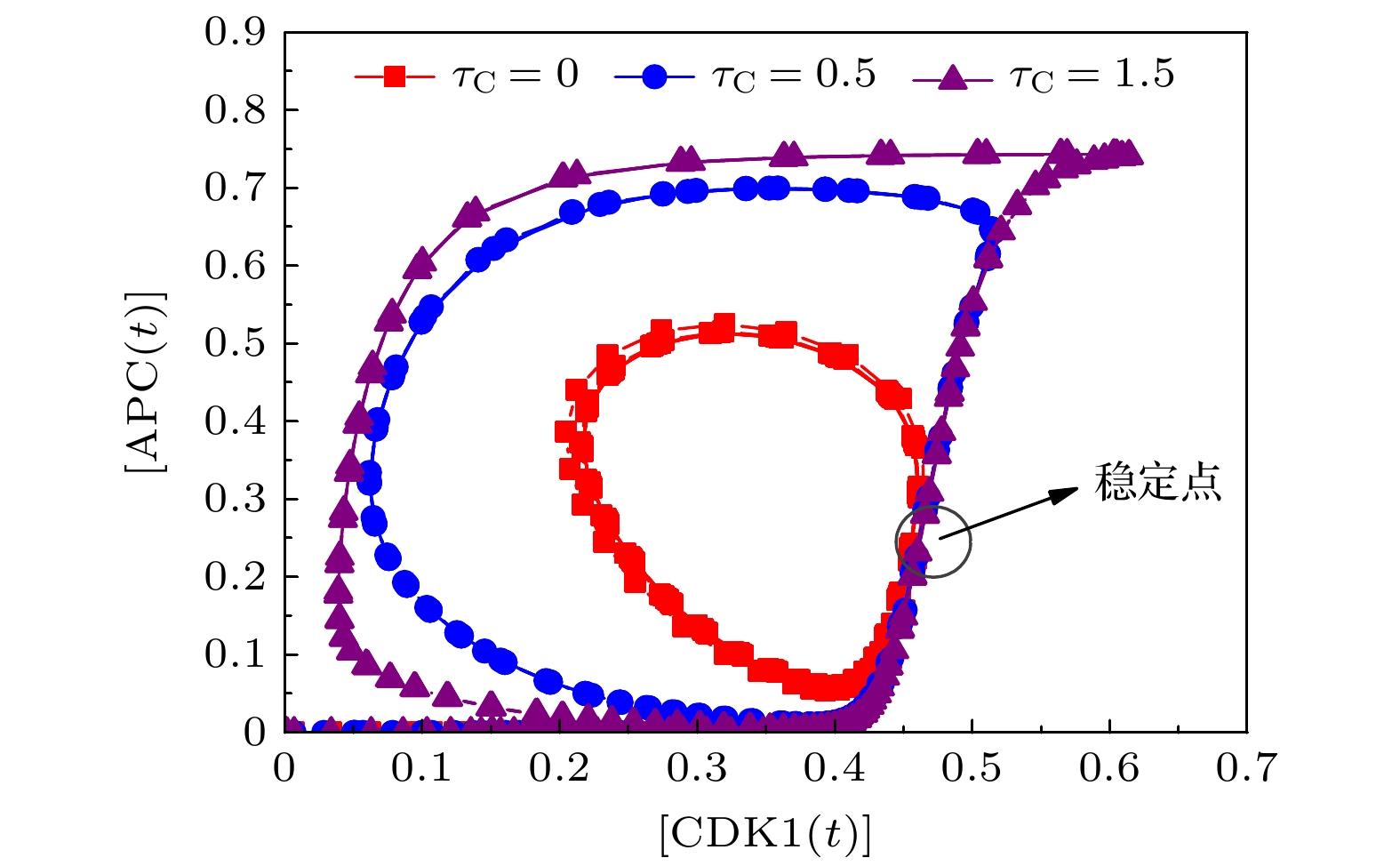
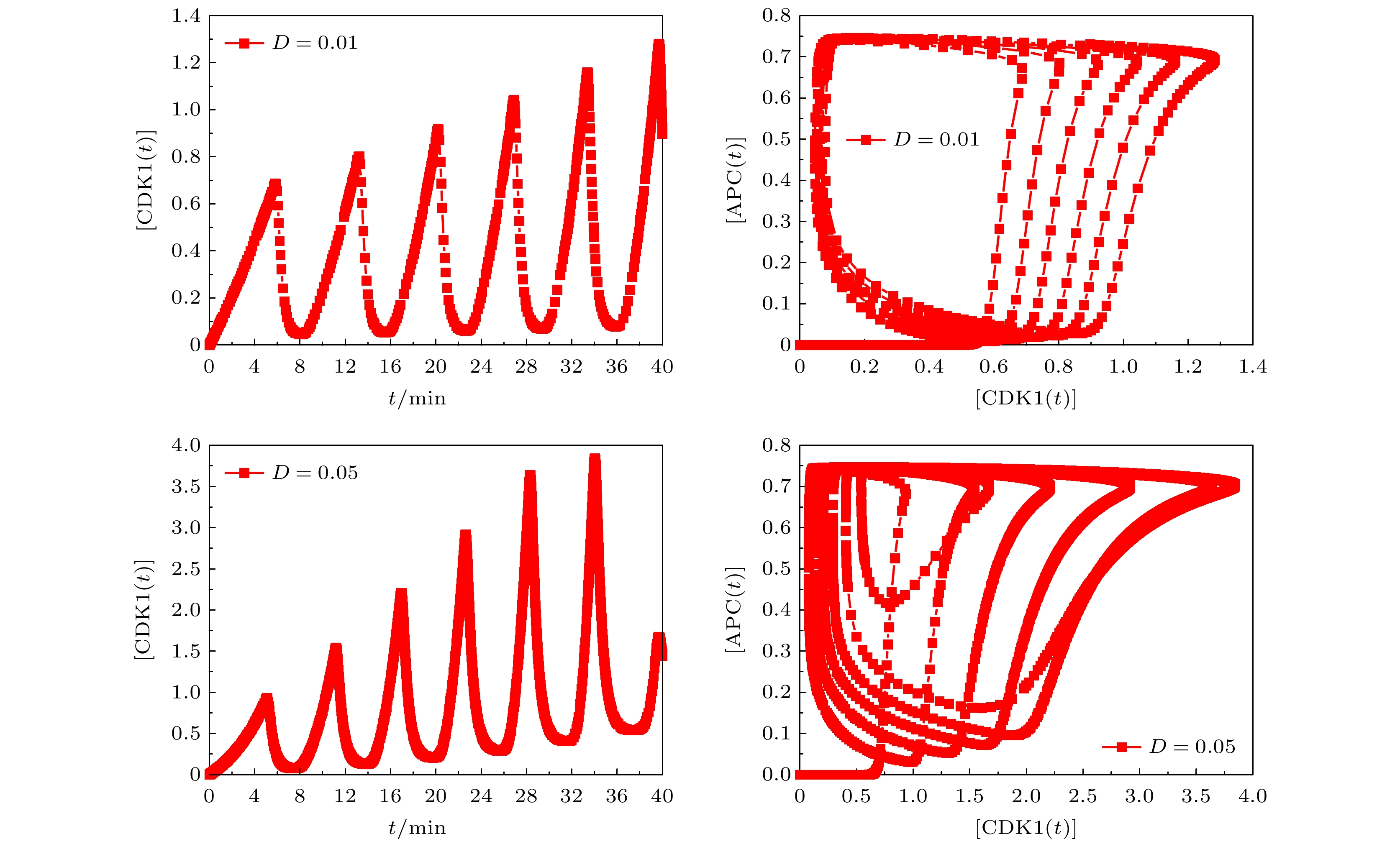
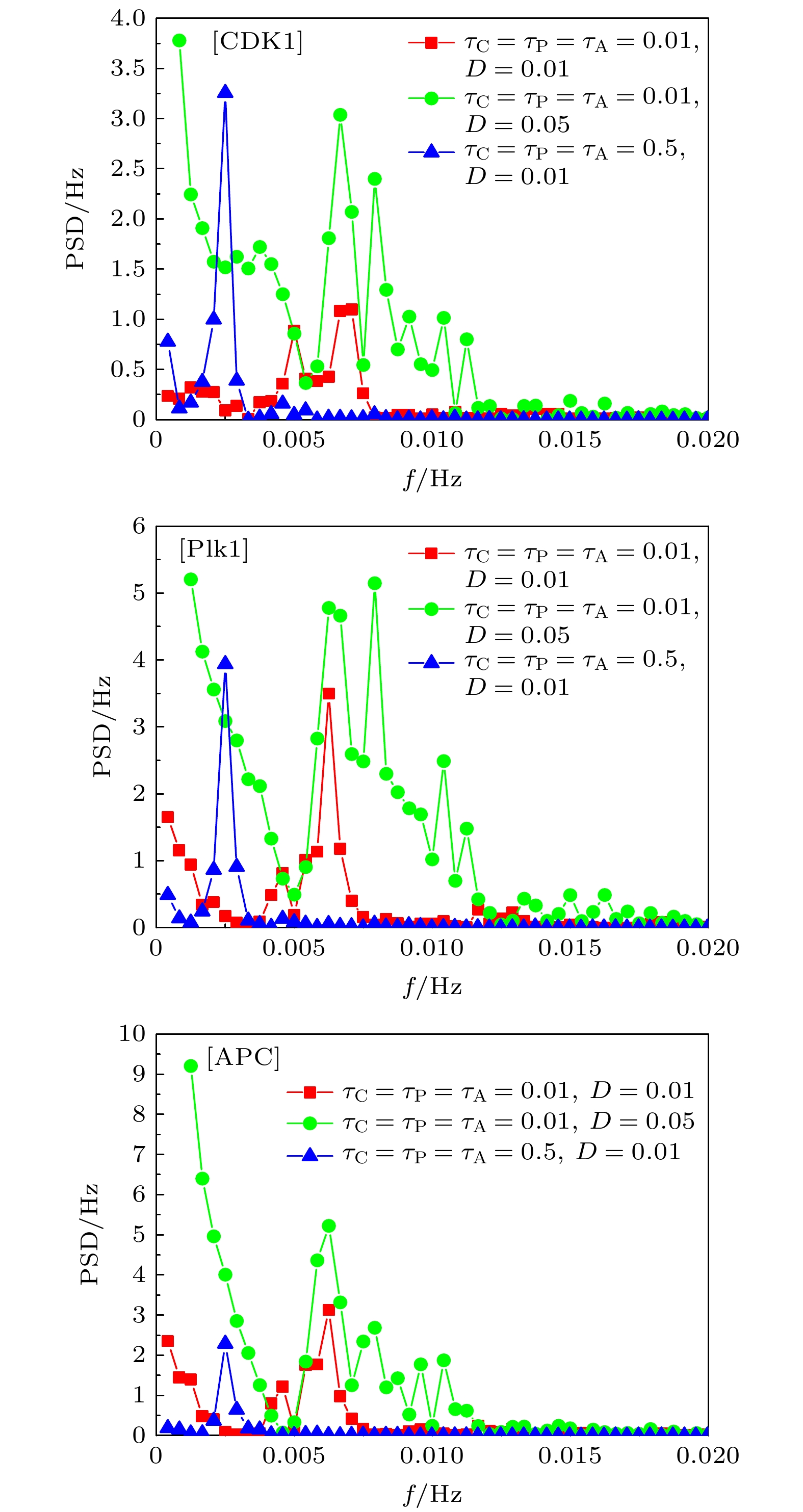
基于Hill动力学与Michaelis-Menten方程, 建立理论模型研究CDK1(细胞周期蛋白依赖性蛋白激酶)/APC(后期促进复合物) 系统振荡过程中, 时间延迟对系统振荡动力学的影响. 理论模型考虑CDK1-Plk1 (Polo样蛋白质激酶)-APC通路中的时间延迟效应, 研究发现, 在不同时间延迟条件下, CDK1, Plk1和APC随时间演化呈现了周期性振荡特性, 表明了细胞周期进程. 随着时间延迟的增加, CDK1, Plk1和APC随时间演化的振荡周期变长、振幅增大, 表明了时间延迟会改变体系的动力学特性. 通过考察在高斯白噪声环境中的时间延迟效应, 研究发现, 噪声扰动明显地改变了CDK1随时间演化的动力学特性. 在较小噪声环境中, CDK1/APC系统通过自调节时间延迟, 改变振幅或振荡周期, 重新自调控, 使系统恢复稳定的周期性振荡. 在较大噪声环境中, CDK1呈现了阻尼振荡模式. 由此表明了较强的噪声, 会使得CDK1/APC系统周期性振荡动力学出现较大改变, 由于时间延迟, CDK1/APC振荡系统表现为从原有的周期性振荡转变为阻尼振荡, 系统原有的振荡模式很难再恢复. 理论结果进一步揭示了诸如非洲爪蟾胚胎等细胞周期过程中的时间延迟效应, 可为设计调控细胞周期、阻断肿瘤转变的通路治疗方案提供理论依据.In this work, based on the Hill dynamics and Michaelis-Menten equation, a theoretical model is built to study the influence of time delay on the oscillation dynamics of a cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1)/ anaphase-promoting complex (APC) system. The theoretical model considers the time delay in the CDK1- polo-like protein kinase (P1K1)-APC pathway. We find that under different time delay conditions, the CDK1, Plk1 and APC exhibit periodic oscillation characteristics over time, indicating cell cycle progression. With the increase of time delay, the oscillation periods and amplitudes of CDK1, Plk1 and APC increase, which indicates that the time delay will change the dynamic characteristics of the system. It implies that during the cell cycle, the status of the CDK1/APC oscillation system will show a long-term correlation with the biochemical reaction time of each component, such as CDK1, Plk1 and APC. This correlation is influenced by its past, and there is a time-delay effect. The additional correction will be made due to time delay. By investigating the time-delay effect in Gaussian white noise environment, we find that in the Gaussian white noise environment, the noise disturbance obviously changes the dynamic characteristics of CDK1 evolution with time. In a low-noise environment, the CDK1/APC system changes the oscillation amplitude or period through self-adjusting time delay, so that the system can restore the stable periodic oscillation, while in a high noise environment, CDK1 exhibits a damped oscillation, indicating that the periodic oscillation dynamics of the CDK1/APC system will be significantly changed by strong noise. In the CDK1/APC system oscillation process, the system adjusts the physiological response through a feedback mechanism. There is a time delay between the perception of the noise effect and the establishment of an appropriate physiological response. By different time delays, the system can adjust complex non-periodic chaotic rhythms with different time delays, and recover to produce a stable periodic physiological process. Owing to the time delay, the CDK1/APC oscillation system changes from the original stable oscillation to a damped oscillation, but the original oscillation mode is difficult to recover. The theoretical results further reveal the time-delay effect in cell cycle processes such as Xenopus embryos, and provide a theoretical basis for designing pathway treatment plans that regulate cell cycle and block tumor transformation.
-
Keywords:
- time delay /
- oscillatory dynamics /
- cell cycle
[1] Hartwell L H, Weinert T A 1989 Science 246 629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Murray A W, Kirschner M W 1989 Nature 339 275
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ben-Sahra I, Howell J J, Asara J M, Manning B D 2013 Science 339 1323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Loh X Y, Sun Q Y, Ding L W, Mayakonda A, Venkatachalam N, Yeo M S, Silva T C, Xiao J F, Doan N B, Said J W, Ran X B, Zhou S Q, Dakle P, Shyamsunder P, Koh A P F, Huang R Y J, Berman B, Tan S Y, Yang H, Lin D C, Koeffler H P 2019 Cancer Res. 80 219
[5] Goldbeter A 2002 Nature 420 238
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Chen K C, Calzone L, Csikasz-Nagy A, Cross F R, Novak B, Tyson J J 2004 Mol. Biol. Cell 15 3841
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Pines J 2011 Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 12 427
[8] Kim S Y, Song E J, Lee K J, Ferrell J E 2005 Mol. Cell Biol. 25 10580
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Murray A W, Kirschner M W 1989 Science 246 614
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Sha W, Moore J, Chen K, Lassaletta A D, Yi C S, Tyson J J, Sible J C 2003 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100 975
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Dasso M, Newport J W 1990 Cell 61 811
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Minshull J, Sun H, Tonks N K, Murray A W 1994 Cell 79 475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Hara K, Tydeman P, Kirschner M 1980 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77 462
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] King R W, Peters J M, Tugendreich S, Rolfe M, Hieter P, Kirschner M W 1995 Cell 81 279
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Gao Z F, Shan H, Wang H 2021 Astron Nachr. 342 369
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Yang Q, Jr J E F 2013 Nat. Cell Biol. 15 518
[17] Doedel E J 1981 Cong. Numer. 30 265
[18] Novak B, Tyson J J 1993 J. Theor. Biol. 165 101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Novak B, Tyson J J 1993 J. Cell Sci. 106 1153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Srividhya J, Gopinathan M S 2006 J. Theor. Biol. 241 617
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ferrell Jr J E, Tsai T Y C, Yang Q 2011 Cell 144 18874
[22] Bae H, Go Y H, Kwon T, Sung B J, Cha H Jin 2019 Pharm. Res. 36 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Seki A, Coppinger J A, Jang C Y, Yates J R, Fang G W 2008 Science 320 1655
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Glass L, Beuter A, Larocque D 1988 Math. Biosci. 90 111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhang C, Du L P, WangT H, Yang T, Zeng C H, Wang C J 2017 Chaos, Solitons & Fractals 96 120
[26] Karamched B R, Bressloff P C 2015 Biophys. J. 108 2408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Steuer R 2004 J. Theor. Biol. 228 293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Kyrychko Y N and Schwartz I B 2018 Chaos 28 063106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] McAdams H H, Arkin A 1999 Trends Gene. 15 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Vilar J M G, Kueh H Y, Barkai N, Leibler S 2002 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99 5988
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Morrison J F, Walsh C T 1988 Adv. Enzymol. Relat. Areas. Mol. Biol. 61 201
[32] Roskoski R, Ritchie P A 2001 Biochemistry 40 9329
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Vodermaier H C 2004 Curr. Biol. 14 R787
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Zitouni S, Nabais C, Jana S C, Guerrero A, Bettencourt-Dias M 2014 Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 15 433
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Glass D S, Jin X F, Riedel-Kruse I H 2021 Nat. Commun. 12 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Huang B, Tian X Y, Liu F, Wang W 2016 Phys. Rev. E 94 052413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Ott W 2008 Comm. Math. Phys. 281 775
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Pomerening J R, Kim S Y, Ferrell J E 2005 Cell 122 565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Lin K K, Young L S 2008 Nonlinearity 21 899
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Kuznetsov A P, Turukina L V, Mosekilde E 2001 Internat. J. Bifur. Chaos Appl. Sci. Engrg. 11 1065
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
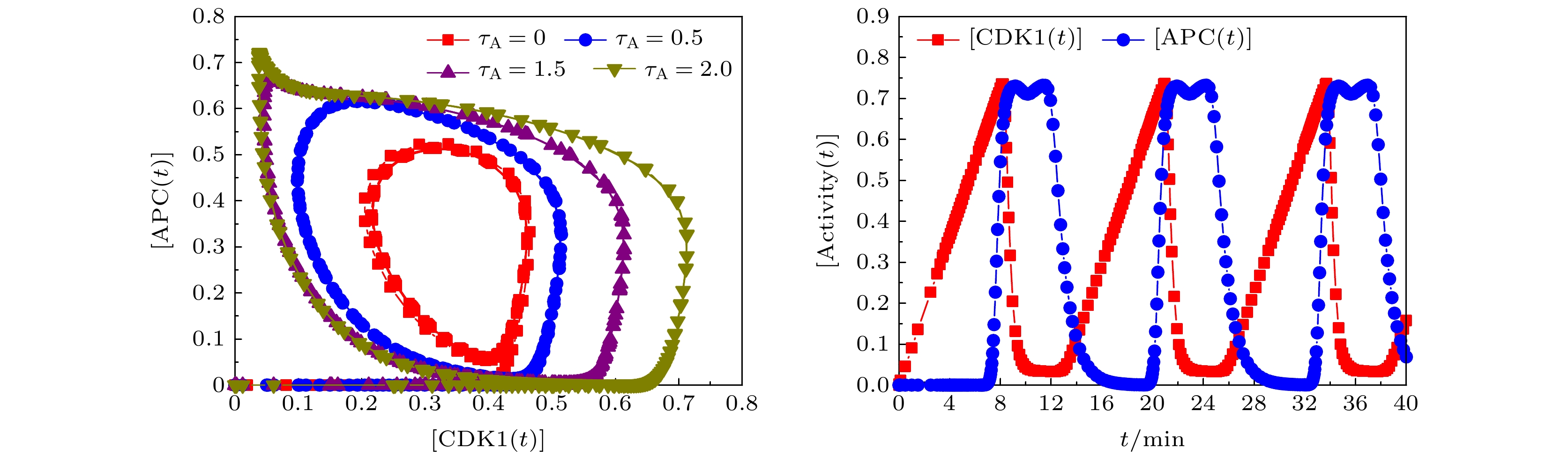
图 4 不同
$ {\tau _{\text{A}}} $ 条件下,$ [{\text{CDK1}}] $ 与$ [{\text{APC}}] $ 对应的相图, 以及$ {\tau _{\text{A}}} = 2.0 $ 时,$ [{\text{CDK1}}] $ 与$ [{\text{APC}}] $ 随时间的演化Fig. 4. Phase plots of
$ [{\text{CDK1}}] $ vs$ [{\text{APC}}] $ different$ {\tau _{\text{A}}} $ , and temporal evolutions of the levels of$ [{\text{CDK1}}] $ and$ [{\text{APC}}] $ for$ {\tau _{\text{A}}} = 2.0 $ . -
[1] Hartwell L H, Weinert T A 1989 Science 246 629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Murray A W, Kirschner M W 1989 Nature 339 275
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ben-Sahra I, Howell J J, Asara J M, Manning B D 2013 Science 339 1323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Loh X Y, Sun Q Y, Ding L W, Mayakonda A, Venkatachalam N, Yeo M S, Silva T C, Xiao J F, Doan N B, Said J W, Ran X B, Zhou S Q, Dakle P, Shyamsunder P, Koh A P F, Huang R Y J, Berman B, Tan S Y, Yang H, Lin D C, Koeffler H P 2019 Cancer Res. 80 219
[5] Goldbeter A 2002 Nature 420 238
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Chen K C, Calzone L, Csikasz-Nagy A, Cross F R, Novak B, Tyson J J 2004 Mol. Biol. Cell 15 3841
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Pines J 2011 Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 12 427
[8] Kim S Y, Song E J, Lee K J, Ferrell J E 2005 Mol. Cell Biol. 25 10580
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Murray A W, Kirschner M W 1989 Science 246 614
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Sha W, Moore J, Chen K, Lassaletta A D, Yi C S, Tyson J J, Sible J C 2003 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100 975
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Dasso M, Newport J W 1990 Cell 61 811
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Minshull J, Sun H, Tonks N K, Murray A W 1994 Cell 79 475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Hara K, Tydeman P, Kirschner M 1980 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77 462
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] King R W, Peters J M, Tugendreich S, Rolfe M, Hieter P, Kirschner M W 1995 Cell 81 279
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Gao Z F, Shan H, Wang H 2021 Astron Nachr. 342 369
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Yang Q, Jr J E F 2013 Nat. Cell Biol. 15 518
[17] Doedel E J 1981 Cong. Numer. 30 265
[18] Novak B, Tyson J J 1993 J. Theor. Biol. 165 101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Novak B, Tyson J J 1993 J. Cell Sci. 106 1153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Srividhya J, Gopinathan M S 2006 J. Theor. Biol. 241 617
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ferrell Jr J E, Tsai T Y C, Yang Q 2011 Cell 144 18874
[22] Bae H, Go Y H, Kwon T, Sung B J, Cha H Jin 2019 Pharm. Res. 36 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Seki A, Coppinger J A, Jang C Y, Yates J R, Fang G W 2008 Science 320 1655
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Glass L, Beuter A, Larocque D 1988 Math. Biosci. 90 111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhang C, Du L P, WangT H, Yang T, Zeng C H, Wang C J 2017 Chaos, Solitons & Fractals 96 120
[26] Karamched B R, Bressloff P C 2015 Biophys. J. 108 2408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Steuer R 2004 J. Theor. Biol. 228 293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Kyrychko Y N and Schwartz I B 2018 Chaos 28 063106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] McAdams H H, Arkin A 1999 Trends Gene. 15 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Vilar J M G, Kueh H Y, Barkai N, Leibler S 2002 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99 5988
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Morrison J F, Walsh C T 1988 Adv. Enzymol. Relat. Areas. Mol. Biol. 61 201
[32] Roskoski R, Ritchie P A 2001 Biochemistry 40 9329
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Vodermaier H C 2004 Curr. Biol. 14 R787
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Zitouni S, Nabais C, Jana S C, Guerrero A, Bettencourt-Dias M 2014 Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 15 433
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Glass D S, Jin X F, Riedel-Kruse I H 2021 Nat. Commun. 12 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Huang B, Tian X Y, Liu F, Wang W 2016 Phys. Rev. E 94 052413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Ott W 2008 Comm. Math. Phys. 281 775
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Pomerening J R, Kim S Y, Ferrell J E 2005 Cell 122 565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Lin K K, Young L S 2008 Nonlinearity 21 899
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Kuznetsov A P, Turukina L V, Mosekilde E 2001 Internat. J. Bifur. Chaos Appl. Sci. Engrg. 11 1065
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 7166
- PDF下载量: 108
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: