-
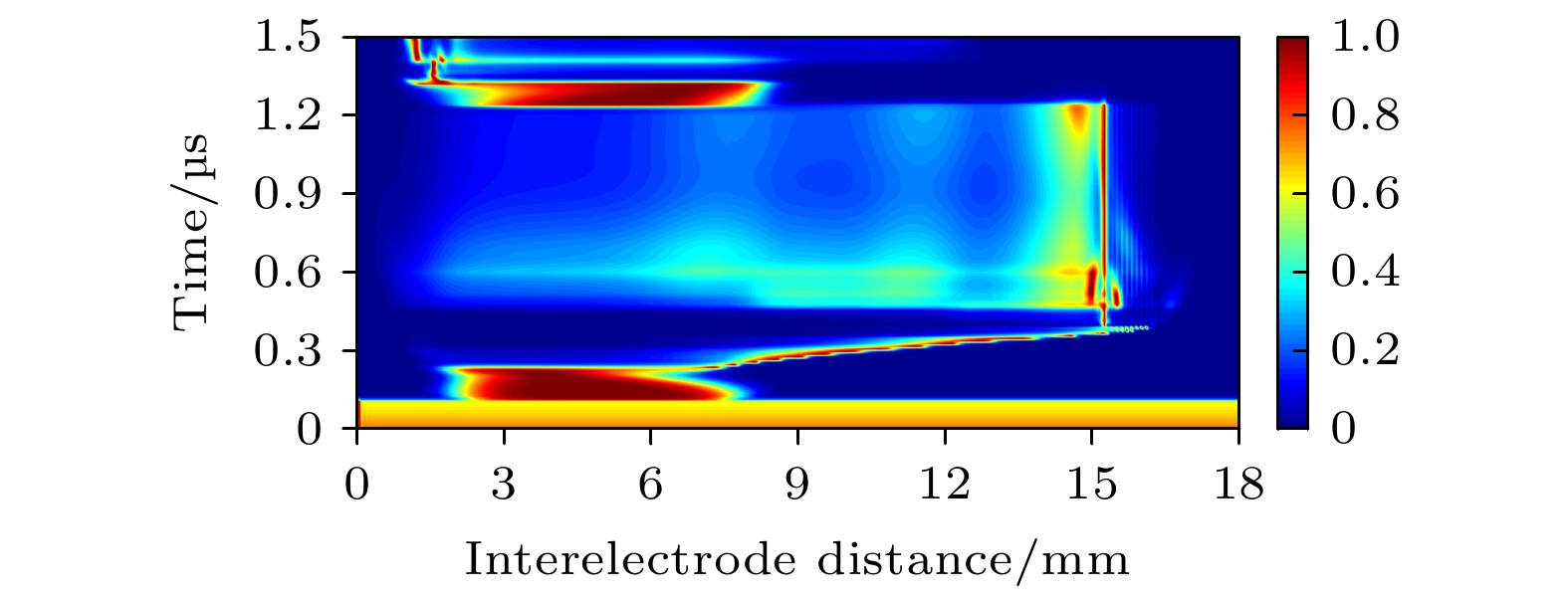
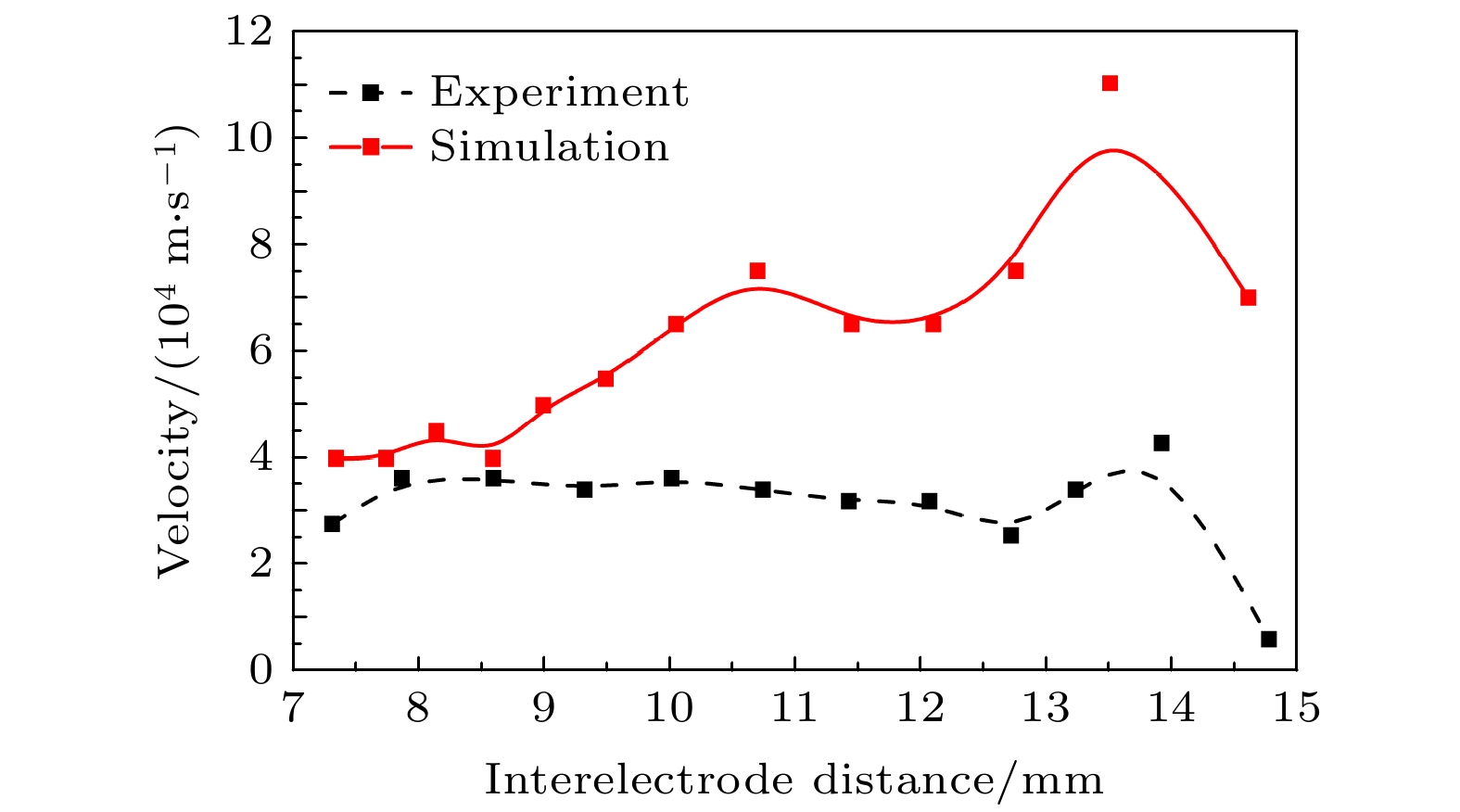
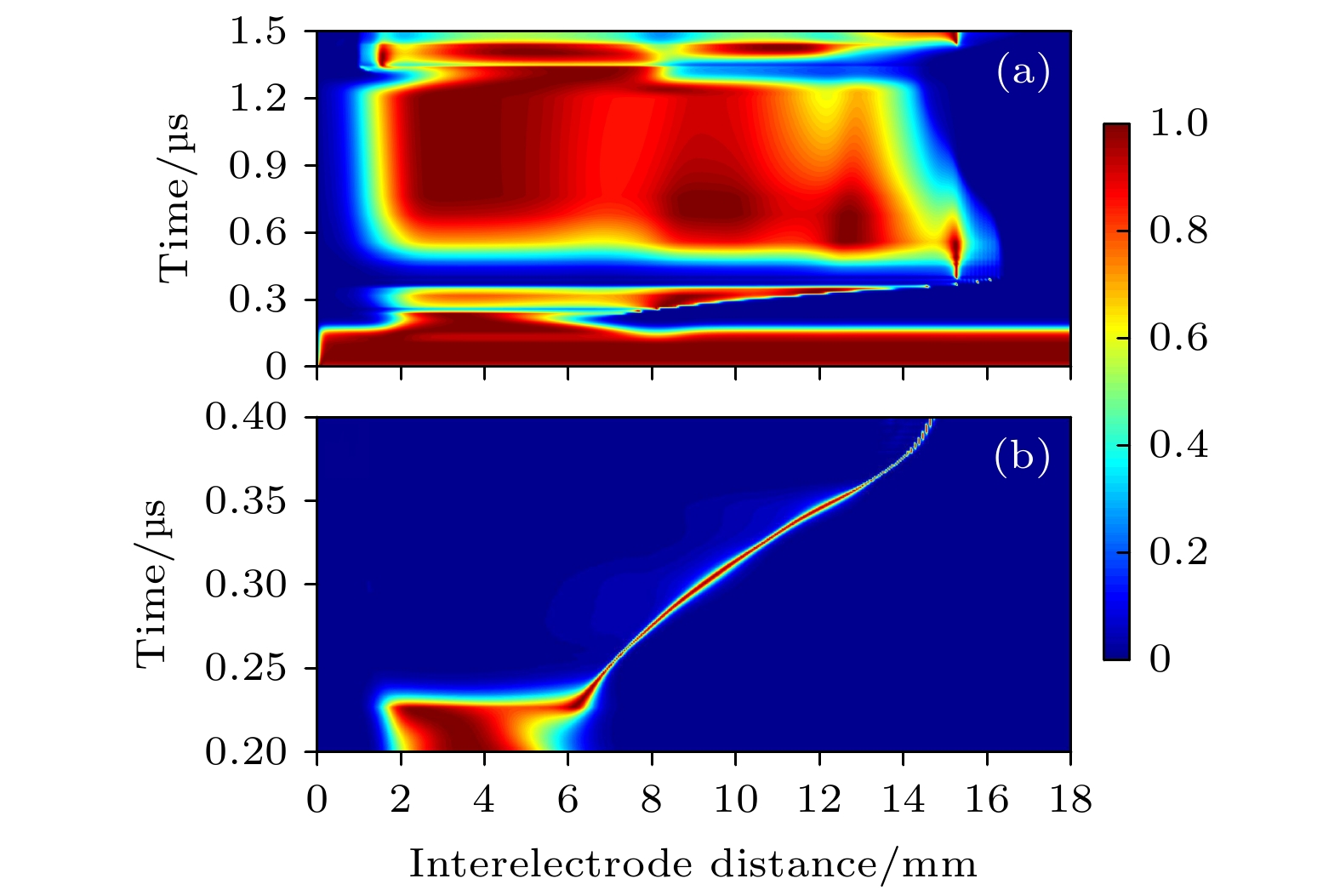
通过实验和数值模拟研究了大气压脉冲放电等离子体射流, 其中在脉冲电压上升沿阶段的放电中形成等离子体子弹并向接地电极输运, 其传播速度在104 m·s–1量级. 数值模拟研究还发现等离子体子弹邻近区域内增强的电场强度可达到106 V·m–1, 说明等离子体子弹的形成主要由放电空间局域增强的电场导致, 在接地电极附近会得到进一步增强. 放电空间的电子密度时空演变过程揭示了等离子体子弹经过的区域会保持较高的电子密度, 说明等离子体子弹的拖尾现象; 而等离子体子弹头部增强的电子产生率与局域增强的电场强度对应, 这说明了等离子体子弹产生的动力学过程. 该大气压脉冲放电等离子体射流中等离子体子弹的特性和机理研究为发展大气压等离子体射流提供了理论和技术基础.Atmospheric pressure plasma plume generated by pulsed discharge is studied by experimental diagnostics and numerical simulations. It is found that the plasma plume is generated in the rising phase of pulse voltage, in which a plasma bullet propagates toward the ground electrode at a speed on the order of 104 m/s. It is also found that the electric field in the vicinity of the plasma bullet reaches 106 V/m, indicating that the formation of plasma bullet can be attributed to the localized enhanced electric field, which will be enhanced near to the grounded electrode. The spatiotemporal evolution of electron density in the discharge reveals that the residual electron density remains after the plasma bullet has passed through, which explains the tailing phenomenon of plasma bullet. The enhanced electron generation rate at the head of plasma bullet corresponds to the localized enhanced electric field, which explains the generation mechanism of plasma bullet. This study of the characteristics and mechanism of plasma bullet provides a theoretical basis for developing the atmospheric plasma plume generated by pulsed discharge.
-
Keywords:
- plasma plume /
- numerical simulation /
- pulsed discharge
[1] Walsh J L, Iza F, Janson N B, Law V J, Kong M G 2010 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 43 075201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Mericam-Bourdet N, Laroussi M, Begum A, Karakas E 2009 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 42 055207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhu P, Meng Z Z, Hu H X, Ouyang J T 2017 Phys. Plasmas 24 103512
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Algwari Q T, O’Connell D 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 99 121501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] O’Neill F T, Twomey B, Law V J, Milosavljevic V, Kong M G, Anghel S D, Dowling D P 2012 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 40 2994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Liu W, Li Z, Ma C, Zhao L 2017 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 50 415201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Lu X, Naidis G V, Laroussi M, Reuter S, Graves D B, Ostrikov K 2016 Phys. Rep. 630 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Deng X L, Nikiforov A Y, Vanraes P, Leys C 2013 J. Appl. Phys. 113 023305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Shaw D, West A, Bredin J, Wagenaars E 2016 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 25 65018
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Nikiforov A Y 2009 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 37 872
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Sun J K, Chung T H 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 20332
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang R X, Zhang C, Shen Y, Zhu W D, Yan P, Shao T, Babaeva N Y, Naidis G V 2015 J. Appl. Phys. 118 123303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Shi J J, Zhong F C, Zhang J 2008 Phys. Plasmas 15 013504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Rong M Z, Xia W J, Wang X H, Liu Z J, Liu D X, Liang Z H, Zhang X N, Kong M G 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 111 074104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Liu Z J, Zhou C X, Liu D X, Xu D H, Xia W J, Cui Q J, Wang B C, Kong M G 2018 Phys. Plasmas 25 013528
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Breden D, Miki K, Raja L L 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 99 111501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hofmans M, Viegas P, Rooij O V, Klarenaar B, Guaitella O, Bourdon A, Sobota A 2020 Appl. Phys. Express 13 086001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Sun Z T, Yan W, Ji L F, Bi Z H, Song Y, Liu D P 2018 Plasma Sci. Technol. 20 085401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Song S T, Guo Y, Choe W, Zhang J, Zhang J, Shi J J 2012 Phys. Plasmas 19 123508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Hagelaar G J M, Pitchford L C 2005 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 14 722
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Sakiyama Y, Graves D B, Stoffels E 2008 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 41 095204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Karakas E, Akman M A, Laroussi M 2012 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 21 034016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Xian Y B, Xu H T, Lu X P, Pei X K, Gong W W, Lu Y, Liu D W, Yang Y 2015 Phys. Plasmas 22 063507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 5 (a) 等离子体子弹在不同位置处的轴向电场强度分布; (b) 等离子体子弹阶段电场强度的时空分布; (c) 等离子体子弹周边典型的电场强度分布
Fig. 5. (a) Spatial profiles of the electric field of plasma bullets at different positions; (b) spatiotemporal evolution of the electric field with the existing of plasma bullet; (c) typical electric field distribution in the domain near the plasma bullet.
表 1 反应方程和速率
Table 1. Elementary reaction and rates.
反应 反应速率 He + e → He* + e $2.308 \times {10^{ - 10} }T_{\rm{e} } ^{0.31}\exp \left( { - \dfrac{ {2.297 \times { {10}^5} } }{ { {T_{\rm{e} } } } } } \right)$/(cm3·s–1) He + e → He+ + 2e $2.584 \times {10^{ - 12} }T_{\rm{e} } ^{0.68}\exp \left( { - \dfrac{ {2.854092 \times { {10}^5} } }{ { {T_{\rm{e} } } } } } \right)$/(cm3·s–1) He* + e → He+ + 2e $4.661 \times {10^{ - 10} }T_{\rm{e} } ^{0.6}\exp \left( { - \dfrac{ {5.546 \times { {10}^4} } }{ { {T_{\rm{e} } } } } } \right)$/(cm3·s–1) ${\rm{He}}_2^+ $ + e → He* + He $5.386 \times {10^{ - 7}}{T_{\rm{e}}}^{ - 0.5}$/(cm3·s–1) He+ + 2He → ${\rm{He}}_2^+ $ + He 1.1 × 10–31/(cm6·s–1) He* + 2He → ${\rm{He}}_2^* $ + He 1.3 × 10–33/(cm6·s–1) He* + e → He + e $1.099 \times {10^{ - 11} }{T_{\rm{e} } ^{0.31}}$/(cm3·s–1) ${\rm{He}}_2^* $ + e →${\rm{He}}_2^+ $ + 2e $1.268 \times {10^{ - 12} }{T_{\rm{e} } ^{0.71}}\exp \left( { - \dfrac{ {3.945 \times { {10}^4} } }{ { {T_{\rm{e} } } } } } \right)$/(cm3·s–1) He* + He* → He+ + He + e $2.7 \times {10^{ - 10}}$/(cm3·s–1) -
[1] Walsh J L, Iza F, Janson N B, Law V J, Kong M G 2010 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 43 075201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Mericam-Bourdet N, Laroussi M, Begum A, Karakas E 2009 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 42 055207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhu P, Meng Z Z, Hu H X, Ouyang J T 2017 Phys. Plasmas 24 103512
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Algwari Q T, O’Connell D 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 99 121501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] O’Neill F T, Twomey B, Law V J, Milosavljevic V, Kong M G, Anghel S D, Dowling D P 2012 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 40 2994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Liu W, Li Z, Ma C, Zhao L 2017 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 50 415201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Lu X, Naidis G V, Laroussi M, Reuter S, Graves D B, Ostrikov K 2016 Phys. Rep. 630 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Deng X L, Nikiforov A Y, Vanraes P, Leys C 2013 J. Appl. Phys. 113 023305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Shaw D, West A, Bredin J, Wagenaars E 2016 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 25 65018
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Nikiforov A Y 2009 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 37 872
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Sun J K, Chung T H 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 20332
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang R X, Zhang C, Shen Y, Zhu W D, Yan P, Shao T, Babaeva N Y, Naidis G V 2015 J. Appl. Phys. 118 123303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Shi J J, Zhong F C, Zhang J 2008 Phys. Plasmas 15 013504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Rong M Z, Xia W J, Wang X H, Liu Z J, Liu D X, Liang Z H, Zhang X N, Kong M G 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 111 074104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Liu Z J, Zhou C X, Liu D X, Xu D H, Xia W J, Cui Q J, Wang B C, Kong M G 2018 Phys. Plasmas 25 013528
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Breden D, Miki K, Raja L L 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 99 111501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hofmans M, Viegas P, Rooij O V, Klarenaar B, Guaitella O, Bourdon A, Sobota A 2020 Appl. Phys. Express 13 086001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Sun Z T, Yan W, Ji L F, Bi Z H, Song Y, Liu D P 2018 Plasma Sci. Technol. 20 085401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Song S T, Guo Y, Choe W, Zhang J, Zhang J, Shi J J 2012 Phys. Plasmas 19 123508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Hagelaar G J M, Pitchford L C 2005 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 14 722
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Sakiyama Y, Graves D B, Stoffels E 2008 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 41 095204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Karakas E, Akman M A, Laroussi M 2012 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 21 034016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Xian Y B, Xu H T, Lu X P, Pei X K, Gong W W, Lu Y, Liu D W, Yang Y 2015 Phys. Plasmas 22 063507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 10026
- PDF下载量: 256
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: