-
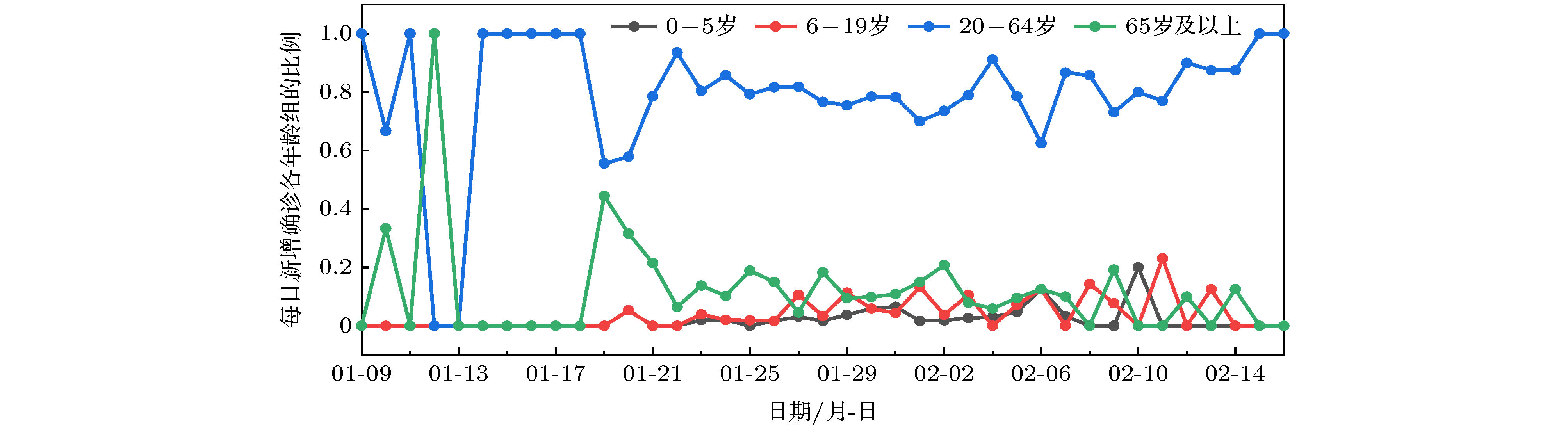
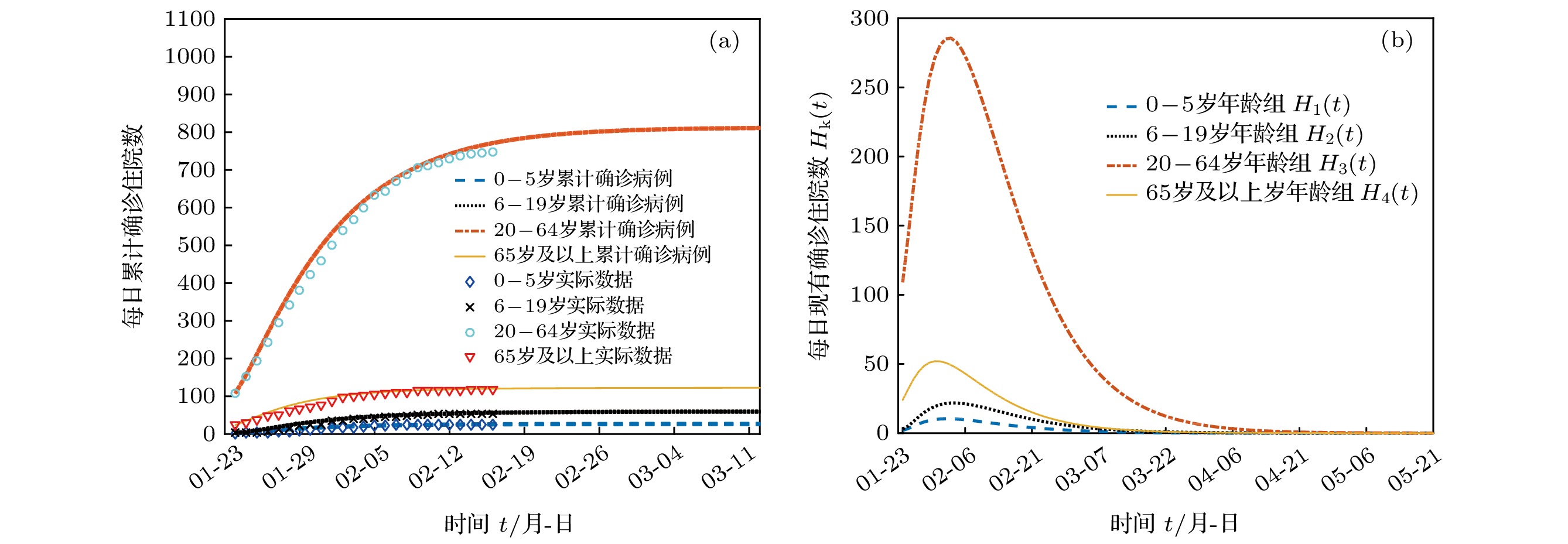
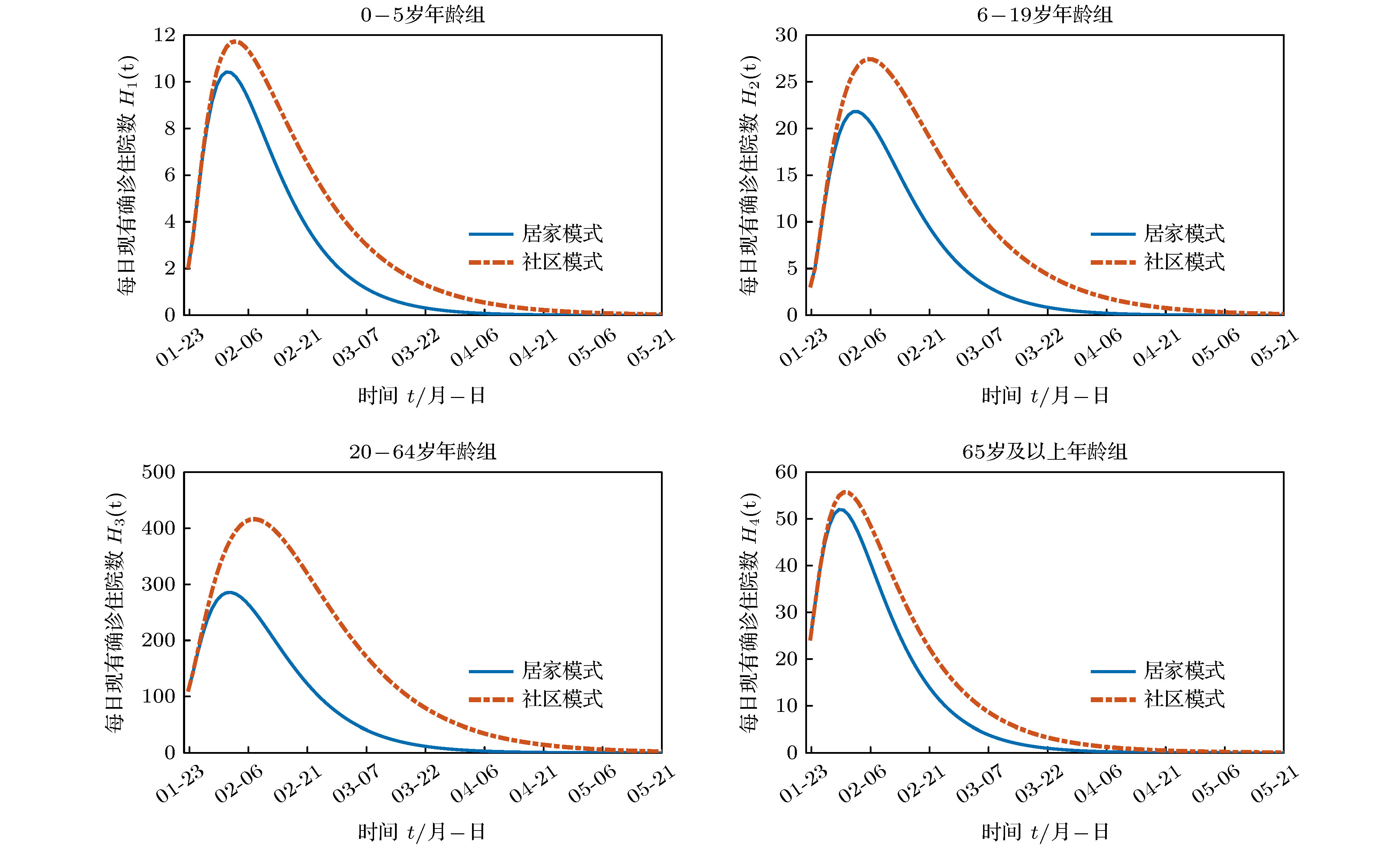
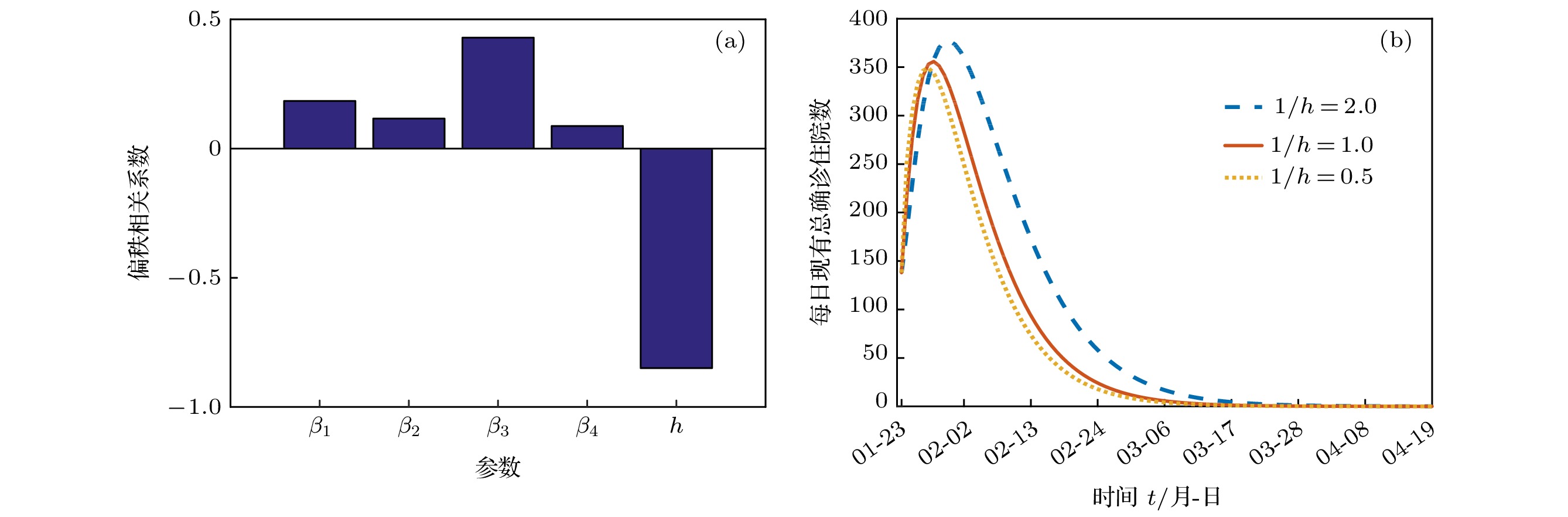
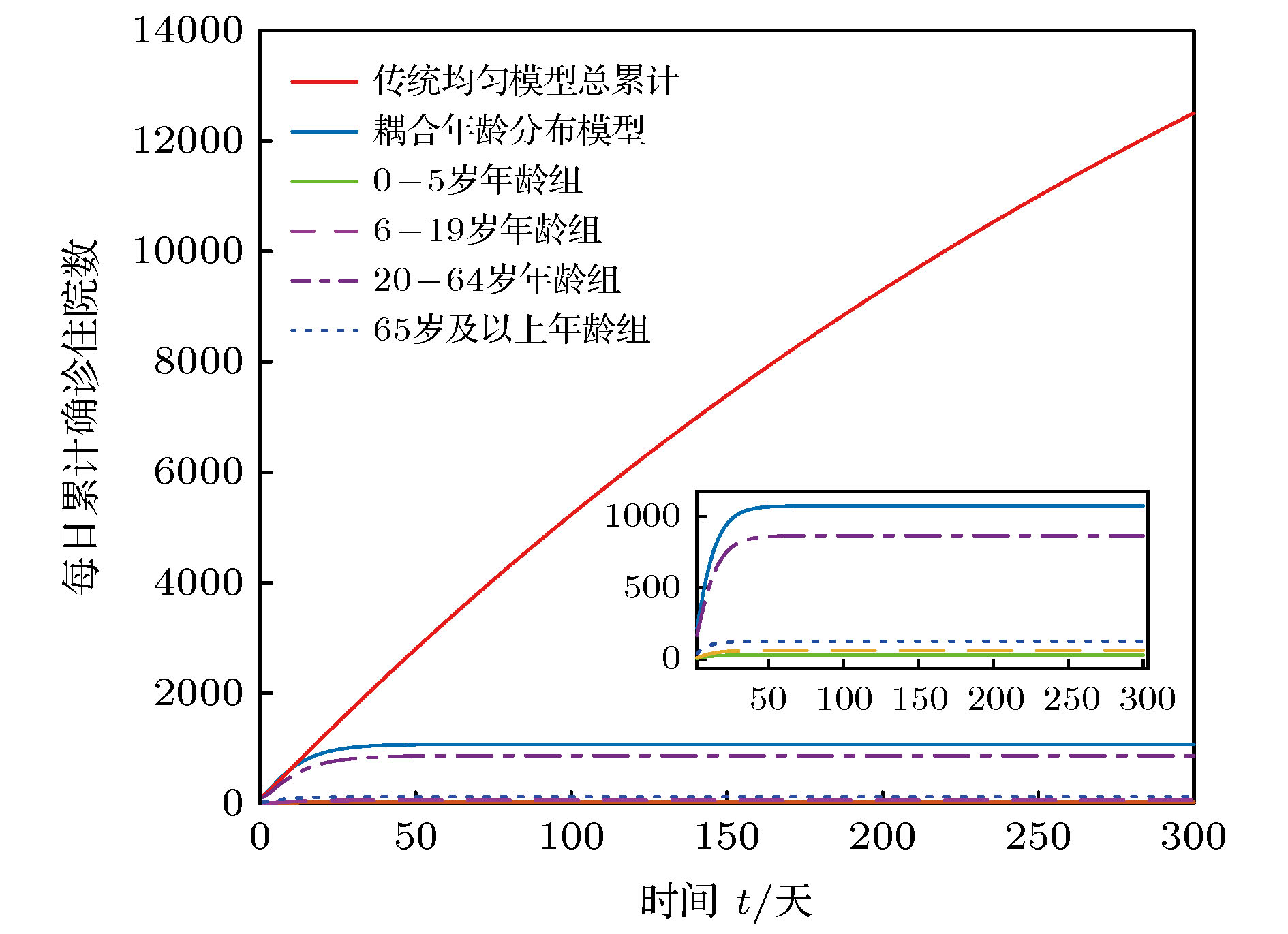
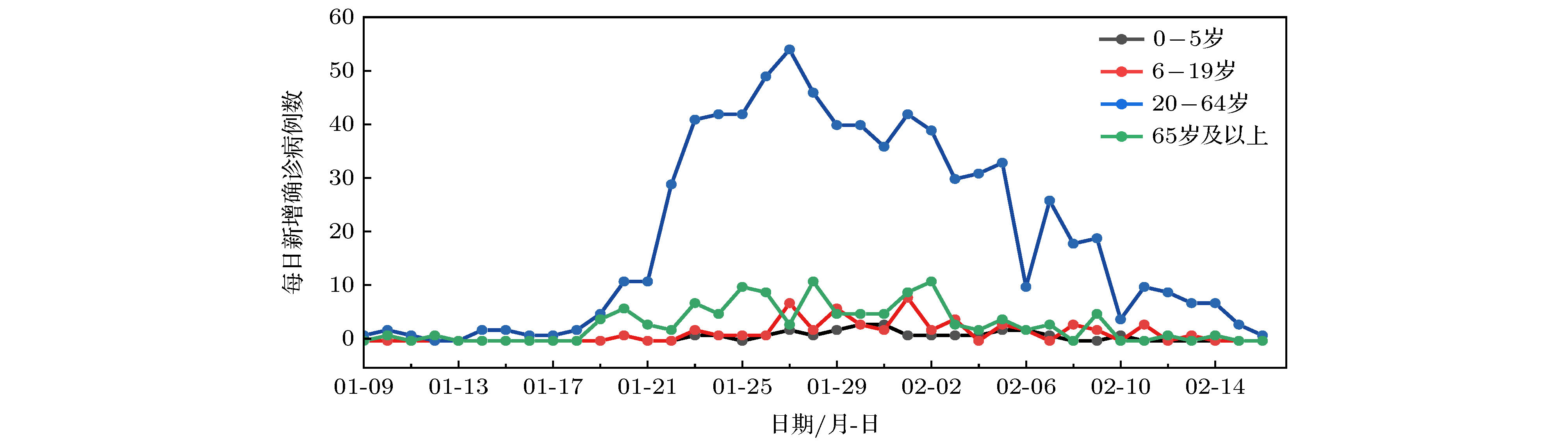
搜集广东省自1月23日到2月16日期间944例新冠肺炎样本信息. 对确诊人群进行年龄特征分析, 将人群分为儿童组(0—5岁)、青少年组(6—19岁)、中青年组(20—64岁)、老年组(65岁及以上), 耦合不同年龄层的接触模式, 建立离散年龄结构新冠肺炎模型, 得出模型的基本再生数及最终规模. 通过蒙特卡罗数值算法(MCMC)辨识模型的参数、拟合累计病例数、计算消亡时间、感染峰值及到达时间等有关生物量. 研究发现中青年人群感染人数最多; 相比于居家模式, 社区模式下中青年人群感染峰值上升41%, 峰值推迟一周到达. 通过分析不同年龄层的最终规模在对应年龄层的占比, 发现老年人的易感性较高, 青少年的易感性相对较低. 在居家模式下, 若各年龄层患者能及时就诊, 住院峰值将进一步减少, 但住院高峰将提前一周到达. 此模型可揭示个体接触行为对新冠肺炎的传播的影响, 定量评价居家隔离措施的有效性.Background: The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has raged more than 10 months and it has become a major public health concern. It is necessary to account for the intrinsic mechanisms and reveal the transmission pattern. Method: We collect detailed information of 944 COVID-19 cases in Guangdong province from January 23rd to February 16th. According to the age-structured characteristics, the population is divided into four groups such as child group (0–5 years old), adolescent group (6–19 years old), young and middle-aged group (20–64 years old), elderly group (65 and over years old). Coupling with different age-structured contact patterns, we establish a discrete age-structured COVID-19 model, obtain the basic reproduction number and final size. By Markov Chain Monte Carlo numerical method (MCMC), we identify the model parameters, fit the cumulative cases, calculate eradiation time of disease, infection peak and the peak arrival time, etc. Results: We found that the most infected people are the young and middle-aged individuals; Compared with household quarantine measure, the peak value of hospitalizations among young and middle-aged group in community mode will increase of 41%, and the peak will delay two weeks. By analyzing the proportions of the final sizes associated age groups, it is found that the elderly have a higher susceptibility, while the adolescents have a lower susceptibility. Under the household quarantine measure, if infected individuals have been confirmed in time of half a day, the peak size of hospitalizations will be further reduced, and the peak hospitalization will advance one week. The model reveals social contact patterns for impacting on COVID-19 transmission, and evaluates the effectiveness of household quarantine.
-
Keywords:
- coronavirus disease 2019 /
- age structured contact pattern /
- Markov Chain Monte Carlo simulation /
- the basic reproduction number
[1] Guangdong Provincial Health Commission. http://www.gd.gov.cn/gdywdt/gdyw/content/post_2878982.html/ [2020-01-24]
[2] Ankarali H, Ankarali S, Caskurlu H 2020 Asia-Pac. J. Public Health 32 157
[3] 金启轩 2020 统计与决策 36 11
Jin Q X 2020 Statistics & Decision 36 11
[4] 张琳 2020 电子科技大学学报 49 345
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang L 2020 J. Univ. Electon. Sci. Technol. China 49 345
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 曹文静, 刘小菲, 韩卓, 冯鑫, 张琳, 刘肖凡, 许小可, 吴晔 2020 69 090203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cao W J, Liu X F, Han Z, Feng X, Zhang L, Liu X F, Xu X K, Wu Y 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 090203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 李盈科, 赵时, 楼一均, 高道舟, 杨琳, 何岱海 2020 69 090202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y K, Zhao S, Lou Y J, Gao D Z, Yang L, He D H 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 090202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yang J Y, Wang G Q, Zhang S 2020 Math. Biol. Eng. 17 4500
[8] Tang B, Wang X, Qian L, Nicola L B, Tang S Y, Xiao Y N, Wu J H 2020 J. Clin. Med. 9 462
[9] 白媛 2017 博士学位论文 (长春: 吉林大学)
Bai Y 2017 Ph. D. Dissertation (Changchun: Jilin University) (in Chinese)
[10] Prem K, Alex R, Mark J 2017 PLOS Comput. Biol. 13 e1005697
[11] Li X Z, Yang J Y, Maia M 2020 Age Structured Epidemic Modelling (Switzerland: Springer) p153
[12] Kiesha P, Liu Y, Timothy W R, Adam J K, Rosalind M E, Nicholas D 2020 Lancet Public Health 5 e261
[13] Zhao H, Feng Z L 2020 Math. Biosci. 326 108405
[14] Read J M, Lessler J, Riley S, Wang S, et al. 2014 Proc. R. Soc. B 281 20140268
[15] The Economic Observer https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1657595901837318521&wfr=spider&for=pc/ [2020-02-04]
[16] Health Commission of Guangdong Province. http://wsjkw.gd.gov.cn/zwyw_yqxx/content/post_2911721.html/ [2020-03-01]
[17] Martcheva M 2015 An Introduction to Mathematical Epidemiology (New York: Springer) p104
[18] Van Den Driessche P, Watmough J 2002 Math. Biosci. 180 29
[19] Horn R A, Jonhson C R 1994 Matrix Analysis (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) p534
[20] Lasalle J P 1976 The Stability of Dynamical Systems (Philadelphia: SIAM) p30
[21] 国务院人口普查办公室, 国家统计局人口和就业统计司2012中国2010年人口普查资料-上 (北京: 中国统计出版社) 第265页
Census Office of the State Council, Division of Population and Employment Statistics 2012 Data from China's 2010 population census-on (Beijing: China Statistical Press) p265
[22] Guangdong Statistical Yearbook 2019 http://stats.gd.gov.cn/gdtjnj/content/post_2639622.html/ [2019-09-29]
[23] Li Q, Guan X H, Wu P, Wang X Y, Zhou L, Tong Y Q, Ren R Q, Kathy S M, Leung, Eric H Y L, Jessica Y W, Xing X S, Xiang N J 2020 N. Engl. J. Med. 382 1199
[24] 肖燕妮, 周义仓, 唐三一 2012 生物数学原理 (西安: 西安交通大学出版社) 第213页
Xiao Y N, Zhou Y C, Tang S Y 2012 Principle of Biomathematics (Xi'an: Xi'an Jiaotong University Press) p213
[25] Moghadas S M, Shoukat A, Fitzpatrick M C, et al. 2020 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 117 9122
[26] Zhang J, Litvinova M, Liang Y, et al. 2020 Science 368 1481
-
表 1 参数定义和参数值
Table 1. Parameter definitions and parameter values
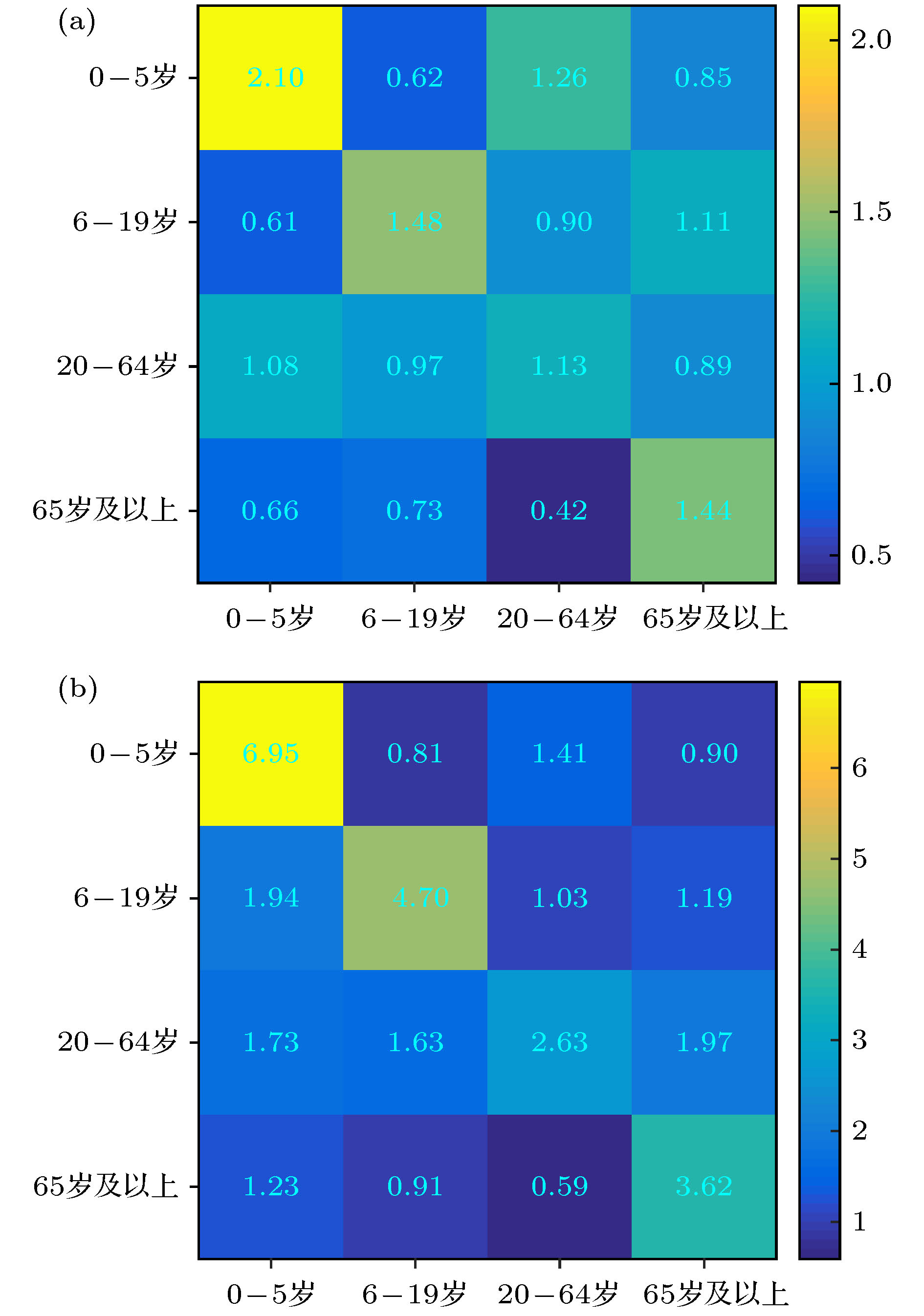
参数 定义 数值 置信区间 数据来源 $\beta_1$ 0—5岁年龄组
感染率0.0164 [0.0163, 0.0165] MCMC $\beta_2$ 6—19岁年龄
组感染率0.0266 [0.0265, 0.0267] MCMC $\beta_3$ 20—64岁年龄
组感染率0.0869 [0.0868, 0.0870] MCMC $\beta_4$ 65岁及以上年
龄组感染率0.0358 [0.0357, 0.0359] MCMC $1/\alpha$ 潜伏期 5.2 — 文献[14] $1/h$ 确诊周期 2.0383 [2.0379, 2.0387] MCMC $1/\gamma$ 康复期 10 — 文献[15] 表 2 变量生物学意义和变量初始值
Table 2. The meaning of variables and initial values
参数 定义 数值 置信区间 数据来源 $S_1(0)$ 初始时刻0—5岁人群
易感者数量7153800 — 表4 $S_2(0)$ 初始时刻6—19岁人
群易感者数量16207482 — 表4 $S_3(0)$ 初始时刻20—64岁
人群易感者数量78760477 — 表4 $S_4(0)$ 初始时刻65岁及以上
人群易感者数量10664042 — 表4 $E_1(0)$ 初始时刻0—5岁
人群潜伏者数量16 [15, 17] MCMC $E_2(0)$ 初始时刻6—19岁
人群潜伏者数量31 [30, 32] MCMC $E_3(0)$ 初始时刻20—64岁
人群潜伏数量317 [316, 318] MCMC $E_4(0)$ 初始时刻65岁及以上
人群潜伏者数量64 [63, 65] MCMC $I_1(0)$ 初始时刻0—5岁人
群染病者数量2 [1, 3] MCMC $I_2(0)$ 初始时刻6—19岁人
群染病者数量2 [1, 3] MCMC $I_3(0)$ 初始时刻20—64岁人
群染病者数量68 [67, 69] MCMC $I_4(0)$ 初始时刻65岁及以上
人群染病者数量17 [16, 18] MCMC $H_1(0)$ 初始时刻0—5岁人
群确诊住院数量2 — 文献[16] $H_2(0)$ 初始时刻6—19岁人
群确诊住院数量3 — 文献[16] $H_3(0)$ 初始时刻20—64岁
人群确诊住院数量109 — 文献[16] $H_4(0)$ 初始时刻65岁及以上
人群确诊住院数量24 — 文献[16] 表 3 2010年广东省各年龄段人口(单位: 1000人)
Table 3. The number of population for each age group of Guangdong province in 2010 (Unit: 1000)
年龄 0 1—4岁 5—9岁 10—14岁 15—19岁 20—24岁 25—29岁 30—34岁 35—39岁 40—44岁 人口 1081 4543 5167 6812 9990 12276 10621 8935 9533 8864 年龄 45—49岁 50—54岁 55—59岁 60—64岁 65—69岁 70—74岁 75—79岁 80—84岁 85岁以上 人口 7047 4899 4399 3066 2168 1911 1494 903 611 表 4 2019年广东省各年龄段人口分布(单位: 人)
Table 4. The number of population for aggregated age groups in Guangdong province in 2019 (unit: person)
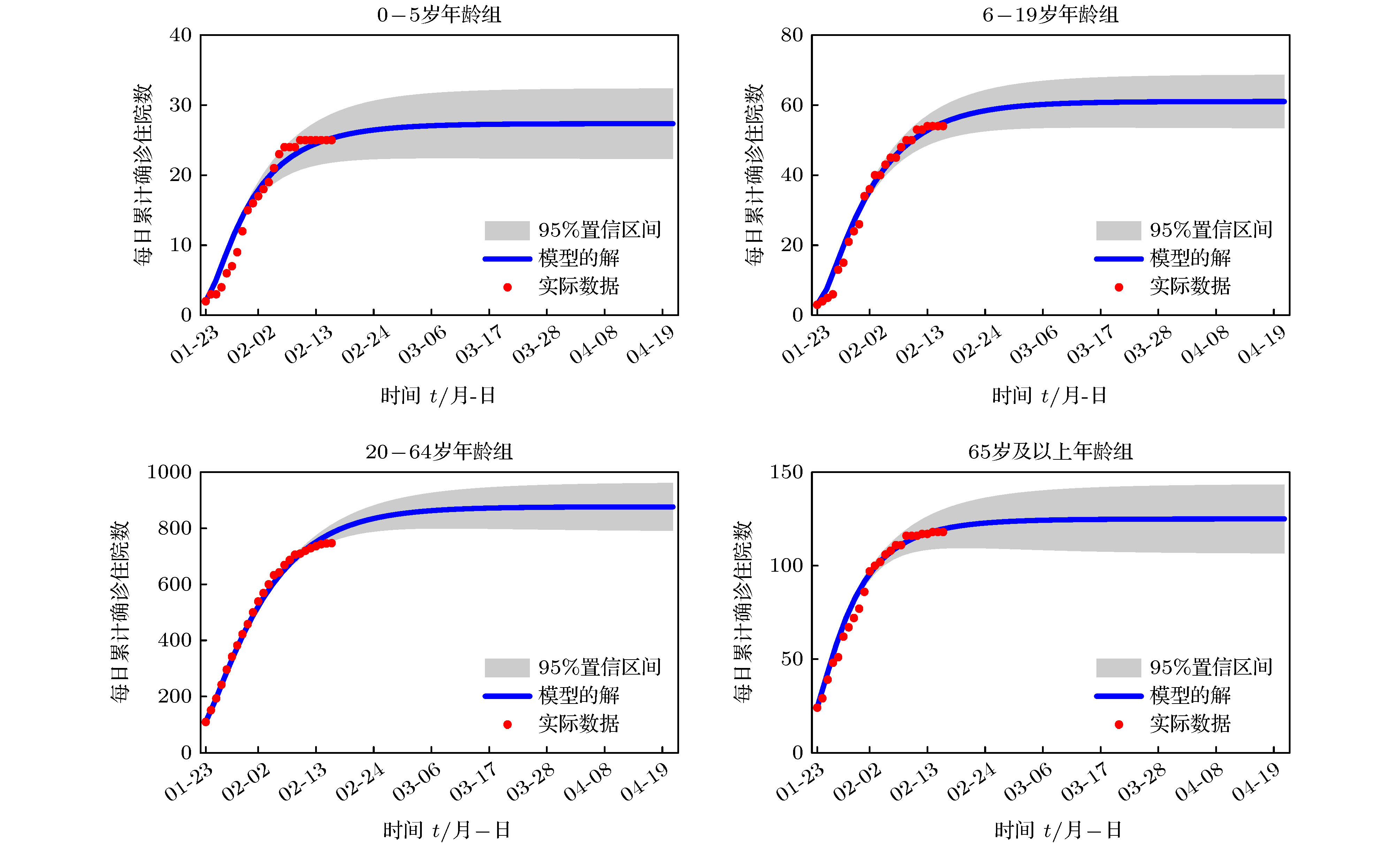
年龄 $N_1$(0—5岁) $N_2$(5—19岁) $N_3$(20—64岁) $N_4$(65岁以上) 人口数 7153800 16207482 78760477 10664042 表 5 拟合结果分析
Table 5. Analysis of fitting results
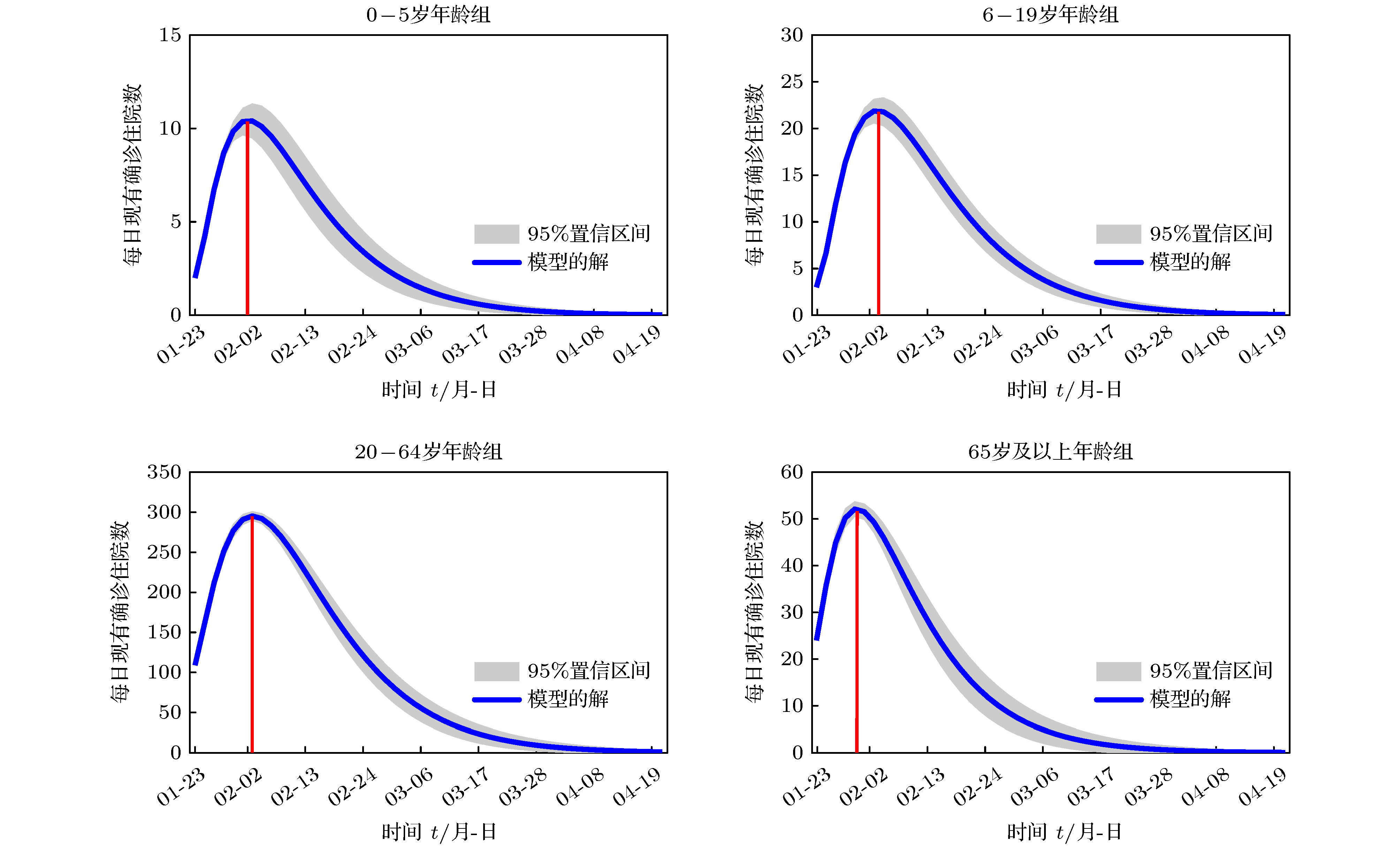
名 称 峰值到达时间 住院峰值/人 最终规模/人 疾病消亡时间 0—5岁年龄组 2月2日 [2月1日, 2月3日] 11 [10, 12] 28 [23, 33] 3月10日 [3月3日, 3月17日] 6—19岁年龄组 2月3日 [2月1日, 2月5日] 21 [20, 23] 61 [54, 69] 3月22日 [3月15日, 3月29日] 20—64岁年龄组 2月3日 [2月2日, 2月4日] 296 [290, 301] 877 [791, 962] 4月22日 [3月31日, 4月30日] 65岁及以上年龄组 1月31日 [1月29日, 2月1日] 52 [50, 54] 125 [107, 144] 3月23日 [3月9日, 4月5日] 表 6 社区模式住院峰值到达时间及峰值
Table 6. Daily peak arrival time and peak values of hospitalized cases in the community mode.
名 称 0—5岁年
龄组6—19岁年
龄组20—64岁
年龄组65岁及以上
年龄组峰值到达时间 2月4日 2月6日 2月8日 2月1日 住院峰值 12 27 417 56 -
[1] Guangdong Provincial Health Commission. http://www.gd.gov.cn/gdywdt/gdyw/content/post_2878982.html/ [2020-01-24]
[2] Ankarali H, Ankarali S, Caskurlu H 2020 Asia-Pac. J. Public Health 32 157
[3] 金启轩 2020 统计与决策 36 11
Jin Q X 2020 Statistics & Decision 36 11
[4] 张琳 2020 电子科技大学学报 49 345
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang L 2020 J. Univ. Electon. Sci. Technol. China 49 345
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 曹文静, 刘小菲, 韩卓, 冯鑫, 张琳, 刘肖凡, 许小可, 吴晔 2020 69 090203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cao W J, Liu X F, Han Z, Feng X, Zhang L, Liu X F, Xu X K, Wu Y 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 090203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 李盈科, 赵时, 楼一均, 高道舟, 杨琳, 何岱海 2020 69 090202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y K, Zhao S, Lou Y J, Gao D Z, Yang L, He D H 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 090202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yang J Y, Wang G Q, Zhang S 2020 Math. Biol. Eng. 17 4500
[8] Tang B, Wang X, Qian L, Nicola L B, Tang S Y, Xiao Y N, Wu J H 2020 J. Clin. Med. 9 462
[9] 白媛 2017 博士学位论文 (长春: 吉林大学)
Bai Y 2017 Ph. D. Dissertation (Changchun: Jilin University) (in Chinese)
[10] Prem K, Alex R, Mark J 2017 PLOS Comput. Biol. 13 e1005697
[11] Li X Z, Yang J Y, Maia M 2020 Age Structured Epidemic Modelling (Switzerland: Springer) p153
[12] Kiesha P, Liu Y, Timothy W R, Adam J K, Rosalind M E, Nicholas D 2020 Lancet Public Health 5 e261
[13] Zhao H, Feng Z L 2020 Math. Biosci. 326 108405
[14] Read J M, Lessler J, Riley S, Wang S, et al. 2014 Proc. R. Soc. B 281 20140268
[15] The Economic Observer https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1657595901837318521&wfr=spider&for=pc/ [2020-02-04]
[16] Health Commission of Guangdong Province. http://wsjkw.gd.gov.cn/zwyw_yqxx/content/post_2911721.html/ [2020-03-01]
[17] Martcheva M 2015 An Introduction to Mathematical Epidemiology (New York: Springer) p104
[18] Van Den Driessche P, Watmough J 2002 Math. Biosci. 180 29
[19] Horn R A, Jonhson C R 1994 Matrix Analysis (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) p534
[20] Lasalle J P 1976 The Stability of Dynamical Systems (Philadelphia: SIAM) p30
[21] 国务院人口普查办公室, 国家统计局人口和就业统计司2012中国2010年人口普查资料-上 (北京: 中国统计出版社) 第265页
Census Office of the State Council, Division of Population and Employment Statistics 2012 Data from China's 2010 population census-on (Beijing: China Statistical Press) p265
[22] Guangdong Statistical Yearbook 2019 http://stats.gd.gov.cn/gdtjnj/content/post_2639622.html/ [2019-09-29]
[23] Li Q, Guan X H, Wu P, Wang X Y, Zhou L, Tong Y Q, Ren R Q, Kathy S M, Leung, Eric H Y L, Jessica Y W, Xing X S, Xiang N J 2020 N. Engl. J. Med. 382 1199
[24] 肖燕妮, 周义仓, 唐三一 2012 生物数学原理 (西安: 西安交通大学出版社) 第213页
Xiao Y N, Zhou Y C, Tang S Y 2012 Principle of Biomathematics (Xi'an: Xi'an Jiaotong University Press) p213
[25] Moghadas S M, Shoukat A, Fitzpatrick M C, et al. 2020 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 117 9122
[26] Zhang J, Litvinova M, Liang Y, et al. 2020 Science 368 1481
计量
- 文章访问数: 14941
- PDF下载量: 262
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: