-
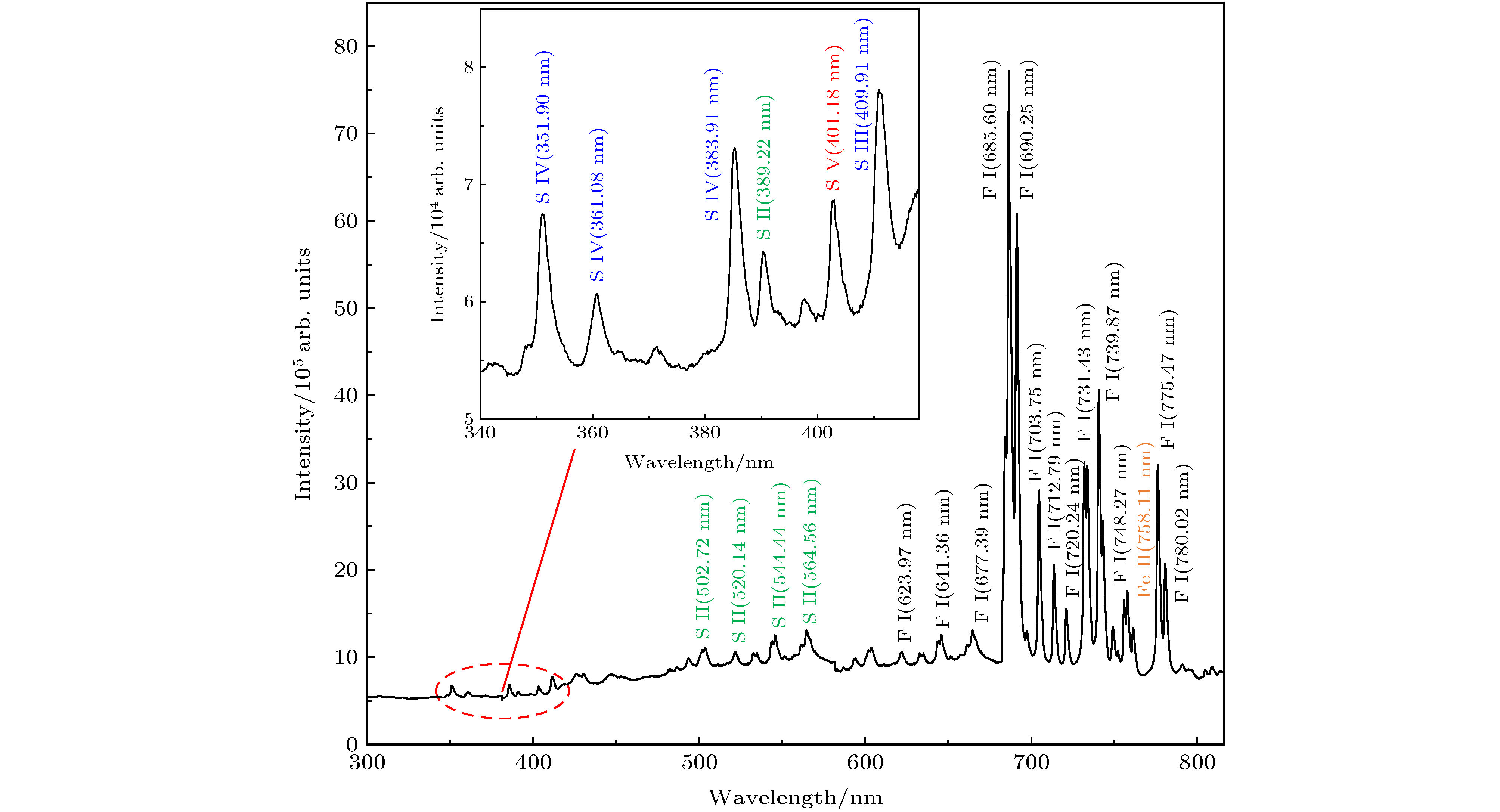
SF6作为气体绝缘介质广泛应用于气体绝缘设备中, 其电弧等离子体得到广泛研究, 但对SF6电弧等离子体时间分辨光谱特性的研究还未见报道. 本文在SF6环境中利用飞秒激光自聚焦产生的光丝引导高压放电, 诱导产生SF6等离子体; 利用光谱系统采集300—820 nm波长范围内的SF6等离子体光谱, 对光谱谱线开展了识别和归属研究, S和F谱线主要分布在300—550 nm和600—800 nm波段, 分析认为S和F原子主要由SF6被高能电子碰撞直接或间接产生, S离子由S原子被高能电子撞击产生. 给出了SF6等离子体的时间分辨光谱, 等离子体光谱强度先增大后减弱, 均由带状光谱和分立光谱叠加而成, 带状光谱主要是由轫致辐射和复合辐射共同作用导致, 基于时间分辨光谱得到了部分S和F的荧光寿命. 给出了电子温度和电子密度随时间的演化规律, 二者演化规律基本相同, 且都随延迟时间呈指数衰减. 最后, 利用Mc Whirter准则得到SF6等离子体处于局部热平衡. 研究结果对于开展SF6分解机理和高压设备运行状态在线监测技术研究具有重要意义.
-
关键词:
- 飞秒激光引导高压放电 /
- 时间分辨光谱 /
- 电子温度和密度 /
- SF6
SF6 is widely used in gas insulated switchgear due to its excellent insulating and arcing performance. SF6 arc plasma has been extensively studied, but time-resolved spectral characteristics of SF6 arc plasma have not been reported. In this paper, the optical filament generated from focused femtosecond laser is used to guide the high-voltage discharge for generating SF6 plasma in SF6 environment. The SF6 plasma spectrum is obtained in a wavelength range of 300–820 nm, and the identification and attribution of the spectral lines are investigated. The S and F lines are mainly in the 300–550 nm band and 600–800 nm band, respectively. The analysis shows that the S and F atoms are mainly directly or indirectly generated by the collision between SF6 and high-energy electrons during the SF6 decomposition caused by discharge. The S ions are generated by the collision of S atoms with high-energy electrons. The time-resolved spectrum of the SF6 plasma superimposed by the continuous spectrum and the line spectrum is given, and its intensity increases and then decreases. The continuous spectrum is mainly generated by the combined effect of bremsstrahlung and recombination radiation. The recombination radiation is mainly generated by the collision of electron with ions and the recombination between molecular and atoms after SF6 decomposition. The fluorescence lifetime of S ion at 409.91 nm is 57 ns, and the fluorescence lifetime of F atom at 685.60 nm is 341 ns. The evolution law of electron temperature and density with time are given. The electron temperature reaches 2047 K in the early stage of plasma formation. After that, the electron temperature quickly falls to about 1600 K within 300 ns due to the rapid expansion of the plasma and the increase in energy loss during electron movement. At the beginning of discharge, a large number of electrons are generated due to the rapid decomposition of SF6, and the electron density is highest ($ 10.1 \times {10^{17}}\;{\rm{c}}{{\rm{m}}^{ - {\rm{3}}}}$ ). After that, the electron density drops rapidly within 200 ns because the recombination between electrons and ions decreases with delay time. Finally, it is proved that the SF6 plasma is in local thermal equilibrium based on the Mc Whirter criterion. The results are of great significance for studying the decomposition mechanism of SF6 and the on-line monitoring technique of high-voltage equipment.-
Keywords:
- femtosecond laser-guided high-voltage discharge /
- time-resolved spectroscopy /
- electron temperature and density /
- SF6
[1] Cui Z, Zhang X X, Cheng Z, Li Y, Xiao H 2019 Spectroc. Acta Pt. A-Molec. Biomolec. Spectr. 215 187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zhong L P, Ji S C, Wang F, Sun Q Q, Chen S, Liu J, Hai B, Tang L 2019 J. Fluor. Chem. 220 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Tang J, Liu F, Zhang X X, Meng Q H, Zhou J B 2012 IEEE Trns. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 19 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Tang J, Liu F, Meng Q H, Zhang X X, Tao J G 2012 IEEE Trns. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 19 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zeng F P, Tang J, Sun H J, Pan J Y, Yao Q, He J J, Hou X Z 2014 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 21 1462
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Liu K, Ji S C, Zhong L P, Zhu L P 2016 International Conference on Condition Monitoring & Diagnosis Xi’an, China, Septenber 25–28, 2016, p578
[7] Swarbrick, P 1967 Br. J. Appl. Phys. 18 419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Gleizes A, Chervy B, Gonzalez J J 1999 J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 32 2060
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Girard R, Belhaouari J B, Gonzalez J J, Gleizes A 1999 J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 32 2890
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Rat V, André P, Aubreton J, Elchinger M F, Fauchais P, Lefort A 2001 J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 34 2191
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Coll I, Casanovas A M, Vial L, Gleizes A, Casanovas J 2000 J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 33 221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Van Brunt R J, Herron J T 1990 IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. 25 75
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Van Brunt R J, Herron J T 1994 Phys. Scr. 1994 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Gao Q Q, Niu C P, Wang X H, Yang A J, Wu Y, Murphy A B, Rong M Z, Fu X X, Liu J L, Xu Y B 2018 J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 51 295202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Gao Q Q, Wang X H, Yang A J, Niu C P, Rong M Z, Jiao L L, Qing M 2019 Phys. Plasmas 26 033508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Vacquie S, Gleizes A, Kafrouni H 1985 J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 18 2193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 徐建源, 王其平 1987 高压电器 1987 9
Xu J Y, Wang Q P 1987 High Voltage Apparatus 1987 9
[18] 林莘, 李鑫涛, 徐建源, 单长旺 2016 中国电机工程学报 36 301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lin X, Li X T, Xu J Y, Shan C W 2016 Proc. Chin. Soc. Elect. Eng. 36 301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 李学斌, 黄旭, 赵义松, 单长旺, 庚振新, 李鑫涛, 林莘 2016 高压电器 52 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X B, Huang X, Zhao Y S, Shan C W, Geng Z X, Li X T, Lin X 2016 High Voltage Apparatus 52 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 庚振新, 石岩, 钟建英, 林莘, 苏镇西, 张友鹏, 徐建源 2017 高压电器 53 18
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Geng Z X, Shi Y, Zhong J Y, Lin X, Su Z X, Zhang Y P, Xu J Y 2017 High Voltage Apparatus 53 18
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 刘玉峰, 丁艳军, 彭志敏, 黄宇, 杜艳君 2014 63 205205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y F, Ding Y J, Peng Z M, Huang Y, Du Y J 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 205205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Eschlböck-Fuchs S, Kolmhofer P J, Bodea M A, Hechenberger J G, Huber N, Rössler R, Pedarniga J D 2015 Spectroc. Acta Pt. B-Atom. Spectr. 109 31
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 王飞鸣, 林莘, 徐建源 2014 高电压技术 40 3073
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang F M, Lin X, Xu J Y 2014 High Voltage Engineering 40 3073
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 刘家合, 鲁佳哲, 雷俊杰, 高勋, 林景全 2020 69 057401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu J H, Lu J Z, Lei J J, Gao X, Lin J Q 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 057401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 董丽芳, 冉俊霞, 毛志国 2005 54 2167
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong L F, Ran J X, Mao Z G 2005 Acta Phys. Sin. 54 2167
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Pagano, C, Hafeez, S, Lunney, J G 2009 J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 42 155205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] Cui Z, Zhang X X, Cheng Z, Li Y, Xiao H 2019 Spectroc. Acta Pt. A-Molec. Biomolec. Spectr. 215 187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zhong L P, Ji S C, Wang F, Sun Q Q, Chen S, Liu J, Hai B, Tang L 2019 J. Fluor. Chem. 220 61
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Tang J, Liu F, Zhang X X, Meng Q H, Zhou J B 2012 IEEE Trns. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 19 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Tang J, Liu F, Meng Q H, Zhang X X, Tao J G 2012 IEEE Trns. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 19 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zeng F P, Tang J, Sun H J, Pan J Y, Yao Q, He J J, Hou X Z 2014 IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 21 1462
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Liu K, Ji S C, Zhong L P, Zhu L P 2016 International Conference on Condition Monitoring & Diagnosis Xi’an, China, Septenber 25–28, 2016, p578
[7] Swarbrick, P 1967 Br. J. Appl. Phys. 18 419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Gleizes A, Chervy B, Gonzalez J J 1999 J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 32 2060
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Girard R, Belhaouari J B, Gonzalez J J, Gleizes A 1999 J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 32 2890
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Rat V, André P, Aubreton J, Elchinger M F, Fauchais P, Lefort A 2001 J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 34 2191
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Coll I, Casanovas A M, Vial L, Gleizes A, Casanovas J 2000 J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 33 221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Van Brunt R J, Herron J T 1990 IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. 25 75
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Van Brunt R J, Herron J T 1994 Phys. Scr. 1994 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Gao Q Q, Niu C P, Wang X H, Yang A J, Wu Y, Murphy A B, Rong M Z, Fu X X, Liu J L, Xu Y B 2018 J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 51 295202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Gao Q Q, Wang X H, Yang A J, Niu C P, Rong M Z, Jiao L L, Qing M 2019 Phys. Plasmas 26 033508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Vacquie S, Gleizes A, Kafrouni H 1985 J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 18 2193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 徐建源, 王其平 1987 高压电器 1987 9
Xu J Y, Wang Q P 1987 High Voltage Apparatus 1987 9
[18] 林莘, 李鑫涛, 徐建源, 单长旺 2016 中国电机工程学报 36 301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lin X, Li X T, Xu J Y, Shan C W 2016 Proc. Chin. Soc. Elect. Eng. 36 301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 李学斌, 黄旭, 赵义松, 单长旺, 庚振新, 李鑫涛, 林莘 2016 高压电器 52 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X B, Huang X, Zhao Y S, Shan C W, Geng Z X, Li X T, Lin X 2016 High Voltage Apparatus 52 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 庚振新, 石岩, 钟建英, 林莘, 苏镇西, 张友鹏, 徐建源 2017 高压电器 53 18
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Geng Z X, Shi Y, Zhong J Y, Lin X, Su Z X, Zhang Y P, Xu J Y 2017 High Voltage Apparatus 53 18
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 刘玉峰, 丁艳军, 彭志敏, 黄宇, 杜艳君 2014 63 205205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y F, Ding Y J, Peng Z M, Huang Y, Du Y J 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 205205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Eschlböck-Fuchs S, Kolmhofer P J, Bodea M A, Hechenberger J G, Huber N, Rössler R, Pedarniga J D 2015 Spectroc. Acta Pt. B-Atom. Spectr. 109 31
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 王飞鸣, 林莘, 徐建源 2014 高电压技术 40 3073
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang F M, Lin X, Xu J Y 2014 High Voltage Engineering 40 3073
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 刘家合, 鲁佳哲, 雷俊杰, 高勋, 林景全 2020 69 057401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu J H, Lu J Z, Lei J J, Gao X, Lin J Q 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 057401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 董丽芳, 冉俊霞, 毛志国 2005 54 2167
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong L F, Ran J X, Mao Z G 2005 Acta Phys. Sin. 54 2167
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Pagano, C, Hafeez, S, Lunney, J G 2009 J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 42 155205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 10540
- PDF下载量: 161
- 被引次数: 0















 下载:
下载: