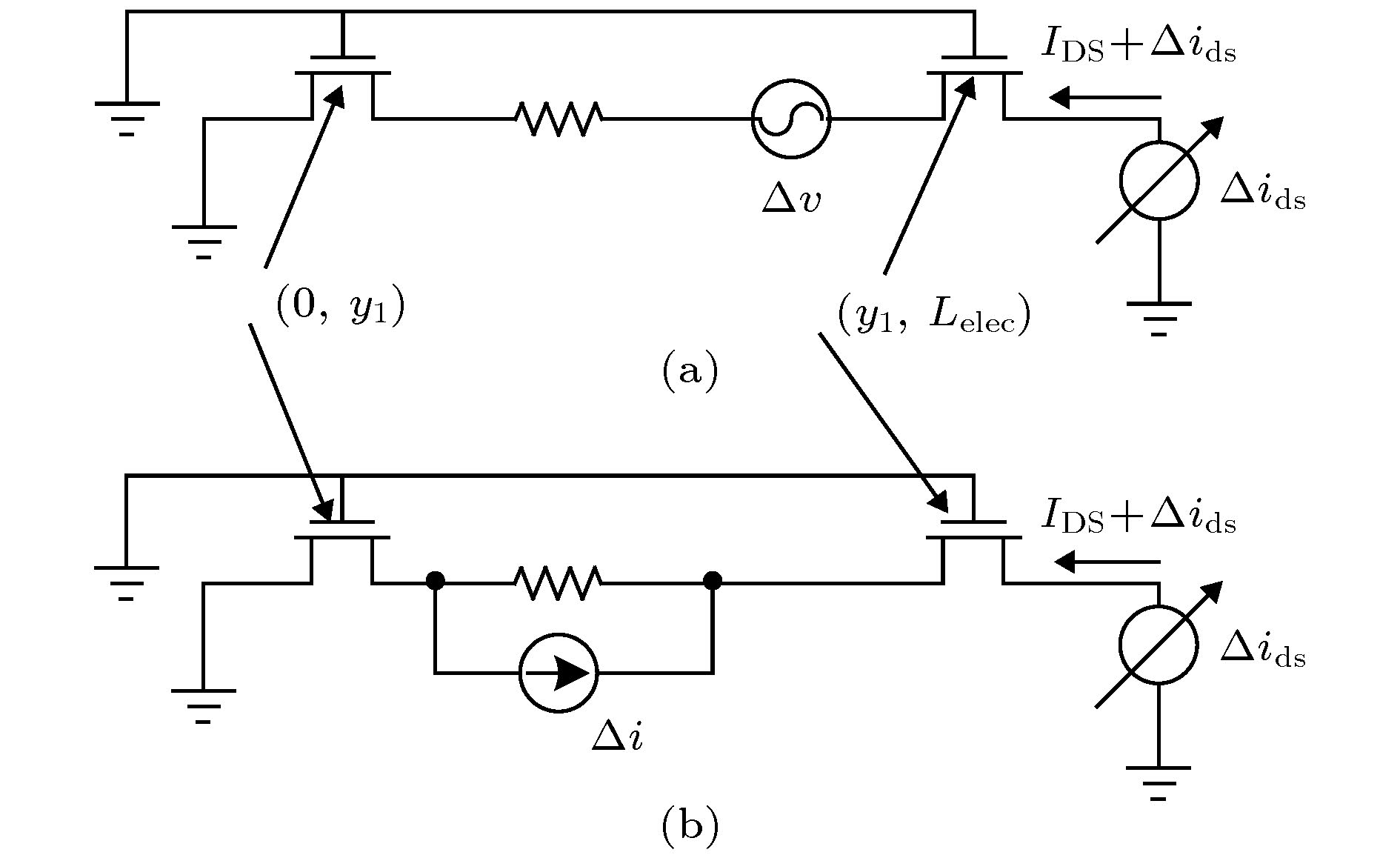
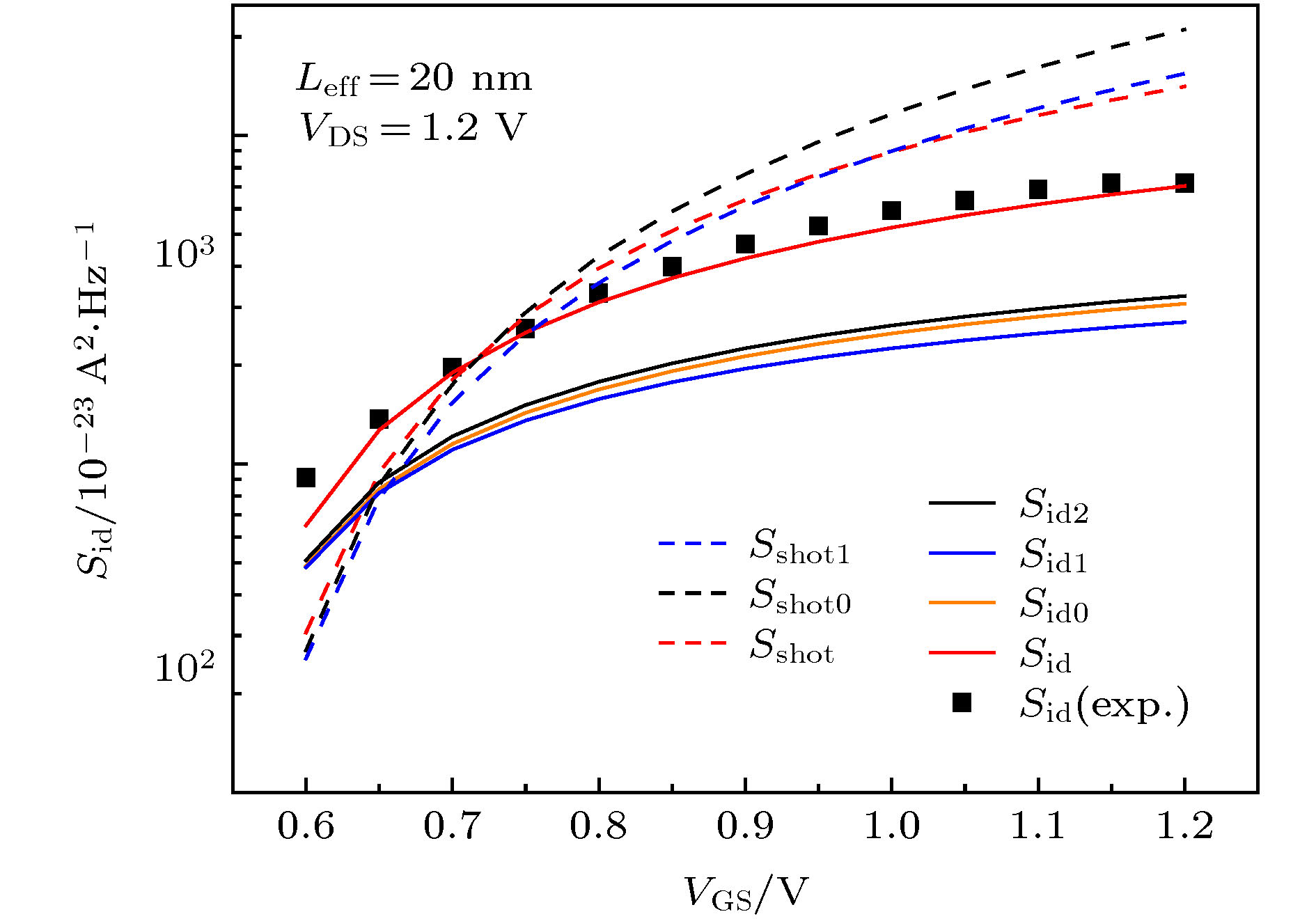
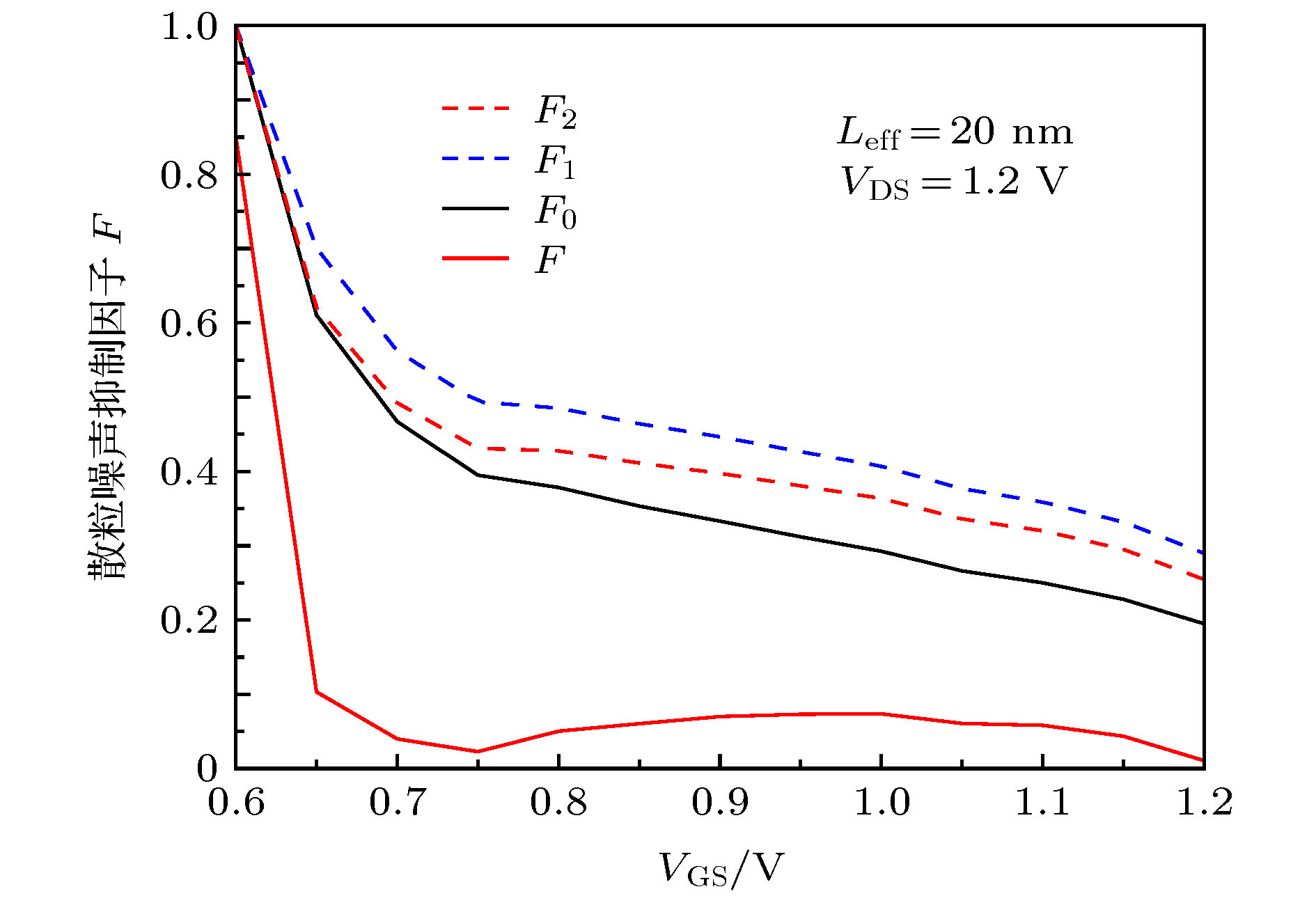
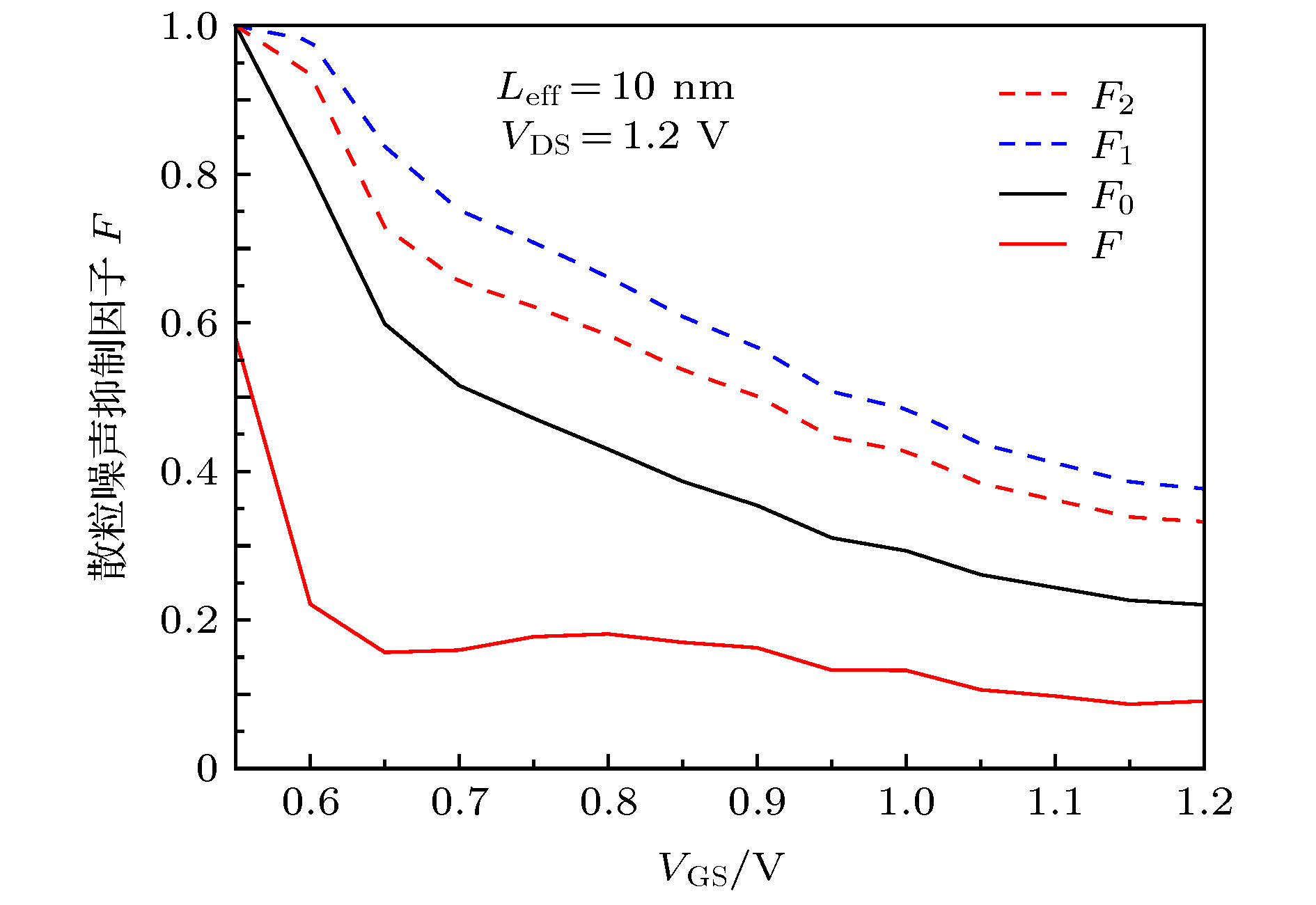
-
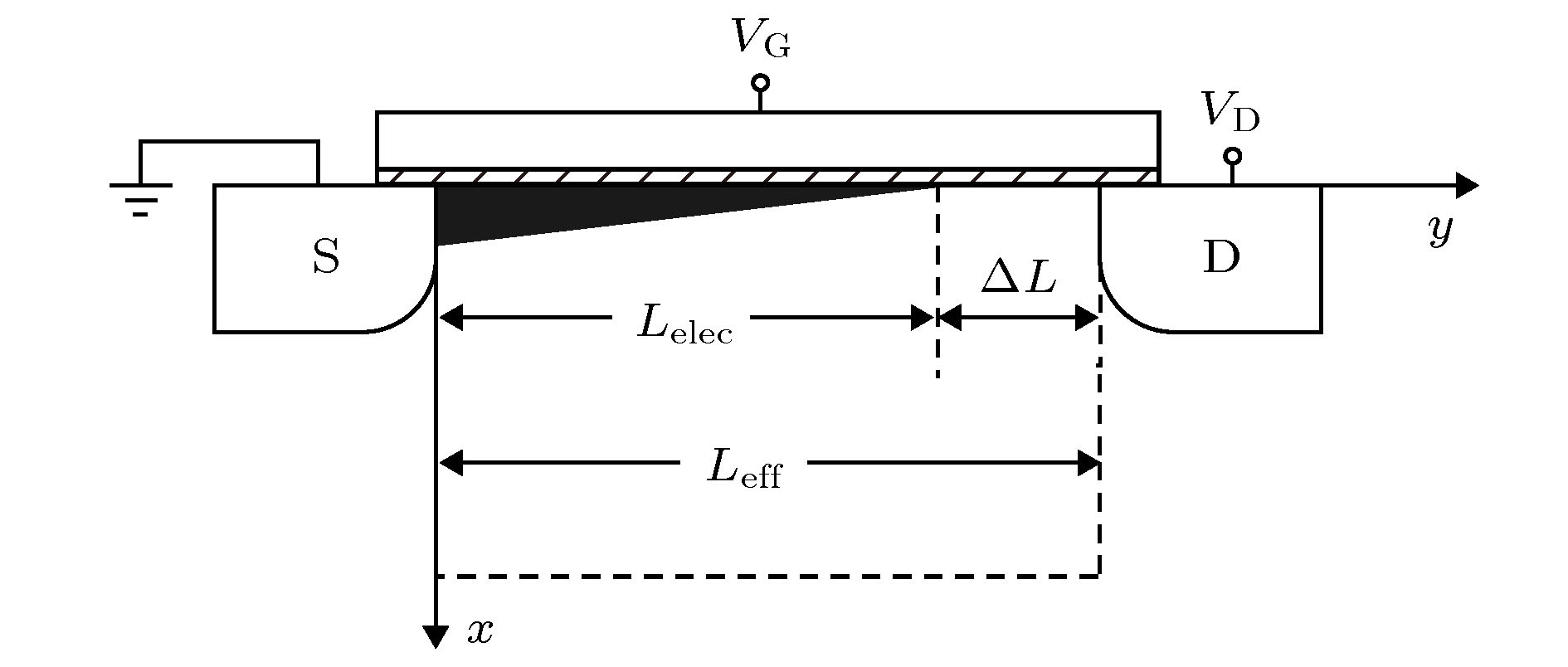
随着金属-氧化物半导体场效应晶体管(MOSFET)器件的尺寸进入到纳米量级, 器件的噪声机理逐渐开始转变. 传统的热噪声与漏源电流模型精度出现下降, 散粒噪声成为器件噪声不可忽略的因素. 本文通过求解能量平衡方程, 推导了短沟道MOSFET器件的沟道电子温度和电子速度表达式, 由此建立了漏源电流模型; 基于漏源电流模型建立了适用于40 nm以下器件的散粒噪声模型和热噪声模型. 研究了n型金属-氧化物半导体场效应晶体管(NMOSFET)器件在不同偏置电压下, 器件尺寸对散粒噪声抑制因子和噪声机理的影响. 研究表明: 已有的热噪声模型与散粒噪声模型的精度随着器件尺寸的减小而下降, 导致相应的散粒噪声抑制因子被高估. 当NMOSFET器件的尺寸减小到10 nm时, 器件的噪声需由热噪声与受抑制的散粒噪声共同表征. 本文建立的短沟道器件散粒噪声模型可应用于纳米尺寸NMOSFET器件噪声性能的分析与建模.
With the development of the semiconductor manufacturing process, the size of the metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) device has been on a tens-of-nanometer scale. The shot noise appears in the excess channel noise of the device, and the noise mechanism of the device begins to change gradually. Due to the fact that the electron temperature gradient is neglected in calculation and the significant enhancement of the lateral channel electric field are not taken into consideration, the traditional electron temperature model and the thermal noise model underestimate the effect of hot carrier effects, resulting in the underestimate of the thermal noise. Moreover, the traditional drain-source current model ignores the electron temperature gradient in the calculation and does not include the effect of the electron temperature on the mobility degradation effect either. Therefore, the calculation accuracy of the shot noise and the Fano factor on the basis of the traditional model will be reduced to a certain extent as the size of the device decreases, thus affecting the analysis of the noise mechanism of the device. In this paper, we establish the channel electron temperature model and the electron velocity model by solving the energy balance equation, and develop the drain source current model based on these two models. Moreover, the shot noise model and the thermal noise model suitable for devices below 40 nm are established based on the drain-source current model. Meanwhile, the Fano factor of the shot noise is calculated. The influence of the MOSFET device size on the noise mechanism and the Fano factor of the shot noise are also investigated when the device is under different bias voltages. The results show that the accuracy of the existing thermal noise model and the shot noise model decline as the device size decreases, which eventually leads the Fano factor of the shot noise to be overestimated. When the size of the NMOSFET device is below 20 nm, the shot noise affects the device noise in the strong inversion region. With the size decreasing, the characteristic of the noise mechanism of the NMOSFET device changes from the characteristic of single thermal noise to the common characteristic of both the thermal noise and the shot noise. When the NMOSFET device size is scaled down to 10 nm, the channel noise of the device can no longer be characterized by the thermal noise alone. Instead, the noise mechanism of the device changes and is characterized by both the channel thermal noise and the suppressed shot noise. The shot noise has become an important factor that contributes to the excessive noise in the device. -
Keywords:
- shot noise /
- Fano factor /
- electron temperature /
- short channel /
- field effect transistor
[1] Scholten A J, Tiemeijer L F, Duijnhoven A T A Z, Havens R J, Kort R, Langevelde R, Klaassen D B M, Jeamsaksiri W, Velghe R M D A 2005 International Conference on Noise and Fluctuations Salamanca, Spain, September 19−23, 2005 p735
[2] 贾晓菲, 杜磊, 唐冬和, 王婷岚, 陈文豪 2012 61 127202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jia X F, Du L, Tang D H, Wang T L, Chen W H 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 127202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Do V A, Dollfus P, Nguyen V L 2007 J. Comput. Electron. 6 125
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Spathis C, Georgakopoulou K, Birbas A 2013 22nd International Conference on Noise and Fluctuations (ICNF) Montpellier, France, June 24−28, 2013 p1
[5] Navid R 2007 J. Appl. Phys. 101 124501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Jia X F, He L 2017 AIP Adv. 7 055202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Teng H F, Jang S L, Juang M H 2003 Solid-State Electron. 47 2043
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Chan L H K, Yeo K S, Chew K W J, Ong S N, Loo X S, Boon C C, Do M A 2012 IEEE Electron Device Lett. 33 1117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 唐冬和, 杜磊, 王婷岚, 陈华, 贾晓菲 2011 60 097202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang D H, Du L, Wang T L, Chen H, Jia X F 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 097202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Jeon J, Kang M 2016 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 55 054102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Jeon J, Lee J, Kim J, Park C H, Lee H, Oh H, Kang H K, Park B G, Shin H 2009 Symposium on VLSI Technology Honolulu, HI, USA, June 15−17, 2009 p48
[12] Smit G D J, Scholten A J, Pijper R M T, Tiemeijer L F, Toorn R V D, Klaassen D B M 2014 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 61 245
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 王军, 王林, 王丹丹 2016 65 237102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J, Wang L, Wang D D 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 237102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang J, Peng X M, Liu Z J, Wang L, Luo Z, Wang D D 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 027201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Mahajan V M, Patalay P R, Jindal R P, Shichijo H, Martin S, Hou F C, Machala C, Trombley D E 2012 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 59 197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Chen X S, Chen C H, Deen M J 2017 International Conference on Noise and Fluctuations (ICNF) Vilnius, Lithuania, June 20−13, 2017 p1
[17] Spathis C, Birbas A, Georgakopoulou K 2015 AIP Adv. 5 087114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang J 2017 Electron. Lett. 53 1671
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Barral V, Poiroux T, Saint-Martin J, Munteanu D, Autran J L, Deleonibus S 2009 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 56 408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Shen Y F, Cui J, Mohammadi S 2017 Solid-State Electron. 131 45
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Chen X S, Chih H C, Ryan L 2018 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 65 1502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Lu Z Q, Lai F C 2009 Analog. Integr. Circ. Process 59 185
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Lee K Y 2017 Solid-State Electron. 130 63
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Chen C H, Deen M J 2002 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 49 1484
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 艾罗拉 N 著 (张兴, 李映雪 译) 1999 用于VLSI模拟的小尺寸MOS器件模型 (北京: 科学出版社) 第248−251页
Arora N (translated by Zhang X, Li Y X) 1999 MOSFET Models for VLSI Circuit Simulation (Beijing: Science Press) pp248−251 (in Chinese)
[26] Lim K Y, Zhou X 2002 Microelectron. Reliab. 42 1857
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Wei C Q, See G H, Zhou X, Chan L 2008 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 55 2378
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Ong S N, Yeo K S, Chew K W J, Chan L H K, Loo X S, Boon C C, Do M A 2012 Solid-State Electron. 68 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Lundstrom M 2009 Fundamentals of Carrier Transport (2nd Ed.) (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) pp230−293
[30] Tsividis Y 2011 Operation and Modeling of the MOS Transistor (3rd Ed.) (New York: Oxford University Press) pp194−201
[31] Ong S N, Yeo K S, Chew K W J, Chan L H K, Loo X S, Boon C C, Do M A 2012 Solid-State Electron. 72 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Paasschens J C J, Scholten A J, van Langevelde R 2005 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 52 2463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Li Z Y, Ma J G, Ye Y Z, Yu M Y 2009 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 56 1300
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] 张梦, 姚若河, 刘玉荣 2020 69 057101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang M, Yao R H, Liu Y R 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 057101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Chen C H, Chen D, Lee R, Lei P, Wan D 2013 Proceedings of the IEEE 2013 Custom Integrated Circuits Conference San Jose, CA, USA, September 22−25, 2013 p1
[36] Yamaguchi K, Sakurai S, Tomizawa K 2010 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 49 024303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] Scholten A J, Tiemeijer L F, Duijnhoven A T A Z, Havens R J, Kort R, Langevelde R, Klaassen D B M, Jeamsaksiri W, Velghe R M D A 2005 International Conference on Noise and Fluctuations Salamanca, Spain, September 19−23, 2005 p735
[2] 贾晓菲, 杜磊, 唐冬和, 王婷岚, 陈文豪 2012 61 127202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jia X F, Du L, Tang D H, Wang T L, Chen W H 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 127202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Do V A, Dollfus P, Nguyen V L 2007 J. Comput. Electron. 6 125
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Spathis C, Georgakopoulou K, Birbas A 2013 22nd International Conference on Noise and Fluctuations (ICNF) Montpellier, France, June 24−28, 2013 p1
[5] Navid R 2007 J. Appl. Phys. 101 124501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Jia X F, He L 2017 AIP Adv. 7 055202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Teng H F, Jang S L, Juang M H 2003 Solid-State Electron. 47 2043
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Chan L H K, Yeo K S, Chew K W J, Ong S N, Loo X S, Boon C C, Do M A 2012 IEEE Electron Device Lett. 33 1117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 唐冬和, 杜磊, 王婷岚, 陈华, 贾晓菲 2011 60 097202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang D H, Du L, Wang T L, Chen H, Jia X F 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 097202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Jeon J, Kang M 2016 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 55 054102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Jeon J, Lee J, Kim J, Park C H, Lee H, Oh H, Kang H K, Park B G, Shin H 2009 Symposium on VLSI Technology Honolulu, HI, USA, June 15−17, 2009 p48
[12] Smit G D J, Scholten A J, Pijper R M T, Tiemeijer L F, Toorn R V D, Klaassen D B M 2014 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 61 245
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 王军, 王林, 王丹丹 2016 65 237102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J, Wang L, Wang D D 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 237102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang J, Peng X M, Liu Z J, Wang L, Luo Z, Wang D D 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 027201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Mahajan V M, Patalay P R, Jindal R P, Shichijo H, Martin S, Hou F C, Machala C, Trombley D E 2012 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 59 197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Chen X S, Chen C H, Deen M J 2017 International Conference on Noise and Fluctuations (ICNF) Vilnius, Lithuania, June 20−13, 2017 p1
[17] Spathis C, Birbas A, Georgakopoulou K 2015 AIP Adv. 5 087114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang J 2017 Electron. Lett. 53 1671
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Barral V, Poiroux T, Saint-Martin J, Munteanu D, Autran J L, Deleonibus S 2009 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 56 408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Shen Y F, Cui J, Mohammadi S 2017 Solid-State Electron. 131 45
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Chen X S, Chih H C, Ryan L 2018 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 65 1502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Lu Z Q, Lai F C 2009 Analog. Integr. Circ. Process 59 185
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Lee K Y 2017 Solid-State Electron. 130 63
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Chen C H, Deen M J 2002 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 49 1484
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 艾罗拉 N 著 (张兴, 李映雪 译) 1999 用于VLSI模拟的小尺寸MOS器件模型 (北京: 科学出版社) 第248−251页
Arora N (translated by Zhang X, Li Y X) 1999 MOSFET Models for VLSI Circuit Simulation (Beijing: Science Press) pp248−251 (in Chinese)
[26] Lim K Y, Zhou X 2002 Microelectron. Reliab. 42 1857
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Wei C Q, See G H, Zhou X, Chan L 2008 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 55 2378
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Ong S N, Yeo K S, Chew K W J, Chan L H K, Loo X S, Boon C C, Do M A 2012 Solid-State Electron. 68 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Lundstrom M 2009 Fundamentals of Carrier Transport (2nd Ed.) (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) pp230−293
[30] Tsividis Y 2011 Operation and Modeling of the MOS Transistor (3rd Ed.) (New York: Oxford University Press) pp194−201
[31] Ong S N, Yeo K S, Chew K W J, Chan L H K, Loo X S, Boon C C, Do M A 2012 Solid-State Electron. 72 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Paasschens J C J, Scholten A J, van Langevelde R 2005 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 52 2463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Li Z Y, Ma J G, Ye Y Z, Yu M Y 2009 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 56 1300
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] 张梦, 姚若河, 刘玉荣 2020 69 057101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang M, Yao R H, Liu Y R 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 057101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Chen C H, Chen D, Lee R, Lei P, Wan D 2013 Proceedings of the IEEE 2013 Custom Integrated Circuits Conference San Jose, CA, USA, September 22−25, 2013 p1
[36] Yamaguchi K, Sakurai S, Tomizawa K 2010 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 49 024303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 11838
- PDF下载量: 157
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: