-
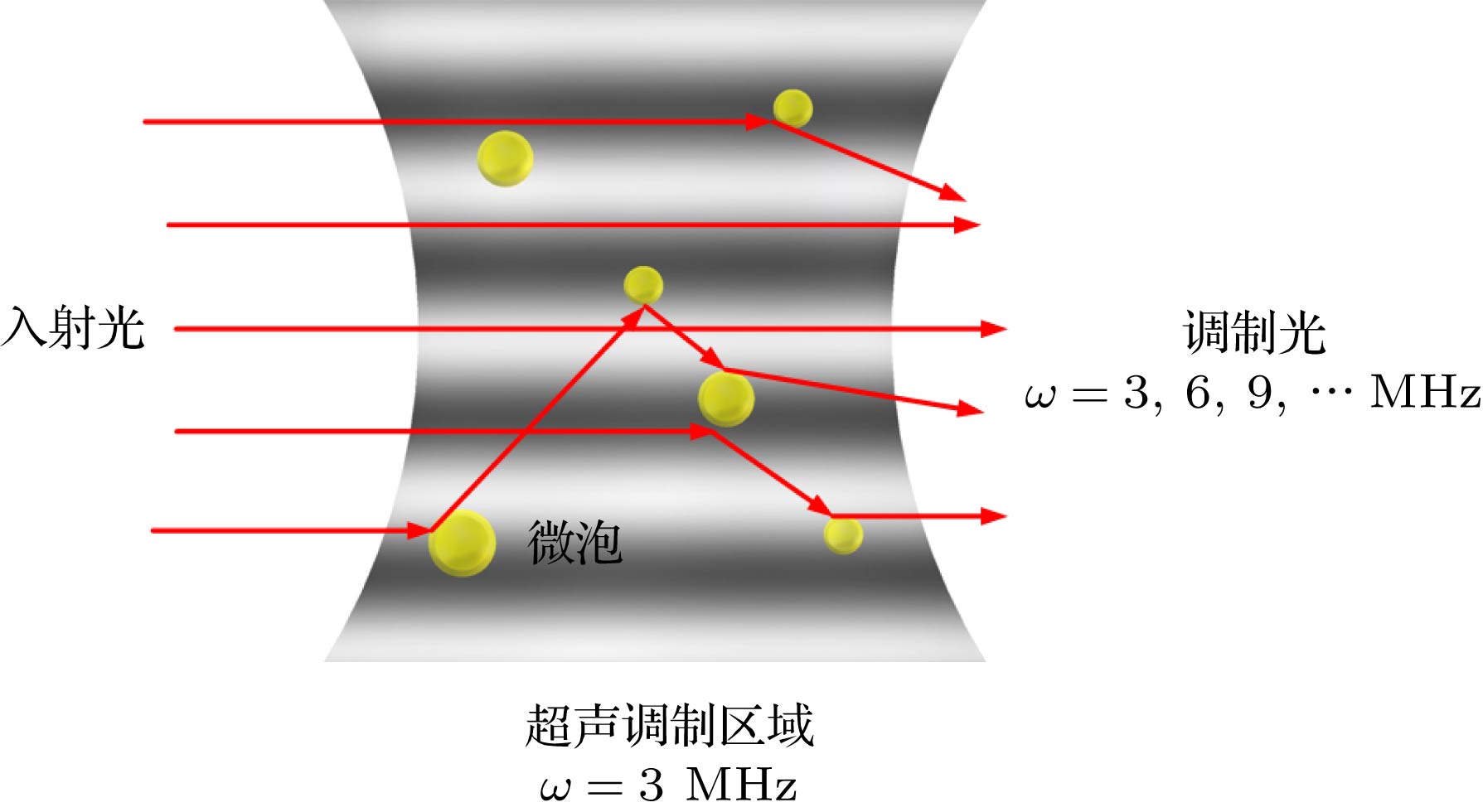
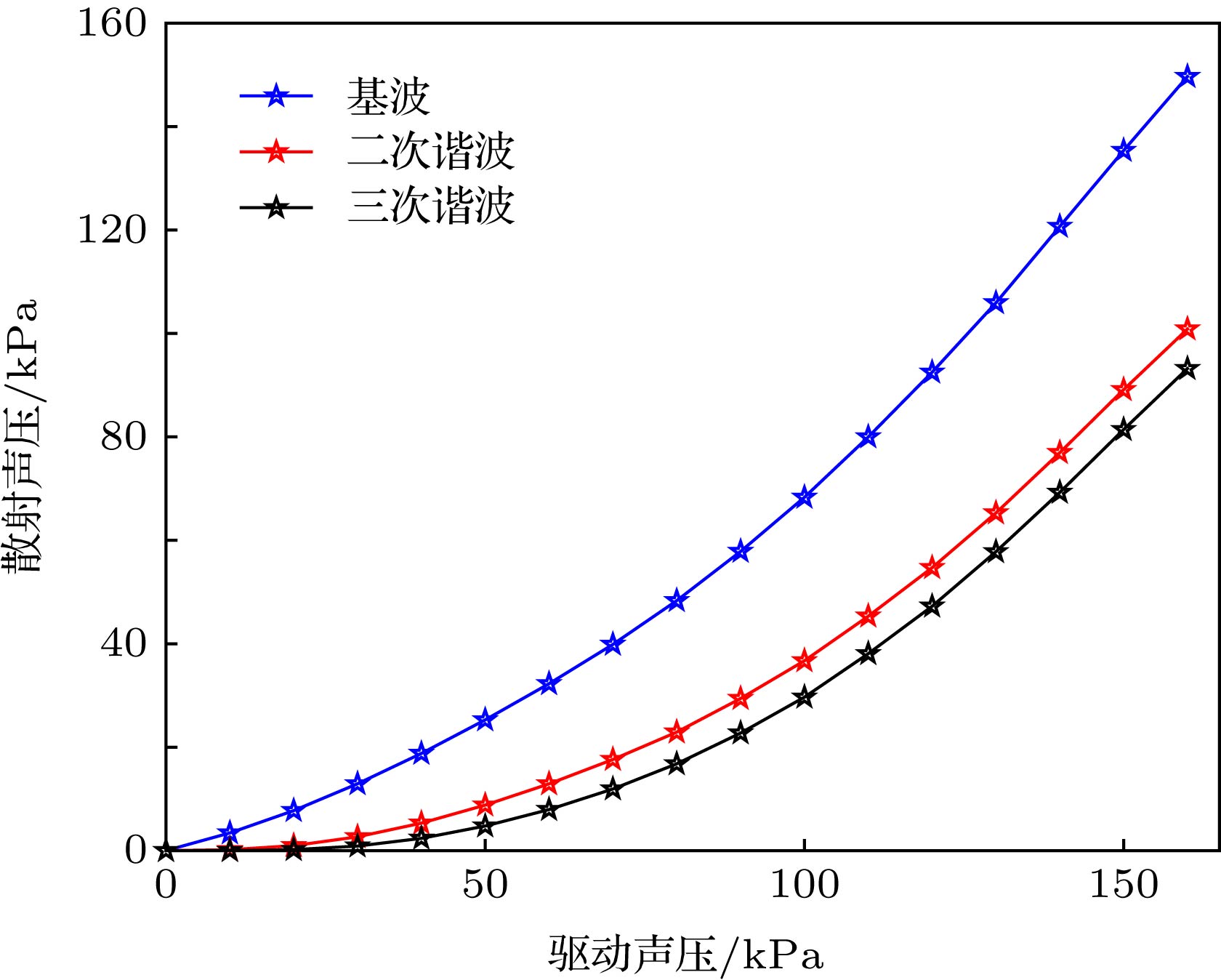
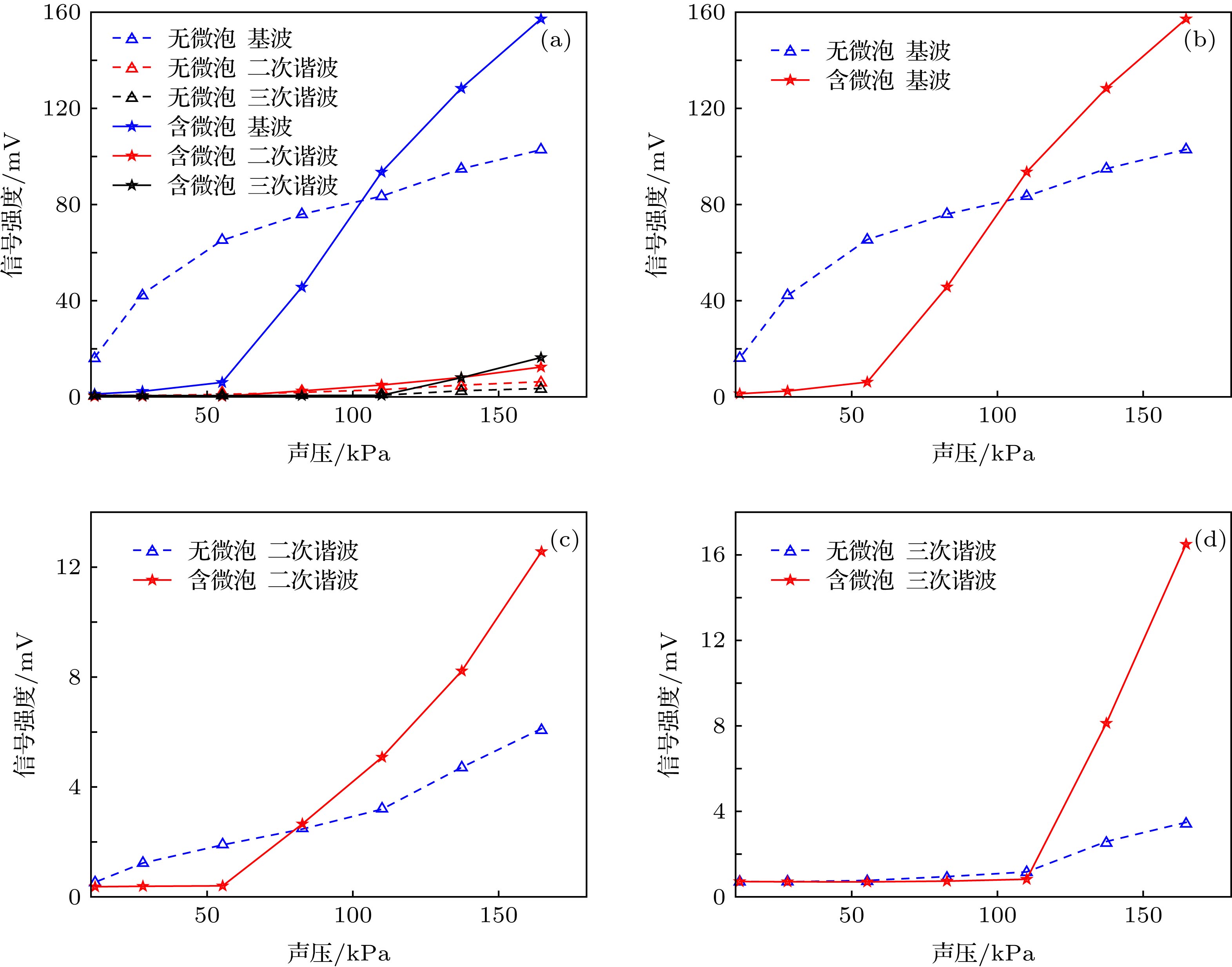
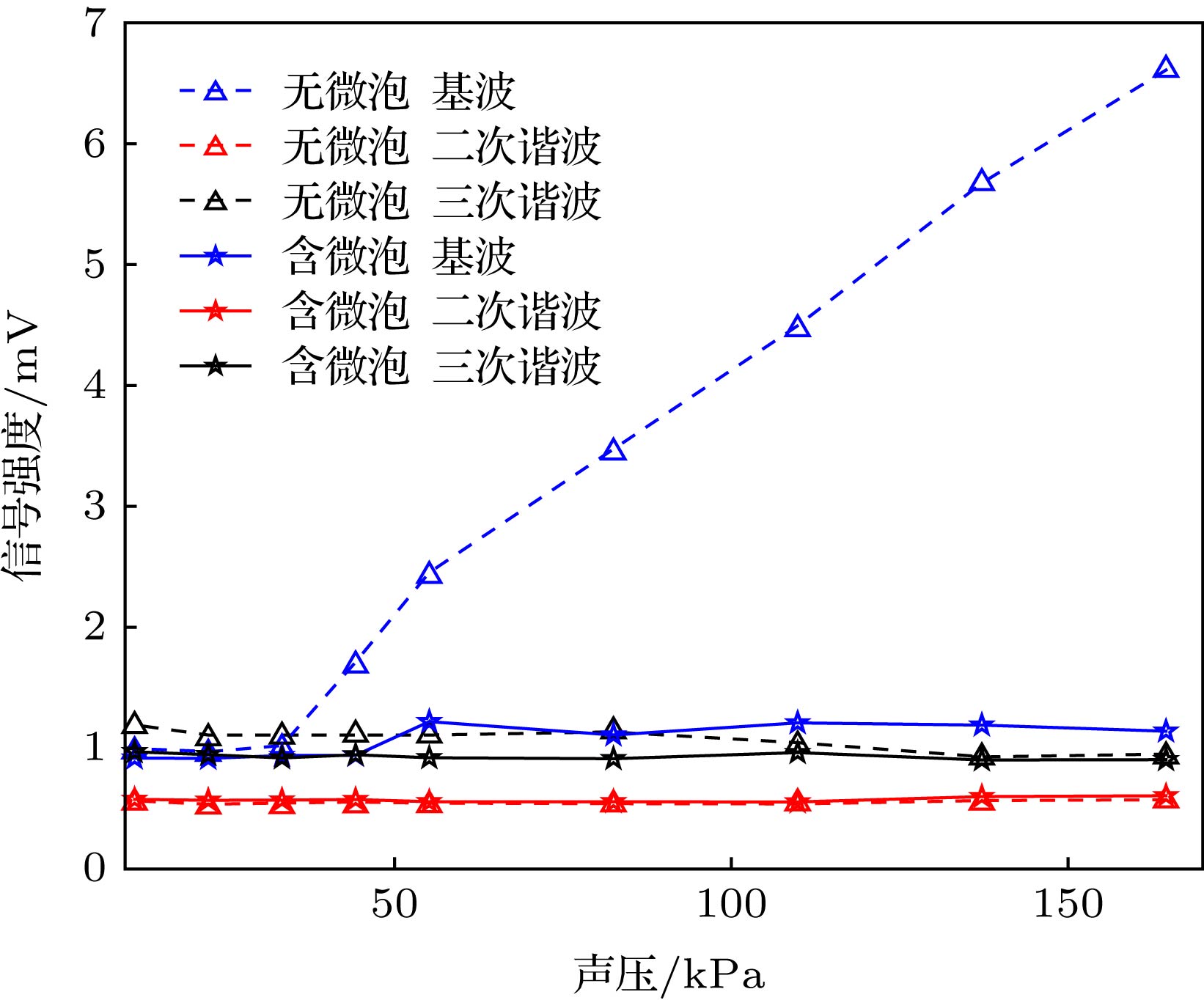
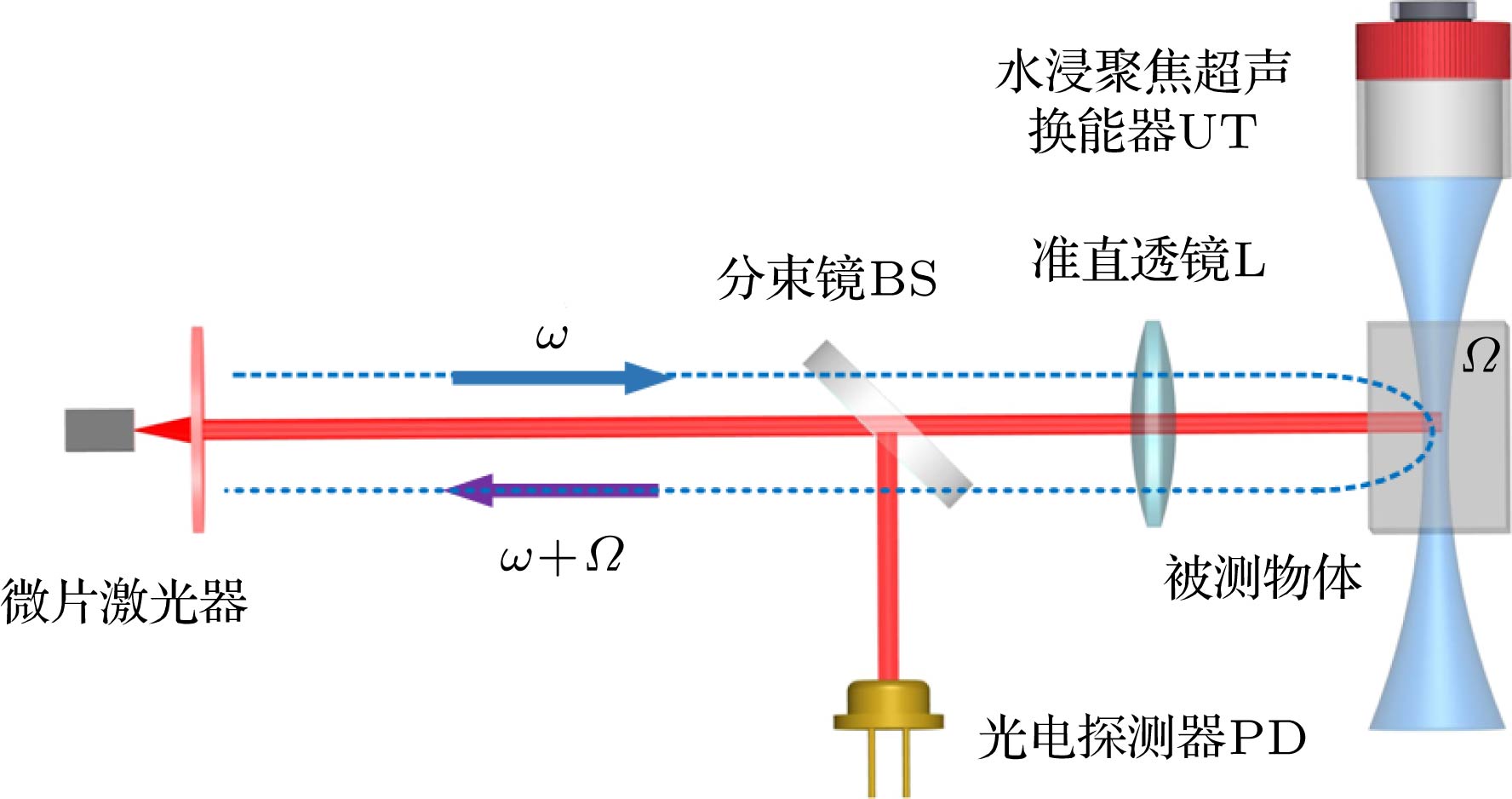
超声调制光学成像技术是一种新型的生物组织光学检测技术, 在癌症的早期检测方面具有巨大的潜力, 但该技术在信噪比和成像对比度方面存在不足. 在超声调制光学成像技术的基础上, 结合高灵敏度的激光回馈技术提出了超声调制激光回馈技术, 建立了含微泡介质的蒙特卡罗光子传输模型, 通过仿真和实验研究了超声微泡造影剂增强超声调制激光回馈成像对比度的作用机理. 结果表明, 在透明溶液中, 超声微泡造影剂可以增强超声调制激光回馈信号, 并产生谐波调制, 通过检测回馈基波和谐波信号增强量的方法可提高成像对比度; 而在仿生物组织环境中, 超声微泡造影剂可显著衰减超声调制激光回馈信号, 通过检测回馈基波和谐波信号衰减量的方法可提高成像对比度.Ultrasound-modulated optical imaging technology is a new type of biological tissue optical detection technology, and sensitive to the change of scattering coefficient and absorption coefficient of biological tissue. This technology is a non-ionizing and non-invasive pathological detection method, which has great potential application in early detection of cancer. However, ultrasound-modulated optical imaging technology is insufficient in signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and imaging contrast. Frequency-shifted laser feedback technology with microchip laser is a new type of highly sensitive interference technology, whose gain coefficient for weak optical signal can reach 106. This technology can greatly improve the SNR of imaging. Combined with the high sensitive laser feedback technology, the ultrasound-modulated laser feedback technology is proposed. The SNR of this technology is better than that of the traditional ultrasound-modulated optical imaging technology. The increase in SNR can achieve greater depth of detection in biological tissue imaging, but there is no significant improvement in imaging contrast. In order to improve the contrast of biological tissue imaging and achieve high resolution imaging of thick biological tissue, we use ultrasound microbubble contrast agent in ultrasound-modulated laser feedback imaging technology. We establish a Monte Carlo photon transport model with microbubbles in order to study the mechanism of contrast enhancement in ultrasound-modulated laser feedback imaging with microbubbles. Finally, we establish an experimental system to verify the correctness of the simulation results. Experimental and simulation results show that in the transparent solution, the ultrasonic microbubble contrast agent can enhance the ultrasound-modulated laser feedback signal and generate harmonic modulation, which can improve the imaging contrast by detecting the enhancement of the fundamental and harmonic signals of the feedback. In the scattering medium, the ultrasonic microbubble contrast agent can significantly attenuate the ultrasound modulated laser feedback signal, and the imaging contrast can be improved by detecting the attenuation of the fundamental and harmonic signal.
-
Keywords:
- acousto-optic imaging /
- laser feedback /
- capsule microbubbles /
- contrast-enhancement
[1] Hussain A, Steenbergen W, Vellekoop I M 2018 J. Biophotonics 11 e201700013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Beard P 2011 Interface Focus 1 602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Lev A, Kotler Z, Sfez B G 2000 Opt. Lett. 25 378
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yao G, Wang L V 2000 Appl. Opt. 39 659
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhang H, Sabooni M, Rippe L, Kim C, Kröll S, Wang L V, Hemmer P R 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 100 131102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Suzuki Y, Xu X, Lai P X, Wang L V 2012 J. Biomed. Opt. 17 080507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Izadifar Z, Babyn P, Chapman D 2019 J. Med. Biol. Eng. 39 259
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Lin L Z, Fan Y, Gao F, Jin L F, Li D, Sun W J, Li F, Qin P, Shi Q S, Shi X Y, Du L F 2018 Theranostics 8 1923
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Song W, Luo Y, Zhao Y, Liu X, Zhao J, Luo J, Zhang Q, Ran H, Wang Z, Guo D 2017 Nanomedicine 12 991
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Qin D W, Li H G, Xie H L 2018 Mol. Med. Rep. 18 3242
[11] Yuan B H, Liu Y, Patrick M, Vignola J 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 95 181113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Hall D J, Hsu M J, Esener S, Robert F, Mattrey R F 2009 Photons Plus Ultrasound: Imaging and Sensing San Jose, United States, February 12, 2009 p71771L
[13] Leung T S, Honeysett J E, Stride E, Deng J 2013 J. Biomed. Opt. 18 015002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Honeysett J E, Stride E, Leung T S 2011 Photons Plus Ultrasound: Imaging and Sensing San Jose, United States, February 10, 2011 p7899
[15] Zhu K Y, Lu Y Y, Zhang S L, Ruan H W, Usuki S, Tan Y D 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 1207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Tan Y D, Wang W P, Xu C X, Zhang S L 2013 Sci. Rep. 3 2971
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 梁金福, 陈伟中, 邵纬航, 周超, 杜联芳, 金利芳 2013 62 084708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang J F, Cheng W Z, Shao W H, Zhou C, Du L F, Jin L F 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 084708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 于洁, 郭霞生, 屠娟, 章东 2015 64 094306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu J, Guo X S, Tu J, Zhang D 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 094306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wu J, Pepe J, Dewitt W 2003 Ultrasound Med. Biol. 29 555
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wang L V 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 87 043903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wang L V, Jacques S L, Zheng L 1995 Comput. Meth. Programs Biomed. 47 131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Periyasamy V, Pramanik M 2013 J. Biomed. Opt. 18 106008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Sivasubramanian K, Periyasamy V, Wen K K, Pramanik M 2016 J. Biomed. Opt. 22 041008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Watté R, Aernouts B, van Beer R, Herremans E, Tri H Q, Verboven P, Nicolaï B, Saeys W 2015 Opt. Express 23 17467
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 玻恩 M, 沃尔夫 E 著(杨葭荪 译) 2009 光学原理 (北京: 电子工业出版社) 第76页
Born M, Wolf E 2009 Principles of Optics: Electromagnetic Theory of Propagation, Interference and Diffraction of Light (Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry) p76 (in Chinese)
-
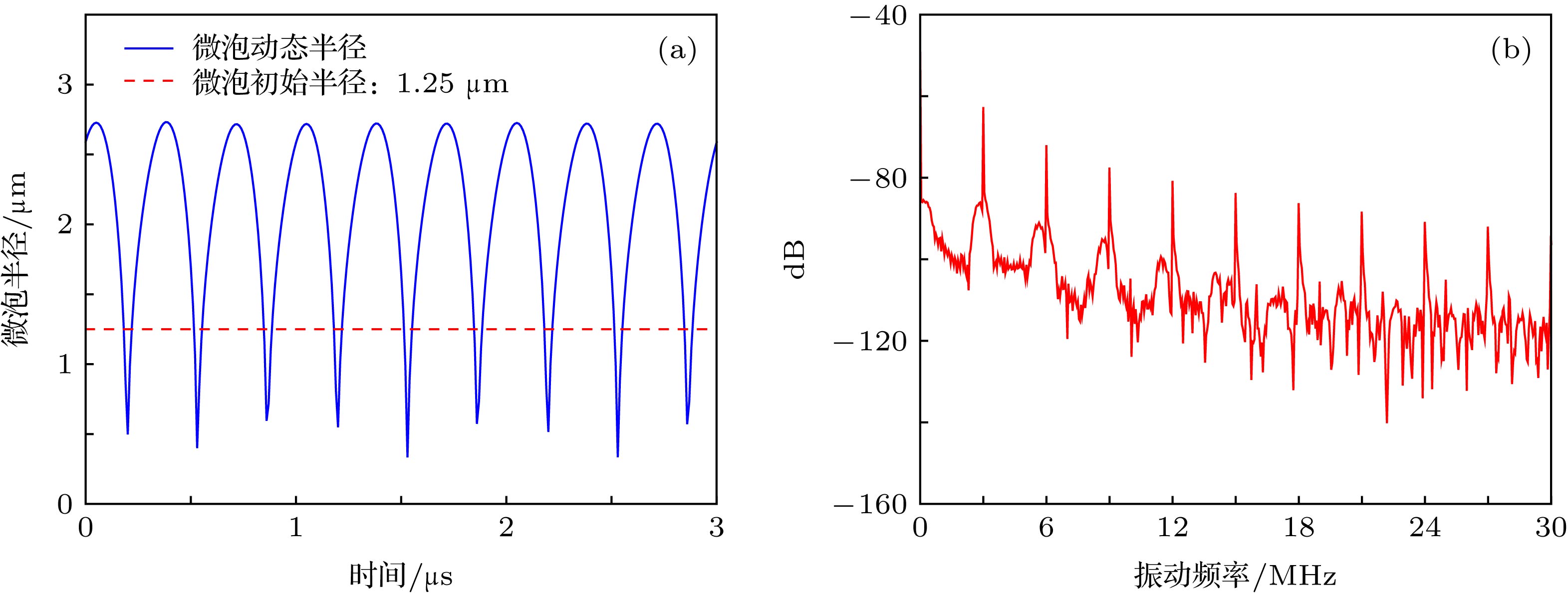
表 1 Rayleigh-Plesset方程仿真参数
Table 1. Rayleigh-Plesset equation simulation parameters.
${\rho _{\rm{L}}}/{\rm{kg}} \cdot {{\rm{m}}^{ - 3}}$ ${P_0}/{\rm{kPa}}$ $\sigma /{\rm{N}} \cdot {{\rm{m}}^{ - 1}}$ $\chi /{\rm{N}} \cdot {{\rm{m}}^{ - 1}}$ $c/{\rm{m}} \cdot {{\rm{s}}^{ - 1}}$ $\varepsilon /{\rm{nm}}$ ${\mu _{{\rm{sh}}}}/{\rm{Pa}} \cdot {\rm{s}}$ $\gamma $ 998 1010 0.051 0.26 1500 5 0.003 1.07 表 2 蒙特卡罗仿真结果
Table 2. Results of Monte Carlo simulation.
溶液种类 背向散射光子数 $\dfrac{{{\simfont\text{调制}} + {\simfont\text{附加调制}}}}{{\simfont\text{未调制}}}$ 调制 未调制 附加调制 0.9%的NaCl溶液 9354 45080 0 20.75% 0.9%的NaCl、微泡混合液 9379 46070 4607 30.36% 1%的脂肪乳剂溶液 843 52966 0 1.59% 1%的脂肪乳剂、微泡混合液 97 52685 7 0.20% -
[1] Hussain A, Steenbergen W, Vellekoop I M 2018 J. Biophotonics 11 e201700013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Beard P 2011 Interface Focus 1 602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Lev A, Kotler Z, Sfez B G 2000 Opt. Lett. 25 378
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yao G, Wang L V 2000 Appl. Opt. 39 659
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhang H, Sabooni M, Rippe L, Kim C, Kröll S, Wang L V, Hemmer P R 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 100 131102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Suzuki Y, Xu X, Lai P X, Wang L V 2012 J. Biomed. Opt. 17 080507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Izadifar Z, Babyn P, Chapman D 2019 J. Med. Biol. Eng. 39 259
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Lin L Z, Fan Y, Gao F, Jin L F, Li D, Sun W J, Li F, Qin P, Shi Q S, Shi X Y, Du L F 2018 Theranostics 8 1923
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Song W, Luo Y, Zhao Y, Liu X, Zhao J, Luo J, Zhang Q, Ran H, Wang Z, Guo D 2017 Nanomedicine 12 991
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Qin D W, Li H G, Xie H L 2018 Mol. Med. Rep. 18 3242
[11] Yuan B H, Liu Y, Patrick M, Vignola J 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 95 181113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Hall D J, Hsu M J, Esener S, Robert F, Mattrey R F 2009 Photons Plus Ultrasound: Imaging and Sensing San Jose, United States, February 12, 2009 p71771L
[13] Leung T S, Honeysett J E, Stride E, Deng J 2013 J. Biomed. Opt. 18 015002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Honeysett J E, Stride E, Leung T S 2011 Photons Plus Ultrasound: Imaging and Sensing San Jose, United States, February 10, 2011 p7899
[15] Zhu K Y, Lu Y Y, Zhang S L, Ruan H W, Usuki S, Tan Y D 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 1207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Tan Y D, Wang W P, Xu C X, Zhang S L 2013 Sci. Rep. 3 2971
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 梁金福, 陈伟中, 邵纬航, 周超, 杜联芳, 金利芳 2013 62 084708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang J F, Cheng W Z, Shao W H, Zhou C, Du L F, Jin L F 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 084708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 于洁, 郭霞生, 屠娟, 章东 2015 64 094306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu J, Guo X S, Tu J, Zhang D 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 094306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wu J, Pepe J, Dewitt W 2003 Ultrasound Med. Biol. 29 555
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wang L V 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 87 043903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wang L V, Jacques S L, Zheng L 1995 Comput. Meth. Programs Biomed. 47 131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Periyasamy V, Pramanik M 2013 J. Biomed. Opt. 18 106008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Sivasubramanian K, Periyasamy V, Wen K K, Pramanik M 2016 J. Biomed. Opt. 22 041008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Watté R, Aernouts B, van Beer R, Herremans E, Tri H Q, Verboven P, Nicolaï B, Saeys W 2015 Opt. Express 23 17467
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 玻恩 M, 沃尔夫 E 著(杨葭荪 译) 2009 光学原理 (北京: 电子工业出版社) 第76页
Born M, Wolf E 2009 Principles of Optics: Electromagnetic Theory of Propagation, Interference and Diffraction of Light (Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry) p76 (in Chinese)
计量
- 文章访问数: 12218
- PDF下载量: 79
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: