-
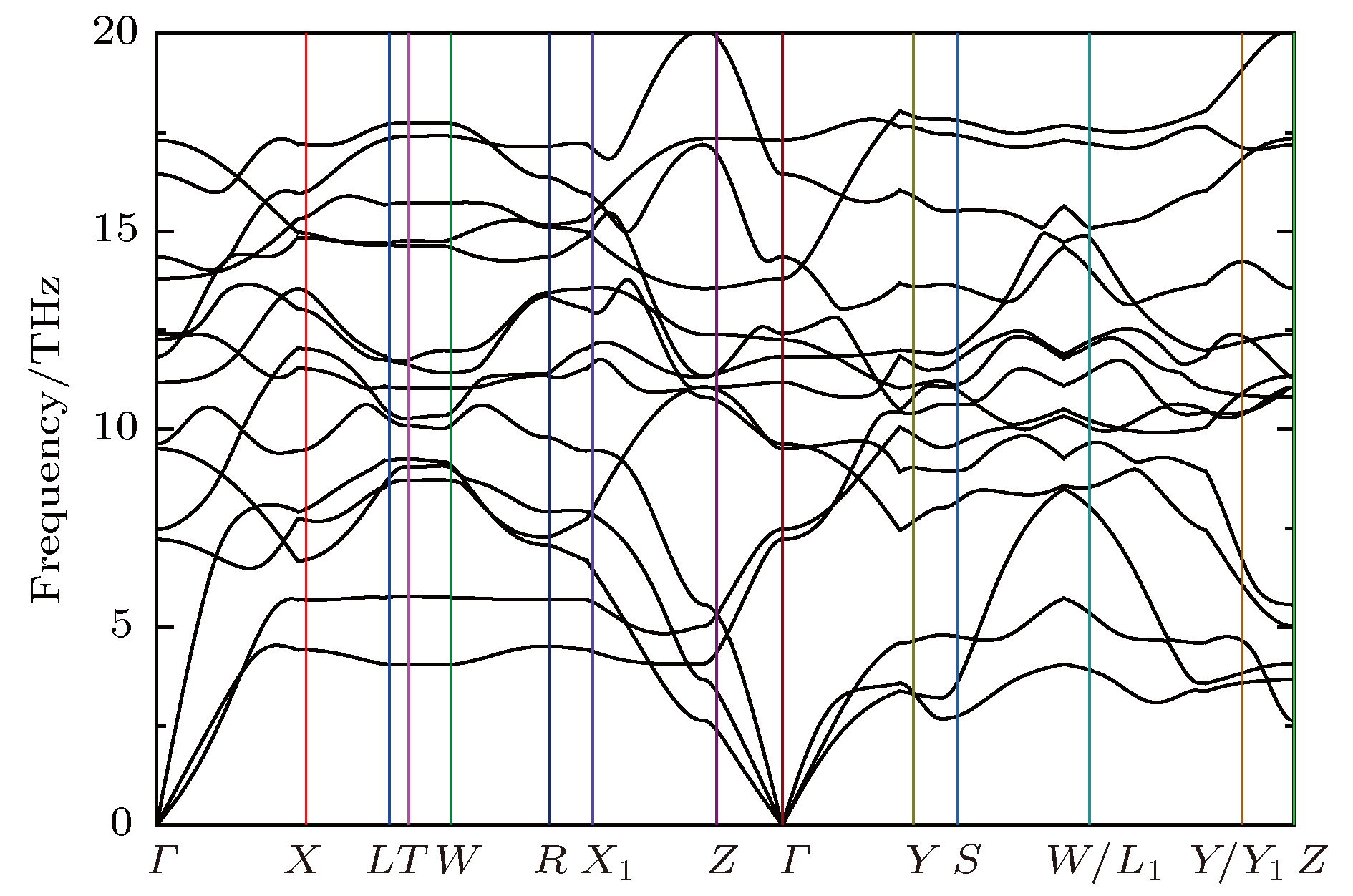
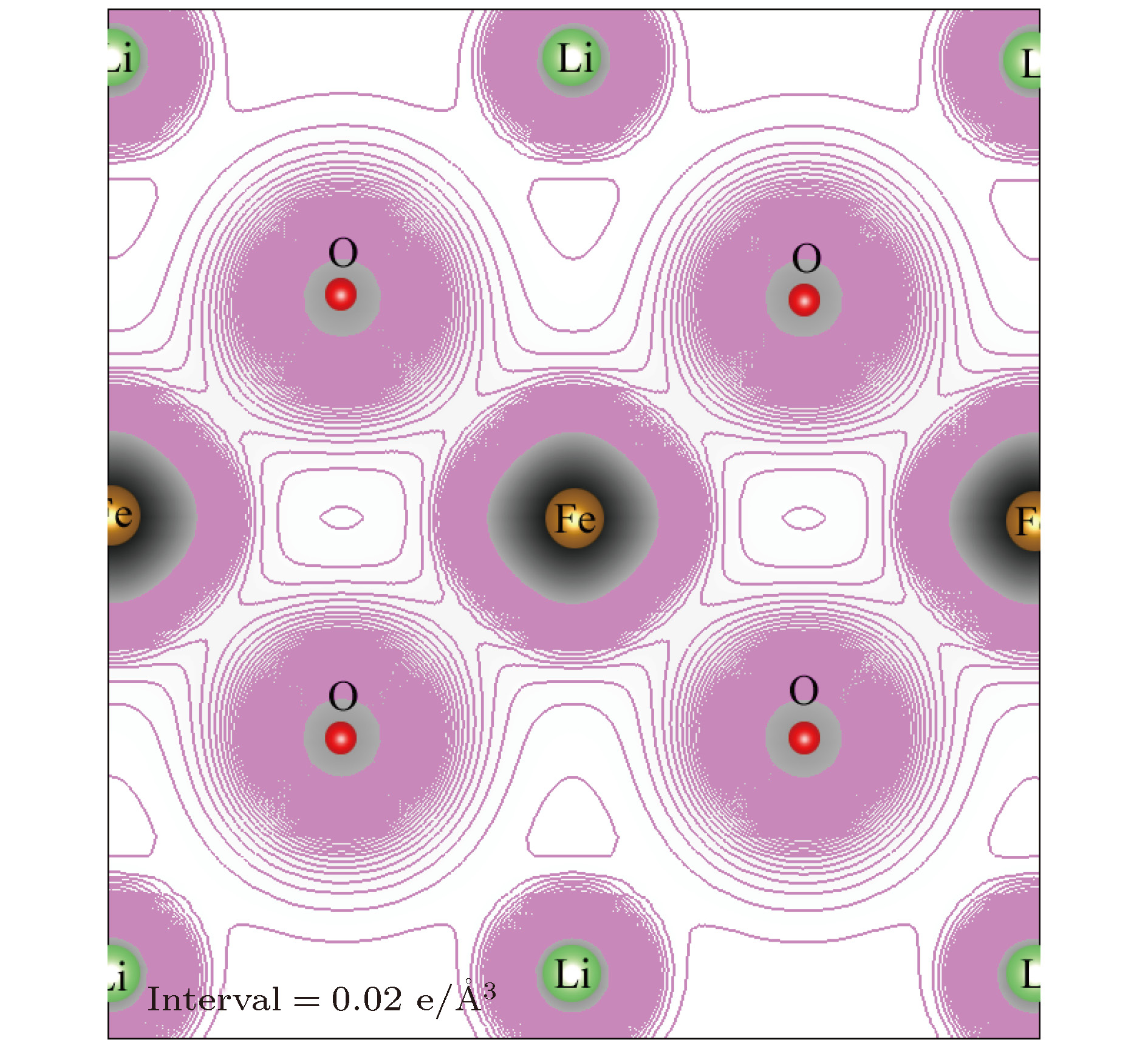
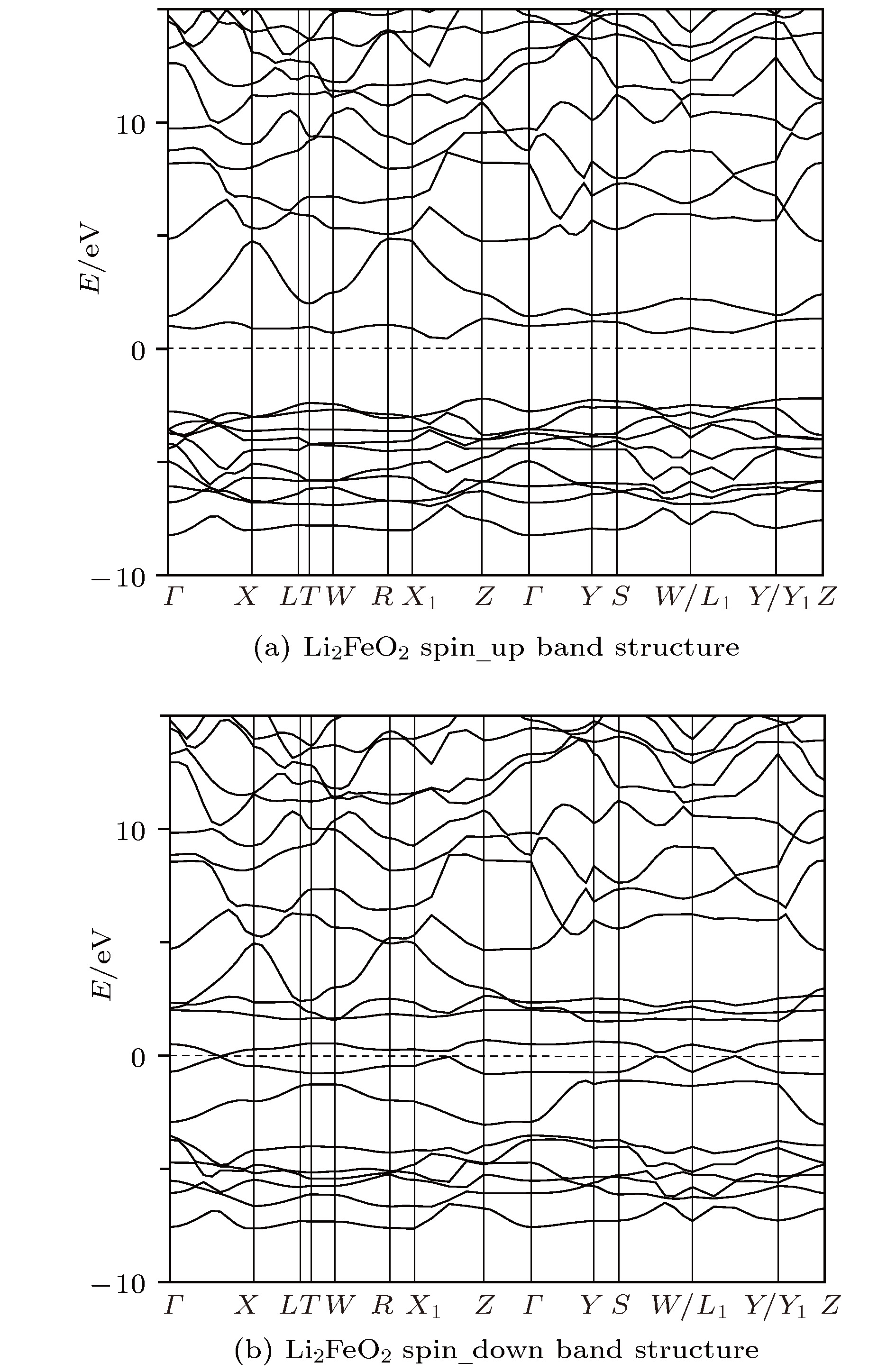
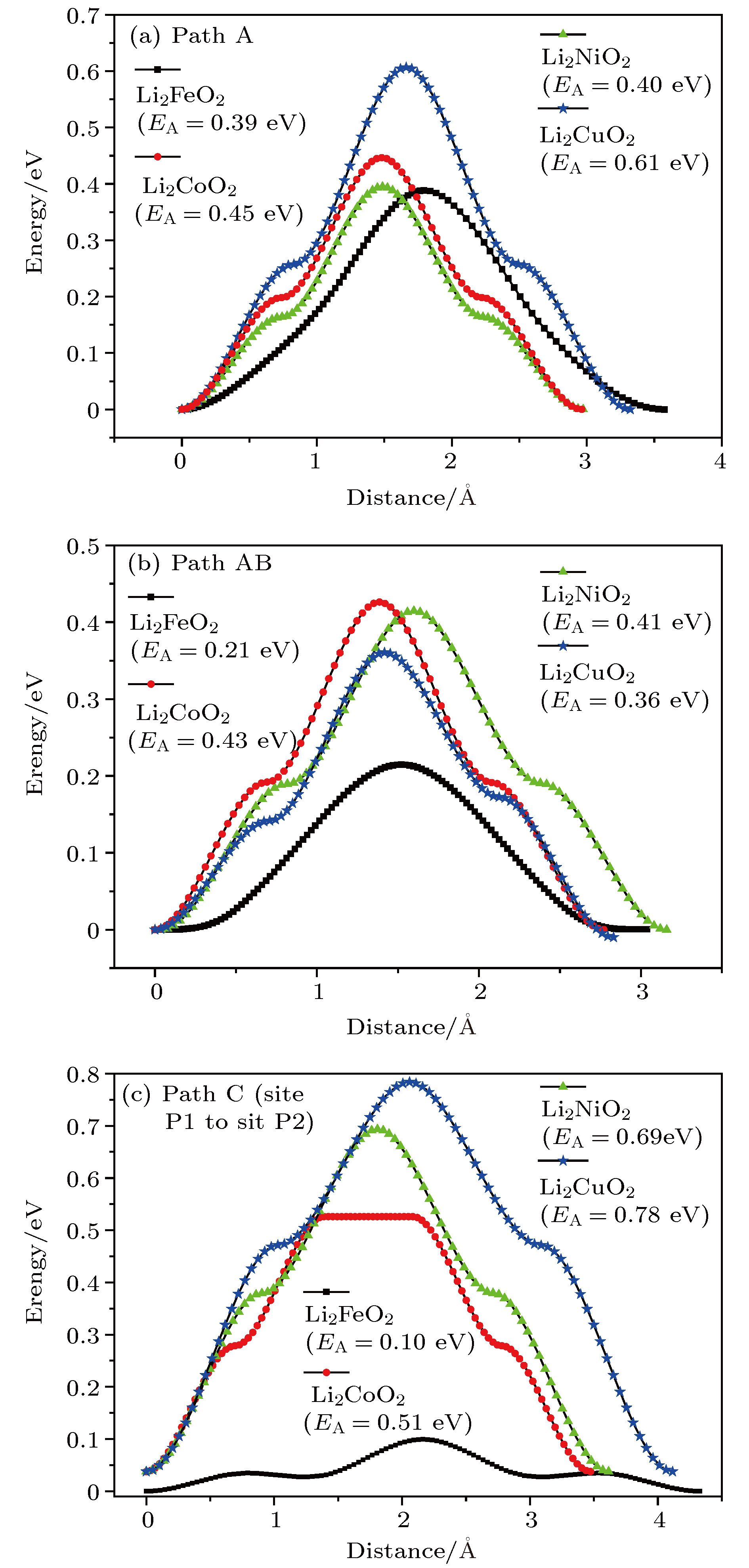
采用基于密度泛函理论的第一性原理方法计算了锂离子电池正极材料Immm-Li2FeO2的声子谱、电子结构性质和Li扩散系数并与Li2MO2 (M = Co, Ni, Cu)材料进行对比. 计算结果显示, Immm-Li2FeO2材料具有结构稳定性, 计算结果呈铁磁性, 能带结构具有半金属的特征. Fe离子外层d电子呈低自旋态, 自旋极化P = 8.01%. 利用分波态密度分析了自旋向上和自旋向下的电子能带结构. 此外, 采用微动弹性带方法计算了各个方向上Li扩散的势垒, 结果表明Li离子比较容易先进行c轴方向的迁移, 迁移势垒为0.1 eV; 然后再沿ab轴方向迁移, 迁移势垒为0.21 eV, 而沿a轴方向迁移的势垒为0.39 eV. 这些势垒值比其他的Li2MO2 (M = Co, Ni, Cu)材料中的势垒值小, 也比其他Fe基Li离子电池正极材料中的势垒值更低, 意味着Li2FeO2中的Li离子将有更高的扩散系数, 这对Li2FeO2作为正极材料具有重要的意义.
-
关键词:
- Immm-Li2FeO2 /
- 电子结构 /
- Li扩散 /
- 第一性原理
The electronic structures and lithium diffusion in the cathode material Immm-Li2FeO2 of lithium-ion batteries are calculated by the first-principles method based on the density functional theory. The calculated results show that Immm-Li2FeO2 is ferromagnetic, and the band structure indicates a semi-metal character. The d-electrons of Fe ions are in the low spin state, with a spin polarization of 8.01%. The spin-up and spin-down band structure are also analyzed by using the l-decomposed electronic density of states. Furthermore, the energy barriers for the lithium ion diffusion in different directions are calculated by the nudged elastic band method. For comparison, the potential barriers for the Li2MO2 (M = Co, Ni, Cu) are also calculated. The results suggest that it is easier for Li ion to diffuse in the c-axis directionof Li2FeO2, with an energy barrier of only 0.1 eV. The energy barrier is 0.21 eV for Li to diffuse in the ab-axis direction, while the diffusion barrier is 0.39 eV along the a-axis direction of Li2FeO2. All these values of energy barriers are lower than those in other Fe-based cathodes mentioned, indicating that the Li diffusion coefficient in Immm-Li2FeO2 should be larger than those of other materials, which also indicates that the Li2FeO2 is of great importance as cathode material.-
Keywords:
- Immm-Li2FeO2 /
- electronic structures /
- Li diffusion /
- first-principles method
[1] Goodenough J B, Park K S 2013 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135 1167
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Goodenough J B, Kim Y 2010 Chem. Mater. 22 587
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Xu L, Tang S, Cheng Y, Wang K, Liang J, Liu C, Cao Y C, Wei F, Mai L Q 2018 Joule 2 1991
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Goodenough J B 2018 Nature Electron. 1 204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Yamada A 2014 Mater. Res. Soc. 39 423
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Robert A, Daniel W T, Fabio L M, Novak P, Bruce P G 2008 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130 3554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Guo S P, Ma Z, Li J C, Xue H G 2017 J. Mater. Sci. 52 1469
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ramos-Sanchez G, Romero-Ibarra I C, Vazquez-Arenas J, Tapia C, Aguilar-Eseiza N, Gonzalez I 2017 Solid State Ionics 303 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Kordatos A, Kuganathan N, Kelaidis N, Iyngaran P, Chroneos A 2018 Sci. Rep. 8 6754
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Back C K, Yin R Z, Shin S J, Lee Y S, Choi W, Kim Y S 2012 J. Electrochem. Soc. 159 A887
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Kang K, Morgan D, Ceder G 2009 Phys. Rev. B 79 014305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Lee H, Chang S K, Goh E Y, Jeong J Y, Lee J H, Kim H J, Cho J J, Hong S T 2008 Chem. Mater. 20 5
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Rose E R, Pandian A S, Yan P F, Weker J N, Wang C M, Nanda J 2017 Chem. Mater. 29 2997
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Perdew J P, Chevary J A, Vosko S H, Jackson K A, Pederson M R, Singh D J, Fiolhais C 1992 Phys. Rev. B 46 6671
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kresse G, Jobert D 1999 Phys. Rev. B 59 1758
[17] Monkhorst H J, Pack J D 1976 Phys. Rev. B 13 5188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Anisimov V I, Zaanen J, Andersen O K 1991 Phys. Rev. B 44 943
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhou F, Cococcioni M, Marianetti C A, Morgan D, Ceder G 2004 Phys. Rev. B 70 235121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Henkelman G, Uberuaga B P, Jónsson H 2000 J. Chem. Phys. 113 9901
[21] Morgan D, van der Ven A, Ceder G 2004 Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 7 A30
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Urban A, Seo D H, Ceder G 2016 njp Computat. Mater. 2 16002
[23] Zhao Y Q, Ma Q R, Liu B, Yu Z L, Yang J L, Cai M Q 2018 Nanoscale 10 8677
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Yu Z L, Ma Q R, Zhao Y Q, Liu B, Cai M Q 2018 J. Phys. Chem. C 112 9275
[25] Zhao Y Q, Ma Q R, Liu Biao, Yu Z L, Cai M Q 2018 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20 14718
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 徐光宪, 王祥云 2010 物质结构 (北京: 科学出版社) 第725−727页
Xu G X, Wang X Y 2010 Material Structure (Beijing: Science Press) pp725−727 (in Chinese)
[27] Huang Z F, Meng X, Wang C Z, Sun Y, Chen G 2006 J.Power Sources 158 1394
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Ramesha K, Seshadri R, Ederer C, He T, Subramanian M A 2004 Phys. Rev. B 70 214409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Krishna G, Dathar P, Sheppard D, Stevenson K J, Henkelman G 2011 Chem. Mater. 23 4032
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Ouyang C, Shi S, Wang Z, Huang X, Chen L 2004 Phys. Rev. B 69 104303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Armstrong A R, Kuganathan N, Islam M S, Bruce P G 2011 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133 13031
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Kutner R 1981 Phys. Lett. A 81 239
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Vineyard G H 1957 J. Phys. Chem. Solids 3 121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 GGA和GGA + U下Li2NiO2的扩散势垒
Table 1. Li2NiO2 diffusion barriers under GGA and GGA + U.
跃迁路径 Path A Path AB Path C Li2NiO2迁移势垒/eV GGA 0.40 0.41 0.69 GGA + U 0.46 0.41 0.89 表 2 Immm-Li2FeO2的结构参数与键长
Table 2. Structural parameters and the bond lengths of Immm-Li2FeO2.
表 3 不同电子自旋组态的Li2FeO2的总结合能与Fe2+磁矩
Table 3. Total cohesive energies and magnetic moments under different spin configurations of Li2FeO2.
电子自旋组态 Li2FeO2结合能(eV/分子式) Fe2+磁矩/μB 高自旋 –3.29 3.92 低自旋 –3.30 2.01 非自旋 –3.22 0 表 4 不同跃迁路径的Li2MO2 (M = Fe, Co, Ni, Cu)的跃迁势垒与跃迁步长
Table 4. Energy barriers and distance for different Li+ migration paths in Li2FeO2
Li2FeO2 Li2CoO2 Li2NiO2 Li2CuO2 Path A 跃迁势垒/eV 0.39 0.45 0.40 0.61 跃迁步长/Å 3.60 2.98 2.98 3.32 Path AB 跃迁势垒/eV 0.21 0.43 0.41 0.36 跃迁步长/Å 3.04 2.76 2.70 2.84 Path C 跃迁势垒/eV 0.10 0.51 0.69 0.78 跃迁步长/Å 4.32 3.50 3.62 4.12 -
[1] Goodenough J B, Park K S 2013 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135 1167
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Goodenough J B, Kim Y 2010 Chem. Mater. 22 587
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Xu L, Tang S, Cheng Y, Wang K, Liang J, Liu C, Cao Y C, Wei F, Mai L Q 2018 Joule 2 1991
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Goodenough J B 2018 Nature Electron. 1 204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Yamada A 2014 Mater. Res. Soc. 39 423
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Robert A, Daniel W T, Fabio L M, Novak P, Bruce P G 2008 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130 3554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Guo S P, Ma Z, Li J C, Xue H G 2017 J. Mater. Sci. 52 1469
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ramos-Sanchez G, Romero-Ibarra I C, Vazquez-Arenas J, Tapia C, Aguilar-Eseiza N, Gonzalez I 2017 Solid State Ionics 303 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Kordatos A, Kuganathan N, Kelaidis N, Iyngaran P, Chroneos A 2018 Sci. Rep. 8 6754
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Back C K, Yin R Z, Shin S J, Lee Y S, Choi W, Kim Y S 2012 J. Electrochem. Soc. 159 A887
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Kang K, Morgan D, Ceder G 2009 Phys. Rev. B 79 014305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Lee H, Chang S K, Goh E Y, Jeong J Y, Lee J H, Kim H J, Cho J J, Hong S T 2008 Chem. Mater. 20 5
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Rose E R, Pandian A S, Yan P F, Weker J N, Wang C M, Nanda J 2017 Chem. Mater. 29 2997
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Perdew J P, Chevary J A, Vosko S H, Jackson K A, Pederson M R, Singh D J, Fiolhais C 1992 Phys. Rev. B 46 6671
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kresse G, Jobert D 1999 Phys. Rev. B 59 1758
[17] Monkhorst H J, Pack J D 1976 Phys. Rev. B 13 5188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Anisimov V I, Zaanen J, Andersen O K 1991 Phys. Rev. B 44 943
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhou F, Cococcioni M, Marianetti C A, Morgan D, Ceder G 2004 Phys. Rev. B 70 235121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Henkelman G, Uberuaga B P, Jónsson H 2000 J. Chem. Phys. 113 9901
[21] Morgan D, van der Ven A, Ceder G 2004 Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 7 A30
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Urban A, Seo D H, Ceder G 2016 njp Computat. Mater. 2 16002
[23] Zhao Y Q, Ma Q R, Liu B, Yu Z L, Yang J L, Cai M Q 2018 Nanoscale 10 8677
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Yu Z L, Ma Q R, Zhao Y Q, Liu B, Cai M Q 2018 J. Phys. Chem. C 112 9275
[25] Zhao Y Q, Ma Q R, Liu Biao, Yu Z L, Cai M Q 2018 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20 14718
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 徐光宪, 王祥云 2010 物质结构 (北京: 科学出版社) 第725−727页
Xu G X, Wang X Y 2010 Material Structure (Beijing: Science Press) pp725−727 (in Chinese)
[27] Huang Z F, Meng X, Wang C Z, Sun Y, Chen G 2006 J.Power Sources 158 1394
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Ramesha K, Seshadri R, Ederer C, He T, Subramanian M A 2004 Phys. Rev. B 70 214409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Krishna G, Dathar P, Sheppard D, Stevenson K J, Henkelman G 2011 Chem. Mater. 23 4032
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Ouyang C, Shi S, Wang Z, Huang X, Chen L 2004 Phys. Rev. B 69 104303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Armstrong A R, Kuganathan N, Islam M S, Bruce P G 2011 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133 13031
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Kutner R 1981 Phys. Lett. A 81 239
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Vineyard G H 1957 J. Phys. Chem. Solids 3 121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 16989
- PDF下载量: 290
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: