-
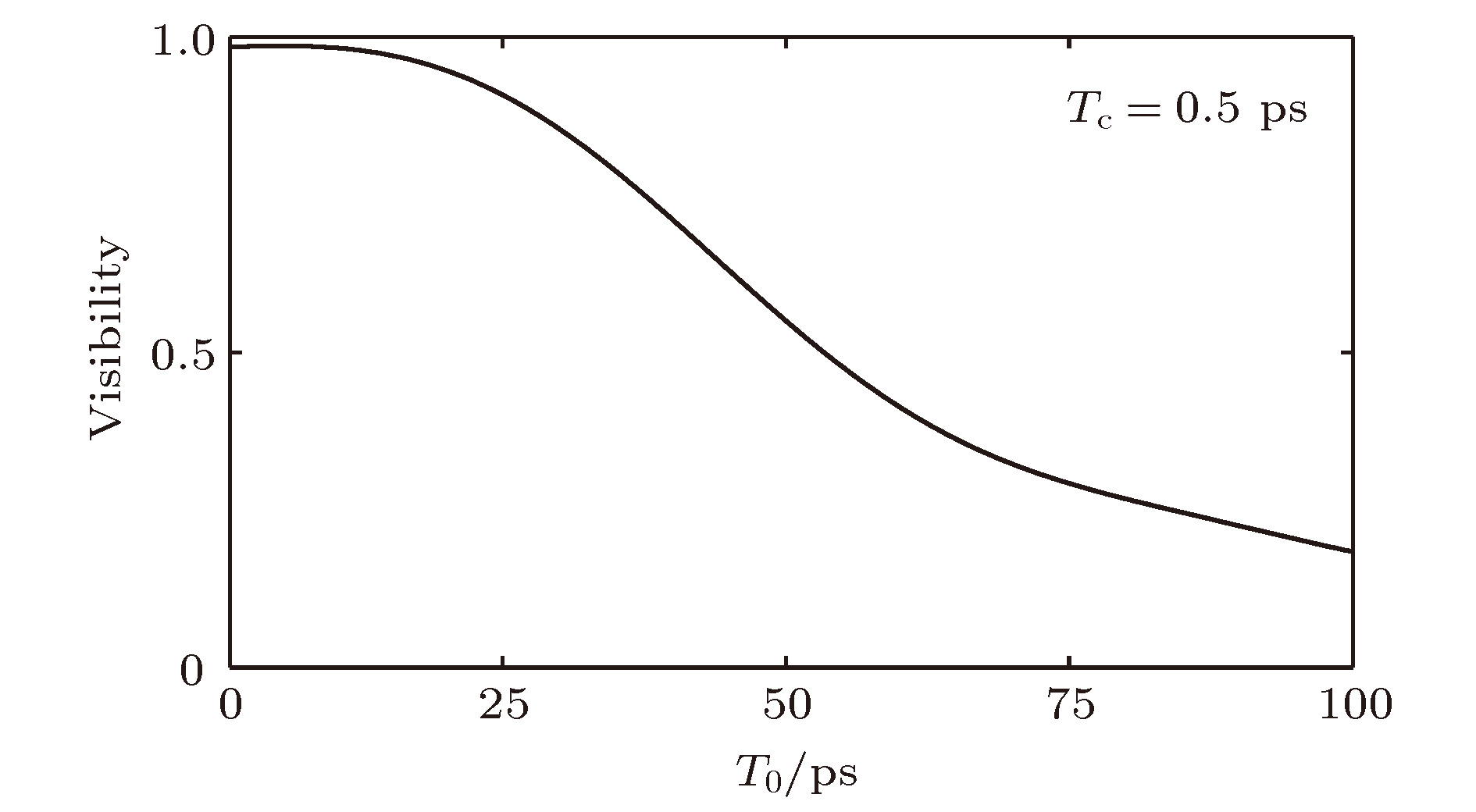
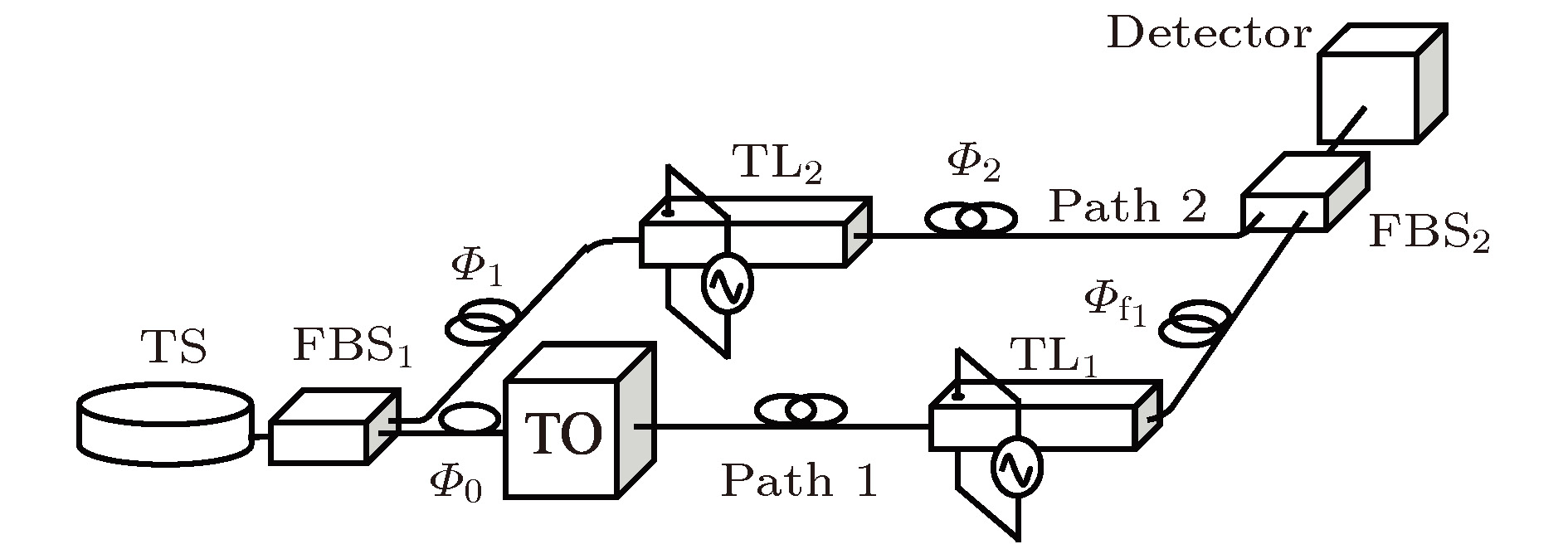
与通常利用二阶强度关联测量实现时域鬼成像不同, 本文利用时域热光源借助干涉仪通过一阶关联实现时域成像. 基于空域光束的近轴衍射和时域窄带脉冲在色散介质中色散之间的空间-时间二象性, 在时域脉冲响应函数的基础上得到了表征一阶关联时域成像的强度表达式, 分析研究了光源脉冲宽度和相干时间对成像可见度和分辨率的影响. 结果一方面表明基于热光场一阶关联的时域成像在不需要额外色散补偿或消除条件下可以实现时域物体信号的再现, 另一方面表明当光源脉冲宽度一定时, 成像可见度随光源脉冲相干时间的增加而增加, 但是成像分辨率逐渐降低, 其中当光源脉冲宽度约为100 ps, 相干时间约为0.5 ps时, 间隔为20 ps, 宽度为8 ps的时域矩形波型物体的成像质量(兼顾可见度和分辨率)较好. 该结果对于基于热光一阶关联的时域成像在时序信号测量中的应用具有重要意义.Different from second-order temporal ghost imaging usually realized by means of second-order correlation measurement, in this paper, we investigate theoretically temporal imaging with temporally thermal light via first-order field correlation based on a Mach-Zehnder interferometer. The paraxial wave equation describing the diffraction of light and the differential equation characterizing the dispersion of light pulse are given. Based on the similarity between these equations, the duality between the paraxial diffraction of the light in the spatial domain and the dispersion of the temporal narrow-band pulse in the dispersive medium (i.e. the space-time duality) is obtained, and the impulse response functions in the time domain for several optical systems are also presented. Then in terms of the space-time duality, we design the scheme for temporal imaging via first-order thermal field correlation based on a Mach-Zehnder interferometer and obtain the intensity expression for first-order temporal imaging according to the temporal impulse response functions, and discuss the influences of the source pulse width and coherence time on the image visibility and resolution. The result shows that the temporal signal can be reconstructed through temporal first-order temporal imaging. Furthermore, when the source’s coherence time is fixed, the image visibility decreases as the pulse width increases. However, the image resolution increases. When the source’s pulse width is fixed, the image visibility increases as the coherence time increases. And yet the image resolution decreases. Specially, when the source’s pulse width is 100 ps and the coherence time is 0.5 ps, the image quality (taking both the visibility and resolution into account) of a temporally rectangular object is satisfactory. In the simulation, the distance and width of the temporal rectangular object are 20 ps and 8 ps, respectively. It is shown that there is a dilemma between the visibility and resolution of first-order temporal imaging which is similar to the result of second-order ghost imaging. Our result discussed herein could be valuable in the reconstruction and detection of temporal signal via first-order temporal ghost imaging with temporally thermal light.
-
Keywords:
- intensity correlation /
- first-order field correlation /
- ghost imaging /
- dispersion
[1] Padgett M J, Boyd R W 2017 Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 375 20160233
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Pittman T B, Shih Y H, Strekalov D V, Sergienko A V 1995 Phys. Rev. A 52 R3429
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Bennink R S, Bentley S J, Boyd R W 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 113601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Gatti A, Brambilla E, Bache M, Lugiato L A 2004 Phys. Rev. A 70 013802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Cheng J, Han S 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 92 093903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Cao D Z, Xiong J, Wang K G 2005 Phys. Rev. A 71 013801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Valencia A, Scarcelli G, D’ Angelo M, Shih Y H 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 063601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ferri F, Magatti D, Gatti A, Bache M, Brambilla E, Lugiato L A 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 183602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Cai Y, Zhu S Y 2005 Phys. Rev. E 71 056607
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang D, Zhai Y H, Wu L A, Chen X H 2005 Opt. Lett. 30 2354
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Cai Y, Wang F 2007 Opt. Lett. 32 205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Liu X F, Chen X H, Yao X R, Yu W K, Zhai G J, Wu L A 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 2314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Sun B, Edgar M P, Bowman R, Vittert L E, Welsh S, Bowman A, Padgett M J 2013 Science 340 844
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Bromberg Y, Katz O, Silberberg Y 2009 Phys. Rev. A 79 053840
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Shapiro J H 2008 Phys. Rev. A 78 061802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhao C Q, Gong W L, Chen M L, Li E R, Wang H, Xu W D, Han S S 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 101 141123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hong Y, Li E R, Gong W L, Han S S 2015 Opt. Express 23 14541
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Chen M, Li E, Gong W L, Bo Z, Xu X, Zhao C, Shen X, Xu W, Han S S 2013 Opt. Photonics J. 3 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Li S, Cropp F, Kabra K, Lane T J, Wetzstein G, Musumeci P, Ratner D 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 121 114801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Cheng J 2009 Opt. Express 17 7916
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Cheng J, Lin J 2013 Phys. Rev. A 87 043810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Cao D Z, Xiong J, Zhang S H, Lin L F, Gao L, Wang K G 2008 Appl. Phys. Lett. 92 201102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chan K W C, O’ Sullivan M N, Boyd R W 2010 Opt. Express 18 5562
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Zhang D J, Li H G, Zhao Q L, Wang S, Wang H B, Xiong J, Wang K G 2015 Phys. Rev. A 92 013823
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Li H G, Zhang D J, Xu D J, Zhao Q L, Wang S, Wang H B, Xiong J, Wang K G 2015 Phys. Rev. A 92 043816
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Katz O, Bromberg Y, Silberberg Y 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 95 131110
[27] 仲亚军, 刘娇, 梁文强, 赵生妹 2015 64 014202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhong Y J, Liu J, Liang W Q, Zhao S M 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 014202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Gao C, Wang X, Wang Z, Li Z, Du G, Chang F, Yao Z 2017 Phys. Rev. A 96 023838
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Cao D H, Li Q H, Zhuang X C, Ren H, Zhang S H, Song X B 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 123401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Yang H, Wu H, Wang H B, Cao D H, Zhang S H, Xiong J, Wang K 2018 Phys. Rev. A 98 053853
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Salem R, Foster M A, Gaeta A L 2013 Adv. Opt. Photonics 5 274
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Foster M A, Salem R, Geraghty D F, Turner-Foster A C, Lipson M, Gaeta A L 2008 Nature 456 81
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Schröder J, Wang F, Clarke A, Ryckeboer E, Pelusi M , Roelens M A, Eggleton B J 2010 Opt. Commun. 283 2611
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Fridman M, Farsi A, Okawachi Y, Gaeta A L 2012 Nature 481 62
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Ryczkowski P, Barbier M, Friberg A T, Dudley J M, Genty G 2016 Nat. Photonics 10 167
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Shirai T, Setälä T, Friberg A T 2010 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 27 2549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Setälä T, Shirai T, Friberg A T 2010 Phys. Rev. A 82 043813
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Chen Z, Li H, Li Y, Shi J, Zeng G 2013 Opt. Eng. 52 076103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Gao L, Zhang S H, Xiong J, Gan S, Feng L J, Cao D Z, Wang K G 2009 Phys. Rev. A 80 021806
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Vabre L, Dubois A, Boccara A C 2002 Opt. Lett. 27 530
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Kolner B H 1994 IEEE J. Quant. Electron. 30 1951
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Cai Y, Zhu S 2004 Opt. Lett. 29 2716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Qu L, Bai Y, Nan S, Shen Q, Li H, Fu X 2018 Opt. Laser Technol. 104 197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] Padgett M J, Boyd R W 2017 Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 375 20160233
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Pittman T B, Shih Y H, Strekalov D V, Sergienko A V 1995 Phys. Rev. A 52 R3429
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Bennink R S, Bentley S J, Boyd R W 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 113601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Gatti A, Brambilla E, Bache M, Lugiato L A 2004 Phys. Rev. A 70 013802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Cheng J, Han S 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 92 093903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Cao D Z, Xiong J, Wang K G 2005 Phys. Rev. A 71 013801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Valencia A, Scarcelli G, D’ Angelo M, Shih Y H 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 063601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ferri F, Magatti D, Gatti A, Bache M, Brambilla E, Lugiato L A 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 183602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Cai Y, Zhu S Y 2005 Phys. Rev. E 71 056607
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang D, Zhai Y H, Wu L A, Chen X H 2005 Opt. Lett. 30 2354
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Cai Y, Wang F 2007 Opt. Lett. 32 205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Liu X F, Chen X H, Yao X R, Yu W K, Zhai G J, Wu L A 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 2314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Sun B, Edgar M P, Bowman R, Vittert L E, Welsh S, Bowman A, Padgett M J 2013 Science 340 844
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Bromberg Y, Katz O, Silberberg Y 2009 Phys. Rev. A 79 053840
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Shapiro J H 2008 Phys. Rev. A 78 061802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhao C Q, Gong W L, Chen M L, Li E R, Wang H, Xu W D, Han S S 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 101 141123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hong Y, Li E R, Gong W L, Han S S 2015 Opt. Express 23 14541
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Chen M, Li E, Gong W L, Bo Z, Xu X, Zhao C, Shen X, Xu W, Han S S 2013 Opt. Photonics J. 3 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Li S, Cropp F, Kabra K, Lane T J, Wetzstein G, Musumeci P, Ratner D 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 121 114801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Cheng J 2009 Opt. Express 17 7916
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Cheng J, Lin J 2013 Phys. Rev. A 87 043810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Cao D Z, Xiong J, Zhang S H, Lin L F, Gao L, Wang K G 2008 Appl. Phys. Lett. 92 201102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chan K W C, O’ Sullivan M N, Boyd R W 2010 Opt. Express 18 5562
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Zhang D J, Li H G, Zhao Q L, Wang S, Wang H B, Xiong J, Wang K G 2015 Phys. Rev. A 92 013823
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Li H G, Zhang D J, Xu D J, Zhao Q L, Wang S, Wang H B, Xiong J, Wang K G 2015 Phys. Rev. A 92 043816
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Katz O, Bromberg Y, Silberberg Y 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 95 131110
[27] 仲亚军, 刘娇, 梁文强, 赵生妹 2015 64 014202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhong Y J, Liu J, Liang W Q, Zhao S M 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 014202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Gao C, Wang X, Wang Z, Li Z, Du G, Chang F, Yao Z 2017 Phys. Rev. A 96 023838
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Cao D H, Li Q H, Zhuang X C, Ren H, Zhang S H, Song X B 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 123401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Yang H, Wu H, Wang H B, Cao D H, Zhang S H, Xiong J, Wang K 2018 Phys. Rev. A 98 053853
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Salem R, Foster M A, Gaeta A L 2013 Adv. Opt. Photonics 5 274
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Foster M A, Salem R, Geraghty D F, Turner-Foster A C, Lipson M, Gaeta A L 2008 Nature 456 81
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Schröder J, Wang F, Clarke A, Ryckeboer E, Pelusi M , Roelens M A, Eggleton B J 2010 Opt. Commun. 283 2611
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Fridman M, Farsi A, Okawachi Y, Gaeta A L 2012 Nature 481 62
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Ryczkowski P, Barbier M, Friberg A T, Dudley J M, Genty G 2016 Nat. Photonics 10 167
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Shirai T, Setälä T, Friberg A T 2010 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 27 2549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Setälä T, Shirai T, Friberg A T 2010 Phys. Rev. A 82 043813
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Chen Z, Li H, Li Y, Shi J, Zeng G 2013 Opt. Eng. 52 076103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Gao L, Zhang S H, Xiong J, Gan S, Feng L J, Cao D Z, Wang K G 2009 Phys. Rev. A 80 021806
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Vabre L, Dubois A, Boccara A C 2002 Opt. Lett. 27 530
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Kolner B H 1994 IEEE J. Quant. Electron. 30 1951
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Cai Y, Zhu S 2004 Opt. Lett. 29 2716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Qu L, Bai Y, Nan S, Shen Q, Li H, Fu X 2018 Opt. Laser Technol. 104 197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 8668
- PDF下载量: 94
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: