-
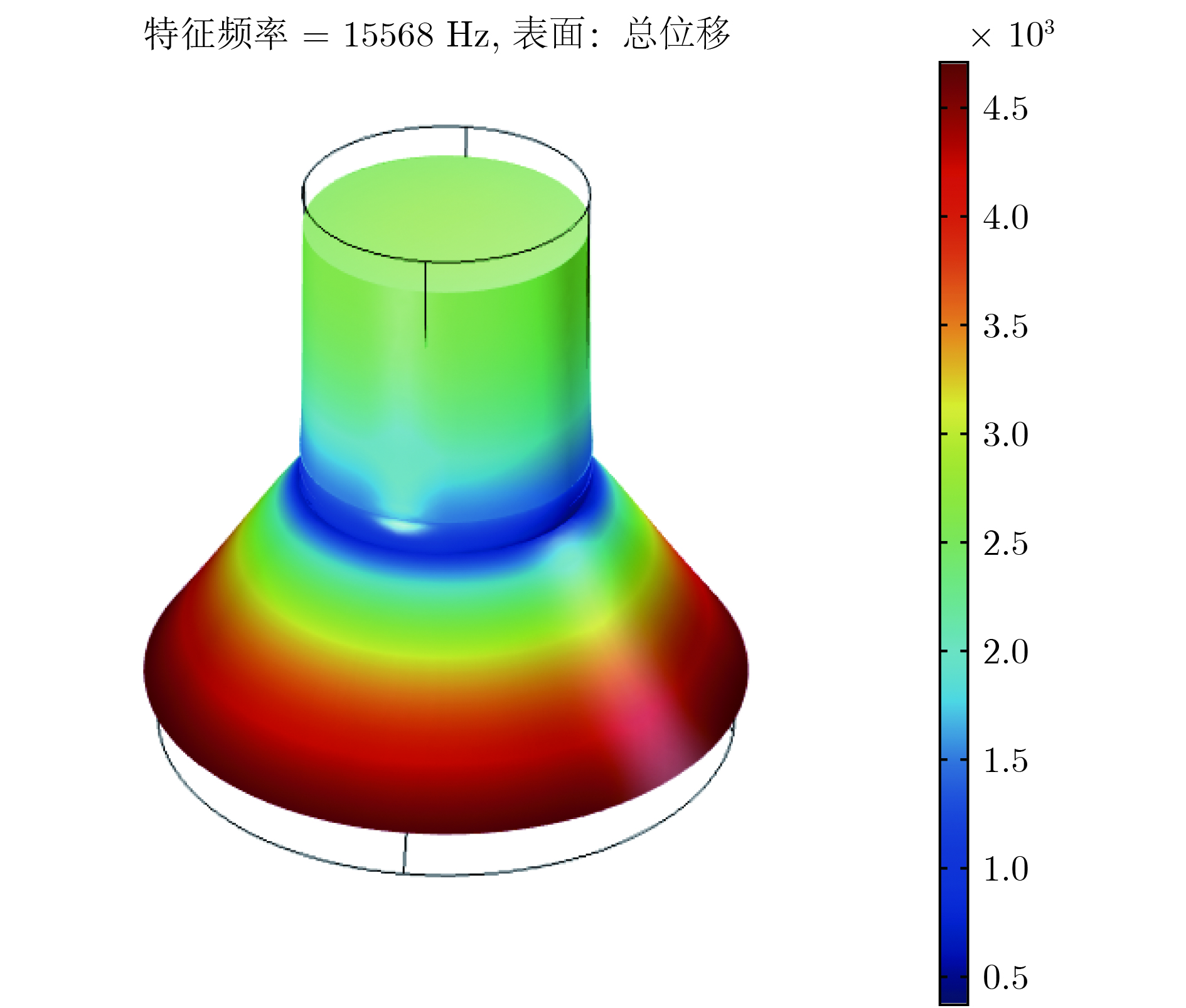
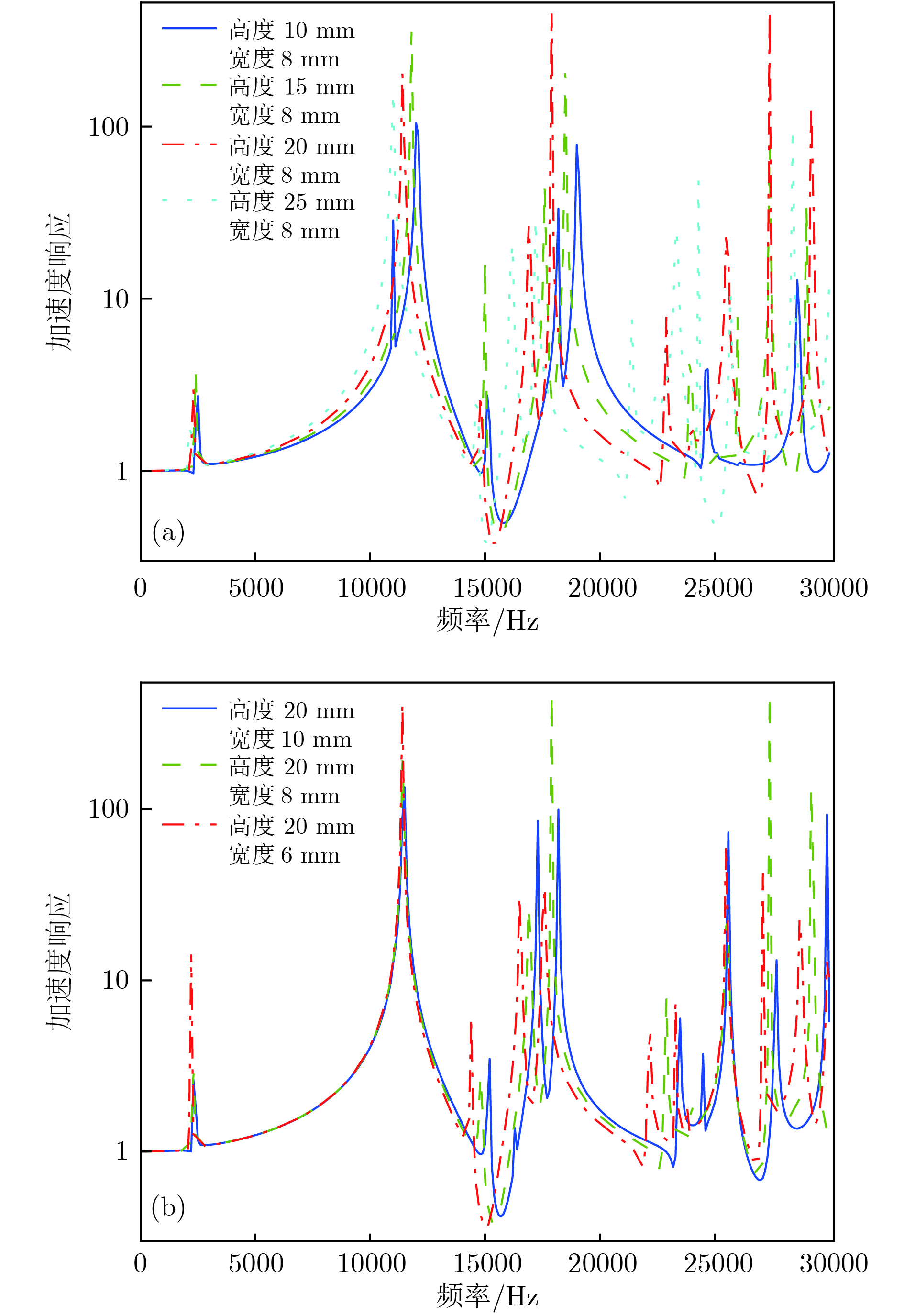
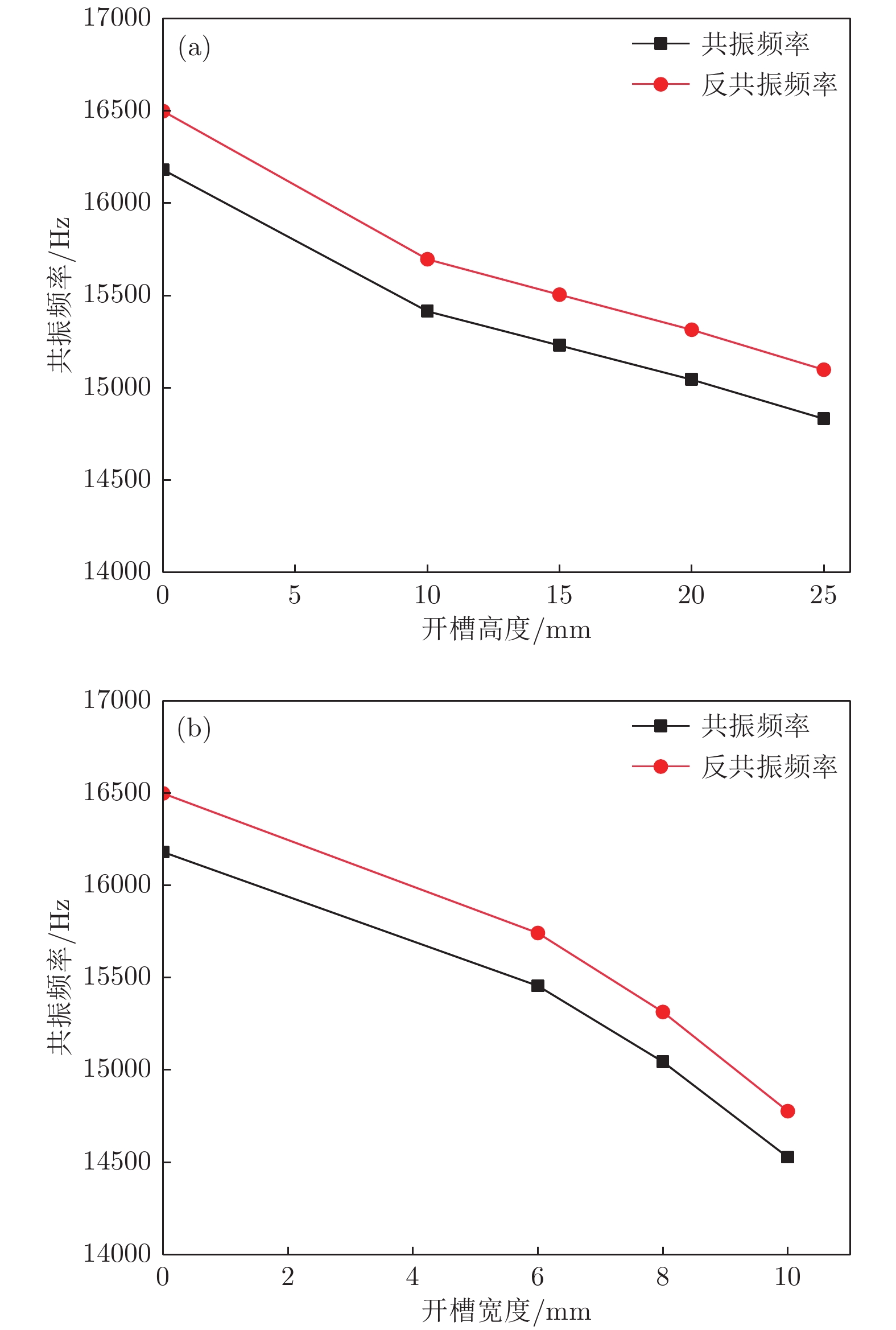
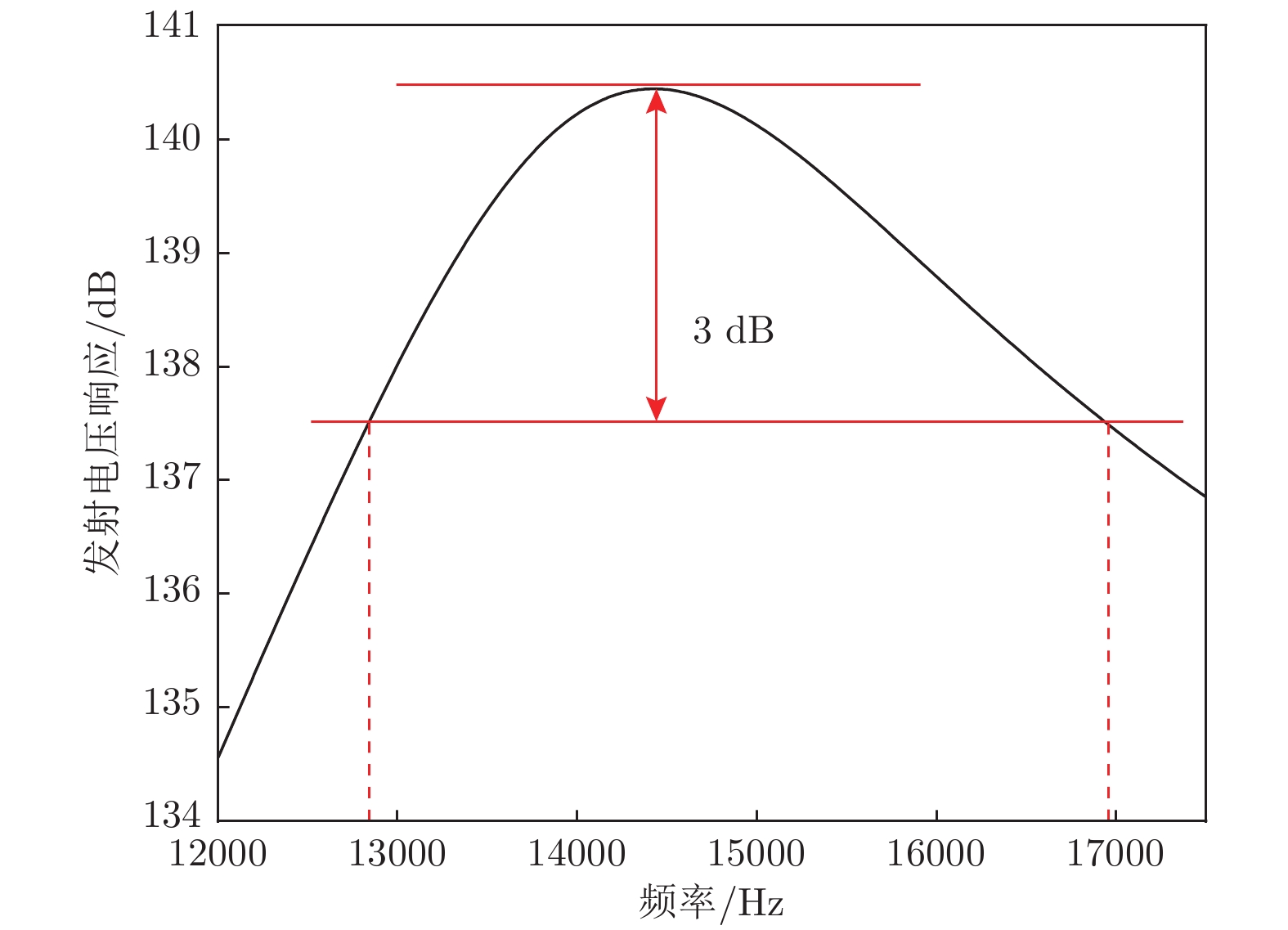
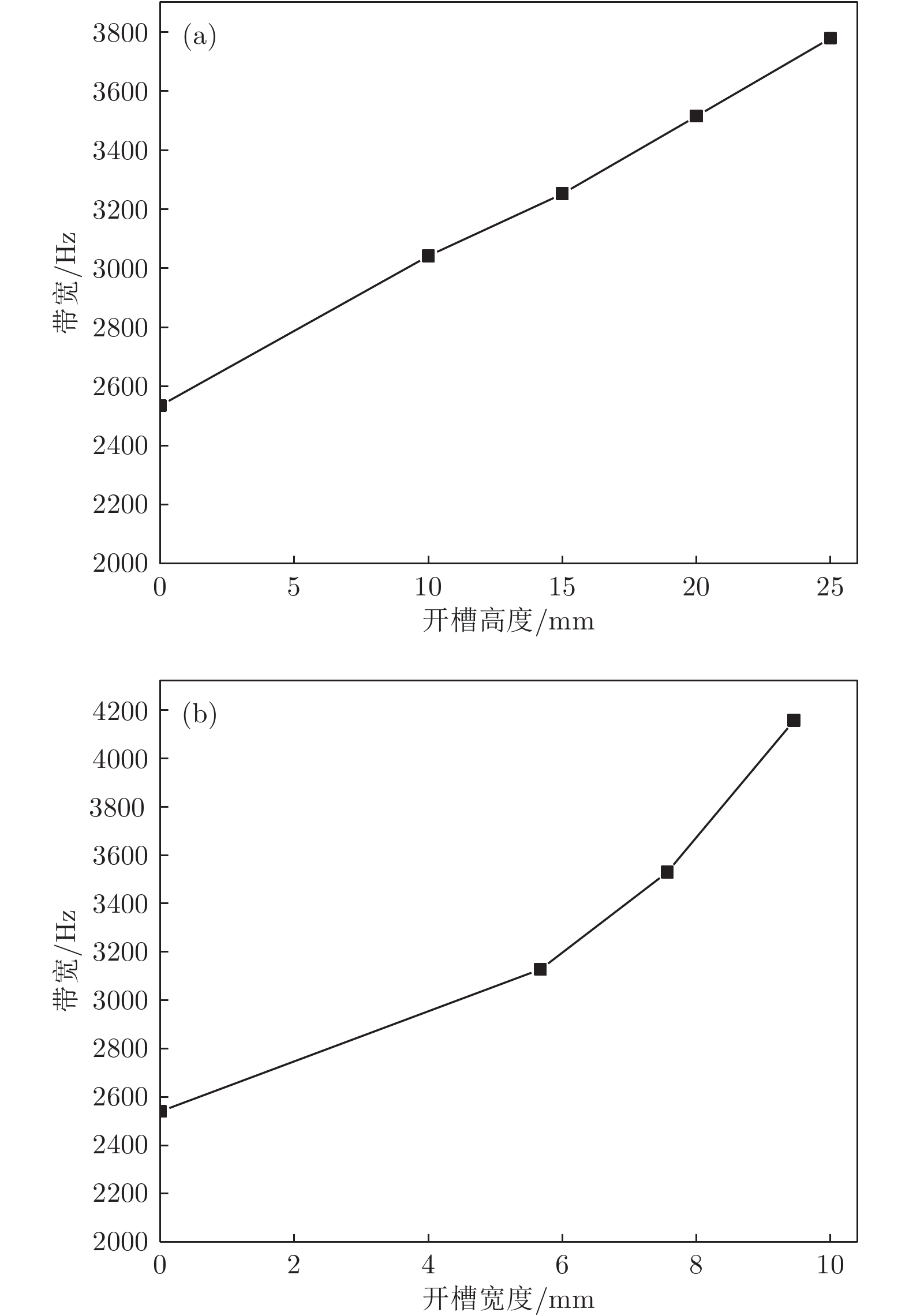
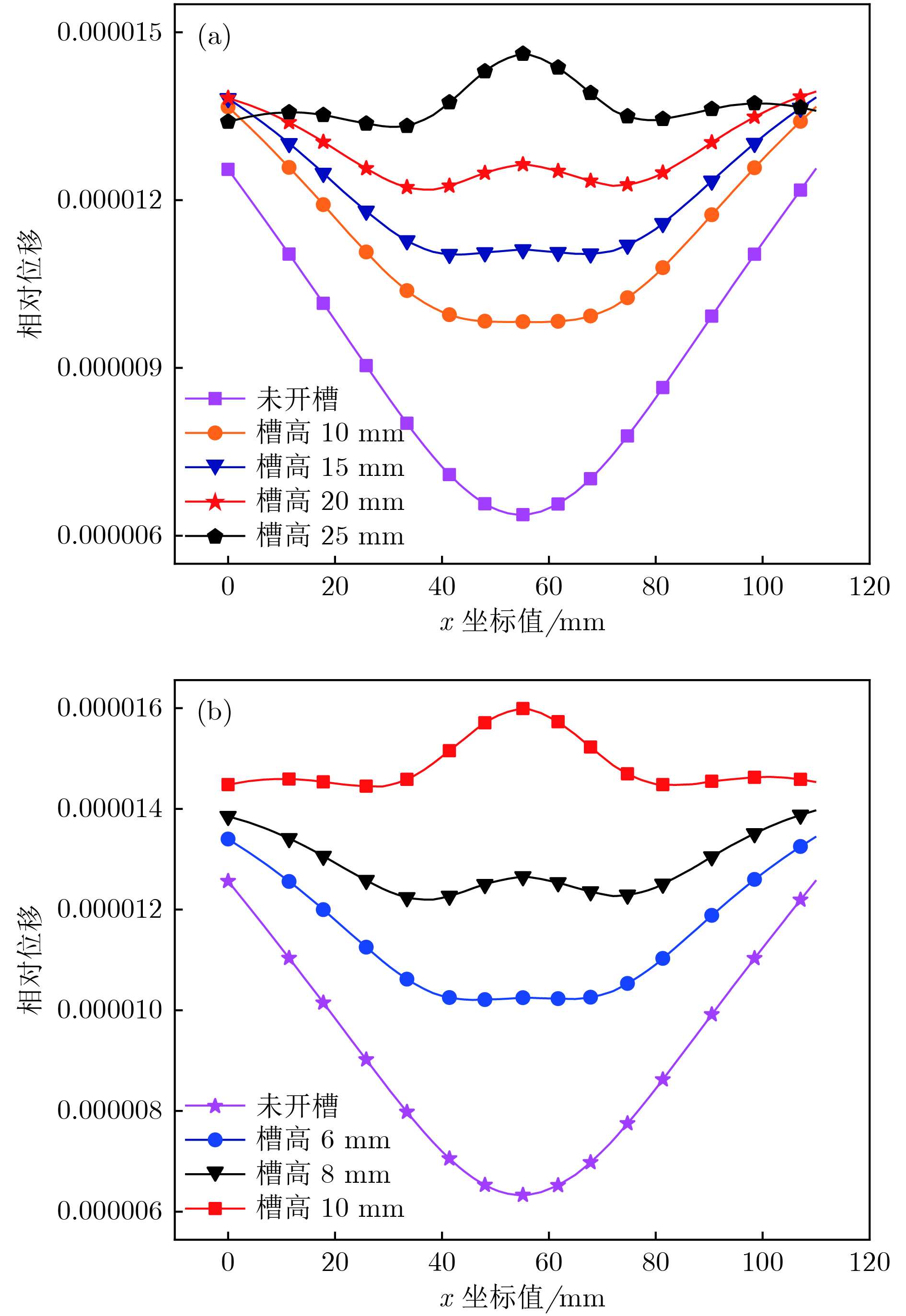
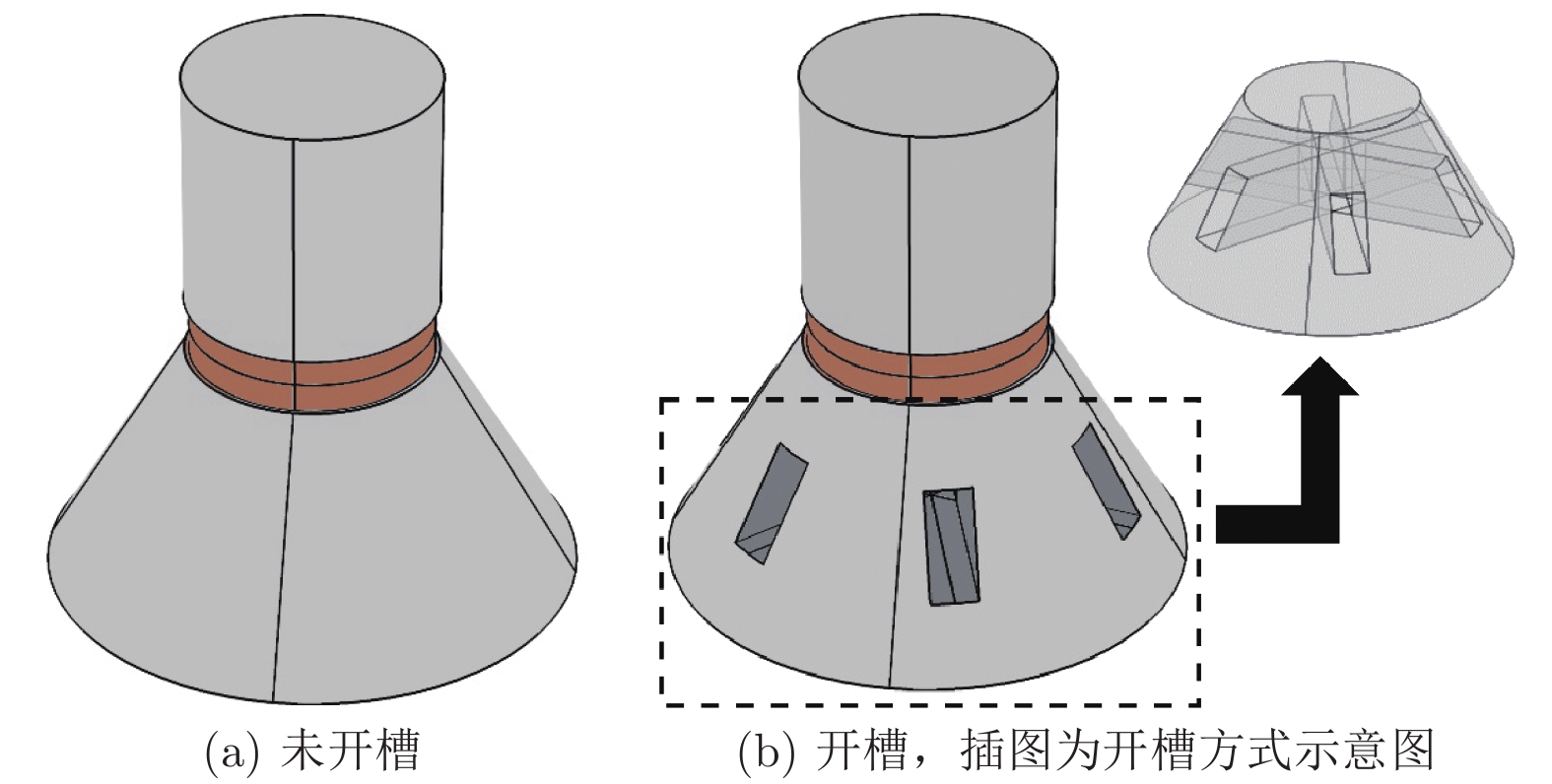
夹心式换能器应用极为广泛, 但当其横向尺寸过大时, 存在耦合振动, 影响其辐射面的位移分布. 本文通过在大尺寸夹心式换能器的前盖板中加工周期排列的槽, 来形成一种二维声子晶体结构. 随后, 采用有限元法对基于二维声子晶体的大尺寸夹心式换能器的振动传输特性、共振频率以及发射电压响应进行仿真模拟, 讨论了开槽高度和开槽宽度对其带隙、共振与反共振频率、带宽以及辐射面位移分布的影响. 研究结果表明, 通过在大尺寸夹心式换能器中应用声子晶体结构可对其进行优化设计. 当大尺寸夹心式换能器的工作频率位于其带隙范围内时, 二维声子晶体结构能有效地抑制其横向振动, 从而改善换能器辐射面位移分布的均匀程度. 此外, 在大尺寸夹心式换能器的前盖板中加工二维声子晶体结构, 能有效提升换能器的带宽, 进而拓宽大尺寸夹心式换能器的工作频带.Sandwich transducers are extremely versatile, but when the lateral dimension is too large, the displacement of the radiating surface is uneven due to the coupling vibration. Due to the unique vibrational band gap characteristics of phononic crystal, vibrations in the bandgap range can be prohibited from propagating for infinite periodic structure or suppressed for finite periodic structure, which makes it widely used in the field of vibration suppression. In this paper, a two-dimensional phononic crystal structure is formed by processing periodically aligned grooves in the front cover of a large-sized sandwich transducer. Since the periodic grooves are formed in the radial direction, the radial waves cannot propagate, and thus the lateral vibration is suppressed. Subsequently, the finite element method is used to simulate the vibration transmission characteristic, resonance frequency and emission voltage response of a large-sized sandwich transducer based on two-dimensional phononic crystal. The effects of slot height and slot width on its bandgap, resonance and anti-resonant frequency, bandwidth, and displacement profile of the radiating surface are discussed. The results show that the phonon crystal structure can be optimized by using a large-sized sandwich transducer. The large-sized sandwich transducer based on two-dimensional phononic crystal has a lateral band gap. When the operating frequency of the large-sized sandwich transducer is within the band gap range, the two-dimensional phononic crystal structure can effectively suppress the lateral vibration, and the uniformity of the displacement distribution of the radiating surface of the transducer is improved. In addition, when the slot width is constant, the bandwidth of the large-sized sandwich transducer based on the two-dimensional phononic crystal increases as the slot height increases. Similarly, when the slot height is constant, the bandwidth of the large-sized sandwich transducer based on the two-dimensional phononic crystal increases as the slot width increases. The two-dimensional phononic crystal structure is processed in the front cover of the large-sized sandwich transducer, and the working frequency band of the large-sized sandwich transducer is effectively broadened.
-
Keywords:
- phononic crystal /
- sandwich piezoelectric transducer /
- lateral vibration /
- broadband
[1] Lin S Y 2005 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 117 653
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Lin S Y 2006 Ultrasonics 44 109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Li X, Yao Z 2016 Smart Mater. Struct. 25 075026
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wei X, Yang Y, Yao W, Zhang L 2017 Sensors 17 2253
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhang Q, Shi S, Chen W 2016 Ultrasonics 66 18
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 左斌, 邵华 2013 机械设计与研究 29 26
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zuo B, Shao H 2013 Machine Design & Research 29 26
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 林书玉 2004 超声换能器的原理及设计 (北京: 科学出版社) 第98页
Lin S Y 2004 The Theory and Design of Ultrasonic Transducers (Beijing: Science Press) p98 (in Chinese)
[8] 林书玉 1993 声学与电子工程 2 34
Lin S Y 1993 Acoust. Electron. Engin. 2 34
[9] 林书玉, 张福成 1994 应用声学 3 30
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lin S Y, Zhang F Z 1994 J. Appl. Acoust. 3 30
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Kushwaha M S, Halevi P, Dobrzynski L, Djafari-Rouhani B 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 73 2022
[11] 唐一璠, 林书玉 2016 65 164202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang Y F, Lin S Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 164202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 张思文, 吴九汇 2013 62 134302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang W S,Wu J H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 134302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Liu Z, Chan C T, Sheng P 2005 Phys. Rev. B 71 014103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 温激鸿 2005 博士学位论文(长沙: 国防科学技术大学)
Wen J H 2005 Ph. D. Dissertation (Changsha: National University of Defense Technology) (in Chinese)
[15] 温熙森, 温激鸿, 郁殿龙, 王刚, 刘耀宗, 韩小云 2004 声子晶体 (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第244页
Wen X S, Wen J H, Yu D L, Wang G, Liu Y Z, Han X Y 2004 Phononic Crystals (Beijing: National Defense Industry Press) p244 (in Chinese)
[16] Ronda S, Aragón J L, Iglesias E, Montero de E F 2017 Sensors 17 729
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Aragón J L, Quinterotorres R, Domínguezjuárez J L, Iglesias E, Ronda S, Montero de E F 2016 Ultrasonics 71 177
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wen J H, Wang G, Yu D L, Zhao H G, Liu Y Z 2005 J. Appl. Phys. 97 141
[19] Wen J H, Yu D L, Liu J W, Xiao Y, Wen X S 2009 Chin. Phys. B 18 2404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhao S Q, Liu B X, Wang Y Q, Chen H L 2013 Adv. Mater. Res. 694 354
-
表 1 大尺寸夹心式换能器的带隙分布情况
Table 1. Band gap distribution of large-size sandwich transducers.
开槽高度/mm 开槽宽度/mm 带隙范围/kHz 10 8 15.3—16.8 15 8 15.1—16.5 20 8 14.9—16.1 25 8 14.8—15.6 20 6 15.3—16.3 20 8 14.9—16.1 20 10 14.5—15.7 -
[1] Lin S Y 2005 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 117 653
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Lin S Y 2006 Ultrasonics 44 109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Li X, Yao Z 2016 Smart Mater. Struct. 25 075026
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wei X, Yang Y, Yao W, Zhang L 2017 Sensors 17 2253
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhang Q, Shi S, Chen W 2016 Ultrasonics 66 18
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 左斌, 邵华 2013 机械设计与研究 29 26
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zuo B, Shao H 2013 Machine Design & Research 29 26
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 林书玉 2004 超声换能器的原理及设计 (北京: 科学出版社) 第98页
Lin S Y 2004 The Theory and Design of Ultrasonic Transducers (Beijing: Science Press) p98 (in Chinese)
[8] 林书玉 1993 声学与电子工程 2 34
Lin S Y 1993 Acoust. Electron. Engin. 2 34
[9] 林书玉, 张福成 1994 应用声学 3 30
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lin S Y, Zhang F Z 1994 J. Appl. Acoust. 3 30
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Kushwaha M S, Halevi P, Dobrzynski L, Djafari-Rouhani B 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 73 2022
[11] 唐一璠, 林书玉 2016 65 164202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang Y F, Lin S Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 164202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 张思文, 吴九汇 2013 62 134302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang W S,Wu J H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 134302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Liu Z, Chan C T, Sheng P 2005 Phys. Rev. B 71 014103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 温激鸿 2005 博士学位论文(长沙: 国防科学技术大学)
Wen J H 2005 Ph. D. Dissertation (Changsha: National University of Defense Technology) (in Chinese)
[15] 温熙森, 温激鸿, 郁殿龙, 王刚, 刘耀宗, 韩小云 2004 声子晶体 (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第244页
Wen X S, Wen J H, Yu D L, Wang G, Liu Y Z, Han X Y 2004 Phononic Crystals (Beijing: National Defense Industry Press) p244 (in Chinese)
[16] Ronda S, Aragón J L, Iglesias E, Montero de E F 2017 Sensors 17 729
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Aragón J L, Quinterotorres R, Domínguezjuárez J L, Iglesias E, Ronda S, Montero de E F 2016 Ultrasonics 71 177
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wen J H, Wang G, Yu D L, Zhao H G, Liu Y Z 2005 J. Appl. Phys. 97 141
[19] Wen J H, Yu D L, Liu J W, Xiao Y, Wen X S 2009 Chin. Phys. B 18 2404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhao S Q, Liu B X, Wang Y Q, Chen H L 2013 Adv. Mater. Res. 694 354
计量
- 文章访问数: 9618
- PDF下载量: 97
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: