-
光子拓扑绝缘体为光子器件的设计和应用带来了新的可能性. 本文研究了基于时间反演对称性破缺的非互易光子拓扑绝缘体多层结构间的Casimir效应. 讨论该多层系统中Casimir排斥作用力的产生, 以及Casimir稳定平衡回复力的实现和调控, 并且着重分析了光子拓扑绝缘体光轴角度差对Casimir作用力的影响. 利用多层系统间的整体相对旋转可得到Casimir作用力的不同取向及其平衡点, 而系统内部各层间的光轴角度差对Casimir效应的影响趋势中存在拐点, 因此可利用多层系统中的旋转自由度来精细控制Casimir相互作用. 本文所提供的新的操控途径和操控自由度, 在实际微纳米系统中减小Casimir效应的不良影响或利用该效应开发其对系统的调控方面具有实际意义.
-
关键词:
- 光子拓扑绝缘体 /
- Casimir效应 /
- Casimir排斥力 /
- 多层系统
The Casimir effect has received extensive attention theoretically and experimentally in recent years. It arises from the macroscopic manifestation of quantum vacuum fluctuations, and this Casimir interaction force can be an effective means of driving and controlling components in micro-electro-mechanical system (MEMS) and nano-electromechanical system (NEMS). Due to the new possibilities provided by photonic topological insulator for designing and using photonic devices, in this work, the Casimir force between the multilayer structures of non-reciprocal photonic topological insulators with broken time-reversal symmetry is investigated, and the influences of the dielectric tensor of the photonic topological insulator, the spatial structural parameters of the multilayer system, and the rotational degree of freedom on the Casimir force are examined. It is found that there exists Casimir repulsive force in such a multilayer system, and the Casimir stable equilibrium and restoring force can be further realized and controlled. Continuous variation between anti-mirror-symmetric configuration and mirror-symmetric configuration is examined. Both the Casimir attraction and repulsion can be generally enhanced through structural optimization by increasing layer number and individual layer thickness. Furthermore, we focus on the detailed analysis of how the optical axis angle difference within the photonic topological insulator layers can be used to adjust the Casimir force. The overall relative rotation of the multilayer system may adjust the magnitude and the direction of the Casimir force, and some inflection points can be found from the influence curve of the optical axis angle difference between internal layers of the multilayer on the Casimir force, allowing the rotational degrees of freedom in the multilayer system to be used for fine-adjusting the Casimir interaction. This work introduces the enhanced degrees of freedom for probing and manipulating the interaction between small objects in micro/nano systems, thereby suppressing adverse Casimir forces and effectively using them.-
Keywords:
- photonic topological insulator /
- Casimir effect /
- repulsive Casimir force /
- multilayered system
[1] Hasan M Z, Kane C L 2010 Rev. Mod. Phys. 82 3045
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Qi X L, Zhang S C 2011 Rev. Mod. Phys. 83 1057
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Xia Y, Qian D, Hsieh D, Wray L, Pal A, Lin H, Bansil A, Grauer D, Hor Y S, Cava R J, Hasan M Z 2009 Nat. Phys. 5 398
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhang H J, Liu C X, Qi X L, Dai X, Fang Z, Zhang S C 2009 Nat. Phys. 5 438
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Luo W, Qi X L 2013 Phys. Rev. B 87 085431
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wang P, Ge J, Li J, Liu Y, Xu Y, Wang J 2021 Innovation 2 100098
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Haldane F D M, Raghu S 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 013904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang Z, Chong Y, Joannopoulos J D, Soljačić M 2009 Nature 461 772
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 王子尧, 陈福家, 郗翔, 高振, 杨怡豪 2024 73 064201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Z Y, Chen F J, Xi X, Gao Z, Yang Y H 2024 Acta Phys. Sin 73 064201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wang Y, Lu Y H, Gao J, Chang Y J, Ren R J, Jiao Z Q, Zhang Z Y, Jin X M 2022 Chip 1 100003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Yang Y H, Yamagami Y, Yu X B, Pitchappa P, Webber J, Zhang B L, Fujita M, Nagatsuma T, Singh R 2020 Nat. Photonics 14 446
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Webber J, Yamagami Y, Ducournau G, Szriftgiser P, Iyoda K, Fujita M 2021 J. Lightwave Technol. 39 7609
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Tschernig K, Jimenez-Galán Á, Christodoulides D N, Ivanov M, Busch K, Bandres M A, Perez-Leija A 2021 Nat. Commun. 12 1974
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chen Y, He X T, Cheng Y J, Qiu H Y, Feng L T, Zhang M, Dai D X, Guo G C, Dong J W, Ren X F 2021 Phys. Rev. Lett. 126 230503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Dai T X, Ao Y T, Bao J M, Mao J, Chi Y L, Fu Z R, You Y L, Chen X J, Zhai C H, Tang B, Yang Y, Li Z H, Yuan L Q, Gao F, Lin X, Thompson M G, O’Brien J L, Li Y, Hu X Y, Gong Q H, Wang J W 2022 Nat. Photonics 16 248
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Tang G J, He X T, Shi F L, Liu J W, Chen X D, Dong J W 2022 Laser Photonics Rev. 16 2100300
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lustig E, Maczewsky L J, Beck J, Biesenthal T, Heinrich M, Yang Z, Plotnik Y, Szameit A, Segev M 2022 Nature 609 931
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Teo H T, Xue H R, Zhang B L 2022 Phys. Rev. A 105 053510
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Devi K M, Jana S, Chowdhury D R 2021 Opt. Mater. Express 11 2445
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Casimir H B G 1948 Proceedings of the Koninklijke Nederlandse Akademie van Wetenschappen 51 793
[21] Palasantzas G, Sedighi M, Svetovoy V B 2020 Appl. Phys. Lett. 117 120501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Vasilyev O A, Marino E, Kluft B B, Schall P, Kondrat S 2021 Nanoscale 13 6475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 周帅, 柳开鹏, 戴士为, 葛力新 2025 74 014202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou S, Liu K P, Dai S W, Ge L X 2025 Acta Phys. Sin 74 014202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Zeng R, Wang C, Zeng X D, Li H Z, Yang S N, Li Q L, Yang Y P 2020 Opt. Express 28 7425
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Küçüköz B, Kotov O V, Canales A, Polyakov A Y, Agrawal A V, Antosiewicz T J, Shegai T O 2024 Sci. Adv. 10 eadn1825
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Grushin A G, Cortijo A 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 106 020403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Fuchs S, Lindel F, Krems R V, Hanson G W, Antezza M, Buhmann S Y 2017 Phys. Rev. A 96 062505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Lindel F, Hanson G W, Antezza M, Buhmann S Y 2018 Phys. Rev. B 98 144101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Masyukov M S, Grebenchukov A N 2021 Phys. Rev. B 104 165308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Nefedov I S, Valagiannopoulos C A, Melnikov L A 2013 J. Opt. 15 114003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Zeng R, Chen L, Nie W, Bi M, Yang Y, Zhu S 2016 Phys. Lett. A 380 2861
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Chiadini F, Fiumara V, Lakhtakia A, Scaglione A 2019 Appl. Opt. 58 1724
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Zeng R, Gao T, Ni P, Fang S, Li H, Yang S, Zeng Z 2024 J. Opt. 26 075602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Kenneth O, Klich I 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 97 160401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Silveirinha M G 2015 Phys. Rev. B 92 125153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Xu J, He P P, Feng D L, Luo Y M, Fan S Q, Yong K L, Tsakmakidis K L 2023 Opt. Express 31 42388
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Holmes A M, Sabbaghi M, Hanson G W 2021 Phys. Rev. B 104 214433
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Bittencourt J A 2004 Fundamentals of Plasma Physics (Springer: New York
[39] Silveirinha M G, Terças H, Antezza M 2023 Phys. Rev. B 108 235154
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
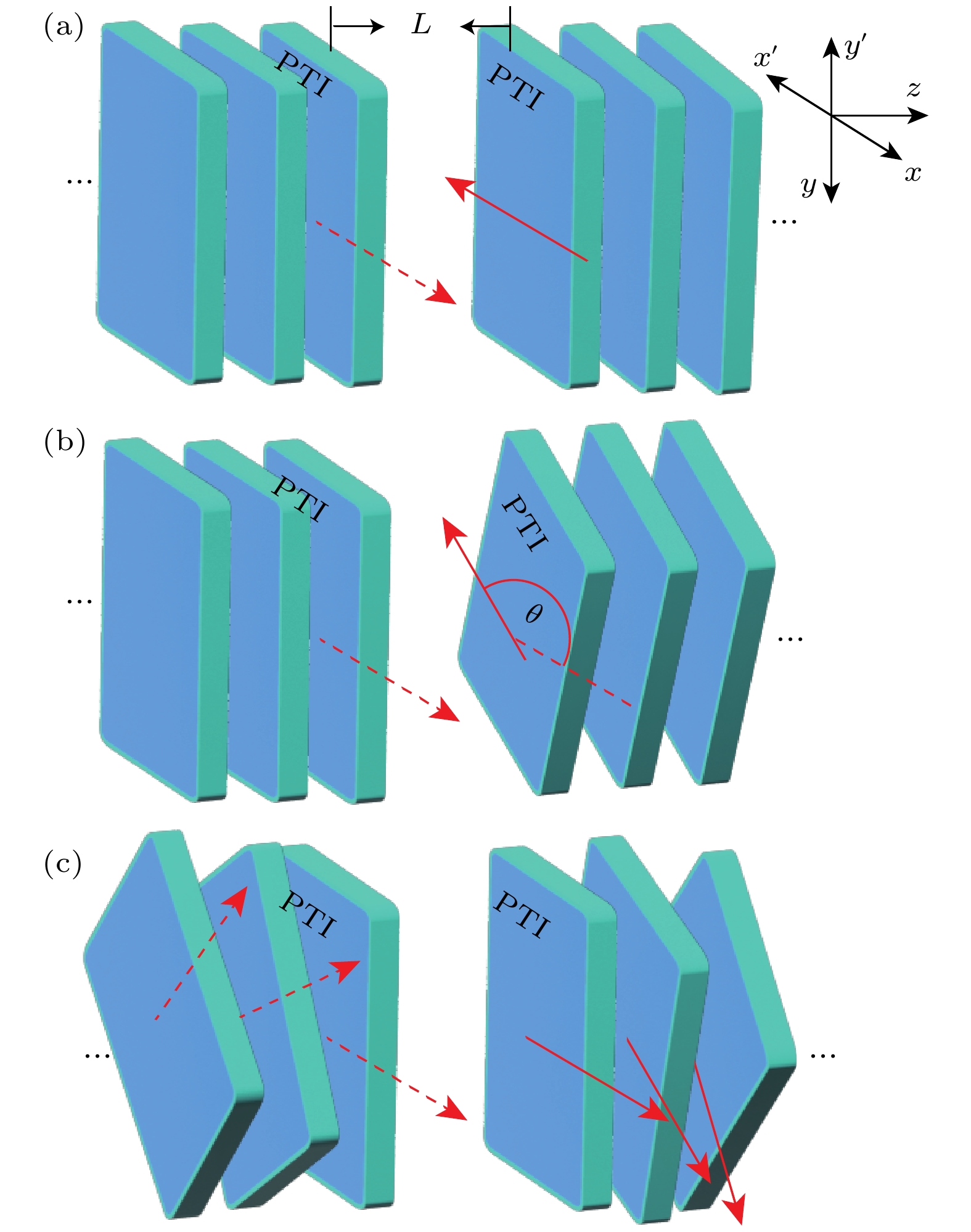
图 1 光子拓扑绝缘体多层结构间Casimir效应示意图, 其中左右多层结构间距L, 左右侧结构相应的参考系分别对应为x-y-z和x'-y'-z坐标系, 红色箭头表示光子拓扑绝缘体的x(x')方向光轴 (a) 两侧结构的该光轴反平行; (b) 两侧结构该光轴的夹角为$\theta $; (c) 系统内部各层相互间也存在光轴夹角
Fig. 1. Sketch of the Casimir effect between multilayered structures made of photonic topological insulators, where L is the separation between two structures, x-y-z and x'-y'-z are the coordinates in the left and right structures, respectively. The red arrows indicate the x(x') optical axes of photonic topological insulators: (a) Anti-parallel on the two sides, (b) an angle $\theta $ between the two sides; (c) exist angles between layers within the system.
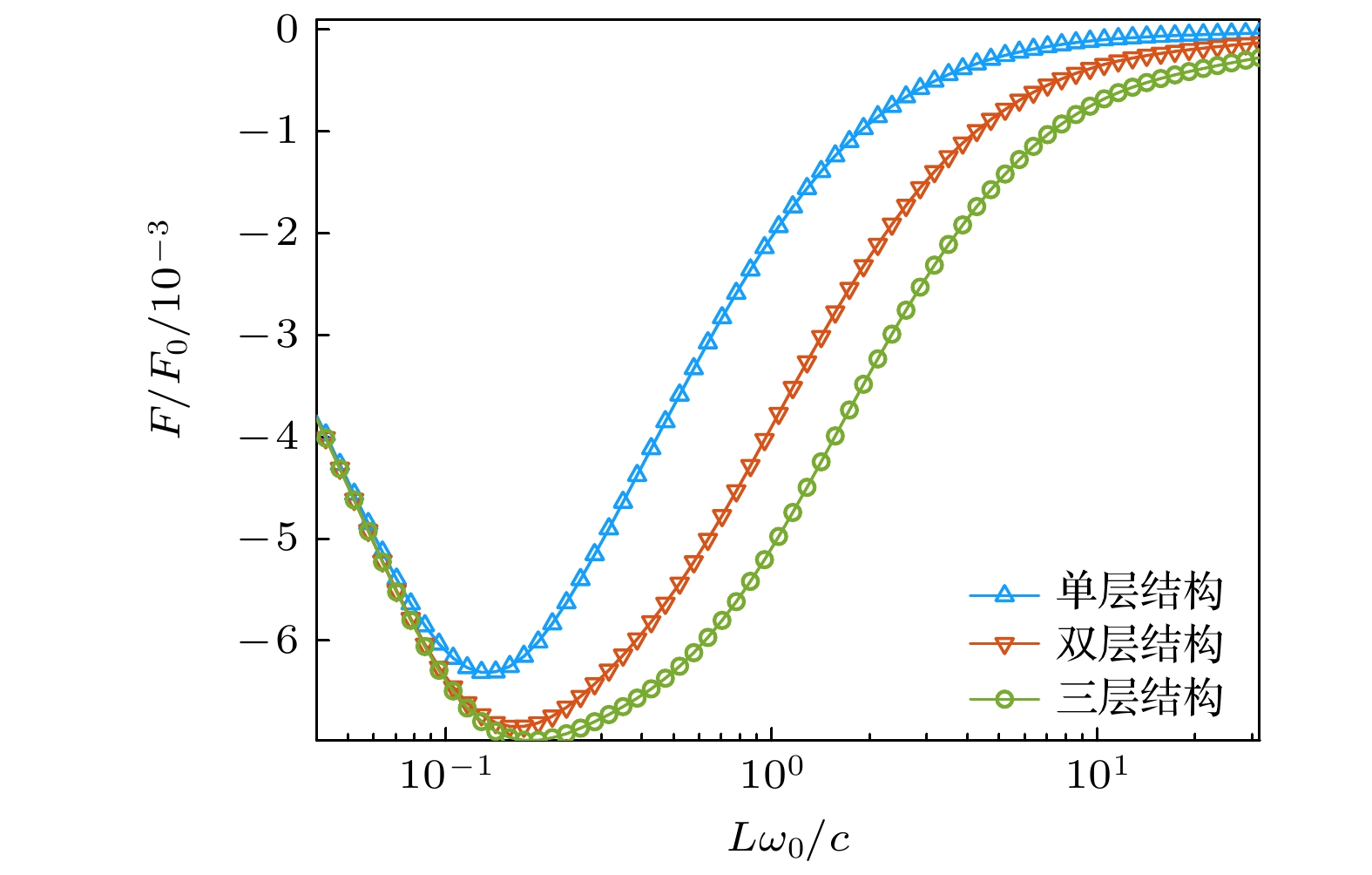
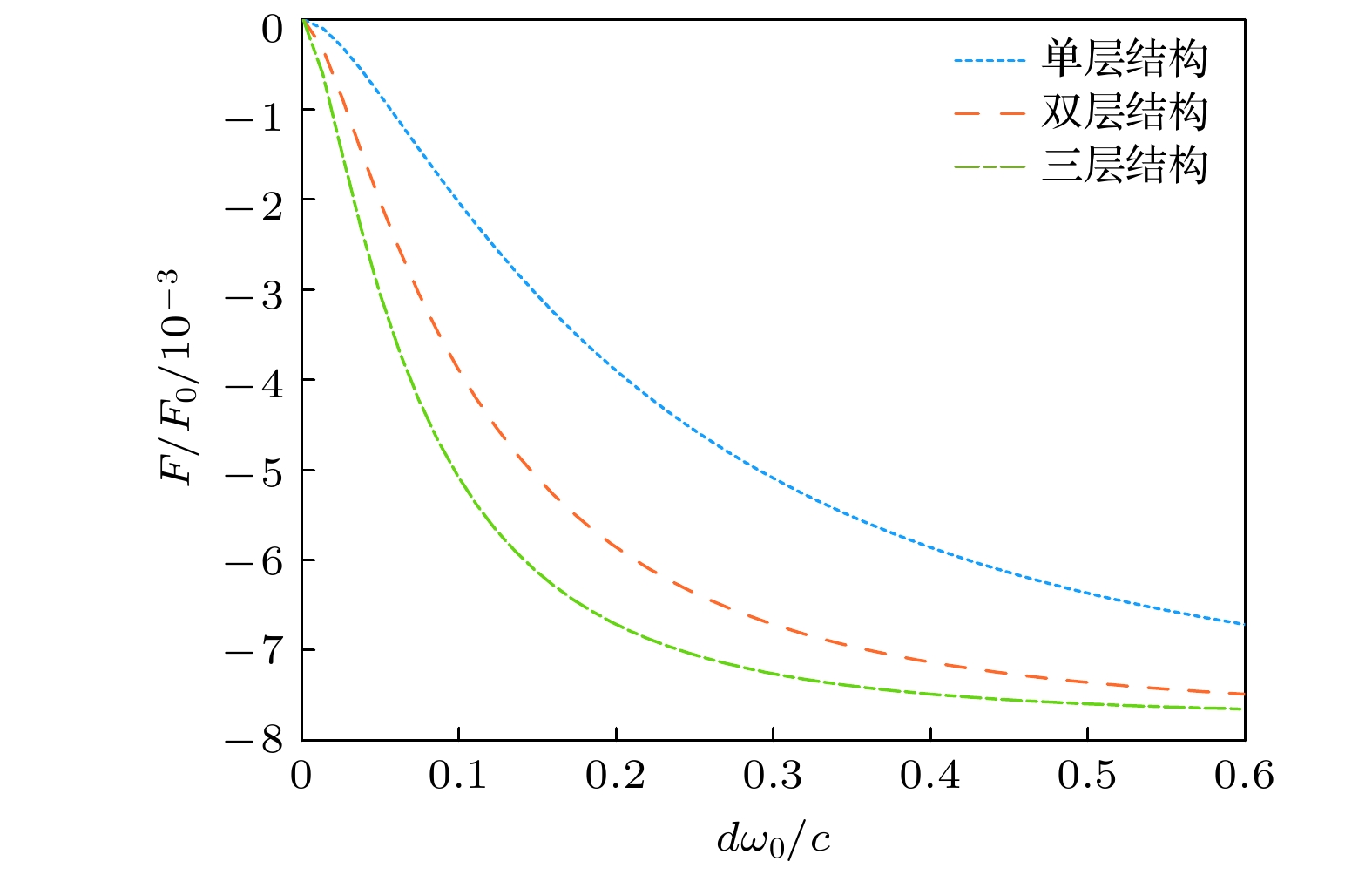
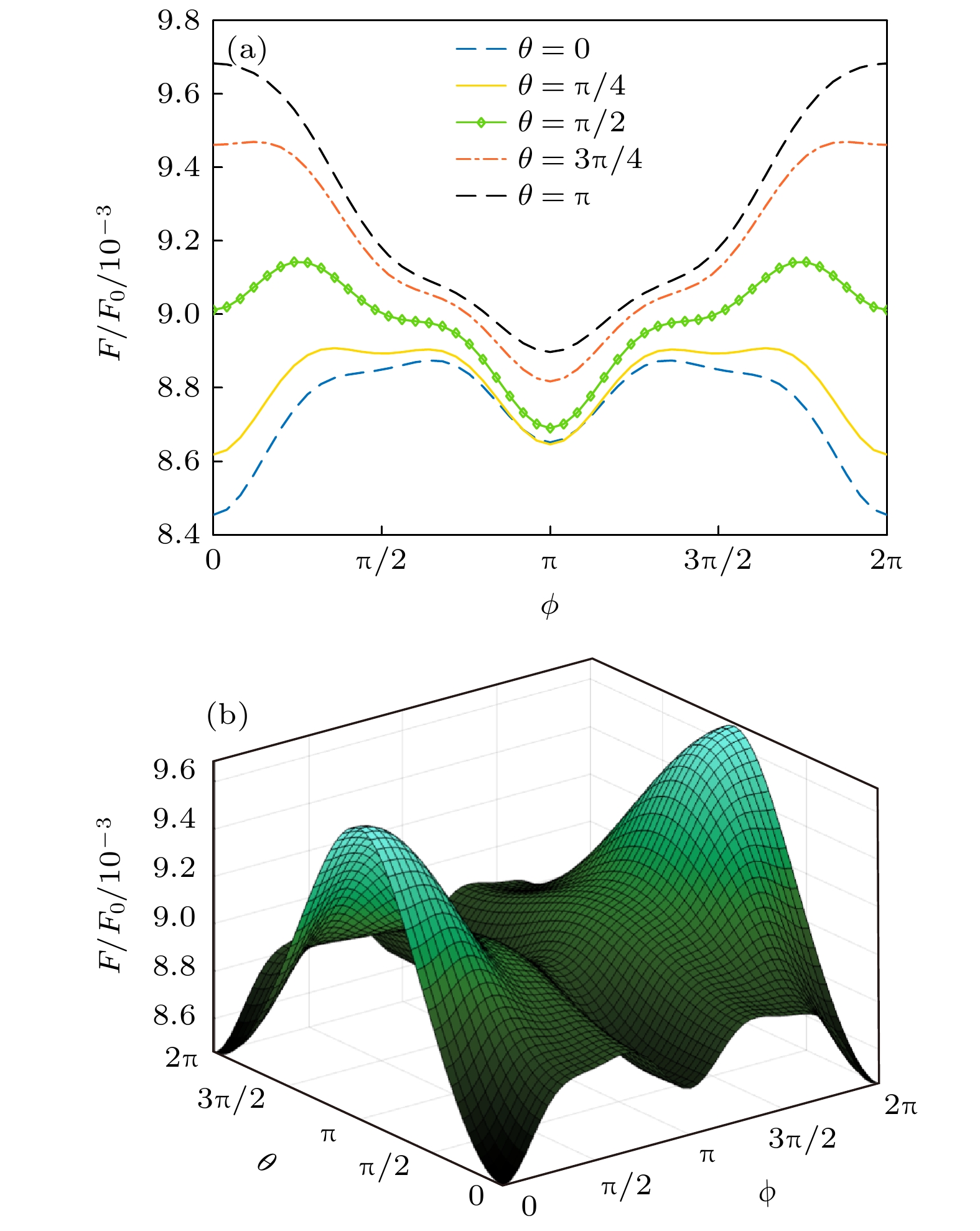
图 4 反镜像对称N层光子拓扑绝缘体结构(N = 1, 2, 3)间的Casimir作用力相对幅值随单元层厚度的变化, 其中结构间距L = 1.0λ, 其他系统参数同图2中的取值
Fig. 4. Relative Casimir force between two N-layer photonic topological insulator structures (N = 1, 2, 3) with inversion-mirror symmetry as a function of the layer thickness, where L = 1.0λ and other parameters are the same as in Fig. 2.
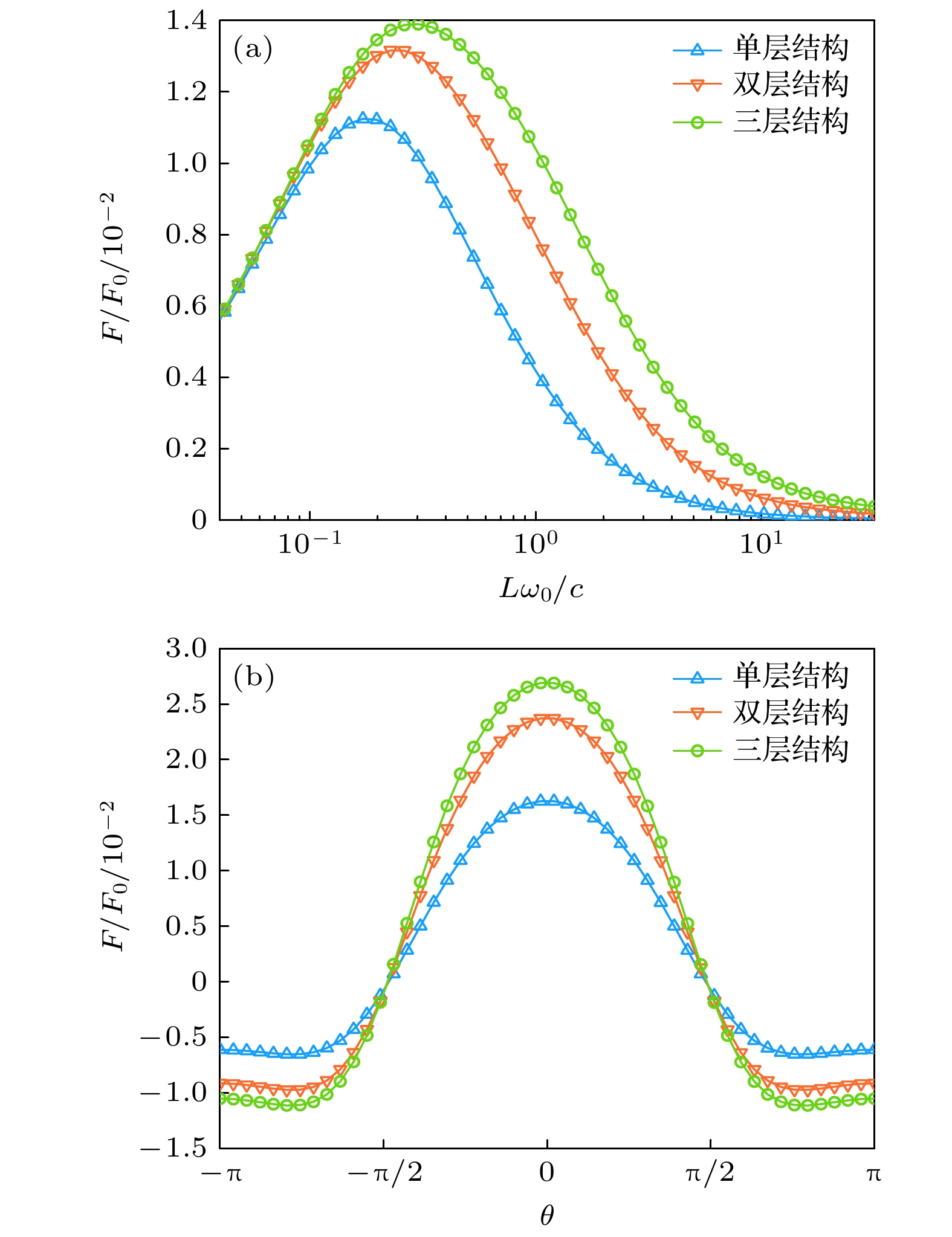
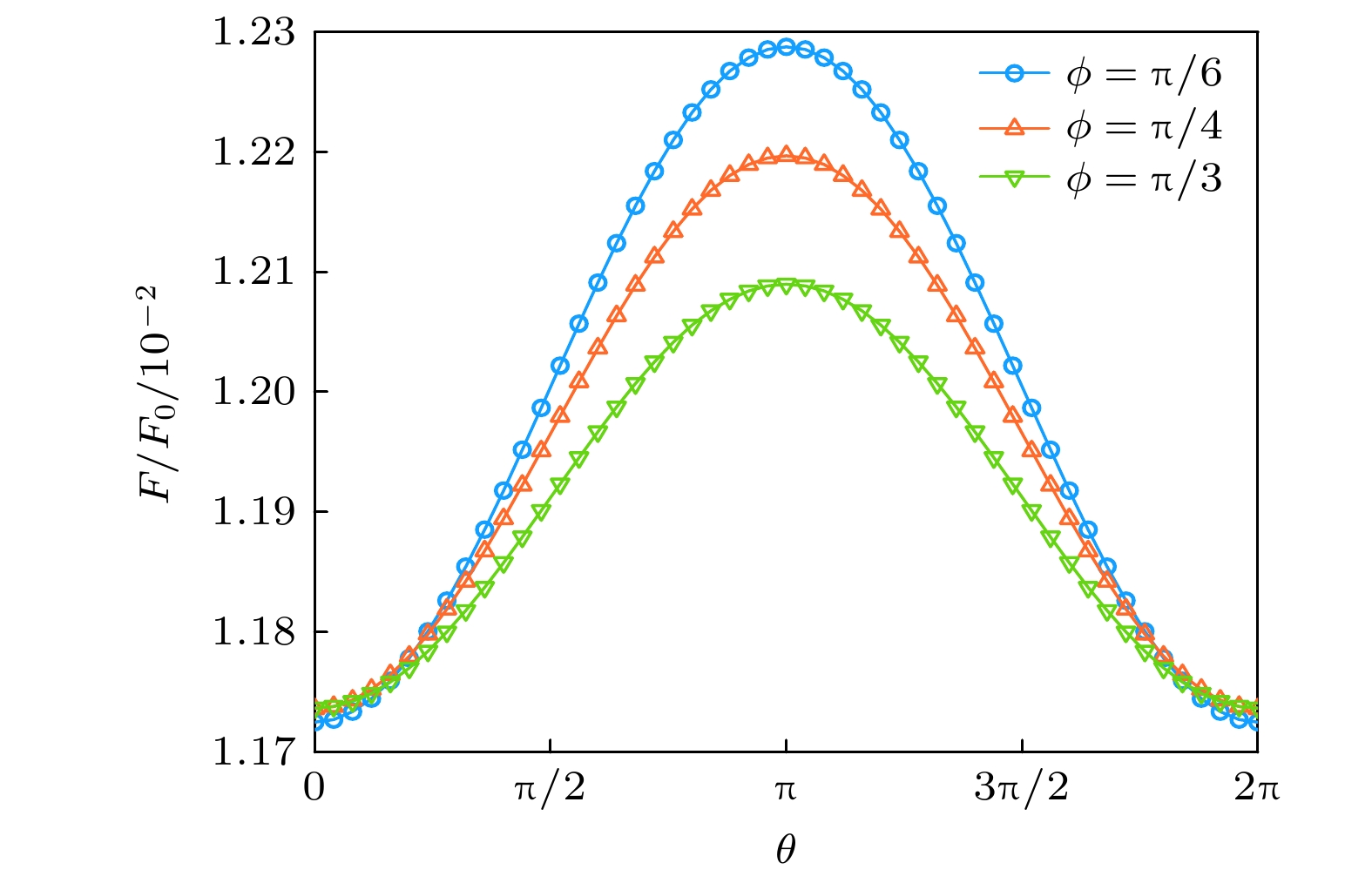
图 6 锑化铟三层系统间Casimir作用力相对幅值在不同 内部层间光轴夹角下随整体旋转角度$\theta $的变化, 其中相 关参数为${\omega _{\text{L}}} = 3.62 \times {10^{13}} {\text{ rad/s}}$, ${\omega _{\text{T}}} = 3.39 \times {10^{13}} {\text{ rad/s}}$, $\varGamma = 5.65 \times {10^{11}} {\text{ rad/s}}$, $\gamma = 3.39 \times {10^{12}} {\text{ rad/s}}$, $N = 1.07 \times $$ {10^{17}}\;{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^{{{ - 3}}}}$, B = 10 T, 其他参数同图4中的取值
Fig. 6. Relative Casimir force between the three-layer InSb systems as a function of the overall rotation angle $\theta $ under different optical axis angles between internal layers, where ${\omega _{\text{L}}} = 3.62 \times {10^{13}}\; {\text{rad/s}}$, ${\omega _{\text{T}}} = 3.39 \times {10^{13}} {\text{ rad/s}}$, $\varGamma = 5.65 \times $$ {10^{11}} {\text{ rad/s}}$, $\gamma = 3.39 \times {10^{12}} {\text{ rad/s}}$, $N = 1.07 \times {10^{17}}\;{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^{{{ - 3}}}}$, B = 10 T, and other parameters are the same as in Fig. 4.
-
[1] Hasan M Z, Kane C L 2010 Rev. Mod. Phys. 82 3045
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Qi X L, Zhang S C 2011 Rev. Mod. Phys. 83 1057
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Xia Y, Qian D, Hsieh D, Wray L, Pal A, Lin H, Bansil A, Grauer D, Hor Y S, Cava R J, Hasan M Z 2009 Nat. Phys. 5 398
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhang H J, Liu C X, Qi X L, Dai X, Fang Z, Zhang S C 2009 Nat. Phys. 5 438
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Luo W, Qi X L 2013 Phys. Rev. B 87 085431
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wang P, Ge J, Li J, Liu Y, Xu Y, Wang J 2021 Innovation 2 100098
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Haldane F D M, Raghu S 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 013904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang Z, Chong Y, Joannopoulos J D, Soljačić M 2009 Nature 461 772
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 王子尧, 陈福家, 郗翔, 高振, 杨怡豪 2024 73 064201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Z Y, Chen F J, Xi X, Gao Z, Yang Y H 2024 Acta Phys. Sin 73 064201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wang Y, Lu Y H, Gao J, Chang Y J, Ren R J, Jiao Z Q, Zhang Z Y, Jin X M 2022 Chip 1 100003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Yang Y H, Yamagami Y, Yu X B, Pitchappa P, Webber J, Zhang B L, Fujita M, Nagatsuma T, Singh R 2020 Nat. Photonics 14 446
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Webber J, Yamagami Y, Ducournau G, Szriftgiser P, Iyoda K, Fujita M 2021 J. Lightwave Technol. 39 7609
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Tschernig K, Jimenez-Galán Á, Christodoulides D N, Ivanov M, Busch K, Bandres M A, Perez-Leija A 2021 Nat. Commun. 12 1974
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chen Y, He X T, Cheng Y J, Qiu H Y, Feng L T, Zhang M, Dai D X, Guo G C, Dong J W, Ren X F 2021 Phys. Rev. Lett. 126 230503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Dai T X, Ao Y T, Bao J M, Mao J, Chi Y L, Fu Z R, You Y L, Chen X J, Zhai C H, Tang B, Yang Y, Li Z H, Yuan L Q, Gao F, Lin X, Thompson M G, O’Brien J L, Li Y, Hu X Y, Gong Q H, Wang J W 2022 Nat. Photonics 16 248
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Tang G J, He X T, Shi F L, Liu J W, Chen X D, Dong J W 2022 Laser Photonics Rev. 16 2100300
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lustig E, Maczewsky L J, Beck J, Biesenthal T, Heinrich M, Yang Z, Plotnik Y, Szameit A, Segev M 2022 Nature 609 931
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Teo H T, Xue H R, Zhang B L 2022 Phys. Rev. A 105 053510
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Devi K M, Jana S, Chowdhury D R 2021 Opt. Mater. Express 11 2445
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Casimir H B G 1948 Proceedings of the Koninklijke Nederlandse Akademie van Wetenschappen 51 793
[21] Palasantzas G, Sedighi M, Svetovoy V B 2020 Appl. Phys. Lett. 117 120501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Vasilyev O A, Marino E, Kluft B B, Schall P, Kondrat S 2021 Nanoscale 13 6475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 周帅, 柳开鹏, 戴士为, 葛力新 2025 74 014202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou S, Liu K P, Dai S W, Ge L X 2025 Acta Phys. Sin 74 014202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Zeng R, Wang C, Zeng X D, Li H Z, Yang S N, Li Q L, Yang Y P 2020 Opt. Express 28 7425
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Küçüköz B, Kotov O V, Canales A, Polyakov A Y, Agrawal A V, Antosiewicz T J, Shegai T O 2024 Sci. Adv. 10 eadn1825
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Grushin A G, Cortijo A 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 106 020403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Fuchs S, Lindel F, Krems R V, Hanson G W, Antezza M, Buhmann S Y 2017 Phys. Rev. A 96 062505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Lindel F, Hanson G W, Antezza M, Buhmann S Y 2018 Phys. Rev. B 98 144101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Masyukov M S, Grebenchukov A N 2021 Phys. Rev. B 104 165308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Nefedov I S, Valagiannopoulos C A, Melnikov L A 2013 J. Opt. 15 114003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Zeng R, Chen L, Nie W, Bi M, Yang Y, Zhu S 2016 Phys. Lett. A 380 2861
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Chiadini F, Fiumara V, Lakhtakia A, Scaglione A 2019 Appl. Opt. 58 1724
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Zeng R, Gao T, Ni P, Fang S, Li H, Yang S, Zeng Z 2024 J. Opt. 26 075602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Kenneth O, Klich I 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 97 160401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Silveirinha M G 2015 Phys. Rev. B 92 125153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Xu J, He P P, Feng D L, Luo Y M, Fan S Q, Yong K L, Tsakmakidis K L 2023 Opt. Express 31 42388
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Holmes A M, Sabbaghi M, Hanson G W 2021 Phys. Rev. B 104 214433
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Bittencourt J A 2004 Fundamentals of Plasma Physics (Springer: New York
[39] Silveirinha M G, Terças H, Antezza M 2023 Phys. Rev. B 108 235154
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 2351
- PDF下载量: 77
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: