-
高空核爆过程会向内磁层注入大量相对论性电子, 形成人工辐射带, 这些高能电子可能对航天器造成显著影响. 本文利用CIMI模型(comprehensive inner magnetosphere-ionosphere model)模拟研究了核爆注入的电子由局地集中分布向环向均匀分布演化的过程, 揭示了人工辐射带形成过程中电子团表现出的螺旋包围、环向膨胀与扩散均匀的行为特征. 对初始时刻集中在$L=1.1—2.2 $、环向覆盖1个时区左右的核爆电子进行的数值模拟表明, 核爆注入电子主要通过螺旋包围过程演化至环向均匀分布, 扩散作用的贡献相对较小. 电子注入后, 在地球磁场的约束下做自西向东环绕地球的漂移运动. 外侧电子漂移速度更快, 因此注入电子团会在环向上剪切拉伸, 以螺旋线结构包围地球. 此外, 研究还发现螺旋结构的形成过程伴随有电子的环向膨胀, 主要由漂移过程中能量色散和投掷角色散机制驱动. 不同能量和投掷角的电子漂移速度不同, 因此逐渐环向分离, 造成环向分布范围扩展, 填充螺旋结构的间隙. 在通过形成螺旋结构与环向膨胀包围地球后, 核爆注入的高能电子进一步通过扩散作用演变为环向均匀分布的结构, 形成相对稳定的人工辐射带.
-
关键词:
- 高空核爆 /
- 人工辐射带 /
- Fokker-Planck 方程 /
- 电子扩散
High-altitude nuclear explosions can inject large amounts of relativistic electrons into the inner magnetosphere, resulting in the formation of artificial radiation belts. These high-energy electrons pose a potential threat to spacecraft due to their long-term stability and influence on space weather. The investigation of the formation and evolution of artificial radiation belts is of great significance for the safety of spacecraft and human space activities. In this study, the comprehensive inner magnetosphere-ionosphere (CIMI) model is used to simulate the transition of electrons from a locally concentrated distribution to an azimuthally uniform distribution, which reveals the spiral encircling, azimuthal expansion, and diffusion behaviors exhibited by the electron cloud during the formation of artificial radiation belts. The CIMI model is a four-dimensional model based on the Fokker-Planck equation. It simulates the evolution of particles across four degrees of freedom: radial, azimuthal, energy, and equatorial pitch angle. Unlike previous studies that mainly focus on the long-term evolution of artificial radiation belts already reaching azimuthal uniformity, this work specifically ascertains the azimuthal evolution process of the injected electrons and how they form the artificial radiation belts. Numerical simulations are conducted on the captured nuclear explosion electrons initially concentrated at L = 1.1–2.2 and covering approximately one time zone azimuthally. The results show that the injected electrons primarily evolve into an azimuthally uniform distribution through a spiral encircling process, with diffusion playing a smaller role. In this process, the electrons undergo eastward drift, with those at higher altitudes exhibiting faster drift velocities. The velocity shear leads to the formation of a helical structure around the Earth. Additionally, the formation of this spiral structure is accompanied by azimuthal expansion, driven mainly by energy and pitch angle dispersion during the drift. Electrons with different energy values and equatorial pitch angles exhibit varying drift speeds, contributing to the azimuthal expansion of electron clusters during the drift. The expansion process can fill the gaps in the helical structure. Ultimately, the electron distribution achieves azimuthal uniformity through energy-pitch angle diffusion.-
Keywords:
- high-altitude nuclear explosions /
- artificial radiation belt /
- Fokker-Planck equations /
- electrons diffusion
[1] Lyons L R 1973 J. Geophys. Res. 78 6793
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zheng Y, Ganushkina N Y, Jiggens P, Jun I, Meier M, Minow J I, O’Brien T P, Pitchford D, Shprits Y, Tobiska W K, Xapsos M A, Guild T B, Mazur J E, Kuznetsova M M 2019 Space Weather 17 1384
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Christofilos N C 1959 J. Geophys. Res. 64 869
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Beall D S, Bostrom C O, Williams D J 1967 J. Geophys. Res. 72 3403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 王建国, 刘利, 牛胜利, 左应红, 高银军, 朱金辉, 张相华, 李桠, 李夏至 2023 现代应用物理 14 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J G, Liu L, Niu S L, Zuo Y H, Gao Y J, Zhu J H, Zhang X H, Li Y, Li X Z 2023 Modern Appl. Phys. 14 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 朱金辉, 左应红, 刘利, 牛胜利, 商鹏, 李夏至, 王学栋 2023 现代应用物理 14 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu J H, Zuo Y H, Liu L, Niu S L, Shang P, Li X Z, Wang X D 2023 Modern Appl. Phys. 14 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 顾旭东, 赵正予, 倪彬彬, 汪枫 2009 58 5871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gu X D, Zhao Z Y, Ni B B, Wang F 2009 Acta Phys. Sin 58 5871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Tu W, Cunningham G S, Chen Y, Morley S K, Reeves G D, Blake J B, Baker D N, Spence H 2014 Geophys. Res. Lett. 41 1359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Fok M C, Buzulukova N Y, Chen S H, Glocer A, Nagai T, Valek P, Perez J D 2014 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 119 7522
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Fok M C, Wolf R A, Spiro R W, Moore T E 2001 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 106 8417
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Fok M C, Kang S B, Ferradas C P, Buzulukova N Y, Glocer A, Komar C M 2021 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 126 e2020JA028987
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Albert J M 2005 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 110 A03218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Albert J M 2008 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 113 A06208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Albert J M, Meredith N P, Horne R B 2009 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 114 1DD
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Weimer D R 2001 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 106 407
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Tsyganenko N A 2012 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 100 5599
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Tsyganenko N A, Stern D P 1996 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 101 27187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Tsyganenko N A, Mukai T 2003 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 108 1136
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Tsyganenko N A, Sitnov M I 2005 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 110 A03208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Meredith N P, Horne R B, Thorne R M, Summers D, Anderson R R 2004 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 109 A06209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Meredith N P, Horne R B, Sicard-Piet A, Boscher D, Yearby K H, Li W, Thorne R M 2012 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 117 A10225
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Rairden R L, Frank L A, Craven J D 2012 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 91 13613
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Gombosi T I, Baker D N, Balogh A, Erickson P J, Huba J D, Lanzerotti L J 2017 Space Sci. Rev. 212 985
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Cowee M, Winske D 2012 Update on the Electron Source Model (Los Alamos National Laboratory) DOI: 10.2172/1046529
[25] Dyal P 2006 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 111 A12211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Wang J G, Niu S L, Zhang D H 2010 The Parameter Manual Book of High-Altitude Nuclear Evplosion Effect (Beijing: Atomic Energy Press) pp259–260 [王建国, 牛胜利, 张殿辉 2010 高空核爆炸效应参数手册 (北京: 原子能出版社) 第259—260页]
Wang J G, Niu S L, Zhang D H 2010 The Parameter Manual Book of High-Altitude Nuclear Evplosion Effect (Beijing: Atomic Energy Press) pp259–260
[27] Vette J I 1991 The AE-8 Trapped Electron Model Environment Report Number: NSSDC/WDC-A-RS-91-24
[28] Hamlin D A, Karplus R, Vik R C, Watson K M 1961 J. Geophys. Res. 66 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Southwood D J, Kivelson M G 1981 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 86 5643
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Southwood D J, Kivelson M G 1982 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 87 1707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Fei Y, Chan A A, Elkington S R, Wiltberger M J 2006 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 111 A12209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Lejosne S, Albert J M 2023 Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences 10 1200485
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Lejosne S, Albert J M, Walton S D 2023 Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences 10 1232512
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Sandhu J K, Rae I J, Wygant J R, Breneman A W, Tian S, Watt C E J, Horne R B, Ozeke L G, Georgiou M, Walach M T 2021 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 126 e2020JA029024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Aryan H, Bortnik J, Meredith N P, Horne R B, Sibeck D G, Balikhin M A 2020 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 126 e2020JA028403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Malaspina D M, Zhu H, Drozdov A Y 2020 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 125 e2019JA027415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
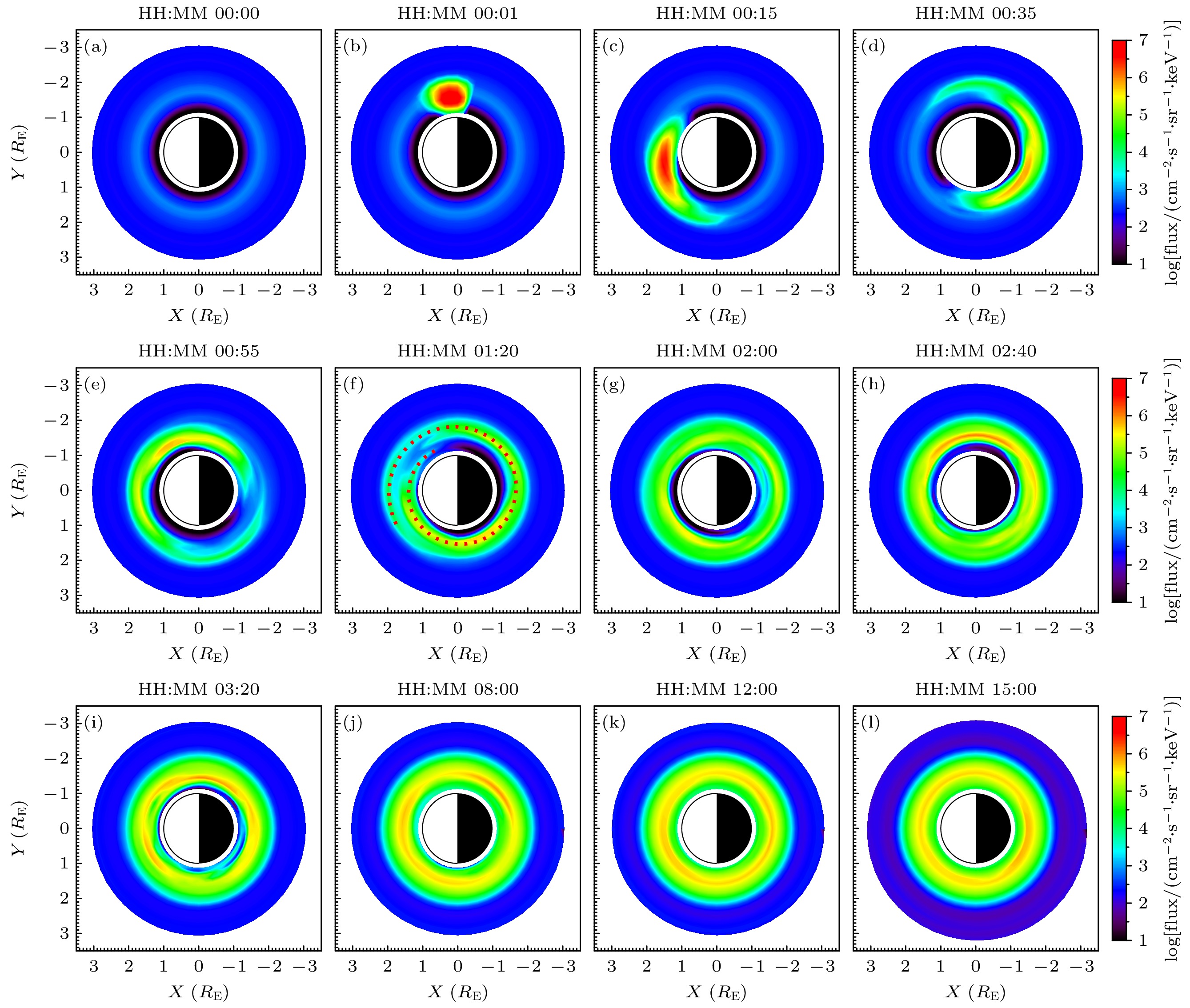
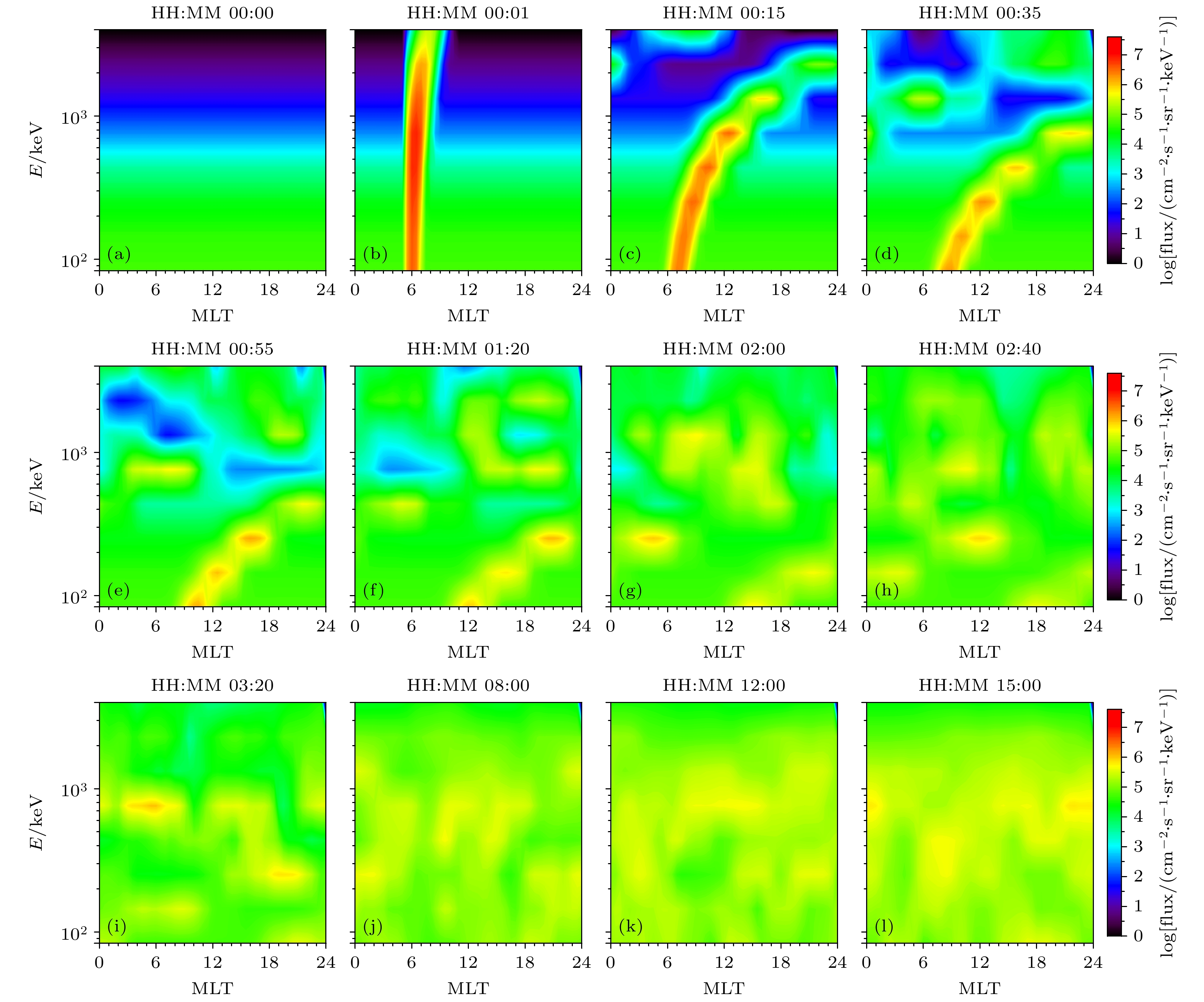
图 2 0.761 MeV电子通量的空间分布随时间的演化过程 (a)—(l)不同时刻电子微分通量在赤道面上的分布, 图中XY平面为从地球北侧看向磁赤道面的俯视图, 太阳位于图片左侧; 图(f)中红色虚线表示注入电子在漂移过程中形成的螺旋线结构
Fig. 2. Temporal evolution of the spatial distribution of 0.761 MeV electrons’ flux: (a)–(l) The differential flux distribution of electrons in the equatorial plane at different times. The XY plane in the figures represents a top-down view of the magnetic equatorial plane from the Earth’s northern side, with the Sun located to the left side. The red dashed line in panel (f) indicates the spiral structure formed by the injected electrons during their drift process.
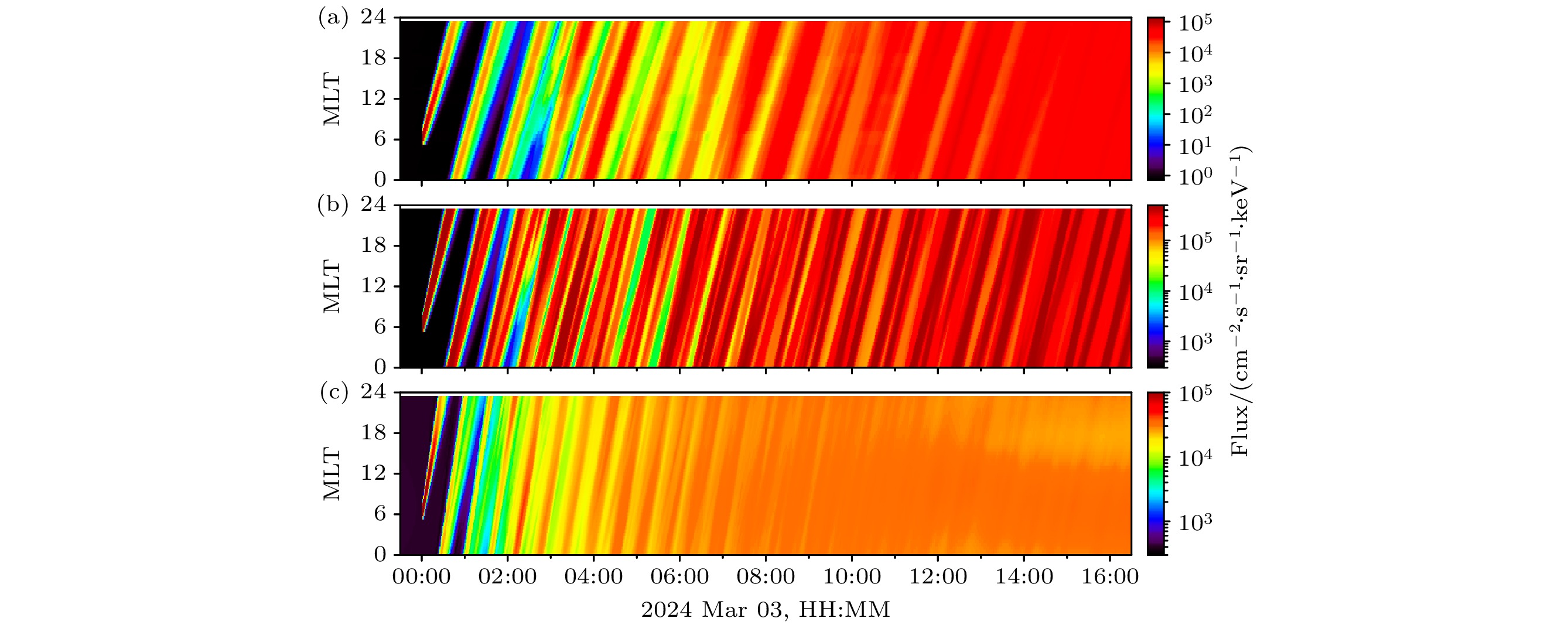
图 3 不同L处电子通量的MLT分布随时间的演化规律, 其中(a)—(c)依次为$ L=1.23 $, $ L=1.45 $, $ L=1.98 $处$ 0.761\;\rm MeV $电子的通量环向分布
Fig. 3. Temporal evolution of the MLT distribution of electron flux at different L values. Panel (a)–(c) show the azimuthal distribution of 0.761 MeV electron flux at $ L=1.23 $, $ L=1.45 $, and $ L=1.98 $, respectively.
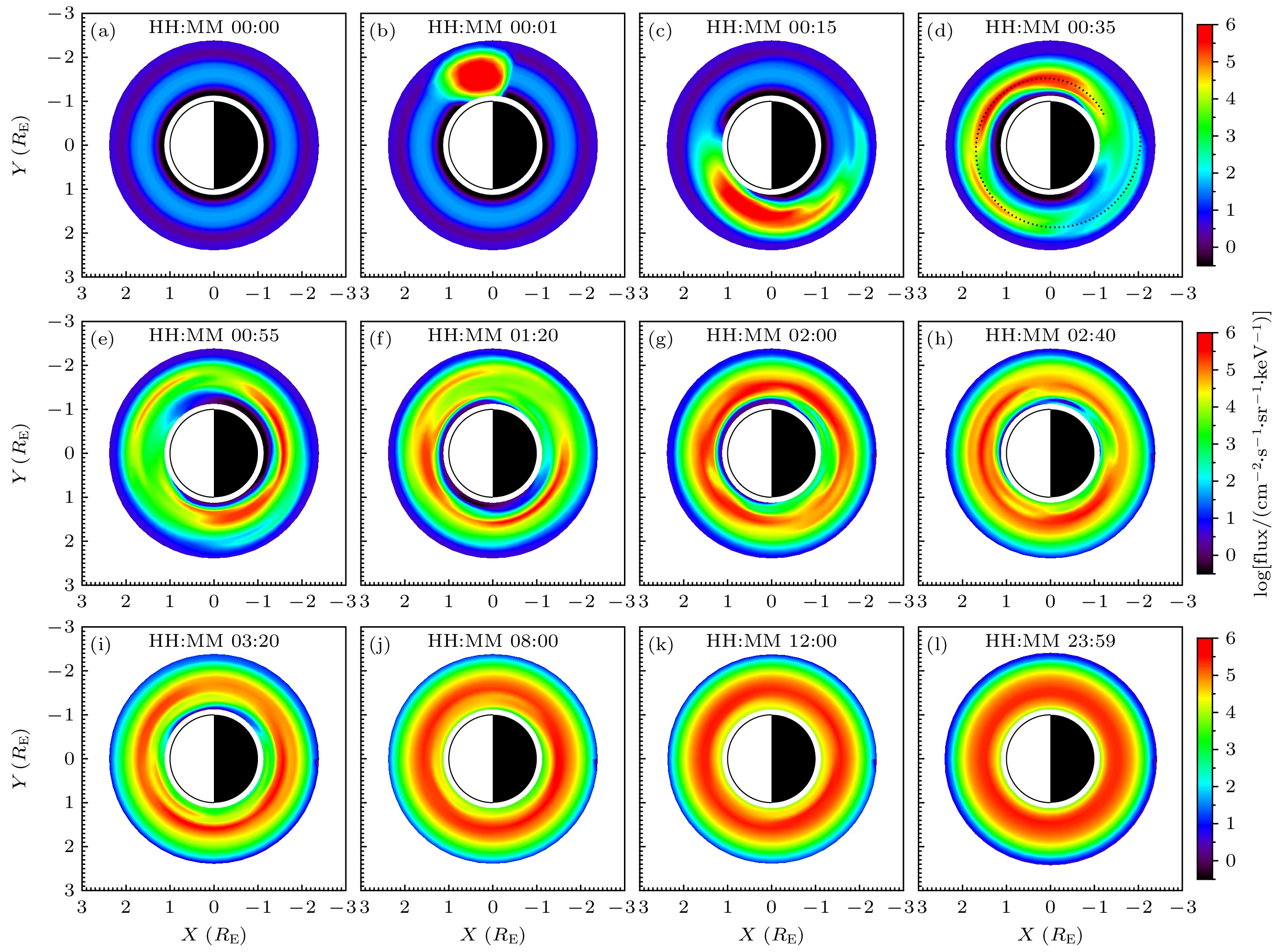
图 4 $ 1.323\;\rm MeV $电子通量的空间分布随时间的演化过程, 其中(a)—(l)为不同时刻电子微分通量在赤道面上的分布; 图(d)中黑色虚线表示注入电子在漂移过程中形成的螺旋线结构
Fig. 4. Temporal evolution of the spatial distribution of 1.323 MeV electrons’ flux. Panel (a)–(l) show the differential flux distribution of electrons in the equatorial plane at different times. The black dashed line in panel (d) indicates the spiral structure formed by the injected electrons during their drift process.
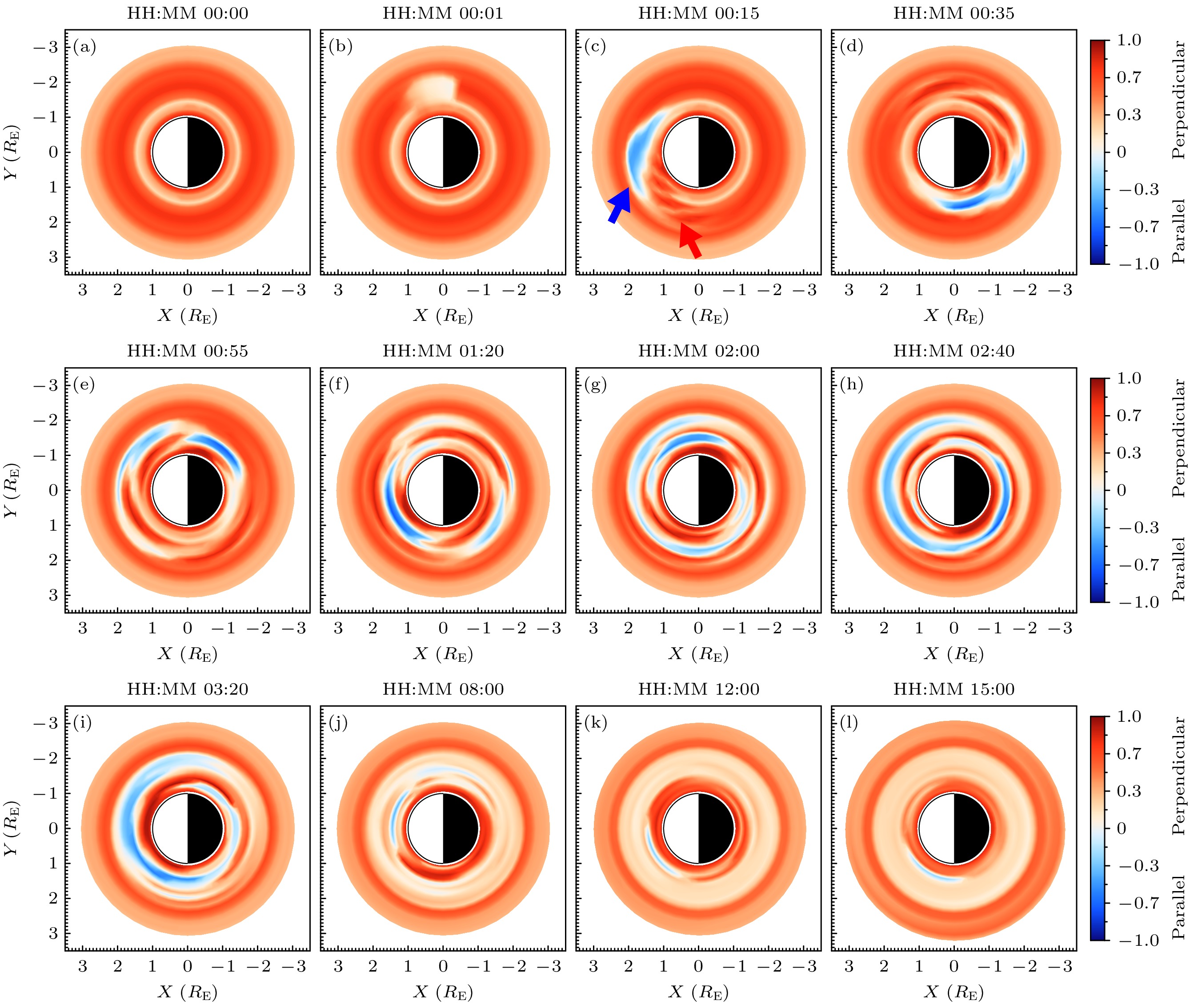
图 5 $ 0.761\;\rm MeV $电子各向异性指数的空间分布随时间的演化过程, 其中(a)—(l)分别为不同时刻电子各向异性指数在磁赤道面中的分布; 图(c)中红色箭头指示注入电子团前端各向异性指数升高的区域, 蓝色箭头指示后端各向异性指数降低的区域
Fig. 5. Temporal evolution of the spatial distribution of the anisotropy index for 0.761 MeV electrons. Panel (a)–(l) show the distribution of the anisotropy index in the magnetic equatorial plane at different times. In panel (c), the red arrow indicates the region where the anisotropy index increases at the front of the injected electron cluster, while the blue arrow indicates the region where the anisotropy index decreases at the rear.
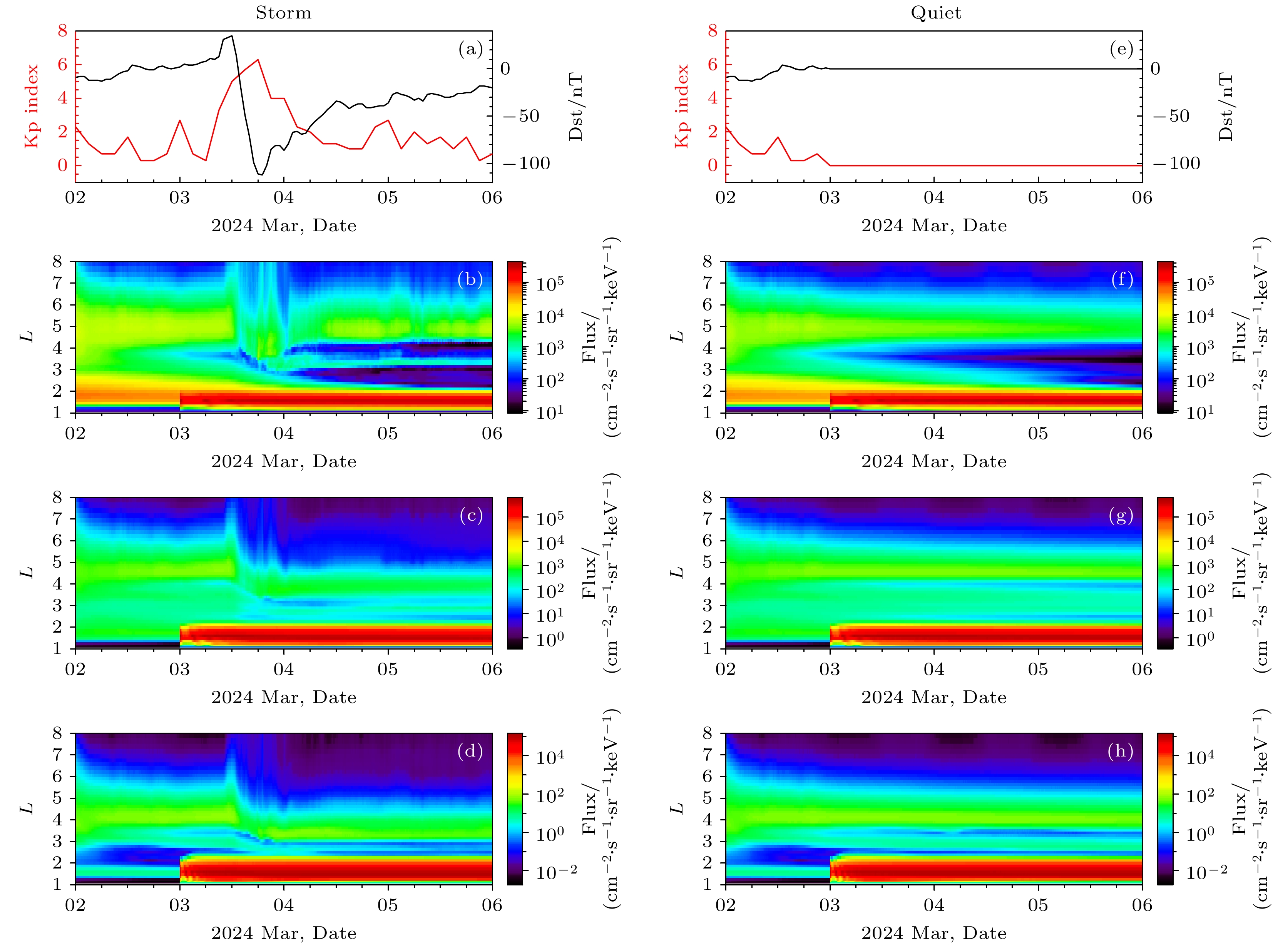
图 7 人工辐射带的长时间演化过程 (a)模拟期间的地磁指数, 红线表示Kp指数, 黑线表示Dst指数; (b)—(d) $ 0.252\;\rm MeV $, $ 0.761\;\rm MeV $, $ 2.301\;\rm MeV $电子通量的L分布随时间的演化过程, 图中通量为对应L上的环向平均通量; (e)—(h)地磁平静条件下左图相应内容
Fig. 7. Long-term evolution of the artificial radiation belt: (a) The geomagnetic indices during the simulation period, with the red line representing the Kp index and the black line representing the Dst index; (b)–(d) the temporal evolution of the L distribution of electron flux for $ 0.252\;\rm MeV $, $ 0.761\;\rm MeV $, and $ 2.301\;\rm MeV $, respectively, where the flux represents the azimuthally averaged flux at the corresponding L; (e)–(h) the corresponding content under geomagnetically quiet conditions.
-
[1] Lyons L R 1973 J. Geophys. Res. 78 6793
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zheng Y, Ganushkina N Y, Jiggens P, Jun I, Meier M, Minow J I, O’Brien T P, Pitchford D, Shprits Y, Tobiska W K, Xapsos M A, Guild T B, Mazur J E, Kuznetsova M M 2019 Space Weather 17 1384
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Christofilos N C 1959 J. Geophys. Res. 64 869
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Beall D S, Bostrom C O, Williams D J 1967 J. Geophys. Res. 72 3403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 王建国, 刘利, 牛胜利, 左应红, 高银军, 朱金辉, 张相华, 李桠, 李夏至 2023 现代应用物理 14 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J G, Liu L, Niu S L, Zuo Y H, Gao Y J, Zhu J H, Zhang X H, Li Y, Li X Z 2023 Modern Appl. Phys. 14 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 朱金辉, 左应红, 刘利, 牛胜利, 商鹏, 李夏至, 王学栋 2023 现代应用物理 14 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu J H, Zuo Y H, Liu L, Niu S L, Shang P, Li X Z, Wang X D 2023 Modern Appl. Phys. 14 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 顾旭东, 赵正予, 倪彬彬, 汪枫 2009 58 5871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gu X D, Zhao Z Y, Ni B B, Wang F 2009 Acta Phys. Sin 58 5871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Tu W, Cunningham G S, Chen Y, Morley S K, Reeves G D, Blake J B, Baker D N, Spence H 2014 Geophys. Res. Lett. 41 1359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Fok M C, Buzulukova N Y, Chen S H, Glocer A, Nagai T, Valek P, Perez J D 2014 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 119 7522
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Fok M C, Wolf R A, Spiro R W, Moore T E 2001 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 106 8417
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Fok M C, Kang S B, Ferradas C P, Buzulukova N Y, Glocer A, Komar C M 2021 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 126 e2020JA028987
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Albert J M 2005 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 110 A03218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Albert J M 2008 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 113 A06208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Albert J M, Meredith N P, Horne R B 2009 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 114 1DD
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Weimer D R 2001 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 106 407
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Tsyganenko N A 2012 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 100 5599
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Tsyganenko N A, Stern D P 1996 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 101 27187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Tsyganenko N A, Mukai T 2003 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 108 1136
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Tsyganenko N A, Sitnov M I 2005 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 110 A03208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Meredith N P, Horne R B, Thorne R M, Summers D, Anderson R R 2004 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 109 A06209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Meredith N P, Horne R B, Sicard-Piet A, Boscher D, Yearby K H, Li W, Thorne R M 2012 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 117 A10225
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Rairden R L, Frank L A, Craven J D 2012 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 91 13613
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Gombosi T I, Baker D N, Balogh A, Erickson P J, Huba J D, Lanzerotti L J 2017 Space Sci. Rev. 212 985
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Cowee M, Winske D 2012 Update on the Electron Source Model (Los Alamos National Laboratory) DOI: 10.2172/1046529
[25] Dyal P 2006 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 111 A12211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Wang J G, Niu S L, Zhang D H 2010 The Parameter Manual Book of High-Altitude Nuclear Evplosion Effect (Beijing: Atomic Energy Press) pp259–260 [王建国, 牛胜利, 张殿辉 2010 高空核爆炸效应参数手册 (北京: 原子能出版社) 第259—260页]
Wang J G, Niu S L, Zhang D H 2010 The Parameter Manual Book of High-Altitude Nuclear Evplosion Effect (Beijing: Atomic Energy Press) pp259–260
[27] Vette J I 1991 The AE-8 Trapped Electron Model Environment Report Number: NSSDC/WDC-A-RS-91-24
[28] Hamlin D A, Karplus R, Vik R C, Watson K M 1961 J. Geophys. Res. 66 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Southwood D J, Kivelson M G 1981 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 86 5643
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Southwood D J, Kivelson M G 1982 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 87 1707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Fei Y, Chan A A, Elkington S R, Wiltberger M J 2006 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 111 A12209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Lejosne S, Albert J M 2023 Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences 10 1200485
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Lejosne S, Albert J M, Walton S D 2023 Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences 10 1232512
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Sandhu J K, Rae I J, Wygant J R, Breneman A W, Tian S, Watt C E J, Horne R B, Ozeke L G, Georgiou M, Walach M T 2021 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 126 e2020JA029024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Aryan H, Bortnik J, Meredith N P, Horne R B, Sibeck D G, Balikhin M A 2020 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 126 e2020JA028403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Malaspina D M, Zhu H, Drozdov A Y 2020 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 125 e2019JA027415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 2998
- PDF下载量: 103
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: