-
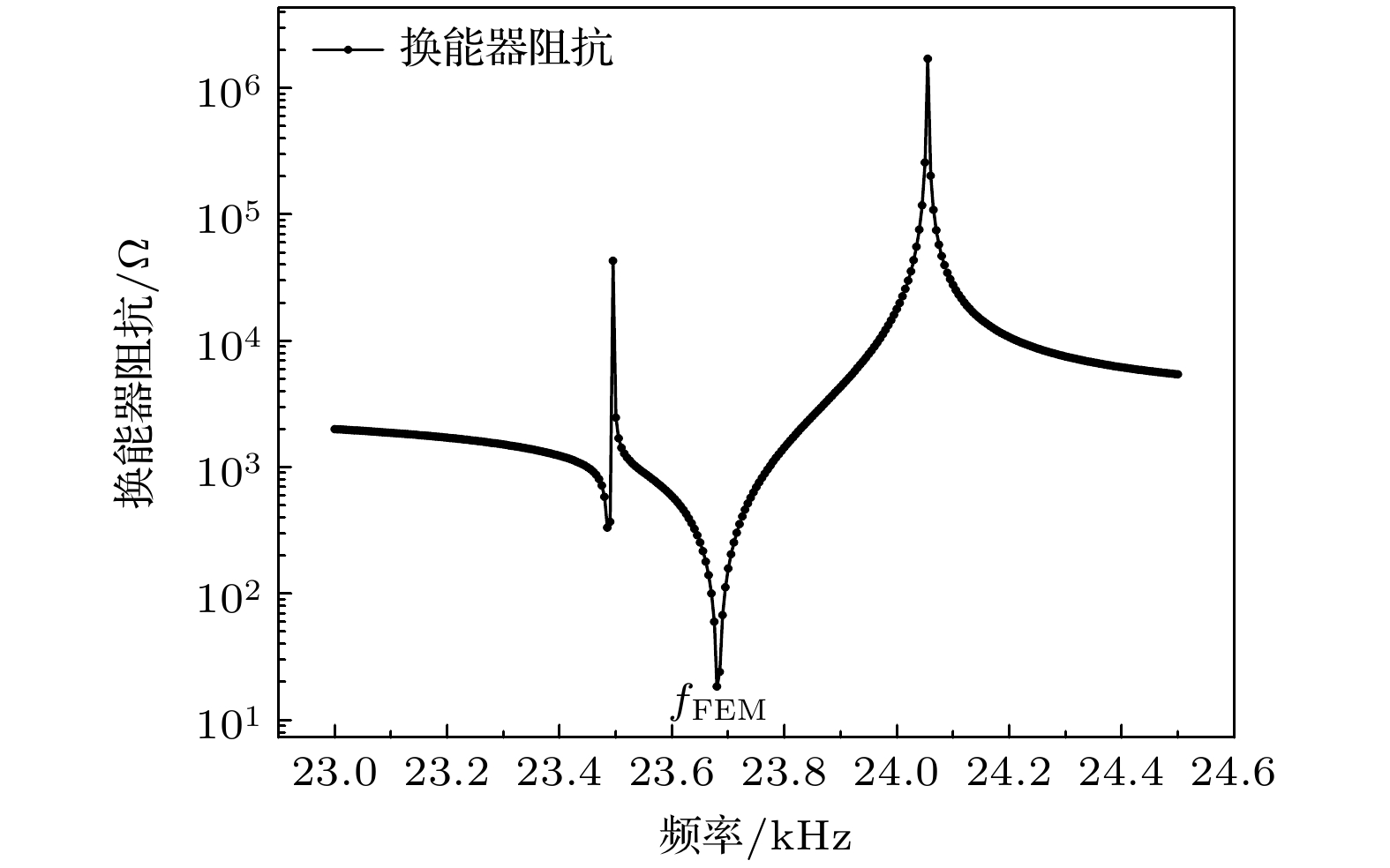
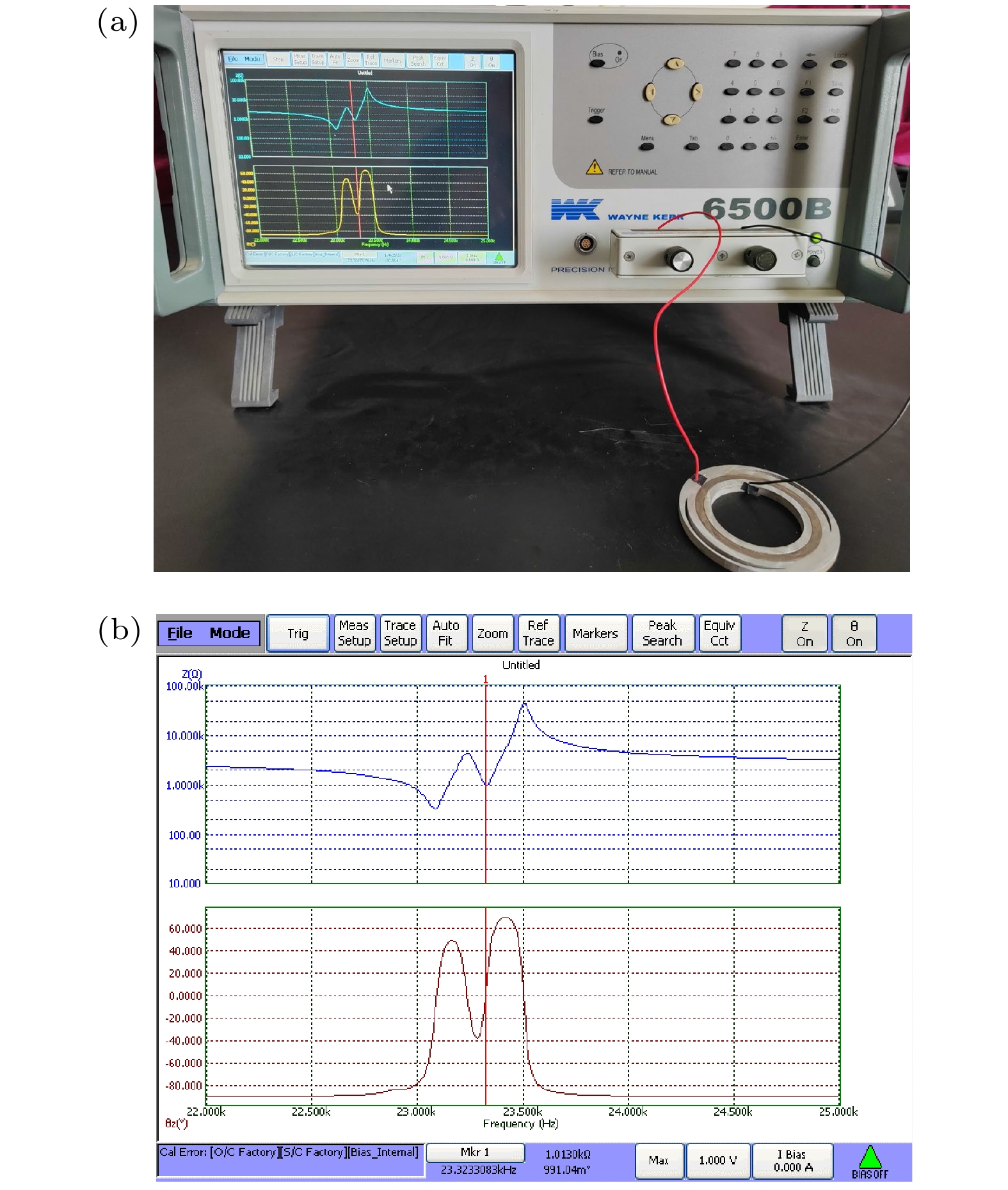
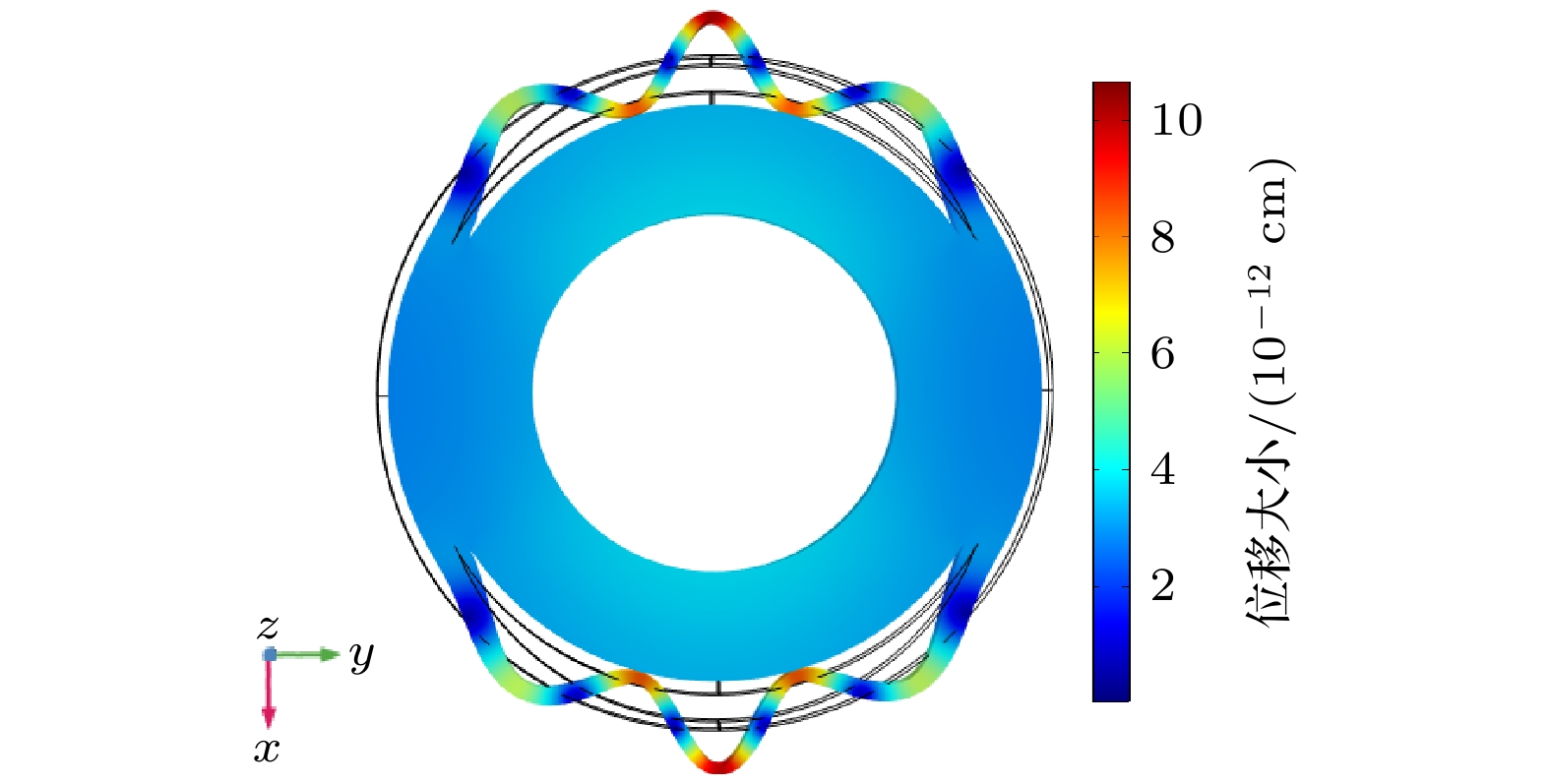
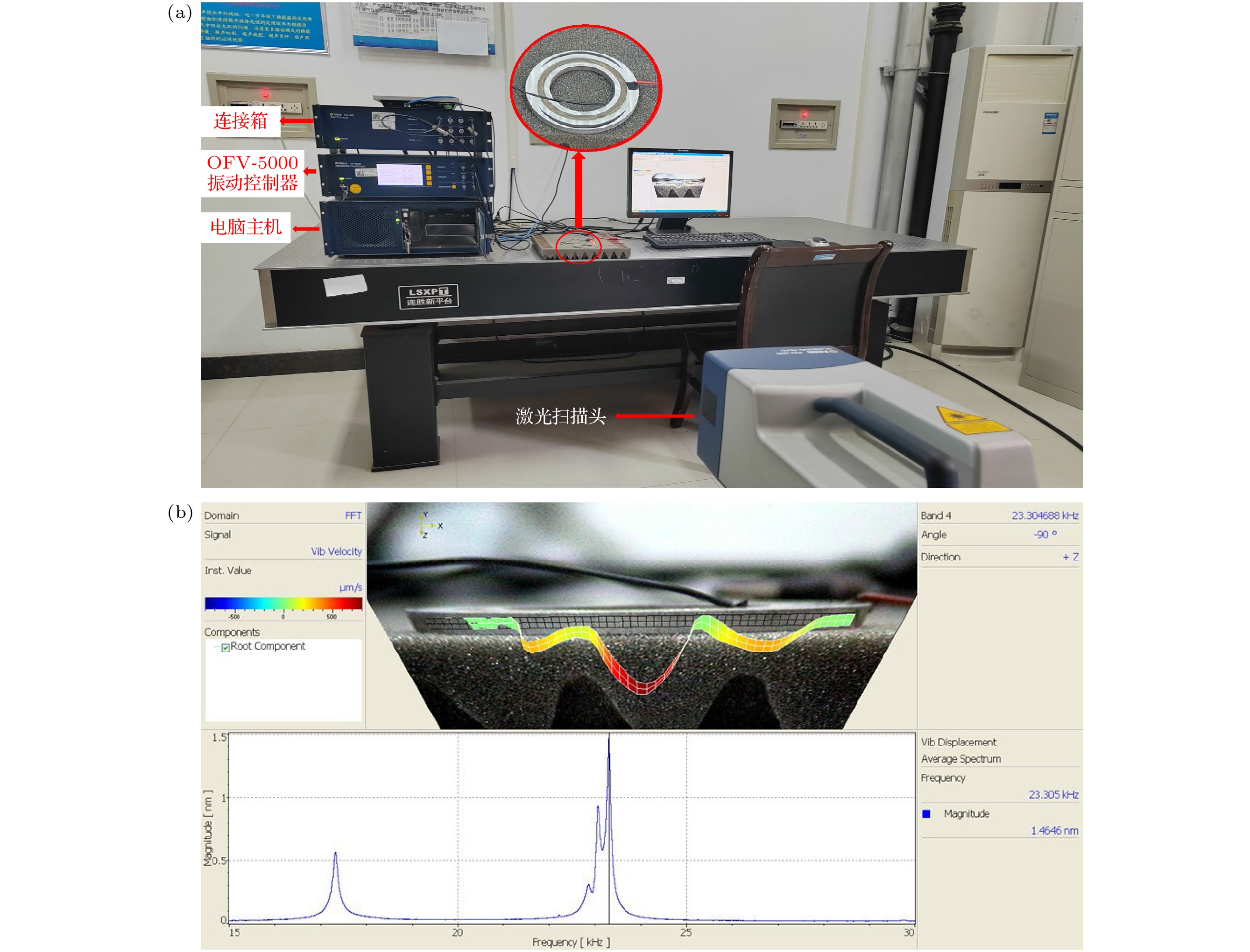
基于弯曲波在声黑洞(acoustic black hole, ABH)结构中振幅不断增大的特性, 提出了一种新型径向夹心式径-弯复合换能器, 该换能器由径向夹心式圆环换能器与外围的环形ABH结构组成. ABH结构的存在实现了换能器径向振动与弯曲振动之间的转换, 提高了换能器的声辐射性能. 利用几何声学的方法建立了ABH结构弯曲振动的解析模型, 给出了其弯曲振动的本征频率, 并结合有限元方法讨论了换能器机电转换性能随尺寸变化的关系. 通过有限元方法给出了该换能器在空气中的辐射声压场、辐射声强以及辐射指向性, 仿真结果表明, ABH结构的存在能够改善换能器弯曲振动的机电转换性能, 提高换能器的声辐射性能, 使换能器呈现出一定的辐射指向性. 最后通过实验对换能器样机的电阻抗特性以及振动模态进行测量, 实验结果与仿真相符合.A novel radial sandwich radial bending composite transducer is proposed based on the increasing amplitude of bending waves in the structure of an acoustic black hole (ABH). The transducer consists of a radial sandwich circular ring transducer and an outer acoustic black hole structure. The existence of the ABH structure realizes the conversion between radial vibration and bending vibration of the transducer, and improves the acoustic radiation performance of the transducer. Based on the one-dimensional acoustic black hole bending vibration theory, the bending vibration equation of the circular ABH structure is given. An analytical model of the ABH structure bending vibration is established by using the method of geometrical-acoustics, and the eigen frequency of its bending vibration is given. The relationship between the electromechanical conversion performance and the size of the transducer is discussed by using the finite element method, and the results show that when the eigen frequency of the bending vibration of the ABH structure is close to the resonant frequency of the transducer, the electromechanical coupling coefficient of the transducer reaches a maximum value. The radiation sound pressure field, radiation sound intensity, and radiation directionality of the transducer in the air are also analyzed by the finite element method. The results indicate that the presence of the ABH structure can improve the electromechanical conversion performance of the bending vibration of the transducer, enhance the acoustic radiation performance of the transducer, make the transducer exhibit radiation directionality and the lower order of the bending vibration mode of the ABH structure, the stronger radiation directionality of the transducer towards the left side and the right side. Finally, in order to verify the accuracy of the simulation and theory, we made a prototype transducer and carried out the experimental test of transducer electrical impedance and vibration mode. The measured results are in good agreement with the simulation results. The displacement distribution of the radiation surface of the transducer at resonance frequency is measured, which verifies the bending vibration mode of the ABH structure. This type of transducer is expected to be used as acoustic projector in the air or water.
-
Keywords:
- acoustic black hole /
- transducer /
- radial vibration /
- bending vibration
[1] 胡银丰 2017 声学与电子工程 39 25
Hu Y F 2017 Acoust Electr Eng. 39 25
[2] 曹雪砷, 王易敏, 王申 2015 测井技术 39 160
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cao X S, Wang Y M, Wang S 2015 Well Logging Technol. 39 160
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 刘世清, 麻磊磊 2020 陕西师范大学学报(自然科学版) 48 60
Liu S Q, Ma L L 2020 J. Shaanxi Normal Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed. ). 48 60
[4] Mironov M A 1988 Sov. Phys. Acoustics. 34 318
[5] Krylov V V 1989 Sov. Phys. Acoustics. 35 176
[6] Krylov V V 1990 Mosc. U. Phys. B+. 45 65
[7] Krylov V V, Tilman F 2004 J. Sound Vib. 274 605
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Remillieux M C, Anderson B E, Le Bas P Y, Ulrich T J 2014 Ultrasonics 54 1409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Anderson B E, Remillieux M C, Le Bas P Y, Ulrich T J, Pieczonka L 2015 Ultrasonics 63 141
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Aronov B S 2013 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 134 1021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Aronov B S 2013 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 133 3875
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 吴德林, 戴郁郁, 陈浩, 张海澜, 王秀明 2020 声学学报 45 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu D L, Dai Y Y, Chen H, Zhang H L, Wang X M 2020 Acta Acustica. 45 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 林书玉, 鲜小军 2014 陕西师范大学学报(自然科学版) 42 31
Lin S Y, Xian X J 2014 J. Shaanxi Normal Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed. ). 42 31
[14] 许龙, 林书玉 2012 声学学报 37 408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu L, Lin S Y 2012 Acta Acustica. 37 408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 李凤鸣, 刘世清, 许龙, 张海岛, 曾小梅, 陈赵江 2023 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 53 198
Li F M, Liu S Q, Xu L, Zhang H D, Zeng X M, Chen Z J 2023 Sci. Sin. Phys. Mech. Astron. 53 198
[16] 董宜雷, 陈诚, 林书玉 2023 72 054304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong Y L, Chen C, Lin S Y 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 054304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 高炳山, 林书玉 2010 应用声学 29 217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao B S, Lin S Y 2010 J. Appl. Acoust. 29 217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 胡静, 林书玉, 王成会, 莫润阳 2015 西北大学学报(自然科学版) 45 709
Hu J, Lin S Y, Wang C H, Mo R Y 2015 J. Northwest Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 45 709
[19] 王帅军, 林书玉 2011 陕西师范大学学报(自然科学版) 39 23
Wang S, Lin S 2011 J. Shaanxi Normal Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 39 23
[20] Krylov V V 2020 J. Sound Vib. 468 115100
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 林书玉 2004 超声换能器的原理及设计 (北京: 科学出版社) 第20页
Lin S Y 2004 The Theory and Design of Ultrasonic Transducers (Beijing: Science Press) p20
-
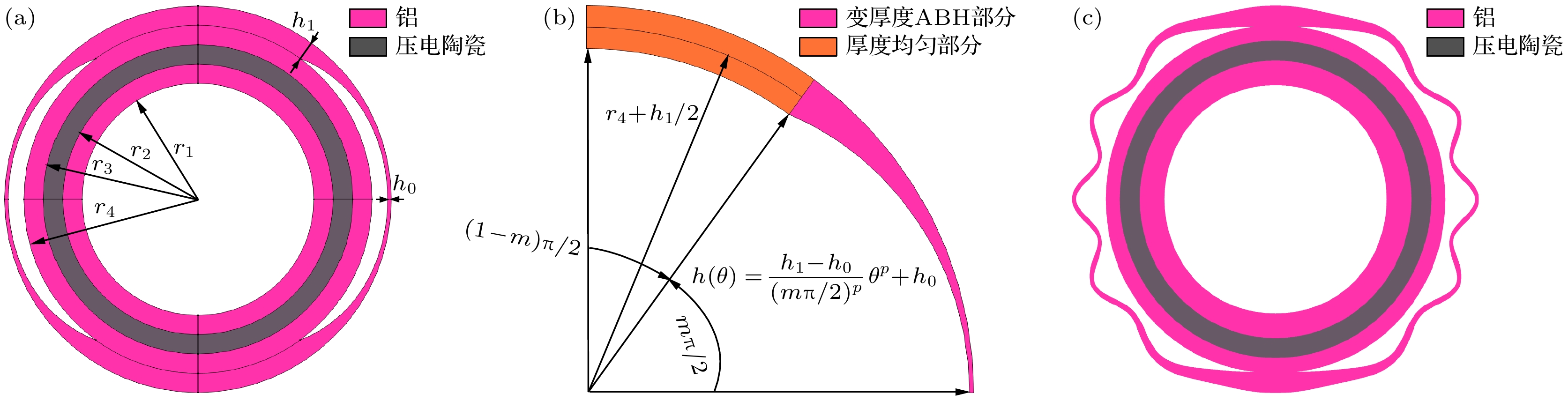
图 1 径向夹心式径-弯复合换能器示意图 (a) 换能器总体示意图; (b) 外围环1/4部分的示意图; (c) 换能器振动模态示意图
Fig. 1. The schematic diagram of a composite radial bending transducer: (a) The overall schematic diagram of the transducer; (b) a schematic diagram of the 1/4 part of the outer ring; (c) a schematic diagram of the vibration mode of the transducer.
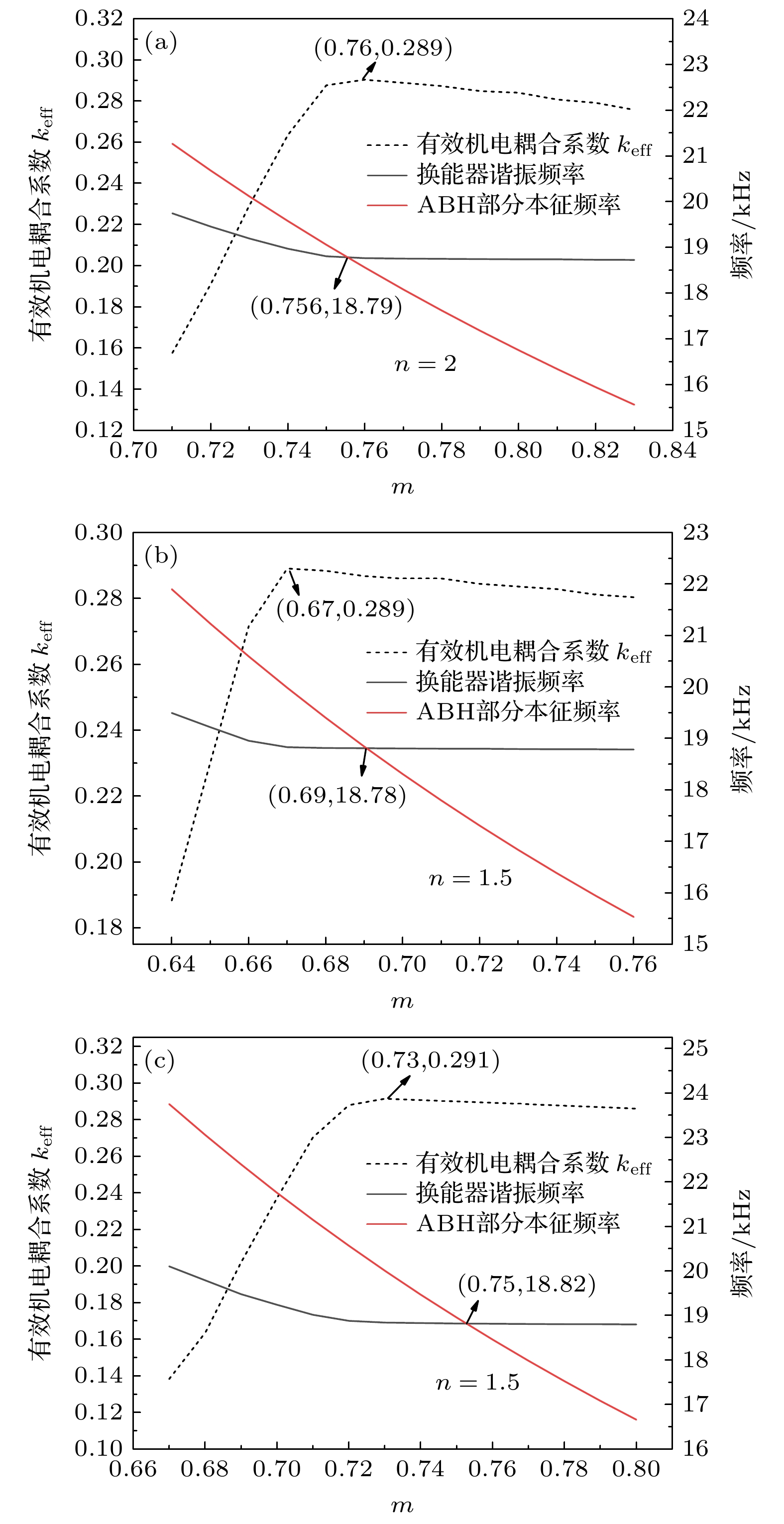
图 2 不同m下换能器的有效机电耦合系数、谐振频率以及ABH部分的弯曲振动本征频率 (a) a型号换能器; (b) b型号换能器; (c) c型号换能器
Fig. 2. Effective electro-mechanical coupling coefficient, resonant frequency of transducer and eigen frequency of bending vibration of ABH part with different m: (a) Model a transducer; (b) model b transducer; (c) model c transducer.
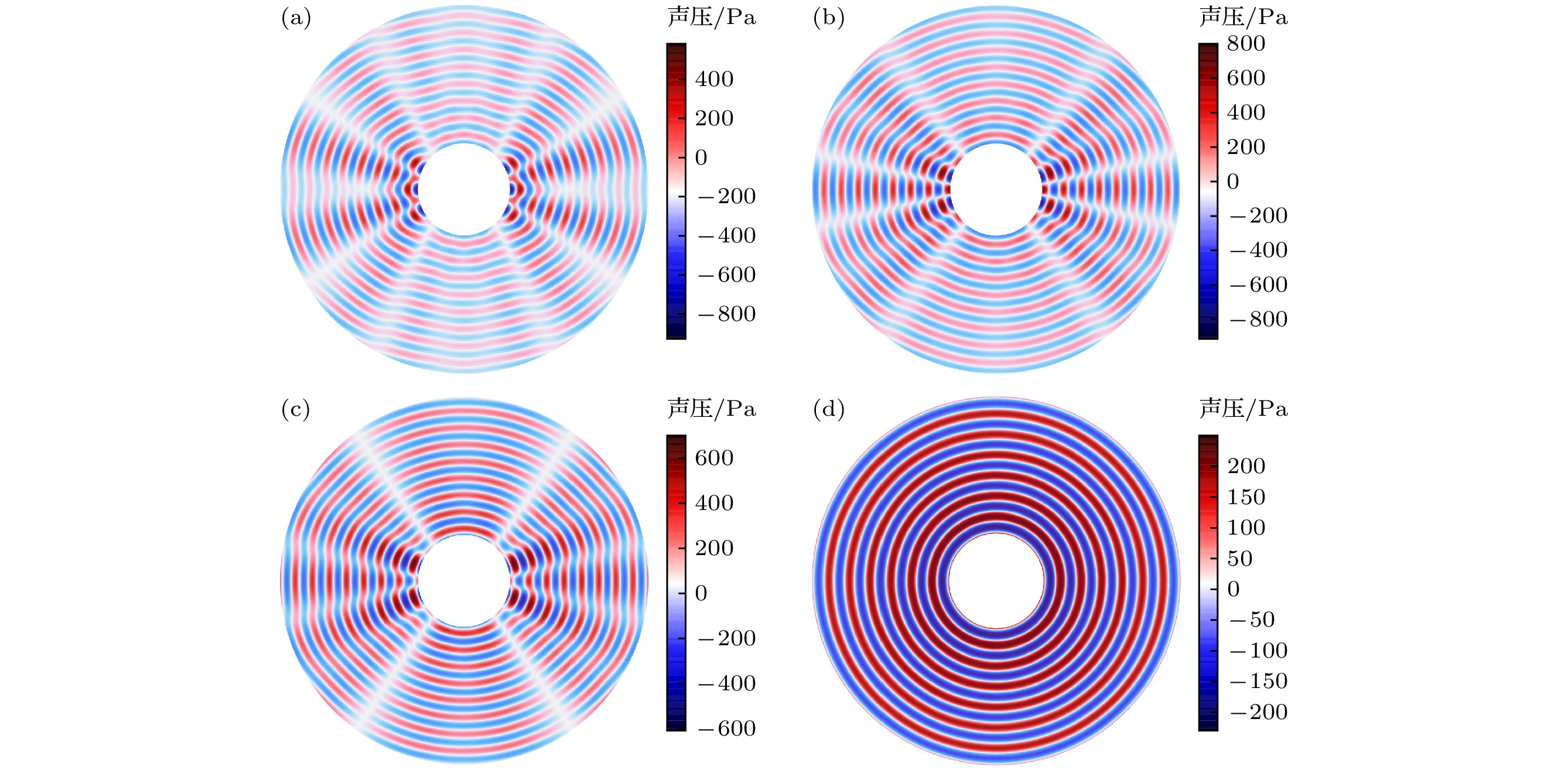
图 3 四种不同换能器在空气中的辐射声压分布图 (a) a型号换能器, fm = 18.766 kHz; (b) b型号换能器, fm = 18.829 kHz; (c) c型号换能器, fm = 18.841 kHz; (d) d型号换能器, fm = 19.01 kHz
Fig. 3. The radiation sound pressure distribution of four different transducers in the air: (a) Model a transducer, fm = 18.766 kHz; (b) model b transducer, fm = 18.829 kHz; (c) model c transducer, fm = 18.841 kHz; (d) model d transducer, fm = 19.01 kHz.
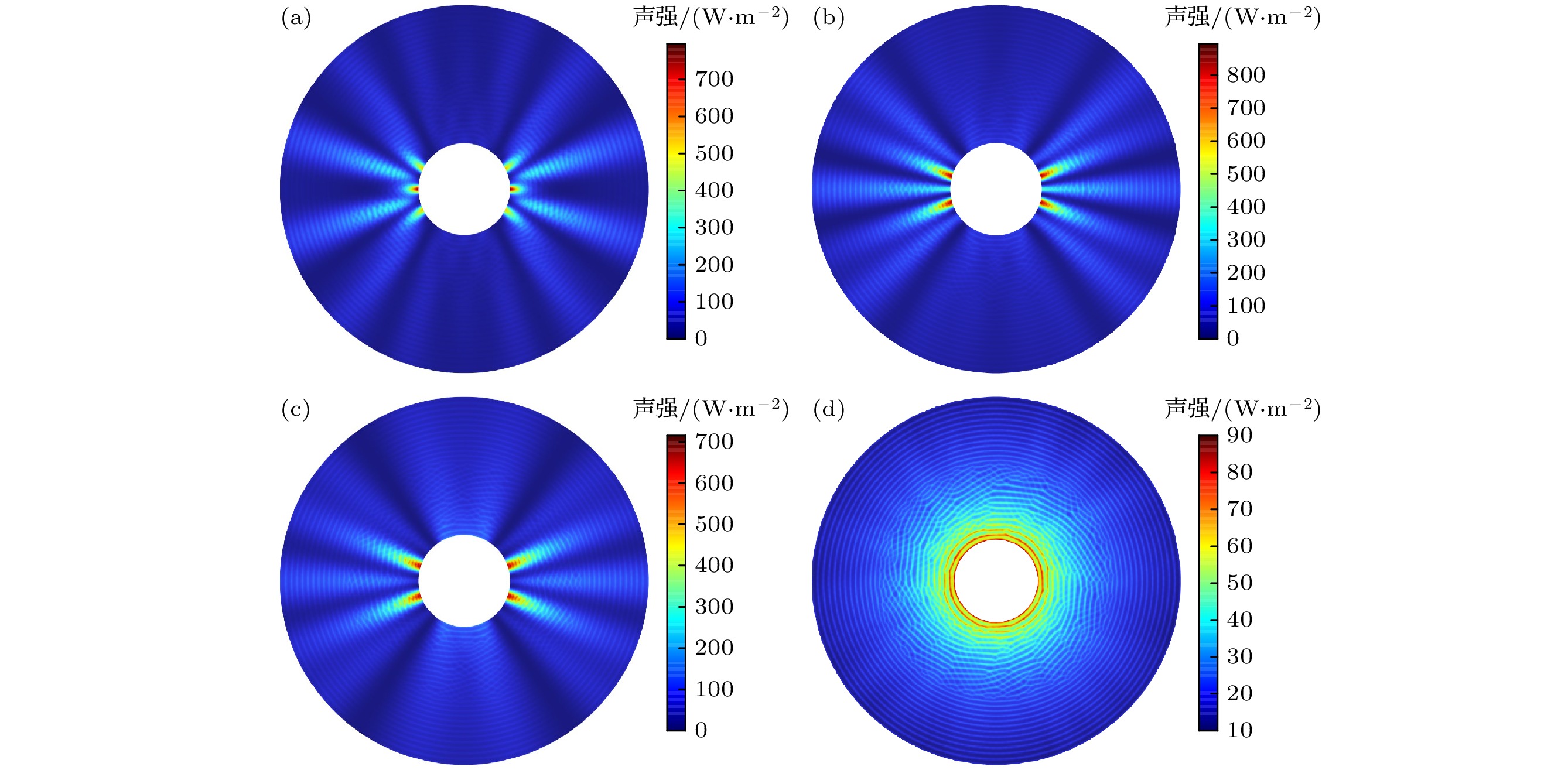
图 4 四种不同换能器在空气中的辐射声强分布图 (a) a型号换能器, fm = 18.766 kHz; (b) b型号换能器, fm = 18.829 kHz; (c) c型号换能器, fm = 18.841 kHz; (d) d型号换能器, fm = 19.01 kHz
Fig. 4. The radiation sound intensity distribution of four different transducers in the air: (a) Model a transducer, fm = 18.766 kHz; (b) model b transducer, fm = 18.829 kHz; (c) model c transducer, fm = 18.841 kHz; (d) model d transducer, fm = 19.01 kHz.
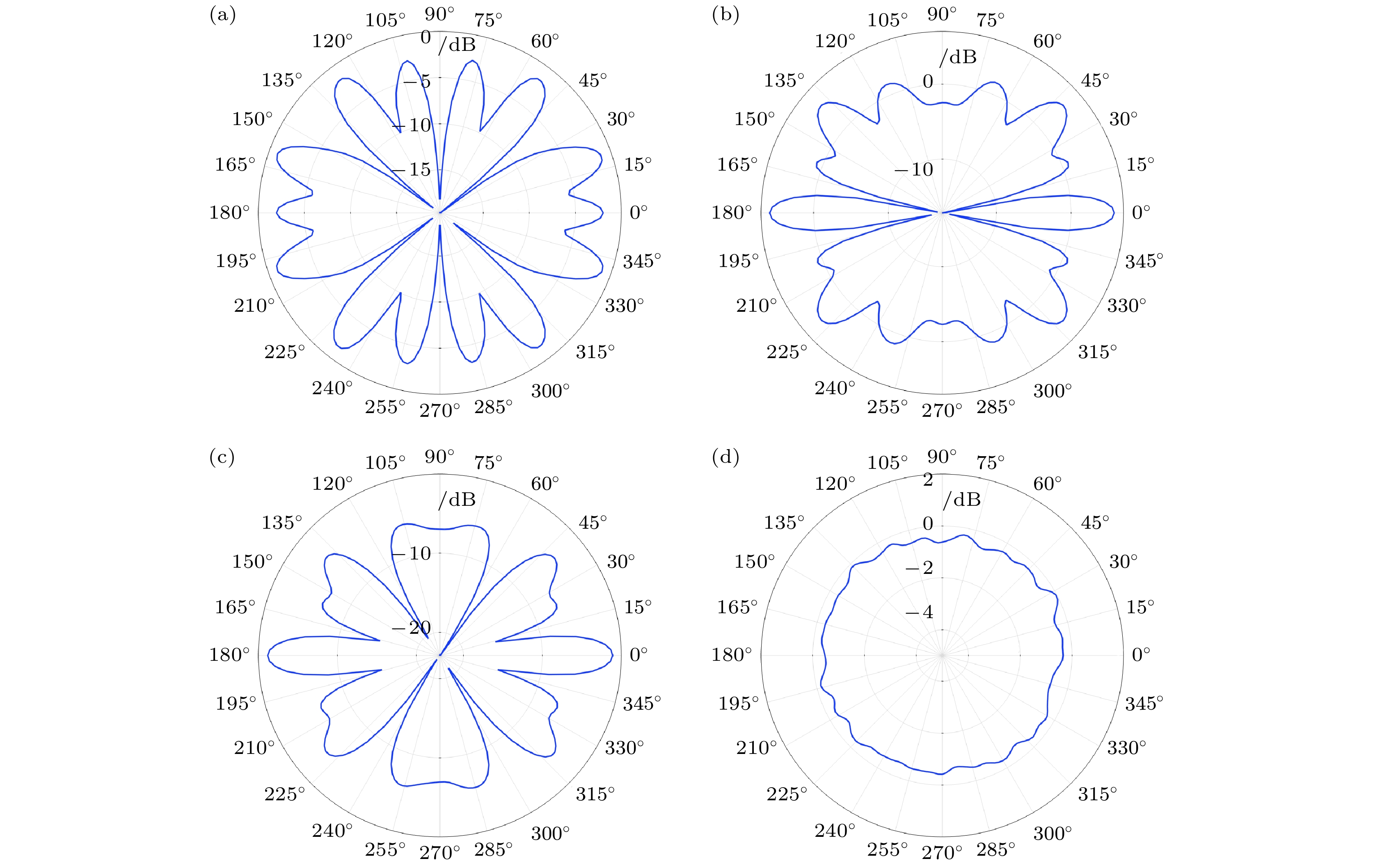
图 5 四种换能器的声场指向性图 (a) a型号换能器, fm = 18.766 kHz; (b) b型号换能器, fm = 18.829 kHz; (c) c型号换能器, fm = 18.841 kHz; (d) d型号换能器, fm = 19.01 kHz
Fig. 5. Four types of transducer sound field directionality graphics: (a) Model a transducer, fm = 18.766 kHz; (b) model b transducer, fm = 18.829 kHz; (c) model c transducer, fm = 18.841 kHz; (d) model d transducer, fm = 19.01 kHz.
表 1 几种不同换能器的尺寸
Table 1. The sizes of several different transducers.
换能器编号 $ {r}_{1}/{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{m}} $ $ {r}_{2}/{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{m}} $ $ {r}_{3}/{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{m}} $ $ {r}_{4}/{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{m}} $ p $ {h}_{1}/{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{m}} $ $ {h}_{0}/{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{m}} $ a 30 35 40 45 3 5 1.0 b 30 35 40 45 2 5 1.5 c 30 35 40 45 2 5 2.0 d 30 35 40 45 — — — 表 2 换能器尺寸参数
Table 2. Size parameters of the transducer.
尺寸
参数r1/mm r2/mm r3/mm r4/mm p h1/mm h0/mm m 22 26 30 34 2 4 1 0.65 -
[1] 胡银丰 2017 声学与电子工程 39 25
Hu Y F 2017 Acoust Electr Eng. 39 25
[2] 曹雪砷, 王易敏, 王申 2015 测井技术 39 160
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cao X S, Wang Y M, Wang S 2015 Well Logging Technol. 39 160
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 刘世清, 麻磊磊 2020 陕西师范大学学报(自然科学版) 48 60
Liu S Q, Ma L L 2020 J. Shaanxi Normal Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed. ). 48 60
[4] Mironov M A 1988 Sov. Phys. Acoustics. 34 318
[5] Krylov V V 1989 Sov. Phys. Acoustics. 35 176
[6] Krylov V V 1990 Mosc. U. Phys. B+. 45 65
[7] Krylov V V, Tilman F 2004 J. Sound Vib. 274 605
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Remillieux M C, Anderson B E, Le Bas P Y, Ulrich T J 2014 Ultrasonics 54 1409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Anderson B E, Remillieux M C, Le Bas P Y, Ulrich T J, Pieczonka L 2015 Ultrasonics 63 141
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Aronov B S 2013 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 134 1021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Aronov B S 2013 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 133 3875
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 吴德林, 戴郁郁, 陈浩, 张海澜, 王秀明 2020 声学学报 45 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu D L, Dai Y Y, Chen H, Zhang H L, Wang X M 2020 Acta Acustica. 45 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 林书玉, 鲜小军 2014 陕西师范大学学报(自然科学版) 42 31
Lin S Y, Xian X J 2014 J. Shaanxi Normal Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed. ). 42 31
[14] 许龙, 林书玉 2012 声学学报 37 408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu L, Lin S Y 2012 Acta Acustica. 37 408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 李凤鸣, 刘世清, 许龙, 张海岛, 曾小梅, 陈赵江 2023 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 53 198
Li F M, Liu S Q, Xu L, Zhang H D, Zeng X M, Chen Z J 2023 Sci. Sin. Phys. Mech. Astron. 53 198
[16] 董宜雷, 陈诚, 林书玉 2023 72 054304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong Y L, Chen C, Lin S Y 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 054304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 高炳山, 林书玉 2010 应用声学 29 217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao B S, Lin S Y 2010 J. Appl. Acoust. 29 217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 胡静, 林书玉, 王成会, 莫润阳 2015 西北大学学报(自然科学版) 45 709
Hu J, Lin S Y, Wang C H, Mo R Y 2015 J. Northwest Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 45 709
[19] 王帅军, 林书玉 2011 陕西师范大学学报(自然科学版) 39 23
Wang S, Lin S 2011 J. Shaanxi Normal Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 39 23
[20] Krylov V V 2020 J. Sound Vib. 468 115100
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 林书玉 2004 超声换能器的原理及设计 (北京: 科学出版社) 第20页
Lin S Y 2004 The Theory and Design of Ultrasonic Transducers (Beijing: Science Press) p20
计量
- 文章访问数: 3629
- PDF下载量: 80
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: