-
采用确切的Muffin-Tin轨道结合相干势近似方法, 本文系统计算研究了0 K下, 磁无序及合金化效应影响Co2CrZ (Z = Ga, Si, Ge)合金L21和D022相稳定性的规律性及物理机理. 研究结果表明, 0 K下, L21相合金晶格常数、体弹性模量、磁矩和弹性常数均与理论和实验值基本吻合; 铁磁下合金具有L21结构, 随磁无序度(y)的增大, L21相能量相对逐渐增大, 最终由低于转变到高于D022相, 因此, 当y ≥ 0.1(0.2)时, Z = Si和Ge(Z = Ga)的合金具有D022相稳定结构; 随y的增大, L21相的四方剪切弹性模量(C' = (C11 –C12)/2)还不断软化, 表明无论在能量还是力学角度上, 磁无序都有利于3种合金发生四方晶格变形; 磁无序影响L21和D022相相对稳定性的电子结构机理归因于Jahn-Teller不稳定性效应; 对于L21相Co2CrGa1–xSix和Co2CrGa1–xGex四元铁磁合金, 随x的增大, 总磁矩均按照Slater-Pauling定律单调增大, C'同时也都变硬, 表明Si和Ge掺杂均有利于增强Co2CrGa合金L21相的力学稳定性, 从而抑制了其四方晶格变形的发生.Using the exact Muffin-Tin orbital method combined with the coherent potential approximation, the effects of magnetic disordering and alloying effects on the phase stability of L21- and D022-Co2CrZ (Z = Ga, Si, Ge) alloys are systematically investigated at 0 K in the present work. It is shown that at 0 K, the lattice parameter, bulk modulus, magnetic moments, and elastic constants of the studied L21 alloys are in line with the available theoretical and experimental data. In the ferromagnetic state, these alloys possess L21 structure; with the magnetic disordering degree (y) increasing, the energy of the phase increases relatively and finally turns from lower than D022 phase to higher than D022 phase. As a result, when y ≥ 0.1 (0.2), then Z = Si and Ge (Z = Ga) alloys are stabilized by the D022 phase. With y increasing, the tetragonal shear elastic modulus (C' = (C11–C12)/2) also turns soft, indicating that the magnetic disorderingis conducive to the lattice tetragonal deformation in the three alloys from both the energetic view and the mechanical view. The electronic origination of the magnetic disordering effect on the stabilities of the L21 and D022 phases can be ascribed to the Jahn-Teller instability effect. In the FM L21-Co2CrGa1–xSix and L21-Co2CrGa1–xGex quaternary alloys, with x increasing, the total magnetic moment increases monotonically according to the Slater-Pauling rule, and C' also stiffens, reflecting that the adding of Si and Ge can promote the mechanical stability of L21-Co2CrGa alloy, thereby depressing the lattice tetragonal deformation.
-
Keywords:
- first-principles calculation /
- phase stability /
- elastic constants /
- Co2CrGa alloy
[1] Heusler F 1903 Deut. Phys. Ges. 5 219
[2] Ram S, Kanchana V 2013 AIP. Conf. Proc. 1512 1102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] AlgethamiO A, 李歌天, 柳祝红, 马星桥 2020 69 058102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Algethami O A, Li G T, Liu Z H, Ma X Q 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 058102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 赵昆, 张坤, 王家佳, 于金, 吴三械 2011 60 127101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhan K, Zhang K, Wang J J, Yu J, Wu S X 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 127101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Krenke T, Acet M, Wassermann E F 2006 Phys. Rev. B. 73 174413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 杜音, 王文洪, 张小明, 刘恩克, 吴光恒 2012 61 147304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Du Y, Wang W H, Zhang X M, Liu E K, Wu G H 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 147304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Terada M, Fujita Y, Endo K 1974 J. Phys. Soc. 36 620
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ritcey S P, Dunlap R A 1984 J. Appl. Phys. 55 2050
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Li Y, Xin Y, Chai L, Ma Y Q, Xu H B 2010 Acta. Mater. 58 3655
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Guezlane M, Baaziz H, Ei Haj Hassan F, Charifi Z, Djaballah Y 2016 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 414 219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Hirata K, Xu X, Omori T, Nagasako M, Kainuma R 2015 J. Alloys Compd. 642 200
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Rai D P, Thapa R K 2012 J. Alloys Compd. 542 257
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Liu C Q, Li Z, Zhang Y L, Huang Y S, Ye M F, Sun X D, Zhang G J, Gao Y M 2018 Appl. Phys. Lett. 112 211903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Shinpei F, Shoji I, Setsuro A 1989 J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 58 3657
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Manfred W, Jian L, Corneliu C 2001 Scr. Mater. 40 2393
[16] Xu X, Omori T, Nagasako M, Okubo A, Umetsu R Y, Kanomata T, Ishida K, Kainuma R 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 103 164104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hirata K, Xu X, Omori T, Kainuma R 2019 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 500 166311
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Umetus R Y, Okubo A, Xu X, Kainuma R 2014 J. Alloys Compd. 588 153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bentouaf A, Mebsout R, Aissa B 2019 J. Alloys Compd. 77 1062
[20] Odaira T, Xu X, Miyake A, Omori T, Tokunaga M, Kainuma R 2018 Scr. Mater. 153 35
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Hu Q M, Li C M, Yang R, Kulkova S E, Bazhanov D I, Johansson B, Vitos L 2009 Phys. Rev. B 79 144112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Li C M, Luo H B, Hu Q M, Yang R, Johansson B, Vitos L 2010 Phys. Rev. B 82 024201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 孙凯晨, 刘爽, 高瑞瑞, 时翔宇, 刘何燕, 罗鸿志 2021 70 137101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun K C, Liu S, Gao R R, Shi X Y, Liu H Y, Luo H Z 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 137101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Li C M, Zhang Y, Feng W J, Huang R Z, Gao M 2020 Phys. Rev. B 101 054106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Vitos L, Abrilsosv I A, Johansson B 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 87 156401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Gyorff B L 1972 Phys. Rev. B 5 2382
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Dutta B, Bhandary S, Ghosh S, Sanyal B 2012 Phys. Rev. B 86 024419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Li C M, Hu Q M, Yang R, Johansson B, Vitos L 2010 Phys. Rev. B 82 094201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 胡岩菲 2020 硕士学位论文 (沈阳: 沈阳师范大学)
Hu Y F 2020 M. S. Dissertation (Shenyang: Shangyang Normal University)(in Chinese)
[30] 张扬 2021硕士学位论文 (沈阳: 沈阳师范大学)
Zhang Y 2021 M. S. Dissertation (Shenyang: Shangyang Normal University)(in Chinese)
[31] Perdew J P, Burke K, Emzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
[32] Vitos L 2007 Computational Quantum Mechanics for Materials Engineers (London: Spring-Verlag) pp98–121
[33] Seema K, Kumar R 2015 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 377 70
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Ram S, Chauhan M R, Agarwal K, Kanchana V 2011 Phil. Mag. Lett. 91 545
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Umetsu R Y, Okubo A, Xu X, Kainuma R 2014 Journal of Alloys and Compounds 588 153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Chen X Q, Podloucky R, Rogl P 2006 J. Appl. Phys. 100 113901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Bai Z Q, Lu Y H, Shen L, Ko V Han G C, Feng Y P 2012 J. Appl. Phys. 111 093911
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Rai D P, Shankar A, Sandeep, Ghimire M P, Thapa R K 2012 Material Science Research India 9 155
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Li C M, Hu Q M, Yang R, Johansson B, Vitos L 2015 Phys. Rev. B 91 174112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Umetsu R Y, Kobayashi K, Kainuma R, Yamaguchi Y, Ohoyama K, Sakuma A, Ishida K 2010 J. Alloys Compd. 499 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Galanakis I, Dederichs P H 2002 Phys. Rev. B 66 174429
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Roy T, Pandey D, Chakrabarti A 2016 Phys. Rev. B 93 184102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Ayuela A, Enkovaara J, Ullakko K, Nieminen E M 1999 J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 11 2017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 2 铁磁状态下L21-Co2CrGa1–xSix和L21-Co2CrGa1–xGex(0 ≤ x ≤ 1)合金晶格常数和体弹性模量随x的变化关系与文献[12, 18, 33, 34, 38]的理论和实验结果的对比 (a) a; (b) B
Fig. 2. x-dependence of the lattice constant and bulk modulus of the FM L21-Co2CrGa1–xSix and L21-Co2CrGa1–xGex (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) alloys are in comparison with the available theoretical and experimental data from Refs. [12, 18, 33, 34, 38]: (a) a; (b) B.
图 3 Co2CrZ(Z = Ga, Si, Ge)合金ΔE随四方晶格c/a的变化关系, 本文ΔE的计算以各合金FM状态下L21相(即y = 0, c/a = 1)的电子总能作为参考值 (a) Z = Ga; (b) Z = Si; (c) Z = Ge
Fig. 3. ΔE of Co2CrZ(Z = Ga, Si, Ge) alloys change with respect to the c/a of tetragonal lattice, here, the electronic energy of the FM L21 structure (y = 0, c/a = 1) is as reference for ΔE calculations of each alloy: (a) Z = Ga; (b) Z = Si; (c) Z = Ge.
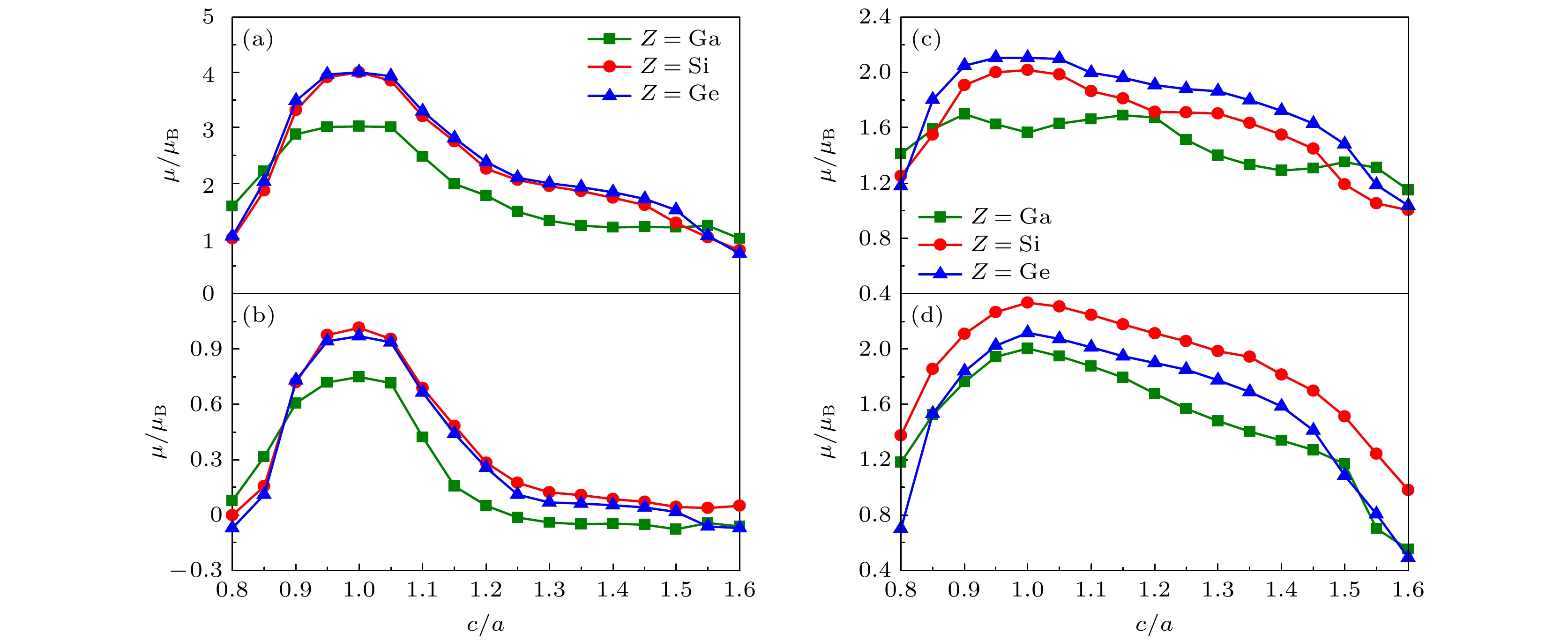
图 4 FM状态下Co2CrZ(Z = Ga, Si, Ge)合金总磁矩(μtot)及Co(μCo), Cr(μCr)原子局域磁矩随四方晶格c/a的变化关系、及其顺磁PM状态下μCr绝对值大小随c/a的变化关系 (a) FM-μtot; (b) FM-μCo; (c) FM-μCr; (d) PM-μCr
Fig. 4. μtot and μCo and μCr atoms of the FM Co2CrZ(Z = Ga, Si, Ge) alloys change with respect to c/a, together with the trends of μCr-x of the three PM alloys in their absolute values: (a) FM-μtot; (b) FM-μCo; (c) FM-μCr; (d) PM-μCr.
图 5 FM状态下L21-Co2CrGa1–xSix和L21-Co2CrGa1–xGex (0 ≤ x ≤ 1)合金μtot与μCo, μCr原子磁矩随x的变化关系、及其与Slater-Pauling(S-P)定律计算给出μtot-x关系的对比
Fig. 5. μtot and μCo, μCr atoms of the FM L21-Co2CrGa1–xSix and L21-Co2CrGa1–xGex (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) alloys change with respect to x, in comparison with their calculated trends of μtot-x according to the Slater-Pauling (S-P) rule.
图 6 FM状态下L21-Co2CrZ (Z = Ga, Si, Ge)合金单晶弹性常数(C44和C '=(C11– C12)/2)和A = C44/C随y的变化关系 (a) (b) Z = Ga; (c) (d) Z = Si; (e) (f) Z = Ge
Fig. 6. Single-crystal elastic constants (C44 and C ' = (C11– C12)/2) and elastic anisotropy (A = C44/C ') of the FM L21-Co2CrZ (Z = Ga, Si, Ge) alloys change with respect to the magnetic disordering degree (y): (a) (b) Z = Ga; (c)(d) Z = Si; (e) (f) Z = Ge.
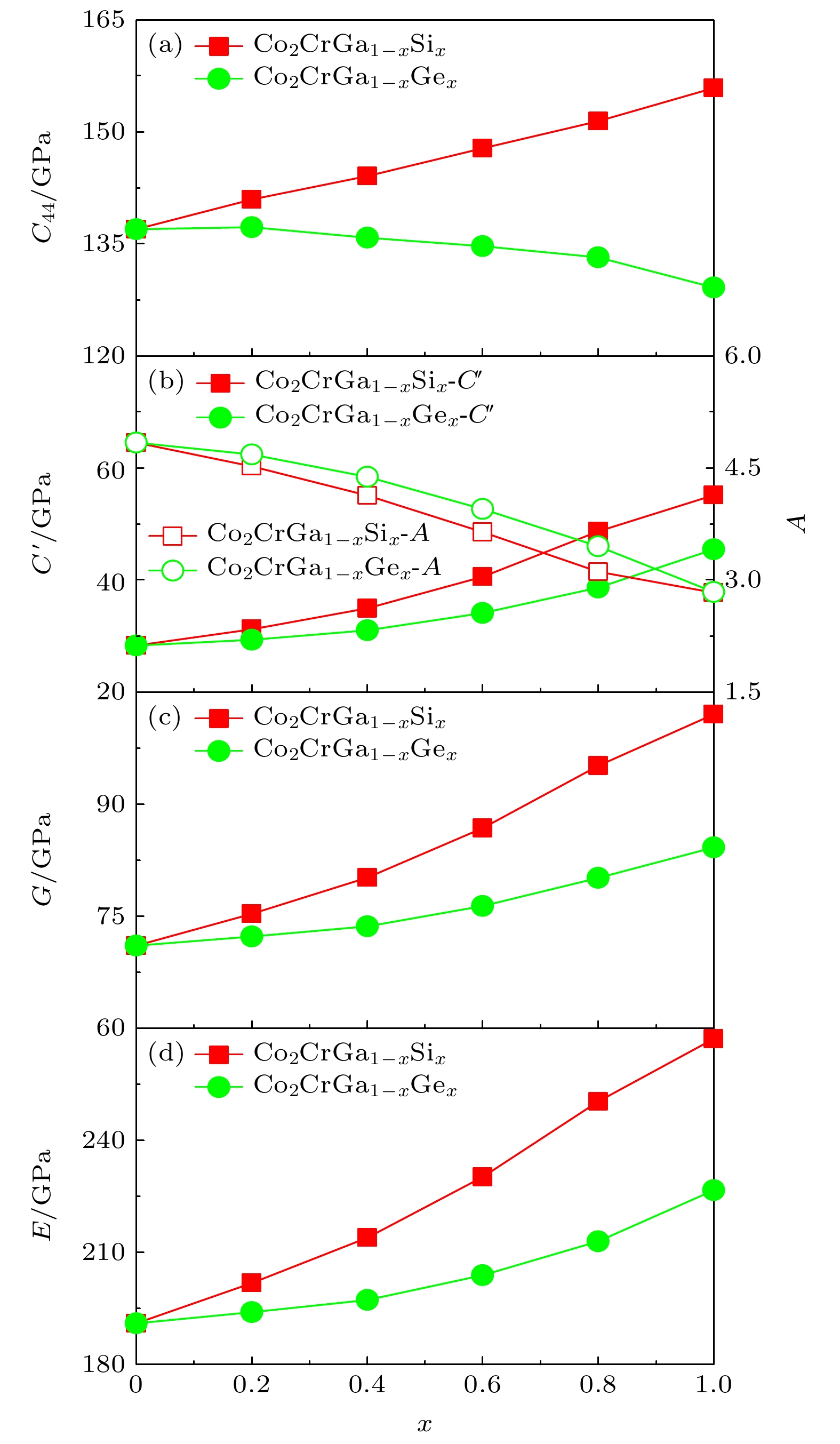
图 7 FM状态下L21-Co2CrGa1–xSix和L21-Co2CrGa1–xGex (0 ≤ x ≤ 1)合金单晶弹性常数(C44和C ' = (C11–C12)/2)、A = C44/C及G和E随x的变化关系 (a) C44–x; (b) C ' –x和A–x; (c)G–x; (d) E–x
Fig. 7. Single-crystal elastic constants (C11, C12, C44, and C ' = (C11–C12)/2), elastic anisotropy (A = C44/C'), polycrystal shear modulus (G), and Young’ modulus (E) of the FM L21-Co2CrGa1–xSix and L21-Co2CrGa1–xGex (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) alloys change with respect to x: (a) C44–x; (b) C ' –x and A–x; (c) G–x; (d) E–x.
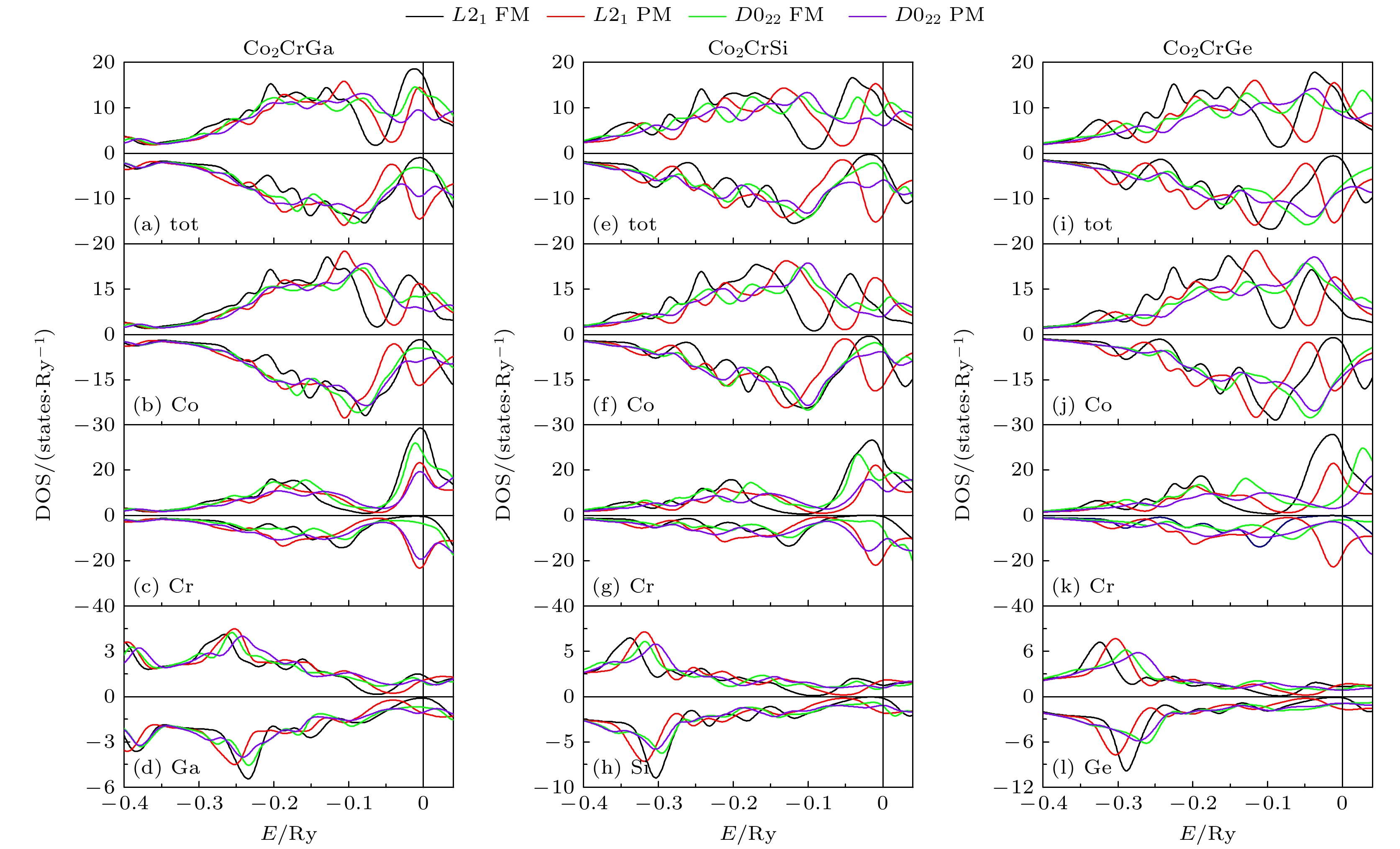
图 8 FM和PM状态下L21-和D022-Co2CrZ (Z = Ga, Si, Ge)合金电子总态密度(DOS)及Co, Cr和Z原子局域DOS的对比: (a)—(d) Z = Ga; (e)—(h) Z = Si; (i)—(l) Z = Ge
Fig. 8. Total electronic density of states (DOS) and local density of states of Co, Cr and Z atoms of the Co2CrZ (Z = Ga, Si, Ge) alloys with both the FM and PM L21 and D022 phases: (a)–(d) Z = Ga; (e)–(h) Z = Si; (i)–(l) Z = Ge.
表 1 铁磁(FM)和顺磁(PM)状态下L21-Co2CrZ (Z = Ga, Si, Ge)合金晶格常数和体弹性模量的EMTO计算结果与其他源于文献[12, 33-38]理论和实验值的对比
Table 1. Lattice constant and bulk modulus of the FM and PM L21-Co2CrZ (Z = Ga, Si, Ge) alloys calculated with the EMTO program are in comparison with the other theoretical and experimental data from Refs. [12, 33-38].
Alloys Phases Methods a/Å B/GPa Co2CrGa FM L21 EMTO 5.736 203.5 The.[12] 5.802 208.8 The.[33] 5.797 204.8 The.[34] 5.720 — Exp.[35] 5.760 — PM L21 EMTO 5.749 177.8 Co2CrSi FM L21 EMTO 5.651 234.3 The.[36] 5.630 227.0 Exp.[37] 5.650 — PM L21 EMTO 5.652 202.4 Co2CrGe FM L21 EMTO 5.755 207.7 The.[38] 5.770 250.4 The.[33] 5.754 227.1 PM L21 EMTO 5.764 180.4 表 2 FM状态下L21-Co2CrZ (Z = Ga, Si, Ge)合金单晶弹性常数(C11, C12, C44, C ' = (C11– C12)/2)、A = C44/C及多晶G和E的EMTO计算结果与源于文献[36, 42]理论值的对比
Table 2. Single-crystal elastic constants (C11, C12, C44, and C ' = (C11 – C12)/2), elastic anisotropy (A = C44/C '), G, and E of the FM L21-Co2CrZ (Z = Ga, Si, Ge) alloys are shown in comparison with the available theoretical results from Refs. [36, 42]
-
[1] Heusler F 1903 Deut. Phys. Ges. 5 219
[2] Ram S, Kanchana V 2013 AIP. Conf. Proc. 1512 1102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] AlgethamiO A, 李歌天, 柳祝红, 马星桥 2020 69 058102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Algethami O A, Li G T, Liu Z H, Ma X Q 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 058102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 赵昆, 张坤, 王家佳, 于金, 吴三械 2011 60 127101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhan K, Zhang K, Wang J J, Yu J, Wu S X 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 127101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Krenke T, Acet M, Wassermann E F 2006 Phys. Rev. B. 73 174413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 杜音, 王文洪, 张小明, 刘恩克, 吴光恒 2012 61 147304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Du Y, Wang W H, Zhang X M, Liu E K, Wu G H 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 147304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Terada M, Fujita Y, Endo K 1974 J. Phys. Soc. 36 620
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ritcey S P, Dunlap R A 1984 J. Appl. Phys. 55 2050
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Li Y, Xin Y, Chai L, Ma Y Q, Xu H B 2010 Acta. Mater. 58 3655
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Guezlane M, Baaziz H, Ei Haj Hassan F, Charifi Z, Djaballah Y 2016 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 414 219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Hirata K, Xu X, Omori T, Nagasako M, Kainuma R 2015 J. Alloys Compd. 642 200
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Rai D P, Thapa R K 2012 J. Alloys Compd. 542 257
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Liu C Q, Li Z, Zhang Y L, Huang Y S, Ye M F, Sun X D, Zhang G J, Gao Y M 2018 Appl. Phys. Lett. 112 211903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Shinpei F, Shoji I, Setsuro A 1989 J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 58 3657
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Manfred W, Jian L, Corneliu C 2001 Scr. Mater. 40 2393
[16] Xu X, Omori T, Nagasako M, Okubo A, Umetsu R Y, Kanomata T, Ishida K, Kainuma R 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 103 164104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hirata K, Xu X, Omori T, Kainuma R 2019 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 500 166311
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Umetus R Y, Okubo A, Xu X, Kainuma R 2014 J. Alloys Compd. 588 153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bentouaf A, Mebsout R, Aissa B 2019 J. Alloys Compd. 77 1062
[20] Odaira T, Xu X, Miyake A, Omori T, Tokunaga M, Kainuma R 2018 Scr. Mater. 153 35
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Hu Q M, Li C M, Yang R, Kulkova S E, Bazhanov D I, Johansson B, Vitos L 2009 Phys. Rev. B 79 144112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Li C M, Luo H B, Hu Q M, Yang R, Johansson B, Vitos L 2010 Phys. Rev. B 82 024201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 孙凯晨, 刘爽, 高瑞瑞, 时翔宇, 刘何燕, 罗鸿志 2021 70 137101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun K C, Liu S, Gao R R, Shi X Y, Liu H Y, Luo H Z 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 137101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Li C M, Zhang Y, Feng W J, Huang R Z, Gao M 2020 Phys. Rev. B 101 054106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Vitos L, Abrilsosv I A, Johansson B 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 87 156401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Gyorff B L 1972 Phys. Rev. B 5 2382
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Dutta B, Bhandary S, Ghosh S, Sanyal B 2012 Phys. Rev. B 86 024419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Li C M, Hu Q M, Yang R, Johansson B, Vitos L 2010 Phys. Rev. B 82 094201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 胡岩菲 2020 硕士学位论文 (沈阳: 沈阳师范大学)
Hu Y F 2020 M. S. Dissertation (Shenyang: Shangyang Normal University)(in Chinese)
[30] 张扬 2021硕士学位论文 (沈阳: 沈阳师范大学)
Zhang Y 2021 M. S. Dissertation (Shenyang: Shangyang Normal University)(in Chinese)
[31] Perdew J P, Burke K, Emzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
[32] Vitos L 2007 Computational Quantum Mechanics for Materials Engineers (London: Spring-Verlag) pp98–121
[33] Seema K, Kumar R 2015 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 377 70
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Ram S, Chauhan M R, Agarwal K, Kanchana V 2011 Phil. Mag. Lett. 91 545
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Umetsu R Y, Okubo A, Xu X, Kainuma R 2014 Journal of Alloys and Compounds 588 153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Chen X Q, Podloucky R, Rogl P 2006 J. Appl. Phys. 100 113901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Bai Z Q, Lu Y H, Shen L, Ko V Han G C, Feng Y P 2012 J. Appl. Phys. 111 093911
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Rai D P, Shankar A, Sandeep, Ghimire M P, Thapa R K 2012 Material Science Research India 9 155
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Li C M, Hu Q M, Yang R, Johansson B, Vitos L 2015 Phys. Rev. B 91 174112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Umetsu R Y, Kobayashi K, Kainuma R, Yamaguchi Y, Ohoyama K, Sakuma A, Ishida K 2010 J. Alloys Compd. 499 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Galanakis I, Dederichs P H 2002 Phys. Rev. B 66 174429
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Roy T, Pandey D, Chakrabarti A 2016 Phys. Rev. B 93 184102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Ayuela A, Enkovaara J, Ullakko K, Nieminen E M 1999 J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 11 2017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 8705
- PDF下载量: 110
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: