-
近年来, 空间结构和社会多样性对群体合作演化的影响吸引了人们极大的关注. 本文在空间公共品博弈中引入了异质增益因子, 研究超图上合作行为的演化. 除所有博弈群组具有相同增益因子的原始模型外, 还考虑了包括均匀分布、指数分布和幂律分布在内的不同异质性强度的三类异质增益因子分布. 数值模拟结果显示, 上述4种增益因子分布对应的公共品博弈中, 均匀随机超图阶数
$g$ 的增大有利于提高群体的合作水平. 更进一步地, 对比超图上原始空间公共品博弈的演化结果, 群体中博弈群组增益因子异质性的引入能够显著促进群体的合作行为, 幂律分布情况下能够使得系统获得最高合作水平. 此外, 研究了超边数目对群体合作演化的影响, 结果表明上述结论对超边数目鲁棒, 并且超边数目$L$ 的增大会抑制公共品博弈中合作行为的涌现. 一定程度上, 本文的研究结果有助于我们更好地理解超图上空间公共品博弈的演化动力学.The spatial structure and social diversity playing a nontrivial role in the emergence and maintenance of cooperation among selfish individuals have been verified. Their effects on the evolution of cooperation have attracted great attention in recent years. Most of previous evolutionary game dynamics is based on pairwise interactions. However, the interactions often take place within groups of people in many real situations and cannot be described simply by dyads. The dynamics of evolutionary games in systems with higher-order interactions has not yet been explored as deserved. In this paper, we introduce heterogeneous multiplication factors into the spatial public goods game to investigate the cooperative behaviors on the hypergraphs. In addition to the original model in which all groups have the same multiplication factor, three types of heterogeneous multiplication factor distributions including uniform, exponential and power-law distributions are considered. The numerical simulation results show that the increase of the order g of the uniform random hypergraphs is conducive to the emergence and prosperity of the individuals' cooperative behavior no matter what types these distributions belong to. Furthermore, compared with the results of the original spatial public goods games on hypergraphs, the heterogeneous multiplication factors following three different distributions can remarkably promote the evolution of cooperation. In particular, for most of ranges of the average rescaling multiplication factor$r_0$ , the highest cooperation level can be obtained under the power-law distribution, while the uniform distribution leads to the lowest cooperation level. We provide an explanation through investigating the number of cooperators in each group. In addition, to probe into the essence that influences the survival of cooperative behaviors, we study the time series of the fraction of groups with different numbers of cooperators. Besides, we also investigate the influence of the number of hyperlinks on cooperation evolution. We find that the results are robust against the number of hyperlinks L, and the emergence of cooperative behaviors in public goods games on hypergraphs is hindered with the value of L increasing. To some extent, these results are helpful in the better understanding of the evolutionary dynamics of the spatial public goods games on hypergraphs with social diversity.[1] Axelrod R, Hamilton W 1981 Science 211 1390
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Szabó G, Fáth G 2007 Phys. Rep. 446 97
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Nowak M A, May R M 1992 Nature 359 826
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Szabó G, Borsos I 2016 Phys. Rep. 624 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Perc M, Jordan J J, Rand D G, Wang Z, Boccaletti S, Szolnoki A 2017 Phys. Rep. 687 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Battiston F, Cencetti G, Iacopini I, Latora V, Lucas M, Patania A, Young J G, Petri G 2020 Phys. Rep. 874 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Santos F C, Santos M D, Pacheco J M 2008 Nature 454 213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Rong Z, Wu Z X 2009 Europhys. Lett. 87 30001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Battiston F, Perc M, Latora V 2017 New J. Phys. 19 073017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Huang C W, Han W C, Li H H, Cheng H Y, Dai Q L, Yang J Z 2019 Appl. Math. Comput. 340 305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Szolnoki A, Perc M 2010 Europhys. Lett. 92 38003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Brandt H, Hauert C, Sigmund K 2003 Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. B 270 1099
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Helbing D, Szolnoki A, Perc M, Szabó G 2010 New J. Phys. 12 083005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chen X, Szolnoki A, Perc M 2014 New J. Phys. 16 083016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Yang H X, Rong Z H 2015 Chaos Solitons Fractals 77 230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Yang H X, Chen X 2018 Appl. Math. Comput. 316 460
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zhang Y C, Wang J, Ding C X, Xia C 2017 Knowledge-Based Systems 136 150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhang L, Xie Y, Huang C W, Li H H, Dai Q L 2020 Chaos, Solitons Fractals 133 109675
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Liu L, Chen X, Perc M 2019 Nonlinear Dynamics 97 749
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Liu L, Chen X 2020 Knowledge-Based Systems 188 104835
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Chen M, Wang L, Wang J, Sun S, Xia C 2015 Appl. Math. Comput. 251 192
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Szolnoki A, Chen X 2015 Phys. Rev. E 92 042813
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Szolnoki A, Perc M 2016 New J. Phys. 18 083021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Javarone M A, Antonioni A, Caravelli F 2016 Europhys. Lett. 114 38001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Pei Z, Wang B, Du J 2017 New J. Phys. 19 013037
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Shi D M, Zhuang Y, Wang B H 2010 Europhys. Lett. 90 58003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Shi D M, Zhuang Y, Wang B H 2012 Physica A 391 1636
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Chen X, Liu Y, Zhou Y, Wang L, Perc M 2012 PLoS One 7 e36895
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Weng Q, He N, Hu L, Chen X 2021 Phys. Lett. A 400 127299
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 郭进利, 祝昕昀 2014 63 090207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo J L, Zhu X Y 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 090207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 卢文, 赵海兴, 孟磊, 胡枫 2021 70 018901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu W, Zhao H X, Meng L, Hu F 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 018901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Vasilyeva E, Kozlov A, Alfaro-Bittner K, Musatov D, Raigorodskii A M, Perc M, Boccaletti S 2021 Sci. Rep. 11 5666
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Battiston F, Amico E, Barrat A, Bianconi G, Ferraz de Arruda G, Franceschiello B, Iacopini I, Kéfi S, Latora V, Moreno Y, Murray M M, Peixoto T P, Vaccarino F, Petri G 2021 Nat. Phys. 17 1093
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Burgio G, Matamalas J T, Gómez S, Arenas A 2020 Entropy 22 744
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Alvarez-Rodriguez U, Battiston F, de Arruda G F, Moreno Y, Perc M, Latora V 2021 Nature Human Behaviour 5 586
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Perc M, Szolnoki A 2008 Phys. Rev. E 77 011904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Taylor P, Jonker L 1978 Math. Biosci. 40 145
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 2
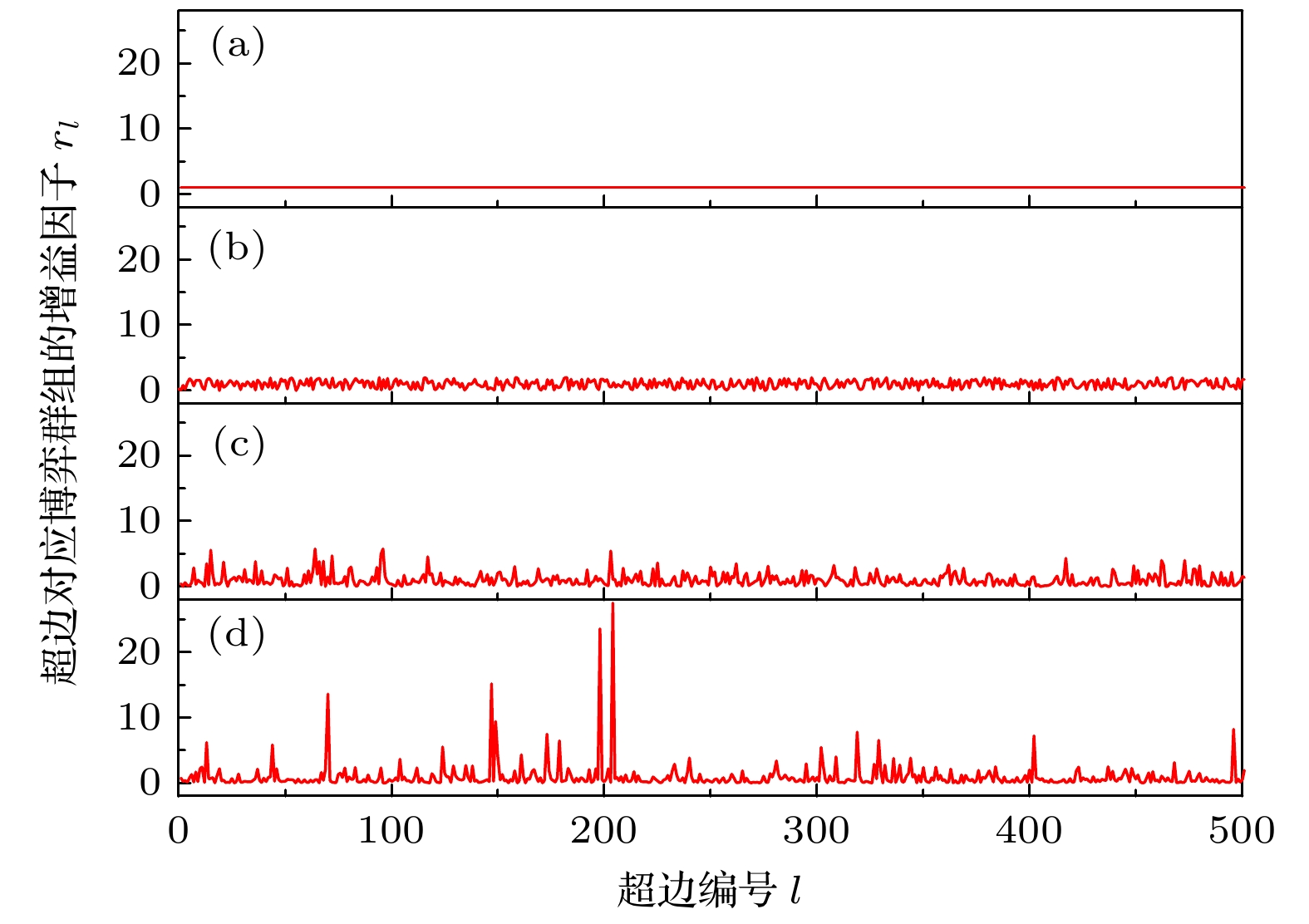
$ r_0 = 1.0 $ 和$ a = 1.0 $ 时4种分布情况下的群体增益因子$ r_{l} = r_0(1 + \xi) $ 的分布 (a) 原始模型; (b) 均匀分布; (c) 指数分布; (d) 幂律分布Fig. 2. Distributions of synergy factors
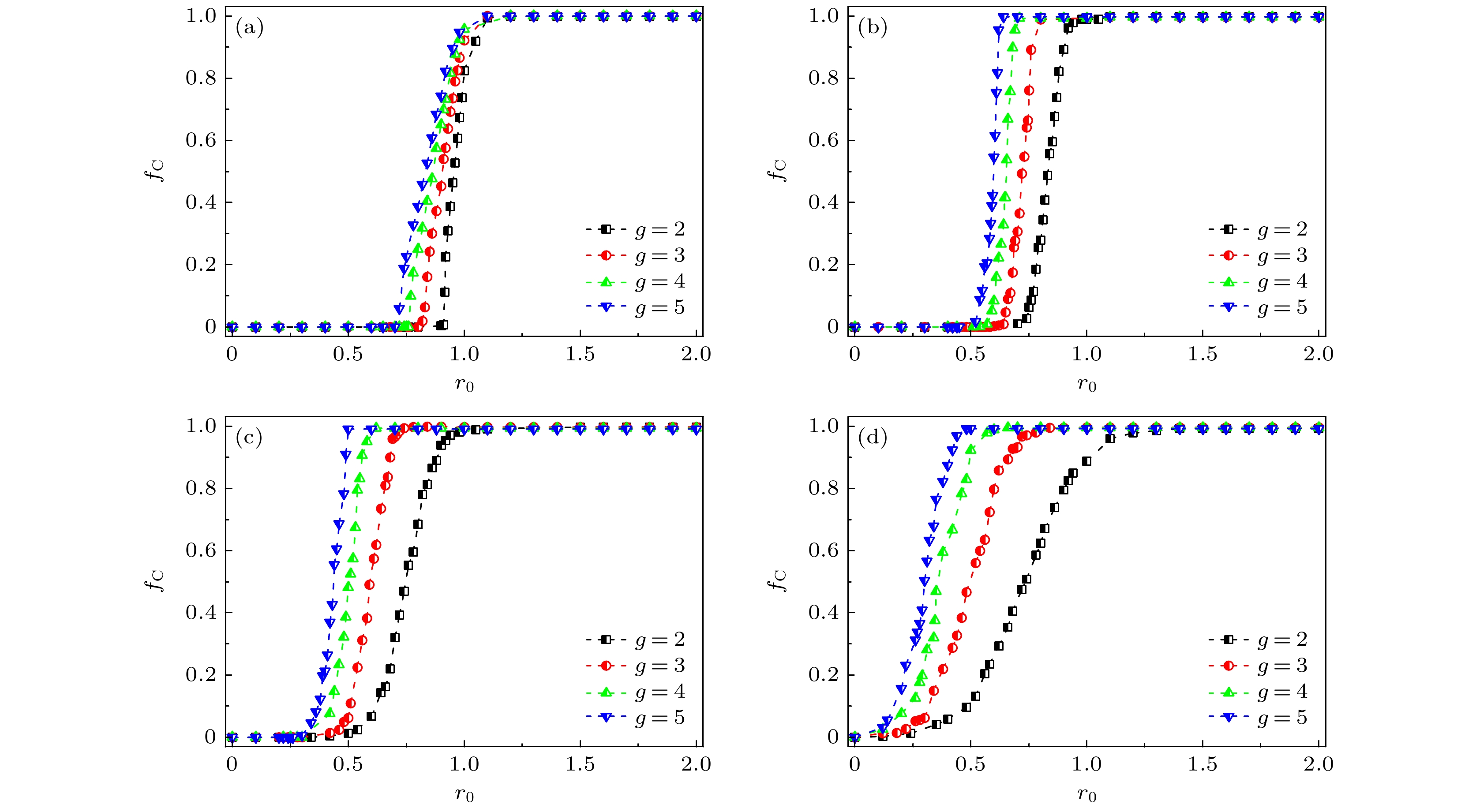
$ r_{l} = r_0(1 + \xi) $ for$ r_0 = 1.0 $ and$ a = 1.0 $ of the four cases: (a) Original model; (b) uniform distribution; (c) exponential distribution; (d) power-law distribution.图 3 4种增益因子分布情况下, 不同阶数
$ g $ 的超图上群体合作水平$f_{\rm{C}}$ 随$ r_0 $ 的变化 (a) 原始模型; (b) 均匀分布; (c) 指数分布; (d) 幂律分布Fig. 3. Fraction of cooperators
$ f_{\rm{C}} $ as a function of$ r_0 $ for hypergraphs with different orders$ g $ : (a) Original model; (b) uniform distribution; (c) exponential distribution; (d) power-law distribution图 6 4种增益因子分布情况下, 参数取
$ g = 5 $ 与$ r_0 = 0.35 $ 时群体合作水平$ f_{\rm{C}} $ 以及群组中合作者数目$ w_{\rm{C}} $ 分别为0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5的博弈群组比例的演化时间序列 (a) 原始模型; (b) 均匀分布; (c) 指数分布; (d) 幂律分布Fig. 6. Time series for the evolution of the fraction of cooperators
$ f_{\rm{C}} $ and the fractions of groups with$ w_{\rm{C}} = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 $ for$ g = 5 $ and$ r_0 = 0.35 $ : (a) Original model; (b) uniform distribution; (c) exponential distribution; (d) power-law distribution图 7 4种增益因子分布情况下, 不同阶数
$ g $ 的超图上临界增益因子均值$r_{\rm{c}}$ 随超边数目$ L $ 与阈值$ L_{\rm{c}} $ 的比值的变化 (a) 原始模型; (b) 均匀分布; (c) 指数分布; (d) 幂律分布Fig. 7. Critical value of the synergy factor
$ r_{\rm{c}} $ as a function of the ratio between the number of hyperlinks$ L $ and the critical value$ L_{\rm{c}} $ in hypergraphs of different orders$ g $ : (a) Original model; (b) uniform distribution; (c) exponential distribution; (d) power-law distribution -
[1] Axelrod R, Hamilton W 1981 Science 211 1390
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Szabó G, Fáth G 2007 Phys. Rep. 446 97
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Nowak M A, May R M 1992 Nature 359 826
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Szabó G, Borsos I 2016 Phys. Rep. 624 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Perc M, Jordan J J, Rand D G, Wang Z, Boccaletti S, Szolnoki A 2017 Phys. Rep. 687 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Battiston F, Cencetti G, Iacopini I, Latora V, Lucas M, Patania A, Young J G, Petri G 2020 Phys. Rep. 874 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Santos F C, Santos M D, Pacheco J M 2008 Nature 454 213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Rong Z, Wu Z X 2009 Europhys. Lett. 87 30001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Battiston F, Perc M, Latora V 2017 New J. Phys. 19 073017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Huang C W, Han W C, Li H H, Cheng H Y, Dai Q L, Yang J Z 2019 Appl. Math. Comput. 340 305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Szolnoki A, Perc M 2010 Europhys. Lett. 92 38003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Brandt H, Hauert C, Sigmund K 2003 Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. B 270 1099
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Helbing D, Szolnoki A, Perc M, Szabó G 2010 New J. Phys. 12 083005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chen X, Szolnoki A, Perc M 2014 New J. Phys. 16 083016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Yang H X, Rong Z H 2015 Chaos Solitons Fractals 77 230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Yang H X, Chen X 2018 Appl. Math. Comput. 316 460
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zhang Y C, Wang J, Ding C X, Xia C 2017 Knowledge-Based Systems 136 150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhang L, Xie Y, Huang C W, Li H H, Dai Q L 2020 Chaos, Solitons Fractals 133 109675
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Liu L, Chen X, Perc M 2019 Nonlinear Dynamics 97 749
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Liu L, Chen X 2020 Knowledge-Based Systems 188 104835
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Chen M, Wang L, Wang J, Sun S, Xia C 2015 Appl. Math. Comput. 251 192
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Szolnoki A, Chen X 2015 Phys. Rev. E 92 042813
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Szolnoki A, Perc M 2016 New J. Phys. 18 083021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Javarone M A, Antonioni A, Caravelli F 2016 Europhys. Lett. 114 38001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Pei Z, Wang B, Du J 2017 New J. Phys. 19 013037
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Shi D M, Zhuang Y, Wang B H 2010 Europhys. Lett. 90 58003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Shi D M, Zhuang Y, Wang B H 2012 Physica A 391 1636
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Chen X, Liu Y, Zhou Y, Wang L, Perc M 2012 PLoS One 7 e36895
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Weng Q, He N, Hu L, Chen X 2021 Phys. Lett. A 400 127299
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 郭进利, 祝昕昀 2014 63 090207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo J L, Zhu X Y 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 090207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 卢文, 赵海兴, 孟磊, 胡枫 2021 70 018901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu W, Zhao H X, Meng L, Hu F 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 018901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Vasilyeva E, Kozlov A, Alfaro-Bittner K, Musatov D, Raigorodskii A M, Perc M, Boccaletti S 2021 Sci. Rep. 11 5666
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Battiston F, Amico E, Barrat A, Bianconi G, Ferraz de Arruda G, Franceschiello B, Iacopini I, Kéfi S, Latora V, Moreno Y, Murray M M, Peixoto T P, Vaccarino F, Petri G 2021 Nat. Phys. 17 1093
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Burgio G, Matamalas J T, Gómez S, Arenas A 2020 Entropy 22 744
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Alvarez-Rodriguez U, Battiston F, de Arruda G F, Moreno Y, Perc M, Latora V 2021 Nature Human Behaviour 5 586
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Perc M, Szolnoki A 2008 Phys. Rev. E 77 011904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Taylor P, Jonker L 1978 Math. Biosci. 40 145
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 7927
- PDF下载量: 155
- 被引次数: 0

















 下载:
下载: