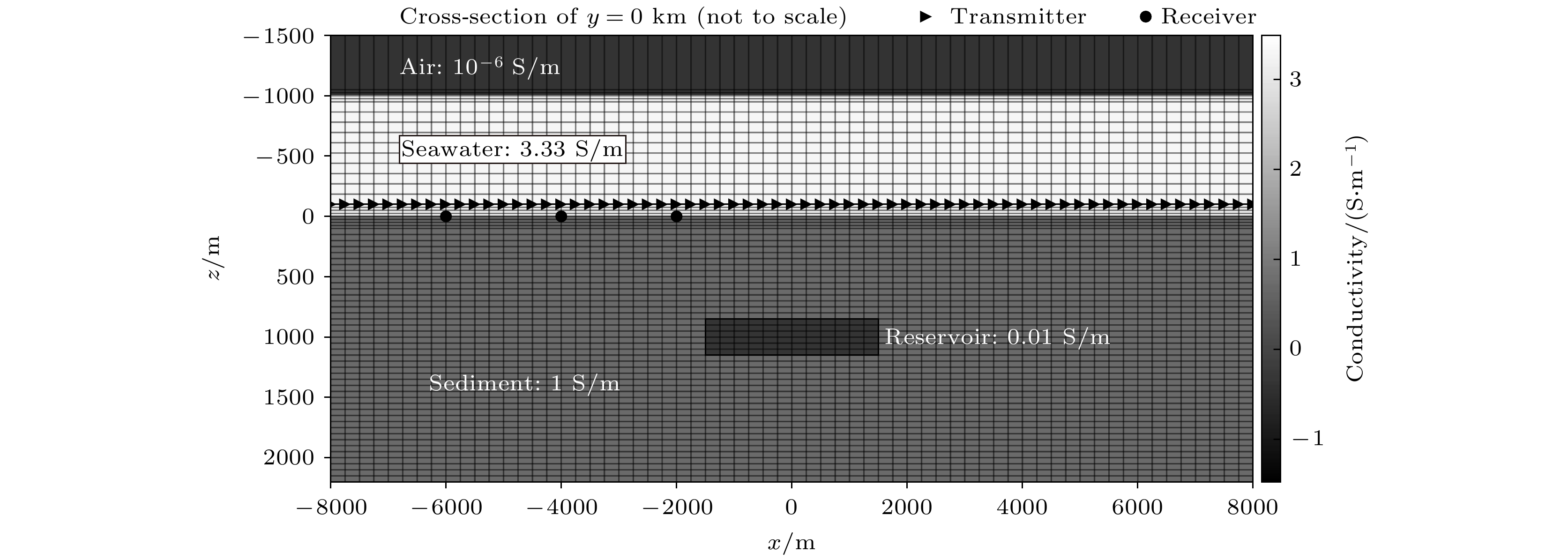
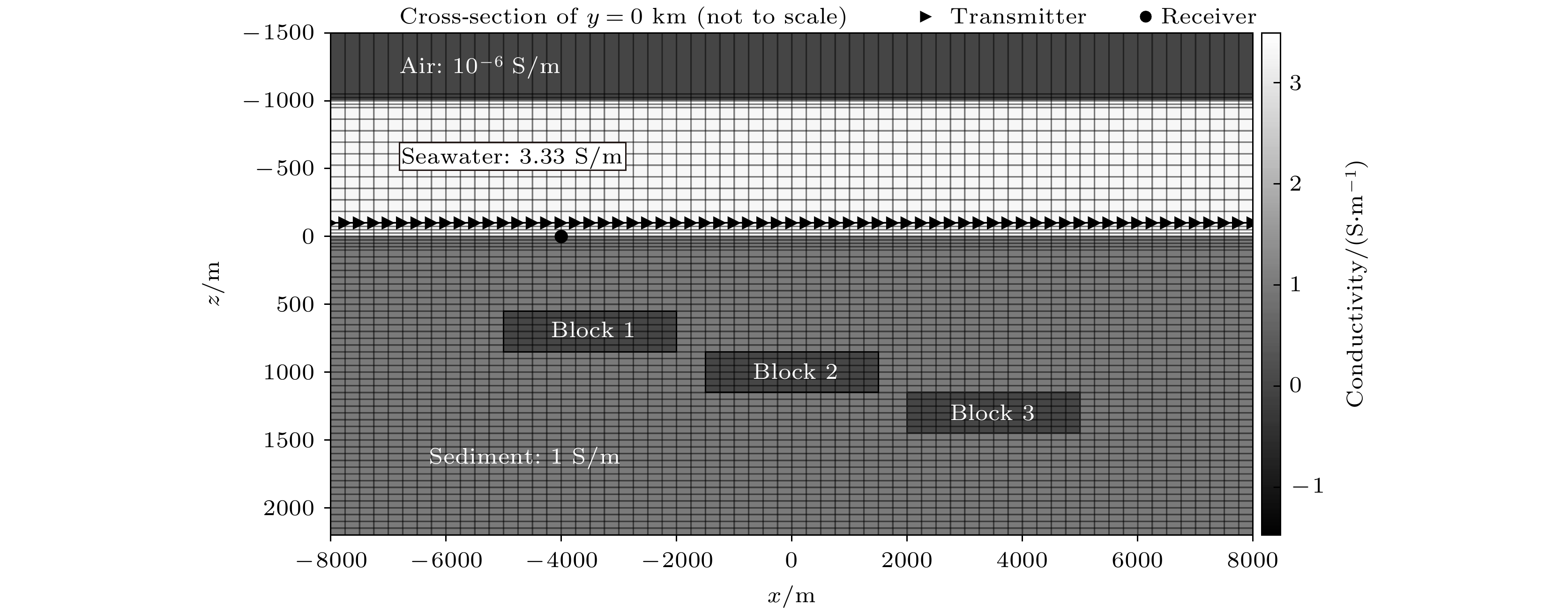
-
借助电场耦合势三维有限体积法与直接求解技术, 研究建立了一套海洋可控源三维电磁响应显式灵敏度矩阵(或称为Fréchet导数)高效算法. 首先, 利用Yee氏交错网格和有限体积法对电场混合势Helmholtz方程进行离散处理, 建立与移动源电磁场正演模拟相对应的大型代数方程组, 再应用直接法得到的逆矩阵和三维线性插值技术事先确定插值算子和投影算子, 并利用投影算子与各个发射源离散向量的乘积计算多发射源电磁响应, 极大地提高了多发射源电磁场正演模拟效率. 在此基础上, 根据块状模型和像素模型中异常体电导率分片常数分布特征, 将电导率摄动产生的一次散射电流场表示成Yee氏剖分网格上散射电流元的叠加, 由投影算子与散射电流元的离散向量的乘积快速计算出电场强度与磁场强度的显式灵敏度矩阵. 最后, 通过数值计算检验算法的有效性, 并通过块状模型与像素模型分别研究海洋可控源电磁响应特征.In this paper, an efficient algorithm of three-dimensional (3D) explicit sensitivity (or called Fréchet derivatives) matrix for marine controlled source electromagnetic measurements is established by combining an electric coupled potential finite volume method with a direct solver PARDISO direct method. Firstly, on the Yee’s staggered grids, the coupled potential Helmholtz equations are discretized to form a large, sparse and complex linear system which is excited by mobile transmitters. Secondly, through the inversion of the discrete matrix and 3D linear interpolation formula, the interpolation operators and projection operators are established for each receiver at different positions. Because these interpolation operators and projection operators are unrelated to transmitters, they can be computed in advance according to the positions of all receivers. Then the multiple projection operators with discrete vector of each transmitter source can efficiently produce the electromagnetic (EM) responses. On the basis, the goal conductivity of block model and pixel model is expressed as a piece-wise constant function. By perturbing the goal conductivity, the scattered electric current density can be decomposed into a series of electric current elements distributed on Yee’s grids. Each scattered current element is equal to the product of relative perturbation of conductivity and the electric intensity on the grid. The discrete vector on the right-hand side is computed by integrating each scattered current element on the Yee’s grid and then being multiplied with the project operator. Then the linear relationship between the changes in EM field and the relative conductivity perturbation on each block or pixel can be fast produced to obtain the explicit sensitivity matrix about EM responses. Finally, numerical results demonstrate the efficiency and accuracy of this method. The characteristics of 3D sensitivity in three different cases are further investigated.
-
Keywords:
- marine controlled source electromagnetic measurement /
- sensitivity matrix /
- finite volume method /
- projection operator
[1] Edwards N 2005 Surv. Geophys. 26 675
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Constable S 2010 Geophysics 75 X75
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Börner R U 2010 Surv. Geophys. 31 225
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Commer M, Newman G A 2008 Geophys. J. Int. 172 513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 汪建勋, 汪宏年, 周建美, 杨守文, 刘晓军, 殷长春 2013 62 224101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J X, Wang H N, Zhou J M, Yang S W, Liu X J, Yin C C 2013 Acta Phy. Sin. 62 224101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 陈桂波, 毕娟, 张烨, 李宗文 2013 62 094102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen G B, Bi J, Zhang Y, Li Z W 2013 Acta Phy. Sin. 62 094102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 姚东华, 汪宏年, 杨守文, 杨海亮 2010 地球 53 3026
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yao D H, Wang H N, Yang S W, Yang H L 2010 Chin. J. Geophys. 53 3026
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 康庄庄, 汪宏年, 王浩森, 杨守文, 殷长春 2020 地球 63 4277
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Kang Z Z, Wang H N, Wang H S, Yang S W, Yin C C 2020 Chin. J. Geophys. 63 4277
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 殷长春, 惠哲剑, 张博, 刘云鹤, 任秀艳 2019 地球 62 1942
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yin C C, Hui Z J, Zhang B, Liu Y H, Ren X Y 2019 Chin. J. Geophys. 62 1942
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Schwarzbach C, Börner R U, Spitzer K 2011 Geophys. J. Int. 187 63
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Haber E, Ascher U M, Aruliah D A, Oldenburg D W 2000 J. Comput. Phys. 163 150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 周建美, 张烨, 汪宏年, 杨守文, 殷长春 2014 63 159101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou J M, Zhang Y, Wang H N, Yang S W, Yin C C 2014 Acta Phy. Sin. 63 159101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 王浩森, 杨守文, 白彦, 陈涛, 汪宏年 2016 65 079101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H S, Yang S W, Bai Y, Chen T, Wang H N 2016 Acta Phy. Sin. 65 079101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang H S, Wang H N, Yang S W, Yin C C 2020 Appl. Geophys. 17 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 陈桂波, 汪宏年, 姚敬金, 韩子夜 2009 58 3848
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen G B, Wang H N, Yao J J, Han Z Y 2009 Acta Phy. Sin. 58 3848
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 林蔺, 焦利光, 陈博, 康庄庄, 马玉刚, 汪宏年 2017 66 139102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lin L, Jiao L G, Chen B, Kang Z Z, Ma Y G, Wang H N 2017 Acta Phy. Sin. 66 139102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Constable S C, Parker R L, Constable C G 1987 Geophysics 52 289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhou J M, Wang J X, Shang Q L, Wang H N, Yin C C 2014 J. Geophys. Eng. 11 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 周建美, 汪宏年, 姚敬金, 杨守文, 马寅芝 2012 61 089101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou J M, Wang H N, Yao J J, Yang S W, Ma Y Z 2012 Acta Phy. Sin. 61 089101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Key K 2009 Geophysics 74 F9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Yang S W, Wang J X, Zhou J M, Zhu T Z, Wang H N 2014 IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 52 6911
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Gribenko A, Zhdanov M 2007 Geophysics 72 WA73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Liu Y H, Yin C C, Qiu C K, Hui Z J, Zhang B, Ren X Y, Weng A H 2019 Geophys. J. Int. 217 301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Hunziker J, Thorbecke J, Brackenhoff J, Slob E 2016 Geophysics 81 F49
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Grayver A V, Streich R, Ritter O 2013 Geophys. J. Int. 193 1432
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Blatter D, Key K, Ray A, Gustafson C, Evans R 2019 Geophys. J. Int. 218 1822
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Ayani M, MacGregor L, Mallick S 2019 Geophys. J. Int. 220 1066
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Abubakar A, Habashy T M, Li M, Liu J 2009 Inverse Prob. 25 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wang H N 2011 IEEE Trans.Geosci. Remote Sen. 49 4483
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Wang H N, Tao H G, Yao J J, Chen G B 2008 IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 46 1525
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Dorn O, Bertete-Aguirre H, Berryman J G, Papanicolaou G C 2002 Inverse Prob. 18 285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Newman G A, Hoversten G M 2000 Inverse Prob. 16 1357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Lien M, Mannseth T 2008 Geophysics 73 F151
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] McGillivray P R, Oldenburg D W, Ellis R G, Habashy T M 1994 Geophys. J. Int. 116 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Chen B, Wang H N, Yang S W 2019 Photonics & Electromagnetics Research Symposium-Fall (PIERS - Fall) Xiamen, China, December 17–20, 2019 p889
[36] Schenk O, Gärtner K 2004 Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 20 475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 3 3个不同位置接收器上电场
${E_x}$ 分量的MVO和PVO曲线以及由EDM和FDM计算得到的振幅与相位灵敏度对比图 (a)${E_x}$ 的MVO正演结果; (b)${E_x}$ 的PVO正演结果; (c)${E_x}$ 振幅灵敏度对比; (d)${E_x}$ 相位灵敏度对比Fig. 3. The
${E_x}$ magnitudes (MVO) and phases (PVO) of 3 receivers at different positions and comparison of Fréchet sensitivity obtained by two different algorithms of EDM and FDM: (a) MVO of${E_x}$ ; (b) PVO of${E_x}$ ; (c) comparison of${E_x}$ amplitude sensitivity; (d) comparison of${E_x}$ phase sensitivity.图 4 3个不同位置接收器上磁场
${H_y}$ 分量MVO和PVO曲线以及由EDM和FDM计算得到的振幅与相位灵敏度对比图 (a)${H_y}$ 的MVO正演结果; (b)${H_y}$ 的PVO正演结果; (c)${H_y}$ 振幅灵敏度对比; (d)${H_y}$ 相位灵敏度对比Fig. 4. The
${H_y}$ magnitudes (MVO) and phases (PVO) of 3 receivers at different position and comparison of Fréchet sensitivity obtained by two different algorithms of EDM and FDM: (a) MVO of${H_y}$ ; (b) PVO of${H_y}$ ; (c) comparison of${H_y}$ amplitude sensitivity; (d) comparison of${H_y}$ phase sensitivity.图 6 位于R2处的接收器上
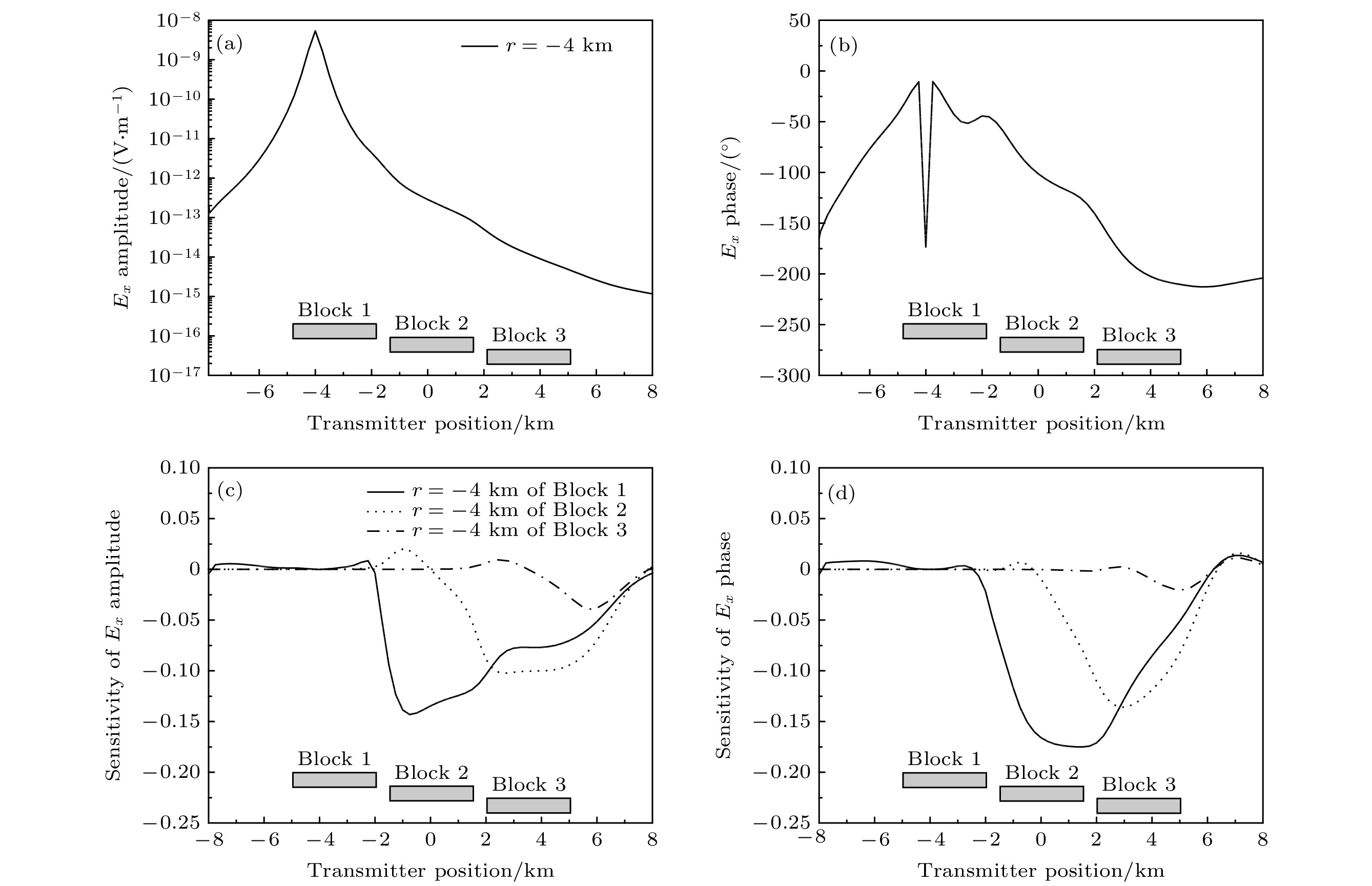
${E_x}$ 的MVO和PVO曲线以及振幅和相位相对于3个块状体电导率灵敏度 (a)${E_x}$ 振幅; (b)${E_x}$ 相位; (c)${E_x}$ 振幅分别对Block 1, Block 2, Block 3的灵敏度; (d)${E_x}$ 相位分别对Block 1, Block 2, Block 3的灵敏度响应Fig. 6. Magnitudes (MVO) and phases (PVO) versus offset of
${E_x}$ at receiver R2 and Fréchet sensitivity about three different Blocks: (a) MVO of${E_x}$ ; (b) PVO of${E_x}$ ; (c) sensitivity of${E_x}$ amplitude about Block 1, Block 2, Block 3; (d) sensitivity of${E_x}$ phase about Block 1, Block 2, Block 3.图 7 位于R2处接收器上磁场
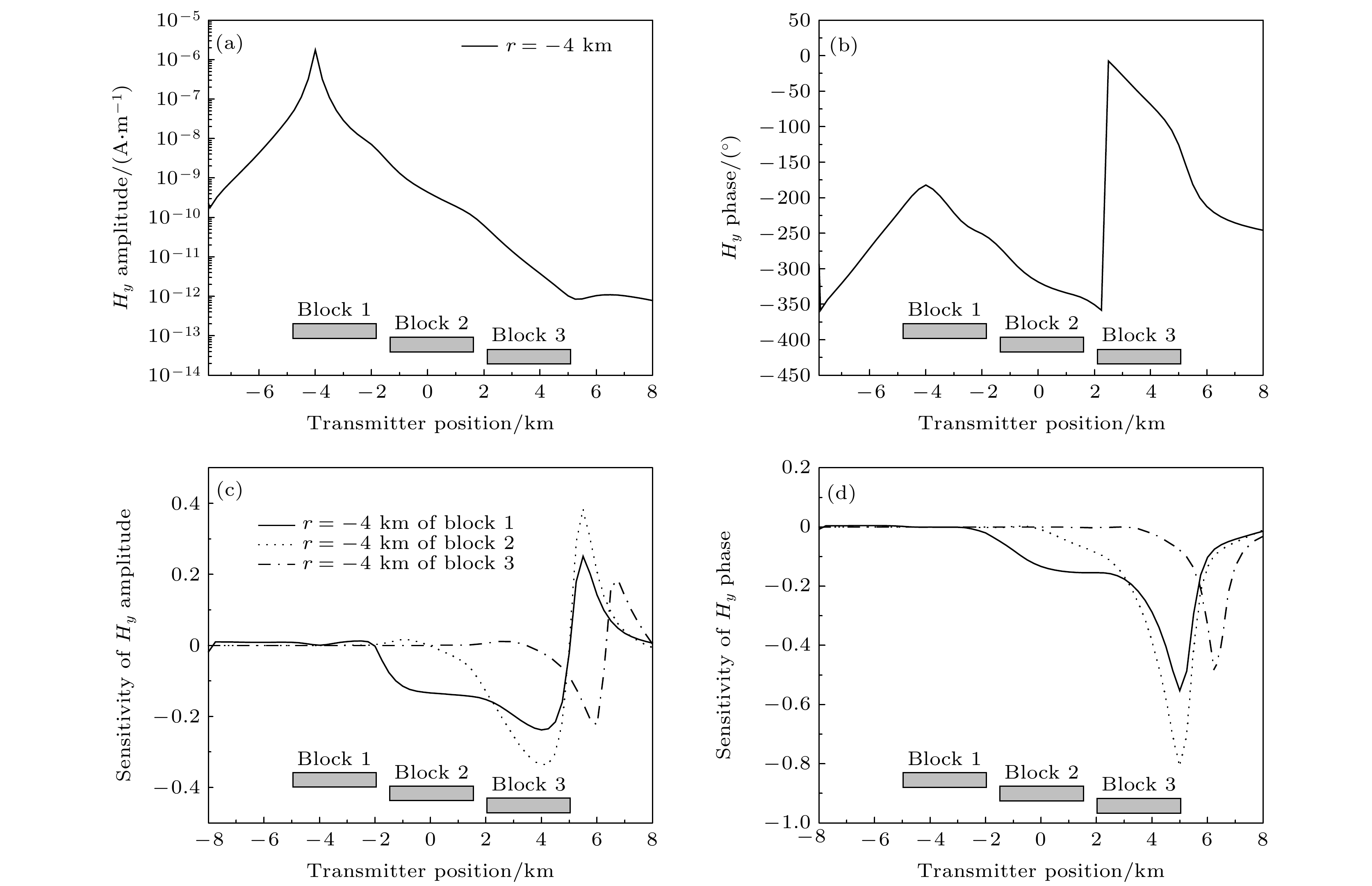
${H_y}$ 分量的MVO和PVO曲线以及振幅和相位相对于3个块状体电导率灵敏度 (a)${H_y}$ 的MVO曲线; (b)${H_y}$ 的PVO曲线; (c)${H_y}$ 振幅对Block 1, Block 2, Block 3的灵敏度; (d)${H_y}$ 相位对Block 1, Block 2, Block 3的灵敏度Fig. 7. The magnitudes (MVO) and phases (PVO) versus offset of
${H_y}$ at receiver R2 and Fréchet sensitivity about three different Blocks: (a) MVO of${H_y}$ ; (b) PVO of${H_y}$ ; (c) sensitivity of${H_y}$ amplitude about Block 1, Block 2, Block 3; (d) sensitivity of${H_y}$ phase about Block 1, Block 2, Block 3图 9 3条不同测线时
${E_x}$ 振幅和相位以及相对于块状异常体的灵敏度对比 (a)振幅; (b)相位; (c)不同测线上振幅灵敏度; (d)不同测线上相位灵敏度Fig. 9. Comparison of magnitudes (MVO), phases (PVO) and Fréchet sensitivity versus offset of
${E_x}$ obtained by three different survey lines: (a) MVO of${E_x}$ ; (b) PVO of${E_x}$ ; (c) comparison of${E_x}$ amplitude sensitivity; (d) comparison of${E_x}$ phase sensitivity.图 10 发射和接收天线固定在不同截面情况下, 主测线和两条旁测线在垂直截面上
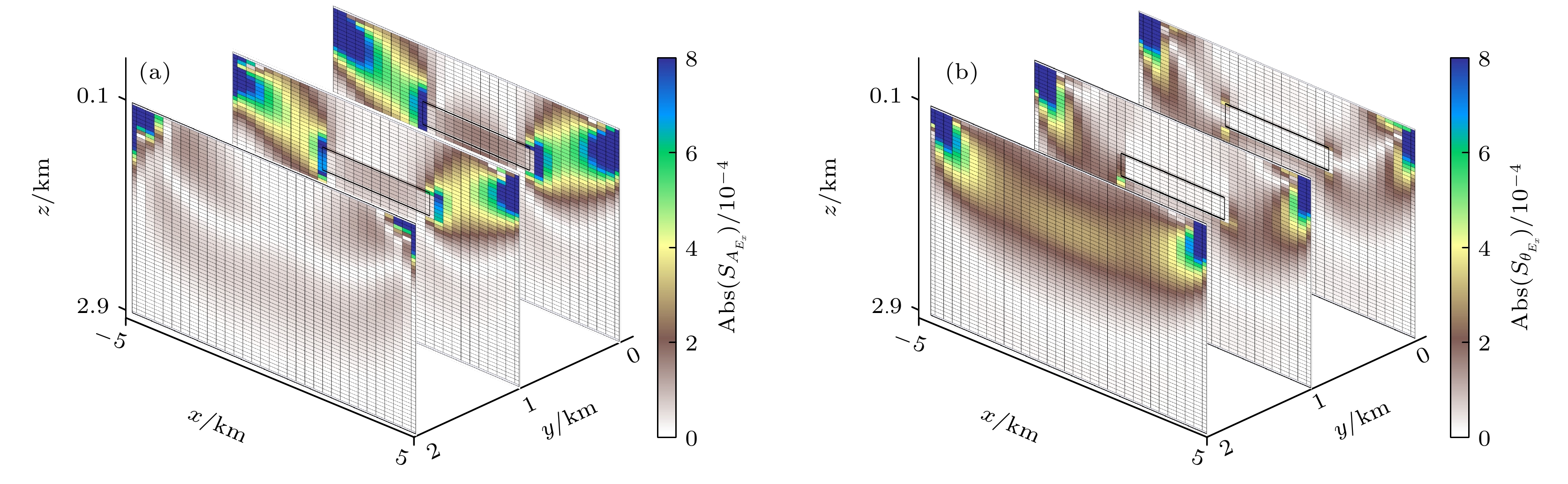
${E_x}$ 振幅和相位的像素灵敏度空间分布(${{{r}}_{\rm{S}}} = (4000,\; 0,\; - 50)$ m和${{{r}}_{\rm{R}}} = (- 4000,\; 0,\; - 50)$ m) (a)${E_x}$ 振幅灵敏度; (b)${E_x}$ 相位灵敏度Fig. 10. The xz cross-sections along inline and two sidelines of
${E_x}$ pixel sensitivity distribution for a given source-receiver combination (${{{r}}_{\rm{S}}} = (4000, \;0, \; - 50)$ m and${{{r}}_{\rm{R}}} = (- 4000,\; 0,\; - 50)$ m): (a) Sensitivity of$ {E}_{x}$ amplitude; (b) sensitivity of${E_x}$ phase.图 11 发射和接收天线固定在不同截面情况下, 3个不同深度的水平截面上
${E_x}$ 振幅和相位的像素灵敏度空间分布(${{{r}}_{\rm{S}}} = $ $ (4000,\; 0,\; - 50)$ m和${{{r}}_{\rm{R}}} = (- 4000,\; 0, \;- 50)$ m) (a)${E_x}$ 振幅灵敏度; (b)${E_x}$ 相位灵敏度Fig. 11. The xy cross-sections at different depth of
${E_x}$ pixel sensitivity distribution for a given source-receiver combination (${{{r}}_{\rm{S}}} = (4000,\; 0,\; - 50)$ m and${{{r}}_{\rm{R}}} = (- 4000,\; 0,\; - 50)$ m): (a) Sensitivity of${E_x}$ amplitude; (b) sensitivity of${E_x}$ phase.表 1 两种算法的计算耗时
Table 1. Computational time cost of EDM and FDM.
Method Number of transmitters Number of receivers Time t/
minEDM-block 65 3 49 FDM 65 3 72 EDM-block 65 5 50 FDM 65 5 108 -
[1] Edwards N 2005 Surv. Geophys. 26 675
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Constable S 2010 Geophysics 75 X75
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Börner R U 2010 Surv. Geophys. 31 225
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Commer M, Newman G A 2008 Geophys. J. Int. 172 513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 汪建勋, 汪宏年, 周建美, 杨守文, 刘晓军, 殷长春 2013 62 224101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J X, Wang H N, Zhou J M, Yang S W, Liu X J, Yin C C 2013 Acta Phy. Sin. 62 224101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 陈桂波, 毕娟, 张烨, 李宗文 2013 62 094102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen G B, Bi J, Zhang Y, Li Z W 2013 Acta Phy. Sin. 62 094102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 姚东华, 汪宏年, 杨守文, 杨海亮 2010 地球 53 3026
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yao D H, Wang H N, Yang S W, Yang H L 2010 Chin. J. Geophys. 53 3026
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 康庄庄, 汪宏年, 王浩森, 杨守文, 殷长春 2020 地球 63 4277
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Kang Z Z, Wang H N, Wang H S, Yang S W, Yin C C 2020 Chin. J. Geophys. 63 4277
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 殷长春, 惠哲剑, 张博, 刘云鹤, 任秀艳 2019 地球 62 1942
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yin C C, Hui Z J, Zhang B, Liu Y H, Ren X Y 2019 Chin. J. Geophys. 62 1942
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Schwarzbach C, Börner R U, Spitzer K 2011 Geophys. J. Int. 187 63
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Haber E, Ascher U M, Aruliah D A, Oldenburg D W 2000 J. Comput. Phys. 163 150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 周建美, 张烨, 汪宏年, 杨守文, 殷长春 2014 63 159101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou J M, Zhang Y, Wang H N, Yang S W, Yin C C 2014 Acta Phy. Sin. 63 159101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 王浩森, 杨守文, 白彦, 陈涛, 汪宏年 2016 65 079101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H S, Yang S W, Bai Y, Chen T, Wang H N 2016 Acta Phy. Sin. 65 079101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang H S, Wang H N, Yang S W, Yin C C 2020 Appl. Geophys. 17 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 陈桂波, 汪宏年, 姚敬金, 韩子夜 2009 58 3848
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen G B, Wang H N, Yao J J, Han Z Y 2009 Acta Phy. Sin. 58 3848
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 林蔺, 焦利光, 陈博, 康庄庄, 马玉刚, 汪宏年 2017 66 139102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lin L, Jiao L G, Chen B, Kang Z Z, Ma Y G, Wang H N 2017 Acta Phy. Sin. 66 139102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Constable S C, Parker R L, Constable C G 1987 Geophysics 52 289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhou J M, Wang J X, Shang Q L, Wang H N, Yin C C 2014 J. Geophys. Eng. 11 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 周建美, 汪宏年, 姚敬金, 杨守文, 马寅芝 2012 61 089101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou J M, Wang H N, Yao J J, Yang S W, Ma Y Z 2012 Acta Phy. Sin. 61 089101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Key K 2009 Geophysics 74 F9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Yang S W, Wang J X, Zhou J M, Zhu T Z, Wang H N 2014 IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 52 6911
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Gribenko A, Zhdanov M 2007 Geophysics 72 WA73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Liu Y H, Yin C C, Qiu C K, Hui Z J, Zhang B, Ren X Y, Weng A H 2019 Geophys. J. Int. 217 301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Hunziker J, Thorbecke J, Brackenhoff J, Slob E 2016 Geophysics 81 F49
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Grayver A V, Streich R, Ritter O 2013 Geophys. J. Int. 193 1432
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Blatter D, Key K, Ray A, Gustafson C, Evans R 2019 Geophys. J. Int. 218 1822
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Ayani M, MacGregor L, Mallick S 2019 Geophys. J. Int. 220 1066
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Abubakar A, Habashy T M, Li M, Liu J 2009 Inverse Prob. 25 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wang H N 2011 IEEE Trans.Geosci. Remote Sen. 49 4483
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Wang H N, Tao H G, Yao J J, Chen G B 2008 IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 46 1525
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Dorn O, Bertete-Aguirre H, Berryman J G, Papanicolaou G C 2002 Inverse Prob. 18 285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Newman G A, Hoversten G M 2000 Inverse Prob. 16 1357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Lien M, Mannseth T 2008 Geophysics 73 F151
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] McGillivray P R, Oldenburg D W, Ellis R G, Habashy T M 1994 Geophys. J. Int. 116 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Chen B, Wang H N, Yang S W 2019 Photonics & Electromagnetics Research Symposium-Fall (PIERS - Fall) Xiamen, China, December 17–20, 2019 p889
[36] Schenk O, Gärtner K 2004 Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 20 475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 6034
- PDF下载量: 83
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: