-
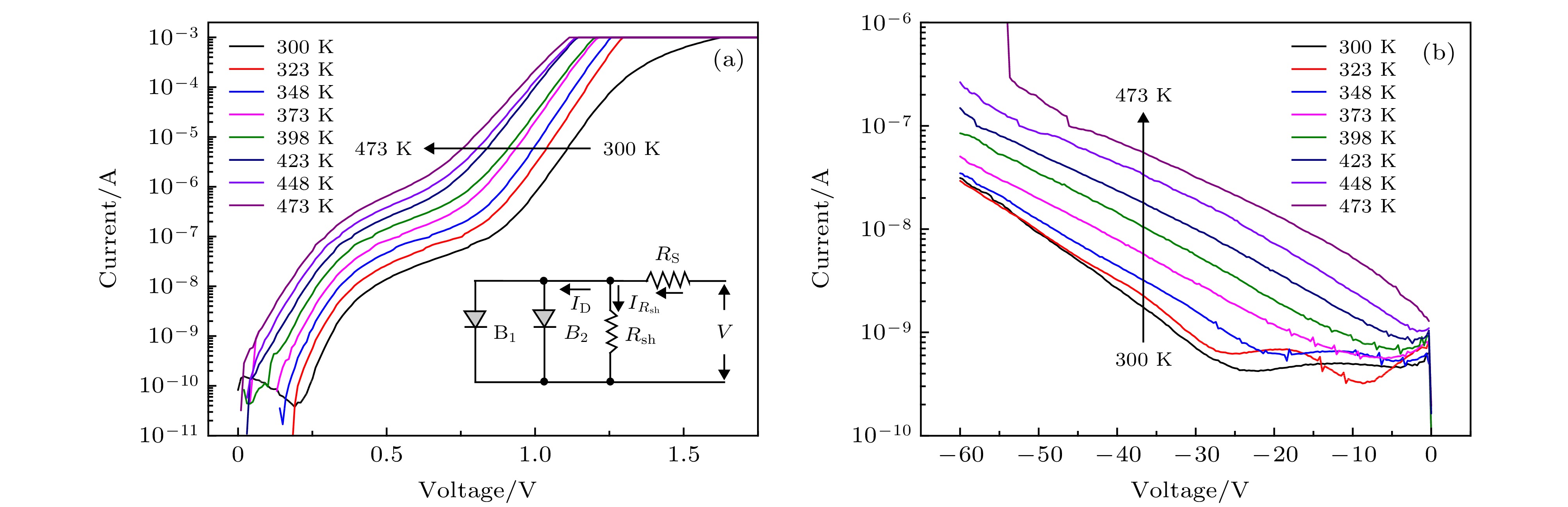
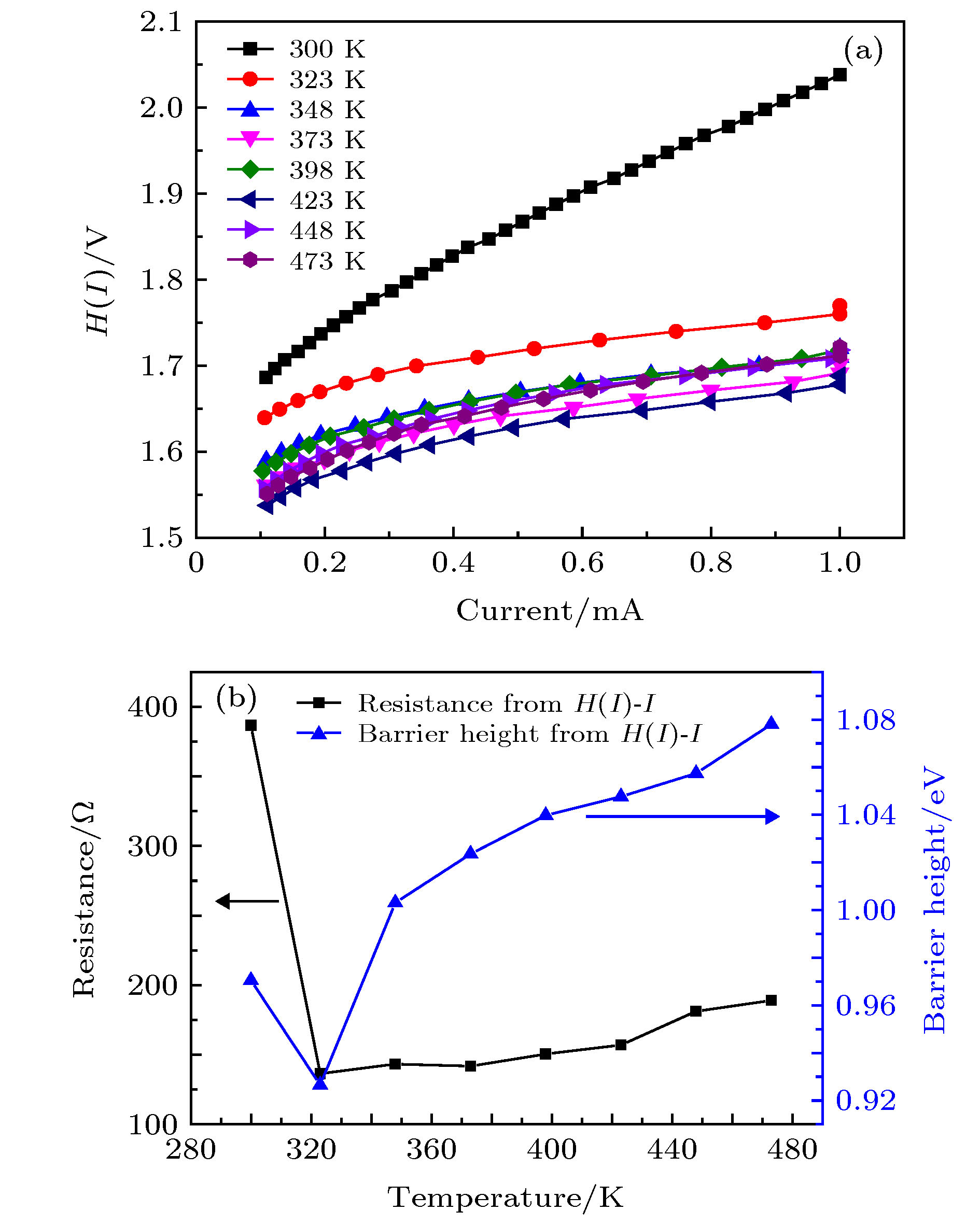
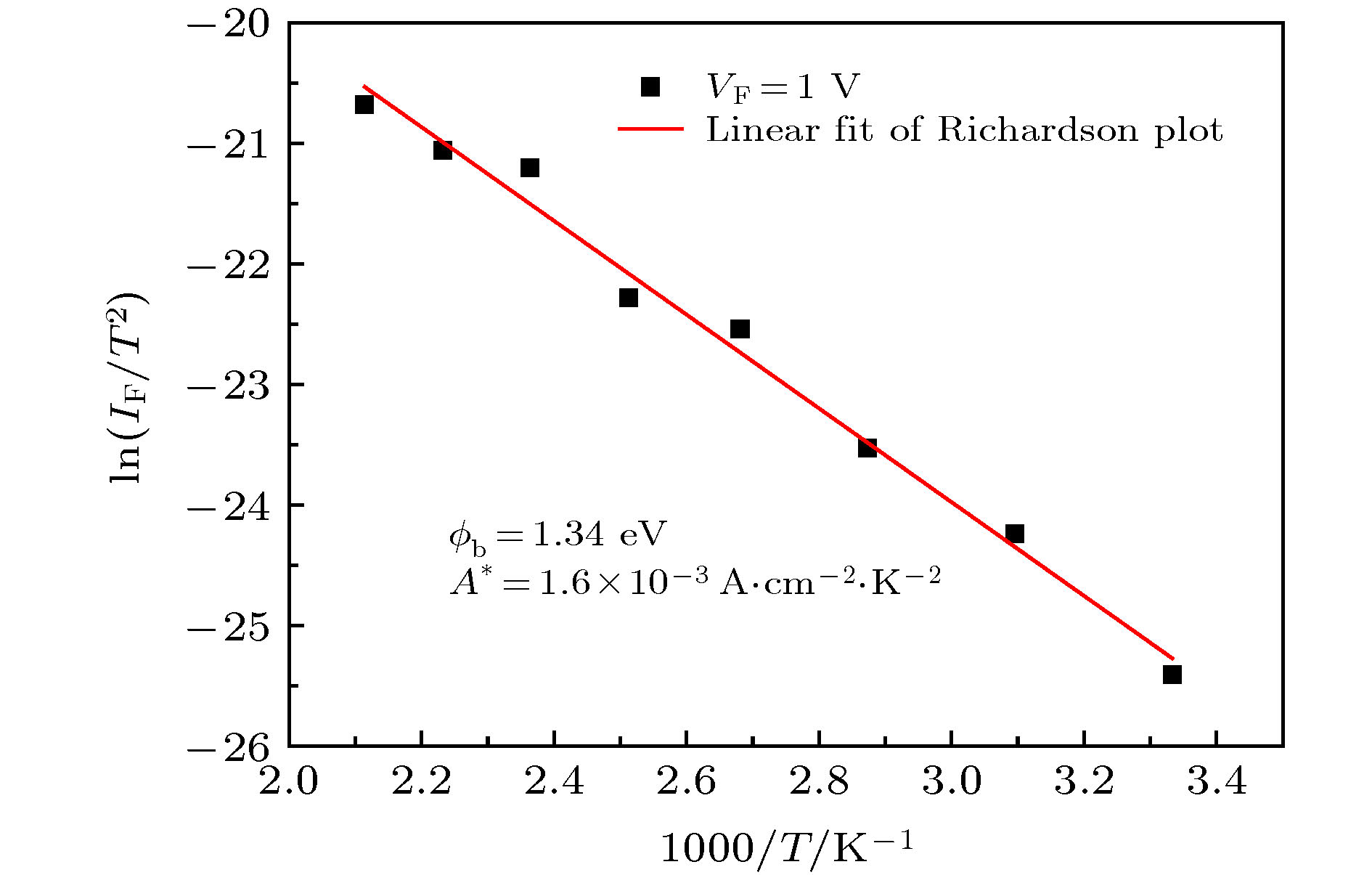
本文制备了基于机械剥离β-Ga2O3的Ni/Au垂直结构肖特基器件, 对该器件进行了温度特性I-V曲线测试. 器件表现出了良好的二极管特性, 随着温度从300 K升高至473 K, 势垒高度从1.08 eV上升至1.35 eV, 理想因子从1.32降低至1.19, 二者表现出了较强的温度依赖特性, 这表明器件的肖特基势垒存在势垒高度不均匀的问题. 串联电阻随温度升高而降低, 这主要是热激发载流子浓度升高导致的. 本文利用势垒高度的高斯分布对器件的温度特性进行了修正, 修正后的势垒高度为1.54 eV, 理查孙常数为26.35 A·cm–2·K–2, 更接近理论值, 这表明利用高斯分布势垒高度的热电子发射模型能够很好地解释Au/Ni/β-Ga2O3肖特基二极管的I-V温度特性问题, 这种方法更适合用来测量β-Ga2O3肖特基二极管的电学参数.In this paper, a Ni/Au vertical structure Schottky diode based on mechanically exfoliated β-Ga2O3 is fabricated. The temperature dependent characteristics of I-V curves are measured. The device shows a good rectifying behavior. As the temperature increases from 300 K to 473 K, the barrier height increases from 1.08 eV to 1.35 eV, and the ideal factor decreases from 1.32 to 1.19. Both of them show strong temperature dependence, which indicates that the Schottky barrier of the device is inhomogeneous. The device has a double exponential forward I-V characteristic curve, which may be related to crystal defects, surface states, surface energy band bending and the effect of mechanical exfoliation from the crystal surface. Through Cheung's method and Norde's method, the series resistances and barrier heights of the device at different temperatures are extracted. It is found that the parameters extracted by the Norde's method are in good agreement with the values obtained from the forward I-V curve. The series resistance decreases with temperature increasing, which is mainly caused by the increase of the concentration of thermally excited carriers. In this paper, the temperature characteristics of the device are modified by the Gauss distribution of the barrier height. The corrected barrier height is 1.54 eV and Richardson's constant is 26.35 A·cm–2·K–2, which is closer to the theoretical value. It shows that the I-V temperature characteristics of Au/Ni/β-Ga2O3 Schottky diodes can be described by the thermionic emission model of the Gauss distribution barrier height accurately. There are a lot of surface states on the surface of Ga2O3 single crystal obtained by Mechanical exfoliation, which has a great influence on the Schottky contact of the device and may lead to the inhomogeneity of Schottky barriers. At the same time, due to mechanical exploiation, the surface of gallium oxide single crystal material is not completely continuous, and the single crystal surface has layered or island structure. This will also cause the inhomogeneous Schottky barrier height. Considering the influence of inhomogeneous barrier on Schottky diode, the method of measuring the temperature characteristics is more suitable to extracting the electrical parameters of β-Ga2O3 Schottky diodes than the method of fitting I-V forward curve by TE model.
-
Keywords:
- Gallium oxide /
- mechanically exfoliated /
- Schottky diode /
- temperature dependent characteristic
[1] 郭道友, 李培刚, 陈政委, 吴真平, 唐为华 2019 68 078501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo D Y, Li P G, Chen Z W, Wu Z P, Tang W H 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 078501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Montes J, Yang C, Fu H, Yang T H, Fu K, Chen H, Zhou J, Huang X, Zhao Y 2019 Appl. Phys. Lett. 114 162103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Barman S K, Huda M N 2019 Phys. Status Solidi-R. 13 1800554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Qian L X, Wang Y, Wu Z H, Sheng T, Liu X Z 2017 Vacuum 140 106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wang X, Liu Z, Zhi Y, Li S, Wu Z, Li P, Tang W 2019 Vacuum 166 79
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Manandhar S, Battu A K, Devaraj A, Shutthanandan V, Thevuthasan S, Ramana C V 2020 Sci. Rep. 10 178
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yang J, Ren F, Tadjer M, Pearton S, Kuramata A 2018 ECS J. Solid State Sc. 7 Q92
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Galazka Z, Irmscher K, Schewski R, Hanke I M, Pietsch M, Ganschow S, Klimm D, Dittmar A, Fiedler A, Schroeder T, Bickermann M 2020 J. Cryst. Growth 529 Unsp 125297
[9] Tang H L, He N T, Zhang H, Liu B, Zhu Z C, Xu M X, Chen L, Liu J L, Ouyang X P, Xu J 2020 Crystengcomm 22 924
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Matsuzaki K, Hiramatsu H, Nomura K, Yanagi H, Kamiya T, Hirano M, Hosono H 2006 Thin Solid Films 496 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wang D, He L N, Le Y, Feng X J, Luan C N, Xiao H D, Ma J 2020 Ceram. Int. 46 4568
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Matsuzaki K, Yanagi H, Kamiya T, Hiramatsu H, Nomura K, Hirano M, Hosono H 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett. 88 92106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Orita M, Ohta H, Hirano M, Hosono H 2000 Appl. Phys. Lett. 77 4166
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Konishi K, Goto K, Murakami H, Kumagai Y, Higashiwaki M 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 110 103506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Pearton S J, Ren F, Tadjer M, Kim J 2018 J. Appl. Phys. 124 220901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Yao Y, Gangireddy R, Kim J, Das K K, Porter L M 2017 J. Vac. Sci. Technol., B 35 03D113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Cheung S K, Cheung N W 1986 Appl. Phys. Lett. 49 85
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Norde H 1979 J. Appl. Phys. 50 5052
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] He Q, Mu W, Dong H, Long S, Jia Z, Lv H, Liu Q, Tang M, Tao X, Liu M 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 110 093503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Ahn S, Ren F, Yuan L, Pearton S J, Kuramata A 2017 ECS J. Solid State Sc. 6 P68
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Jian G, He Q, Mu W, Fu B, Dong H, Qin Y, Zhang Y, Xue H, Long S, Jia Z, Lv H, Liu Q, Tao X, Liu M 2018 AIP Adv. 8 015316
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Fares C, Ren F, Pearton S J 2018 ECS J. Solid State Sc. 8 Q3007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Reddy P R S, Janardhanam V, Shim K H, Reddy V R, Lee S N, Park S J, Choi C J 2020 Vacuum 171 109012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 施敏, 伍国珏(耿莉, 张瑞智译) 2008 半导体器件物理(第3版) (西安: 西安交通大学出版社) 第118−119页
Sze S M, Kwok K N (translated by Geng L, Zhang R) 2008 Physics of Semiconductor Devices (3rd Ed.) (Xi'an: Xi'an Jiaotong University Press) pp118−119 (in Chinese)
[25] Shi J J, Xia X C, Liang H W, Abbas Q, Liu J, Zhang H Q, Liu Y 2019 J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. 30 3860
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Ohdomari I, Tu K N 1980 J. Appl. Phys. 51 3735
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Tung R T 1992 Phys. Rev. B 45 13509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Güçlü Ç Ş, Özdemir A F, Altindal Ş 2016 Appl. Phys. A 122 1032.1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Marıl E, Altındal Ş, Kaya A, Koçyiğit S, Uslu İ 2015 Philos. Mag. 95 1049
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Garrido-Alzar C L 1997 Renewable Energy 10 4
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Janardhanam V, Jyothi I, Sekhar Reddy P R, Cho J, Cho J M, Choi C J, Lee S N, Rajagopal Reddy V 2018 Superlattices Microstruct. 120 508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Jyothi I, Seo M W, Janardhanam V, Shim K H, Lee Y B, Ahn K S, Choi C J 2013 J. Alloys Compd. 556 252
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Mönch W 2007 Appl. Phys. A 87 359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Li A, Feng Q, Zhang J, Hu Z, Feng Z, Zhang K, Zhang C, Zhou H, hao Y 2018 Superlattices Microstruct. 119 212
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Shen Y, Feng Q, Zhang K, Hu Z, Yan G, Cai Y, Mu W, Jia Z, Zhang C, Zhou H, Zhang J, Lian X, Lai Z, Hao Y 2019 Superlattices Microstruct. 133 106179
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] 施敏, 伍国珏 (耿莉, 张瑞智译) 2008 半导体器件物理 (第3版) (西安: 西安交通大学出版社) 第132−133页
Sze S M, Kwok K N (translated by Geng L, Zhang R) 2008 Physics of Semiconductor Devices (3rd Ed.) (Xi'an: Xi'an Jiaotong University Press) pp132−133 (in Chinese)
[37] Sasaki K, Higashiwaki M, Kuramata A, Masui T, Yamakoshi S 2013 IEEE Electron Device Lett. 34 493
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Werner J H, Güttler H H 1991 J. Appl. Phys. 69 1522
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 I-V温度特性曲线提取数据表
Table 1. The parameters from temperature dependent I-V characteristic curves.
温度/K 势垒高度/eV 理想因子n 阈值电压/V Barrier 1 Barrier 2 Barrier 1 Barrier 2 Barrier 1 Barrier 2 300 1.01 1.08 1.32 2.11 1.02 1.77 323 1.00 1.17 1.74 1.81 1.28 1.64 348 1.08 1.23 1.46 1.71 1.16 1.61 373 1.13 1.25 1.36 1.69 1.11 1.58 398 1.17 1.29 1.37 1.67 1.14 1.59 423 1.22 1.30 1.28 1.65 1.10 1.56 448 1.27 1.32 1.24 1.71 1.09 1.59 473 1.31 1.35 1.19 1.69 1.06 1.58 表 2 H(I)-I与F(V)-V曲线提取数据表
Table 2. The parameters from H(I)-I curves and F(V)-V curves.
温度/K 势垒高度/eV 串联电阻/Ω H(I)-I F(V)-V H(I)-I F(V)-V 300 0.97 1.07 386.62 12299.25 323 0.93 1.10 136.38 6184.64 348 1.00 1.15 143.32 3086.28 373 1.02 1.19 141.79 1603.53 398 1.04 1.23 150.50 838.20 423 1.05 1.27 157.03 379.21 448 1.06 1.29 181.14 381.55 473 1.08 1.34 189.04 157.33 -
[1] 郭道友, 李培刚, 陈政委, 吴真平, 唐为华 2019 68 078501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo D Y, Li P G, Chen Z W, Wu Z P, Tang W H 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 078501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Montes J, Yang C, Fu H, Yang T H, Fu K, Chen H, Zhou J, Huang X, Zhao Y 2019 Appl. Phys. Lett. 114 162103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Barman S K, Huda M N 2019 Phys. Status Solidi-R. 13 1800554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Qian L X, Wang Y, Wu Z H, Sheng T, Liu X Z 2017 Vacuum 140 106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wang X, Liu Z, Zhi Y, Li S, Wu Z, Li P, Tang W 2019 Vacuum 166 79
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Manandhar S, Battu A K, Devaraj A, Shutthanandan V, Thevuthasan S, Ramana C V 2020 Sci. Rep. 10 178
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yang J, Ren F, Tadjer M, Pearton S, Kuramata A 2018 ECS J. Solid State Sc. 7 Q92
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Galazka Z, Irmscher K, Schewski R, Hanke I M, Pietsch M, Ganschow S, Klimm D, Dittmar A, Fiedler A, Schroeder T, Bickermann M 2020 J. Cryst. Growth 529 Unsp 125297
[9] Tang H L, He N T, Zhang H, Liu B, Zhu Z C, Xu M X, Chen L, Liu J L, Ouyang X P, Xu J 2020 Crystengcomm 22 924
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Matsuzaki K, Hiramatsu H, Nomura K, Yanagi H, Kamiya T, Hirano M, Hosono H 2006 Thin Solid Films 496 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wang D, He L N, Le Y, Feng X J, Luan C N, Xiao H D, Ma J 2020 Ceram. Int. 46 4568
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Matsuzaki K, Yanagi H, Kamiya T, Hiramatsu H, Nomura K, Hirano M, Hosono H 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett. 88 92106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Orita M, Ohta H, Hirano M, Hosono H 2000 Appl. Phys. Lett. 77 4166
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Konishi K, Goto K, Murakami H, Kumagai Y, Higashiwaki M 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 110 103506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Pearton S J, Ren F, Tadjer M, Kim J 2018 J. Appl. Phys. 124 220901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Yao Y, Gangireddy R, Kim J, Das K K, Porter L M 2017 J. Vac. Sci. Technol., B 35 03D113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Cheung S K, Cheung N W 1986 Appl. Phys. Lett. 49 85
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Norde H 1979 J. Appl. Phys. 50 5052
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] He Q, Mu W, Dong H, Long S, Jia Z, Lv H, Liu Q, Tang M, Tao X, Liu M 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 110 093503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Ahn S, Ren F, Yuan L, Pearton S J, Kuramata A 2017 ECS J. Solid State Sc. 6 P68
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Jian G, He Q, Mu W, Fu B, Dong H, Qin Y, Zhang Y, Xue H, Long S, Jia Z, Lv H, Liu Q, Tao X, Liu M 2018 AIP Adv. 8 015316
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Fares C, Ren F, Pearton S J 2018 ECS J. Solid State Sc. 8 Q3007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Reddy P R S, Janardhanam V, Shim K H, Reddy V R, Lee S N, Park S J, Choi C J 2020 Vacuum 171 109012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 施敏, 伍国珏(耿莉, 张瑞智译) 2008 半导体器件物理(第3版) (西安: 西安交通大学出版社) 第118−119页
Sze S M, Kwok K N (translated by Geng L, Zhang R) 2008 Physics of Semiconductor Devices (3rd Ed.) (Xi'an: Xi'an Jiaotong University Press) pp118−119 (in Chinese)
[25] Shi J J, Xia X C, Liang H W, Abbas Q, Liu J, Zhang H Q, Liu Y 2019 J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. 30 3860
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Ohdomari I, Tu K N 1980 J. Appl. Phys. 51 3735
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Tung R T 1992 Phys. Rev. B 45 13509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Güçlü Ç Ş, Özdemir A F, Altindal Ş 2016 Appl. Phys. A 122 1032.1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Marıl E, Altındal Ş, Kaya A, Koçyiğit S, Uslu İ 2015 Philos. Mag. 95 1049
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Garrido-Alzar C L 1997 Renewable Energy 10 4
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Janardhanam V, Jyothi I, Sekhar Reddy P R, Cho J, Cho J M, Choi C J, Lee S N, Rajagopal Reddy V 2018 Superlattices Microstruct. 120 508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Jyothi I, Seo M W, Janardhanam V, Shim K H, Lee Y B, Ahn K S, Choi C J 2013 J. Alloys Compd. 556 252
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Mönch W 2007 Appl. Phys. A 87 359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Li A, Feng Q, Zhang J, Hu Z, Feng Z, Zhang K, Zhang C, Zhou H, hao Y 2018 Superlattices Microstruct. 119 212
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Shen Y, Feng Q, Zhang K, Hu Z, Yan G, Cai Y, Mu W, Jia Z, Zhang C, Zhou H, Zhang J, Lian X, Lai Z, Hao Y 2019 Superlattices Microstruct. 133 106179
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] 施敏, 伍国珏 (耿莉, 张瑞智译) 2008 半导体器件物理 (第3版) (西安: 西安交通大学出版社) 第132−133页
Sze S M, Kwok K N (translated by Geng L, Zhang R) 2008 Physics of Semiconductor Devices (3rd Ed.) (Xi'an: Xi'an Jiaotong University Press) pp132−133 (in Chinese)
[37] Sasaki K, Higashiwaki M, Kuramata A, Masui T, Yamakoshi S 2013 IEEE Electron Device Lett. 34 493
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Werner J H, Güttler H H 1991 J. Appl. Phys. 69 1522
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 11692
- PDF下载量: 216
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: