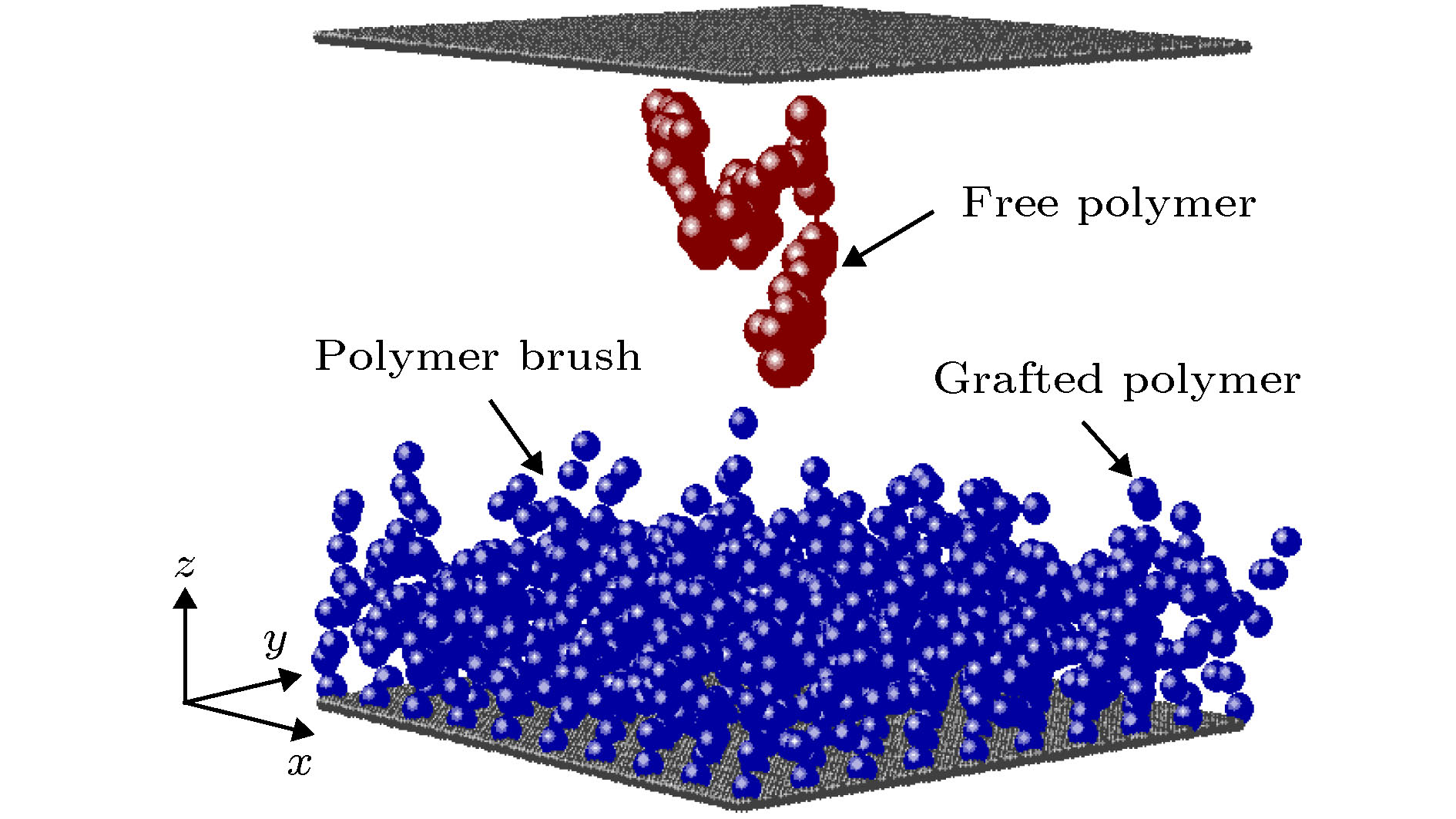
-
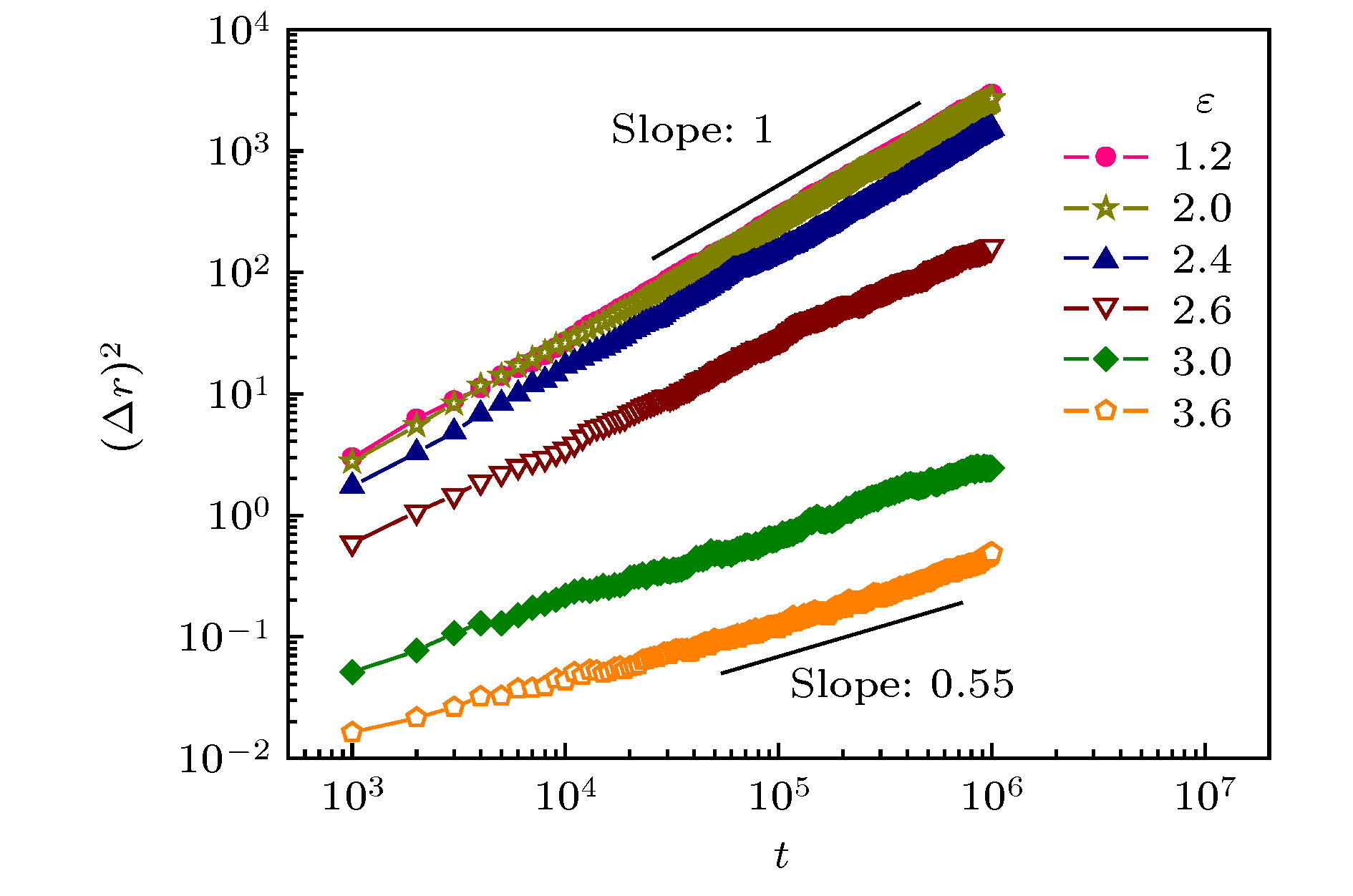
用Monte Carlo方法模拟研究了一条自由高分子链在分子刷表面吸附的静态和动态特性. 结果表明, 随着自由链与分子刷之间吸附作用能(ε)的增大, 自由链出现由脱吸附态到吸附态的相转变, 同时链的扩散由正常模式转为亚扩散模式. 临界吸附能(εC)几乎与自由链长度无关, 但随着分子刷链长度的减小或分子刷链间距的增大而不断增大. 在εC附近, 自由链嵌入分子刷内部, 同时链尺寸达到极小, 而当ε
$\gg $ εC时, 自由链处于强吸附态, 链节主要分布于分子刷表层, 同时整个吸附动态过程可分为自由链吸附和分子刷扩散两个阶段.-
关键词:
- 高分子链 /
- 分子刷 /
- 吸附 /
- Monte Carlo模拟
The adsorption of polymer on surface is a hot topic in physical, chemical and biological communities, which is influenced by many factors, such as the topological structure and the flexibility of the polymer, the attractive interaction between the polymer and the surface, the detailed structure of the surface, etc. The adsorption of polymers on solid surfaces is extensively studied, while the adsorption behaviors of polymers on soft surfaces are still unclear. In this work, the static and dynamical characters of the adsorption of a free polymer chain on polymer brushes are studied by using Monte Carlo simulation. The brush is formed by grafted polymers with length Nb and distance d. Results indicate that, with increasing the adsorption energy (ε) between the free polymer and the brush, the free polymer shows a phase transition from a desorbed state to an adsorbed state. Based on the dependence of the number of the adsorption segment of the free polymer (mad) on the adsorption energy ε, we defined the critical adsorption point (εC) where the phase transition occurs. εC is nearly independent of the length of the free polymer, but it increases with decreasing the length of the grafted polymer or increasing the distance between the grafted polymers. When ε < εC, the free polymer is desorbed and its size is the same as that in free space. When ε ≈ εC, the free polymer is sucked into the brush and meanwhile the size is compressed. While when ε $\gg $ εC, the free polymer is strongly adsorbed on the surface of the brush and forms a quasi two-dimensional conformation, and meanwhile the whole adsorption process contains two stages: the adsorption process of the free polymer and the diffusion process of the brush. Moreover, with the increase of ε, the diffusion of the free polymer shows an obvious transition from the normal model to the sub-diffusion model near εC. The transition of the diffusion model maybe useful for separation of polymers with different attractive polymer-brush interactions. For example, one may construct a brush surface and use it as a polymer separation device. Under weak driving force parallel to the surface, polymers with polymer-brush interaction ε < εC can move quickly, while polymers with ε > εC will move slowly or be trapped on the brush.-
Keywords:
- polymer Chain /
- polymer brush /
- adsorption /
- Monte Carlo simulation
[1] Liu J, Wu Y, Shen J, Gao Y, Zhang L, Cao D 2011 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13 13058
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Macosko C W, Guegan P, Khandpur A 1996 Macromolecules 29 5590
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Bikiaris D, Panayiotou C 1998 J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 70 1503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Díaz M F, Barbosa S E, Capiati N J 2007 Polymer 48 1058
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Neyret S, Ouali L, Candau F, Pefferkorn E 1995 J. Colloid Interface Sci. 176 86
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Meredith J C, Johnston K P 1998 Macromolecules 31 5518
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Teraoka I 1996 Prog. Polym. Sci. 21 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Jun S, Mulder B 2006 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103 12388
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Williams M C 2007 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104 11125
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Sheng J F, Luo K F 2015 RSC Advances 5 2056
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Douah S, Sabeur S A 2018 Macromol. Theory Simul. 27 1700074
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Ziebarth J D, Gardiner A A, Wang Y M, Jeong Y, Ahn J, Jin Y, Chang T 2016 Macromolecules 49 8780
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li B, Sun Z Y, An L J 2015 J. Chem. Phys. 143 024908
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Li H, Qian C J, Luo M B 2016 J. Chem. Phys. 144 164901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Yang X. Yang Q H, Fu Y, Wu F, Huang J H, Luo M B 2019 Polymer 172 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Yang X, Wu F, Hu D D, Zhang S, Luo M B 2019 Chin. Phys. Lett. 36 098202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] de Carvalho S J, Metzler R, Cherstvy A G 2015 Soft Matter 11 4430
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 鲁旸, 瞿立建 2017 高分子学报 3 549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu Y, Zhai L J 2017 Acta Polym. Sin. 3 549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 王禹, 章林溪 2008 高分子学报 3 216
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y, Zhang L X 2008 Acta Polym. Sin. 3 216
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 王禹, 章林溪 2008 57 3281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y, Zhang L X 2008 Acta. Phys. Sin. 57 3281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 李洪, 艾倩雯, 汪鹏君, 高和蓓, 崔毅, 罗孟波 2018 67 168201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li H, Ai Q W, Wang P J, Gao H B, Cui Y, Luo M B 2018 Acta. Phys. Sin. 67 168201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Descas R, Sommer J, Blumen A 2004 J. Chem. Phys. 120 8831
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Luo M B 2008 J. Chem. Phys. 128 044912
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Yang Q H, Luo M B 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 37156
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Cerda J J, Sintes T 2005 Biophys. Chem. 115 277
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Li H, Gong B, Qian C J, Luo M B 2015 Soft Matter 11 3222
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Yang Q H, Yang X, Luo M B 2019 Polymer 180 121677
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Milchev A, Egorov S A, Binder K 2014 Soft Matter 10 5974
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Tessier F, Labrie J, Slater G W 2002 Macromolecules 35 4791
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Cherstvy A G, Metzler R 2014 Phys. Rev. E 90 012134
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Morrin G T, Schwartz D K 2018 Macromolecules 51 1207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
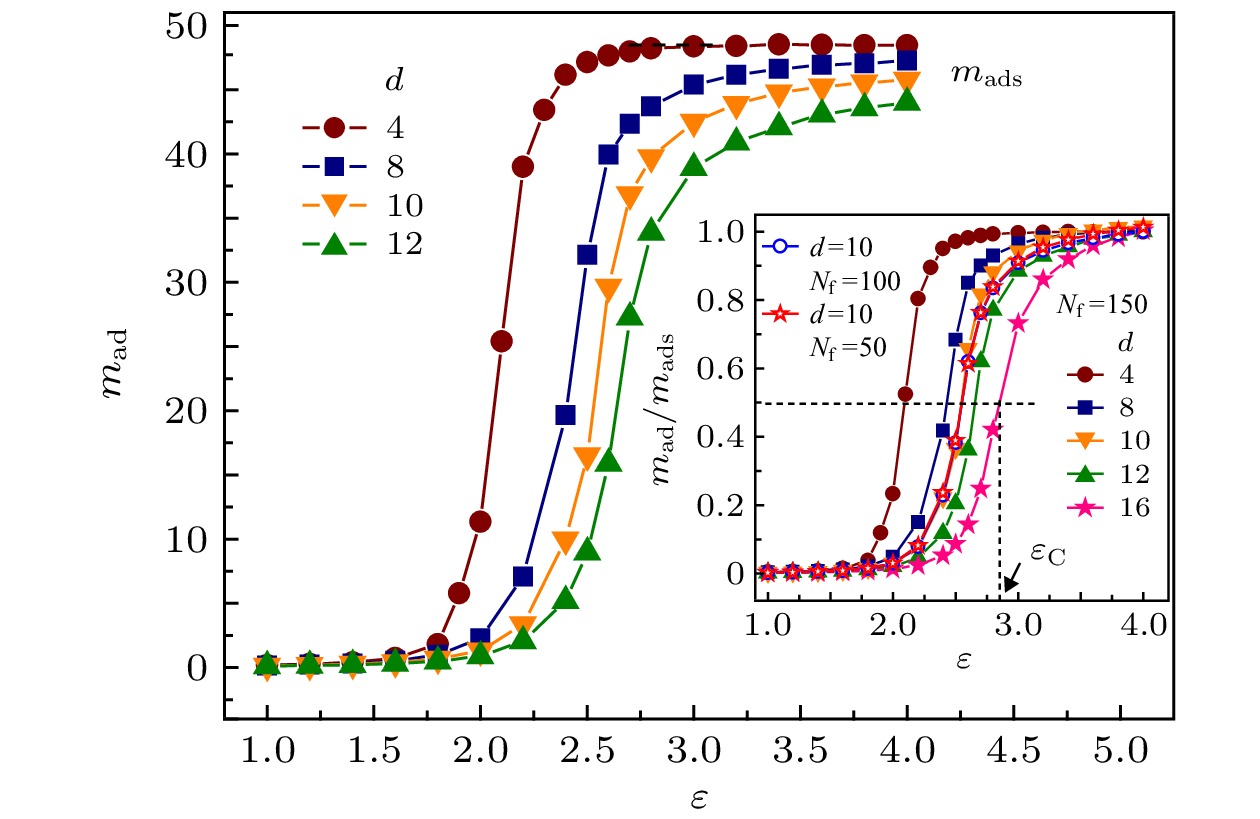
图 2 d取不同值时, 自由链吸附链节数mad随吸引作用能ε的变化, 其中Nf = 50, Nb = 10. 插图: Nf和d不同时, 比值mad/mads随ε的变化
Fig. 2. The number of the adsorbed segment of the free polymer mad as a function of the adsorption energy ε for different d, where Nf = 50 and Nb = 10. The inset presents the dependence of the ratio mad/mads on ε for different Nf and d.
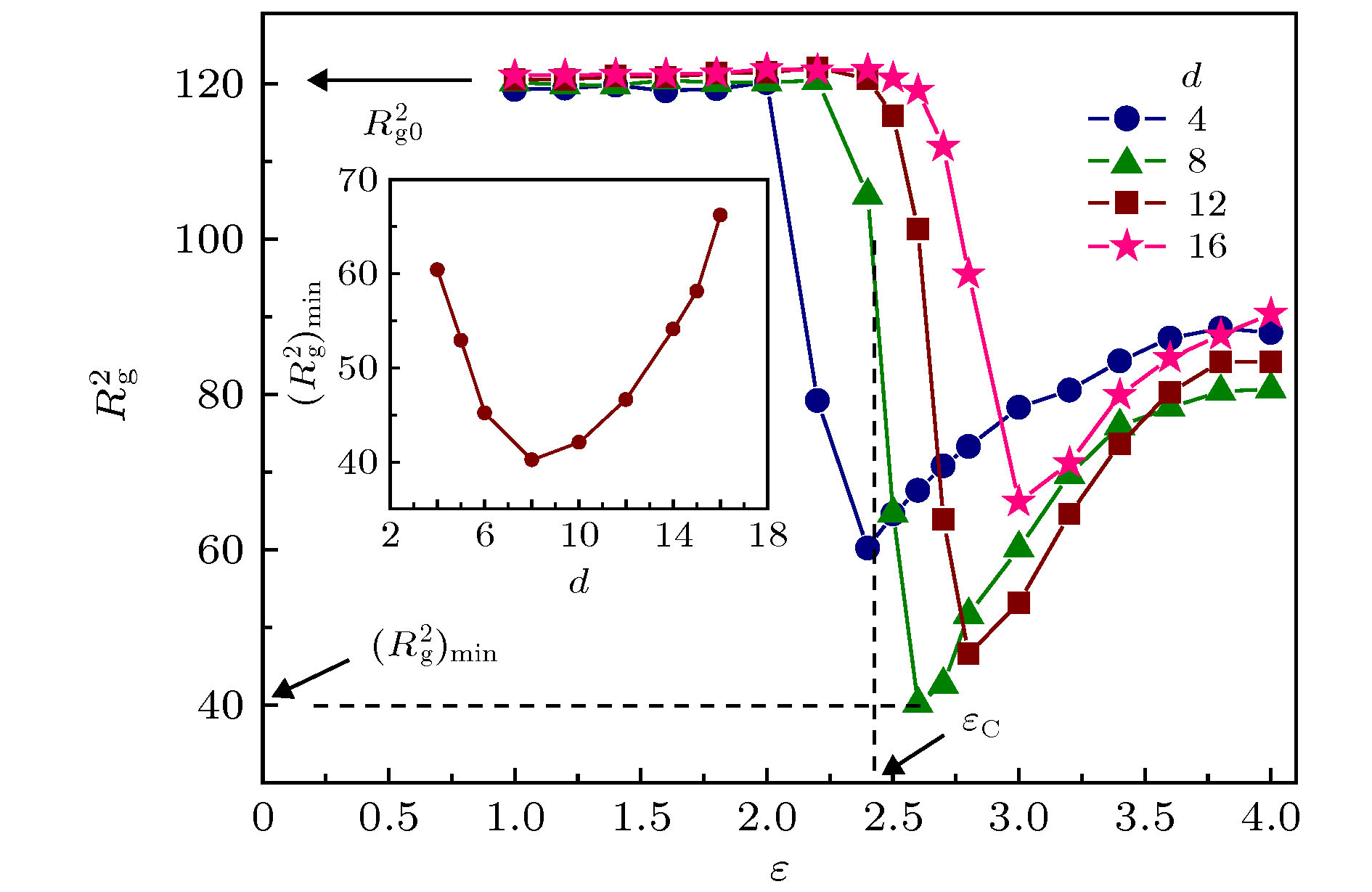
图 3 d取不同值时, 自由链均方回转半径
$R_{\rm{g}}^{\rm{2}}$ 随ε的变化, 其中Nf = 50, Nb = 10. 插图:$R_{\rm{g}}^{\rm{2}}$ 的最小值${(R_{\rm{g}}^{\rm{2}})_{\min }}$ 随d的变化Fig. 3. The mean square radius of the free polymer
$R_{\rm{g}}^{\rm{2}}$ as a function of ε, where Nf = 50 and Nb = 10. The inset presents the dependence of the minimum of$R_{\rm{g}}^2$ ,${(R_{\rm{g}}^{\rm{2}})_{\min }}$ , on d.图 7 自由链吸附链节数mfa和自由链-分子刷链节接触对数mfb随时间t的演化, 其中Nf = 50, Nb = 10, d = 10, ε = 3. 插图: (a)弛豫函数qfa(t)和qfb(t)随时间的演化; (b)自由链吸附时间τfa以及自由链-分子刷链节接触对数弛豫时间τfb随吸引作用能ε的变化, 其中Nf = 50, Nb = 10, d = 10
Fig. 7. The evolution of the number of the adsorbed segment of the free polymer (mfa) and that of the number the segment of polymer brush contacting with the free polymer (mfb), where Nf = 50, Nb = 10, d = 10 and ε = 3. The insets: (a) The evolution of the relaxation function qfa(t) and qfb(t); (b) the dependence of the adsorption time τfa of the free polymer and the relaxation time of the number of segment of brush contacting with the free polymer τfb on the adsorption energy ε, where Nf = 50, Nb = 10 and d = 10.
-
[1] Liu J, Wu Y, Shen J, Gao Y, Zhang L, Cao D 2011 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13 13058
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Macosko C W, Guegan P, Khandpur A 1996 Macromolecules 29 5590
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Bikiaris D, Panayiotou C 1998 J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 70 1503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Díaz M F, Barbosa S E, Capiati N J 2007 Polymer 48 1058
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Neyret S, Ouali L, Candau F, Pefferkorn E 1995 J. Colloid Interface Sci. 176 86
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Meredith J C, Johnston K P 1998 Macromolecules 31 5518
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Teraoka I 1996 Prog. Polym. Sci. 21 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Jun S, Mulder B 2006 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103 12388
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Williams M C 2007 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104 11125
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Sheng J F, Luo K F 2015 RSC Advances 5 2056
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Douah S, Sabeur S A 2018 Macromol. Theory Simul. 27 1700074
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Ziebarth J D, Gardiner A A, Wang Y M, Jeong Y, Ahn J, Jin Y, Chang T 2016 Macromolecules 49 8780
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li B, Sun Z Y, An L J 2015 J. Chem. Phys. 143 024908
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Li H, Qian C J, Luo M B 2016 J. Chem. Phys. 144 164901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Yang X. Yang Q H, Fu Y, Wu F, Huang J H, Luo M B 2019 Polymer 172 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Yang X, Wu F, Hu D D, Zhang S, Luo M B 2019 Chin. Phys. Lett. 36 098202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] de Carvalho S J, Metzler R, Cherstvy A G 2015 Soft Matter 11 4430
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 鲁旸, 瞿立建 2017 高分子学报 3 549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu Y, Zhai L J 2017 Acta Polym. Sin. 3 549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 王禹, 章林溪 2008 高分子学报 3 216
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y, Zhang L X 2008 Acta Polym. Sin. 3 216
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 王禹, 章林溪 2008 57 3281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y, Zhang L X 2008 Acta. Phys. Sin. 57 3281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 李洪, 艾倩雯, 汪鹏君, 高和蓓, 崔毅, 罗孟波 2018 67 168201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li H, Ai Q W, Wang P J, Gao H B, Cui Y, Luo M B 2018 Acta. Phys. Sin. 67 168201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Descas R, Sommer J, Blumen A 2004 J. Chem. Phys. 120 8831
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Luo M B 2008 J. Chem. Phys. 128 044912
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Yang Q H, Luo M B 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 37156
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Cerda J J, Sintes T 2005 Biophys. Chem. 115 277
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Li H, Gong B, Qian C J, Luo M B 2015 Soft Matter 11 3222
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Yang Q H, Yang X, Luo M B 2019 Polymer 180 121677
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Milchev A, Egorov S A, Binder K 2014 Soft Matter 10 5974
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Tessier F, Labrie J, Slater G W 2002 Macromolecules 35 4791
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Cherstvy A G, Metzler R 2014 Phys. Rev. E 90 012134
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Morrin G T, Schwartz D K 2018 Macromolecules 51 1207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 10207
- PDF下载量: 133
- 被引次数: 0















 下载:
下载: