-
机械振子的基态冷却是腔量子光力学中的基本问题之一. 所谓的基态冷却就是让机械振子的稳态声子数小于1. 本文通过光压涨落谱和稳态声子数研究双光腔光力系统(标准单光腔光力系统中引入第二个光腔, 并与第一个光腔直接耦合)的基态冷却. 首先得到系统的有效哈密顿量, 然后给出朗之万方程和速率方程, 最后分别给出空腔和原子腔的光压涨落谱、冷却率和稳态声子数. 通过光压涨落谱、冷却率和稳态声子数表达式, 重点讨论空腔时机械振子的基态冷却, 发现当满足最佳参数条件(机械振子的冷却跃迁速率对应光压涨落谱的最大值, 而加热跃迁速率对应光压涨落谱的最小值)时, 机械振子可以被冷却到稳态声子数足够少. 此外分析: 当辅助腔内注入原子系综时, 若参数选择恰当可能更利于基态冷却.
The ground-state cooling of mechanical resonator is one of the fundamental problems in cavity quantum photomechanics. The so-called ground-state cooling is to make the number of steady-state phonons of the mechanical resonator less than one. In this paper, we first propose an electromagnetically-induced-transparency-like cooling mechanism in a double-cavity optomechanical system to cool a mechanical resonator. In the double-optical cavity optomechanical system, the right additional cavity, which is directly coupled to a standard optomechanical system, contains an ultra-cold two-level atomic ensemble. By selecting the optimal parameters to meet the cooling process of the mechanical resonator corresponding to the maximum value of the optical fluctuation spectrum and the heating process of the mechanical resonator corresponding to the minimum value of the optical fluctuation spectrum, the mechanical resonator can be cooled by monitoring the phonon number. We also exert the effects of the atomic additional cavity on the quantum Langevin equations and optical fluctuation spectrum. We find that the atomic double-cavity system may have a better ground-state cooling than the double-cavity in certain parameters. To date, the researchers have proposed a number of theoretical cooling schemes in order to achieve the ground-state cooling of mechanical resonator. As far as we know, the sideband cooling for just a standard optomechanical system is a most famous scheme and the mechanical resonator is coupled to the optical field via radiation pressure force. By the quantum theory of mechanical resonator’s sideband cooling, the optical fluctuation spectrum determines the transition rate of both cooling and heating process of the mechanical resonator. That’s to say, the optical fluctuation spectrum at a mechanical resonator frequency ωm is corresponding to the cooling transition, whereas the optical fluctuation spectrum at –ωm is corresponding to the heating transition. They respectively correspond to anti-Stokes and Stokes effect in physics. Under resolvable sideband conditions, the optical field’s decay rate (the half-width of the single Lorentzian peak of optical fluctuation spectrum) is less than the frequency of the mechanical resonator. So, the ground-state cooling of the mechanical resonator can be obtained by making the maximum and minimum value of the optical fluctuation spectrum respectively correspond to the cooling anti-Stokes process and heating Stokes process. In this paper, we mainly observe the electromagnetically-induced-transparency-like ground-state cooling in a double-cavity optomechanical system with an ensemble of two-level atoms. By adjusting the maximum and minimum value of the optical fluctuation spectrum at the position of ω = ωm and ω = –ωm, the mechanical resonator could be cooled down approximately to the ground state. Even when there exists an ensemble of two-level atoms in the right additional cavity, the mechanical resonator can be better cooled than just a cavity. These results may be conducive to the ground-state cooling of the mechanical resonator in the future experiment. -
Keywords:
- double-optical cavity /
- ground state cooling /
- Langevin equation /
- rate equation
[1] Kippenberg T J, Vahala K J 2007 Opt. Express 15 17172
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Aspelmeyer M, Meystre P, Schwab K 2012 Phys. Today 65 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Metzger C H, Karrai K 2004 Nature 432 1002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Machnes S, Cerrillo J, Aspelmeyer M, Wieczorek W, Plenio M B, Retzker A 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 153601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] O’Connell A D, Hofheinz M, Ansmann M, Bialczak R C, Lenander M, Lucero E, Neeley M, Sank D, Wang H, Weides M, Wenner J, Martinis J M, Cleland A N 2010 Nature 464 697
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Teufel J D, Donner T, Li D, Harlow J W, Allmanet M S, Cicak K, Sirois A J, Whittaker J D, Lehnert K W, Simmonds R W 2011 Nature 475 359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wilson-Rae I, Zoller P, Imamoglu A 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 92 075507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Liu Y C, Xiao Y F, Luan X, Wong C W 2013 Phys. Rev.Lett. 110 153606
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhu J P, Li G X, Ficek Z 2012 Phys. Rev. A 85 033835
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 陈华俊, 米贤武 2011 60 124206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen H J, Mi X W 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 124206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wilson-Rae I, Nooshi N, Zwerger W, Kippenberg T J 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 99 093901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Marquardt F, Chen J P, Clerk A A, Girvin S M 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 99 093902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Liu Y C, Luan X, Li H K, Gong Q, Wong C W, Xiao Y F 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 112 213602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Jing H, Özdemir S K, Lü X Y, Zhang J, Yang L, Nori F 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 113 053604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Chen H J 2018 J. Appl. Phys. 124 153102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang P, Wang Y D, Sun C P 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 95 097204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Xia K, Evers J 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 227203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] EversJ, Keitel C H 2004 Europhys. Lett. 68 370
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Harris S E 1997 Phys. Today 50 36
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Fleischhauer M, Imamoglu A, Marangos J P 2005 Rev. Mod. Phys. 77 633
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Genes C, Ritsch H, Drewsen M, Dantan A 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 051801(R)
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 谷开慧, 严冬, 张孟龙, 殷景志, 付长宝 2019 68 054201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gu K H, Yan D, Zhang M L, Yin J Z, Fu C B 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 054201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Grudinin I S, Lee H, Painter O, Vahala K J 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 083901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Di K, Xie C, Zhang J 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 106 153602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Gu W J, Li G X 2013 Phys. Rev. A 87 025804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Ojanen T, Børkje K 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 013824
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Giovannetti V, Vitali D 2001 Phys. Rev. A 63 023812
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Guo Y J, Li K, Nie W J, Li Y 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 053841
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Garrido Alzar C L, Martinez M A G, Nussenzeig P 2002 Am. J. Phys. 70 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] AnetsbergerG, Rivière R, Schliesser A, Arcizet O, Kippenberg T J 2008 Nat. Photonics 2 627
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 2 双腔间耦合系数J影响下涨落谱
$S\left( \omega \right)$ 随频率$\omega $ 的变化(左腔和右腔的有效失谐和对应的耗散率分别为${\varDelta _1} = {\omega _{\rm{m}}}, {\kappa _1} = 5{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ ;${\varDelta _2} = - {\omega _{\rm{m}}}, {\kappa _2} = 0.05{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ )Fig. 2. Fluctuation spectrum
$S\left( \omega \right)$ as a function of the frequency$\omega $ with different double-cavity coupling coefficient J. The effective detunings of the left cavity mode and right cavity mode and the corresponding decay rates are respectively are${\varDelta _1} = {\omega _{\rm{m}}}, {\kappa _1} = 5{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ ;${\varDelta _2} = - {\omega _{\rm{m}}}, {\kappa _2} = 0.05{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ .图 3 不同衰减率
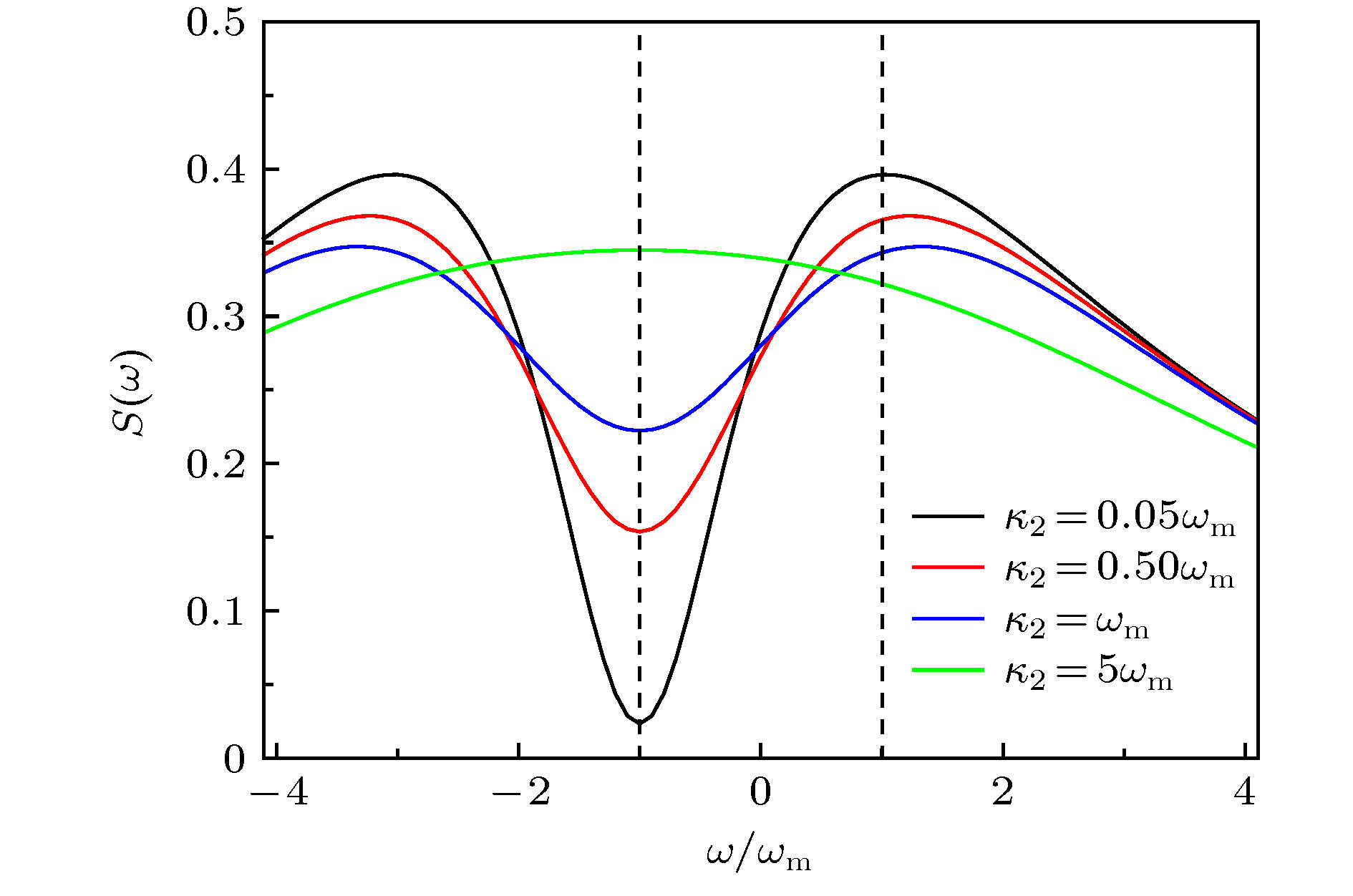
${\kappa _2}$ 影响下的涨落谱(给定的参数分别为${\varDelta _1} = - {\omega _{\rm{m}}}, {\kappa _1} = 5{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ ;${\varDelta _2} = - {\omega _{\rm{m}}}, J = 2{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ )Fig. 3. Optical fluctuation spectrum with different decay rates
${\kappa _2}$ . The given parameters are${\varDelta _1} = - {\omega _{\rm{m}}}, {\kappa _1} = 5{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ ;${\varDelta _2} = - {\omega _{\rm{m}}}, J = 2{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ .图 4 参数影响下空腔和原子腔涨落谱
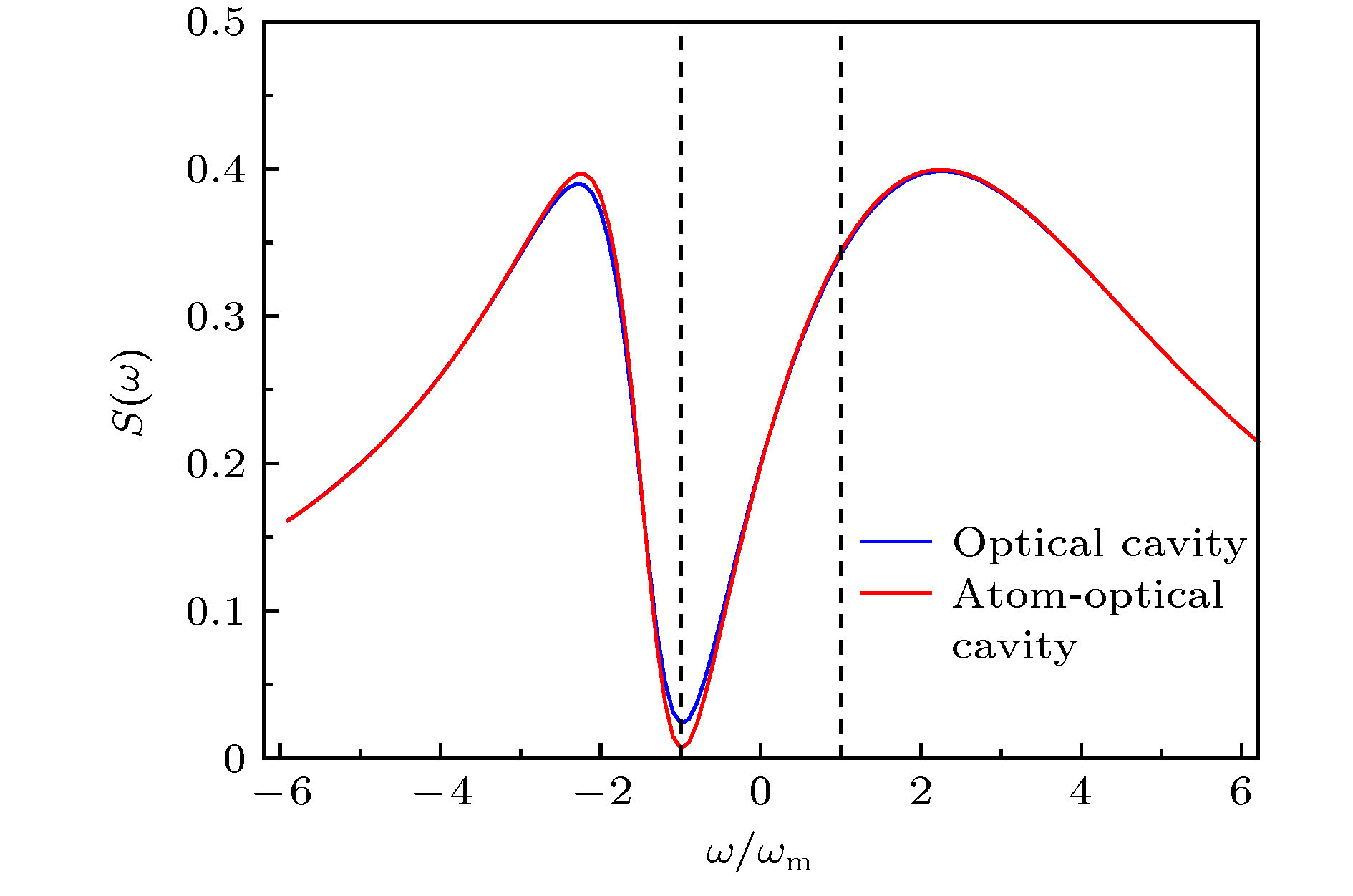
$S\left( \omega \right)$ 随频率$\omega $ 的变化(左腔和右腔的有效失谐和对应的耗散率分别为${\varDelta _1} = {\omega _{\rm{m}}},\; {\kappa _1} = 5{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ ;${\varDelta _2} = - {\omega _{\rm{m}}}, \;{\kappa _2} = 0.05{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ ; 原子的有效失谐和相干衰减率是${\varDelta _{\rm{a}}} = {\omega _{\rm{m}}},\; {\gamma _{\rm{a}}} = 10{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ ; 原子-场耦合系数${g_{\rm{a}}} = 0.62 \times {10^{ - 4}}{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ , 原子数$N = {10^8}$ )Fig. 4. Optical and atom-optical fluctuation spectrum
$S\left( \omega \right)$ as a function of the frequency$\omega $ under the influence of parameters. The effective detunings of the left cavity mode and right cavity mode and the corresponding decay rates are respectively are${\varDelta _1} = {\omega _{\rm{m}}},\; {\kappa _1} = 5{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ ;${\varDelta _2} = - {\omega _{\rm{m}}}, $ ${\kappa _2} = 0.05{\omega _{\rm{m}}} $ . The atomic effective detuning and the coherent decay rates are respectively are${\varDelta _{\rm{a}}} = {\omega _{\rm{m}}}, {\gamma _a} = 10{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ . The atom-field coupling strength is${g_{\rm{a}}} = 0.62 \times {10^{ - 4}}{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ . The atomic number is$N = {10^8}$ .图 5 衰减率
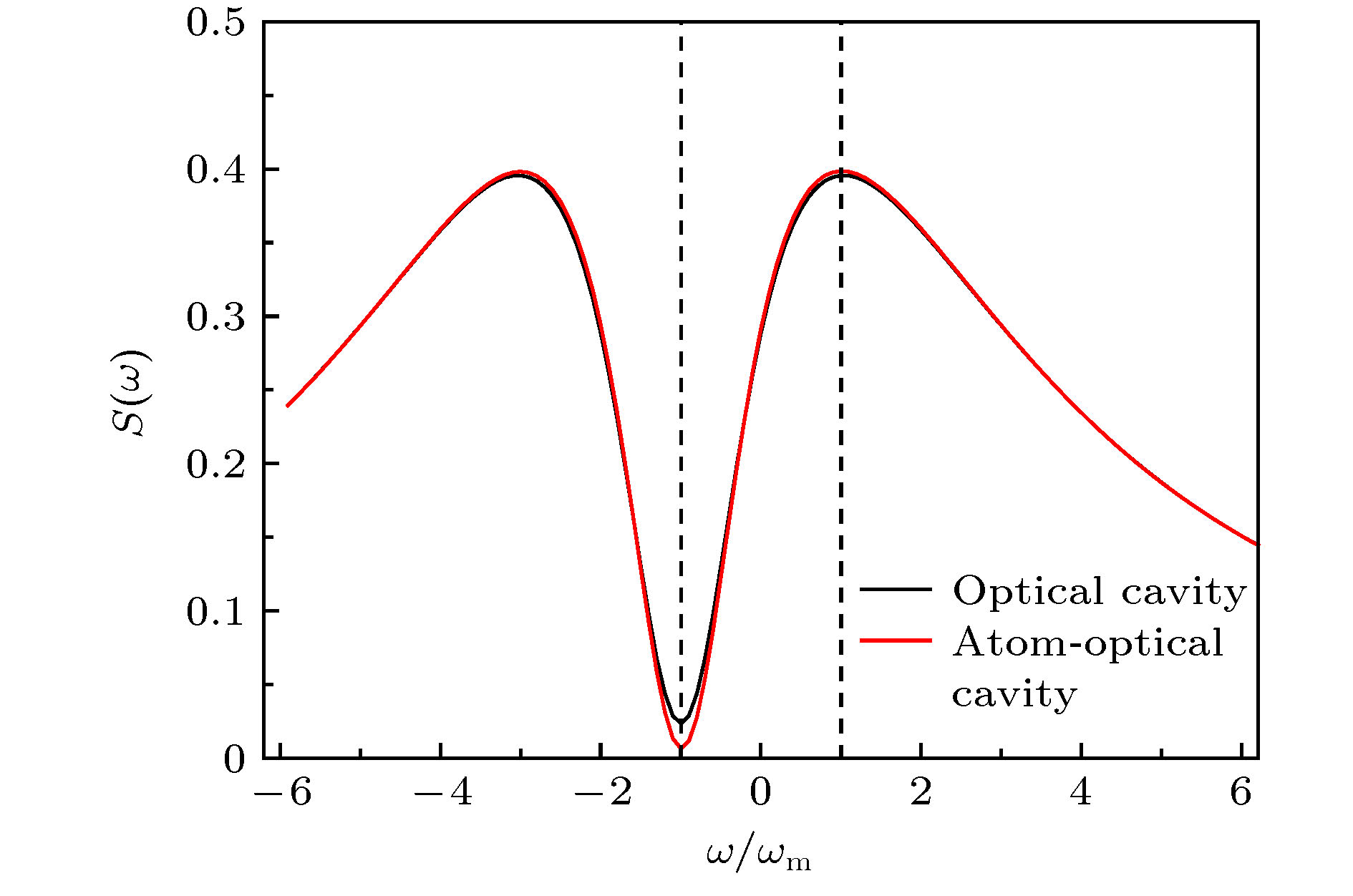
${\kappa _2} = 0.05{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ 影响下空腔和原子腔涨落谱(给定的参数分别为${\varDelta _1} = - {\omega _{\rm{m}}},\; {\kappa _1} = 5{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ ;${\varDelta _2} = - {\omega _{\rm{m}}}, J =$ $ 2{\omega _{\rm{m}}} $ ;${\varDelta _{\rm{a}}} = {\omega _{\rm{m}}}, {\gamma _{\rm{a}}} = 10{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ ;${g_{\rm{a}}} \!=\! 0.62 \!\times\! {10^{ - 4}}{\omega _{\rm{m}}},$ $N \!=\! {10^8}$ )Fig. 5. Fluctuation spectrum and atom-optical fluctuation spectrum with given decay rates
${\kappa _2} = 0.05{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ . The given parameters are${\varDelta _1} = - {\omega _{\rm{m}}}, \;{\kappa _1} = 5{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ ,${\varDelta _2} = - {\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ , J =$ 2{\omega _{\rm{m}}} $ ,${\varDelta _{\rm{a}}} = {\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ ,$ {\gamma _{\rm{a}}} = 10{\omega _{\rm{m}}} $ ;${g_{\rm{a}}} = 0.62 \!\times\! {10^{ - 4}}{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ ,$N \!= \!{10^8}$ 图 6 冷却速率
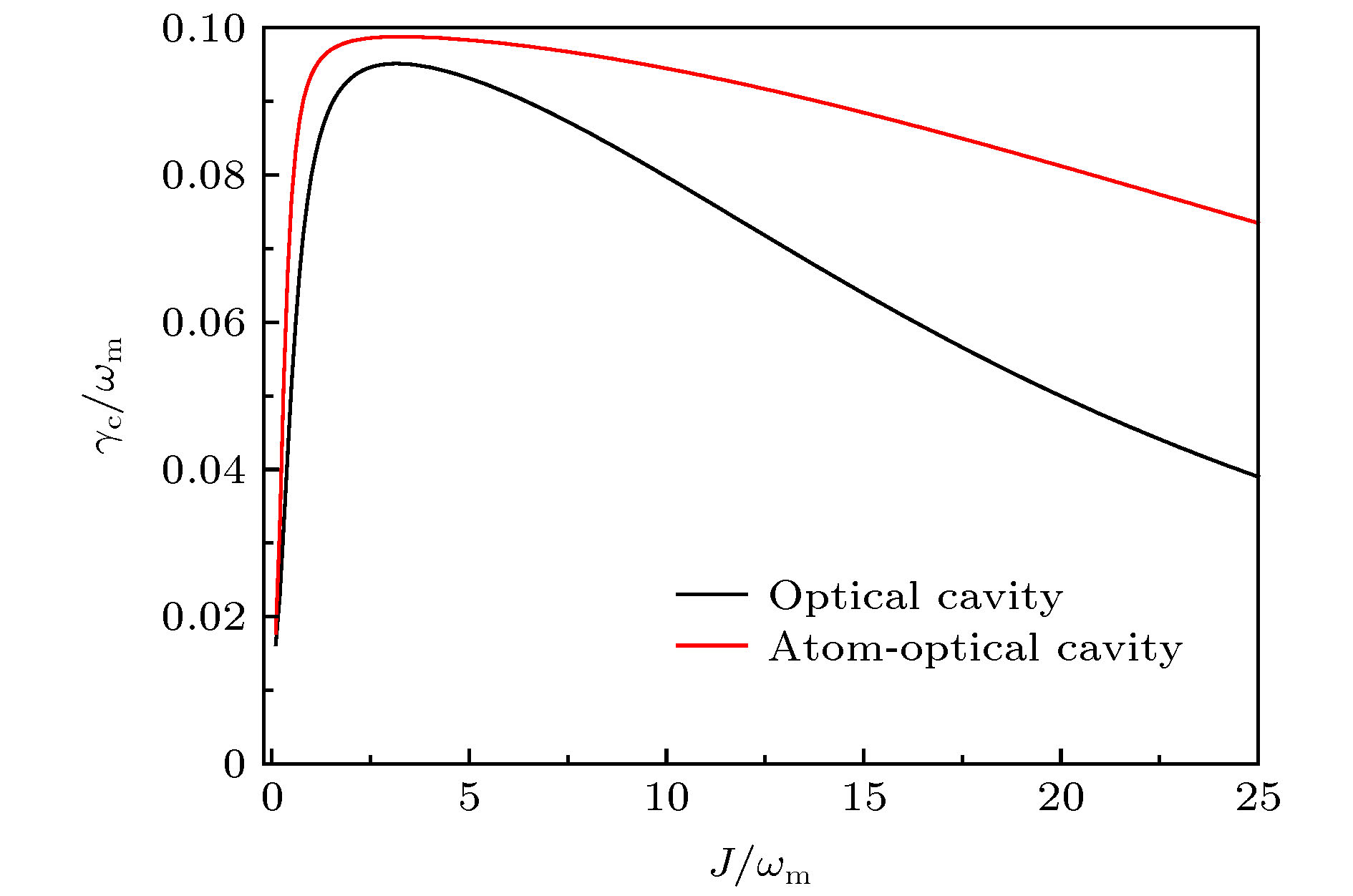
${\gamma _{\rm{c}}}$ 在不同衰减率${\kappa _2}$ 影响下随光腔耦合系数J的函数(给定的参数是$g = 0.5{\omega _{\rm{m}}}, {\varDelta _2} = - {\omega _{\rm{m}}},\; {\kappa _1} = 5{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ , 最优失谐${\varDelta _1}$ 满足(66)式)Fig. 6. Cooling rate
${\gamma _c}$ as a function of optical coupling coefficient J in the case of different decay rates${\kappa _2}$ . The given parameters are$g = 0.5{\omega _{\rm{m}}},\; {\varDelta _2} = - {\omega _{\rm{m}}}, \;{\kappa _1} = 5{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ , and the optimal detuning${\varDelta _1}$ satisfied the Eq. (66).图 7 参数影响下平均声子数
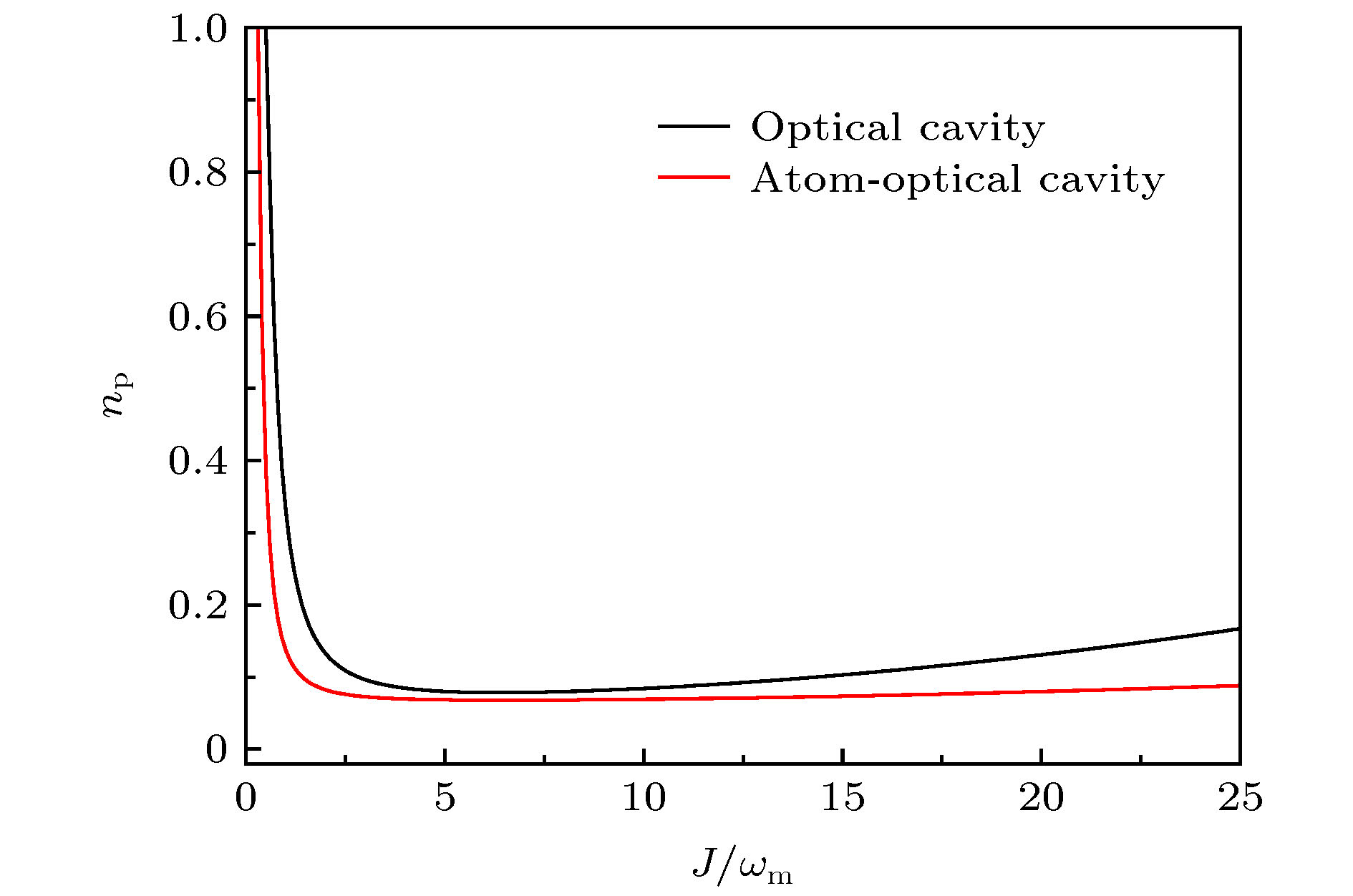
${n_{\rm{p}}}$ 随最佳光腔耦合系数J的变化(给定的参数是${\omega _{\rm{m}}} \!= \!1.55{\text{π}} \times 20\;{\rm{MHz}}$ ,$ {Q_{\rm{m}}} \!=\! {{{\omega _{\rm{m}}}} / {{\gamma _{\rm{m}}}}} =$ $ 6.2 \times {10^4}, {n_m} = 403 $ ,$g = 0.5{\omega _{\rm{m}}} $ ,${\kappa _1} = 5{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ ,${\kappa _2} = 0.05{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ ,${\varDelta _2} = - {\omega _{\rm{m}}} $ , 最优失谐${\varDelta _1}$ 满足(66)式)Fig. 7. Mean phonon number
${n_{\rm p}}$ as a function of optical coupling coefficient J. The given parameters are${\omega _{\rm{m}}} \!=\! 1.55{\text{π}} \times $ $20\;{\rm{MHz}},\;{Q_{\rm{m}}} = {{{\omega _{\rm{m}}}} / {{\gamma _{\rm{m}}}}} = 6.2 \times {10^4} $ ,${n_{\rm{m}}} = 403$ ,$g = 0.5{\omega _{\rm{m}}} $ ,${\kappa _1} \!=\! 5{\omega _{\rm{m}}}, {\kappa _2} \!=\! 0.05{\omega _{\rm{m}}}, {\varDelta _2} \!=\! - {\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ , and the optical detuning${\varDelta _1}$ satisfied the Eq. (66).图 8 平均声子数
${n_{\rm{p}}}$ 随有效初始温度T的变化(给定的参数是${\omega _{\rm{m}}} = 1.55{\text{π}} \times 20\;{\rm{MHz}}$ ,${Q_{\rm{m}}} = {{{\omega _{\rm{m}}}} / {{\gamma _{\rm{m}}}}} = 6.2 \times {10^4} $ ,$J = 10{\omega _{\rm{m}}} $ ,$ g = 0.5{\omega _{\rm{m}}} $ ,${\kappa _1} = 5{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ ,${\kappa _2} = 0.05{\omega _{\rm{m}}} $ ,${\varDelta _2} =$ $ - {\omega _{\rm{m}}} $ , 最优失谐${\varDelta _1}$ 满足(66)式)Fig. 8. Mean phonon number
${n_{\rm{p}}}$ as a function of effective initial temperature T. The given parameters are${\omega _{\rm{m}}} =$ $ 1.55{\text{π}} \times 20\;{\rm{MHz}} $ ,$ {Q_{\rm{m}}} = {{{\omega _{\rm{m}}}} / {{\gamma _{\rm{m}}}}} = 6.2 \times {10^4} $ ,$ J = 10{\omega _{\rm{m}}} $ ,$ g = 0.5{\omega _{\rm{m}}} $ ,${\kappa _1} = 5{\omega _{\rm{m}}}, {\kappa _2} = 0.05{\omega _{\rm{m}}}, {\varDelta _2} = - {\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ and the optical detuning${\varDelta _1}$ satisfied the Eq. (66).图 9 冷却速率
${\gamma _{\rm{c}}}$ 随最佳光腔耦合系数J的变化(给定的参数是${\omega _{\rm{m}}} = 1.55{\text{π}} \times 20\;{\rm{MHz}}$ ,${Q_{\rm{m}}} = {{{\omega _{\rm{m}}}} / {{\gamma _{\rm{m}}}}} = 6.2 \times {10^4}$ ,${n_{\rm{m}}} \!=\! 403$ ,$g \!=\! 0.5{\omega _{\rm{m}}} $ ,${\kappa _1} \!=\! 5{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ ,${\kappa _2} \!=\! 0.05{\omega _{\rm{m}}} $ ,${\varDelta _1} \!=\! {\varDelta _2} \!=\!$ $ - {\omega _{\rm{m}}} $ ,${\varDelta _{\rm{a}}} = {\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ ,$ {\gamma _{\rm{a}}} = 10{\omega _{\rm{m}}} $ ,$ {g_{\rm{a}}} = 0.62 \times {10^{ - 4}}{\omega _{\rm{m}}} $ ,$N = {10^8} $ )Fig. 9. Cooling rate
${\gamma _{\rm{c}}}$ as a function of optical coupling coefficient J. The given parameters are${\omega _{\rm{m}}}\! =\! 1.55{\text{π}} \!\times \!20\;{\rm{MHz}}$ ,$ {Q_{\rm{m}}} = {{{\omega _{\rm{m}}}} / {{\gamma _{\rm{m}}}}} = 6.2\! \times \!{10^4} $ ,${n_{\rm{m}}} = 403$ ,$g \!=\! 0.5{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ ,${\kappa _1} \!=\! 5{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ ,${\kappa _2} = 0.05{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ ,$ {\varDelta _1} = {\varDelta _2} = - {\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ ,${\varDelta _{\rm{a}}} = {\omega _{\rm{m}}} $ ,${\gamma _{\rm{a}}} = 10{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ ,$ {g_{\rm{a}}} = 0.62 \times {10^{ - 4}}{\omega _{\rm{m}}}$ ,$ N = {10^8} $ . -
[1] Kippenberg T J, Vahala K J 2007 Opt. Express 15 17172
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Aspelmeyer M, Meystre P, Schwab K 2012 Phys. Today 65 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Metzger C H, Karrai K 2004 Nature 432 1002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Machnes S, Cerrillo J, Aspelmeyer M, Wieczorek W, Plenio M B, Retzker A 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 153601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] O’Connell A D, Hofheinz M, Ansmann M, Bialczak R C, Lenander M, Lucero E, Neeley M, Sank D, Wang H, Weides M, Wenner J, Martinis J M, Cleland A N 2010 Nature 464 697
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Teufel J D, Donner T, Li D, Harlow J W, Allmanet M S, Cicak K, Sirois A J, Whittaker J D, Lehnert K W, Simmonds R W 2011 Nature 475 359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wilson-Rae I, Zoller P, Imamoglu A 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 92 075507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Liu Y C, Xiao Y F, Luan X, Wong C W 2013 Phys. Rev.Lett. 110 153606
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhu J P, Li G X, Ficek Z 2012 Phys. Rev. A 85 033835
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 陈华俊, 米贤武 2011 60 124206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen H J, Mi X W 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 124206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wilson-Rae I, Nooshi N, Zwerger W, Kippenberg T J 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 99 093901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Marquardt F, Chen J P, Clerk A A, Girvin S M 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 99 093902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Liu Y C, Luan X, Li H K, Gong Q, Wong C W, Xiao Y F 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 112 213602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Jing H, Özdemir S K, Lü X Y, Zhang J, Yang L, Nori F 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 113 053604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Chen H J 2018 J. Appl. Phys. 124 153102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang P, Wang Y D, Sun C P 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 95 097204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Xia K, Evers J 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 227203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] EversJ, Keitel C H 2004 Europhys. Lett. 68 370
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Harris S E 1997 Phys. Today 50 36
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Fleischhauer M, Imamoglu A, Marangos J P 2005 Rev. Mod. Phys. 77 633
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Genes C, Ritsch H, Drewsen M, Dantan A 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 051801(R)
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 谷开慧, 严冬, 张孟龙, 殷景志, 付长宝 2019 68 054201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gu K H, Yan D, Zhang M L, Yin J Z, Fu C B 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 054201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Grudinin I S, Lee H, Painter O, Vahala K J 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 083901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Di K, Xie C, Zhang J 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 106 153602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Gu W J, Li G X 2013 Phys. Rev. A 87 025804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Ojanen T, Børkje K 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 013824
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Giovannetti V, Vitali D 2001 Phys. Rev. A 63 023812
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Guo Y J, Li K, Nie W J, Li Y 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 053841
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Garrido Alzar C L, Martinez M A G, Nussenzeig P 2002 Am. J. Phys. 70 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] AnetsbergerG, Rivière R, Schliesser A, Arcizet O, Kippenberg T J 2008 Nat. Photonics 2 627
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 9134
- PDF下载量: 203
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: