-
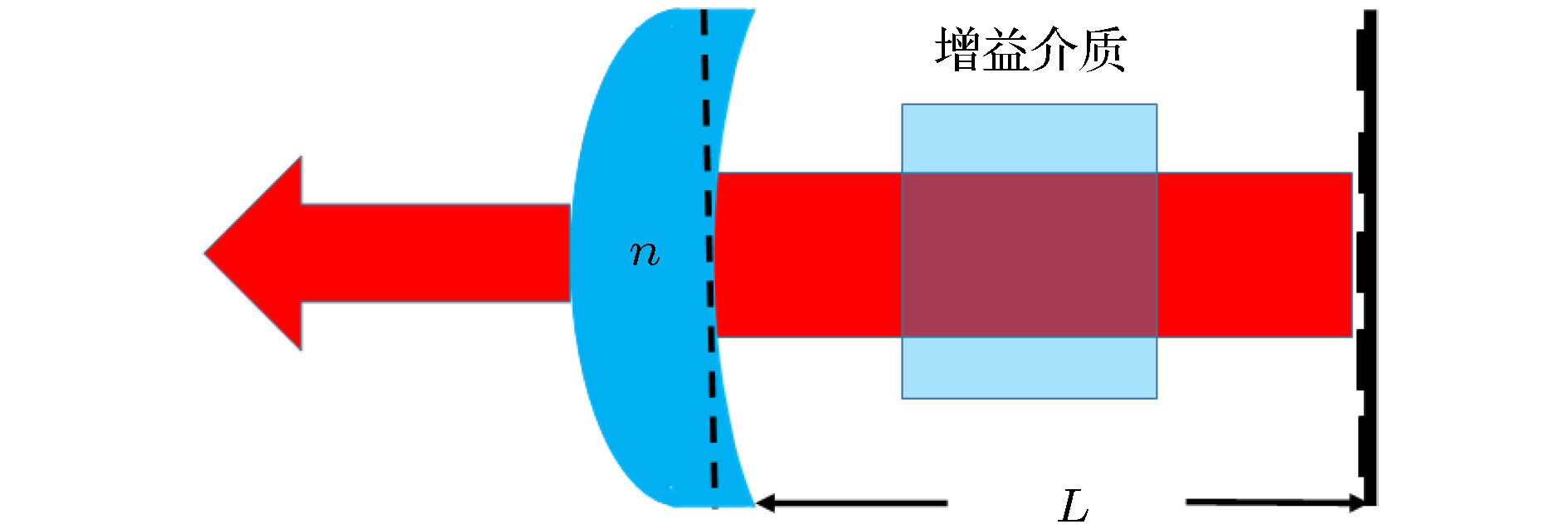
A scheme for forming high-quality circular Airy beams inside the laser resonator is presented theoretically. The desired circular Airy beam can be generated when the common reflective mirror is replaced by a designed diffractive optical element. The mode generated in the proposed cavity can be stimulated by using the so-called eigenvector method. The calculated results show that the parameters of the beams can be controlled by changing the phase distribution of the diffractive optical element. The loss of the generated mode is very low, which is close to that of the fundamental Gaussian mode. The purity of the generated mode is very high, which is much better than that from the phase-only encoding method in Fourier space. The phase distribution of the diffractive optical element needs designing for a fixed resonator length. In practice, the real resonator length may not be equal to the designed resonator length. Thus, the influence of the alignment error of the resonator length is discussed in detail. The results show that the diffraction loss of the proposed system is still very small even when the error reaches up to 2 mm. Meanwhile, the purity of the generated mode decreases little. Then, the influence of etching depth errors and the decenter of the reflective mirrors are discussed in detail. Here we assume that the fluctuations are randomly distributed. The value of the maximum fluctuation is used to represent the etching depth error degree. The results show that the diffraction loss of the proposed system is more sensitive to production error, and the purity of the generated mode is more sensitive to alignment error. Thus, we estimate that the maximum etching depth error should be less than six percent of the wavelength, and the vertical distance between the centers of the two reflective mirrors should be less than 7 μm if one wants to obtain high-quality CAB with high efficiency. The requirements for precision are acceptable for existing microfabrication and operation technologies.
[1] Siviloglou G A, Broky J, Dogariu A, Christodoulides D N 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 99 213901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Minovich A E, Klein A E, Neshev D N, Pertsch T, Kivshar Y S, Christodoulides D N 2014 Laser. Photon. Rev. 8 221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Qian J, Liu B Y, Sun H X, Yuan S Q, Yu X Z 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 114304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 崔省伟, 陈子阳, 胡克磊, 蒲继雄 2013 62 094205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cui S W, Chen Z Y, Hu K L, Pu J X 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 094205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 张泽, 刘京郊, 张鹏, 倪培根, Prakash J, 胡洋, 姜东升, Christodoulides D N, 陈志刚 2013 62 034209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Z, Liu J J, Zhang P, Ni P G, Prakash J, Hu Y, Jiang D S, Christodoulides D N, Chen Z G 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 034209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Guo Y H, Huang Y J, Li X, Pu M B, Gao P, Jin J J, Ma X L, Luo X G 2019 Adv. Opt. Mater. 7 1900503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Li Z, Cheng H, Liu Z, Chen S, Tian J 2016 Adv. Opt. Mater. 4 1230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Fan Q, Zhu W, Liang Y, Huo P, Zhang C, Agrawal A, Huang K, Luo X, Lu Y, Qiu C, Lezec H J, Xu T 2019 Nano Lett. 19 1158
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Efremidis N K, Christodoulides D N 2010 Opt. Lett. 35 4045
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Papazoglou D G, Efremidis N K, Christodoulides D N, Tzortzakis S 2011 Opt. Lett. 36 1842
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Liu K, Koulouklidis A D, Papazoglou D G, Tzortzakis S, Zhang X C 2016 Optica 3 605
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Manousidaki M, Papazoglou D G, Farsari M, Tzortzakis S 2016 Optica 3 525
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Manousidaki M, Fedorov V Y, Papazoglou D G, Farsari M, Tzortzakis S 2018 Opt. Lett. 4 3
[14] Zhang P, Prakash J, Zhang Z, Mills M S, Efremidis N K, Christodoulides D N, Chen Z 2011 Opt. Lett. 36 2883
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Davis J A, Cottrell D M, Zinn J M 2013 Appl. Opt. 52 1888
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Davis J A, Cottrell D M, Sand D 2012 Opt. Express 20 13302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 刘正楠, 耿滔, 邓攀 2019 中国激光 46 0209001
Liu Z N, Geng T, Deng P 2019 Chin. J. Lasers 46 0209001
[18] Fox A G, Li T 1961 Bell System Techical Journal 40 453
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Chao J, Li B, Cheng Y, Wang Y 2007 Opt. Laser Technol. 39 490
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Cheng Y Y, Wang Y Q, Hu J, Li J R 2004 Opt. Commun. 234 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Bélanger P A, Paré C 1991 Opt. Lett. 16 1057
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Leger J R, Chen D, Wang Z 1994 Opt. Lett. 19 108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Jiang Y, Zhu X, Yu W, Shao H, Zheng W, Lu X 2015 Opt. Express 23 29834
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Li N, Jiang Y, Huang K, Lu X 2014 Opt. Express 22 22847
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhou W, Bovik A C, Sheikh H R, Simoncelli E P 2004 IEEE Trans. Image Process 13 600
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
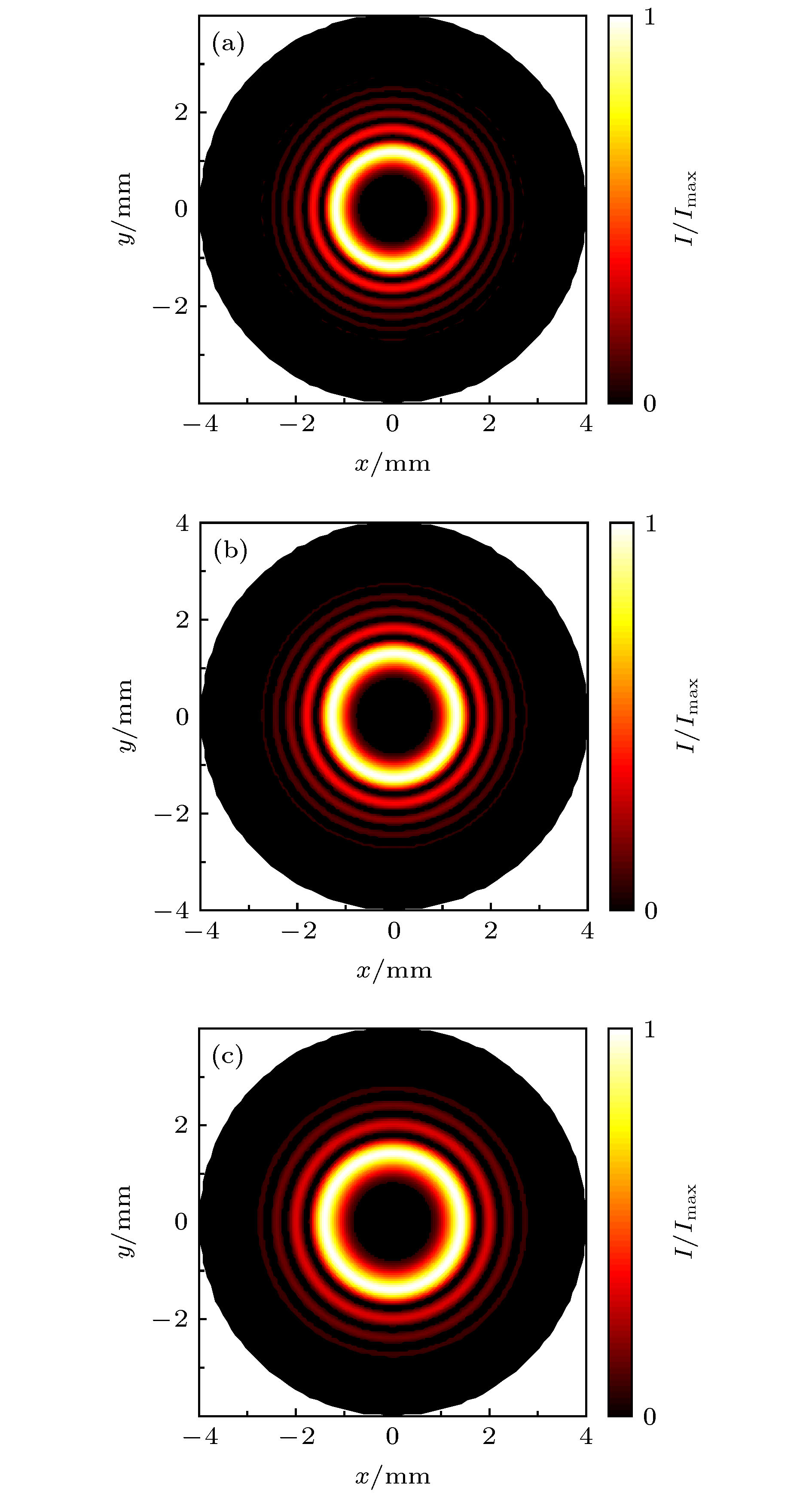
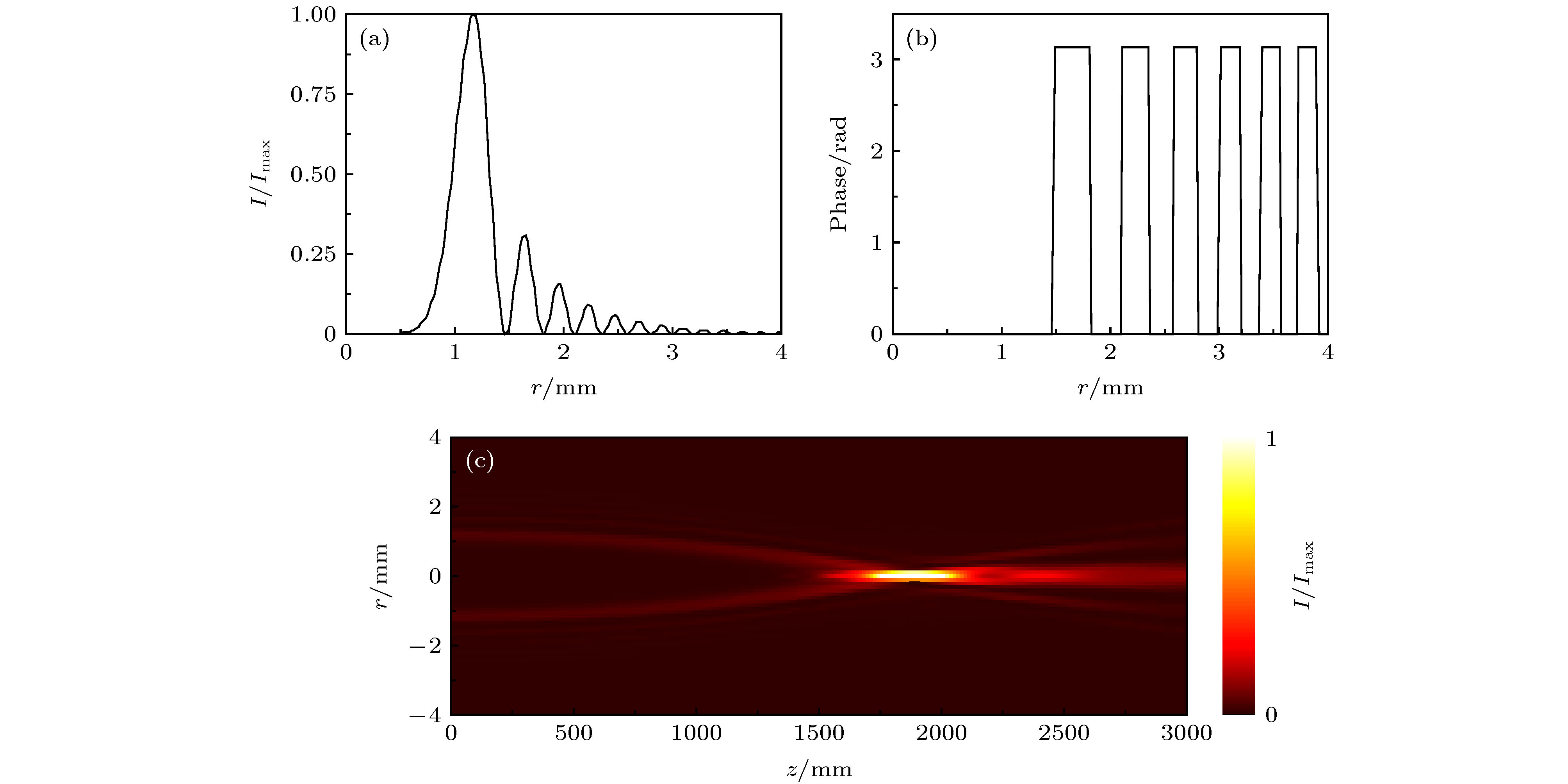
图 3 不同参数条件下, 使用Fox-Li方法计算获得的腔内光场模式分布 (a) r0 = 1 mm, w = 0.2 mm和a = 0.15; (b) r0 = 1.1 mm, w = 0.22 mm和a = 0.17; (c) r0 = 1.2 mm, w = 0.25 mm和a = 0.2
Fig. 3. Calculation results of the intensity distributions of the modes by using Fox-Li method with different parameters: (a) r0 = 1 mm, w = 0.2 mm and a = 0.15; (b) r0 = 1.1 mm, w = 0.22 mm and a = 0.17; (c) r0 = 1.2 mm, w = 0.25 mm and a = 0.2.
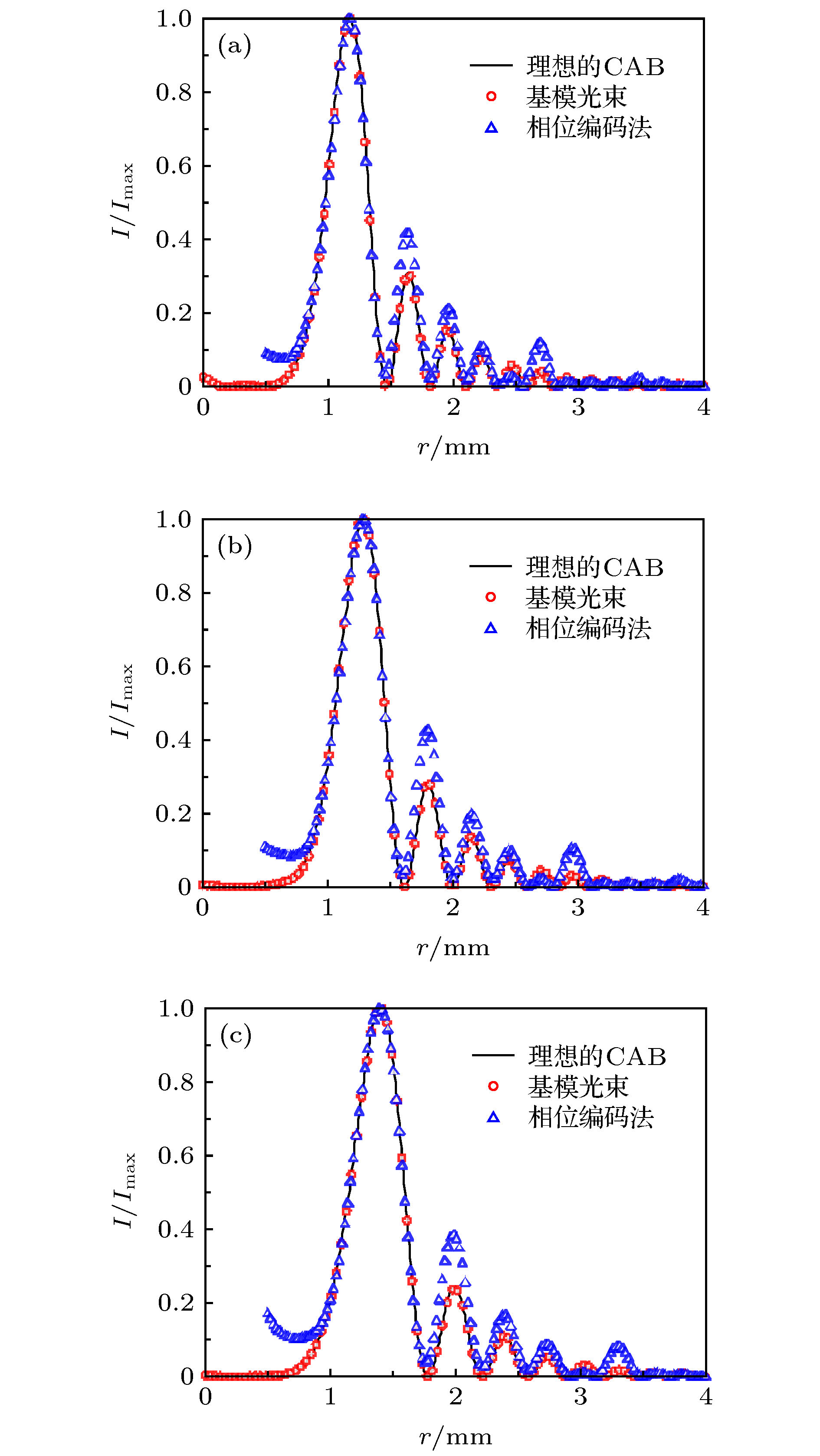
图 4 理想CAB和使用不同方法产生的光束的径向光强分布 (a) r0 = 1 mm, w = 0.2 mm和a = 0.15; (b) r0 = 1.1 mm, w = 0.22 mm和a = 0.17; (c) r0 = 1.2 mm, w = 0.25 mm和a = 0.2
Fig. 4. Radial intensity distributions of the ideal CAB and the beams produced by different methods: (a) r0 = 1 mm, w = 0.2 mm and a = 0.15; (b) r0 = 1.1 mm, w = 0.22 mm and a = 0.17; (c) r0 = 1.2 mm, w = 0.25 mm and a = 0.2.
图 5 理想CAB和使用不同方法产生的光束的光轴光强分布 (a) r0 = 1 mm, w = 0.2 mm和a = 0.15; (b) r0 = 1.1 mm, w = 0.22 mm和a = 0.17; (c) r0 = 1.2 mm, w = 0.25 mm和a = 0.2
Fig. 5. On-axis intensity contrast of the ideal CAB and the beams produced by different methods: (a) r0 = 1 mm, w = 0.2 mm and a = 0.15; (b) r0 = 1.1 mm, w = 0.22 mm and a = 0.17; (c) r0 = 1.2 mm, w = 0.25 mm and a = 0.2.
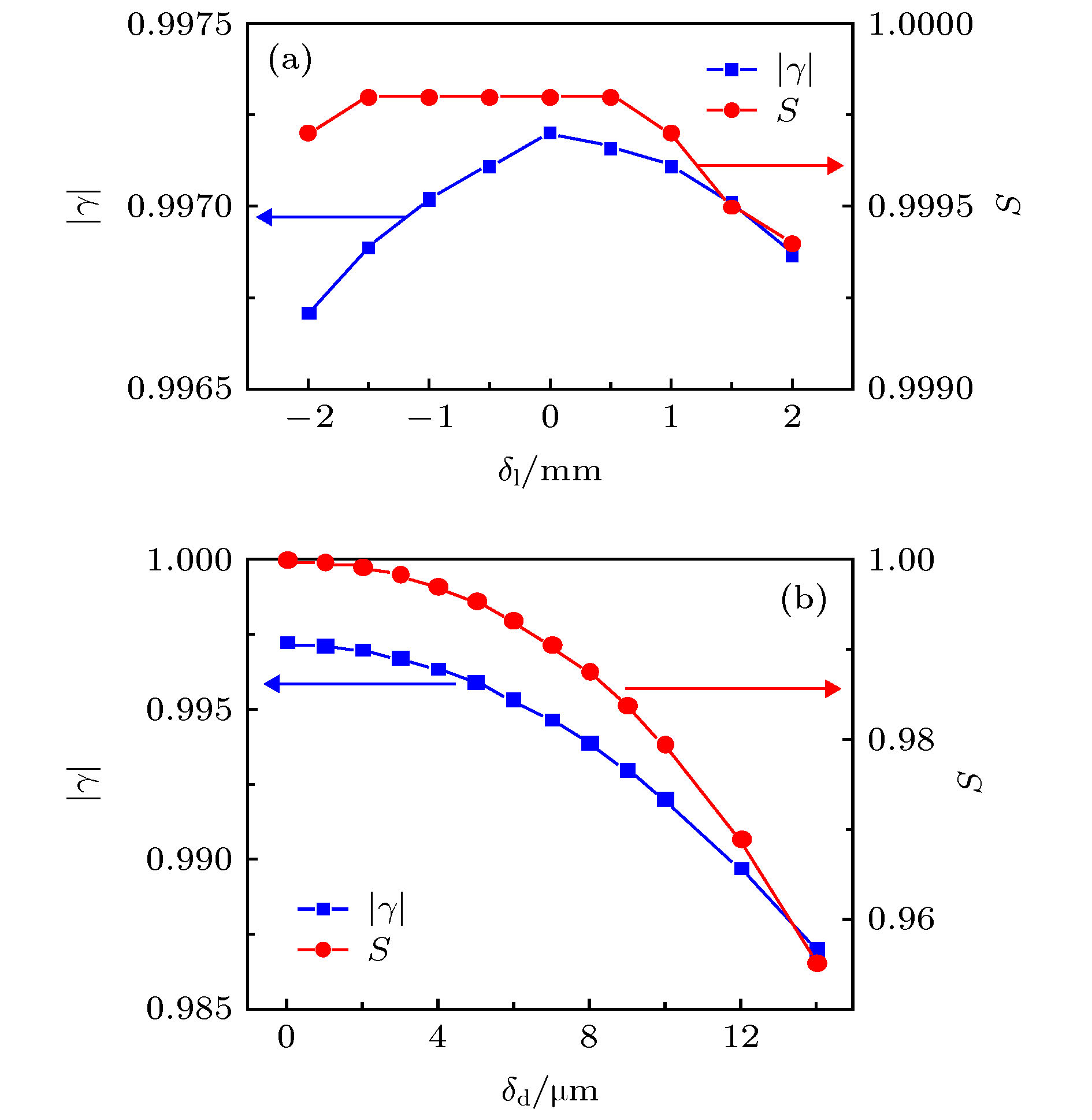
图 6 光束参数为
${r_0} = 1\;{\rm{mm}}$ ,$w = 0.2\;{\rm{mm}}$ 和$a = 0.15$ 时, 系统对准误差对产生光束质量的影响 (a)基模的$\left| \gamma \right|$ 以及S与腔长误差${\delta _{\rm{l}}}$ 的关系; (b)基模的$\left| \gamma \right|$ 以及S与同轴度误差${\delta _{\rm{d}}}$ 的关系Fig. 6. The influence of the alignment errors on formation of the fundamental mode with
${r_0} = 1\;{\rm{mm}}$ ,$w = 0.2\;{\rm{mm}}$ and$a = 0.15$ : (a)$\left| \gamma \right|$ and S of the fundamental mode as a function of$\delta_{\rm l}$ ; (b)$\left| \gamma \right|$ and S of the fundamental mode as a function of$\delta _{\rm d}$ 表 1 不同参数条件下的衍射光学元件上的相位分布和计算获得的最大3个
$\left| \gamma \right|$ 对应模式的光强分布Table 1. The phase distributions of the diffractive optical elements, the three largest
$\left| \gamma \right|$ and the calculated intensity distributions of corresponding modes with different parameters.CAB的参数 衍射光学元件上的相位分布/rad $\left| \gamma \right|$ 光强分布 r0 = 1 mm
w = 0.2 mm
a = 0.15
0.9972 
0.9898 
0.9898 
r0 = 1.1 mm
w = 0.22 mm
a = 0.17
0.9970 
0.9845 
0.9845 
r0 = 1.2 mm
w = 0.25 mm
a = 0.2
0.9960 
0.9804 
0.9804 
-
[1] Siviloglou G A, Broky J, Dogariu A, Christodoulides D N 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 99 213901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Minovich A E, Klein A E, Neshev D N, Pertsch T, Kivshar Y S, Christodoulides D N 2014 Laser. Photon. Rev. 8 221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Qian J, Liu B Y, Sun H X, Yuan S Q, Yu X Z 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 114304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 崔省伟, 陈子阳, 胡克磊, 蒲继雄 2013 62 094205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cui S W, Chen Z Y, Hu K L, Pu J X 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 094205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 张泽, 刘京郊, 张鹏, 倪培根, Prakash J, 胡洋, 姜东升, Christodoulides D N, 陈志刚 2013 62 034209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Z, Liu J J, Zhang P, Ni P G, Prakash J, Hu Y, Jiang D S, Christodoulides D N, Chen Z G 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 034209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Guo Y H, Huang Y J, Li X, Pu M B, Gao P, Jin J J, Ma X L, Luo X G 2019 Adv. Opt. Mater. 7 1900503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Li Z, Cheng H, Liu Z, Chen S, Tian J 2016 Adv. Opt. Mater. 4 1230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Fan Q, Zhu W, Liang Y, Huo P, Zhang C, Agrawal A, Huang K, Luo X, Lu Y, Qiu C, Lezec H J, Xu T 2019 Nano Lett. 19 1158
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Efremidis N K, Christodoulides D N 2010 Opt. Lett. 35 4045
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Papazoglou D G, Efremidis N K, Christodoulides D N, Tzortzakis S 2011 Opt. Lett. 36 1842
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Liu K, Koulouklidis A D, Papazoglou D G, Tzortzakis S, Zhang X C 2016 Optica 3 605
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Manousidaki M, Papazoglou D G, Farsari M, Tzortzakis S 2016 Optica 3 525
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Manousidaki M, Fedorov V Y, Papazoglou D G, Farsari M, Tzortzakis S 2018 Opt. Lett. 4 3
[14] Zhang P, Prakash J, Zhang Z, Mills M S, Efremidis N K, Christodoulides D N, Chen Z 2011 Opt. Lett. 36 2883
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Davis J A, Cottrell D M, Zinn J M 2013 Appl. Opt. 52 1888
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Davis J A, Cottrell D M, Sand D 2012 Opt. Express 20 13302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 刘正楠, 耿滔, 邓攀 2019 中国激光 46 0209001
Liu Z N, Geng T, Deng P 2019 Chin. J. Lasers 46 0209001
[18] Fox A G, Li T 1961 Bell System Techical Journal 40 453
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Chao J, Li B, Cheng Y, Wang Y 2007 Opt. Laser Technol. 39 490
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Cheng Y Y, Wang Y Q, Hu J, Li J R 2004 Opt. Commun. 234 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Bélanger P A, Paré C 1991 Opt. Lett. 16 1057
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Leger J R, Chen D, Wang Z 1994 Opt. Lett. 19 108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Jiang Y, Zhu X, Yu W, Shao H, Zheng W, Lu X 2015 Opt. Express 23 29834
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Li N, Jiang Y, Huang K, Lu X 2014 Opt. Express 22 22847
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zhou W, Bovik A C, Sheikh H R, Simoncelli E P 2004 IEEE Trans. Image Process 13 600
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 10522
- PDF下载量: 133
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: