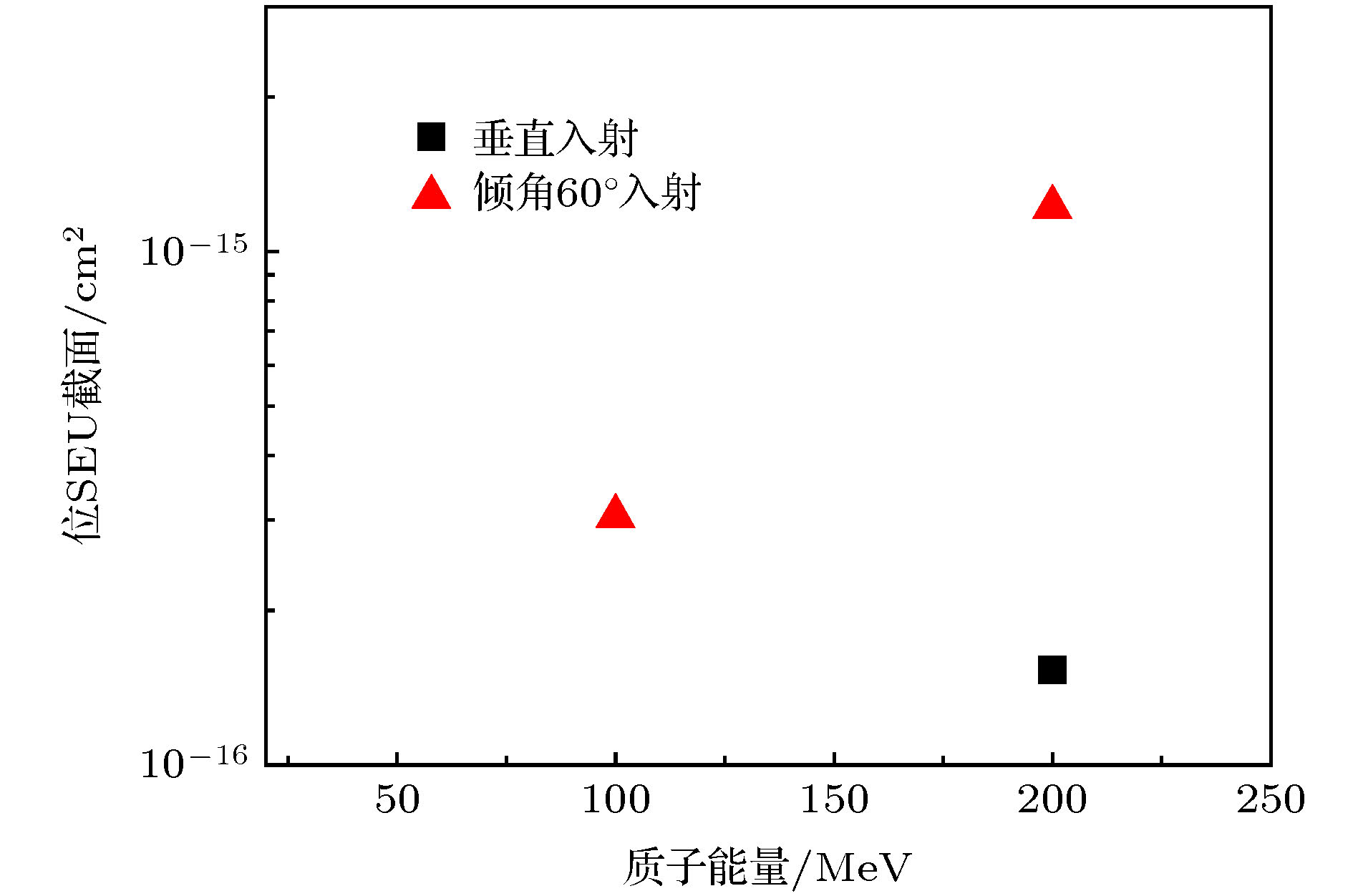
-
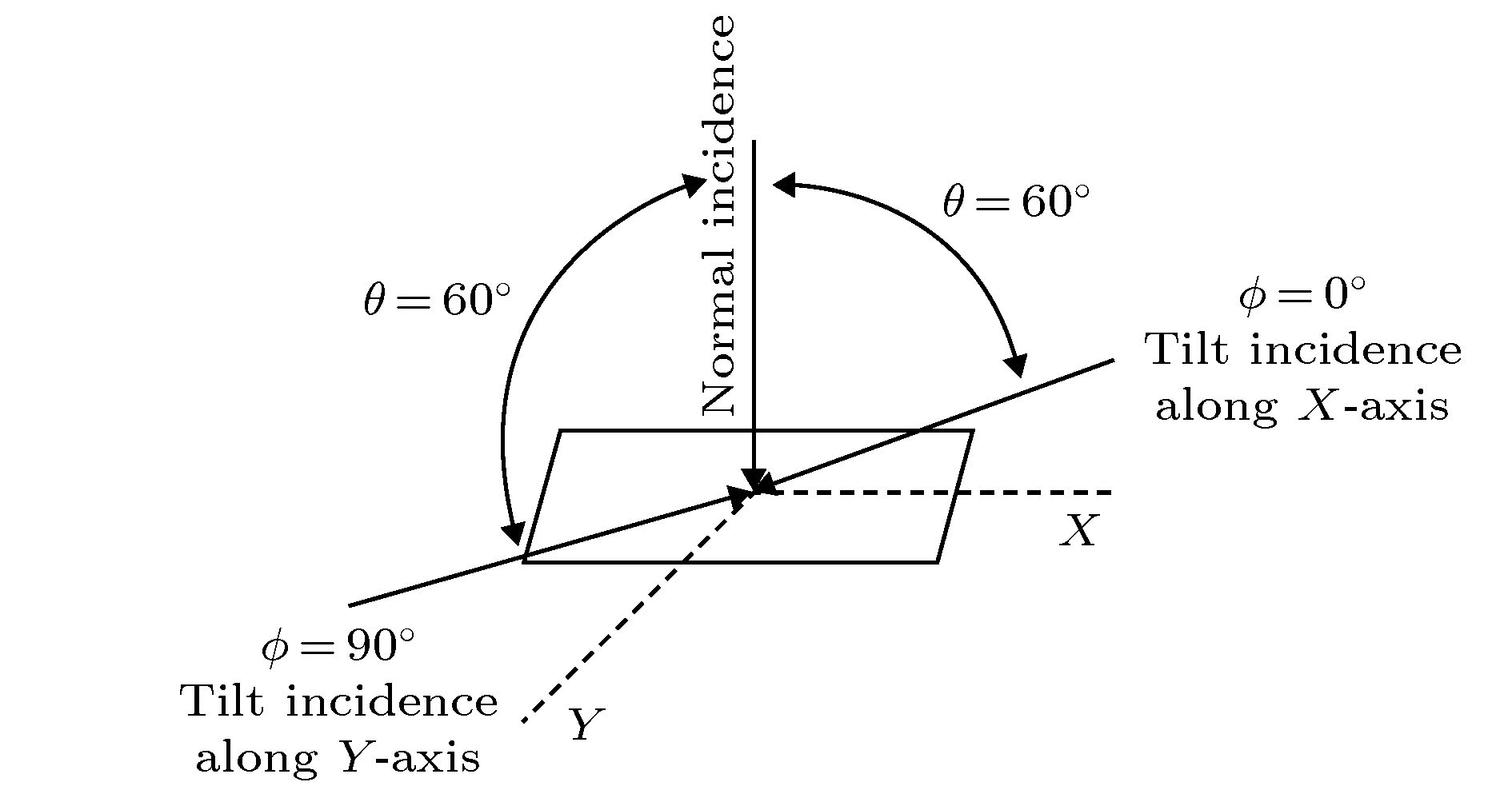
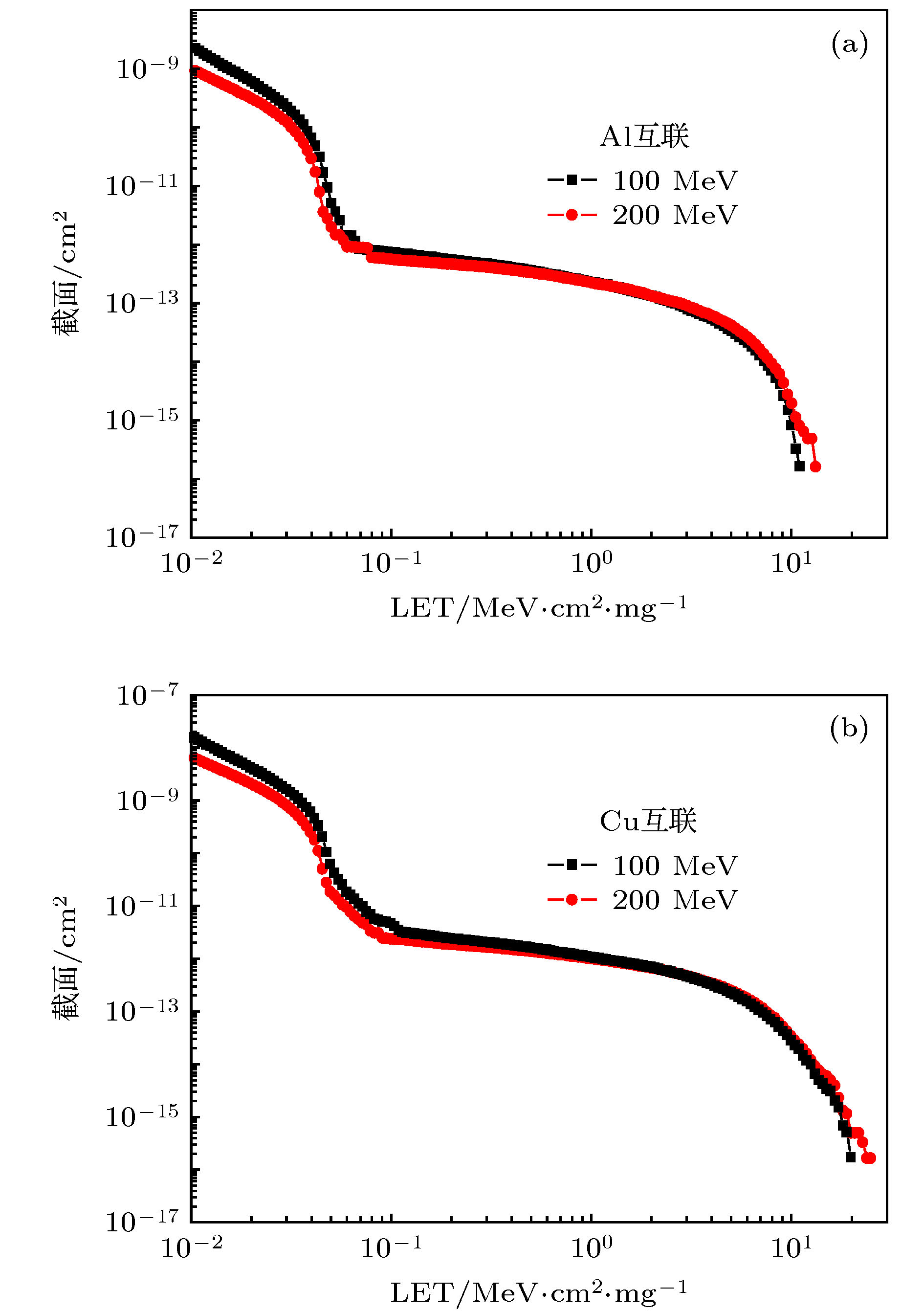
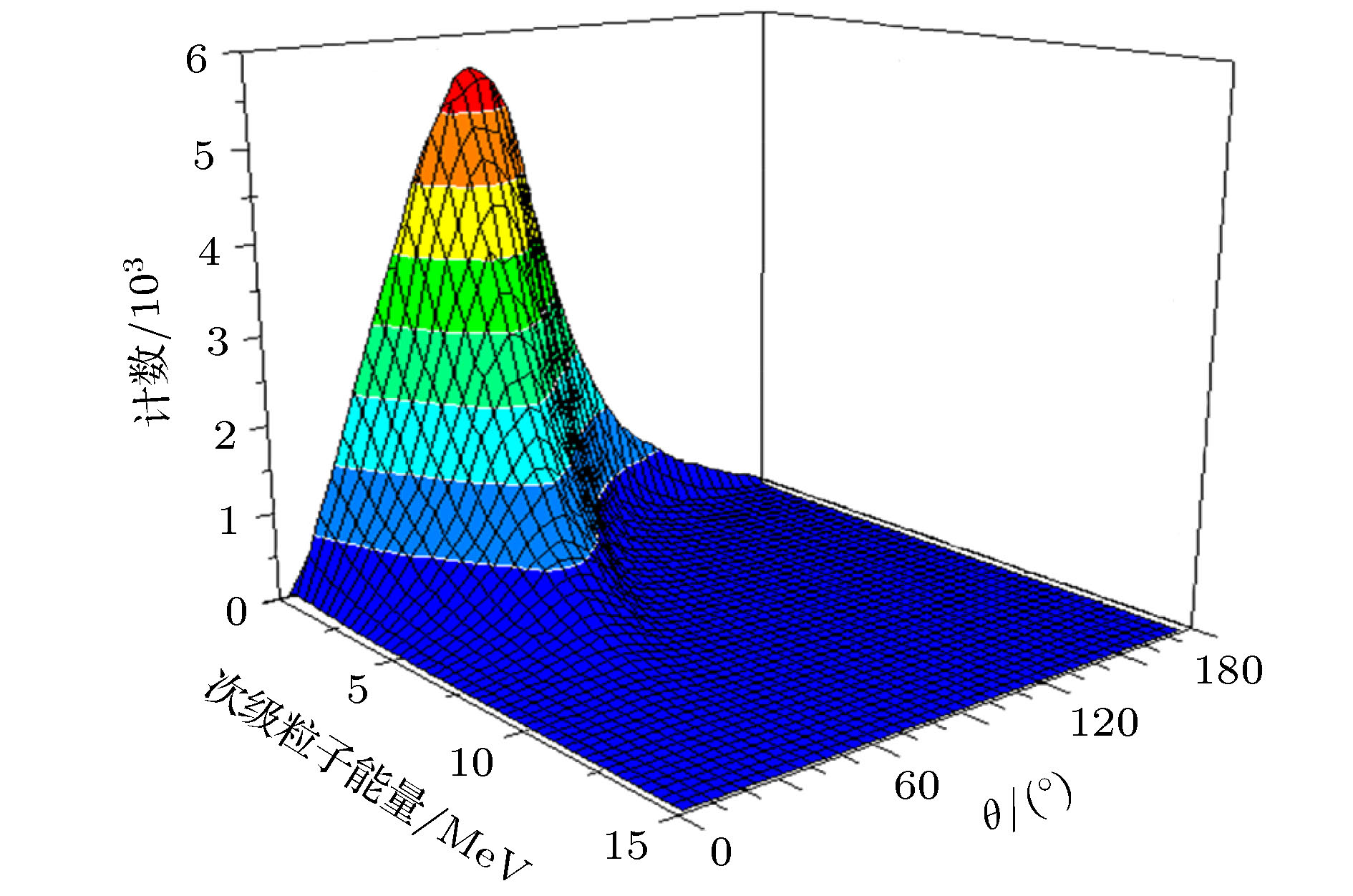
为实现对纳米DICE (dual interlocked cell)加固器件抗质子单粒子能力的准确评估, 通过对65 nm双DICE加固静态随机存储器(static random access memory, SRAM)重离子单粒子翻转试验数据的分析, 获取了其在重离子垂直和倾角入射时的单粒子翻转 (single event upset, SEU)阈值以及离子入射最劣方位角, 并结合蒙卡仿真获取不同能量质子与器件多层金属布线层发生核反应产生的次级粒子LET(linear energy transfer)值最大值以及角度分布特性, 对器件在不同能量下的质子单粒子效应敏感性进行了预测, 质子单粒子效应实验结果验证了预测方法的有效性以及预测结果的准确性, 并提出针对DICE加固类器件在重离子和质子单粒子效应试验评估中均应开展离子最劣方位角下的倾角入射试验.
-
关键词:
- 双双互锁存储单元加固 /
- 单粒子翻转 /
- 质子 /
- 最劣方位角
In order to evaluate the radiation tolerance to proton single event effect(SEE) in nanometer dual interlocked cell (DICE) hardening device accurately, single event upset (SEU) linear energy transfer (LET) threshold at heavy ion normal and tilt incidence, and the worst case SEU orientational angle are acquired based on the analysis of heavy ion SEU testing data in 65 nm dual DICE static random access memory (SRAM). It is proved that dual DICE design is effective for improving the LET threshold against SEU. Howerer, heavy ion tilt incidence at the worst orientational angle will significantly reduce the SEU threshold and increase the SEU cross section. The worst orientational angle for SEU in DICE SRAM is the large tilting angle along the well. The maximum LET value and the emission angle distribution of secondary particle induced by the nuclear reaction between protons with different energy and layers with different multiple metallization are obtained by using Monte-Carlo simulation. The maximum LET value of secondary particle from proton-copper spallation reaction is higher than 15 MeV·cm2/mg for 100 MeV and 200 MeV protons. Secondary particles with the maximum energy and longest range are emitted preferentially in the forward direction. Proton SEU sensitivity is further predicted through combining heavy ion test data with Monte-Carlo simulation. Proton SEU test data verify the effectiveness of the prediction method and the accuracy of the prediction results. The research results indicate that the tolerance of nanometer DICE hardening technique against proton SEU will be overestimated if SEE evaluation test is carried out with only 100 MeV proton accelerator or normal incidence. Proton single event upset in nanometer dual DICE SRAM has an evident dependence on tilt angle and orientational angle. By adopting the above prediction method, whether proton SEE test needs performing or not in nanometer radiation-hardening device can be judged and screened. The requirements for the maximum energy of proton accelerator can be ascertained. In order to ensure that the devices are applied to space with high reliability, SEE test should be carried out including tilt incidence at the worst orientational angle in nanometer DICE hardening device in the process of heavy ion and proton SEE test evaluation.-
Keywords:
- double dual interlocked cell hardening /
- single event upset /
- proton /
- the worst orientational angle
[1] Hoeffgen S K, Durante M, Ferlet-Cavrois V, Harboe-Sørensen R, Lennartz W, Kuendgen T, Kuhnhenn J, Latessa C, Mathes M, Menicucci A, Metzger S, Nieminen P, Pleskac R, Poivey C, Schardt D, Weinand U 2012 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 59 1161
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Falguere D, Boscher D, Nuns T, Duzellier S, Bourdarie S, Ecoffet R, Barde S, Cueto J, Alonzo C, Hoffman C 2002 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 49 2782
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Peterson E L 1992 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 39 1600
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Calvel P, Barillot C, Lamothe P, Ecoffet R, Duzellier S, Falguere D 1996 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 43 2827
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Edmonds L D 2000 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 47 1713
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Barak J 2006 .IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 53 3336
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Koga R, George J, Swift G, Yui C, Edmonds L, Carmichael C, Langley T, Murray P, Lanes K, Napier M 2004 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 51 2825
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Hansen D L 2015 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 62 2874
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Sierawski B D, Pellish J A, Reed R A, Schrimpf R D, Warren K M, Weller R A, Mendenhall M H, Black J D, Tipton A D, Xapsos M A, Baumann R C, Deng X, Campola M J, Friendlich M R, Kim H S, Phan A M, Seidleck C M 2009 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 56 3085
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Warren K M, Weller R A, Sierawski B D, Reed R A, Mendenhall M H, Schrimph R D, Massengill L W, Porter M E, Wilkinson J D, Label K A, Adams J H 2007 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 54 898
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Xi K, Geng C, Zhang Z G, Hou M D, Sun Y M, Luo J, Liu T Q, Wang B, Ye B, Yin Y N, Liu J 2016 Chin. Phys. C 40 066001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Warren K M, Sierawski B D, Reed R A, Weller R A, Carmichael C, Lesea A, Mendenhal M H, Dodd P E, Schrimpf R D, Massengill L W, Hoang T, Wan H, De Jong J L, Padovani R, Fabula J J 2007 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 54 2419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Gorbunov M S, Boruzdina A B, Dolotov P S 2016 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 63 2250
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Loveless T D, Jagannathan S, Reece T, Chetia J, Bhuva B L, McCurdy M W, Massengill L W, Wen S J, Wong R, Rennie D 2011 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 58 1008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Amusan O A, Massengill L W, Baze M. P., Bhuva B L, Witulski A F, DasGupta S, Sternberg A L, Fleming P R, Heath C C, Alles M L 2007 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 52 2584
[16] Gorbunov M S, Dolotov P S, Antonov A A, Zebrev G.I, Emeliyanov V V, Boruzdina A B, Petrov A G, Ulanova A V 2014 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 61 1575
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Liu L, Yue S G, Lu S J 2015 J. Semicond. 36 115007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Cabanas-Holmen M, Cannon E H, Rabaa S, Amort T, Ballast J, Carson M, Lam D, Brees R 2013 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 60 4374
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] European Space Agency 2014 ESCC Basic Specification NO. 25100
[20] Turflinger T L, Clymer D A, Mason L W, Stone S, George J S, Koga R, Beach E, Huntington K, Turflinger T L 2017 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 64 309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Schwank J R, Shaneyfelt M R, Baggio J, Dodd P E, Felix J A, Ferlet-Cavrois V, Paillet P, Lambert D, Sexton F W, Hash G L, Blackmore E 2006 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 52 2622
[22] 罗尹虹, 张凤祁, 王燕萍, 王圆明, 郭晓强, 郭红霞 2016 65 068501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Luo Y H, Zhang F Q, Wang Y P, Wang Y M, Guo X Q, Guo H X 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 068501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
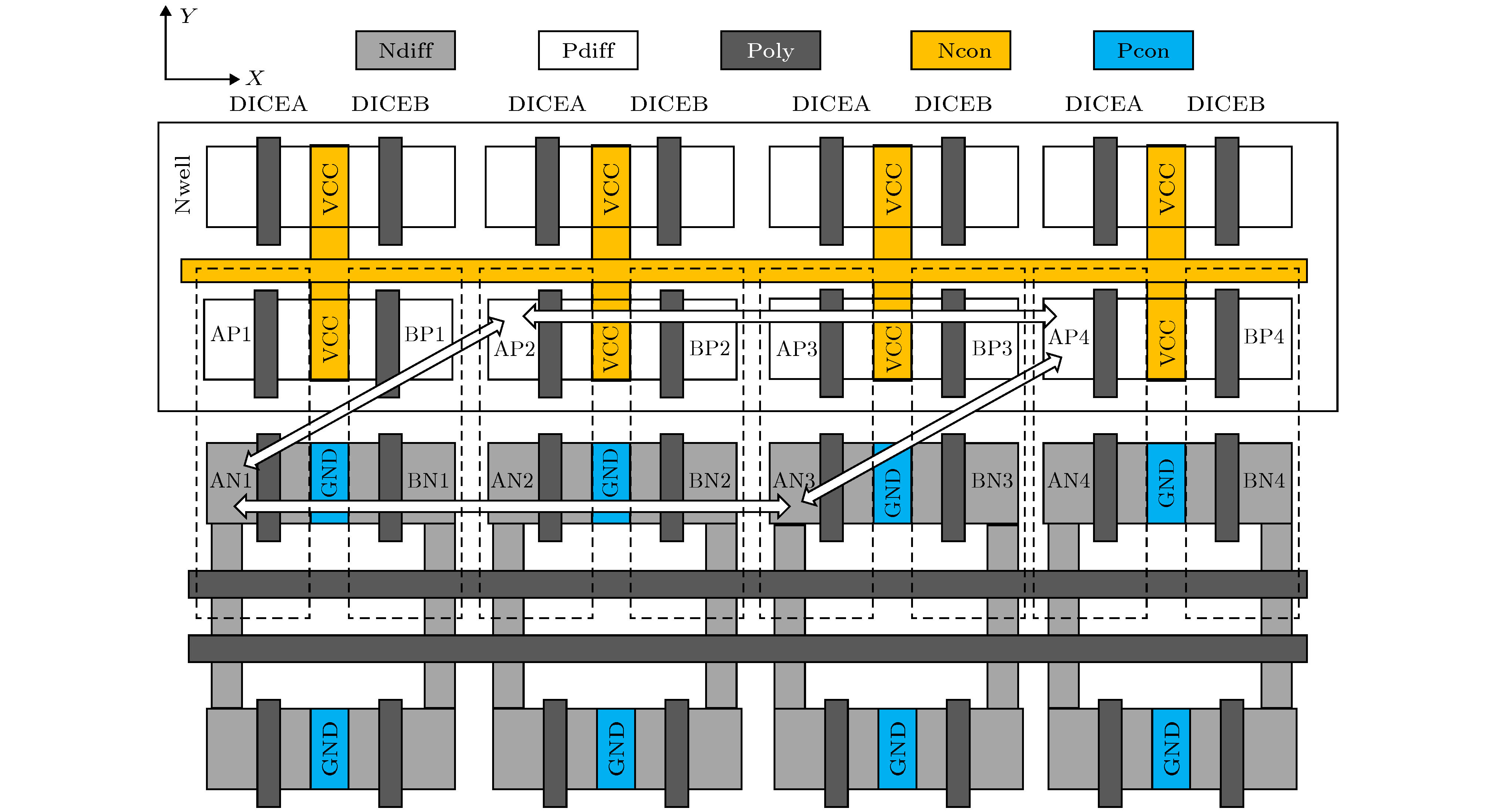
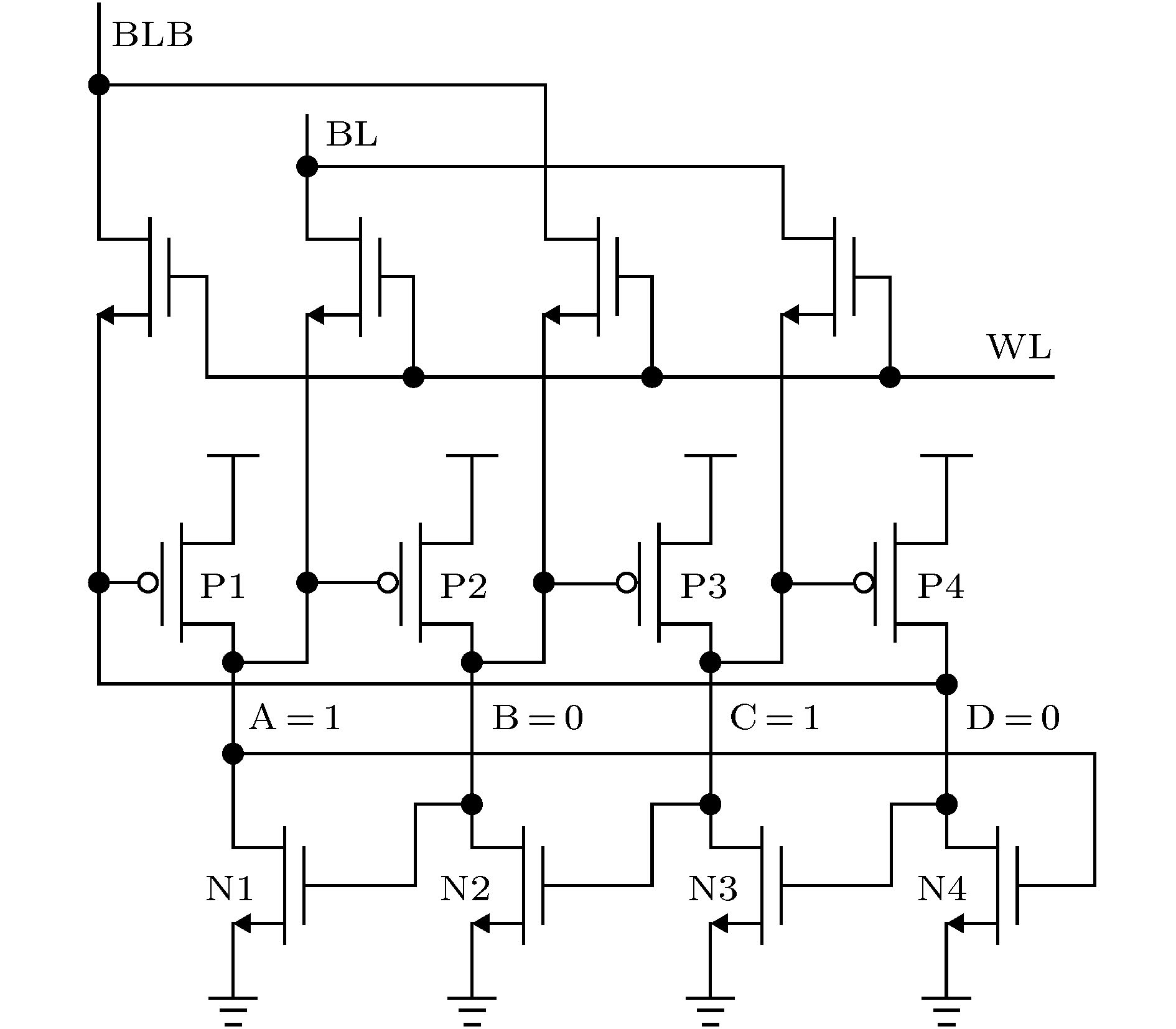
表 1 双DICE存储单元存储不同数据时的灵敏节点对
Table 1. Sensitive pairs with different data stored in dual DICE cell.
存储数据 灵敏节点对 存储数据 灵敏节点对 BL = 1, (A, B, C, D) = (1, 0, 1, 0) N1/N3 BL = 0, (A, B, C, D) = (0, 1, 0, 1) N2/N4 P2/P4 P1/P3 N1/P2 N2/P3 N3/P4 N4/P1 表 2 试验离子种类信息
Table 2. Ion species in Heavy ion testing.
序号 离子种类 能量/MeV 射程/μm 垂直入射时有效LET/(MeV·cm2/mg) 倾角30°、60°时对应的有效LET/(MeV·cm2/mg) 1 19F9+ 110 82.7 4.4 5.1/9.3 2 35Cl11, 14+ 160 46.0 14.0 16.5/30.7 3 48Ti10, 15+ 169 34.7 23.5 4 74Ge11, 20+ 210 30.5 37.4 5 79Br13, 21+ 220 30.4 40.5 45.8/63.3 6 127I15, 25+ 265 28.8 52.7 57.7/68.0 7 209Bi31+ 923 53.7 99.8 -
[1] Hoeffgen S K, Durante M, Ferlet-Cavrois V, Harboe-Sørensen R, Lennartz W, Kuendgen T, Kuhnhenn J, Latessa C, Mathes M, Menicucci A, Metzger S, Nieminen P, Pleskac R, Poivey C, Schardt D, Weinand U 2012 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 59 1161
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Falguere D, Boscher D, Nuns T, Duzellier S, Bourdarie S, Ecoffet R, Barde S, Cueto J, Alonzo C, Hoffman C 2002 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 49 2782
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Peterson E L 1992 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 39 1600
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Calvel P, Barillot C, Lamothe P, Ecoffet R, Duzellier S, Falguere D 1996 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 43 2827
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Edmonds L D 2000 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 47 1713
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Barak J 2006 .IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 53 3336
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Koga R, George J, Swift G, Yui C, Edmonds L, Carmichael C, Langley T, Murray P, Lanes K, Napier M 2004 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 51 2825
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Hansen D L 2015 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 62 2874
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Sierawski B D, Pellish J A, Reed R A, Schrimpf R D, Warren K M, Weller R A, Mendenhall M H, Black J D, Tipton A D, Xapsos M A, Baumann R C, Deng X, Campola M J, Friendlich M R, Kim H S, Phan A M, Seidleck C M 2009 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 56 3085
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Warren K M, Weller R A, Sierawski B D, Reed R A, Mendenhall M H, Schrimph R D, Massengill L W, Porter M E, Wilkinson J D, Label K A, Adams J H 2007 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 54 898
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Xi K, Geng C, Zhang Z G, Hou M D, Sun Y M, Luo J, Liu T Q, Wang B, Ye B, Yin Y N, Liu J 2016 Chin. Phys. C 40 066001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Warren K M, Sierawski B D, Reed R A, Weller R A, Carmichael C, Lesea A, Mendenhal M H, Dodd P E, Schrimpf R D, Massengill L W, Hoang T, Wan H, De Jong J L, Padovani R, Fabula J J 2007 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 54 2419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Gorbunov M S, Boruzdina A B, Dolotov P S 2016 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 63 2250
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Loveless T D, Jagannathan S, Reece T, Chetia J, Bhuva B L, McCurdy M W, Massengill L W, Wen S J, Wong R, Rennie D 2011 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 58 1008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Amusan O A, Massengill L W, Baze M. P., Bhuva B L, Witulski A F, DasGupta S, Sternberg A L, Fleming P R, Heath C C, Alles M L 2007 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 52 2584
[16] Gorbunov M S, Dolotov P S, Antonov A A, Zebrev G.I, Emeliyanov V V, Boruzdina A B, Petrov A G, Ulanova A V 2014 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 61 1575
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Liu L, Yue S G, Lu S J 2015 J. Semicond. 36 115007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Cabanas-Holmen M, Cannon E H, Rabaa S, Amort T, Ballast J, Carson M, Lam D, Brees R 2013 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 60 4374
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] European Space Agency 2014 ESCC Basic Specification NO. 25100
[20] Turflinger T L, Clymer D A, Mason L W, Stone S, George J S, Koga R, Beach E, Huntington K, Turflinger T L 2017 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 64 309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Schwank J R, Shaneyfelt M R, Baggio J, Dodd P E, Felix J A, Ferlet-Cavrois V, Paillet P, Lambert D, Sexton F W, Hash G L, Blackmore E 2006 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 52 2622
[22] 罗尹虹, 张凤祁, 王燕萍, 王圆明, 郭晓强, 郭红霞 2016 65 068501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Luo Y H, Zhang F Q, Wang Y P, Wang Y M, Guo X Q, Guo H X 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 068501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 11666
- PDF下载量: 114
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: