-
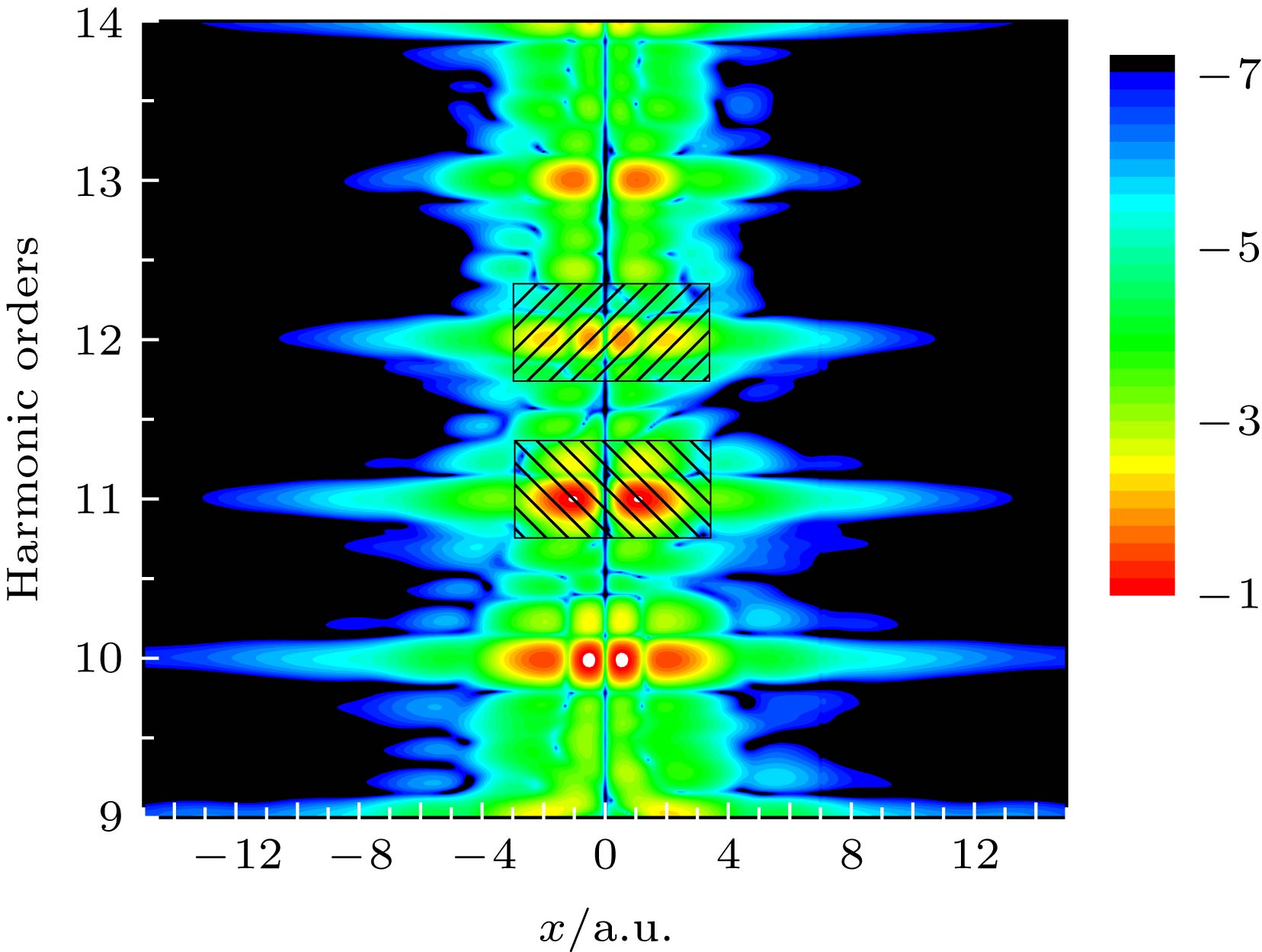
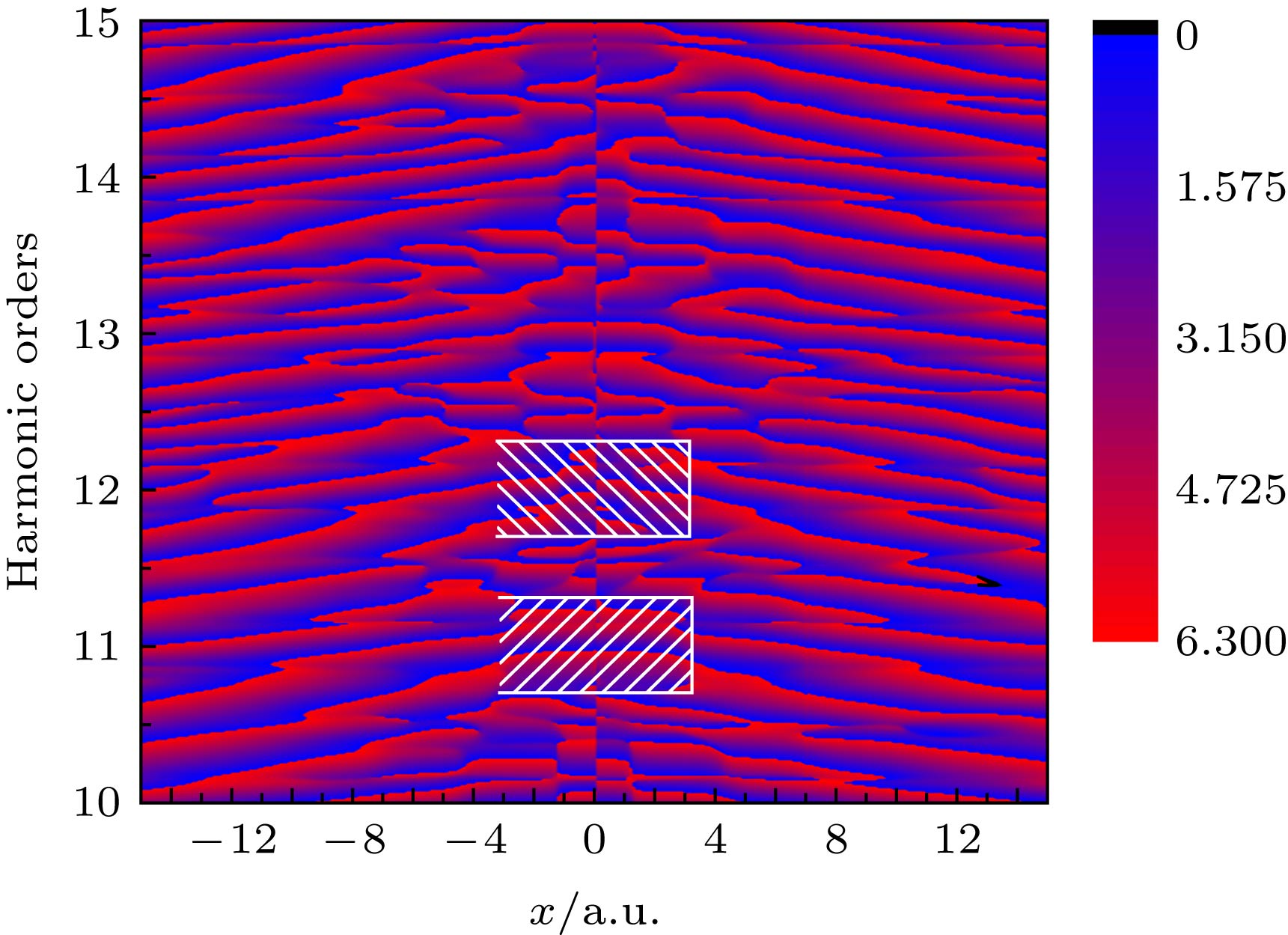
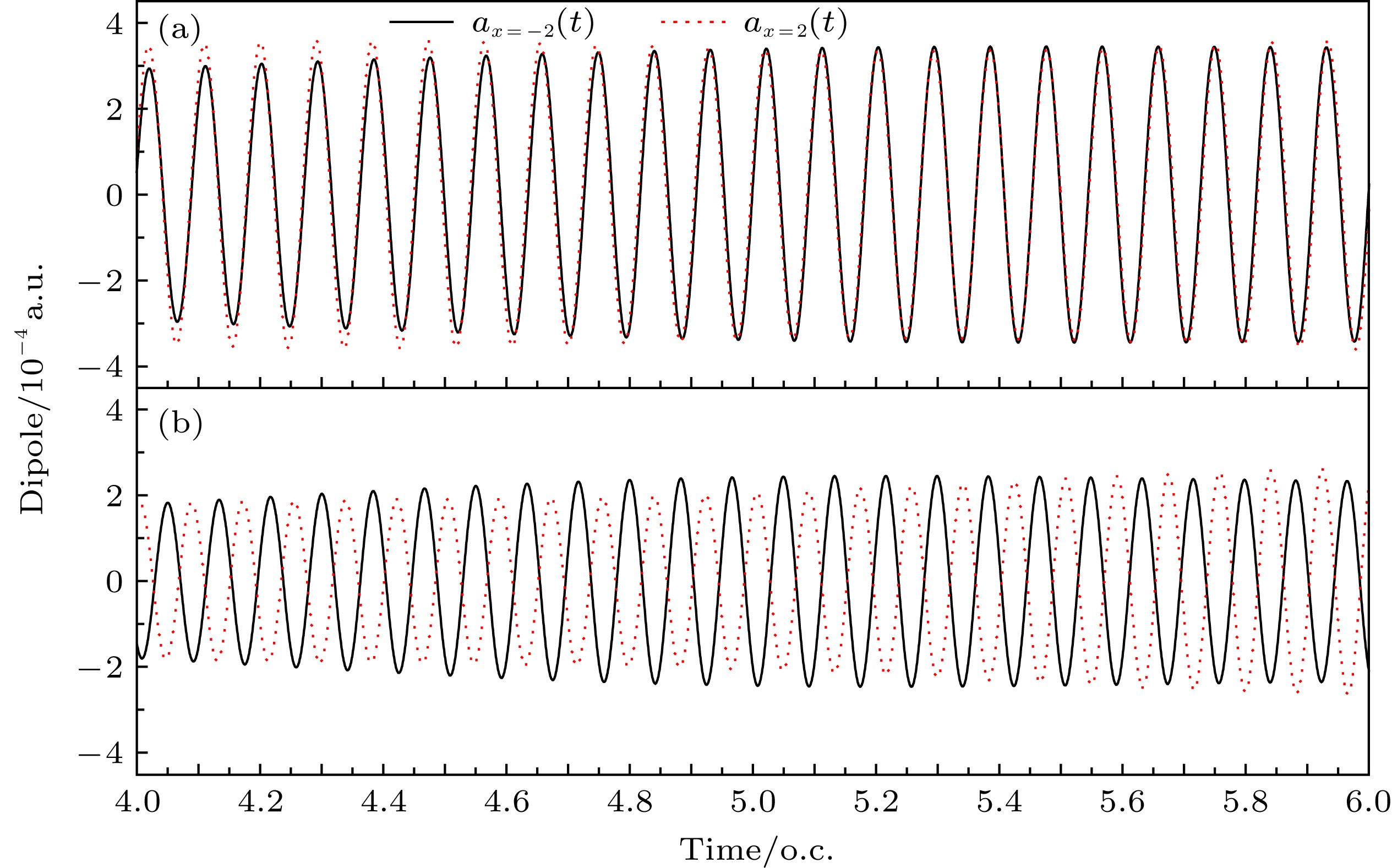
激光与原子、分子相互作用的高次谐波是产生超短阿秒脉冲和相干高频XUV光源的重要手段之一. 为了产生高强度的XUV光源, 需要对谐波产生机制深入研究. 本文通过数值求解含时薛定谔方程, 计算了不同空间位置的含时偶极矩进而得到不同空间位置的高次谐波发射. 对不同空间位置的谐波发射谱的分析发现, 谐波发射的主要空间位置在核区附近, 不同空间位置的谐波中奇次和偶次谐波均能被观察到, 整数阶谐波能量辐射强度较大. 进一步研究不同空间位置的谐波相位发现, 在x = 0左右两侧发射的奇次谐波相位相同, 偶次谐波相位相反. 通过滤波方法分析了不同空间位置的相同次谐波的含时偶极矩信息, 发现该相位特征导致了奇次谐波的增强, 偶次谐波的消失.
The higher-order harmonics generated from an atom irradiated by ultarashort laser pulses is one of the important ways to obtain ultrashort attosecond pulses and coherent XUV sources. In order to produce a high-inntensity XUV source, one needs to study the mechanism of harmonic generation. The mechanism of the atomic high harmonic generation can be well understood by the semi-classical three-step model. First, the electron tunnels the barrier formed by the atomic potential and laser electric field, and then it propagates freely in the laser field and can be driven back to the mother ion where it recombines with the ground state of ion. Although the cutoff energy of the high harmonic can be predicted by this model, it cannot provide more information about the harmonic efficiency and the spectral structure. Recently, the generation mechanism of high harmonic has been studied by using the Bohmian trajectory scheme based on the time dependent wave packet. It is found that the harmonic structure can be reconstructed qualitatively by using a single Bohmian trajectory. The more accurate structure of harmonic spectrum needs more Bohmian trajectories. The calculation of these trajectories requires a lot of computation resources because the trajectory calculation is from the numerical solution for the time-dependent Schrödinger equation. In this work, we numerically solve the time-dependent Schrödinger equation of a model atom irradiated by ultrashort laser pulses. The time-dependent dipole moments at different spatial locations are calculated from the time-dependent wave function. The harmonic spectra are calculated from the Fourier transform of the time dipole moments. The harmonic spectra of different spatial locations show that the main emission positions of harmonic emission are near the nuclear region. One can observe the odd- and even-order harmonics at the different spatial positions. There has a larger radiation intensity for the integer-order harmonic. For the odd-order harmonics, their harmonic phases are the same on both sides of x = 0. For the even-order harmonics, their harmonic phases each have a pi difference on both side of x = 0. By using the filtering scheme, we analyze the phases of an harmonic at different spatial locations. It is found that the phase difference leads the odd-order harmonics to increase and the even-order harmonics to disappear. These findings contribute to the understanding of the physical mechanism of higher harmonic generated from an atom irradiated by strong laser pulses. -
Keywords:
- high-order harmonic emission /
- spatial distribution /
- wave packet
[1] Ozaki T, Ganeev R A, Ishizawa A, Kanai T, Kuroda H 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 253902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Dromey B, Zepf M, Gopal A, Wei M S, Tatarakis M 2006 Nat. Phys. 2 456
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Krausz F, Brabec T 1998 Opt. Photonics News 9 46
[4] Emma P, Akre R, Arthur J, Bionta R, Bostedt C, BozekJ, Brachmann A, Bucksbaum P, Coffee R, Decker F G, Ding Y, Dowell D, Edstrom S 2010 Nat. Photonics 4 641
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Gibsone A, Paul A, Wagner N 2003 Science 302 95
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Cingoz A, Yost D C, Allison T K, Ruehl A, Fermann M E, Hart I, Ye J 2012 Nature 482 68
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Goulielmakis E, Schultze M, Hofstetter M, Yakovlev V S, Gagnon J, Uiberacker M, Aquila A L 2008 Science 320 1614
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Qin M, Zhu X, Zhang Q, Lu P 2012 Opt. Lett. 37 5208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Curkum P B 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 71 1994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Pan Y, Guo F M, Jin C, Yang Y J, Ding D J 2019 Phys. Rev. A 99 033411
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Botheron P, Pons B 2010 Phys. Rev. A 82 021404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wei S S, Li S Y, Guo F M, Yang Y J, Wang B B 2013 Phys. Rev. A 87 063418
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Song Y, Li S Y, Liu X S, Chen J G, Zeng S L, Yang Y J 2012 Phys. Rev. A 86 033424
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Song Y, Li S Y, Liu X S, Guo F M, Yang Y J 2013 Phys. Rev. A 88 053419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 田原野, 郭福明, 曾思良, 杨玉军 2013 62 113201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tian Y Y, Guo F M, Zeng S L, Yang Y J 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 113201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Han J X, Wang J, Qiao Y, Liu A H, Guo F M, Yang Y J 2019 Opt. Express 27 8768
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yang Y J, Chen G, Chen J G, Zhu Q R 2004 Chin. Phys. Lett. 21 652
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 刘艳, 贾成, 郭福明, 杨玉军 2016 65 033201
Liu Y, Jia C, Guo F M, Yang Y Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 033201
[19] Tian Y Y, Li S Y, Wei S S, Guo F M, Zeng S L, Chen J G, Yang Y J 2014 Chin. Phys. B 23 053202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 宋文娟, 郭福明, 陈基根, 杨玉军 2018 67 033201
Song W J, Guo F M, Chen J G, Yang Y J 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 033201
[21] He X, Miranda M, Schwenke J, Giulbaud O, Ruchon T, Heyl C, Georgadiou E 2009 Phys. Rev. A 79 063829
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Chen Y J, Zhang B 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 053402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
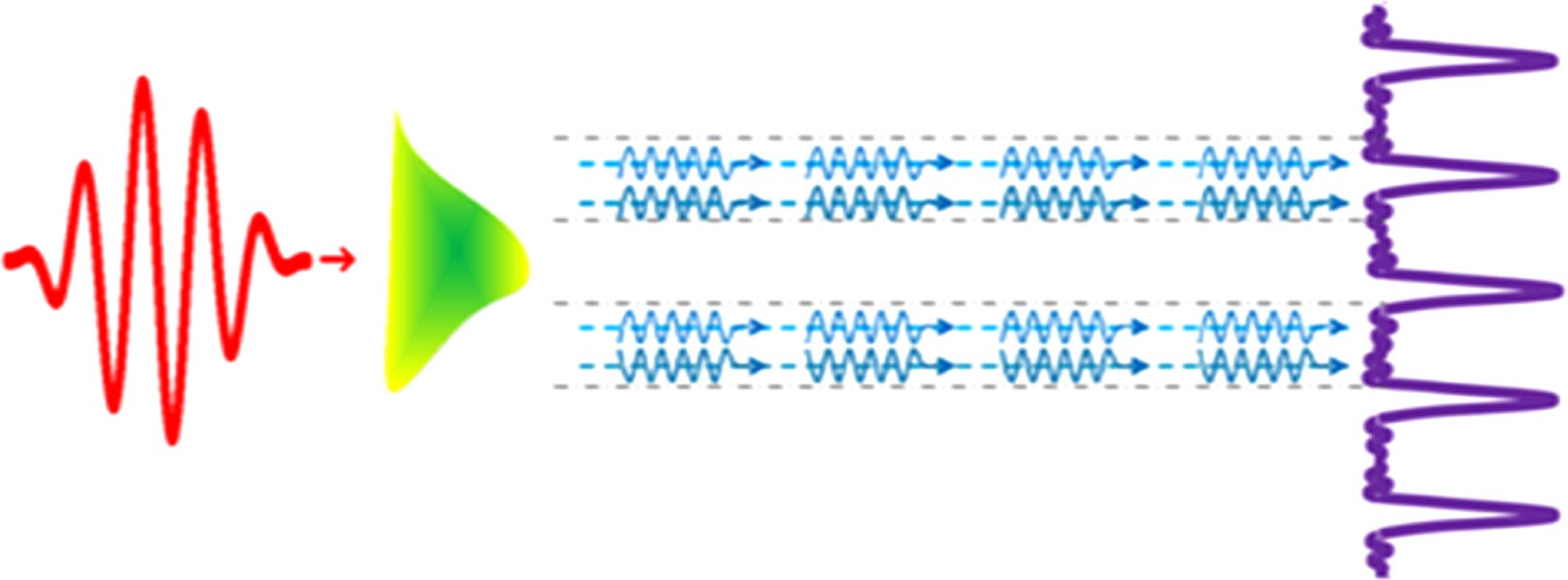
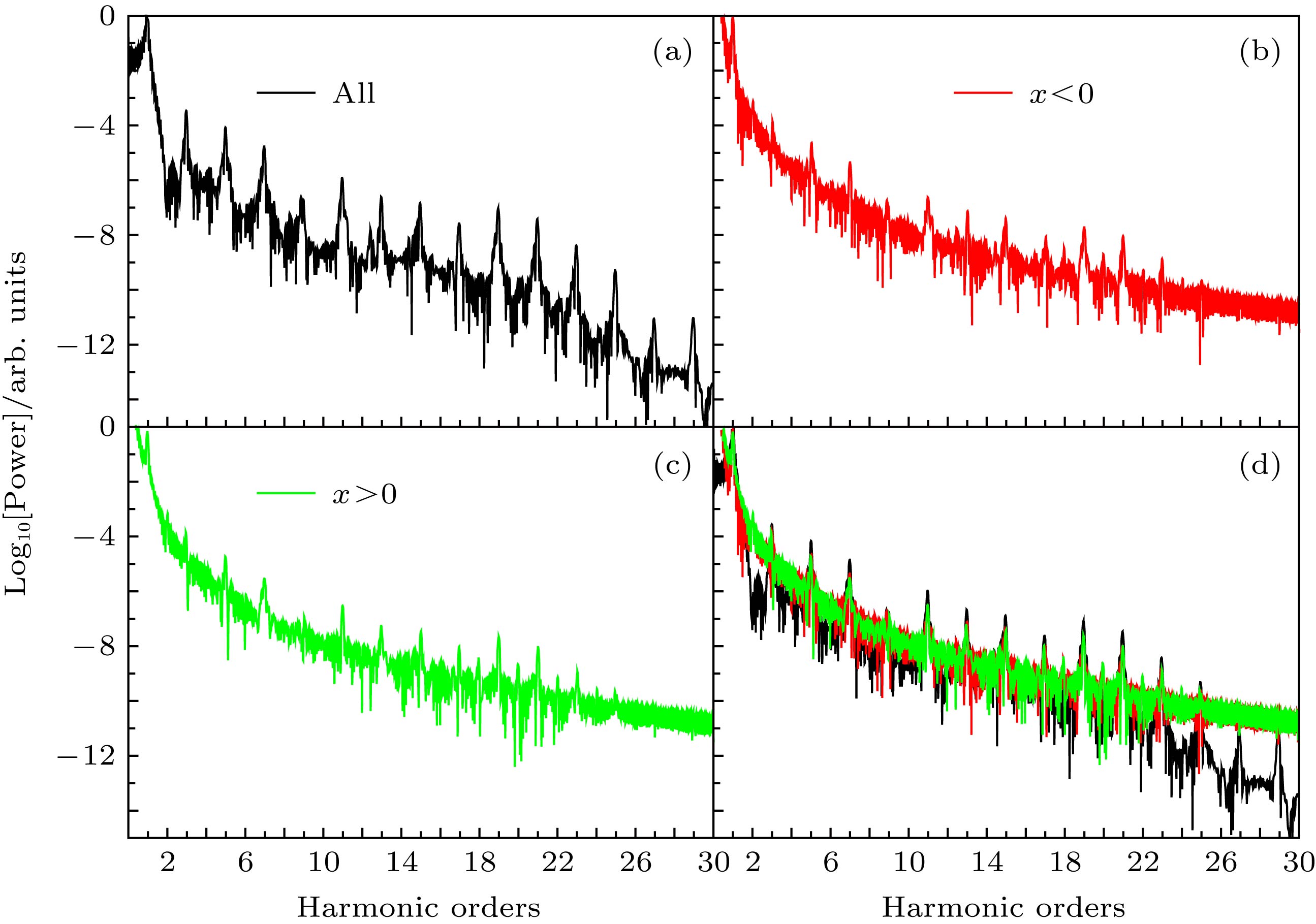
图 1 (a) 激光脉冲辐照下原子的高次谐波发射; (b)
${a_{x < 0}}(t)$ 计算得到的谐波谱; (c)${a_{x > 0}}(t)$ 计算得到的谐波谱; (d) 三个谐波谱的对比Fig. 1. (a) High-order harmonic emission of atoms irradiated by laser pulses; (b) harmonic spectra calculated from
${a_{x < 0}}(t)$ ; (c) harmonic spectra calculated from${a_{x > 0}}(t)$ ; (d) the comparison of three harmonic spectra. -
[1] Ozaki T, Ganeev R A, Ishizawa A, Kanai T, Kuroda H 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 253902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Dromey B, Zepf M, Gopal A, Wei M S, Tatarakis M 2006 Nat. Phys. 2 456
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Krausz F, Brabec T 1998 Opt. Photonics News 9 46
[4] Emma P, Akre R, Arthur J, Bionta R, Bostedt C, BozekJ, Brachmann A, Bucksbaum P, Coffee R, Decker F G, Ding Y, Dowell D, Edstrom S 2010 Nat. Photonics 4 641
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Gibsone A, Paul A, Wagner N 2003 Science 302 95
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Cingoz A, Yost D C, Allison T K, Ruehl A, Fermann M E, Hart I, Ye J 2012 Nature 482 68
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Goulielmakis E, Schultze M, Hofstetter M, Yakovlev V S, Gagnon J, Uiberacker M, Aquila A L 2008 Science 320 1614
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Qin M, Zhu X, Zhang Q, Lu P 2012 Opt. Lett. 37 5208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Curkum P B 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 71 1994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Pan Y, Guo F M, Jin C, Yang Y J, Ding D J 2019 Phys. Rev. A 99 033411
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Botheron P, Pons B 2010 Phys. Rev. A 82 021404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wei S S, Li S Y, Guo F M, Yang Y J, Wang B B 2013 Phys. Rev. A 87 063418
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Song Y, Li S Y, Liu X S, Chen J G, Zeng S L, Yang Y J 2012 Phys. Rev. A 86 033424
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Song Y, Li S Y, Liu X S, Guo F M, Yang Y J 2013 Phys. Rev. A 88 053419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 田原野, 郭福明, 曾思良, 杨玉军 2013 62 113201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tian Y Y, Guo F M, Zeng S L, Yang Y J 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 113201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Han J X, Wang J, Qiao Y, Liu A H, Guo F M, Yang Y J 2019 Opt. Express 27 8768
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yang Y J, Chen G, Chen J G, Zhu Q R 2004 Chin. Phys. Lett. 21 652
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 刘艳, 贾成, 郭福明, 杨玉军 2016 65 033201
Liu Y, Jia C, Guo F M, Yang Y Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 033201
[19] Tian Y Y, Li S Y, Wei S S, Guo F M, Zeng S L, Chen J G, Yang Y J 2014 Chin. Phys. B 23 053202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 宋文娟, 郭福明, 陈基根, 杨玉军 2018 67 033201
Song W J, Guo F M, Chen J G, Yang Y J 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 033201
[21] He X, Miranda M, Schwenke J, Giulbaud O, Ruchon T, Heyl C, Georgadiou E 2009 Phys. Rev. A 79 063829
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Chen Y J, Zhang B 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 053402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 9198
- PDF下载量: 81
- 被引次数: 0

















 下载:
下载: