-
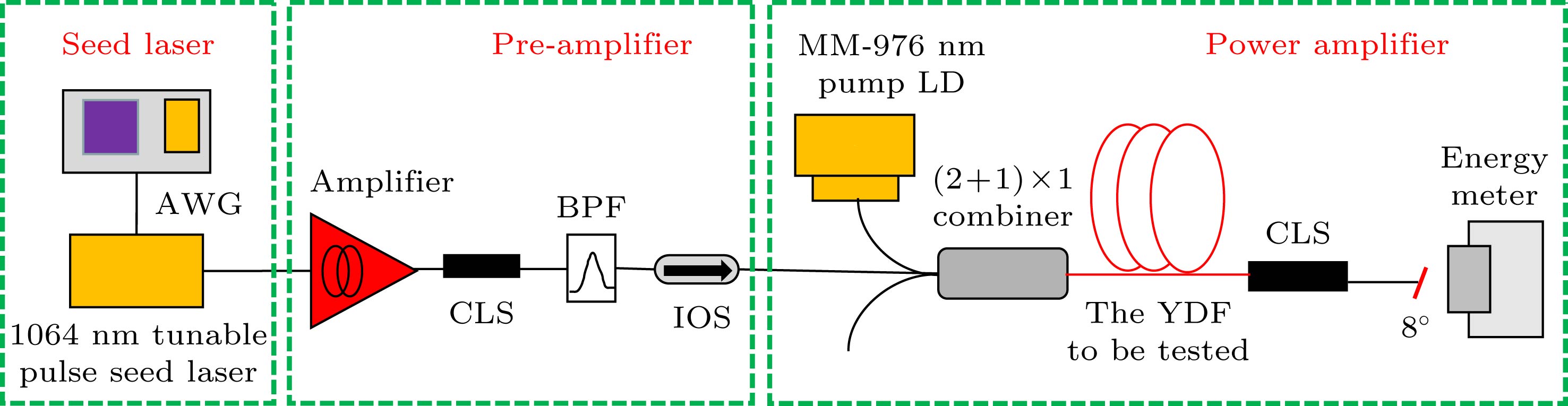
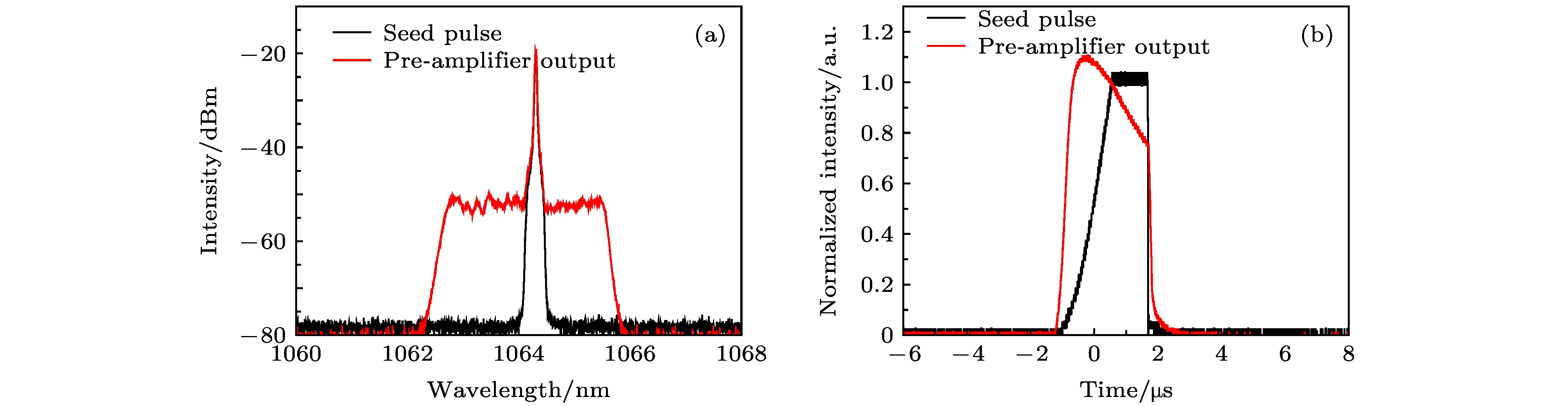
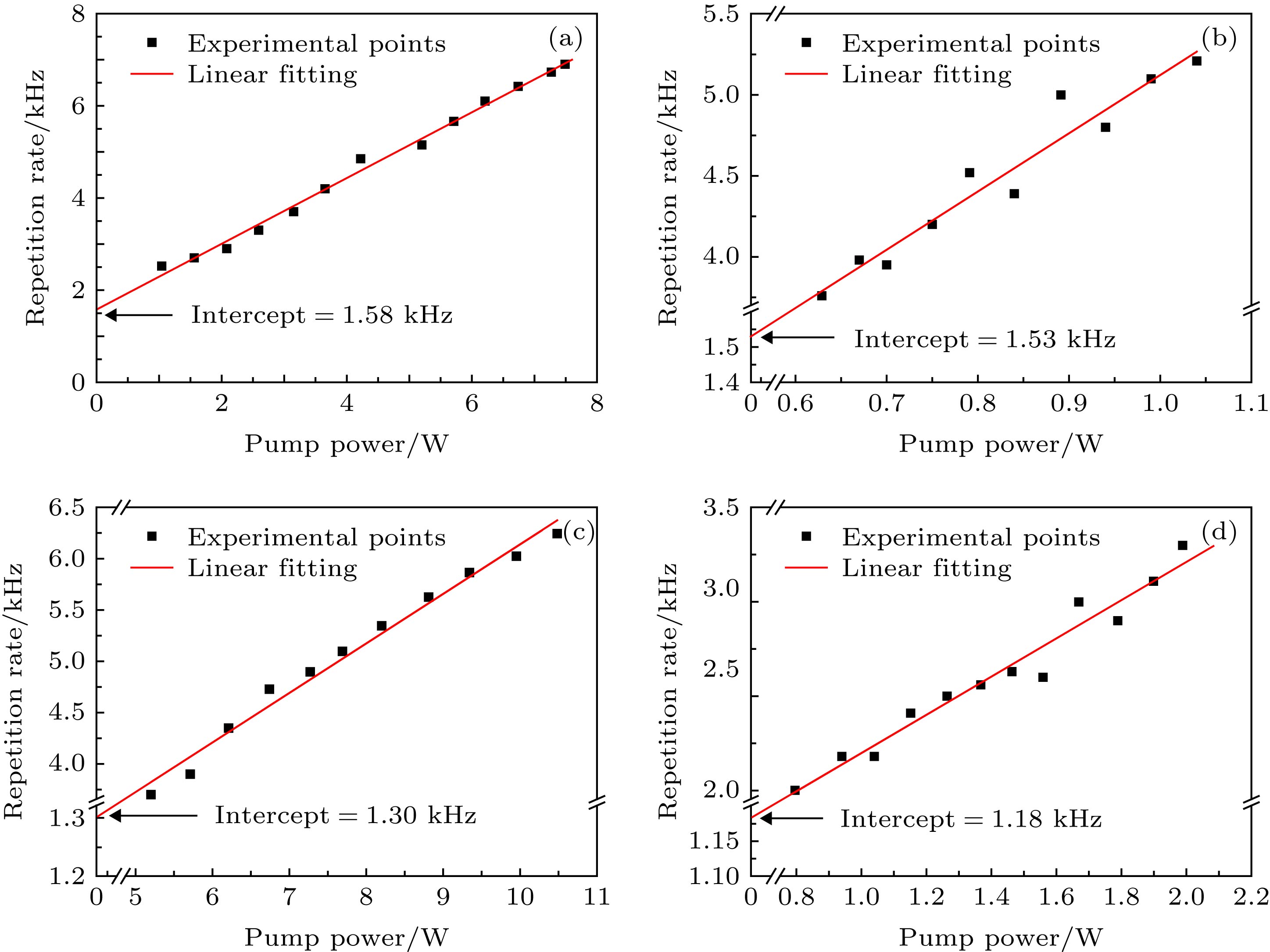
提出了一种基于脉冲光纤激光放大器能量特性测量有源光纤中稀土离子上能级寿命的方法. 根据光纤激光器速率方程, 能够确定有源光纤中反转粒子数储能随抽运功率和时间的变化关系; 实验测量不同种子光脉冲重复频率下放大器输出单脉冲能量的变化, 可以反映出反转粒子数随时间的变化情况, 进而根据理论模型得到激活离子的激光上能级寿命. 实验搭建了1.06 μm掺镱(Yb3+)光纤激光放大系统对该测量方法理论模型的合理性进行了验证, 对几种常见商用掺Yb3+有源光纤激光上能级寿命分别进行了多次测量和数据处理, 测量结果以及变化趋势与其他相关报道中的结果相符.The upper-laser-level lifetime (fluorescence lifetime) of the rear earth dopant in the active fiber is a key parameter which indicates the performance of the fiber, and takes an important role in designing the laser system. However, the accurate measurement of fluorescence lifetime in active fiber remains challenging, which mainly rely on the direct measurement of laser induced fluorescence lifetime of the active fiber or lifetime measurement of bulk laser glass. The former method suffers the error due to the amplified spontaneous emission and the reabsorption process, while the latter ignores the influence of high temperature and tension produced during the fiber drawing on the emission behavior of the material. Therefore, the accuracy of these measurements can become a problem. In this work, we propose a new approach to measuring the upper-laser-level lifetime of the rear earth dopant in the active fiber based on the power/energy performance of the fiber amplifier. The population inversion, i. e. the energy storage, in the active fiber of a fiber amplifier is a function of upper-laser-level lifetime. Therefore, the upper-laser-level lifetime can be derived by measuring the average power or output pulse energy of the amplifier, given that the energy storage in the active fiber is extracted adequately by a seed laser. Using the rate equations, we model the population inversion and energy storage in the active fiber each as a function of pump power and time, and the resulting relationship between the upper-laser-level lifetime and the average output power. The upper-laser-level lifetimes of several commercial Yb-doped active fibers are experimentally measured by this method through using the fibers as the gain media of the amplifier operated at 1064 nm. The convenience of experimental data processing is also discussed. The measured lifetime and evolution trend of the lifetime with dopant concentration exhibitthat they are in good agreement with those from other reports and the theoretical model, which verifies the feasibility of this method.
-
Keywords:
- upper-laser-level lifetime /
- active fiber /
- fiber laser /
- fiber amplifier
[1] Fu S J, Shi W, Feng Y, Zhang L, Yang Z G, Xu S H, Zhu X S, Norwood R A, Peyghambarian N 2017 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 34 A49
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Pask H M, Carman R J, Hanna D C, Tropper A C, Mackechnie C J, Barber P R, Dawes J M 1995 IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. 1 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Sintov Y, Glick Y, Koplowitch T, Nafcha Y 2008 Opt. Commun. 281 1162
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Geng J H, Wu J F, Jiang S B, Yu J R 2007 Opt. Lett. 32 355
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Vivona M, Kim J, Zervas M N 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 4097
[6] Paschotta R, Nilsson J, Barber P R, Caplen J E, Tropper A C, Hanna D C 1997 Opt. Commun. 136 375
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Guo Y, Zheng X, Ming H, Zhang Q J 2001 Chin. Phys. Lett. 18 1337
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 蒋红玫, 杨博思, 李贺龙, 徐淮良 2013 中国光学 6 5
Jiang H M, Yang B S, Li H L, Xu H L 2013 Chin. Opt. 6 5
[9] 陆同兴, 路轶群 2009 激光光谱技术原理及应用 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社) 第170−193页
Lu T X, Lu Y Q 2009 Principle and Application of Laser Spectroscopy (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China Press) pp170−193 (in Chinese)
[10] Li A H, Zheng Z R, Lü Q, Xu Z P, Xu C, Xu Y H, Liu W L 2011 Opt. Lett. 36 1056
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Biémont E, Quinet P, Dai Z W, Jiang Z K, Zhang Z G, Xu H L, Svanberg S 2002 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 35 4743
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tang G W, Qian G Q, Shi Z G, Liu Y, Huang B W, He Y C, Jiang L C, Sun M, Qian Q, Yang Z M 2019 Opt. Mater. Express 9 362
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Piccoli R, Mechin D, Robin T, Taccheo S 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 4370
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Newell T C, Peterson P, Gavrielides A, Sharma M P 2007 Opt. Commun. 273 256
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 欧攀 2014 高等光学仿真(第2版)(北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社) 第296页
Ou P 2014 Advanced Optical Simulation (second edition) (Beijing: Beihang University Press) p296 (in Chinese)
[16] Giles C R, Desurvire E 1991 J. Lightwave Technol. 9 271
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang Y, Martinez-Rios A, Po H 2003 Opt. Commun. 224 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Hardy A, Oron R 1997 IEEE J. Quantum Elect. 33 307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 黄琳, 代志勇, 刘永智 2009 58 6992
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang L, Dai Z Y, Liu Y Z 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 6992
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
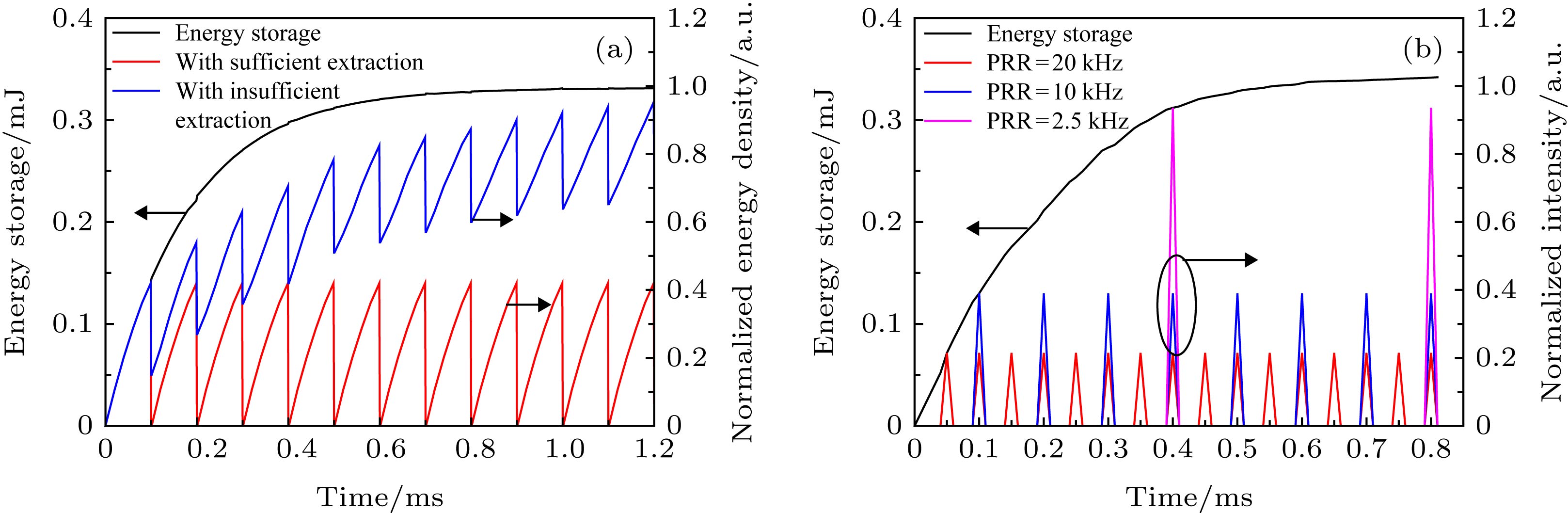
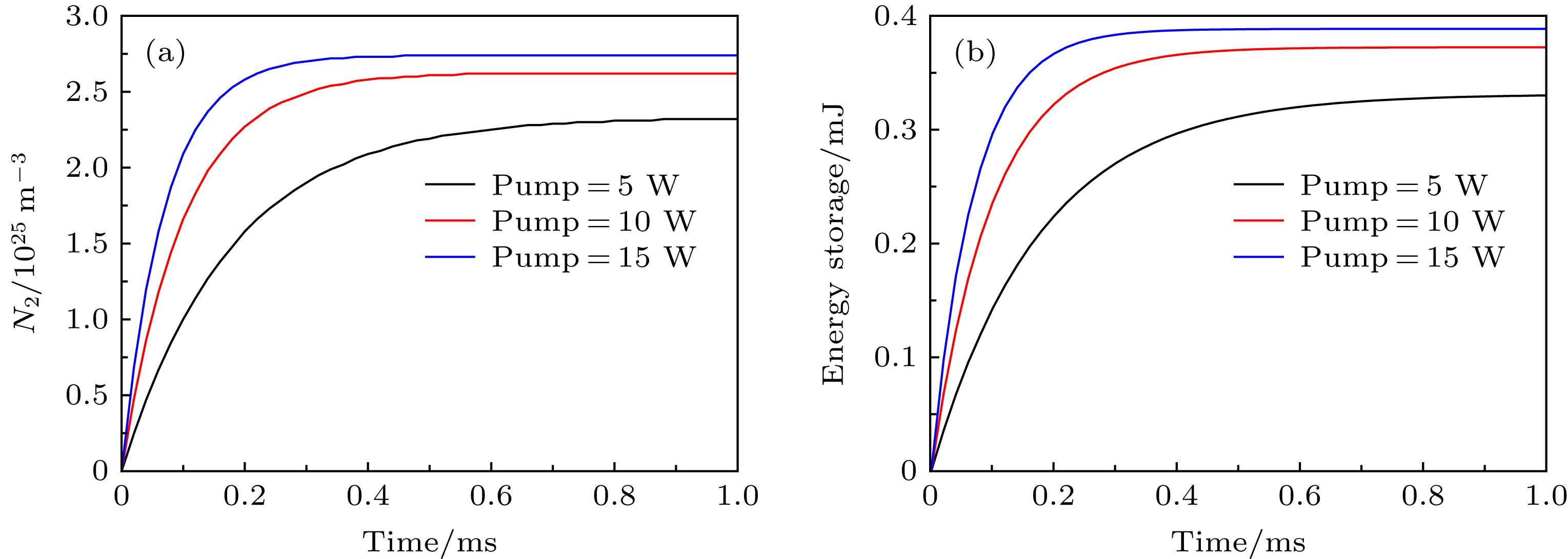
图 2 抽运功率5 W时有源纤储能及(a)不同提取效率下归一化储能密度随时间的变化(PRR = 10 kHz), (b)放大级输出脉冲强度与种子光重复频率之间的关系
Fig. 2. Energy storage with 5 W launched pump power and (a) normalized energy density with different extraction efficiency as a function of time (PRR = 10 kHz), (b) the relationship between output pulse intensity and seed PRR.
表 1 公式中各参数的物理意义及参考值
Table 1. The physical meaning and their reference value in the theoretical model.
符号/单位 物理意义 参考值 λp/nm 抽运光波长 976 σa/m2 抽运光受激吸收截面 2.6 × 10–26 σe/m2 抽运光受激发射截面 2.6 × 10–26 Γp 抽运光重叠因子 0.0024 N/m–3 有源光纤掺杂粒子密度 6 × 1025 h/J·s 普朗克常量 6.62 × 10–34 c/m·s–1 真空中光速 3 × 108 τ/ms 上能级寿命 0.8 A/m3 纤芯横截面积 7 × 10–11 -
[1] Fu S J, Shi W, Feng Y, Zhang L, Yang Z G, Xu S H, Zhu X S, Norwood R A, Peyghambarian N 2017 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 34 A49
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Pask H M, Carman R J, Hanna D C, Tropper A C, Mackechnie C J, Barber P R, Dawes J M 1995 IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. 1 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Sintov Y, Glick Y, Koplowitch T, Nafcha Y 2008 Opt. Commun. 281 1162
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Geng J H, Wu J F, Jiang S B, Yu J R 2007 Opt. Lett. 32 355
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Vivona M, Kim J, Zervas M N 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 4097
[6] Paschotta R, Nilsson J, Barber P R, Caplen J E, Tropper A C, Hanna D C 1997 Opt. Commun. 136 375
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Guo Y, Zheng X, Ming H, Zhang Q J 2001 Chin. Phys. Lett. 18 1337
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 蒋红玫, 杨博思, 李贺龙, 徐淮良 2013 中国光学 6 5
Jiang H M, Yang B S, Li H L, Xu H L 2013 Chin. Opt. 6 5
[9] 陆同兴, 路轶群 2009 激光光谱技术原理及应用 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社) 第170−193页
Lu T X, Lu Y Q 2009 Principle and Application of Laser Spectroscopy (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China Press) pp170−193 (in Chinese)
[10] Li A H, Zheng Z R, Lü Q, Xu Z P, Xu C, Xu Y H, Liu W L 2011 Opt. Lett. 36 1056
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Biémont E, Quinet P, Dai Z W, Jiang Z K, Zhang Z G, Xu H L, Svanberg S 2002 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 35 4743
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tang G W, Qian G Q, Shi Z G, Liu Y, Huang B W, He Y C, Jiang L C, Sun M, Qian Q, Yang Z M 2019 Opt. Mater. Express 9 362
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Piccoli R, Mechin D, Robin T, Taccheo S 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 4370
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Newell T C, Peterson P, Gavrielides A, Sharma M P 2007 Opt. Commun. 273 256
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 欧攀 2014 高等光学仿真(第2版)(北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社) 第296页
Ou P 2014 Advanced Optical Simulation (second edition) (Beijing: Beihang University Press) p296 (in Chinese)
[16] Giles C R, Desurvire E 1991 J. Lightwave Technol. 9 271
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang Y, Martinez-Rios A, Po H 2003 Opt. Commun. 224 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Hardy A, Oron R 1997 IEEE J. Quantum Elect. 33 307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 黄琳, 代志勇, 刘永智 2009 58 6992
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang L, Dai Z Y, Liu Y Z 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 6992
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 11432
- PDF下载量: 196
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: