-
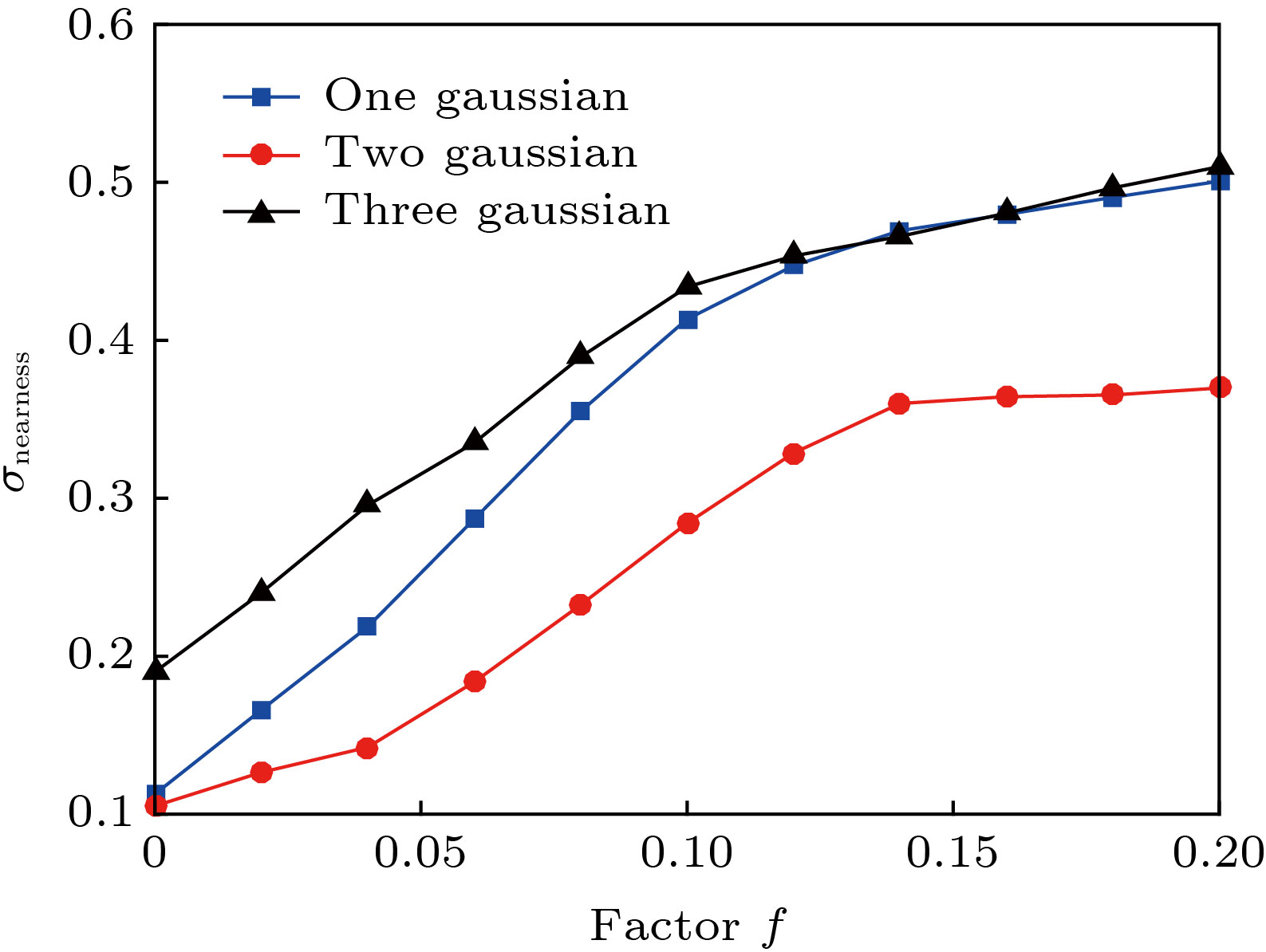
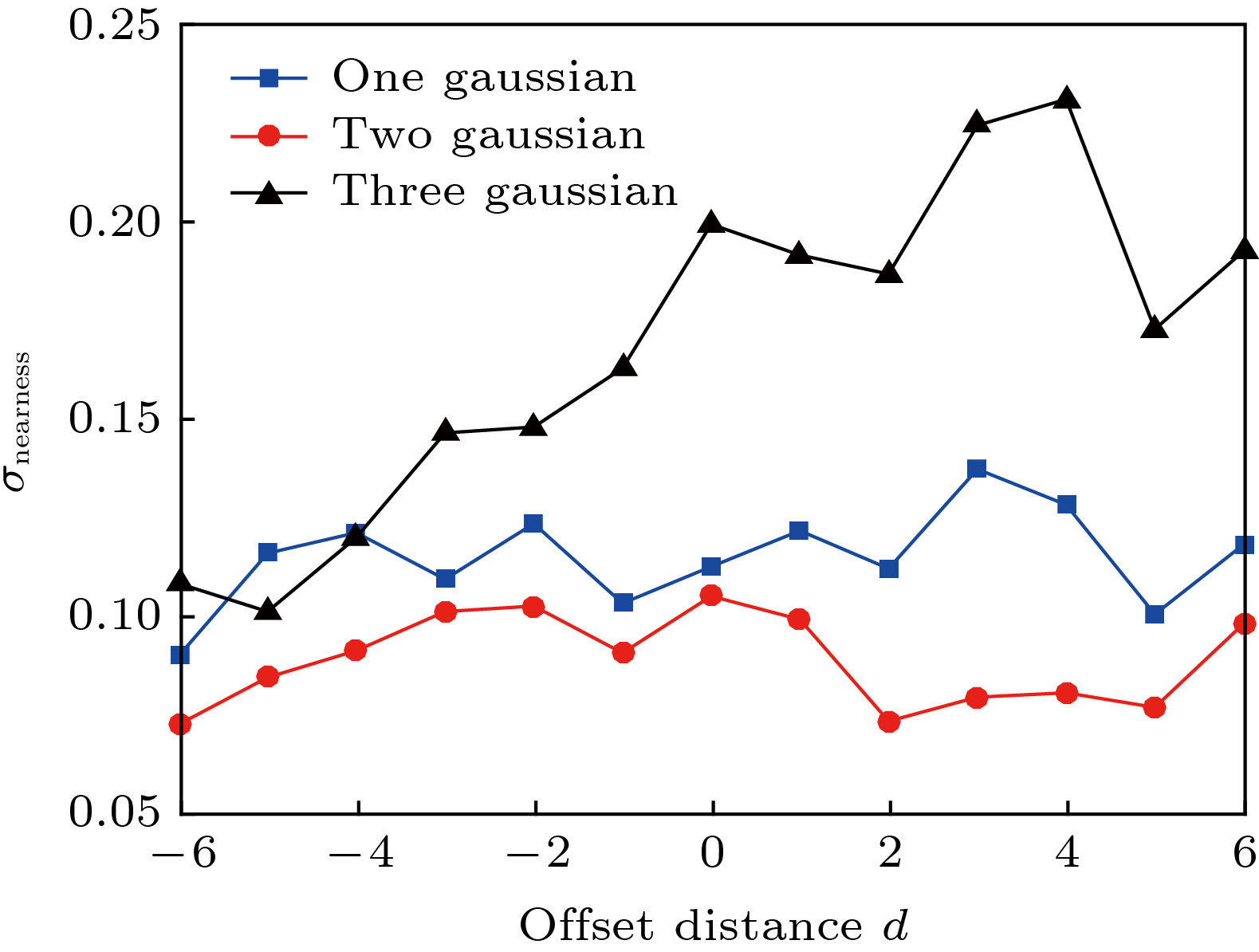
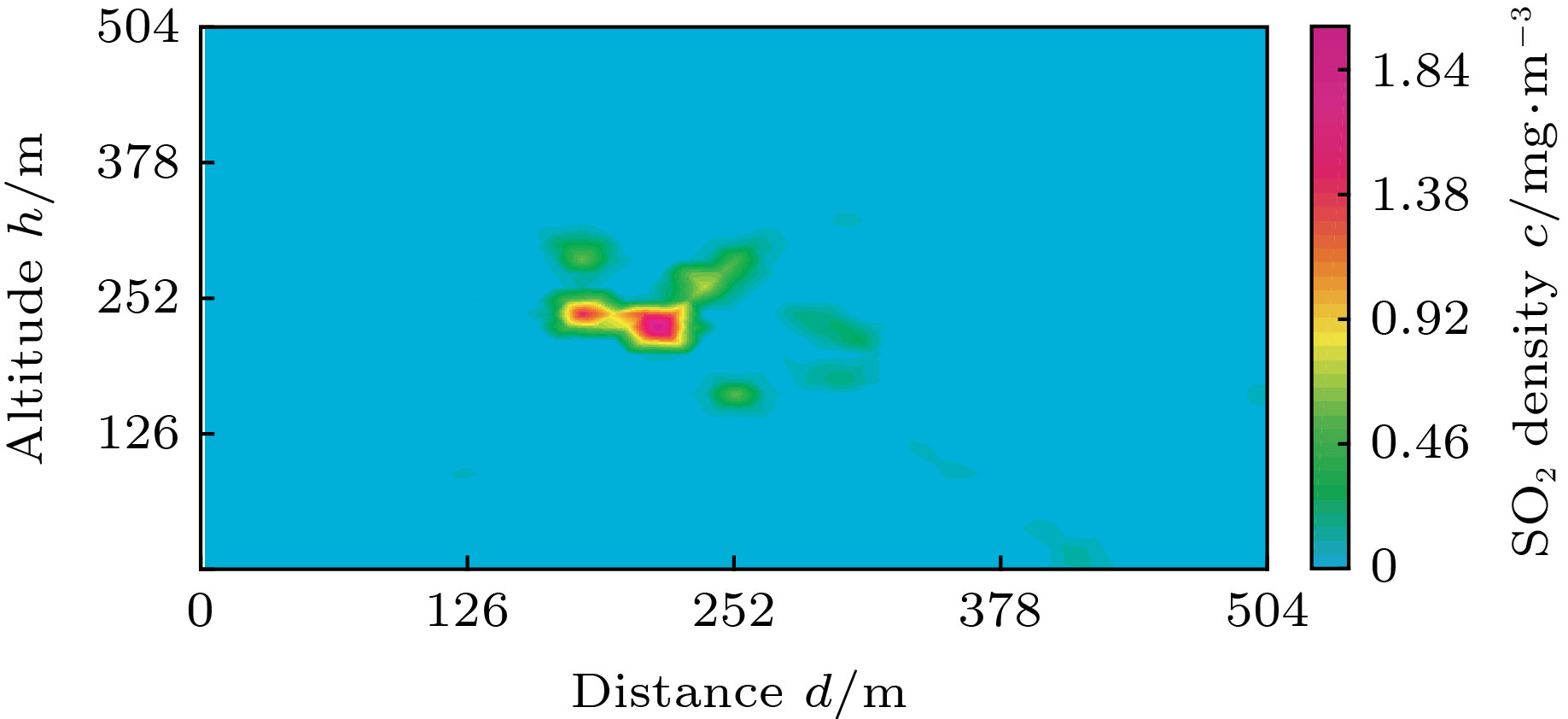
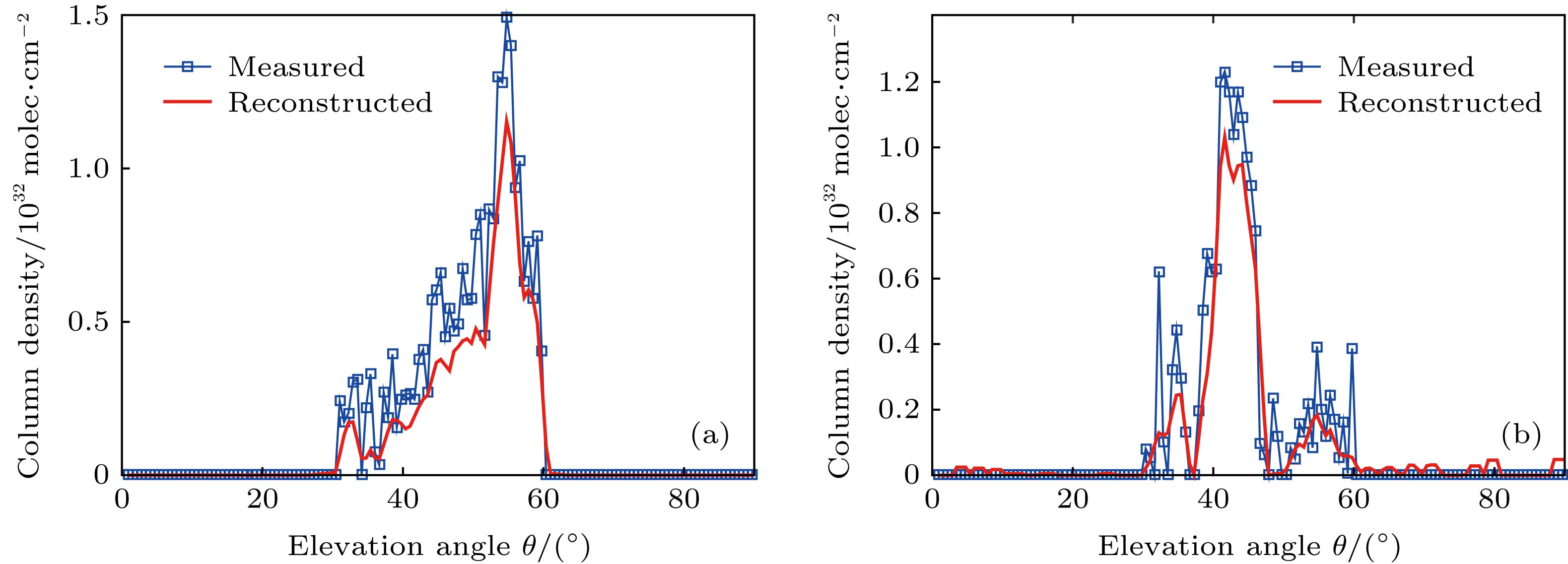
烟羽断层重建一般使用两台光谱仪采集数据, 属于典型的不完全角度重建. 为了提高重建结果的稳定性和接近度, 将压缩感知理论引入气体分布重建领域. 提出了一种新的计算机层析算法——低三阶导数全变分法, 用于重建电厂烟囱排放的SO2截面的二维分布. 使用低三阶导数模型模拟气体扩散, 认为气体浓度对位置的三阶导数是稀疏的. 将重建图像的全变分作为目标函数, 并通过数值最优化方法求得气体浓度分布的最优解. 数值模拟的结果表明, 与传统的低三阶导数法相比, 低三阶导数全变分法将接近度提高了80%以上. 外场实验表明, 重建图像的一致性相关因子达0.9023. 低三阶导数全变分法能有效消除测量误差对图像重建的影响, 提高重建图像的质量.In this paper, we present a novel method of computing tomography , i.e. the low third deviation total variation (LTD-TV) method to reconstruct the two-dimensional distribution of SO2 of stack plume. The path-integral data of the plume are collected by only two imaging differential absorption spectrometers (IDOASs). However, due to the insufficient number of IDOASs, conventional reconstruction methods result in severe streaking artifacts. The traditional low third derivative method is widely used to reconstruct the gas distribution. It suggests a spatial distribution of gas concentrations, which has a low third spatial derivative in every direction and at every point. The derivatives are usually set to be zero. The method improves the reconstructed images by providing extra information which contains the gas concentration in line with the distribution of the second order polynomial, but it also gives rise to the extra artifacts. To address this issue, we further improve the traditional low third deviation (LTD) method by suggesting that the third derivative of gas concentration is sparse. We therefore adopt the compressed sensing (CS) based total variation (TV) optimization framework. In the LTD-TV method, a logarithmic barrier function with TV is used as an objective function. The objective function is then optimized by numerical optimization method, in which the gradient projection is used to determine its descent direction and a Barzilai-Borwein scheme to determine its step-size. The final results are obtained by iterative optimization. Numerical simulations are performed to simulate the reconstruction of gas distribution which is in line with Gaussian distribution. Compared with the conventional LTD method, the LTD-TV method enhances the proximity by 20%—80%, and greatly corrects the artifacts near the edges of images. The result of field campaign suggests that concordance correlation factor between the collected data and reconstructed image is 0.9023. It also shows that it has good noise immunity. In summary, it is the first time that we have introduced the CS theory into the field of gas plume reconstruction. Compared with the existing methods, the LTD-TV method can greatly reduce the artifacts and increase the credibility of the reconstruction.
-
Keywords:
- spectral absorption by atmospheric gases /
- plume reconstruction /
- low-third-deviation total variational method /
- imaging differential optical absorption spectrometer
[1] Yao L, Garmash O, Bianchi F, Zheng J, Yan C, Kontkanen 2018 Science 361 278
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 饶瑞中 2012 现代大气光学(北京: 科学出版社) 第551页
Rao R Z 2012 Modern Atmospheric Optics (Beijing: Science Press)p551(in Chinese)
[3] Samanta A, Todd L A 2000 Atmos. Environ. 34 699
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Todd L A, Ramachandran G 1994 Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 55 403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 韦民红, 童敏明, 李素文, 肖建于 2015 光谱学与光谱分析 35 2252
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wei M H, Tong M M, Li S W, Xiao J Y 2015 Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 35 2252
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Drescher A C, Gadgil A J, Price P N, Nazaroff W W 1996 Atmos. Environ. 30 929
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Price P N, Fischer M L, Gadgil A J, Sextro R G 2001 Atmos. Environ. 35 2827
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Olaguer E P 2011 Atmos. Environ. 45 6980
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Olaguer E P, Erickson M H, Wijesinghe A, Neish B S 2016 J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc. 66 164
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Olaguer E P, Stutz Jochen, Erickson M H, Hurlock S C, Cheung R, Tsai C, Colosimo S F, Festa J, Wijesinghe A, Neish B S 2017 Atmos. Environ. 150 220
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Johansson M, Bo G, Rivera C, Zhang Y 2009 Bull. Volcanol. 71 1169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Kazahaya R, Mori T, Kazahaya K, Hirabayashi J 2008 Geophys. Res. Lett. 35 344
[13] Casaballe N, Osorio M, Martino M D, Frins E 2017 Earth Space Sci. 4 723
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 杨富强, 张定华, 黄魁东, 王鹍, 徐哲 2014 63 058701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang F Q, Zhang D H, Huang K D, Wang K, Xu Z 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 058701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Sidky E Y, Kao C M, Pan X 2006 J. X-Ray Sci. Technol. 14 119
[16] Sidky E Y, Pan X C 2008 Phys. Med. Biol. 53 4777
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Niu T, Zhu L 2012 Med. Phys. 39 4588
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Barzilai J, Borwein J M 1988 IMA J. Numer. Anal. 8 141
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 司福祺, 谢品华, Heue K P, 刘诚, 彭夫敏, 刘文清 2008 57 6018
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Si F Q, Xie P H, Heue K P, Liu C, Peng F M, Liu W Q 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 6018
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 周海金 2013 博士学位论文 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
Zhou H J 2013 Ph. D. Dissertation (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China) (in Chinese)
[21] Wu C F, Chang S Y 2011 Atmos. Environ. 45 1476
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 周斌, 刘文清, 齐锋, 李振璧, 崔延军 2002 光学学报 22 957
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou B, Liu W Q, Qi F, Li Z B, Cui Y J 2002 Acta Opt. Sin. 22 957
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 刘世胜 魏庆农 王峰平 詹锴 2009 大气与环境光学学报 4 118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu S S, Wei Q N, Wang F P, Zhan K 2009 J. Atmos. Environ. Opt. 4 118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Hartl A, Song B C, Pundt I 2006 Atmos. Chem. Phys. 6 847
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 2 传统LTD法与LTD-TV法比较 (a), (b), (c)测试图形; (d), (e), (f)传统LTD法重建图形; (g), (h), (i) LTD-TV法20000次迭代重建图形
Fig. 2. Comparison between traditional LTD algorithm and LTD-TV algorithm: (a), (b), (c) Test distribution; (d), (e), (f) reconstruction of distribution using traditional LTD algorithm; (g), (h), (i) reconstruction of distribution using LTD-TV algorithm with 20000 iterations.
-
[1] Yao L, Garmash O, Bianchi F, Zheng J, Yan C, Kontkanen 2018 Science 361 278
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 饶瑞中 2012 现代大气光学(北京: 科学出版社) 第551页
Rao R Z 2012 Modern Atmospheric Optics (Beijing: Science Press)p551(in Chinese)
[3] Samanta A, Todd L A 2000 Atmos. Environ. 34 699
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Todd L A, Ramachandran G 1994 Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 55 403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 韦民红, 童敏明, 李素文, 肖建于 2015 光谱学与光谱分析 35 2252
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wei M H, Tong M M, Li S W, Xiao J Y 2015 Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 35 2252
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Drescher A C, Gadgil A J, Price P N, Nazaroff W W 1996 Atmos. Environ. 30 929
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Price P N, Fischer M L, Gadgil A J, Sextro R G 2001 Atmos. Environ. 35 2827
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Olaguer E P 2011 Atmos. Environ. 45 6980
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Olaguer E P, Erickson M H, Wijesinghe A, Neish B S 2016 J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc. 66 164
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Olaguer E P, Stutz Jochen, Erickson M H, Hurlock S C, Cheung R, Tsai C, Colosimo S F, Festa J, Wijesinghe A, Neish B S 2017 Atmos. Environ. 150 220
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Johansson M, Bo G, Rivera C, Zhang Y 2009 Bull. Volcanol. 71 1169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Kazahaya R, Mori T, Kazahaya K, Hirabayashi J 2008 Geophys. Res. Lett. 35 344
[13] Casaballe N, Osorio M, Martino M D, Frins E 2017 Earth Space Sci. 4 723
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 杨富强, 张定华, 黄魁东, 王鹍, 徐哲 2014 63 058701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang F Q, Zhang D H, Huang K D, Wang K, Xu Z 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 058701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Sidky E Y, Kao C M, Pan X 2006 J. X-Ray Sci. Technol. 14 119
[16] Sidky E Y, Pan X C 2008 Phys. Med. Biol. 53 4777
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Niu T, Zhu L 2012 Med. Phys. 39 4588
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Barzilai J, Borwein J M 1988 IMA J. Numer. Anal. 8 141
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 司福祺, 谢品华, Heue K P, 刘诚, 彭夫敏, 刘文清 2008 57 6018
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Si F Q, Xie P H, Heue K P, Liu C, Peng F M, Liu W Q 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 6018
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 周海金 2013 博士学位论文 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
Zhou H J 2013 Ph. D. Dissertation (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China) (in Chinese)
[21] Wu C F, Chang S Y 2011 Atmos. Environ. 45 1476
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 周斌, 刘文清, 齐锋, 李振璧, 崔延军 2002 光学学报 22 957
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou B, Liu W Q, Qi F, Li Z B, Cui Y J 2002 Acta Opt. Sin. 22 957
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 刘世胜 魏庆农 王峰平 詹锴 2009 大气与环境光学学报 4 118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu S S, Wei Q N, Wang F P, Zhan K 2009 J. Atmos. Environ. Opt. 4 118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Hartl A, Song B C, Pundt I 2006 Atmos. Chem. Phys. 6 847
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 8414
- PDF下载量: 49
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: