-
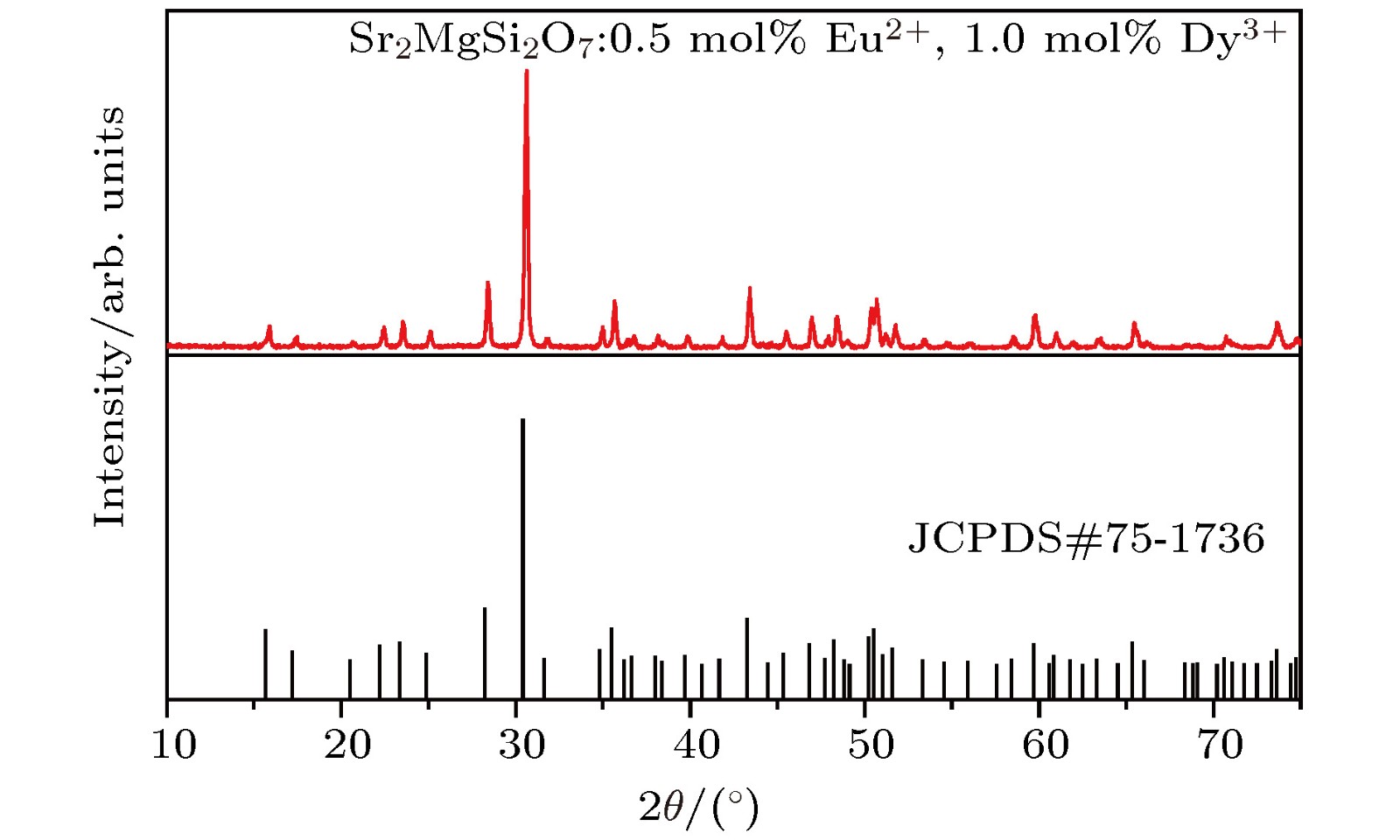
为了得到最长有效余辉时间的Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+, Dy3+荧光粉, 应用二次通用旋转组合设计对实验进行全程优化, 建立了稀土离子掺杂浓度Eu2+, Dy3+和有效余辉时间的二元二次回归方程模型, 应用遗传算法计算得到有效余辉时间的理论最大值. 采用高温固相法合成了最优掺杂浓度Sr2MgSi2O7:0.5 mol%Eu2+, 1.0 mol%Dy3+的荧光粉, 在370 nm激发下观察到了465 nm的特征发射, 这归因于Eu2+的4f65d1—4f7跃迁. 测量了最优荧光粉的热释发光特性, 计算得到了陷阱深度为0.688 eV, 讨论了长余辉发光的特性.An optimization method is used to obtain the longest effective afterglow time in the rare earth ions doped long lasting phosphors. The effective afterglow time is defined as the time for the intensity to decays to 10% of the initial intensity. In this paper, we choose the Eu2+ and Dy3+ coped Sr2MgSi2O7 as the experimental objects. In order to obtain the longest effective afterglow time of Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+, Dy3+ phosphor, the experiment is optimized by quadratic general rotation combination design. The Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+, Dy3+ phosphor are synthesized via a solid-state reaction. The effective afterglow time is obtained by the afterglow decay curve. A binary quadratic regression equation model relating the rare earth ions Eu2+/Dy3+ doping concentrations to the effective afterglow time is established. The genetic algorithm is used to solve the equation. The optimal doping concentration of Eu2+ and Dy3+ are 0.5 mol% and 1.0 mol%, respectively. The theoretical maximum value of effective afterglow time is calculated to be 321 s. The phosphor with the optimal doping concentration Sr2MgSi2O7:0.5 mol% Eu2+, 1.0 mol% Dy3+ are synthesized by the same method as that of synthesizing the frontal samples. The X-ray diffraction shows that the optimal sample prepared is of pure phase, and the doping ions have no effect on the lattice structure of the matrix. A characteristic emission at 465 nm due to the 4f65d1−4f7 transition of Eu2+is observed under the 370 nm excitation. The afterglow curve of the optimal sample is measured and the effective afterglow time is 333 s which has a good match with the theoretically calculated value of 321 s. The thermoluminescence spectrum of the optimal phosphor is measured, and the trap depth is calculated to be 0.688 eV according to the Chen’s model. Moreover, the long-lasting luminescence process of Eu2+ as the luminescence center of Sr2MgSi2O7 matrix is discussed in the energy level diagram.
-
Keywords:
- experimental optimization design /
- long afterglow /
- Sr2MgSi2O7 /
- Eu2+/Dy3+
[1] Chang C K, Mao D L, Shen J F, Feng C L 2003 J. Alloy. Compd. 348 224
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Johnson E J, Kafalas J, Dyes W A 1982 Appl. Phys. Lett. 40 993
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 梅屹峰, 唐远河, 梅小宁, 刘汉臣, 刘骞, 余洋, 李宁远, 高恒 2016 65 170701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mei Q F, Tang Y H, Mei X N, Liu H C, Liu Q, Yu Y, Li N Y, Gao H 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 170701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 彭玲玲, 曹仕秀, 赵聪, 刘碧桃, 韩涛, 李凤, 黎小敏 2018 67 187801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Peng L L, Cao S X, Zhao C, Liu B T, Han T, Li F, Li X M 2018 Acta Phys Sin. 67 187801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 刘文全, 朝克夫, 武文杰, 包富泉, 周炳卿 2018 65 207801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu W Q, Zhao K F, Wu W J, Bao F Q, Zhou B Q 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 207801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Lindmayer J 1988 Solid State Technol. 31 135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Fan W H, Wang Y C, Xu H, Li D, Wei Z, Yang B Z, Niu L H 1999 J. Appl. Phys. 85 451
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhang Y, Wang B, Liu X, Xiao M 2010 J. Appl. Phys. 107 103502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Yamashita S A, Ogawa N 1989 Phys. States Solidi B 118 89
[10] Ou Y Y, Zhou W J, Liu C M, Lin L T, Brik G M, Dorenbos P 2018 J. Phys. Chem. C 122 2959
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Yan J, Liu C M, Vlieland J, Zhou J B, Dorenbos P, Huang Y, Tao Y, Liang H B 2017 J. Lumin. 183 97
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Liu F, Yan W, Chuang Y J, Zhen Z, Xie J, Pan Z 2013 Sci. Rep. 3 1554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Xu X, He Q, Yan L 2013 J. Alloy. Compd. 574 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang J, Ma Q, Wang Y, Shen H, Yuan Q 2017 Nanoscale 9 6204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 孙佳石, 李香萍, 李树伟, 吴金磊, 石琳琳, 徐赛, 张金苏, 程丽红, 陈宝玖 2017 66 100201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun J S, Li X P, Wu J L, Li S W, Shi L L, Xu S, Zhang J S, Cheng L H, Chen B J 2017 Acta Phys Sin. 66 100201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 田碧凝 2013 硕士学位论文 (大连: 大连海事大学)
Tian B N 2013 M. S. Thesis (Dalian: Dalian Mar-itime University) (in Chinese)
[17] 任露泉 2009 试验优化设计与分析 (北京: 科学出版社) 第172—185页
Ren L Q 2009 Design of Experiment and Optimization (Beijing: Science Press) pp172–185 (in Chinese)
[18] 王志军, 刘海燕, 杨勇, 蒋海峰, 段平光, 李盼来, 杨志平, 郭庆林 2014 63 077802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Z J, Liu H Y, Yang Y, Jiang H F, Duan P G, Li P L, Yang Z P, Guo Q L 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 077802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 何为, 薛卫东, 唐斌 2012 优化试验设计方法及数据分析 (北京: 化学工业出版社) 第185—190页
He W, Xue W D, Tang B 2012 The Method of Opti-mal Design of Experiment and Data Analysis (Beijing: Chemical Industry Press) pp185–190 (in Chinese)
[20] 翟梓会, 孙佳石, 张金苏, 李香萍, 程丽红, 仲海洋, 李晶晶, 陈宝玖 2013 62 203301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhai Z H, Sun J S, Zhang J S, Li X P, Cheng L H, Zhong H Y, Li J J, Chen B J 2013 Acta Phys Sin. 62 203301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 程仕平, 徐慧, 王德志, 王光君, 吴壮志 2007 稀有金属材料与工程 36 1933
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cheng S P, Xu H, Wang D Z, Wang G J, Wu Z Z 2007 Rare Metal. Mat. Eng. 36 1933
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 高大海, 罗军, 葛明桥 2013 化工新型材料 41 30
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao D H, Luo J, Ge M Q 2013 New Chem. Mater. 41 30
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Xiong W W, Yin C L, Zhang Y, Zhang J L 2009 Chin. J. Mech. Eng-En. 22 862
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Tan G Z, Zhou D M, Jiang B J, Dioubate M I 2008 J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 15 845
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 石琳琳, 孙佳石, 翟梓会, 李香萍, 张金苏, 陈宝玖 2014 光子学报 43 1116002
Shi L L, Sun J S, Zhai Z H, Li X P, Zhang J S, Chen B J 2014 Acta Photo. Sin. 43 1116002
[26] Wu H, Hu Y, Chen L, Wang X 2011 J. Alloy. Compd. 509 4304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Chen R 1969 J. Appl. Phys. 40 570
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 张哲, 徐旭辉, 邱建备, 张新, 余雪 2014 光谱学与光谱分析 34 1486
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Z, Xu X H, Qiu J B, Zhang X, Yu X 2014 Spetroscopy Spectral Anal. 34 1486
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 齐智坚, 黄维刚 2013 62 197801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi Z J, Huang W G 2013 Acta Phys Sin. 62 197801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 自然因素水平编码表
Table 1. Natural factor level coding table
Zj(xj) x1(Eu2+)/% x2(Dy3+)/% Z2j(r) 5 10 Z0j + $\varDelta_j$(1) 4.341 8.682 Z0j(0) 2.75 5.5 Z0j – $\varDelta_j$(–1) 1.159 2.318 Z1j(–r) 0.5 1 $\varDelta_j$ = (Z2j – Z1j)/2r 1.591 3.182 xj = (Zj – Z0j)/$\varDelta_j$ x1 = (Z1 – 2.75)/1.591 x2 = (Z2 – 5.5)/3.182 表 2 二次通用旋转组合设计实验方案及余辉时间
Table 2. Quadratic general rotation combination design experimental scheme and afterglow time.
Number x0 x1 x2 x1x2 x12 x22 Afterglow time/s 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 132 2 1 1 –1 –1 1 1 80 3 1 –1 1 –1 1 1 212 4 1 –1 –1 1 1 1 184 5 1 r 0 0 r2 0 116 6 1 –r 0 0 r2 0 290 7 1 0 r 0 0 r2 172 8 1 0 –r 0 0 r2 138 9 1 0 0 0 0 0 141 10 1 0 0 0 0 0 104 11 1 0 0 0 0 0 102 12 1 0 0 0 0 0 101 13 1 0 0 0 0 0 105 表 3 显著性检验分析
Table 3. Significant test analysis.
Afterglow time/s 方差或 t 统计量 显著性水平$\alpha$ 显著性水平$\alpha$ x0 14.490 0.001 *** x1 5.193 0.01 ** x2 1.546 0.2 * x1x2 0.703 0.6 Insignificant x12 6.116 0.01 *** x22 2.408 0.2 * F回 18.07 0.001 *** 注: ***极显著水平($\alpha$ ≤ 0.01); **显著水平($\alpha$ ≤ 0.1); *较显著水平($\alpha$ ≤ 0.25). 表 5 Sr2MgSi2O7:0.5 mol% Eu2+, 1.0 mol% Dy3+的陷阱深度参数
Table 5. Trap depth parameter of Sr2MgSi2O7:0.5 mol% Eu2+, 1.0 mol% Dy3+.
T1/K Tm/K T2/K $\tau$/K $\delta$/K $\omega$/K ${\mu _{\rm g}}$/K ${E_\tau }$/eV ${E_\delta }$/eV ${E_\omega }$/eV E/eV 339* 365 393 26 28 54 0.528 0.673 0.701 0.690 0.688 $\tau$ $\delta$ $\omega$ ${c_\alpha }$ 1.81 1.71 3.54 ${b_\alpha }$ 2 0 1 -
[1] Chang C K, Mao D L, Shen J F, Feng C L 2003 J. Alloy. Compd. 348 224
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Johnson E J, Kafalas J, Dyes W A 1982 Appl. Phys. Lett. 40 993
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 梅屹峰, 唐远河, 梅小宁, 刘汉臣, 刘骞, 余洋, 李宁远, 高恒 2016 65 170701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mei Q F, Tang Y H, Mei X N, Liu H C, Liu Q, Yu Y, Li N Y, Gao H 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 170701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 彭玲玲, 曹仕秀, 赵聪, 刘碧桃, 韩涛, 李凤, 黎小敏 2018 67 187801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Peng L L, Cao S X, Zhao C, Liu B T, Han T, Li F, Li X M 2018 Acta Phys Sin. 67 187801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 刘文全, 朝克夫, 武文杰, 包富泉, 周炳卿 2018 65 207801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu W Q, Zhao K F, Wu W J, Bao F Q, Zhou B Q 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 207801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Lindmayer J 1988 Solid State Technol. 31 135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Fan W H, Wang Y C, Xu H, Li D, Wei Z, Yang B Z, Niu L H 1999 J. Appl. Phys. 85 451
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhang Y, Wang B, Liu X, Xiao M 2010 J. Appl. Phys. 107 103502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Yamashita S A, Ogawa N 1989 Phys. States Solidi B 118 89
[10] Ou Y Y, Zhou W J, Liu C M, Lin L T, Brik G M, Dorenbos P 2018 J. Phys. Chem. C 122 2959
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Yan J, Liu C M, Vlieland J, Zhou J B, Dorenbos P, Huang Y, Tao Y, Liang H B 2017 J. Lumin. 183 97
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Liu F, Yan W, Chuang Y J, Zhen Z, Xie J, Pan Z 2013 Sci. Rep. 3 1554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Xu X, He Q, Yan L 2013 J. Alloy. Compd. 574 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang J, Ma Q, Wang Y, Shen H, Yuan Q 2017 Nanoscale 9 6204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 孙佳石, 李香萍, 李树伟, 吴金磊, 石琳琳, 徐赛, 张金苏, 程丽红, 陈宝玖 2017 66 100201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun J S, Li X P, Wu J L, Li S W, Shi L L, Xu S, Zhang J S, Cheng L H, Chen B J 2017 Acta Phys Sin. 66 100201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 田碧凝 2013 硕士学位论文 (大连: 大连海事大学)
Tian B N 2013 M. S. Thesis (Dalian: Dalian Mar-itime University) (in Chinese)
[17] 任露泉 2009 试验优化设计与分析 (北京: 科学出版社) 第172—185页
Ren L Q 2009 Design of Experiment and Optimization (Beijing: Science Press) pp172–185 (in Chinese)
[18] 王志军, 刘海燕, 杨勇, 蒋海峰, 段平光, 李盼来, 杨志平, 郭庆林 2014 63 077802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Z J, Liu H Y, Yang Y, Jiang H F, Duan P G, Li P L, Yang Z P, Guo Q L 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 077802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 何为, 薛卫东, 唐斌 2012 优化试验设计方法及数据分析 (北京: 化学工业出版社) 第185—190页
He W, Xue W D, Tang B 2012 The Method of Opti-mal Design of Experiment and Data Analysis (Beijing: Chemical Industry Press) pp185–190 (in Chinese)
[20] 翟梓会, 孙佳石, 张金苏, 李香萍, 程丽红, 仲海洋, 李晶晶, 陈宝玖 2013 62 203301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhai Z H, Sun J S, Zhang J S, Li X P, Cheng L H, Zhong H Y, Li J J, Chen B J 2013 Acta Phys Sin. 62 203301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 程仕平, 徐慧, 王德志, 王光君, 吴壮志 2007 稀有金属材料与工程 36 1933
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cheng S P, Xu H, Wang D Z, Wang G J, Wu Z Z 2007 Rare Metal. Mat. Eng. 36 1933
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 高大海, 罗军, 葛明桥 2013 化工新型材料 41 30
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao D H, Luo J, Ge M Q 2013 New Chem. Mater. 41 30
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Xiong W W, Yin C L, Zhang Y, Zhang J L 2009 Chin. J. Mech. Eng-En. 22 862
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Tan G Z, Zhou D M, Jiang B J, Dioubate M I 2008 J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 15 845
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 石琳琳, 孙佳石, 翟梓会, 李香萍, 张金苏, 陈宝玖 2014 光子学报 43 1116002
Shi L L, Sun J S, Zhai Z H, Li X P, Zhang J S, Chen B J 2014 Acta Photo. Sin. 43 1116002
[26] Wu H, Hu Y, Chen L, Wang X 2011 J. Alloy. Compd. 509 4304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Chen R 1969 J. Appl. Phys. 40 570
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 张哲, 徐旭辉, 邱建备, 张新, 余雪 2014 光谱学与光谱分析 34 1486
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Z, Xu X H, Qiu J B, Zhang X, Yu X 2014 Spetroscopy Spectral Anal. 34 1486
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 齐智坚, 黄维刚 2013 62 197801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi Z J, Huang W G 2013 Acta Phys Sin. 62 197801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 12144
- PDF下载量: 119
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: