-
Co-Al-W基高温合金具有类似于Ni基高温合金的
$\gamma + \gamma′$ 相组织结构. 根据面心立方固溶体的团簇加连接原子结构模型, Ni基高温合金的成分式即最稳定的化学近程序结构单元可以描述为第一近邻配位多面体团簇加上次近邻的三个连接原子. 本文应用类似方法, 首次给出了Co-Al-W基高温合金的团簇成分式. 利用原子半径和团簇共振模型, 可计算出Co-Al-W三元合金的团簇成分通式, 为[Al-Co12](Co,Al,W)3, 即以Al为中心原子、Co为壳层原子的[Al-Co12]团簇加上三个连接原子. 对于多元合金, 需要先将元素进行分类: 溶剂元素—类Co元素$\overline {{\rm{Co}}} $ (Co, Cr, Fe, Re, Ni, Ir, Ru)和溶质元素—类Al元素$\overline {{\rm{Al}}} $ (Al, W, Mo, Ta, Ti, Nb, V等); 进而根据合金元素的配分行为, 将类Co元素分为${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^\gamma }$ (Cr, Fe, Re)和${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′}}$ (Ni, Ir, Ru); 根据混合焓, 将类Al元素分为Al,$\overline {\rm{W}} $ (W, Mo)和$\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} $ (Ta, Ti, Nb, V等). 由此, 任何多元Co-Al-W基高温合金均可简化为$\overline {{\rm{Co}}} \text{-} \overline {{\rm{Al}}} $ 伪二元体系或者$\overline {{\rm{Co}}} \text{-} {\rm{Al}} \text{-}\left( {\overline {\rm{W}}, \overline {{\rm{Ta}}} } \right)$ 伪三元体系, 其团簇加连接原子成分式为$\left[ {\overline {{\rm{Al}}} \text{-} {{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} }_{12}}} \right]$ $\left( {{{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} }_{1.0}}{{\overline {{\rm{Al}}} }_{2.0}}} \right)$ (或$\left[ {{\rm{Al}} \text{-} {{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} }_{12}}} \right]{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} _{1.0}}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.5}}{\left( {\overline {\rm{W}},\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} } \right)_{1.5}}$ =${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} _{81.250}}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{9.375}}{\left( {\overline {\rm{W}},\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} } \right)_{9.375}}$ at.%). 其中,${\gamma }$ 与${\gamma′}$ 相的团簇成分式分别为$\left[ {\overline {{\rm{Al}}} \text{-} {{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} }_{12}}} \right]\!\left( {{{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} }_{1.5}}{{\overline {{\rm{Al}}} }_{1.5}}} \right)$ (或$\left[ {{\rm{Al}} \text{-} {{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} }_{12}}} \right]{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} _{1.5}}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.5}}{\left( {\overline {\rm{W}},\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} } \right)_{1.0}}$ =${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} _{84.375}}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{9.375}}$ ${\left( {\overline {\rm{W}},\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} } \right)_{6.250}}$ at.%)和$\left[ {\overline {{\rm{Al}}} \text{-} {{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} }_{12}}} \right]\left( {{{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} }_{0.5}}{{\overline {{\rm{Al}}} }_{2.5}}} \right)$ (或$\left[ {{\rm{Al}} \text{-} {{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} }_{12}}} \right]{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} _{0.5}}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.5}}{\left( {\overline {\rm{W}},\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} } \right)_{2.0}}$ =$ {\overline {{\rm{Co}}} _{78.125}}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{9.375}}{\left( {\overline {\rm{W}},\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} } \right)_{12.500}}$ at.%). 例如, Co82Al9W9合金的团簇成分式为[Al-Co12]Co1.1Al0.4W1.4 (~[Al-Co12]Co1.0Al0.5W1.5), 其中${\gamma }$ 相的团簇成分式为[Al-Co12]Co1.6Al0.4W1.0 (~[Al-Co12]Co1.5Al0.5W1.0),${\gamma′}$ 相的团簇成分式为[Al-Co12]Co0.3Al0.5W2.2 (~[Al-Co12]Co0.5Al0.5W2.0).-
关键词:
- Co-Al-W基高温合金 /
- 成分式 /
- 团簇加连接原子模型 /
- 化学近程序
Having a$\gamma /\gamma′ $ microstructure similar to Ni-base superalloys and also including various alloying elements such as Al and W, new Co-base superalloy, namely Co-Al-W-base alloy, has been widely studied as a kind of potential alternative of Ni-base superalloy, which is the most important high-temperature structural material in industrial applications. Besides, Co-Al-W-base alloy has also excellent mechanical properties, for example, creep properties comparable to those of the first-generation Ni-base single crystal superalloys. In our previous work, the ideal composition formula of Ni-base superalloy has been obtained by applying the cluster-plus-glue-atom structure model of faced centered cubic solid solution, which shows that the most stable chemical short-range-order unit is composed of a nearest-neighbor cluster and three next-neighbor glue atoms. In this paper, the ideal cluster formula of Co-Al-W-base superalloy is addressed by using the same approach. Based on cluster-plus-glue-atom model theory, according to lattice constants and atom radii, calculations are carried out. The results show that the atom radius of Al is equal to Covalent radius (0.126 nm) and for$\gamma′ $ phase the atom radius of W changes obviously (0.1316 nm). After analyzing atomic radii, the chemical formula for Co-Al-W ternary alloy is calculated to be [Al-Co12](Co,Al,W)3, which signifies an Al centered atom and twelve Co nearest-neighbored cluster atoms plus three glue atoms, which is in good consistence with that for Ni-base single crystal superalloy. For multi-element alloy, the alloying elements are classified, according to the heat of mixing between the alloying elements and Co as well as partition behavior of alloying elements, as solvent elements-Co-like elements$\overline {{\rm{Co}}} $ (Co, Ni, Ir, Ru, Cr, Fe, and Re) and solute elements-Al-like elements$\overline {{\rm{Al}}} $ (Al, W, Mo, Ta, Ti, Nb, V, etc.). The solvent elements can be divided into two kinds according to partition behaves:${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma }}$ (Cr, Fe, and Re) and${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′}}$ (Ni, Ir, and Ru). The latter is further grouped into Al,${\overline {\rm{W}} }$ (W and Mo, which have weaker heat of mixing than Al-Co ) and${\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} }$ (Ta, Ti, Nb, V, etc., which have stronger heat of mixing than Al-Co). Then all chemically complex Co-Al-W-base superalloys are simplified into$\overline {{\rm{Co}}} \text{-} \overline {{\rm{Al}}} $ pseudo-binary or$\overline {{\rm{Co}}} \text{-} {\rm{Al}} \text{-} \left( {\overline {\rm{W}},\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} } \right)$ pseudo-ternary system. Within the framework of the cluster-plus-glue-atom formulism and by analyzing the compositions of alloy, it is shown that the Co-Al-W-base superalloy satisfies the ideal formula$\left[ {\overline {{\rm{Al}}} \text{-} {{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} }_{12}}} \right]\left( {{{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} }_{1.0}}{{\overline {{\rm{Al}}} }_{2.0}}} \right)$ (or$\left[ {{\rm{Al}} \text{-} {{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} }_{12}}} \right]{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} _{1.0}}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.5}}{\left( {\overline {\rm{W}},\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} } \right)_{1.5}}$ =${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} _{81.250}}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{9.375}}{\left( {\overline {\rm{W}},\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} } \right)_{9.375}}$ at.%). In the same way, those of$\gamma $ and$\gamma′ $ phases are respectively$\left[ {\overline {{\rm{Al}}} \text{-} {{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} }_{12}}} \right]\left( {{{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} }_{1.5}}{{\overline {{\rm{Al}}} }_{1.5}}} \right)$ (or$\left[ {{\rm{Al}} \text{-} {{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} }_{12}}} \right]{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} _{1.5}}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.5}}{\left( {\overline {\rm{W}},\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} } \right)_{1.0}}$ =${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} _{84.375}}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{9.375}}{\left( {\overline {\rm{W}},\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} } \right)_{6.250}}$ at.%) and$\left[ {\overline {{\rm{Al}}} \text{-} {{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} }_{12}}} \right]\left( {{{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} }_{0.5}}{{\overline {{\rm{Al}}} }_{2.5}}} \right)$ (or$\left[ {{\rm{Al}} \text{-} {{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} }_{12}}} \right]{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} _{0.5}}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.5}}{\left( {\overline {\rm{W}},\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} } \right)_{2.0}}$ =${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} _{78.125}}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{9.375}}{\left( {\overline {\rm{W}},\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} } \right)_{12.500}}$ at.%). For example, alloy Co82Al9W9 and its$\gamma $ and$\gamma′ $ phases are formulated respectively as [Al-Co12]Co1.1Al0.4W1.4 (~ [Al-Co12]Co1.0Al0.5W1.5), [Al-Co12]Co1.6Al0.4W1.0 (~ [Al-Co12]Co1.5Al0.5W1.0), and [Al-Co12]Co0.3Al0.5W2.2 (~[Al-Co12]Co0.5Al0.5W2.0).-
Keywords:
- Co-Al-W-base superalloys /
- composition formula /
- cluster-plus-glue-atom model /
- chemical short-range order
[1] Sims C T, Hagel W C 1972 The Superalloys (New York: John Wiley & Sons) p1
[2] Sato J, Omori T, Oikawa K, Ohnuma I, Kainuma R, Ishida K 2006 Science 312 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Suzuki A, Pollock T M 2008 Acta Mater. 56 1288
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Bauer A, Neumeiera S, Pyczakb F, Singer R F, Göken M 2012 Mater. Sci. Eng. 550 333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Klein L, Shen Y, Killian M S, Virtanen S 2011 Corros. Sci. 53 2713
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Ooshima M, Tanaka K, Okamoto N L, Kishida K, Inui H 2010 J. Alloys Compd. 508 71
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Chen M, Wang C Y 2009 Scr. Mater. 60 659
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bauer A, Neumeier S, Pyczakc F, Göken M 2010 Scr. Mater. 63 1197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Kobayashi S, Tsukamoto Y, Takasugi T 2012 Intermetallics 31 94
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Meher S, Yan H Y, Nag S, Dye D, Banerjee R 2012 Scr. Mater. 67 850
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Morinaga M, Yukawa N, Ezaki H, Adachi H 1984 Superalloys (Warrendale, PA: The Metallurgical Society of AIME) p523
[12] 张继山, 崔华, 胡壮麟, 村田纯教, 森永正彦, 汤川夏夫 1993 金属学报 29 289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang J S, Cui H, Hu Z L, Murata Y, Morinaga M, Yukawa N 1993 Acta Metall. Sin. 29 289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Dong C, Wang Q, Qiang J B, Wang Y M, Jiang N, Han G, Li Y H, Wu J, Xia J H 2007 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 40 R273
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Han G, Qiang J B, Li F W, Yuan L, Quan S G, Wang Q, Wang Y M, Dong C, Häussler P 2011 Acta Mater. 59 5917
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Luo L J, Chen H, Wang Y M, Qiang J B, Wang Q, Dong C, Häussler P 2014 Philos. Mag. 94 2520
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 张宇, 王清, 董红刚, 董闯, 张洪宇, 孙晓峰 2017 金属学报 54 591
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y, Wang Q, Dong H G, Dong C, Zhang H Y, Sun X F 2017 Acta Metall. Sin. 54 591
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Bragg W L, Williams E J 1934 Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 151 699
[18] Williams E 1935 Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 152 231
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bethe H 1935 Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 150 552
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Cowly J 1950 Phys. Rev. 77 669
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Cowly J 1960 Phys. Rev. 120 1648
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Cowly J 1965 Phys. Rev. 138 A1384
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chen H, Wang Q, Wang Y M, Qiang J B, Dong C 2010 Philos. Mag. 90 3935
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Chen H, Wang Q, Wang Y M, Wang Y, Dong C 2011 Isr. J. Chem. 51 1226
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wang Y, Wang Q, Zhao J, Dong C 2010 Scr. Mater. 63 178
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Yuan L, Pang C, Wang Y M, Wang Q, Qiang J B, Dong C 2010 Intermetallics 18 1800
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Li F W, Qiang J B, Wang Q, Wang Y M, Dong X L, Dong C, Zhu S J 2012 Intermetallics 30 86
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wang Z R, Dong D D, Qiang J B, Wang Q, Wang Y M, Dong C 2013 Sci. China: Phys. Mech. Astron. 56 1419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wang Q, Zhu C L, Li Y H, Wu J, Dong C, Qiang J B, Zhang W, Inoue A 2007 Mater. Sci. Forum 561−565 1275
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 谷俊杰 2011 硕士学位论文 (大连: 大连理工大学)
Gu J J 2011 M. S. Thesis (Dalian: Dalian University of Technology) (in Chinese)
[31] Wang Q, Li Q, Li X N, Zhang R Q, Gao X X, Dong C, Liaw P K 2015 Metall. Mater. Trans. A 46 3924
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 王清, 查钱锋, 刘恩雪, 董闯, 王学军, 谭朝鑫, 龚春俊 2012 金属学报 48 1201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Q, Zha Q F, Liu E X, Dong C, Wang X J, Tan C X, Gong C J 2012 Acta Metall. Sin. 48 1201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] 马仁涛, 郝传璞, 王清, 任明法, 王英敏, 董闯 2010 金属学报 46 1034
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma R T, Hao C P, Wang Q, Ren M F, Wang Y M, Dong C 2010 Acta Metall. Sin. 46 1034
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] 董丹丹 2017 博士学位论文 (大连: 大连理工大学)
Dong D D 2017 Ph. D. Dissertation (Dalian: Dalian University of Technology) (in Chinese)
[35] 董闯, 董丹丹, 王清 2018 金属学报 54 293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong C, Dong D D, Wang Q 2018 Acta Metall. Sin. 54 293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Hong H L, Wang Q, Dong C 2015 Sci. China: Mater. 58 355
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Hong H L, Wang Q, Dong C, Liaw P K 2014 Sci. Rep. 4 7065
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] 洪海莲, 董闯, 王清, 张宇, 耿遥祥 2016 65 036101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hong H L, Dong C, Wang Q, Zhang Y, Geng Y X 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 036101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Pearson W B 1973 J. Appl. Cryst. 6 306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Pyczak F, Bauer A, Göken M, Lorenz U, Neumeier S, Oehring M, Paul J, Schell N, Schreyer A, Stark A, Symanzik F 2015 J. Alloys Compd. 632 110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Povstugar I, Zenk C H, Li R, Choi P P, Neumeier S, Dolotko O, Hoelzel M, Göken M, Raabe D 2016 Mater. Sci. Technol. 32 220
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Shinagawa K, Omori T, Sato J, Oikawa K, Ohnuma I, Kainuma R, Ishida K 2008 Mater. Trans. 49 1474
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Wang Y J, Wang C Y 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 94 261909
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Bocchini P J, Lass E A, Moon K W, Williams M E, Campbell C E, Kattner U R, Dunand D C, Seidman D N 2013 Scr. Mater. 68 563
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Povstugar I, Choi P P, Neumeier S, Bauer A, Zenk C H, Göken M, Raabe D 2014 Acta Mater. 78 78
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Meher S, Banerjee R 2014 Intermetallics 49 138
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Lass E A, Williams M E, Campbell C E, Moon K W, Kattner U R 2014 J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 35 711
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] Zhong F, Li S S, Sha J B 2015 Mater. Sci. Eng. A 637 175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[49] Sauza D J, Bocchini P J, Dunand D C, Seidman D N 2016 Acta Mater. 117 135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[50] Zhou H J, Xue F, Chang H, Feng Q 2018 J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 34 799
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[51] Takeuchi A, Inoue A 2005 Mater. Trans. 46 2817
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[52] Shinagawa K, Omori T, Oikawa K, Kainuma R, Ishida K 2009 Scr. Mater. 61 612
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[53] Chen M, Wang C Y. 2010 Phys. Lett. A 374 3238
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[54] Ping D H, Cui C Y, Gu Y F, Harada H 2007 Ultramicroscopy 107 791
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[55] Makineni S K, Nithin B, Chattopadhyay K 2015 Scr.Mater. 98 36
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[56] Makineni S K, Samanta A, Rojhirunsakool T, Alam T, Nithin B, Singh A K, Banerjee R, Chattopadhyay K 2015 Acta Mater. 97 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[57] Pollock T M, Dibbern J, Tsunekane M, Suzuki 2010 JOM 62 58
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[58] Yan H Y, Vorontsov V A, Dye D 2014 Intermetallics 48 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[59] Xue F, Zhou H J, Ding X F, Wang M L, Feng Q 2013 Mater. Lett. 112 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[60] Xue F, Zhou H J, Feng Q 2014 JOM 66 2486
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[61] Titus M S, Suzuki A, Pollock T M 2012 High Temperature Creep of New L12 Containing Cobalt‐Base Superalloys (New York: John Wiley Sons. Inc.) p823
[62] Shi L, Yu J J, Cui C Y, Sun X F 2015 Mater. Lett. 149 58
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
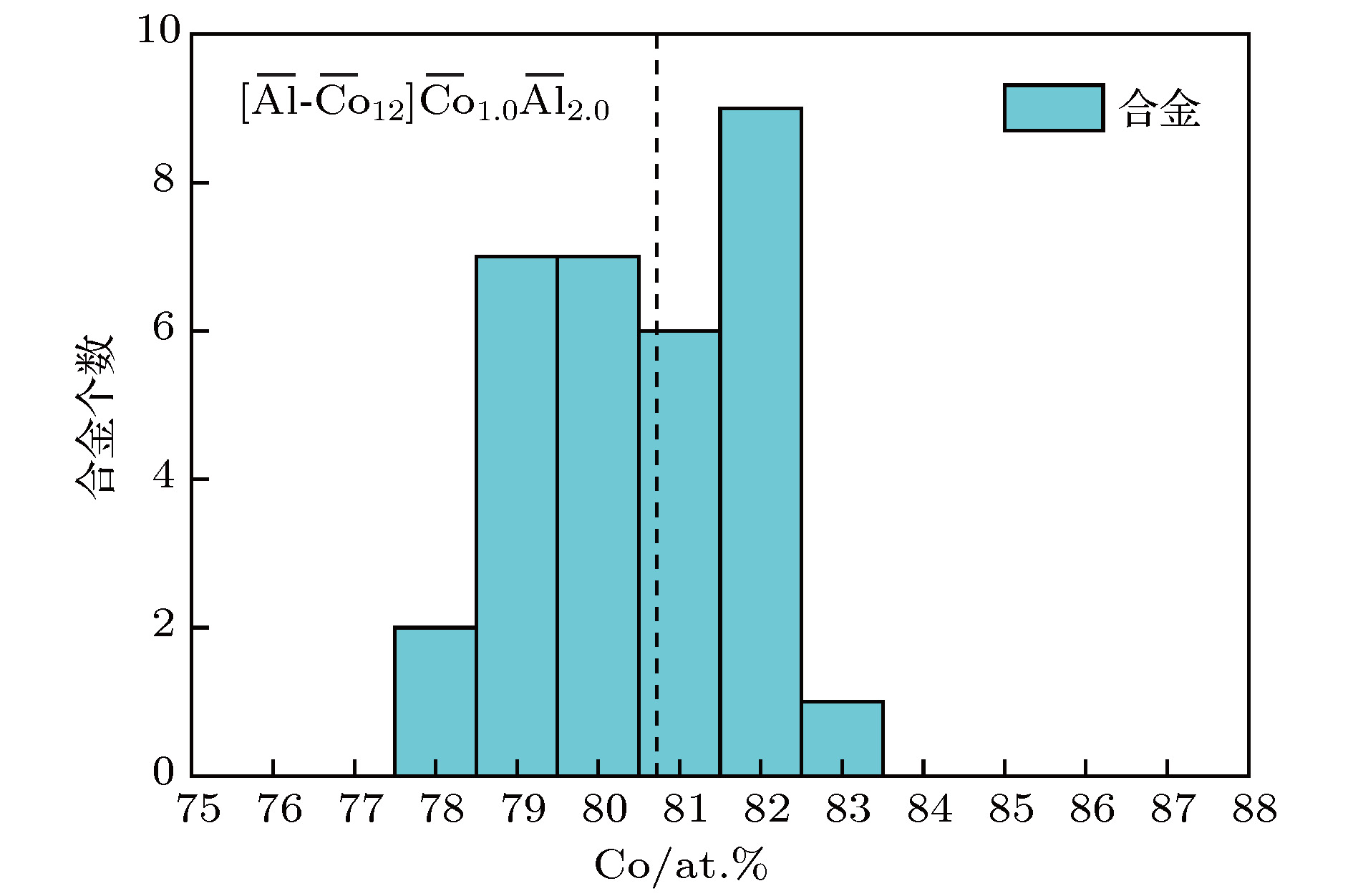
图 2 合金数量随Co含量的变化, 虚线表示平均成分式
$\left[ {\overline {{\rm{Al}}} \text{-} {{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} }_{12}}} \right]{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} _{1.0}}{\overline {{\rm{Al}}} _{2.0}}$ Fig. 2. Statistical distribution of alloy compositions as a function of at.% Co. The dashed vertical line represents the ideal composition formula
$\left[ {\overline {{\rm{Al}}} \text{-} {{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} }_{12}}} \right]{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} _{1.0}}{\overline {{\rm{Al}}} _{2.0}}$ 图 3
$\overline {{\rm{Co}}} \text{-} {\rm{Al}} \text{-} \left( {\overline {\rm{W}},\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} } \right)$ 伪三元成分分布 (a) 合金成分; (b)$\gamma $ 和$\gamma′ $ 两相成分; 图中虚线为 Co-Al-W三元相图中富Co端1173 K等温截面相图[2], 中心成分点${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} _{81.250}}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{9.375}}$ ${\left( {\overline {\rm{W}} ,\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} } \right)_{9.375}}$ 用蓝色空心三角形标出Fig. 3.
$\overline {{\rm{Co}}} \text{-} {\rm{Al}} \text{-} \left( {\overline {\rm{W}} ,\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} } \right)$ pseudo-ternary composition diagram: (a) Alloy compositions; (b)$\gamma $ and$\gamma′ $ two phases compositions, where the dashed lines represent the isothermal section of the Co-Al-W ternary system in the Co-rich portion at 1173 K[2], and the blue hollow triangle points to the center composition${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} _{81.250}}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{9.375}}{\left( {\overline {\rm{W}} ,\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} } \right)_{9.375}}$ 表 1 实测的
$\gamma $ 相成分和晶格常数[40-42], 以及按照(7)式计算的晶格常数Table 1. Measured compositions and lattice constants of
$\gamma $ phase in Co-Al-W-base superalloys[40-42], in comparison with the calculated lattice constants合金成分/at.% $\gamma $相成分/at.% 晶格常数实验值/nm 晶格常数计算值/nm 绝对误差$\varDelta $ Co82Al9W9 Co81.7Al9.3W9 0.3580 0.3579 0.0001 Co83Al9W8 Co81.9Al10.0W8.1 0.3576 0.3575 0.0001 Co80Al9W11 Co80.7Al9.2W10.2 0.3586 0.3588 0.0002 Co74Al9W9Cr8 Co73.9Al8.0W6.8Cr11.2 0.3578 0.3575 0.0003 Co64Al9W9Ni18 Co69.1Al6.8W7.0Ni16.9 0.3577 0.3562 0.0015 Co65Al9W9Ni9Cr8 Co66.7Al7.8W6.7Ni8.3Cr10.7 0.3581 0.3584 0.0003 Co56Al9W9Ni18Cr8 Co59.2Al6.0W7.4Ni15.6Cr11.8 0.3583 0.3581 0.0002 Co72.5Ni10Al10W7.5 Co76.2Al8.7W5.4Ni9.7 0.3578 0.3562 0.0016 表 2 实测
$\gamma′ $ 相成分和晶格常数[40-42]以及根据(9)式计算的W原子半径Table 2. Atomic radii of W fitted from measured compositions and lattice constants
$\gamma′$ phases in different alloys[40-42]合金成分/at.% $\gamma′ $相成分/at.% 晶格常数实验值/nm W原子半径/nm Co82Al9W9 Co77.49Al10.03W12.48 0.3594 0.1317 Co83Al9W8 Co76.6Al9.4W14 0.3589 0.1306 Co80Al9W11 Co75.1Al9.1W15.8 0.3595 0.1311 Co74Al9W9Cr8 Co73.9Al9.4W10.4Cr6.3 0.3587 0.1314 Co64Al9W9Ni18 Co58.9Al10.8W11.0Ni19.3 0.3590 0.1317 Co65Al9W9Ni9Cr8 Co64.2Al10.1W9.9Ni9.4Cr6.4 0.3587 0.1317 Co56Al9W9Ni18Cr8 Co54.5Al10.5W9.7Ni19.7Cr5.6 0.3587 0.1319 Co72.5Ni10Al10W7.5 Co68.8Al10.8W9.9Ni10.5 0.3593 0.1324 表 3 合金化组元与基体组元Co之间的混合焓
$\Delta H$ (单位: kJ/mol)及在$\gamma / \gamma′ $ 两相中的配分系数(${K_x} = {C_x}^{\gamma′}/{C_x}^\gamma $ )[9,10,40-42,44-52]Table 3. Heats of mixing
$\Delta H$ (unit: kJ/mol) between alloying elements and matrix element Co and their partition coefficients (${K_x} = {C_x}^{\gamma′ }/$ ${C_x}^\gamma $ ) for$\gamma$ and$\gamma′$ [9,10,40-42,44-52]元素
分类合金化
元素混合焓
$\Delta H$/kJ·mol元素配分
系数K${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma }}$ Cr –4 0.48—0.60 Fe –1 Re 2 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}$ Ni –2 1.08—1.27 Ru –1 Ir –3 Al Al –19 0.93—1.60 ${\overline {\rm{W}} }$ W –1 1.03—6.21 Mo –5 ${\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} }$ V –14 1.57—8.67 Ta –24 Nb –25 Ti –28 Sc –30 Hf –35 表 4 Co-Al-W基多元合金的团簇成分式, 所列成分源自文献[2-4, 6, 8, 10, 39, 40-42, 44, 45, 48, 51, 57-62]
Table 4. Compositions formulas of Co-Al-W-base multi-element superalloys. The alloy compositions are taken from references [2-4, 6, 8, 10, 39, 40-42, 44, 45, 48, 51, 57-62]
合金成分/at.% 团簇成分式-[团簇](连接原子)3 连接原子 Co78Al10W10Ta2 [Al-Co12]Co0.5Al0.6W1.6Ta0.3 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{0.5}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.6}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.6}}{\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} _{0.3}}$ Co78Al9W10Mo3 [Al-Co12]Co0.5Al0.4W1.6Mo0.5 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{0.5}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.4}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{2.1}}$ Co79Al9W10Ti2 [Al-Co12]Co0.6Al0.4W1.6Ti0.3 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{0.6}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.4}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.6}}{\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} _{0.3}}$ Co79Al9W10V2 [Al-Co12]Co0.6Al0.4W1.6V0.3 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{0.6}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.4}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.6}}{\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} _{0.3}}$ Co79Al9W10Si2 [Al-Co12]Co0.6Al0.4W1.6Si0.3 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{0.6}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.4}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.6}}{\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} _{0.3}}$ Co79Al9W8Ta2Nb2 [Al-Co12]Co0.6Al0.4W1.3Ta0.3Nb0.3 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{0.6}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.4}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.3}}{\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} _{0.6}}$ Co79Al9W8Ta2V2 [Al-Co12]Co0.6Al0.4W1.3Ta0.3V0.3 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{0.6}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.4}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.3}}{\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} _{0.6}}$ Co79Al8W9Ta2Ti2 [Al-Co12]Co0.6Al0.3W1.4Ta0.3Ti0.3 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{0.6}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.3}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.4}}{\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} _{0.6}}$ Co79.5Al9.7W10.8 [Al-Co12]Co0.7Al0.6W1.7 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{0.7}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.6}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.7}}$ Co79.9Al9.4W10.7 [Al-Co12]Co0.8Al0.5W1.7 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{0.8}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.5}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.7}}$ Co80Al9W11 [Al-Co12]Co0.8Al0.4W1.8 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{0.8}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.4}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.8}}$ Co80Al9W9Ti2 [Al-Co12]Co0.8Al0.4W1.4Ti0.3 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{0.8}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.4}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.4}}{\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} _{0.3}}$ Co80Al9W9V2B0.04 [Al-Co12]Co0.8Al0.4W1.4V0.3 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{0.8}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.4}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.4}}{\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} _{0.3}}$ Co80Al9W9Ta2 [Al-Co12]Co0.8Al0.4W1.4Ta0.3 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{0.8}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.4}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.4}}{\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} _{0.3}}$ Co80.3Al9.3W10.4 [Al-Co12]Co0.8Al0.5W1.7 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{0.8}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.5}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.7}}$ Co80.5Al9W10Si0.5 [Al-Co12]Co0.9Al0.4W1.6Si0.1 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{0.9}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.4}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.6}}{\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} _{0.1}}$ Co81Al9W9Mo1B0.04 [Al-Co12]Co1.0Al0.4W1.4Mo0.2 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{1.0}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.4}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.6}}$ Co81Al9W8Ta2 [Al-Co12]Co1.0Al0.4W1.3Ta0.3 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{1.0}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.4}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.3}}{\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} _{0.3}}$ Co81.3Al9.2W9.5 [Al-Co12]Co1.0Al0.5W1.5 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{1.0}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.5}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.5}}$ Co81.5Al9W9Nb0.5 [Al-Co12]Co1.0Al0.4W1.4Nb0.1 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{1.0}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.4}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.4}}{\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} _{0.1}}$ Co81.5Al9W5.5Ta2Mo2 [Al-Co12]Co1.0Al0.4W0.9Ta0.3Mo0.3 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{1.0}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.4}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.2}}{\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} _{0.3}}$ Co82Al9W9 [Al-Co12]Co1.1Al0.4W1.4 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{1.1}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.4}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.4}}$ Co72Al9W9Ni10 [Al-Co11.7Ni0.3]Ni1.1Al0.4W1.4 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{1.1}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.4}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.4}}$ Co82Al9W7.5Mo1.5 [Al-Co12]Co1.1Al0.4W1.4 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{1.1}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.4}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.4}}$ Co80Al9W9Cr2B0.04 [Al-Co12]Co0.8Cr0.3Al0.4W1.4 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{0.8}{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^\gamma }_{0.3}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.4}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.6}}$ Co78Al9W9Cr4 [Al-Co12]Co0.6Cr0.6Al0.4W1.4 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{0.6}{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^\gamma }_{0.6}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.4}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.4}}$ Co73Al9W9Ni9 [Al-Co11.7Ni0.3]Ni1.1Al0.4W1.4 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{1.1}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.4}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.4}}$ Co64Al9W9Ni18 [Al-Co10.2Ni1.8]Ni1.1Al0.4W1.4 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{1.1}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.4}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.4}}$ Co81.8Al9.2W9 [Al-Co12]Co1.1Al0.5W1.4 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{1.1}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.5}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.4}}$ Co72.5Al10W7.5Ni10 [Al-Co11.6Ni0.4]Ni1.2Al0.4W1.4 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{1.2}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.4}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.4}}$ Co81.5Al9W5.5Ta2Ir2 [Al-Co2]Co1.0Al0.4W0.9Ta0.3Ir0.3 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{1.3}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.4}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{0.9}}{\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} _{0.3}}$ Co79Al9W8Ta2Cr2 [Al-Co12]Co0.6Cr0.3Al0.4W1.3Ta0.3 ${\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^{\gamma′ }}_{0.6}{\overline {{\rm{Co}}} ^\gamma }_{0.3}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{l}}_{0.4}}{\overline {\rm{W}} _{1.3}}{\overline {{\rm{Ta}}} _{0.3}}$ 表 5 部分Co-Al-W基高温合金中
$\gamma $ 和$\gamma′ $ 两相团簇式[40,42,44,45]Table 5. Composition formulas of
$\gamma $ and$\gamma′ $ phases in some Co-Al-W-base superalloys[40,42,44,45]合金成分/at.% $\gamma $相团簇成分式 $\gamma′ $相团簇成分式 Co82Al9W9 [Al-Co12]Co1.6Al0.4W1.0 [Al-Co12]Co0.3Al0.5W2.2 Co78Al9W9Cr4 [Al-Co12]Co0.9Al0.3W0.9Cr0.9 [Al-Co12]Co0.2Al0.5W1.8Cr0.5 Co73Al9W9Ni18 [Al-Co11.1Ni0.9]Al0.1W1.1Ni1.8 [Al-Co9.4Ni2.6]Al0.7W1.8Ni0.5 Co79.5Al9.7W10.8 [Al-Co12]Co1.7Al0.4W0..9 [Al-Co12]Co0.4Al0.6W2.0 Co80Al9W9Ti2 [Al-Co12]Co1.6Al0.4W0.8Ti0.2 [Al-Co12]Co0.2Al0.4W1.9Ti0.4 Co80Al9W9Ta2 [Al-Co12]Co1.8Al0.4W0.7Ta0.1 [Al-Co12]Co0.2Al0.4W1.9Ta0.5 Co79Al8W9Ta2Ti2 [Al-Co12]Co2.0Al0.3W0.5Ta0.04Ti0.1 [Al-Co12]Co0.1Al0.4W1.9Ta0.3Ti0.3 Co78Al10W10Ta2 [Al-Co12]Co1.6Al0.7W0.7Ta0.1 [Al-Co12]Al0.7W1.9Ta0.4 Co78Al9W10Mo3 [Al-Co12]Co1.7Al0.1W0.8Mo0.4 [Al-Co12]Co0.2Al0.6W1.7Mo0.5 -
[1] Sims C T, Hagel W C 1972 The Superalloys (New York: John Wiley & Sons) p1
[2] Sato J, Omori T, Oikawa K, Ohnuma I, Kainuma R, Ishida K 2006 Science 312 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Suzuki A, Pollock T M 2008 Acta Mater. 56 1288
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Bauer A, Neumeiera S, Pyczakb F, Singer R F, Göken M 2012 Mater. Sci. Eng. 550 333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Klein L, Shen Y, Killian M S, Virtanen S 2011 Corros. Sci. 53 2713
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Ooshima M, Tanaka K, Okamoto N L, Kishida K, Inui H 2010 J. Alloys Compd. 508 71
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Chen M, Wang C Y 2009 Scr. Mater. 60 659
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bauer A, Neumeier S, Pyczakc F, Göken M 2010 Scr. Mater. 63 1197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Kobayashi S, Tsukamoto Y, Takasugi T 2012 Intermetallics 31 94
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Meher S, Yan H Y, Nag S, Dye D, Banerjee R 2012 Scr. Mater. 67 850
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Morinaga M, Yukawa N, Ezaki H, Adachi H 1984 Superalloys (Warrendale, PA: The Metallurgical Society of AIME) p523
[12] 张继山, 崔华, 胡壮麟, 村田纯教, 森永正彦, 汤川夏夫 1993 金属学报 29 289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang J S, Cui H, Hu Z L, Murata Y, Morinaga M, Yukawa N 1993 Acta Metall. Sin. 29 289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Dong C, Wang Q, Qiang J B, Wang Y M, Jiang N, Han G, Li Y H, Wu J, Xia J H 2007 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 40 R273
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Han G, Qiang J B, Li F W, Yuan L, Quan S G, Wang Q, Wang Y M, Dong C, Häussler P 2011 Acta Mater. 59 5917
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Luo L J, Chen H, Wang Y M, Qiang J B, Wang Q, Dong C, Häussler P 2014 Philos. Mag. 94 2520
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 张宇, 王清, 董红刚, 董闯, 张洪宇, 孙晓峰 2017 金属学报 54 591
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y, Wang Q, Dong H G, Dong C, Zhang H Y, Sun X F 2017 Acta Metall. Sin. 54 591
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Bragg W L, Williams E J 1934 Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 151 699
[18] Williams E 1935 Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 152 231
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bethe H 1935 Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 150 552
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Cowly J 1950 Phys. Rev. 77 669
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Cowly J 1960 Phys. Rev. 120 1648
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Cowly J 1965 Phys. Rev. 138 A1384
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chen H, Wang Q, Wang Y M, Qiang J B, Dong C 2010 Philos. Mag. 90 3935
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Chen H, Wang Q, Wang Y M, Wang Y, Dong C 2011 Isr. J. Chem. 51 1226
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wang Y, Wang Q, Zhao J, Dong C 2010 Scr. Mater. 63 178
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Yuan L, Pang C, Wang Y M, Wang Q, Qiang J B, Dong C 2010 Intermetallics 18 1800
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Li F W, Qiang J B, Wang Q, Wang Y M, Dong X L, Dong C, Zhu S J 2012 Intermetallics 30 86
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wang Z R, Dong D D, Qiang J B, Wang Q, Wang Y M, Dong C 2013 Sci. China: Phys. Mech. Astron. 56 1419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wang Q, Zhu C L, Li Y H, Wu J, Dong C, Qiang J B, Zhang W, Inoue A 2007 Mater. Sci. Forum 561−565 1275
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 谷俊杰 2011 硕士学位论文 (大连: 大连理工大学)
Gu J J 2011 M. S. Thesis (Dalian: Dalian University of Technology) (in Chinese)
[31] Wang Q, Li Q, Li X N, Zhang R Q, Gao X X, Dong C, Liaw P K 2015 Metall. Mater. Trans. A 46 3924
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 王清, 查钱锋, 刘恩雪, 董闯, 王学军, 谭朝鑫, 龚春俊 2012 金属学报 48 1201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Q, Zha Q F, Liu E X, Dong C, Wang X J, Tan C X, Gong C J 2012 Acta Metall. Sin. 48 1201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] 马仁涛, 郝传璞, 王清, 任明法, 王英敏, 董闯 2010 金属学报 46 1034
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma R T, Hao C P, Wang Q, Ren M F, Wang Y M, Dong C 2010 Acta Metall. Sin. 46 1034
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] 董丹丹 2017 博士学位论文 (大连: 大连理工大学)
Dong D D 2017 Ph. D. Dissertation (Dalian: Dalian University of Technology) (in Chinese)
[35] 董闯, 董丹丹, 王清 2018 金属学报 54 293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong C, Dong D D, Wang Q 2018 Acta Metall. Sin. 54 293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Hong H L, Wang Q, Dong C 2015 Sci. China: Mater. 58 355
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Hong H L, Wang Q, Dong C, Liaw P K 2014 Sci. Rep. 4 7065
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] 洪海莲, 董闯, 王清, 张宇, 耿遥祥 2016 65 036101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hong H L, Dong C, Wang Q, Zhang Y, Geng Y X 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 036101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Pearson W B 1973 J. Appl. Cryst. 6 306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Pyczak F, Bauer A, Göken M, Lorenz U, Neumeier S, Oehring M, Paul J, Schell N, Schreyer A, Stark A, Symanzik F 2015 J. Alloys Compd. 632 110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Povstugar I, Zenk C H, Li R, Choi P P, Neumeier S, Dolotko O, Hoelzel M, Göken M, Raabe D 2016 Mater. Sci. Technol. 32 220
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Shinagawa K, Omori T, Sato J, Oikawa K, Ohnuma I, Kainuma R, Ishida K 2008 Mater. Trans. 49 1474
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Wang Y J, Wang C Y 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 94 261909
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Bocchini P J, Lass E A, Moon K W, Williams M E, Campbell C E, Kattner U R, Dunand D C, Seidman D N 2013 Scr. Mater. 68 563
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Povstugar I, Choi P P, Neumeier S, Bauer A, Zenk C H, Göken M, Raabe D 2014 Acta Mater. 78 78
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Meher S, Banerjee R 2014 Intermetallics 49 138
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Lass E A, Williams M E, Campbell C E, Moon K W, Kattner U R 2014 J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 35 711
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] Zhong F, Li S S, Sha J B 2015 Mater. Sci. Eng. A 637 175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[49] Sauza D J, Bocchini P J, Dunand D C, Seidman D N 2016 Acta Mater. 117 135
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[50] Zhou H J, Xue F, Chang H, Feng Q 2018 J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 34 799
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[51] Takeuchi A, Inoue A 2005 Mater. Trans. 46 2817
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[52] Shinagawa K, Omori T, Oikawa K, Kainuma R, Ishida K 2009 Scr. Mater. 61 612
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[53] Chen M, Wang C Y. 2010 Phys. Lett. A 374 3238
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[54] Ping D H, Cui C Y, Gu Y F, Harada H 2007 Ultramicroscopy 107 791
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[55] Makineni S K, Nithin B, Chattopadhyay K 2015 Scr.Mater. 98 36
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[56] Makineni S K, Samanta A, Rojhirunsakool T, Alam T, Nithin B, Singh A K, Banerjee R, Chattopadhyay K 2015 Acta Mater. 97 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[57] Pollock T M, Dibbern J, Tsunekane M, Suzuki 2010 JOM 62 58
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[58] Yan H Y, Vorontsov V A, Dye D 2014 Intermetallics 48 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[59] Xue F, Zhou H J, Ding X F, Wang M L, Feng Q 2013 Mater. Lett. 112 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[60] Xue F, Zhou H J, Feng Q 2014 JOM 66 2486
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[61] Titus M S, Suzuki A, Pollock T M 2012 High Temperature Creep of New L12 Containing Cobalt‐Base Superalloys (New York: John Wiley Sons. Inc.) p823
[62] Shi L, Yu J J, Cui C Y, Sun X F 2015 Mater. Lett. 149 58
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 12130
- PDF下载量: 83
- 被引次数: 0
























































 下载:
下载: