-
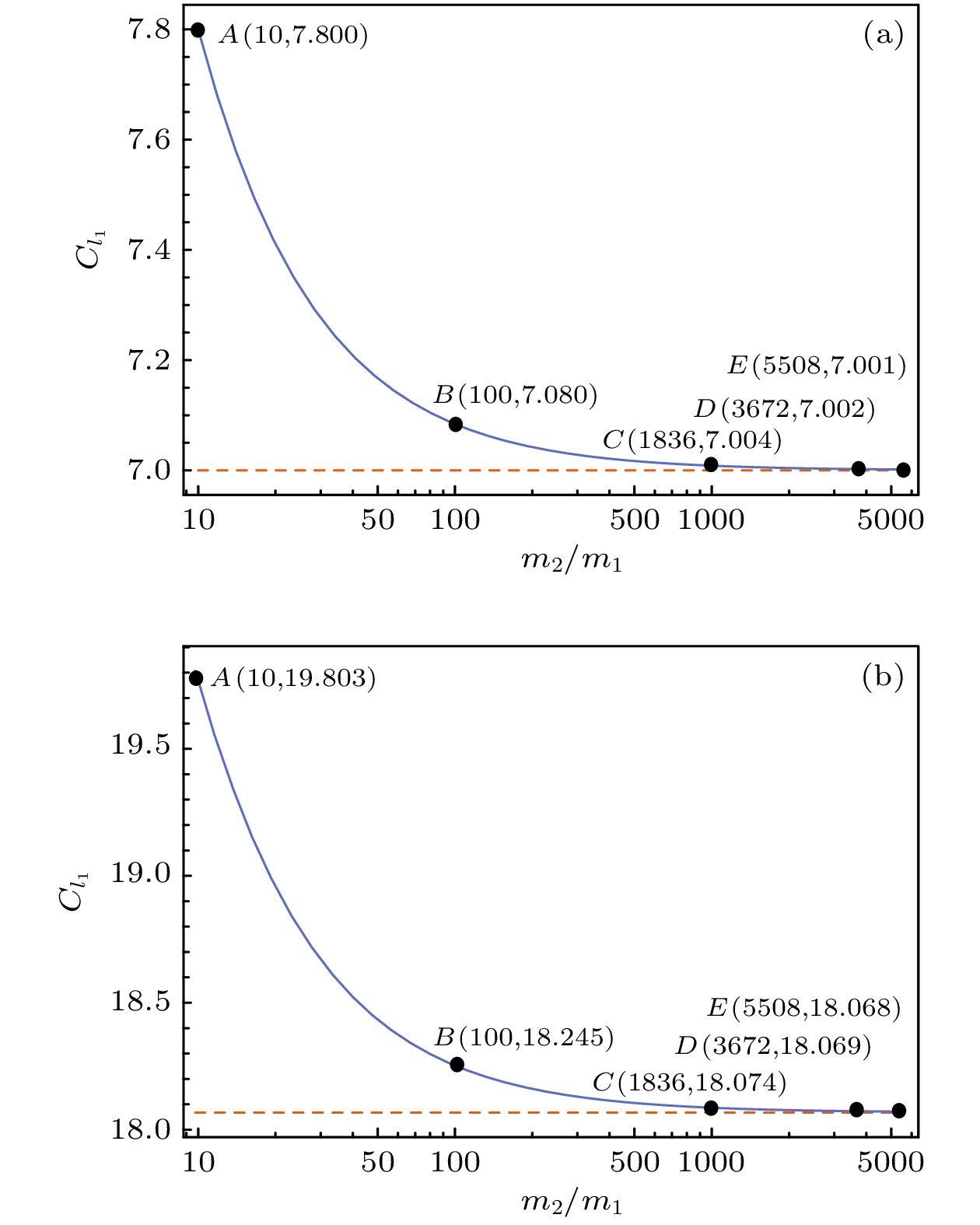
In an isolated two-body composite system, the discussion of how the change of one body affects the state of the other will help to know the relation of a single particle's mixed and pure states. Given 5 one-dimensional hydrogen-like atoms models, each Coulomb interaction potential keeps invariant, while the masses of the nuclei are different. These two-body composite systems stay in their respective entangled state, each electron stays in a mixed state. If we suppose a one-dimensional hydrogen atom model having infinite nuclear mass, the electron stays in a pure state. We select position representation. The wave function of the ground state of the atom has the form of the square root of a δ function. To avoid calculation trouble of δ function, we select the first excited state and the superposed state of the first and the second excited states. We compare the two pure states, the first excited state and the superposed state, with those corresponding mixed states by fidelity and l1 norm coherence, and calculate the purities of the mixed states. The summations become integrations due to the position variable having a continuous eigenvalue spectrum. We investigate the changes in these quantities with the increase of the nuclear mass. The results show that the purities of the mixed states and the fidelities increase with the nuclear mass increasing. However, the coherences of the mixed states decrease with the nuclear mass increasing. This can be explained as that a mixed state with non-zero coherence may approach to a pure eigenstate, while the latter has zero coherence in the eigenspace. These mean that the greater a nuclear mass is, the closer the mixed state approaches to the corresponding pure state. Therefore, the two pure states are the approximations of the corresponding mixed states. The entangled state of the electron and the nucleus is related with the nuclear mass and the Coulomb interaction potential. So, each electron mixed state and its coherence are related with the nucleus and their Coulomb interaction potential. If the nuclear mass is great, the nucleus is approximately motionless or its state is approximately unchanged, and the Coulomb interaction potential approximates to the external Coulomb potential of the electron. The electron approximately stays in a pure state. The state and its coherence are related with the nucleus and the Coulomb interaction. From other point of view, the entangled state of the nucleus and the electron approximates to the product state of the unchanged nucleus state and the electron state. In this case, an electron mixed state approximates to its corresponding pure state, and then these states and their coherences are all related with the nucleus and the Coulomb interaction.
-
Keywords:
- mixed state /
- fidelity /
- coherence /
- continuous variable
[1] 曾谨言 2007 量子力学 (卷Ⅰ) (北京: 科学出版社) 第305−307, 235−238 页
Zeng J Y 2007 Quantum Mechanics (Vol. 1) (Beijing: Science Press) pp305−307, 235−238 (in Chinese)
[2] 张永德 2017 量子力学(北京: 科学出版社) 第21 页
Zhang Y D 2017 Quantum Mechanics (Beijing: Science Press) p21 (in Chinese)
[3] Landau L D, Lifshitz E M 2007 Quantum Mechanics (Singapore: Elsevier Pte Ltd.) pp39, 51
[4] 喀兴林 2001 高等量子力学(北京: 高等教育出版社) 第192−199, 84−88页
Ka X L 2001 Advanced Quantum Mechanics (Bijing: Higher Education Press) pp192−199, 84−88 (in Chinese)
[5] Gamel O, James D F V 2012 Phys. Rev. A 86 033830
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Uhlmann A 1976 Rep. Math. Phys. 9 273
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Jozsa R 1994 J. Mod. Opt. 41 2315
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Nielsen M A, Chuang I L 2003 Quantum Computation and Quantum Information (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) pp409−413
[9] 李承祖, 黄明球, 陈平行, 梁林梅 2000 量子通信和量子计算 (长沙: 国防科技大学出版社) 第130−131页
Li C Z, Huang M Q, Chen P X, Liang L M 2000 Quantum Communication and Quantum Computation (Changsha: University of National Defence Technology Press) pp130−131 (in Chinese)
[10] Hou J C, Qi X F 2012 Sci. China, Ser. G 55 1820
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Aberg J 2006 arXiv: 0612146 [quant-ph]
[12] Bartlett S D, Rudolph T, Spekkens R W, Turner P S 2006 New J. Phys. 8 58
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Baumgratz T, Cramer M, Plenio M B 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 113 140401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chen J X, Grogan S, Johnston N, Li C K, Plosker S 2016 Phys. Rev. A 94 042313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Yu X D, Zhang D J, Liu C L, Tong D M 2016 Phys. Rev. A 93 060303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Hu M L, Hu X, Wang J C, Peng Y, Zhang Y R, Fan H 2017 arXiv 1703.01852 [quant-ph
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Qi X F, Gao T, Yan F L 2017 J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 50 285301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Song X K, Huang Y Q, Ling J J, Yung M H 2018 Phys. Rev. A 98 050302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhou G Y, Huang L J, Pan J Y, Hu L Y, Huang J H 2018 Front. Phys. 13 130701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Yu C S, Li D M, Zhou N N 2019 EPL 125 50001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Li K, Liu Z B, Zeng T H 2019 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58 3252
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 吕鑫 2020 69 070301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lü X 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 070301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Loudon R 1959 Am. J. Phys. 27 649
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 钱伯初 1989 大学物理 7 5
Qian B C 1989 College Physics 7 5
[25] Bertet P, Osnaghi S, Rauschenbeutel A, Nogues G, Auffeves A, Brune M, Raimond J M, Haroche S 2001 Nature 411 166
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zeng T H 2013 arXiv: 1307.1851 [gen-ph]
[27] Fayngold M, Fayngold V 2013 Quantum Mechanics and Quantum Information (Germany: Wiley-VCH) p603
[28] 曾天海 2016 大学物理 35 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zeng T H 2016 College Physics 35 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 曾天海 2017 现代物理 7 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zeng T H 2017 Modern Physics 7 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Zeng T H, Sun Z Z, Shao B 2020 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 59 229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] 曾谨言 2007 量子力学 (卷Ⅰ) (北京: 科学出版社) 第305−307, 235−238 页
Zeng J Y 2007 Quantum Mechanics (Vol. 1) (Beijing: Science Press) pp305−307, 235−238 (in Chinese)
[2] 张永德 2017 量子力学(北京: 科学出版社) 第21 页
Zhang Y D 2017 Quantum Mechanics (Beijing: Science Press) p21 (in Chinese)
[3] Landau L D, Lifshitz E M 2007 Quantum Mechanics (Singapore: Elsevier Pte Ltd.) pp39, 51
[4] 喀兴林 2001 高等量子力学(北京: 高等教育出版社) 第192−199, 84−88页
Ka X L 2001 Advanced Quantum Mechanics (Bijing: Higher Education Press) pp192−199, 84−88 (in Chinese)
[5] Gamel O, James D F V 2012 Phys. Rev. A 86 033830
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Uhlmann A 1976 Rep. Math. Phys. 9 273
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Jozsa R 1994 J. Mod. Opt. 41 2315
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Nielsen M A, Chuang I L 2003 Quantum Computation and Quantum Information (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) pp409−413
[9] 李承祖, 黄明球, 陈平行, 梁林梅 2000 量子通信和量子计算 (长沙: 国防科技大学出版社) 第130−131页
Li C Z, Huang M Q, Chen P X, Liang L M 2000 Quantum Communication and Quantum Computation (Changsha: University of National Defence Technology Press) pp130−131 (in Chinese)
[10] Hou J C, Qi X F 2012 Sci. China, Ser. G 55 1820
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Aberg J 2006 arXiv: 0612146 [quant-ph]
[12] Bartlett S D, Rudolph T, Spekkens R W, Turner P S 2006 New J. Phys. 8 58
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Baumgratz T, Cramer M, Plenio M B 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 113 140401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chen J X, Grogan S, Johnston N, Li C K, Plosker S 2016 Phys. Rev. A 94 042313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Yu X D, Zhang D J, Liu C L, Tong D M 2016 Phys. Rev. A 93 060303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Hu M L, Hu X, Wang J C, Peng Y, Zhang Y R, Fan H 2017 arXiv 1703.01852 [quant-ph
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Qi X F, Gao T, Yan F L 2017 J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 50 285301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Song X K, Huang Y Q, Ling J J, Yung M H 2018 Phys. Rev. A 98 050302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhou G Y, Huang L J, Pan J Y, Hu L Y, Huang J H 2018 Front. Phys. 13 130701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Yu C S, Li D M, Zhou N N 2019 EPL 125 50001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Li K, Liu Z B, Zeng T H 2019 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58 3252
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 吕鑫 2020 69 070301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lü X 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 070301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Loudon R 1959 Am. J. Phys. 27 649
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 钱伯初 1989 大学物理 7 5
Qian B C 1989 College Physics 7 5
[25] Bertet P, Osnaghi S, Rauschenbeutel A, Nogues G, Auffeves A, Brune M, Raimond J M, Haroche S 2001 Nature 411 166
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zeng T H 2013 arXiv: 1307.1851 [gen-ph]
[27] Fayngold M, Fayngold V 2013 Quantum Mechanics and Quantum Information (Germany: Wiley-VCH) p603
[28] 曾天海 2016 大学物理 35 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zeng T H 2016 College Physics 35 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 曾天海 2017 现代物理 7 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zeng T H 2017 Modern Physics 7 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Zeng T H, Sun Z Z, Shao B 2020 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 59 229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 8833
- PDF Downloads: 132
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: