-
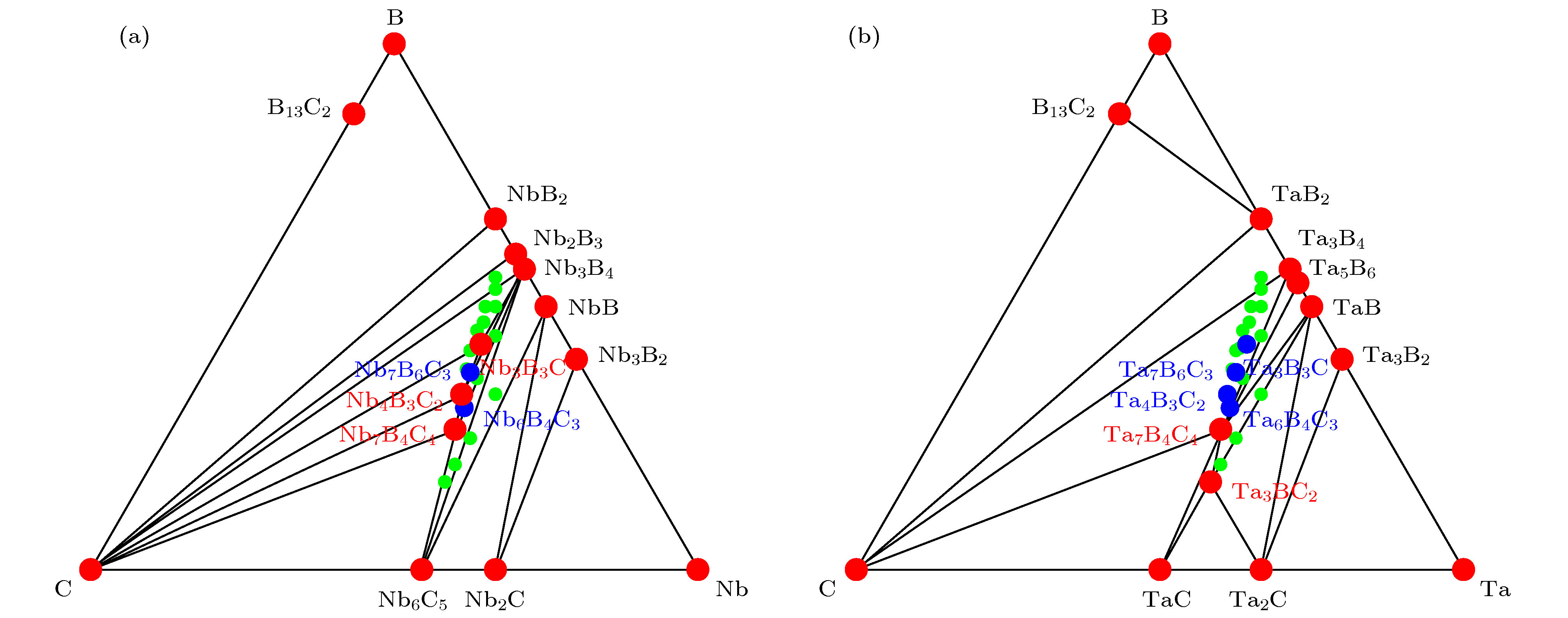
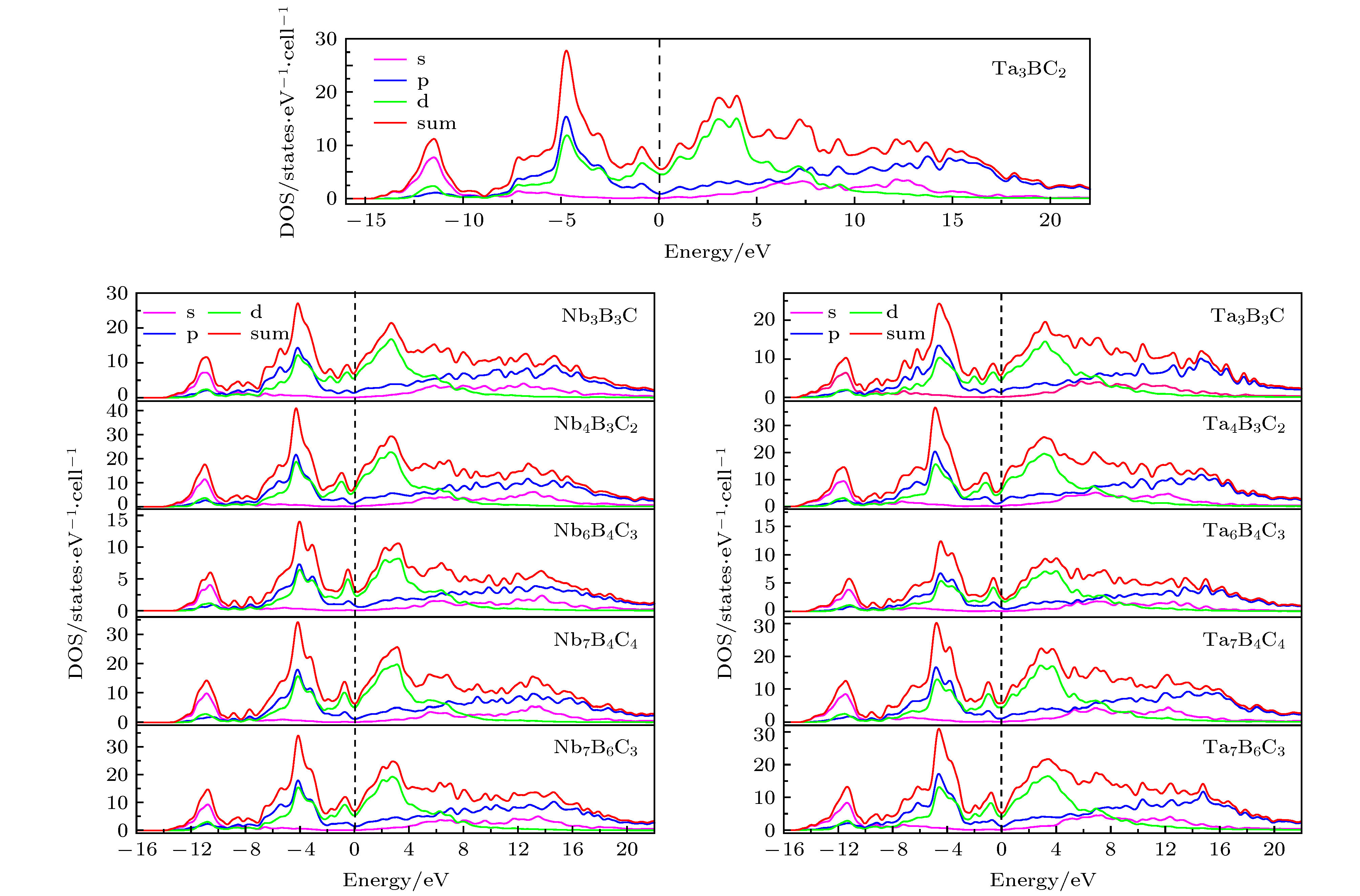
Transition-metal light-element compounds are potential candidates for hard materials. In the past, most of studies focused on the binary transition metal borides, carbides and nitrides, while the researches of ternary phases are relatively rare. In this paper, the structure units of the known Nb3B3C and Nb4B3C2 phases are first analyzed to be Nb6C octahedron and Nb6B triangular prism, respectively. By stacking the Nb6C octahedron and Nb6B triangular prism, twenty ternary Nb-B-C and twenty ternary Ta-B-C configurations with different compositions are constructed. The chemical formula of these Nb-B-C and Ta-B-C configurations can be defined to be Nb(m + n + 2)B(2m + 2)Cn and Ta(m + n + 2)B(2m + 2)Cn, respectively. Using first-principles density functional calculations, thermodynamical, dynamical and mechanical stabilities of the constructed ternary Nb-B-C and Ta-B-C configurations are investigated through calculating their enthalpies of formation, phonon dispersions and elastic constants. Five Nb-B-C (Nb3B3C, Nb4B3C2, Nb6B4C3, Nb7B4C4 and Nb7B6C3) phases and six Ta-B-C (Ta3B3C, Ta4B3C2, Ta6B4C3, Ta7B4C4, Ta7B6C3 and Ta3BC2) phases are predicted to be stable by analyzing the constructed ternary Nb-B-C and Ta-B-C phase diagrams, in which the seven phases (Nb6B4C3, Ta3B3C, Ta4B3C2, Ta6B4C3, Ta7B4C4, Ta7B6C3 and Ta3BC2) are first predicted to be stable. The Nb6B4C3, Ta6B4C3, Ta4B3C2 and Ta3B3C phases are stable when temperature is higher than 1730, 210, 360 and 1100 K, respectively. And the Ta3BC2 phase is stable only when temperature is lower than 130 K. The calculated results about mechanical and electric properties show that these Nb-B-C and Ta-B-C phases are conductive materials with a high hardness in a range of 23.8–27.4 GPa.
-
Keywords:
- hard materials /
- phase diagram /
- first-principles calculations /
- stability
[1] Tian Y J, Xu B, Zhao Z S 2012 Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 33 93
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 包括, 马帅领, 徐春红, 崔田 2017 66 036104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bao K, Ma S L, Xu C H, Cui T 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 036104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhou X F, Sun J, Fan Y X, Chen J, Wang H T, Guo X J, He J L, Tian Y J 2007 Phys. Rev. B 76 100101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wu Q H, Hu Q K, Hou Y M, Wang H Y, Zhou A G, Wang L B 2018 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 30 385402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Tian Y J, Xu B, Yu D L, Ma Y M, Wang Y B, Jiang Y B, Hu W T, Tang C C, Gao Y F, Luo K, Zhao Z S, Wang L M, Wen B, He J L, Liu Z Y 2013 Nature 493 385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Huang Q, Yu D L, Xu B, Hu W T, Ma Y M, Wang Y B, Zhao Z S, Wen B, He J L, Liu Z Y, Tian Y J 2014 Nature 510 250
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 徐波, 田永君 2017 66 036201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu B, Tian Y J 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 036201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wu Q H, Hu Q K, Hou Y M, Wang H Y, Zhou A G, Wang L B, Cao G H 2018 Mater. Des. 140 45
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Cumberland R W, Weinberger M B, Gilman J J, Clark S M, Tolbert S H, Kaner R B 2005 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127 7264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chung H Y, Weinberger M B, Levine J B, Kavner A, Yang J M, Tolbert S H, Kaner R B 2007 Science 316 436
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Gregoryanz E, Sanloup C, Somayazulu M, Badro J, Fiquet G, Mao H K, Hemley R J 2004 Nat. Mater. 3 294
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Young A F, Sanloup C, Gregoryanz E, Scandolo S, Hemley R J, Mao H K 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 96 155501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Ivanovskii A L 2012 Prog. Mater. Sci. 57 184
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 陶强, 马帅领, 崔田, 朱品文 2017 66 036103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tao Q, Ma S L, Cui T, Zhu P W 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 036103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Hillebrecht H, Gebhardt K 2001 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 40 1445
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 胡前库, 侯一鸣, 吴庆华, 秦双红, 王李波, 周爱国 2019 68 096201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu Q K, Hou Y M, Wu Q H, Qin S H, Wang L B, Zhou A G 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 096201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang P F, Weng M Y, Xiao Y, Hu Z X, Li Q H, Li M, Wang Y D, Chen X, Yang X N, Wen Y R, Yin Y X, Yu X Q, Xiao Y G, Zheng J X, Wan L J, Pan F, Guo Y G 2019 Adv. Mater. 31 1903483
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Xiao W J, Xin C, Li S B, Jie J S, Gu Y, Zheng J X, Pan F 2018 J. Mater. Chem. A 6 9893
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Kresse G, Furthmüller J 1996 Phys. Rev. B 54 11169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Le Page Y, Saxe P 2002 Phys. Rev. B 65 104104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Togo A, Tanaka I 2015 Scr. Mater. 108 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Togo A, Chaput L, Tanaka I, Hug G 2010 Phys. Rev. B 81 174301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Mouhat F, Coudert F X 2014 Phys. Rev. B 90 224104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wu Z J, Zhao E J, Xiang H P, Hao X F, Liu X J, Meng J 2007 Phys. Rev. B 76 054115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Pugh S F 1954 Philos. Mag. 45 823
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Chen X Q, Niu H Y, Li D Z, Li Y Y 2011 Intermetallics 19 1275
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
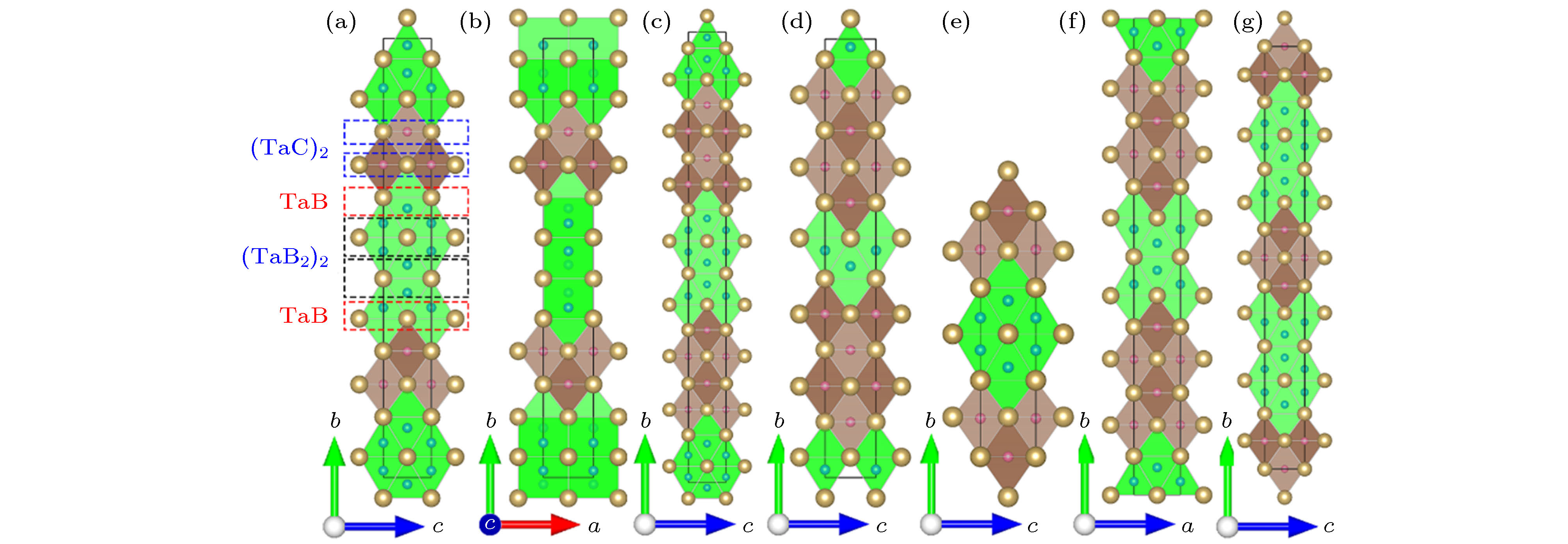
图 1 (a), (b) Ta3B3C; (c) Ta4B3C2; (d) Ta3BC2; (e) Ta6B4C3; (f) Ta7B4C4; (g) Ta7B6C3的晶体结构. 棕球: Ta原子; 蓝球: B原子; 粉球: C原子. Ta6B三棱柱和Ta6C八面体分别用绿色和褐色表示
Figure 1. The crystal structures of (a), (b) Ta3B3C; (c) Ta4B3C2; (d) Ta3BC2; (e) Ta6B4C3; (f) Ta7B4C4; (g) Ta7B6C3. The light brown, blue and pink spheres represent Ta, B, and C atoms, respectively. The Ta6B triangular prisms and Ta6C octahedrons are painted green and dark brown.
表 1 不同成分Nb(m + n + 2)B(2m + 2)Cn和Ta(m + n + 2)B(2m + 2)Cn晶体的结构参数
Table 1. Structural parameters of Nb(m + n + 2)B(2m + 2)Cn and Ta(m + n + 2)B(2m + 2)Cn crystals.
m n 空间群 模型 晶格参数/Å 模型 晶格参数/Å a b c a b c 0 1 Cmmm Nb3B2C 3.254 13.808 3.141 Ta3B2C 3.240 13.697 3.127 0 2 Cmcm Nb2BC 3.235 18.330 3.153 Ta2BC 3.220 18.165 3.140 0 3 Cmmm Nb5B2C3 3.225 22.903 3.153 Ta5B2C3 3.199 22.659 3.138 0 4 Cmcm Nb3BC2 3.214 27.376 3.156 Ta3BC2 3.198 27.132 3.150 1 1 Pmmm Nb4B4C 3.290 18.994 3.145 Ta4B4C 3.277 18.878 3.127 1 2 Immm Nb5B4C2 3.267 23.600 3.150 Ta5B4C2 3.248 23.377 3.138 1 3 Pmmm Nb6B4C3 3.243 28.028 3.154 Ta6B4C3 3.225 27.872 3.141 1 4 Immm Nb7B4C4 3.242 32.545 3.158 Ta7B4C4 3.224 32.315 3.147 2 1 Cmmm Nb5B6C 3.302 24.414 3.134 Ta5B6C 3.289 24.208 3.122 2 2 Cmcm Nb3B3C 3.284 28.877 3.144 Ta3B3C 3.267 28.688 3.133 2 3 Cmmm Nb7B6C3 3.264 33.364 3.148 Ta7B6C3 3.246 33.164 3.136 2 4 Cmcm Nb4B3C2 3.257 37.874 3.153 Ta4B3C2 3.243 37.609 3.141 3 1 Pmmm Nb6B8C 3.309 14.889 3.137 Ta6B8C 3.298 14.788 3.122 3 2 Immm Nb7B8C2 3.290 34.247 3.144 Ta7B8C2 3.276 34.007 3.131 3 3 Pmmm Nb8B8C3 3.276 19.350 3.148 Ta8B8C3 3.258 19.235 3.135 3 4 Immm Nb9B8C4 3.268 43.255 3.151 Ta9B8C4 3.252 42.977 3.138 4 1 Cmmm Nb7B10C 3.312 35.192 3.131 Ta7B10C 3.299 34.990 3.116 4 2 Cmcm Nb4B5C 3.296 39.694 3.139 Ta4B5C 3.280 39.441 3.125 4 3 Cmmm Nb9B10C3 3.281 44.206 3.142 Ta9B10C3 3.263 43.924 3.130 4 4 Cmcm Nb5B5C2 3.273 48.729 3.145 Ta5B5C2 3.257 48.400 3.134 表 2 不同成分Nb-B-C相和Ta-B-C相的形成焓 (单位: eV/atom),
$ \Delta{H}_{\rm{elements}} $ 表示单质为反应物,$ \Delta{H}_{\rm{comp}} $ 表示最稳定竞争组合为反应物Table 2. Calculated formation enthalpies of different Nb-B-C and Ta-B-C phases (in eV/atom).
$ \Delta{H}_{\rm{elements}} $ represents the elements as the reactants, and$\Delta{H}_{\rm{comp}}$ indicates the most stable composite as the reactants.Phases $ \Delta{H}_{\rm{elements}} $ $ \Delta{H}_{\rm{comp}} $ 最稳定竞争组合 Phases $ \Delta{H}_{\rm{elements}} $ $ \Delta{H}_{\rm{comp}} $ 最稳定竞争组合 Nb3B2C –0.620 0.070 Nb3B4 + 6NbB + Nb6C5 = 5Nb3B2C Ta3B2C –0.651 0.086 Ta3BC2 + 3TaB = 2Ta3B2C Nb2BC –0.619 0.029 Nb3B4 + NbB + Nb6C5 = 5Nb2BC Ta2BC –0.664 0.035 Ta3BC2 + TaB = 2Ta2BC Nb5B2C3 –0.586 0.036 3Nb3B4 + Nb7B4C4 + 4Nb6C5 = 8Nb5B2C3 Ta5B2C3 –0.655 0.021 3Ta3BC2 + TaB = 2Ta5B2C3 Nb3BC2 –0.586 0.019 Nb3B4 + 3Nb7B4C4 + 4Nb6C5 = 16Nb3BC2 Ta3BC2 –0.660 –0.002 TaB + 2TaC = Ta3BC2 Nb4B4C –0.679 0.030 3Nb3B4 + Nb7B4C4 = 4Nb4B4C Ta4B4C –0.691 0.044 Ta7B4C4 + 3Ta3B4 = 4Ta4B4C Nb5B4C2 –0.668 0.006 Nb3B4 + Nb7B4C4 = 2Nb5B4C2 Ta5B4C2 –0.694 0.019 Ta7B4C4 + Ta3B4 = 2Ta5B4C2 Nb6B4C3 –0.645 0.005 Nb3B4 + 3Nb7B4C4 = 4Nb6B4C3 Ta6B4C3 –0.693 0.004 3Ta7B4C4 + Ta3B4 = 4Ta6B4C3 Nb7B4C4 –0.632 –0.006 3Nb3B4 + 2C + 2Nb6C5 = 3Nb7B4C4 Ta7B4C4 –0.685 –0.017 3Ta3B4 + 4TaC = Ta7B4C4 Nb5B6C –0.697 0.015 3Nb3B4 + C + 2Nb3B3C = 3Nb5B6C Ta5B6C –0.697 0.024 C + Ta5B6 = Ta5B6C Nb3B3C –0.685 –0.001 3Nb3B4 + C + 3Nb4B3C2 = 7Nb3B3C Ta3B3C –0.699 0.010 3Ta7B4C4 + 9Ta3B4 + 4C = 16Ta3B3C Nb7B6C3 –0.664 0.0005 Nb3B3C + Nb4B3C2 = Nb7B6C3 Ta7B6C3 –0.695 0.0008 5Ta7B4C4 + 7Ta3B4 + 4C = 8Ta7B6C3 Nb4B3C2 –0.648 –0.001 5Nb3B4 + 4C + 7Nb7B4C4 = 16Nb4B3C2 Ta4B3C2 –0.684 0.002 7Ta7B4C4 + 5Ta3B4 + 4C = 16Ta4B3C2 Nb6B8C –0.695 0.019 2Nb3B4 + C = Nb6B8C Ta6B8C –0.685 0.034 2Ta3B4 + C = Ta6B8C Nb7B8C2 –0.683 0.008 3Nb3B4 + 2C + 4Nb3B3C = 3Nb7B8C2 Ta7B8C2 –0.686 0.020 Ta7B4C4 + 7Ta3B4 + 4C = 4Ta7B8C2 Nb8B8C3 –0.665 0.008 C + 8Nb3B3C = 3Nb8B8C3 Ta8B8C3 –0.684 0.012 Ta7B4C4 + 3Ta3B4 + 2C = 2Ta8B8C3 Nb9B8C4 –0.651 0.008 C + 5Nb3B3C + 3Nb4B3C2 = 3Nb9B8C4 Ta9B8C4 –0.675 0.013 3Ta7B4C4 + 5Ta3B4 + 4C = 4Ta9B8C4 Nb7B10C –0.693 0.021 C + 2Nb2B3 + Nb3B4 = Nb7B10C Ta7B10C –0.677 0.030 TaB2 + 2Ta3B4 + C = Ta7B10C Nb4B5C –0.684 0.011 2C + Nb3B3C + 3Nb3B4 = 3Nb4B5C Ta4B5C –0.679 0.026 Ta7B4C4 + 19Ta3B4 + 12C = 16Ta4B5C Nb9B10C3 –0.668 0.012 C + 2Nb3B3C + Nb3B4 = Nb9B10C3 Ta9B10C3 –0.677 0.019 3Ta7B4C4 + 17Ta3B4 + 12C = 8Ta9B10C3 Nb5B5C2 –0.655 0.011 C + 5Nb3B3C = 3Nb5B5C2 Ta5B5C2 –0.670 0.018 5Ta7B4C4 + 15Ta3B4 + 12C = 16Ta5B5C2 表 3 Nb-B-C和Ta-B-C三元相的弹性常数Cij、体模量B、剪切模量 G和维氏硬度Hv (单位: GPa)
Table 3. Elastic constants Cij, bulk modulus B, shear modulus G, Vickers hardness Hv of Nb-B-C and Ta-B-C ternary phases (in GPa).
结构 弹性常数 力学性能a 硬度 C11 C22 C33 C44 C55 C66 C12 C13 C23 B G B/G HChen HTian Nb3B3C 544.3 479.8 522.8 181.5 171.9 245.3 170.9 132.9 162.2 275.3 189.7 1.45 24.8 24.7 Nb4B3C2 551.5 499.2 548.5 184.0 175.1 257.1 183.2 132.7 157.8 282.9 195.8 1.44 25.5 25.4 Nb6B4C3 533.3 493.8 548.1 174.9 161.3 255.2 175.4 138.9 151.7 278.5 189.5 1.47 24.4 24.3 Nb7B4C4 535.9 505.9 526.4 172.2 161.3 259.1 184.0 142.8 152.6 280.6 188.3 1.49 23.9 23.8 Nb7B6C3 553.1 494.5 563.2 188.7 179.6 255.6 176.4 132.1 157.7 282.5 198.9 1.42 26.3 26.2 Ta3B3C 569.6 514.4 563.5 194.1 180.0 261.8 187.1 147.3 173.9 295.9 200.8 1.47 25.3 25.3 Ta4B3C2 581.1 535.3 602.1 197.3 185.1 275.8 200.3 146.0 170.2 305.7 209.0 1.46 26.2 26.2 Ta3BC2 550.0 547.7 550.0 159.8 159.5 292.1 216.7 160.0 149.2 299.6 191.8 1.56 22.7 22.9 Ta6B4C3 584.7 539.6 614.2 203.0 189.9 279.9 195.5 168.0 144.1 305.9 213.9 1.43 27.4 27.3 Ta7B4C4 563.1 547.5 571.5 183.6 170.4 281.4 200.2 162.0 164.3 303.9 200.8 1.51 24.4 24.5 Ta7B6C3 584.7 540.0 614.2 203.0 190.0 280.0 195.5 168.0 144.1 305.9 213.9 1.43 27.4 27.3 TaB2 302 200 1.51 24.4 24.5 NbB2 287 195 1.47 24.8 24.8 TaC 324 215 1.51 25.6 25.9 NbC 239 161 1.48 21.6 21.4 SiC 213 187 1.14 33.6 32.2 Al2O3 232 147 1.58 18.7 18.7 TiN 259 180 1.44 24.3 24.0 注: a二元相力学性能数据来自Materials Project网站. -
[1] Tian Y J, Xu B, Zhao Z S 2012 Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 33 93
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 包括, 马帅领, 徐春红, 崔田 2017 66 036104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bao K, Ma S L, Xu C H, Cui T 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 036104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhou X F, Sun J, Fan Y X, Chen J, Wang H T, Guo X J, He J L, Tian Y J 2007 Phys. Rev. B 76 100101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wu Q H, Hu Q K, Hou Y M, Wang H Y, Zhou A G, Wang L B 2018 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 30 385402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Tian Y J, Xu B, Yu D L, Ma Y M, Wang Y B, Jiang Y B, Hu W T, Tang C C, Gao Y F, Luo K, Zhao Z S, Wang L M, Wen B, He J L, Liu Z Y 2013 Nature 493 385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Huang Q, Yu D L, Xu B, Hu W T, Ma Y M, Wang Y B, Zhao Z S, Wen B, He J L, Liu Z Y, Tian Y J 2014 Nature 510 250
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 徐波, 田永君 2017 66 036201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu B, Tian Y J 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 036201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wu Q H, Hu Q K, Hou Y M, Wang H Y, Zhou A G, Wang L B, Cao G H 2018 Mater. Des. 140 45
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Cumberland R W, Weinberger M B, Gilman J J, Clark S M, Tolbert S H, Kaner R B 2005 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127 7264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chung H Y, Weinberger M B, Levine J B, Kavner A, Yang J M, Tolbert S H, Kaner R B 2007 Science 316 436
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Gregoryanz E, Sanloup C, Somayazulu M, Badro J, Fiquet G, Mao H K, Hemley R J 2004 Nat. Mater. 3 294
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Young A F, Sanloup C, Gregoryanz E, Scandolo S, Hemley R J, Mao H K 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 96 155501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Ivanovskii A L 2012 Prog. Mater. Sci. 57 184
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 陶强, 马帅领, 崔田, 朱品文 2017 66 036103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tao Q, Ma S L, Cui T, Zhu P W 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 036103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Hillebrecht H, Gebhardt K 2001 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 40 1445
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 胡前库, 侯一鸣, 吴庆华, 秦双红, 王李波, 周爱国 2019 68 096201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu Q K, Hou Y M, Wu Q H, Qin S H, Wang L B, Zhou A G 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 096201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang P F, Weng M Y, Xiao Y, Hu Z X, Li Q H, Li M, Wang Y D, Chen X, Yang X N, Wen Y R, Yin Y X, Yu X Q, Xiao Y G, Zheng J X, Wan L J, Pan F, Guo Y G 2019 Adv. Mater. 31 1903483
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Xiao W J, Xin C, Li S B, Jie J S, Gu Y, Zheng J X, Pan F 2018 J. Mater. Chem. A 6 9893
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Kresse G, Furthmüller J 1996 Phys. Rev. B 54 11169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Le Page Y, Saxe P 2002 Phys. Rev. B 65 104104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Togo A, Tanaka I 2015 Scr. Mater. 108 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Togo A, Chaput L, Tanaka I, Hug G 2010 Phys. Rev. B 81 174301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Mouhat F, Coudert F X 2014 Phys. Rev. B 90 224104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wu Z J, Zhao E J, Xiang H P, Hao X F, Liu X J, Meng J 2007 Phys. Rev. B 76 054115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Pugh S F 1954 Philos. Mag. 45 823
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Chen X Q, Niu H Y, Li D Z, Li Y Y 2011 Intermetallics 19 1275
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 13510
- PDF Downloads: 208
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: