-
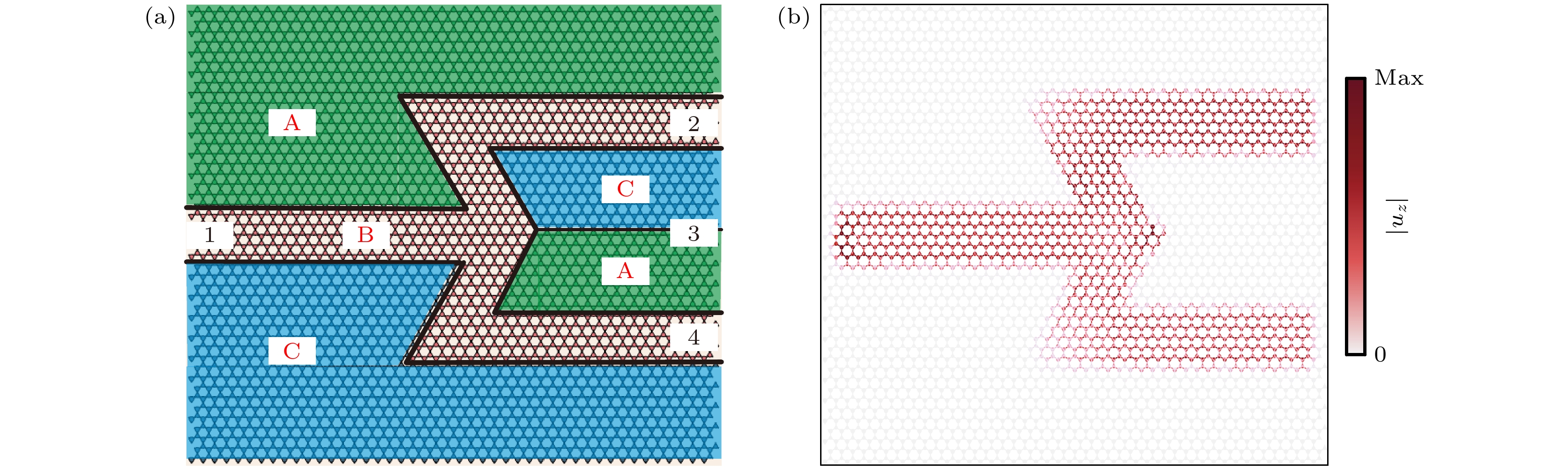
自拓扑绝缘体概念从量子波领域拓展到经典波领域以来, 谷霍尔拓扑绝缘体因其新奇的物理特性、丰富的波调控方式等优势, 引起了大量的关注, 相关研究得到了快速发展. 本文针对传统谷拓扑绝缘体中边缘态输运容量小、结构不灵活等缺陷, 基于谷锁定原理设计了一种拓扑波导结构. 该结构的原始构形具有矩形脉连接的蜂窝晶格, 利用等效结构参数方法计算了模型的能带结构、输运特性, 发现其布里渊区角点K处有3个狄拉克点. 通过改变结构参数打破体系的空间反演对称性, 实现了3个频段的弹性波模式的拓扑相变; 在两个拓扑绝缘体中间插入具有狄拉克点的声子晶体组成拓扑异质结构, 展示了该结构的拓扑波导态具有多频段、宽度可调、强鲁棒性等优点. 基于该结构设计了能量分束器、能量汇聚器, 实现了对弹性波的多种灵活操控. 此研究不仅丰富了拓扑声学, 所设计的拓扑异质结构在多频段通信与信息处理方面具有潜在的应用前景.Since the topological insulator concept was expanded from the field of quantum waves to the field of elastic waves, the research related to the elastic system valley Hall insulator has been developed rapidly because of its novel physical properties, rich design ability for wave modulation and simple implementation conditions. To address the limitations of small energy and inflexible structure of the edge-state transmission of valley Hall insulators in traditional structure, a topological waveguide heterostructure is designed based on the valley locking principle. The original configuration of this structure features a honeycomb lattice connected by rectangular veins. The energy band structure and transmission characteristics of the model are calculated using the equivalent structural parameter method. It is found that there are three Dirac points at the corner point K of the Brillouin zone, and the spatial inversion symmetry of the system can be broken by changing the structural parameters, so as to realize the topological phase transition of the out-of-plane body elastic mode in three frequency bands. The topological heterogeneous structure is formed by superimposing Dirac point phonon crystals between two topological insulators, and the topological waveguide state possesses advantages, such as multiband, tunability, and robustness. The structure can be used to design energy splitters and energy convergers to achieve flexible manipulation of elastic waves. This study enriches topological acoustics, and the designed multi-band elastic topological insulator has potential applications in multi-band communication and information processing.
-
Keywords:
- phononic crystals /
- elastic waves /
- topological waveguide states /
- multiband
[1] Bernevig B A, Hughes T L, Zhang S C 2006 Science 314 1757
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Moore J E 2010 Nature 464 194
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] He C, Ni X, Ge H, Sun X C, Chen Y B, Lu M H, Liu X P, Chen Y F 2016 Nat. Phys. 12 1124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Miniaci M, Pal R, Morvan B, Ruzzene M 2018 Phys. Rev. X 8 031074
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhou W J, Wu B, Su Y, Liu D Y, Chen W Q, Bao R H 2021 Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 28 221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zeng Y, Zhang S Y, Zhou H T, et al. 2021 Mater. Des. 208 109906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wang K, Zhou J X, Chang Y P, Ouyang H J, Xu D L, Yang Y 2020 Nonlinear Dyn. 101 755
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ding Y J, Peng Y G, Zhu Y F, et al. 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 122 014302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Yang Z J, Gao F, Shi X H, Lin X, Gao Z, Chong Y D, Zhang B L 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 114301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wang P, Lu L, Bertoldi K 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 115 104302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Gao N, Qu S C, Si L, Wang J, Chen W Q 2021 Appl. Phys. Lett. 118 063502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Chen Y F, Meng F, Huang X D 2021 Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 146 107054
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Huo S Y, Chen J J, Huang H B, Wei Y J, Tan Z H, Feng L Y, Xie X P 2021 Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 154 107543
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Lu J Y, Qiu C Y, Ye L P, Fan X Y, Ke M Z, Zhang F, Liu Z Y 2017 Nat. Phys. 13 369
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Brendel C, Peano V, Painter O, Marquardt F 2018 Phys. Rev. B 97 020102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lin J H, Qi Y J, He Z J, Bi R G, Dong K 2024 Appl. Phys. Lett. 124 082202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 王一鹤, 张志旺, 程营, 刘晓峻 2019 68 227805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y H, Zhang Z W, Cheng Y, Liu X J 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 227805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 贾鼎, 葛勇, 袁寿其, 孙宏祥 2019 68 224301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jia D, Ge Y, Yuan S Q, Sun H X 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 224301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 郑周甫, 尹剑飞, 温激鸿, 郁殿龙 2020 69 156201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zheng Z F, Yin J F, Wen J H, Yu D L 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 156201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Jiang Z, Zhou Y Y, Zheng S J, Liu J T, Xia B Z 2023 Int. J. Mech. Sci. 255 108464
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Huo S, Chen J, Huang H, 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 10335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Yang Z Z, Li X, Peng Y Y, 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 125 255502.
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Xu G G, Sun X W, Wen X D 2023 J Appl Phys. 133 095110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang M D, Zhou W Y, Bi L, Qiu C Y, Ke M Z, Liu Z Y 2020 Nat. Commun. 11 3000
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Huo S Y, Xie G H, Qiu S J, Gong X C, Fan S Z, Fu C M, Li Z Y 2022 Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 29 7772
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Wang J Q, Zhang Z D, Yu S Y, Ge H, Liu K F, Wu T, Sun X C, Liu L, Chen H Y, He C 2022 Nat. Commun. 13 1324
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Liu S, Deng W Y, Huang X Q, Lu J Y, Ke M Z, Liu Z Y 2022 Phys. Rev. Appl. 18 034066
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Chen Y, Guo Z, Liu Y 2024 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 57 465306.
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 王艳锋 2015 博士学位论文 (北京: 北京交通大学)
Wang Y F 2015 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijin: Beijinjiaotong University
[30] Lai Y, Zhang Z Q 2003 Appl. Phys. Lett. 83 3900-
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Mei J, Liu Z Y, Shi J, et al. 2003 Phys. Rev. B. 67 245107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
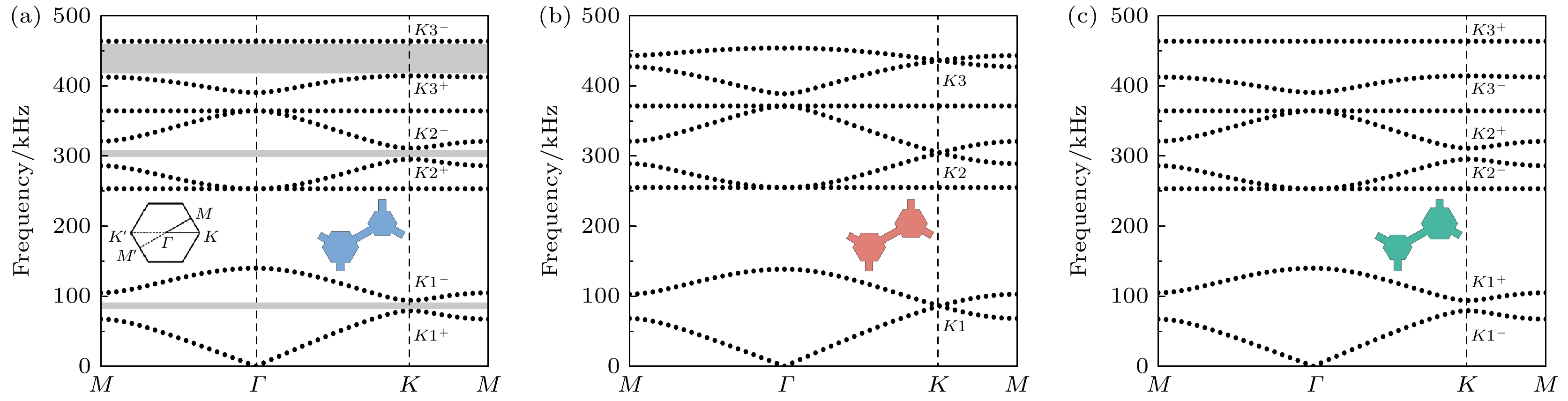
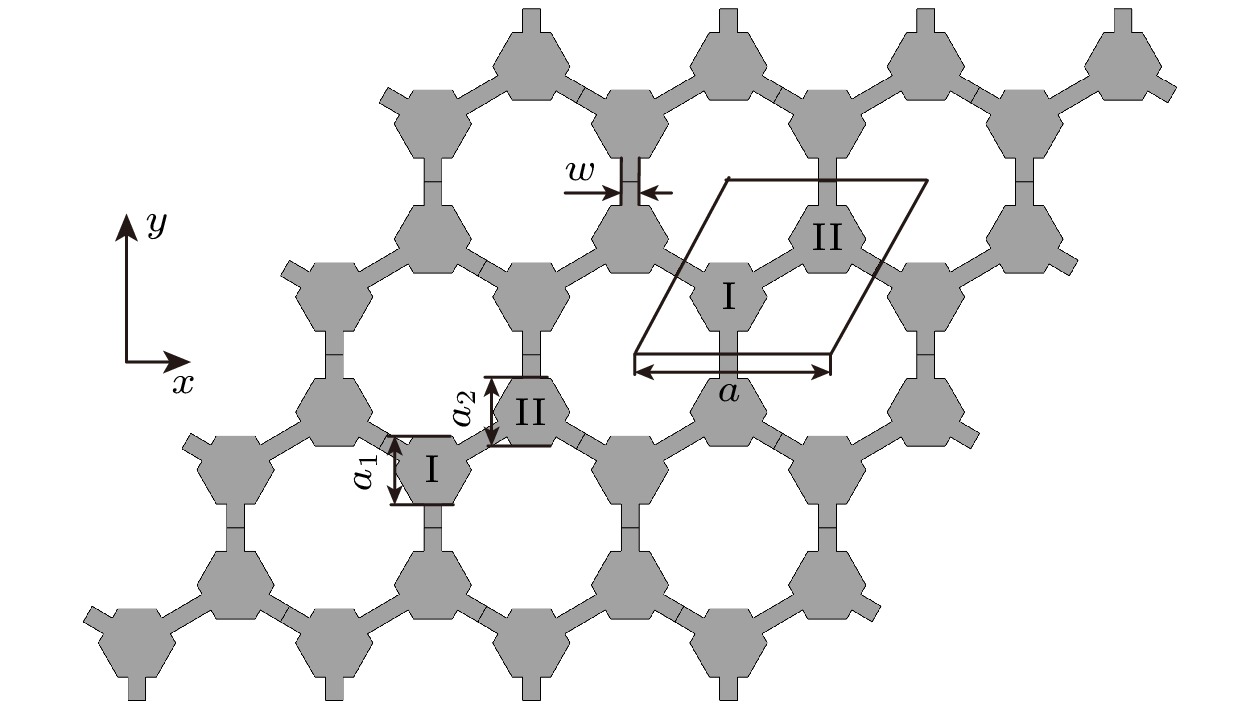
图 2 面外弹性波模式的能带结构图 (a) 当$ {a_1} > {a_2} $时, 几何模型及能带图, 阴影部分表示带隙; (b) 当$ {a_1}={a_2} $时, 几何模型及能带结构; (c) 当$ {a_1} < {a_2} $时, 几何模型及能带结构
Fig. 2. Energy band structure diagrams of the out-of-plane body elastic wave mode: (a) When $ {a_1} > {a_2} $, geometric model energy band diagram and its band gap (shaded); (b) when $ {a_1}={a_2} $, geometric model and energy band structure; (c) when $ {a_1} < {a_2} $, geometric model and energy band structure.
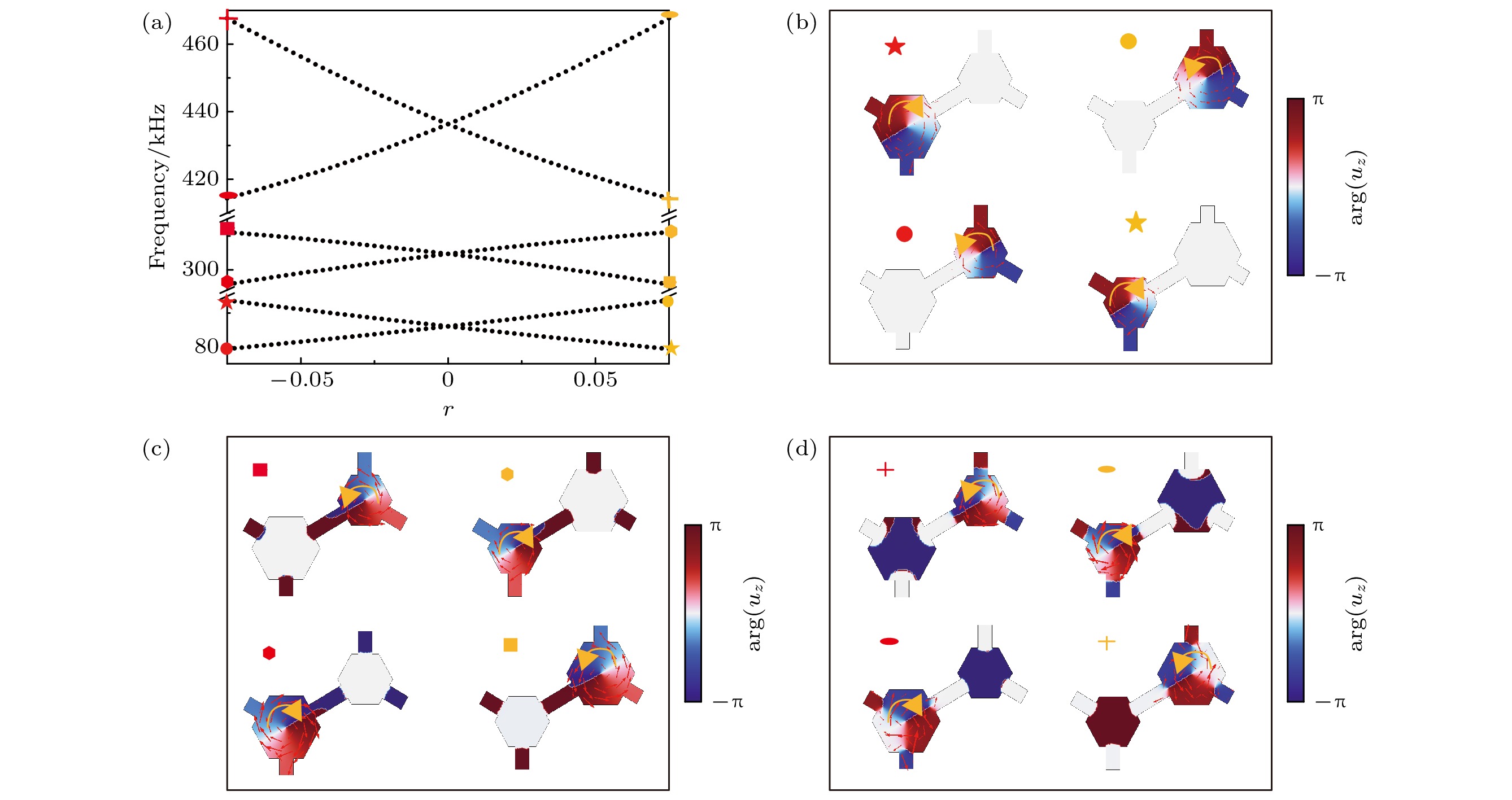
图 3 拓扑相变图 (a) 3组$K^+ $和$K^- $特征态频率随着r的变化; (b)第1频段的谷态本征位移场图; (c)第2频段的谷态本征位移场图; (d)第3频段的谷态本征位移场图
Fig. 3. Topological phase transition diagrams: (a) Variation of 3 sets of $ K^+ $ and $K^- $ eigenstate frequencies with r ; (b) valley eigenshift field map for the first frequency band; (c) valley eigenshift field map for the second frequency band; (d) valley eigenshift field map for the third frequency band.
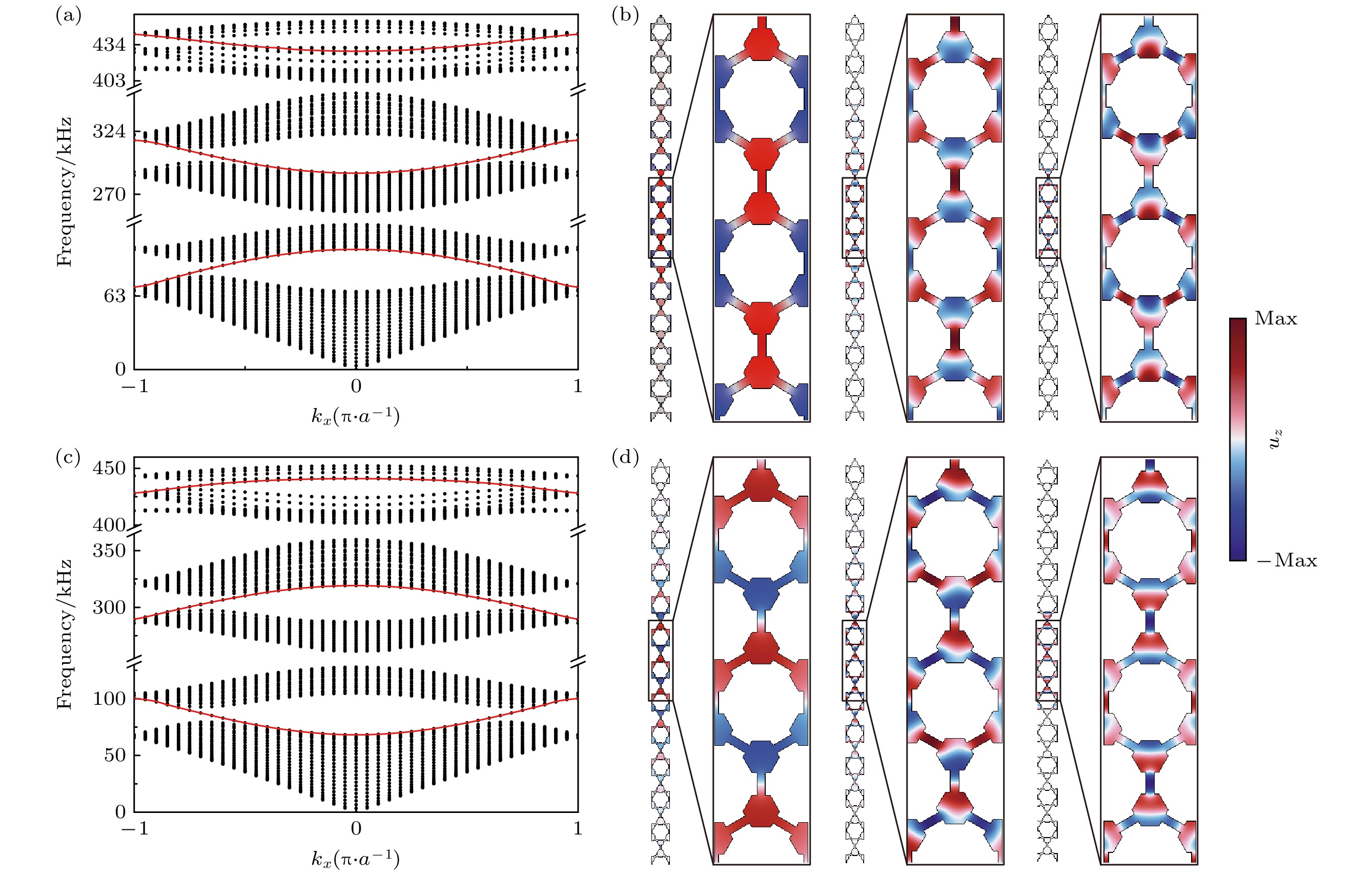
图 5 (a) U1U2U3型超胞投影能带; (b) kx = 0.6时91.4 kHz, 300.9 kHz, 435.2 kHz三个频段内U1U2U3型超胞的谷波导态; (c) U3U2U1型超胞投影能带; (d) kx = 0.6时82.9 kHz, 306.9 kHz, 436.7 kHz三个频段内U3U2U1型超胞的谷波导态
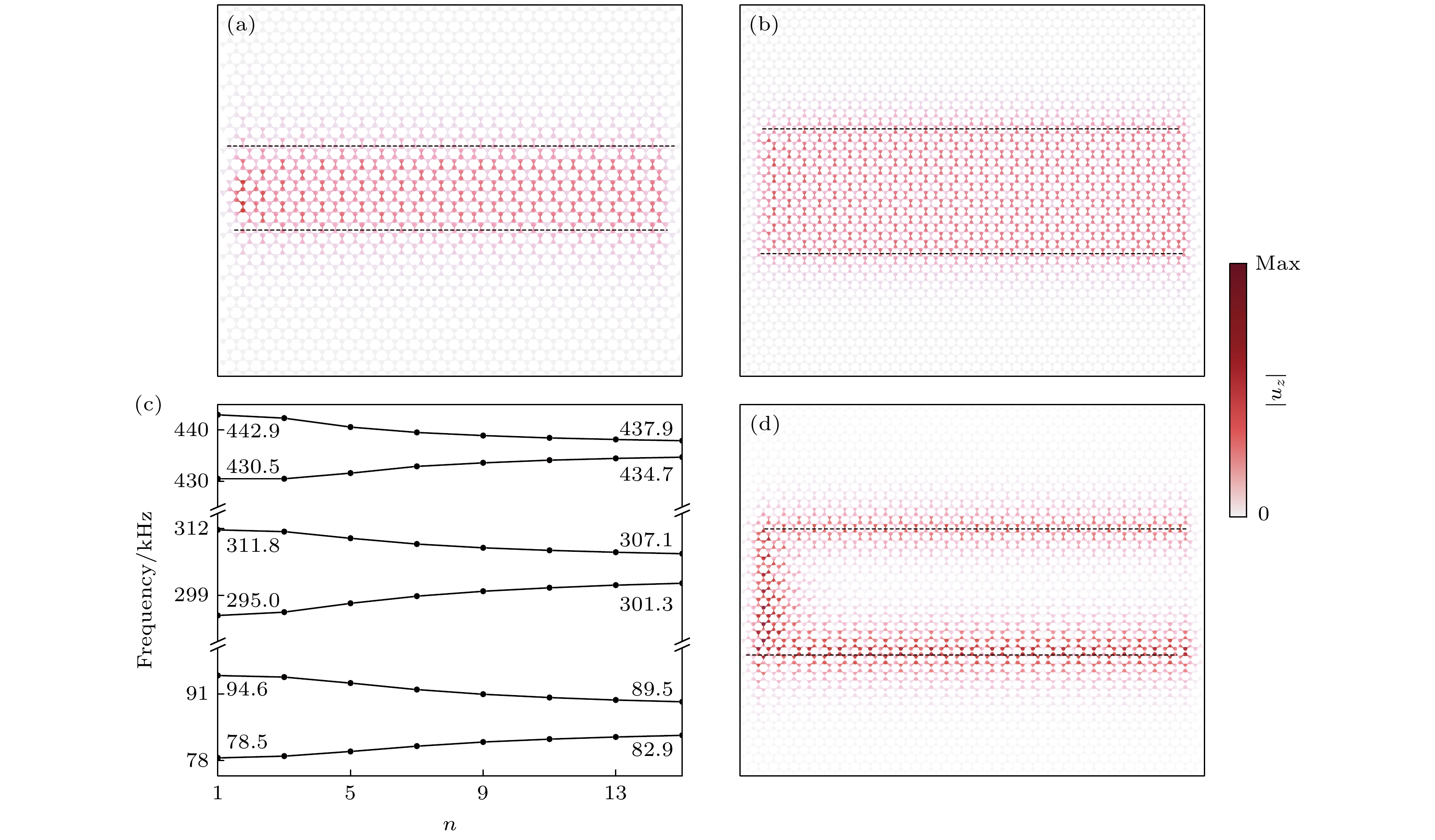
Fig. 5. (a) Projected energy bands of U1U2U3-type supercells; (b) the valley waveguide states of U1U2U3-type supercells at 91.4 kHz, 300.9 kHz, and 435.2 kHz bands for kx = 0.6; (c) the projected energy bands of U3U2U1-type supercells; (d) the valley waveguide states of U3U2U1-type supercells at 82.9 kHz, 306.9 kHz, and 436.7 kHz bands for kx = 0.6.
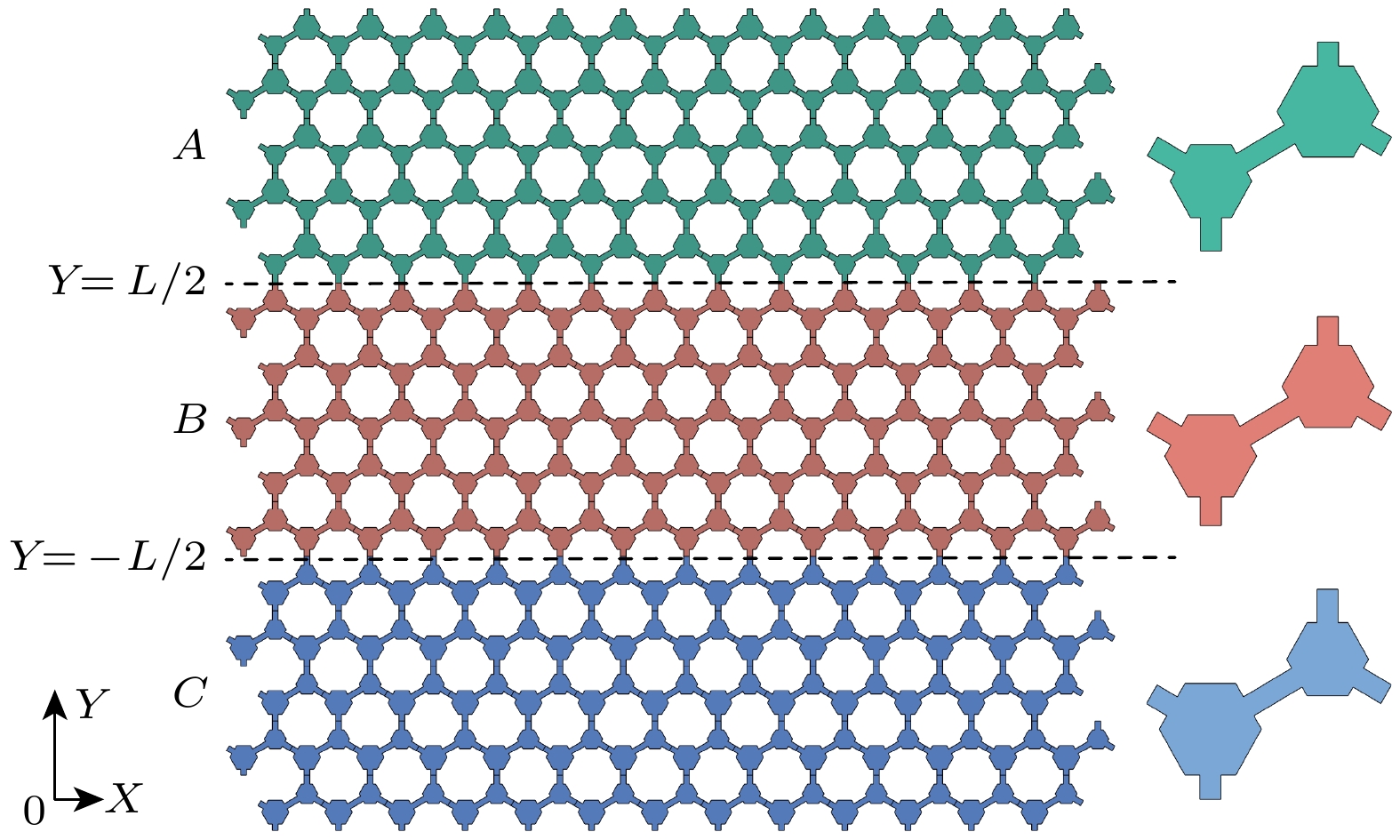
图 6 面外弹性波模式的波导输运 (a) A_{15}|B_5 |C_{15}型波导, 在左侧施加激励的${u_z}$绝对值场图; (b) A_{15}|B_15 |C_{15}型波导, 在左侧施加激励的${u_z}$绝对值场图; (c) A_{15}|B_n|C_{15}型波导, 波导频宽随着B域层数n的变化; (d) A_{15}|C_15 |A_{15}型波导, 在左侧施加激励的${u_z}$绝对值场图
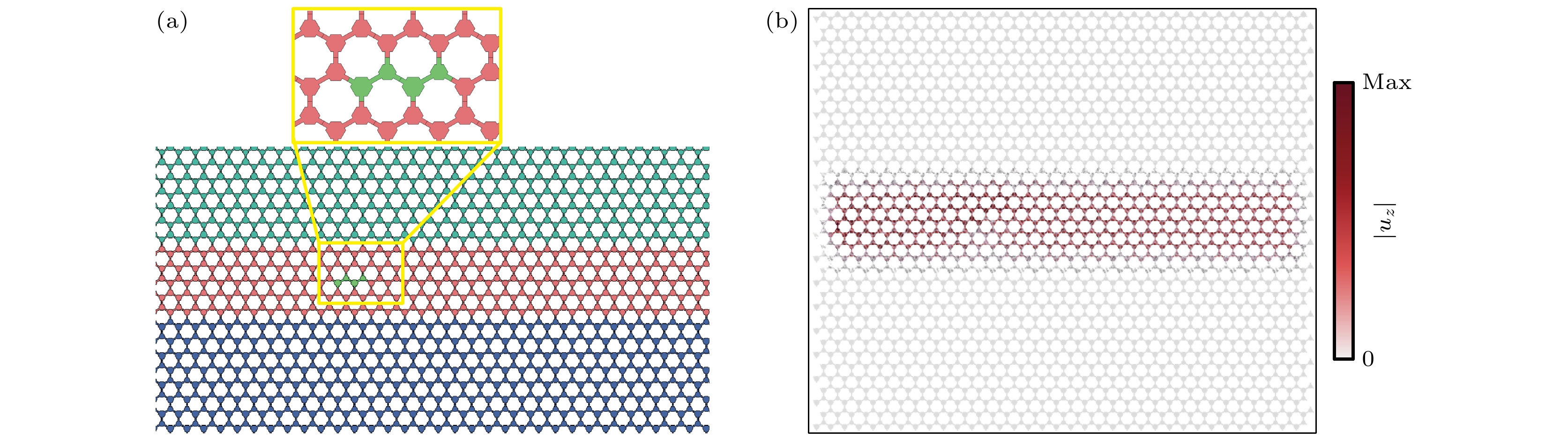
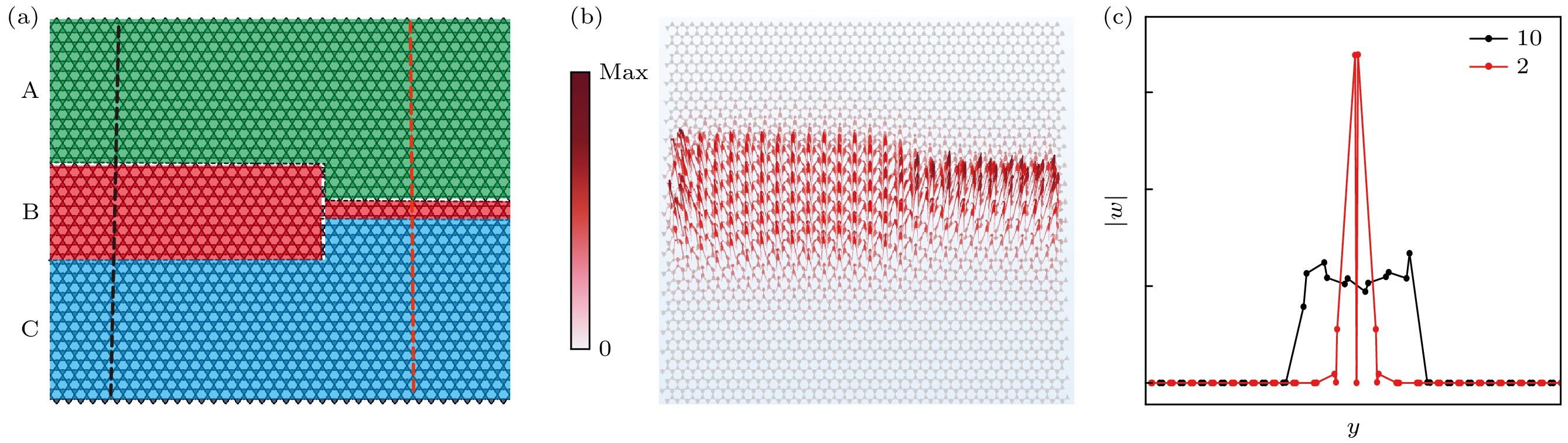
Fig. 6. Waveguide transmission in the out-of-plane elastic wave mode: (a) ${u_z}$ absolute value field plot for waveguide type A_{15}|B_5 |C_{15} with excitation applied on the left side. (b) ${u_z}$ absolute value field plot for waveguide type A_{15}|B_15 |C_{15} with excitation applied on the left side. (c) Variation of waveguide frequency band of A_{15}|B_n|C_{15} waveguide with the number of B-domain layers n. The waveguide frequency band is the same as the number of II-domain layers. (d) ${u_z}$ absolute value field plot for waveguide type A_{15}|C_15 |A_{15} with excitation applied on the left side.
-
[1] Bernevig B A, Hughes T L, Zhang S C 2006 Science 314 1757
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Moore J E 2010 Nature 464 194
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] He C, Ni X, Ge H, Sun X C, Chen Y B, Lu M H, Liu X P, Chen Y F 2016 Nat. Phys. 12 1124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Miniaci M, Pal R, Morvan B, Ruzzene M 2018 Phys. Rev. X 8 031074
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhou W J, Wu B, Su Y, Liu D Y, Chen W Q, Bao R H 2021 Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 28 221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zeng Y, Zhang S Y, Zhou H T, et al. 2021 Mater. Des. 208 109906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wang K, Zhou J X, Chang Y P, Ouyang H J, Xu D L, Yang Y 2020 Nonlinear Dyn. 101 755
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Ding Y J, Peng Y G, Zhu Y F, et al. 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 122 014302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Yang Z J, Gao F, Shi X H, Lin X, Gao Z, Chong Y D, Zhang B L 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 114 114301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wang P, Lu L, Bertoldi K 2015 Phys. Rev. Lett. 115 104302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Gao N, Qu S C, Si L, Wang J, Chen W Q 2021 Appl. Phys. Lett. 118 063502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Chen Y F, Meng F, Huang X D 2021 Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 146 107054
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Huo S Y, Chen J J, Huang H B, Wei Y J, Tan Z H, Feng L Y, Xie X P 2021 Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 154 107543
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Lu J Y, Qiu C Y, Ye L P, Fan X Y, Ke M Z, Zhang F, Liu Z Y 2017 Nat. Phys. 13 369
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Brendel C, Peano V, Painter O, Marquardt F 2018 Phys. Rev. B 97 020102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lin J H, Qi Y J, He Z J, Bi R G, Dong K 2024 Appl. Phys. Lett. 124 082202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 王一鹤, 张志旺, 程营, 刘晓峻 2019 68 227805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y H, Zhang Z W, Cheng Y, Liu X J 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 227805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 贾鼎, 葛勇, 袁寿其, 孙宏祥 2019 68 224301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jia D, Ge Y, Yuan S Q, Sun H X 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 224301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 郑周甫, 尹剑飞, 温激鸿, 郁殿龙 2020 69 156201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zheng Z F, Yin J F, Wen J H, Yu D L 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 156201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Jiang Z, Zhou Y Y, Zheng S J, Liu J T, Xia B Z 2023 Int. J. Mech. Sci. 255 108464
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Huo S, Chen J, Huang H, 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 10335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Yang Z Z, Li X, Peng Y Y, 2020 Phys. Rev. Lett. 125 255502.
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Xu G G, Sun X W, Wen X D 2023 J Appl Phys. 133 095110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang M D, Zhou W Y, Bi L, Qiu C Y, Ke M Z, Liu Z Y 2020 Nat. Commun. 11 3000
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Huo S Y, Xie G H, Qiu S J, Gong X C, Fan S Z, Fu C M, Li Z Y 2022 Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 29 7772
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Wang J Q, Zhang Z D, Yu S Y, Ge H, Liu K F, Wu T, Sun X C, Liu L, Chen H Y, He C 2022 Nat. Commun. 13 1324
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Liu S, Deng W Y, Huang X Q, Lu J Y, Ke M Z, Liu Z Y 2022 Phys. Rev. Appl. 18 034066
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Chen Y, Guo Z, Liu Y 2024 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 57 465306.
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 王艳锋 2015 博士学位论文 (北京: 北京交通大学)
Wang Y F 2015 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijin: Beijinjiaotong University
[30] Lai Y, Zhang Z Q 2003 Appl. Phys. Lett. 83 3900-
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Mei J, Liu Z Y, Shi J, et al. 2003 Phys. Rev. B. 67 245107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 2020
- PDF下载量: 98
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: