-
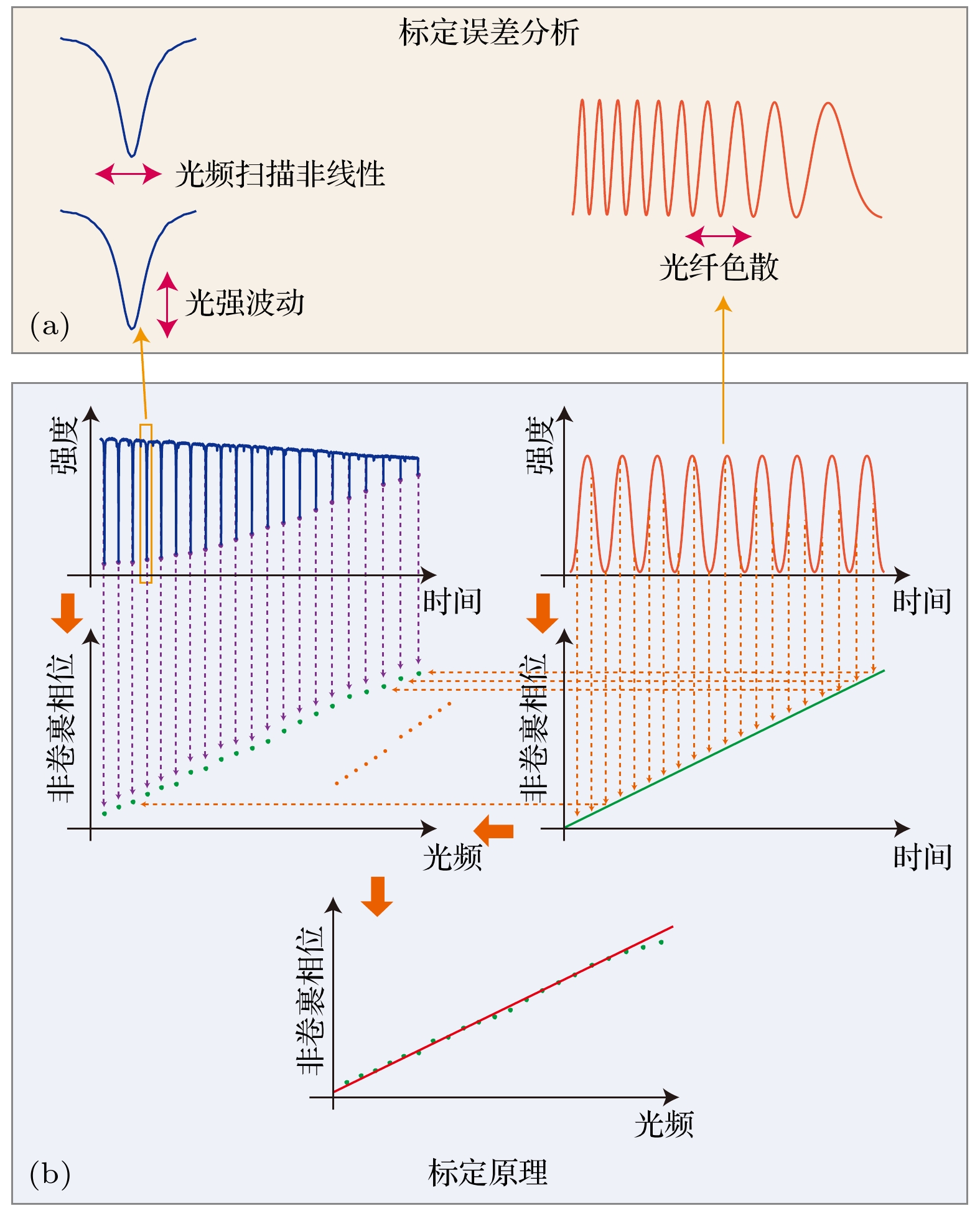
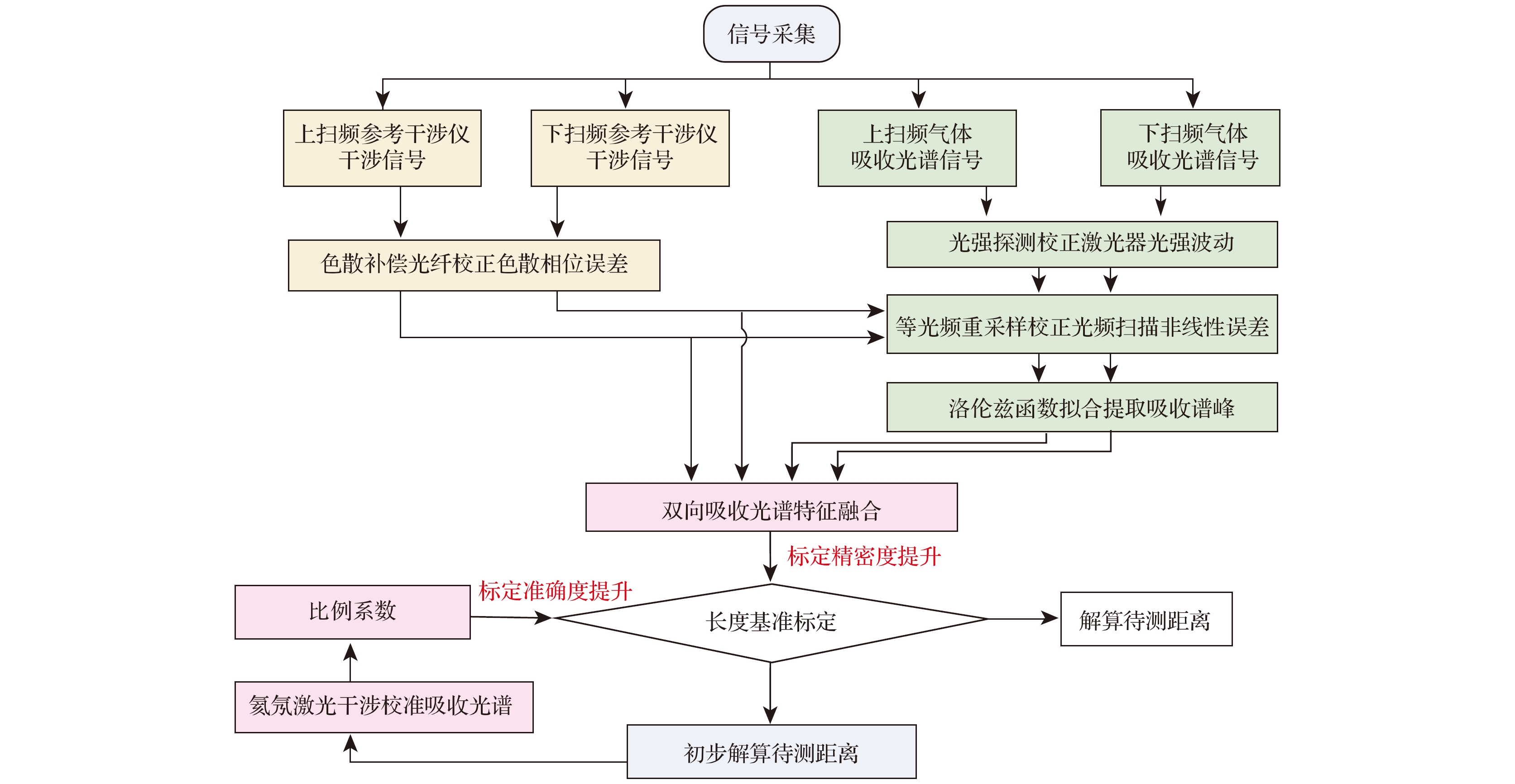
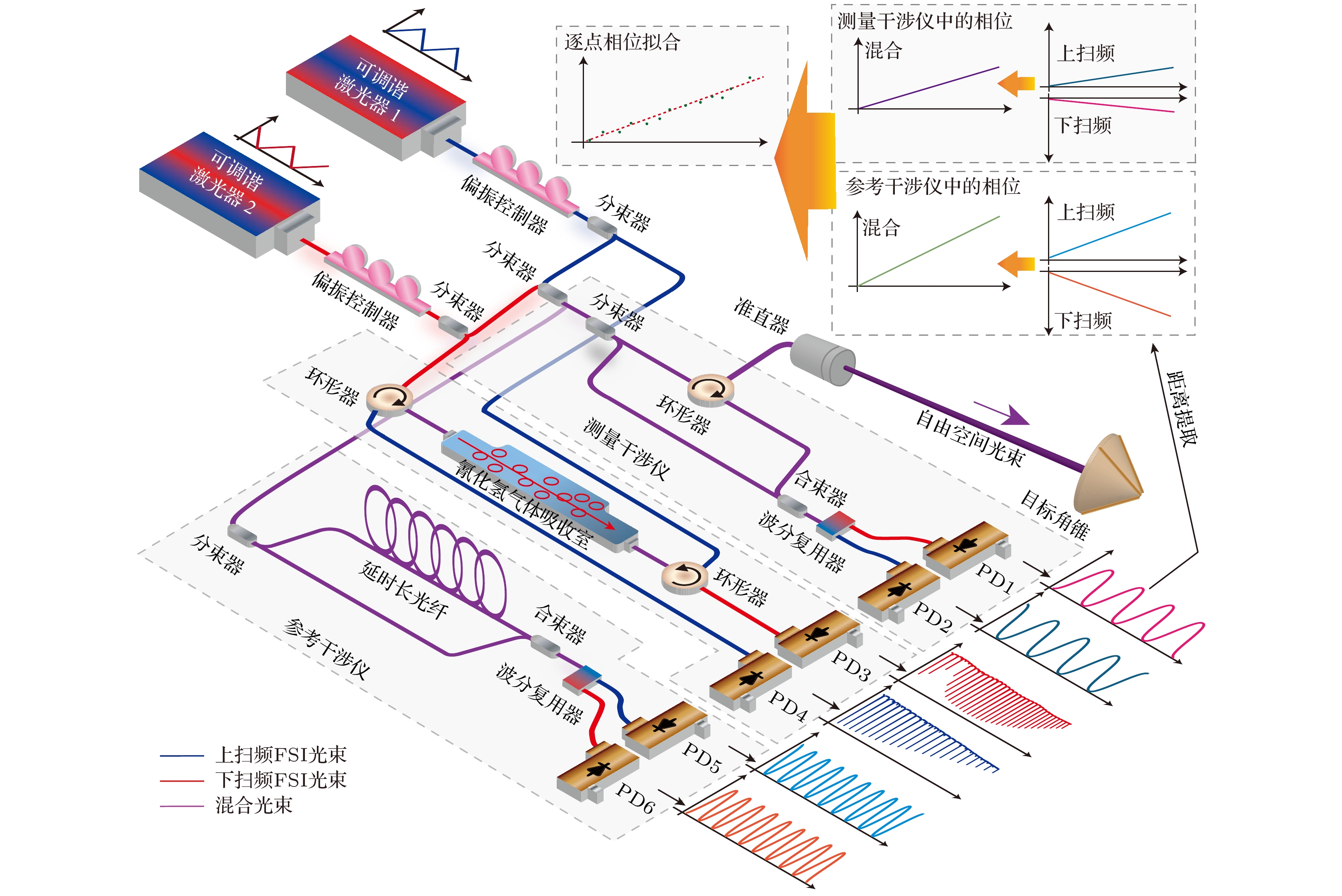
本文研究了光频扫描干涉绝对测距的长度基准精准标定方法. 利用气体吸收光谱在线标定测距系统中作为长度基准的延时长光纤光程, 并提出利用加权线性最小二乘方法解决不同吸收谱峰不确定度的差异. 针对吸收光谱标定光纤光程重复精度低的问题, 提出了利用双向吸收光谱特征融合的方法提升光纤光程标定精密度. 针对吸收谱峰绝对光频准确性不足的问题, 提出单一吸收光谱比例系数的标定方法, 相较于逐一校准谱峰光频的思路更为简单直接, 提升了光纤光程标定准确度. 为验证上述方法的有效性, 分别进行了重复精度评估实验、比例系数标定实验以及精度比对实验. 实验结果表明, 标定164 m光纤光程的标准差为10—30 μm, 在系统温度上升及温度稳定条件下, 0—10 m及0—15 m的测量范围内, 测距标准差不大于5 μm, 测距比对残差不大于± 4 μm, 显示了该系统良好的测距性能.Accurate measurement of length is an important foundation for ensuring the quality of advanced manufacturing equipment. In recent years, absolute ranging technology represented by frequency scanning interferometry (FSI) has gradually become a widely used ranging method in the manufacturing industry due to its advantages of high precision, high flexibility, and no range ambiguity. To address the repeatability and accuracy of length reference calibration in FSI absolute ranging, this paper proposes a method of accurately calibrating length reference based on bidirectional absorption spectrum feature fusion and proportional coefficient calibration, by using gas absorption spectroscopy to calibrate the delayed long fiber path length as a length reference in the distance measurement system online, and by using weighted linear least squares method to solve the differences in uncertainty among different absorption spectrum peaks. To address the problem of low repeatability in optical fiber path length calibration by using absorption spectroscopy, a method of utilizing bidirectional absorption spectrum feature fusion is proposed, thereby improving the precision of optical fiber path length calibration. To address the issue of insufficient accuracy in absolute optical frequency of absorption spectrum peaks, a calibration method by using a single absorption spectrum proportional coefficient is proposed. Compared with the idea of calibrating the optical frequency of each peak one by one, this method is simple and direct, thus improving the accuracy of fiber path length calibration. To verify the effectiveness of the above methods, the experiments on repeated precision evaluation, proportional coefficient calibration, and accuracy comparison are conducted separately. The experimental results show that the standard deviation for calibrating the optical path length of 164 m fiber is 10–30 μm. Under the conditions of system temperature rise and temperature stability, the distance measurement standard deviations are not greater than 5 μm in the measurement ranges of 0–10 m and 0–15 m, and the distance comparison residuals are not greater than ±4 μm, demonstrating the good distance measurement performance of the system. In the future, we will carry out thermal insulation and temperature control of the gas absorption chamber and the entire ranging optical path, and study the stability of the spectral proportionality coefficient and absorption peaks while controlling external environmental factors.
-
Keywords:
- frequency scanning interferometry /
- gas absorption spectroscopy /
- absolute ranging /
- weighted least squares
[1] Schmitt R H, Peterek M, Morse E, Knapp W, Galetto M, Härtig F, Goch G, Ben H, Forbes A 2016 CIRP Annals - Manuf. Techn. 65 643
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Gao W, Kim S W, Bosse H, Haitjema H, Chen Y L, Lu X D, Knapp W, Weckenmann, Estler W T, Kunzmann H A 2015 CIRP Annals - Manuf. Techn. 64 773
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Pellegrini S, Buller G S, Smith J M, Wallace A M, Cova S 2000 Meas. Sci. Technol. 11 712
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yang S, Yang L H, Wu T F, Shi S D, Ma L Y, Zhu J G 2023 Opt. Express 31 42595
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 林嘉睿, 邾继贵, 张皓琳, 杨学友, 叶声华 2012 仪器仪表学报 33 463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lin J R, Zhu J G, Zhang H L, Yang X Y, Ye S H 2012 Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 33 463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Deng R, Shi S D, Yang L H, Lin J R, Zhu J G 2023 Meas. Sci. Technol. 34 085007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Falaggis K, Towers D P, Towers C E 2009 Opt. Lett. 34 950
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 梁旭, 林嘉睿, 吴腾飞, 赵晖, 邾继贵 2022 71 090602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang X, Lin J R, Wu T F, Zhao H, Zhu J G 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 090602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 时光, 张福民, 曲兴华, 孟祥松 2014 63 184209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shi G, Zhang F M, Qu X H, Meng X S 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 184209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhou Q, Wu T F, Liu Y, Shang Y, Lin J R, Yang L H, Li J S, Zeng Z M, Zhu J G 2021 Opt. Express 29 42127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Pan H, Zhang F M, Shi C Z, Qu X H 2017 Appl. Opt. 56 6956
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Schneider R, Thuermel P, Stockmann M 2001 Opt. Eng. 40 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Cui P F, Yang L H, Guo Y, Lin J R, Liu Y, Zhu J G 2018 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 30 744
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhou Q, Wu T F, Lin J R, Liang X, Zeng Z M 2022 Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Optical Instruments and Technology, China, Apirl 8–10, 2022 p12282
[15] Jia X Y, Liu Z G, Tao L, Deng Z W 2017 Opt. Express 25 25782
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jia L H, Wang Y, Wang X Y, Zhang F M, Wang W Q, Wang J D, Zheng J H, Chen J W, Song M Y, Ma X, Yuan M Y, Little B, Chu S T, Cheng D, Qu X H, Zhao W, Zhang W F 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 1025
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Dale J, Hughes B, Lancaster A J, Lewis A J, Reichold J H, Warden M S 2014 Opt. Express 22 24869
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] DiLazaro T, Nehmetallah G 2018 Appl. Opt. 57 6260
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 潘浩 2018 博士学位论文(天津: 天津大学)
Pan H 2018 Ph. D. Dissertation (Tianjin: Tianjin University
[20] 许新科 2016 博士学位论文(哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学)
Xu X K 2016 Ph. D. Dissertation (Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology
[21] 路程 2017 博士学位论文(哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学)
Lu C 2017 Ph. D. Dissertation (Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology
[22] William C, Swann, Sarah L G 2005 Opt. Soc. Am. B 22 1749
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhou Q, Wu T F, Long X Y, Zeng Z M, Zhu J G 2024 J. Lightwave Technol. 42 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 伊灵平, 张福民, 曲兴华, 李雅婷 2020 红外与毫米波学报 39 331
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yi L P, Zhang F M, Qu X H, Li Y T 2020 J. Infrared Millim. Waves 39 331
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
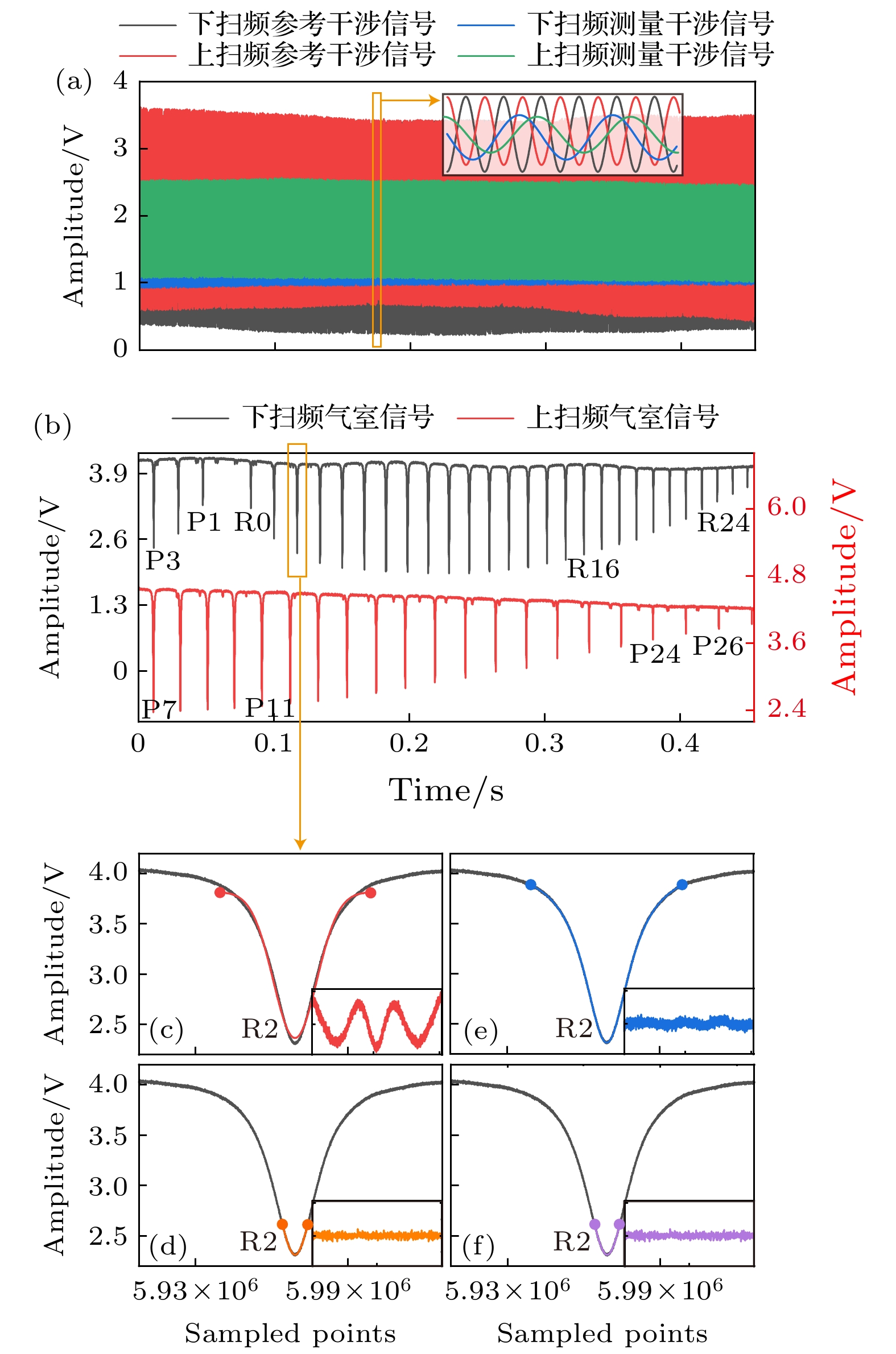
图 5 信号采集和处理结果 (a) 扫频干涉原信号; (b) 双向吸收光谱原信号; (c) 宽区间的高斯拟合函数拟合R2谱峰; (d) 窄区间的高斯拟合函数拟合R2谱峰; (e) 宽区间的洛伦兹拟合函数拟合R2谱峰; (f) 窄区间的洛伦兹拟合函数拟合R2谱峰
Fig. 5. Signal acquisition and processing results: (a) Original signals of frequency scanning interferometry; (b) original signal of bidirectional absorption spectroscopy; (c) wide range Gaussian fitting function to fit the R2 spectral peak; (d) narrow range Gaussian fitting function to fit the R2 spectral peak; (e) wide range Lorentz fitting function to fit the R2 spectral peak; (f) narrow range Lorentz fitting function to fit the R2 spectral peak.
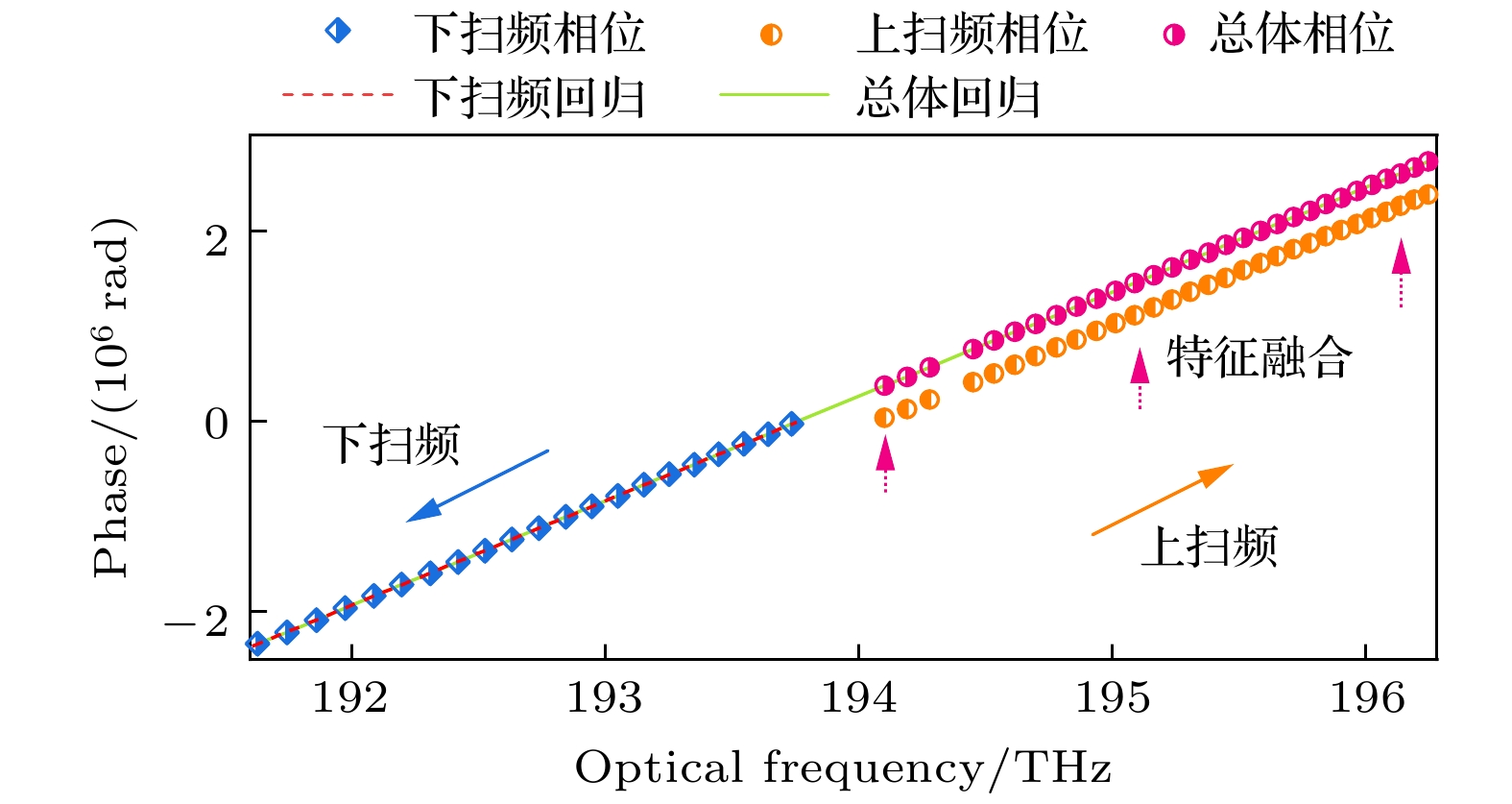
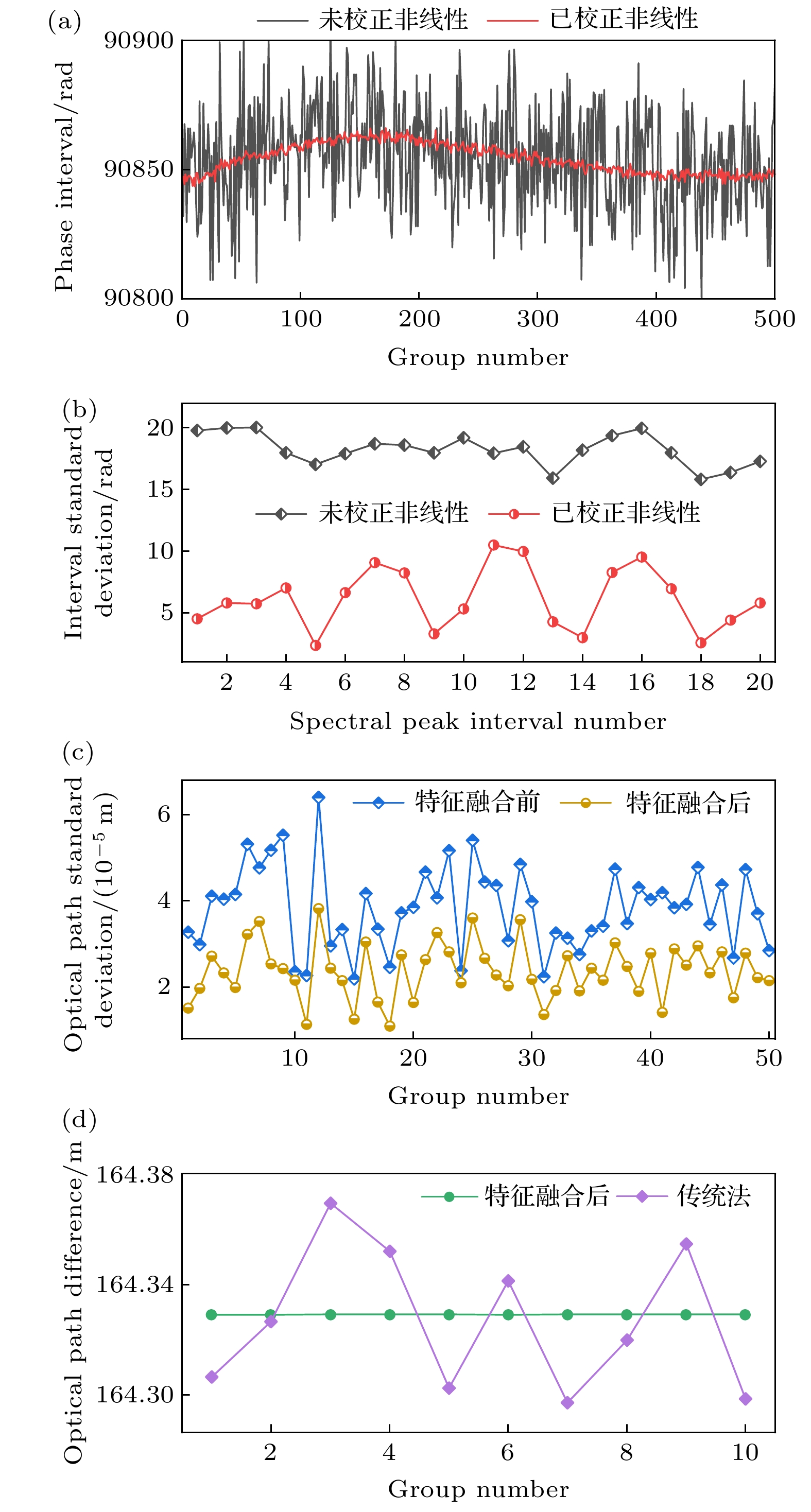
图 6 重复精度评估 (a) 气室信号校正非线性前后的R9和R10的相位间隔值; (b) 气室信号校正非线性前后的谱峰间相位间隔标准差; (c) 双向吸收光谱特征融合前后延时长光纤光程标定的标准差; (d) 传统标定方法与本文方法的精度比较
Fig. 6. Precision evaluation: (a) Phase interval of R9 and R10 before and after correcting the nonlinearity of gas absorption signal; (b) phase interval standard deviation of spectral peak to peak before and after correcting the nonlinearity; (c) optical path standard deviation of calibration for the long delay optical fiber before and after bidirectional spectrum feature integration; (d) comparison of precision between traditional calibration method and our method.
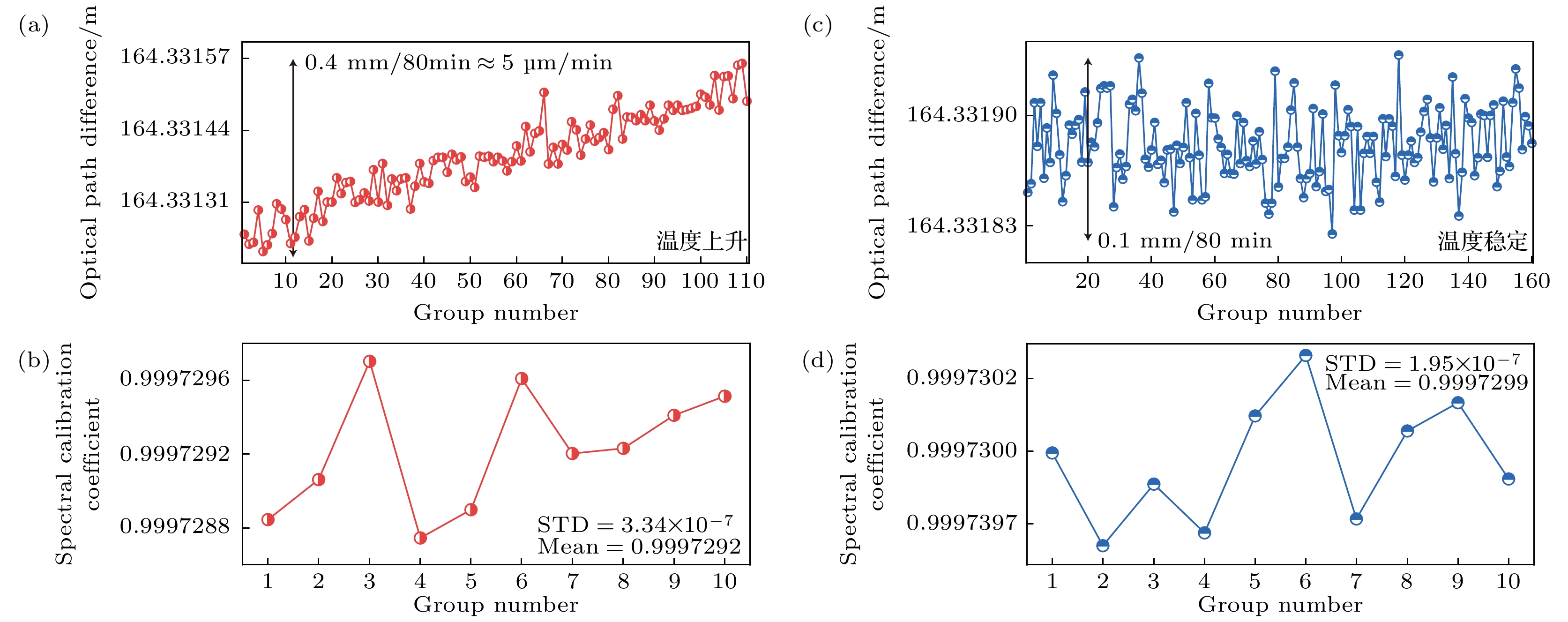
图 9 不同温度变化条件下的实验结果 (a) 升温时的光纤光程变化; (b) 升温时气体吸收光谱比例系数; (c) 温度稳定时光纤光程变化; (d) 温度稳定时气体吸收光谱比例系数
Fig. 9. The experimental results under different temperature variation conditions: (a) The optical path variation during temperature rising; (b) calibration coefficient of gas absorption spectrum during temperature rising; (c) the optical path variation at stable temperature; (d) calibration coefficient of gas absorption spectrum at stable temperature.
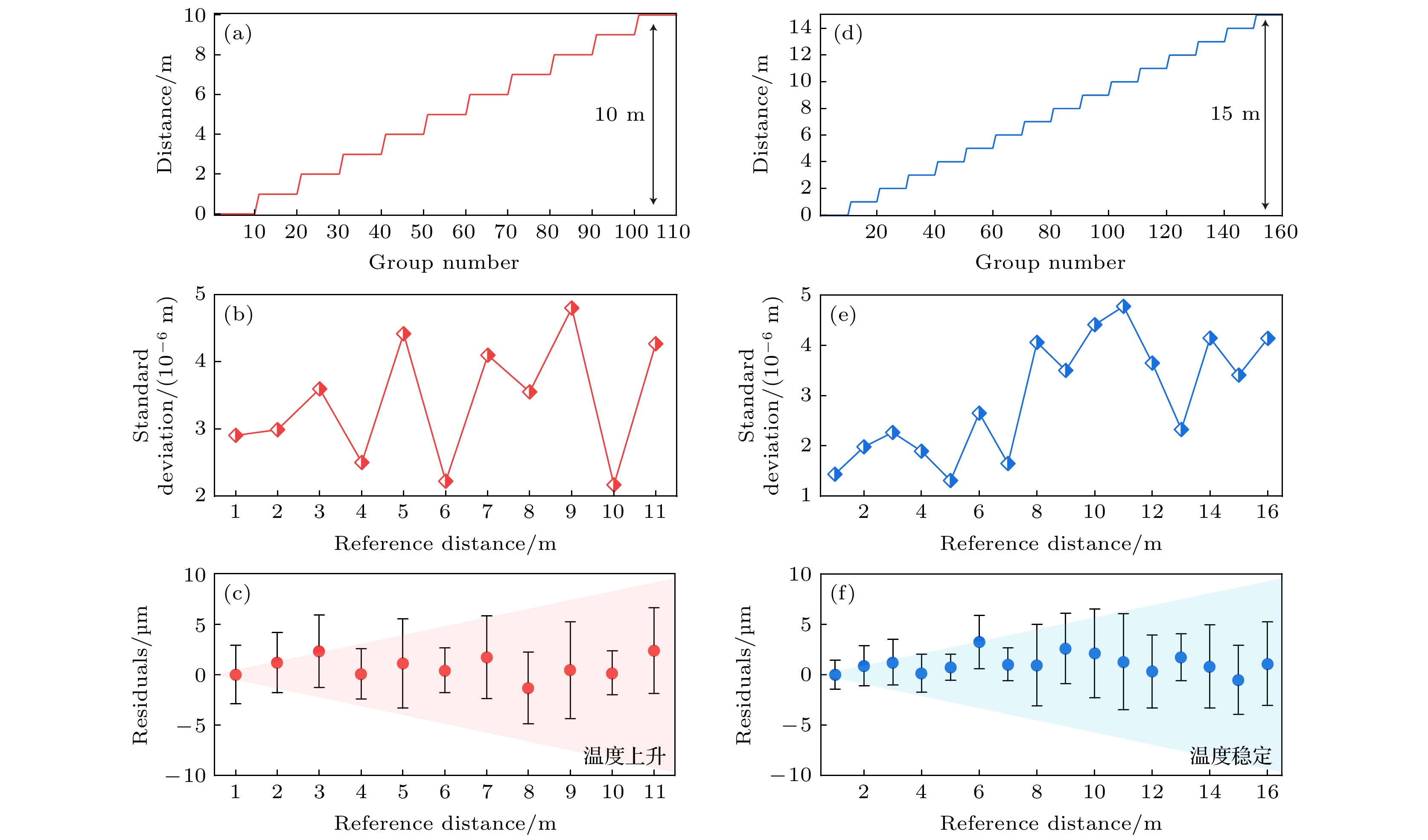
图 10 测距系统准确度评估结果 (a) 升温时的FSI系统测距值; (b) 升温时的FSI系统测距标准差; (c) 升温时的FSI系统与干涉仪比对残差; (d) 温度稳定时的FSI系统测距值; (e) 温度稳定时的FSI系统测距标准差; (f) 温度稳定时的FSI系统与干涉仪比对残差
Fig. 10. The accuracy evaluation results: (a) FSI system ranging value during temperature rising; (b) FSI system ranging standard deviation during temperature rising; (c) residual during temperature rising; (d) FSI system ranging value at stable temperature; (e) FSI system ranging standard deviation at stable temperature; (f) residual at stable temperature.
-
[1] Schmitt R H, Peterek M, Morse E, Knapp W, Galetto M, Härtig F, Goch G, Ben H, Forbes A 2016 CIRP Annals - Manuf. Techn. 65 643
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Gao W, Kim S W, Bosse H, Haitjema H, Chen Y L, Lu X D, Knapp W, Weckenmann, Estler W T, Kunzmann H A 2015 CIRP Annals - Manuf. Techn. 64 773
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Pellegrini S, Buller G S, Smith J M, Wallace A M, Cova S 2000 Meas. Sci. Technol. 11 712
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yang S, Yang L H, Wu T F, Shi S D, Ma L Y, Zhu J G 2023 Opt. Express 31 42595
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 林嘉睿, 邾继贵, 张皓琳, 杨学友, 叶声华 2012 仪器仪表学报 33 463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lin J R, Zhu J G, Zhang H L, Yang X Y, Ye S H 2012 Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 33 463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Deng R, Shi S D, Yang L H, Lin J R, Zhu J G 2023 Meas. Sci. Technol. 34 085007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Falaggis K, Towers D P, Towers C E 2009 Opt. Lett. 34 950
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 梁旭, 林嘉睿, 吴腾飞, 赵晖, 邾继贵 2022 71 090602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang X, Lin J R, Wu T F, Zhao H, Zhu J G 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 090602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 时光, 张福民, 曲兴华, 孟祥松 2014 63 184209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shi G, Zhang F M, Qu X H, Meng X S 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 184209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhou Q, Wu T F, Liu Y, Shang Y, Lin J R, Yang L H, Li J S, Zeng Z M, Zhu J G 2021 Opt. Express 29 42127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Pan H, Zhang F M, Shi C Z, Qu X H 2017 Appl. Opt. 56 6956
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Schneider R, Thuermel P, Stockmann M 2001 Opt. Eng. 40 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Cui P F, Yang L H, Guo Y, Lin J R, Liu Y, Zhu J G 2018 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 30 744
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhou Q, Wu T F, Lin J R, Liang X, Zeng Z M 2022 Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Optical Instruments and Technology, China, Apirl 8–10, 2022 p12282
[15] Jia X Y, Liu Z G, Tao L, Deng Z W 2017 Opt. Express 25 25782
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jia L H, Wang Y, Wang X Y, Zhang F M, Wang W Q, Wang J D, Zheng J H, Chen J W, Song M Y, Ma X, Yuan M Y, Little B, Chu S T, Cheng D, Qu X H, Zhao W, Zhang W F 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 1025
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Dale J, Hughes B, Lancaster A J, Lewis A J, Reichold J H, Warden M S 2014 Opt. Express 22 24869
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] DiLazaro T, Nehmetallah G 2018 Appl. Opt. 57 6260
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 潘浩 2018 博士学位论文(天津: 天津大学)
Pan H 2018 Ph. D. Dissertation (Tianjin: Tianjin University
[20] 许新科 2016 博士学位论文(哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学)
Xu X K 2016 Ph. D. Dissertation (Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology
[21] 路程 2017 博士学位论文(哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学)
Lu C 2017 Ph. D. Dissertation (Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology
[22] William C, Swann, Sarah L G 2005 Opt. Soc. Am. B 22 1749
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhou Q, Wu T F, Long X Y, Zeng Z M, Zhu J G 2024 J. Lightwave Technol. 42 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 伊灵平, 张福民, 曲兴华, 李雅婷 2020 红外与毫米波学报 39 331
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yi L P, Zhang F M, Qu X H, Li Y T 2020 J. Infrared Millim. Waves 39 331
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 581
- PDF下载量: 34
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: