-
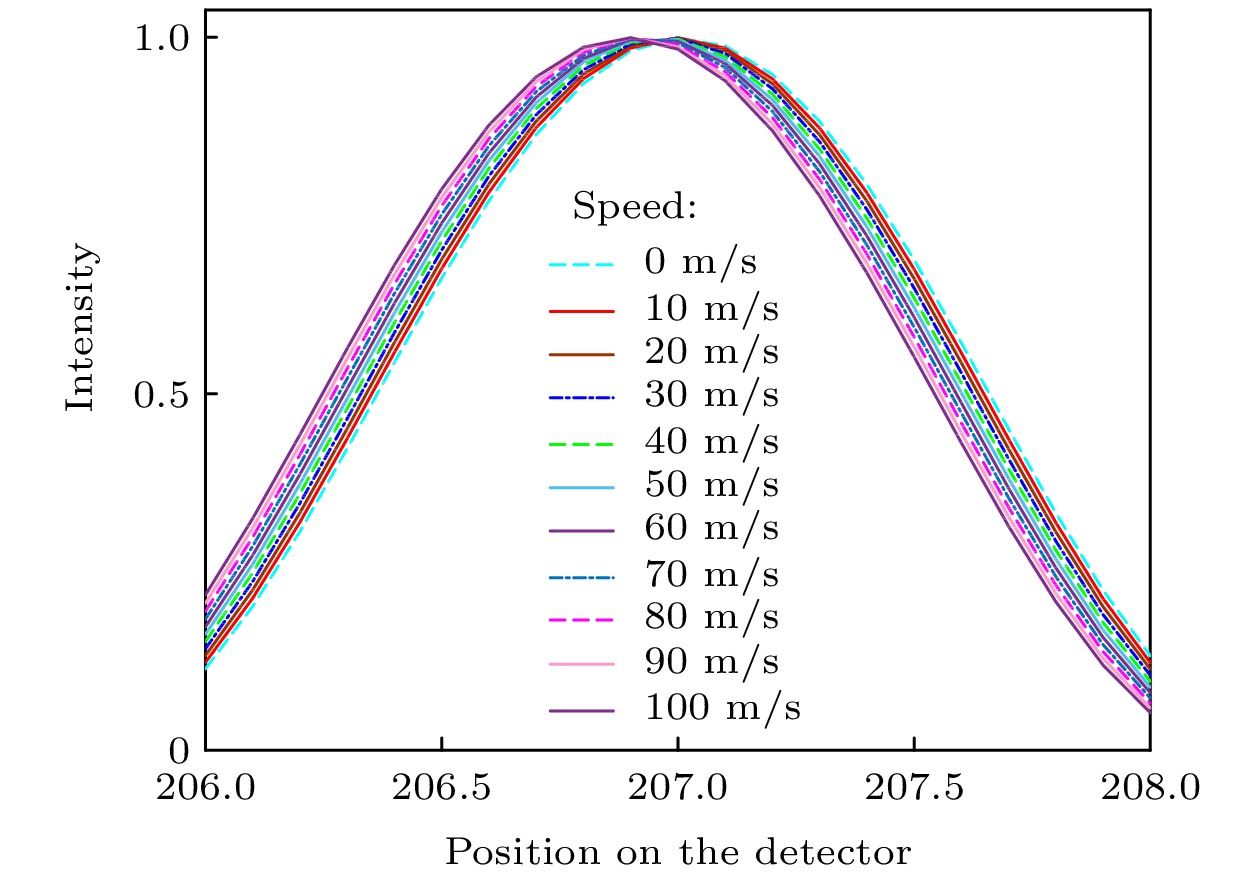
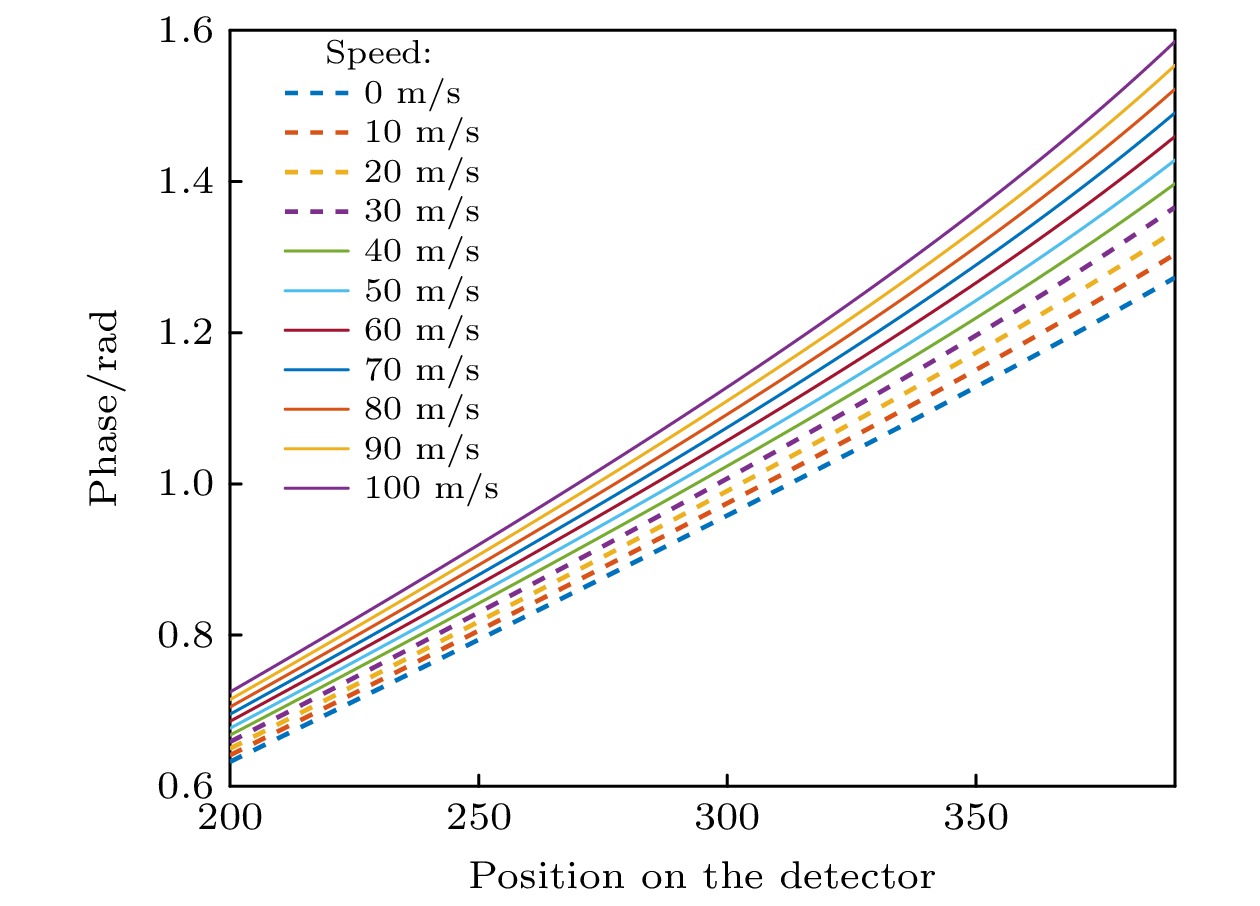
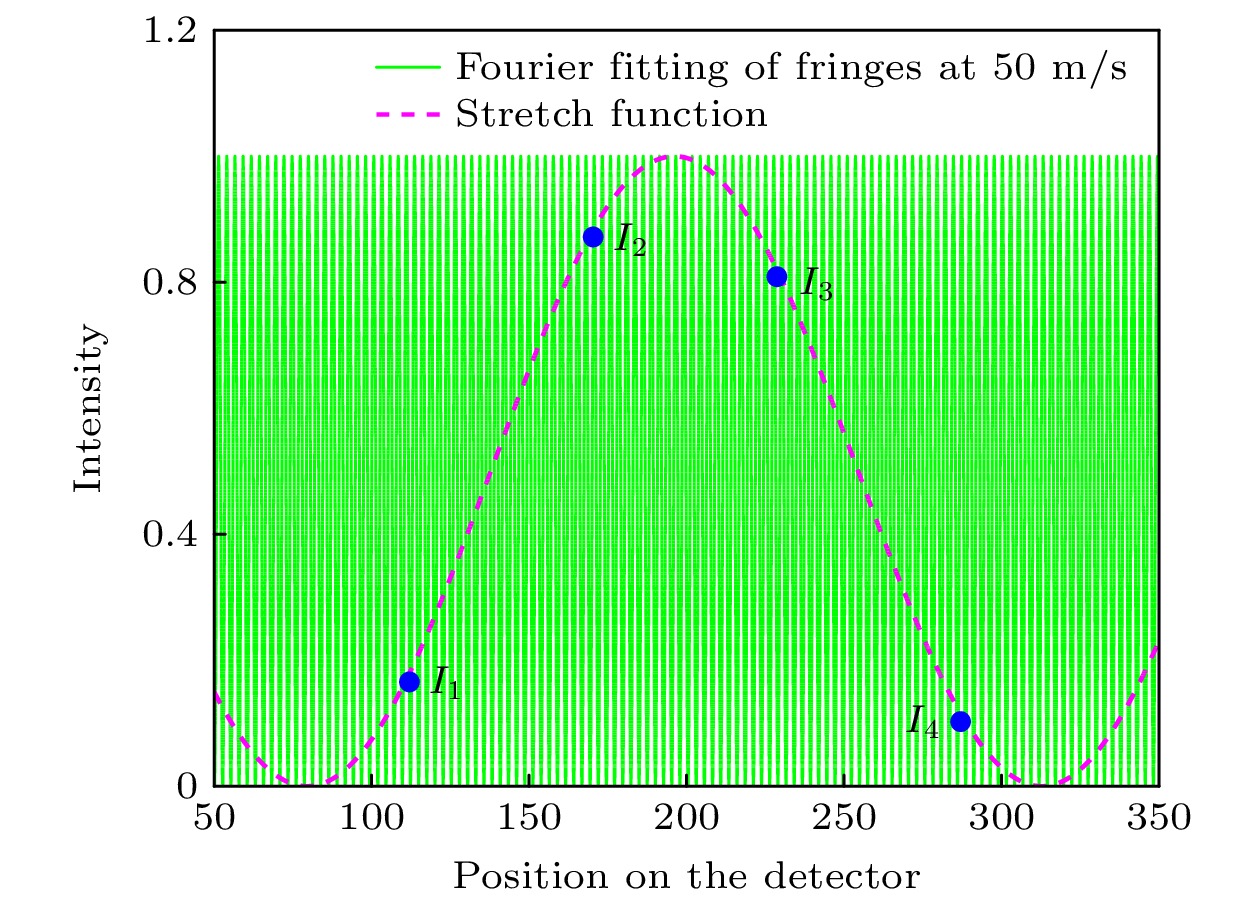
采用多普勒非对称空间外差仪(Doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne, DASH)被动遥感探测高层大气风速, 目前有傅里叶级数法和流行的傅里叶变换两种测风方法. 本文提出“四强度法”测风. 比较研究了傅里叶级数法、傅里叶变换法和“四强度法”测风的原理、正演、噪声和反演等内容, 3种测风方法均从DASH斐索干涉条纹的相位差变换而来. 假设风速为0—100 m/s, 利用傅里叶级数法、傅里叶变换法和“四强度法”得到正演的斐索干涉图后, 再对应得到正演风速的误差分别为2.93%, 4.67%和3.00%. 人为添加均值为0、标准差为0.1的高斯噪声后, 假设风速是0—100 m/s, 用傅里叶级数、傅里叶变换和“四强度法”分别对平场后的数据正演, 得到相对误差对应分别为2.30%, 11.66%, 2.27%. 人为添加高斯噪声后, 假设风速为31—39 m/s和30.1—30.9 m/s, 用傅里叶级数法和“四强度法”得到正演风速值, 两种情况的傅里叶级数法的测风误差是3.55%和4.15%, 均高于“四强度法”的测风误差2.20%和2.69%. 利用GBAII-DASH野外拍摄西安上空98 km的O(1S) 557.7 nm气辉, 得到天顶角为0°和45°的成像干涉图, 再用傅里叶级数、傅里叶变换和“四强度法”得到反演风速分别为32.21 m/s, 43.55 m/s和32.17 m/s. 从DASH的正演、反演结果看, 本文提出的“四强度法”探测高层大气风速的结果较好, 计算简便, 测风精度相对较高.
-
关键词:
- 非对称空间外差光谱仪 /
- “四强度法” /
- 傅里叶变换 /
- 测风
The DASH (Doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne) is used to detect the upper atmospheric wind speed by its imaging Fizeau interference fringes. There are two wind measurement methods: Fourier series method (FSM) and popular Fourier transform method (FTM). However, the wind speed measurement accuracy of FTM is greatly influenced by window function, and the calculation is relatively complicated. The Four-point algorithm (FPA) for DASH’s wind speed measurement is proposed in this paper. The contents of wind speed measurement principle, forward modeling, noise and inversion by the FSM, FTM and FPA are wholly compared and studied. The three wind speed measurement methods are all derived from the phase difference transformation of DASH Fizeau interference fringes. The Fizeau interference fringes with wind speed of 0–100 m/s at the interval of 10 m/s are simulated, and the forward wind speeds are obtained by FSM, FTM and FPA, and the corresponding wind measurement errors are 2.93%, 4.67% and 3.00%, respectively. After artificially adding Gaussian noise with a mean value of 0 and a standard deviation of 0.1, FSM, FTM and FPA are used to forward the Fizeau interference fringes after flat field, and the corresponding relative errors are 2.30%, 11.66% and 2.27%, respectively. After artificially adding Gaussian noise, the Fizeau interference fringes of wind speeds of 31–39 m/s with 1 m/s interval and 30.1–30.9 m/s with 0.1 m/s interval are simulated, and the forward wind speeds are obtained by FSM and FPA. In both cases, the wind speed measurement errors of FSM are 3.55% and 4.15% higher than those of FPA. The O(1S) 557.7 nm airglow at peak altitude of 98 km in Xi’an was photographed by using our GBAII (ground based airglow imaging interferometer)-DASH, and the imaging interferograms with zenith angles of 0° and 45° were obtained. Then by the methods of Fourier series, Fourier transform and FPA are used to obtain the inversion wind speed of 32.21 m/s, 43.55 m/s and 32.17 m/s, respectively. From the forward and inversion results of DASH, we can see that the FPA has a better result for detecting the upper atmospheric wind due to its simple calculation and smaller wind measurement error.-
Keywords:
- asymmetric spatial heterodyne spectrometer /
- four-point algorithm /
- Fourier transform /
- wind measurement
[1] 易帆 1997 中国科学基金 11 43
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yi F 1997 Fundamental Research 11 43
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 任志鹏 2020 科学通报 65 1320
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ren Z P 2020 Sci. Bull. 65 1320
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Shepherd G G, Thuillier G, Gault W A, Solheim B H, Hersom C, Alunni J M, Brun J F, Brune S, Charlot P, Cogger L L, Desaulniers D L, Evans W F J, Gattinger R L, Girod F, Harvie D, Hum R H, Kendall D J W, Llewellyn E J, Lowe R P, Ohrt J, Pasternak F, Peillet O, Powell I, Rochon Y, Ward W E, Wiens R H, Wimperis J 1993 J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 98 10725
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Bird J C, Facheng L, Solheim B H, Shepherd G G 1995 Meas. Sci. Technol. 6 1368
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Piotrowski McCall S H C, Dobrowolski J A, Shepherd G G 1989 Appl. Opt. 28 2854
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Shepherd G G, Gault W A, Koehler R A 1991 Can. J. Phys. 69 1175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Englert C R, Babcock D D, Harlander J M 2007 Appl. Opt. 46 307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Englert C R, Harlander J M, Brown C M, Marr K D, Miller I J, Stump J E, Hancock J, Peterson J Q, Kumler J, Morrow W H, Mooney T A, Ellis S, Mende S B, Harris S E, Stevens M H, Makela J J, Harding B J, Immel T J 2017 Space Sci. Rev. 212 553
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Englert C R, Harlander J M, Marr K D, Harding B J, Makela J J, Fae T, Brown C M, Ratnam M V, Rao S V B, Immel T J 2023 Space Sci. Rev. 219 27
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 陈洁婧, 冯玉涛, 胡炳樑, 李娟, 孙剑, 郝雄波, 白清兰 2017 光学学报 37 92
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen J J, Feng Y T, Hu B L, Li J, Sun J, Hao X B, Bai Q L 2017 Acta Opt. Sin. 37 92
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 彭翔, 刘恩海, 田书林, 方亮 2022 71 240601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Peng X, Liu E H, Tian S L, Fang L 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 240601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Ning T 2012 M. S. Thesis (Toronto: York University
[13] Gao H Y, Tang Y H, Hua D X, Liu H C, Cao X G, Duan X D, Jia Q J, Qu O Y, Wu Y 2013 Appl. Opt. 52 8650
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Tang Y H, Duan X D, Gao H Y, Qu O Y, Jia Q J, Cao X G, Wei S N, Yang R 2014 Appl. Opt. 53 2273
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 唐远河, 崔进, 郜海阳, 屈欧阳, 段晓东, 李存霞, 刘丽娜 2017 66 130601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang Y H, Cui J, Gao H Y, Qu O Y, Duan X D, Li C X, Liu L N 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 130601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Tang Y, Yang R, Gao H, Zhai F, Yu Y, Cui J 2017 Proc. SPIE 10256 102563C
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 赵博, 晏磊, 李颜青, 齐向东, 高键翔 2011 光学技术 27 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao B, Yan L, Li Y Q, Qi X D, Gao J X 2011 Opt. Techn. 27 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhang S P, Shepherd G G 2005 J. Geophys. Res. Space 110 A03304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Shepherd G G 2002 Spectral Imaging of the Atmosphere (London: Academic Press) p113
[20] 沈静, 熊伟, 施海亮, 李志伟, 胡广骁, 乔延利 2016 光谱学与光谱分析 36 3014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shen J, Xiong W, Shi H L, Li Z W, Hu G X, Qiao Y L 2016 Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 36 3014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 1 DASH的光路图[7]
Fig. 1. Optical path diagram of DASH.
表 1 三种测风方法的正演结果
Table 1. Forward wind speed results by three methods.
Calculated
wind/(m·s–1)Method category Fourier series Fourier transformation Four-point algorithm ϕ/rad v/(m·s–1) Φ/rad v/(m·s–1) ϕ/rad v/(m·s–1) 0 –0.7114 1.2615 0.7338 10 –0.6833 9.69 1.2917 10.43 0.7619 9.69 20 –0.6551 19.41 1.3220 20.86 0.7901 19.41 30 –0.6271 29.07 1.3523 31.32 0.8181 29.07 40 –0.5988 38.83 1.3827 41.79 0.8464 38.83 50 –0.5706 48.55 1.4131 52.29 0.8745 48.52 60 –0.5426 58.21 1.4436 62.81 0.9025 58.19 70 –0.5144 67.93 1.4742 73.36 0.9307 67.92 80 –0.4864 77.59 1.5049 83.94 0.9588 77.58 90 –0.4581 87.34 1.5357 94.56 0.9870 87.33 100 –0.4299 97.07 1.5666 105.21 1.0152 97.05 表 2 加入噪声后的3种测风方法的正演误差
Table 2. Speed Error after adding noise by three methods.
Calculated
wind/(m·s–1)Method category Fourier series Fourier transformation Four-point algorithm v/(m·s–1) Relative error/% v/(m·s–1) Relative error/% v/(m·s–1) Relative error/% 10 9.45 5.52 7.85 21.47 9.47 5.28 20 20.28 1.38 13.25 33.76 20.30 1.49 30 29.55 1.49 28.70 4.34 29.57 1.42 40 40.03 0.09 35.13 12.19 40.04 0.10 50 49.10 1.79 55.03 10.07 49.04 1.74 60 58.76 2.07 69.15 15.25 58.77 2.05 70 67.93 2.96 65.15 6.34 67.93 2.96 80 77.83 2.72 81.17 1.46 77.85 2.69 90 87.96 2.26 92.80 3.11 87.97 2.25 100 97.31 2.69 108.67 8.67 97.33 2.67 表 3 三种方法反演室外测风结果
Table 3. Inversion wind speed outdoor experiment by three methods.
Method category ϕ0/rad ϕ0 + ϕv
/radϕv/rad v
/(m·s–1)Fourier series –0.7129 –0.8063 0.0934 32.21 Fourier transformation –0.0152 0.1111 0.1263 43.55 Four-point algorithm 0.1362 0.2295 0.0933 32.17 -
[1] 易帆 1997 中国科学基金 11 43
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yi F 1997 Fundamental Research 11 43
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 任志鹏 2020 科学通报 65 1320
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ren Z P 2020 Sci. Bull. 65 1320
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Shepherd G G, Thuillier G, Gault W A, Solheim B H, Hersom C, Alunni J M, Brun J F, Brune S, Charlot P, Cogger L L, Desaulniers D L, Evans W F J, Gattinger R L, Girod F, Harvie D, Hum R H, Kendall D J W, Llewellyn E J, Lowe R P, Ohrt J, Pasternak F, Peillet O, Powell I, Rochon Y, Ward W E, Wiens R H, Wimperis J 1993 J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 98 10725
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Bird J C, Facheng L, Solheim B H, Shepherd G G 1995 Meas. Sci. Technol. 6 1368
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Piotrowski McCall S H C, Dobrowolski J A, Shepherd G G 1989 Appl. Opt. 28 2854
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Shepherd G G, Gault W A, Koehler R A 1991 Can. J. Phys. 69 1175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Englert C R, Babcock D D, Harlander J M 2007 Appl. Opt. 46 307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Englert C R, Harlander J M, Brown C M, Marr K D, Miller I J, Stump J E, Hancock J, Peterson J Q, Kumler J, Morrow W H, Mooney T A, Ellis S, Mende S B, Harris S E, Stevens M H, Makela J J, Harding B J, Immel T J 2017 Space Sci. Rev. 212 553
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Englert C R, Harlander J M, Marr K D, Harding B J, Makela J J, Fae T, Brown C M, Ratnam M V, Rao S V B, Immel T J 2023 Space Sci. Rev. 219 27
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 陈洁婧, 冯玉涛, 胡炳樑, 李娟, 孙剑, 郝雄波, 白清兰 2017 光学学报 37 92
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen J J, Feng Y T, Hu B L, Li J, Sun J, Hao X B, Bai Q L 2017 Acta Opt. Sin. 37 92
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 彭翔, 刘恩海, 田书林, 方亮 2022 71 240601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Peng X, Liu E H, Tian S L, Fang L 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 240601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Ning T 2012 M. S. Thesis (Toronto: York University
[13] Gao H Y, Tang Y H, Hua D X, Liu H C, Cao X G, Duan X D, Jia Q J, Qu O Y, Wu Y 2013 Appl. Opt. 52 8650
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Tang Y H, Duan X D, Gao H Y, Qu O Y, Jia Q J, Cao X G, Wei S N, Yang R 2014 Appl. Opt. 53 2273
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 唐远河, 崔进, 郜海阳, 屈欧阳, 段晓东, 李存霞, 刘丽娜 2017 66 130601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang Y H, Cui J, Gao H Y, Qu O Y, Duan X D, Li C X, Liu L N 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 130601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Tang Y, Yang R, Gao H, Zhai F, Yu Y, Cui J 2017 Proc. SPIE 10256 102563C
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 赵博, 晏磊, 李颜青, 齐向东, 高键翔 2011 光学技术 27 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao B, Yan L, Li Y Q, Qi X D, Gao J X 2011 Opt. Techn. 27 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhang S P, Shepherd G G 2005 J. Geophys. Res. Space 110 A03304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Shepherd G G 2002 Spectral Imaging of the Atmosphere (London: Academic Press) p113
[20] 沈静, 熊伟, 施海亮, 李志伟, 胡广骁, 乔延利 2016 光谱学与光谱分析 36 3014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shen J, Xiong W, Shi H L, Li Z W, Hu G X, Qiao Y L 2016 Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 36 3014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 3452
- PDF下载量: 199
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: